Renal Tubular Epithelial TRPA1 Acts as An Oxidative Stress Sensor to Mediate Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Kidney Injury through MAPKs/NF-κB Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
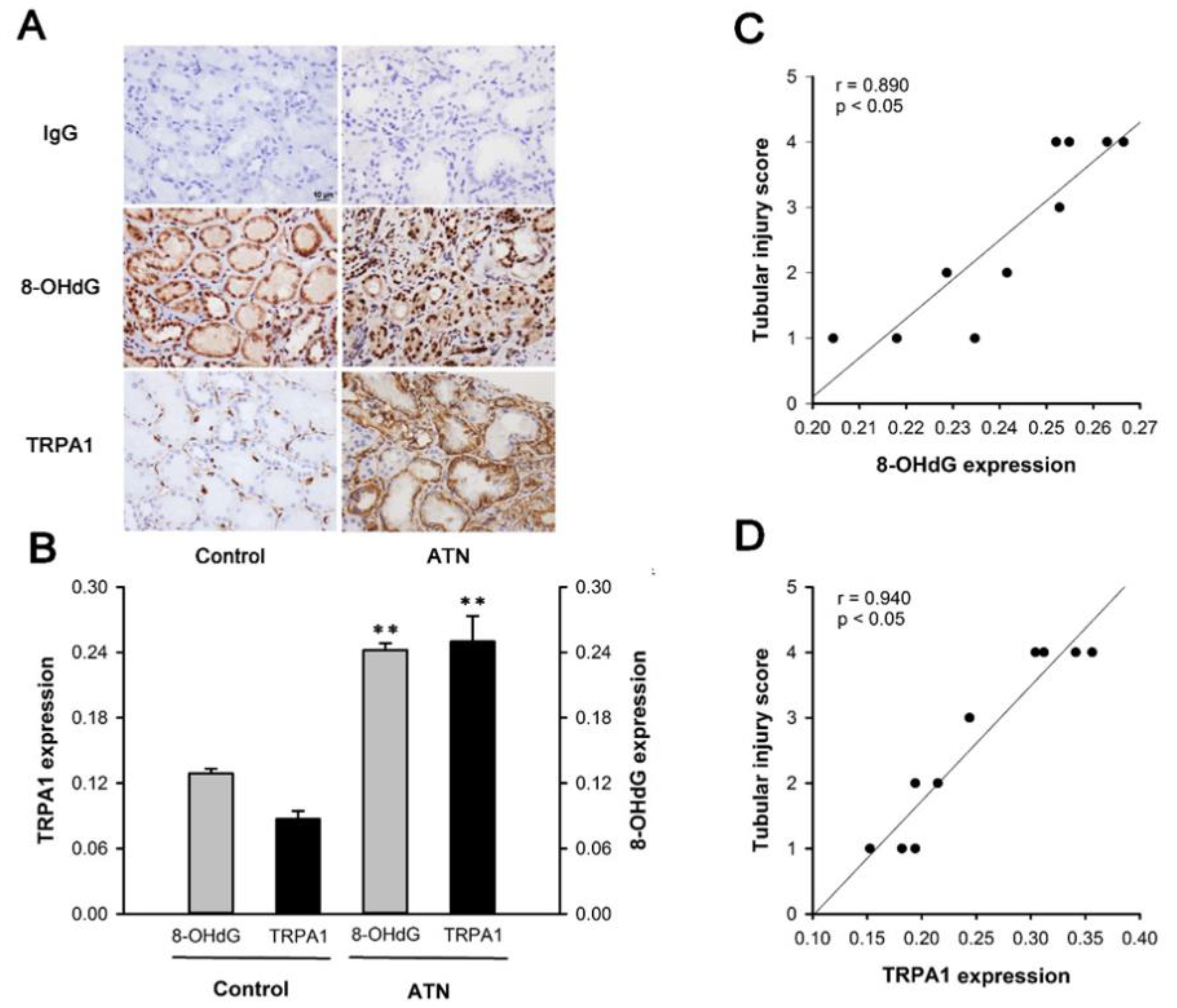
2.1. Patients with ATN and AKI Display Increased Expression of Renal Tubular TRPA1 and 8-OHdG
2.2. IR Increases the Expression of TRPA1 in Renal Tubular Epithelia and Renal Tissues in WT Mice, but Not in trpa1−/− Mice
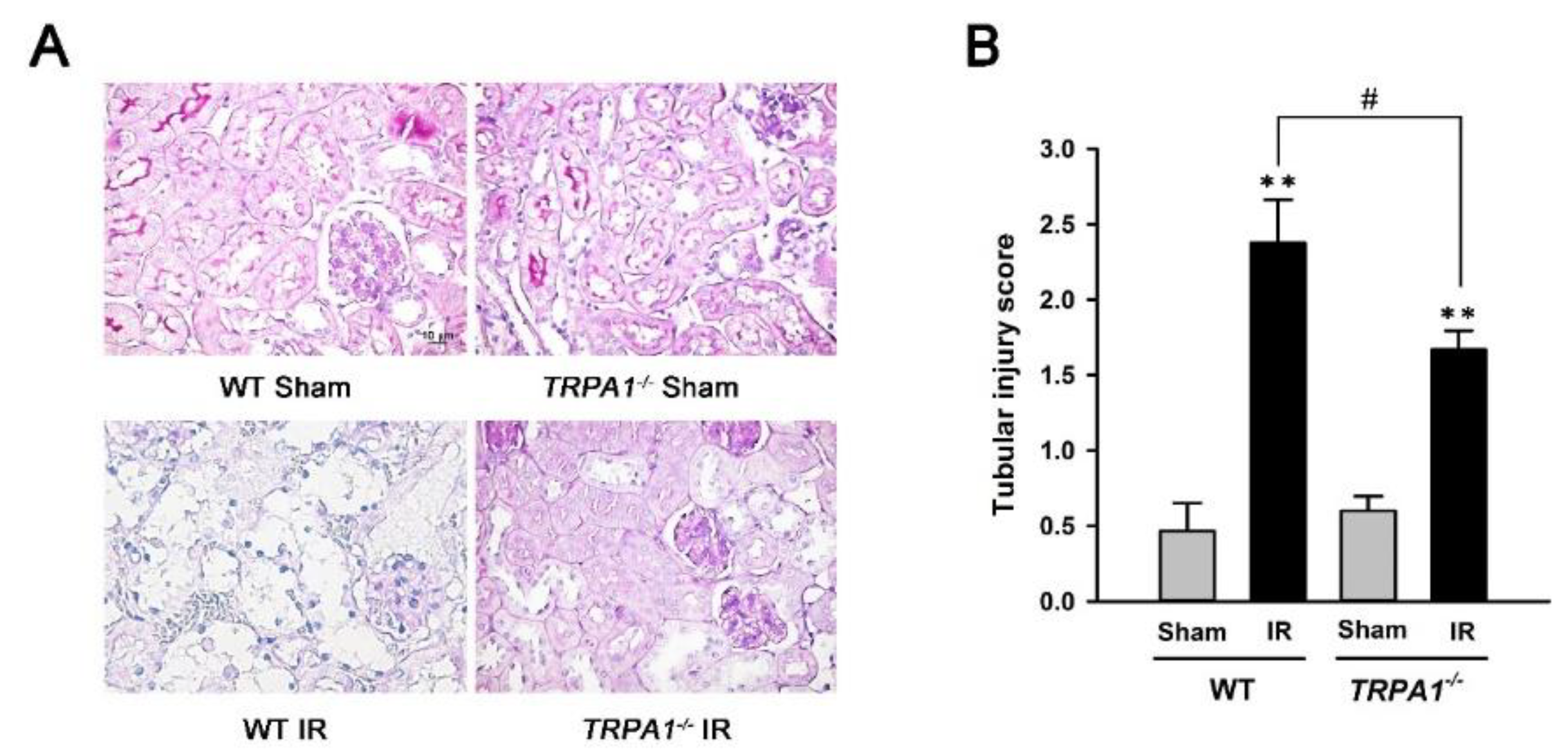
2.3. Renal Tubular Injury Induced by IR Is Lessened in trpa1−/− Mice
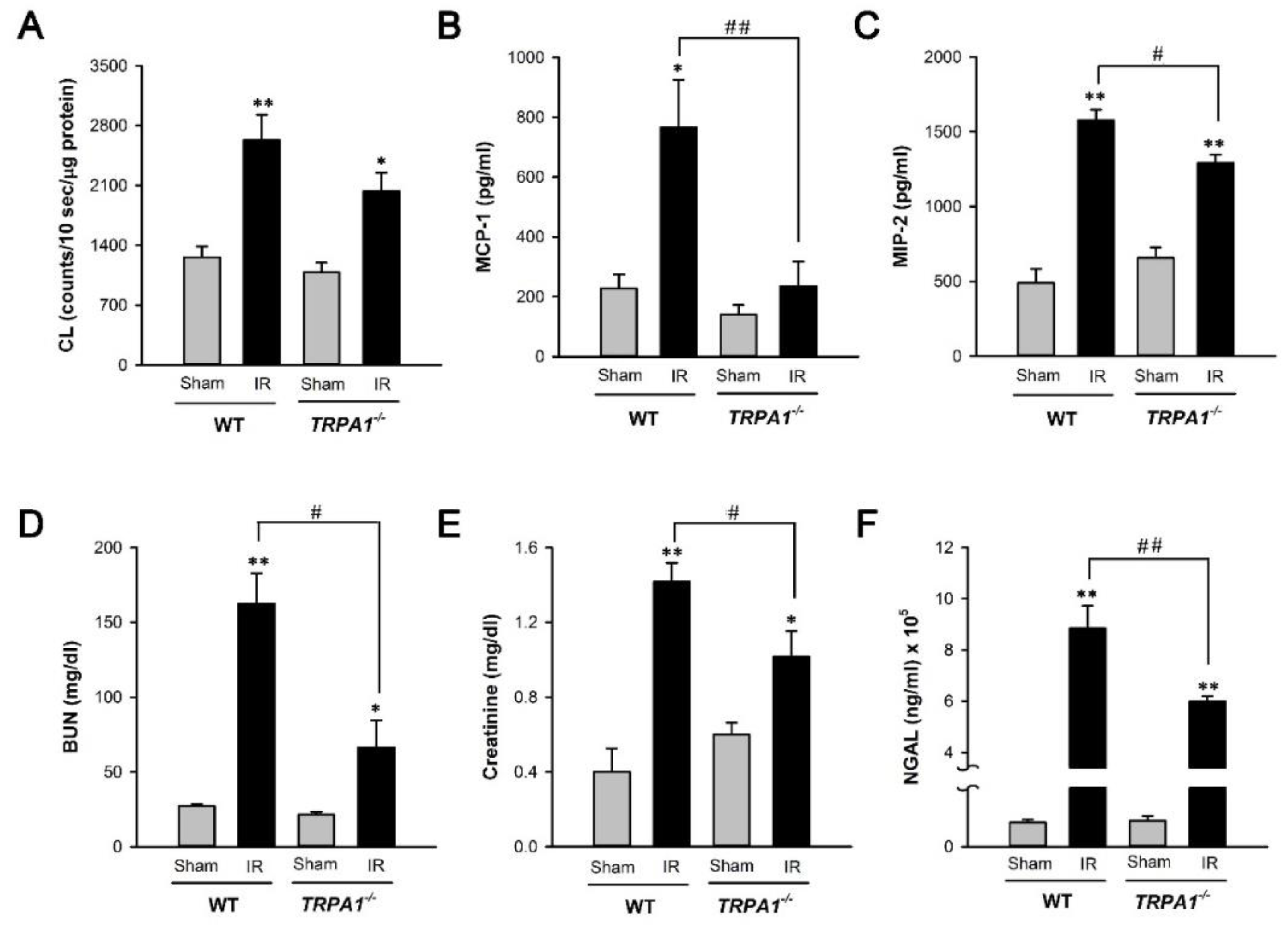
2.4. I/R-Induced Increase in Biomarker Levels of Renal Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Dysfunction, and Injury Is Alleviated in Trpa1−/− Mice
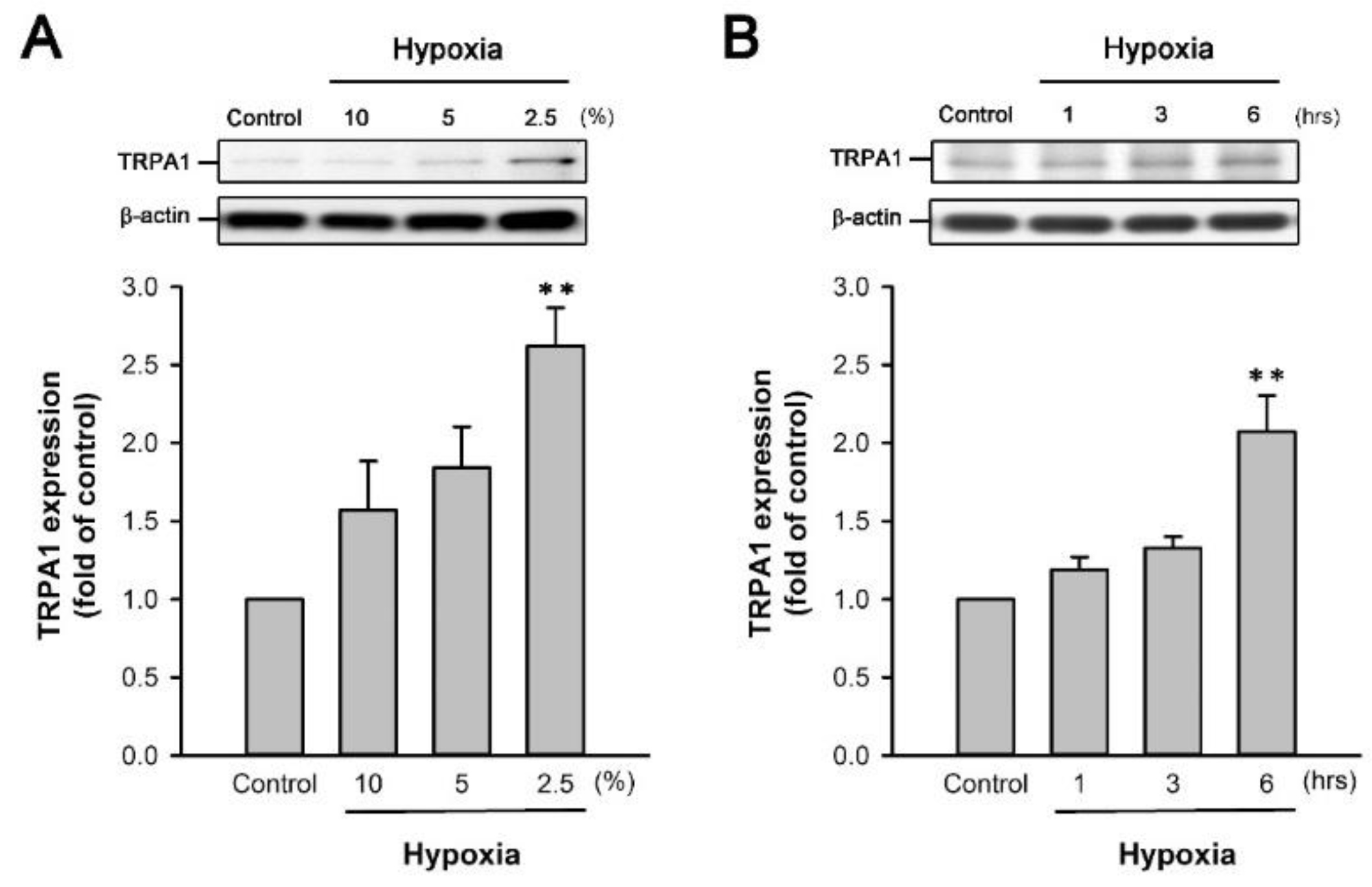
2.5. H/R Increases the TRPA1 Expression in HK-2 Cells
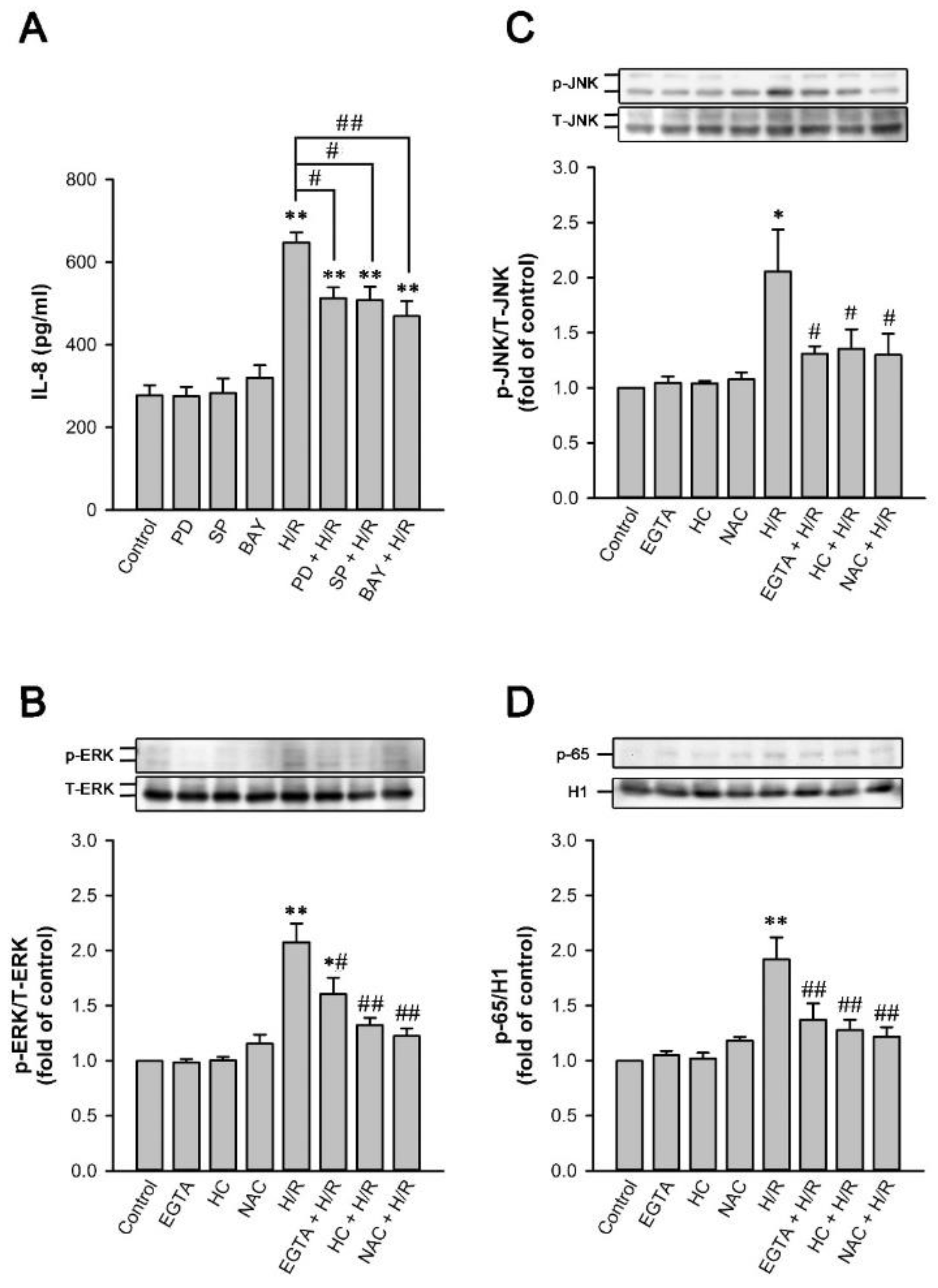
2.6. TRPA1 Mediates the Induction of IL-8 by H/R in HK-2 Cells
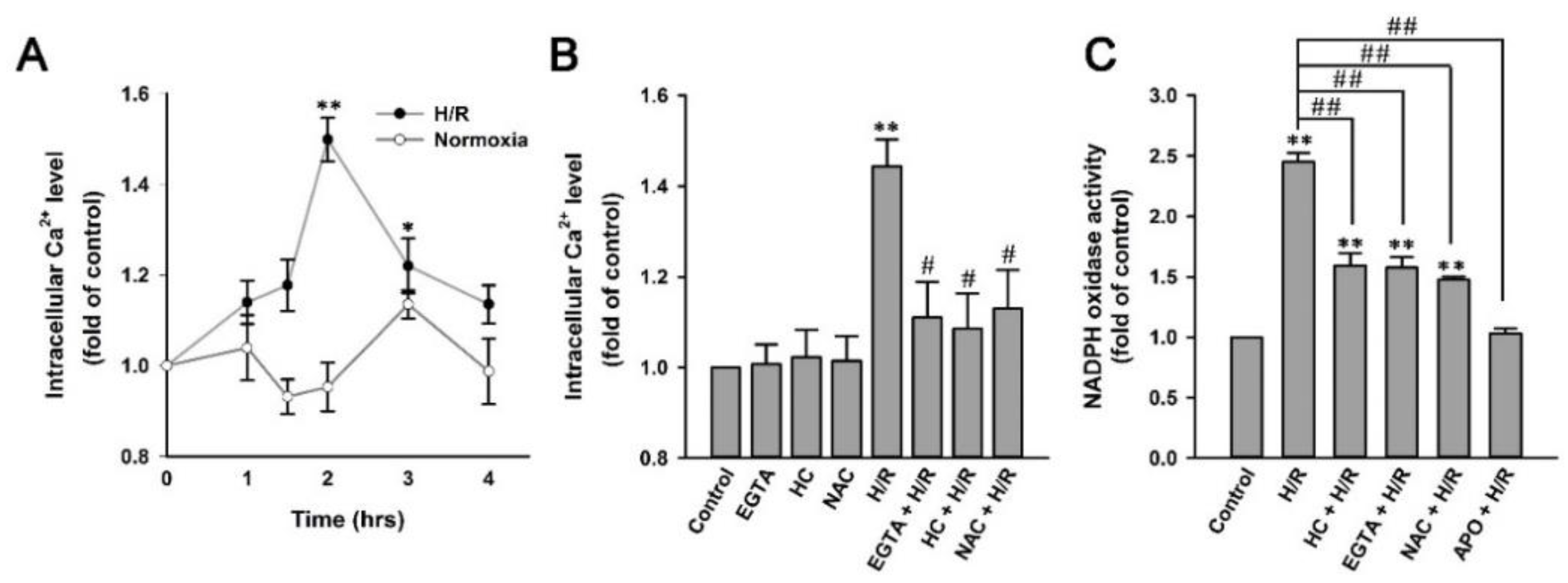
2.7. H/R Causes ROS-Dependent, TRPA1-Mediated Increases in Intracellular Ca2+ and NADPH Oxidase Activity in HK-2 Cells
2.8. H/R-Induced Intracellular ROS Increase via a ROS-Dependent, TRPA1-Mediated, and NOX-Released Pathway in HK-2 Cells
2.9. MAPKs/NF-κB Pathway Is Vital for the TRPA1-Mediated Induction of IL-8 by H/R in HK-2 Cells
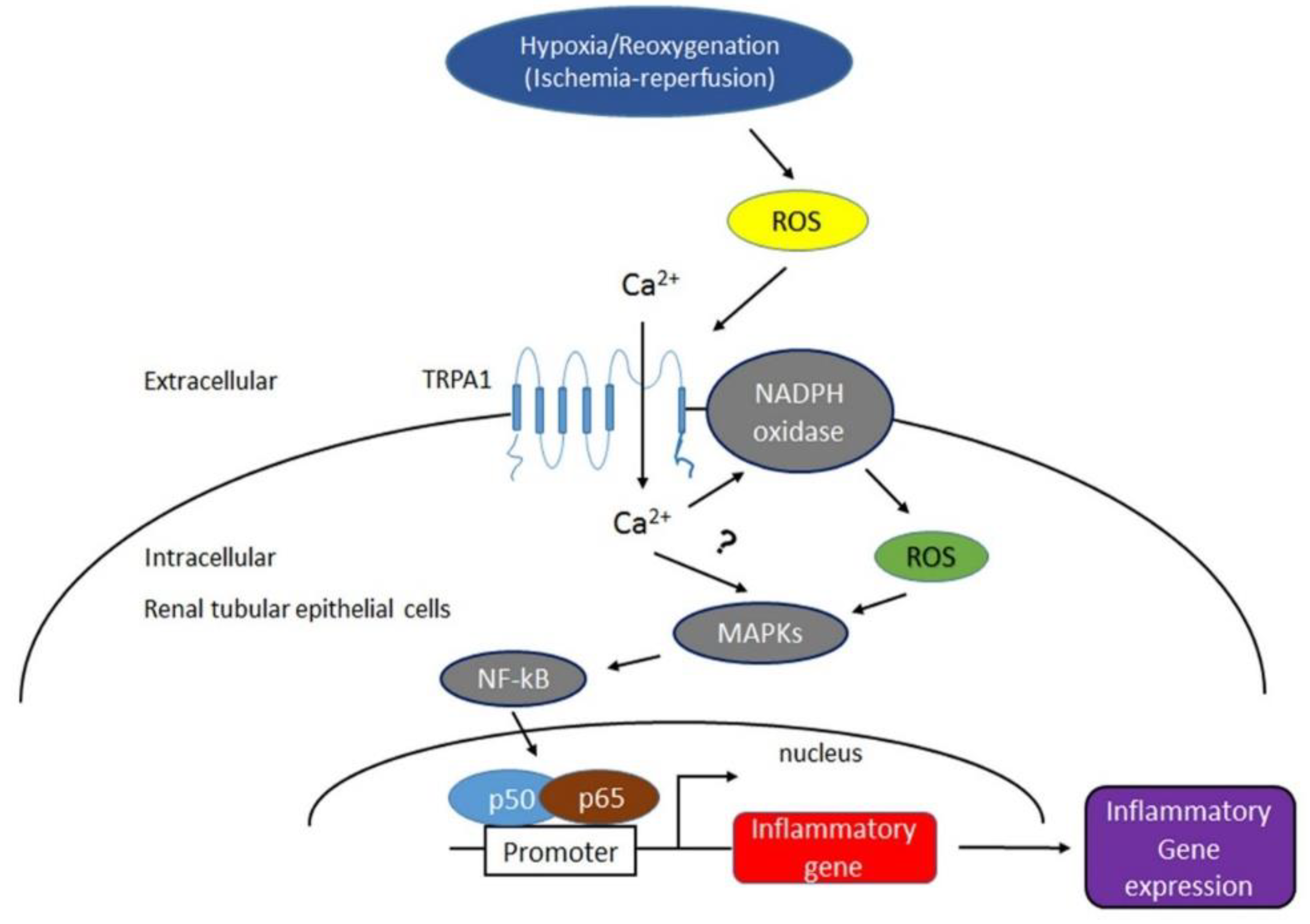
3. Discussion
4. Materials and methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Human Study
4.3. Animals and Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Model
4.4. Cell Culture and H/R Model
4.5. Histopathology and Tubular Injury Score
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Serum BUN and Creatinine
4.8. Tissue Superoxide Production
4.9. Inflammatory Chemokines and NGAL
4.10. Western Blot
4.11. siRNA Transfection
4.12. Intracellular Ca2+ Levels and NADPH Oxidase Activity
4.13. Detection of ROS by Flow Cytometry
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kusch, A.; Hoff, U.; Bubalo, G.; Zhu, Y.; Fechner, M.; Schmidt-Ullrich, R.; Marko, L.; Muller, D.N.; Schmidt-Ott, K.M.; Gurgen, D.; et al. Novel signalling mechanisms and targets in renal ischaemia and reperfusion injury. Acta Physiol. 2013, 208, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, M.; Nematbakhsh, M. Renal ischemia/reperfusion injury; from pathophysiology to treatment. J. Ren. Inj. Prev. 2015, 4, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.Y.; Chien, Y.; Chiou, G.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Chiou, C.H.; Tarng, D.C. Induced pluripotent stem cells without c-Myc attenuate acute kidney injury via downregulating the signaling of oxidative stress and inflammation in ischemia-reperfusion rats. Cell Transpl. 2012, 21, 2569–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rovcanin, B.; Medic, B.; Kocic, G.; Cebovic, T.; Ristic, M.; Prostran, M. Molecular Dissection of Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion: Oxidative Stress and Cellular Events. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 1965–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarng, D.C.; Tseng, W.C.; Lee, P.Y.; Chiou, S.H.; Hsieh, S.L. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Conditioned Medium Attenuates Acute Kidney Injury by Downregulating the Oxidative Stress-Related Pathway in Ischemia-Reperfusion Rats. Cell Transpl. 2016, 25, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thurman, J.M. Triggers of inflammation after renal ischemia/reperfusion. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 123, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basile, D.P.; Anderson, M.D.; Sutton, T.A. Pathophysiology of acute kidney injury. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 1303–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Nezu, M.; Souma, T.; Yu, L.; Suzuki, T.; Saigusa, D.; Ito, S.; Suzuki, N.; Yamamoto, M. Transcription factor Nrf2 hyperactivation in early-phase renal ischemia-reperfusion injury prevents tubular damage progression. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, H.; Xue, X.; Liu, G.; Guan, G.; Liu, H.; Sun, L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z. Nitro-oleic acid ameliorates oxygen and glucose deprivation/re-oxygenation triggered oxidative stress in renal tubular cells via activation of Nrf2 and suppression of NADPH oxidase. Free Radic. Res. 2016, 50, 1200–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altintas, R.; Polat, A.; Vardi, N.; Oguz, F.; Beytur, A.; Sagir, M.; Yildiz, A.; Parlakpinar, H. The protective effects of apocynin on kidney damage caused by renal ischemia/reperfusion. J. Endourol. 2013, 27, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, D.N.; Kvietys, P.R. Reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species: The evolution of a concept. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 524–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bedard, K.; Krause, K.H. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: Physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuichi, K.; Wada, T.; Kaneko, S.; Murphy, P.M. Roles of chemokines in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 4021–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Xiong, M.; Zeng, Y.; Sun, X.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z. Mechanistic studies of a novel mycophenolic acid-glucosamine conjugate that attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3503–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, K.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, D.W.; Han, D.; Noh, S.J.; Jung, H.S. Aminophylline Effect on Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Mice. Transpl. Proc. 2017, 49, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, C.; Zang, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, L.; Masucci, M.V.; Tang, J.; Li, X.; Liu, N.; Bayliss, G.; Zhao, T.C.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of Src kinase protects against acute kidney injury in a murine model of renal ischemia/reperfusion. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 31238–31253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Xu, J.; Feng, D.G.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.X.; Zhao, H. DUSP14 knockout accelerates cardiac ischemia reperfusion (IR) injury through activating NF-kappaB and MAPKs signaling pathways modulated by ROS generation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 501, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, D.; Na, N.; Li, H.; Miao, B.; Hong, L.; Huang, Z. Renoprotective effect of erythropoietin via modulation of the STAT6/MAPK/NF-kappaB pathway in ischemia/reperfusion injury after renal transplantation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bessac, B.F.; Sivula, M.; von Hehn, C.A.; Escalera, J.; Cohn, L.; Jordt, S.E. TRPA1 is a major oxidant sensor in murine airway sensory neurons. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viana, F. TRPA1 channels: Molecular sentinels of cellular stress and tissue damage. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 4151–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, D.A.; Gentry, C.; Moss, S.; Bevan, S. Transient receptor potential A1 is a sensory receptor for multiple products of oxidative stress. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 2485–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dembla, S.; Hasan, N.; Becker, A.; Beck, A.; Philipp, S.E. Transient receptor potential A1 channels regulate epithelial cell barriers formed by MDCK cells. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 1509–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanda, Y.; Yamasaki, Y.; Sasaki-Yamaguchi, Y.; Ida-Koga, N.; Kamisuki, S.; Sugawara, F.; Nagumo, Y.; Usui, T. TRPA1-dependent reversible opening of tight junction by natural compounds with an alpha,beta-unsaturated moiety and capsaicin. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, E.S.; Fernandes, M.A.; Keeble, J.E. The functions of TRPA1 and TRPV1: Moving away from sensory nerves. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nassini, R.; Pedretti, P.; Moretto, N.; Fusi, C.; Carnini, C.; Facchinetti, F.; Viscomi, A.R.; Pisano, A.R.; Stokesberry, S.; Brunmark, C.; et al. Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 channel localized to non-neuronal airway cells promotes non-neurogenic inflammation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, A.H.; Liu, M.H.; Ko, H.K.; Perng, D.W.; Lee, T.S.; Kou, Y.R. Lung Epithelial TRPA1 Transduces the Extracellular ROS into Transcriptional Regulation of Lung Inflammation Induced by Cigarette Smoke: The Role of Influxed Ca(2)(+). Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 148367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, S.; Geng, Y.; Song, Y. Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 protects against sepsis-induced kidney injury by modulating mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 4163–4172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, K.; Wang, P.; Wang, D.H. Knockout of TRPA1 exacerbates angiotensin II-induced kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2019, 317, F623–F631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, D.H. Knockout of Trpa1 exacerbates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury with classical activation of macrophages. Am. J. Hypertens. 2021, 34, 110–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, E.; Alegre, L.; Blanco-Sanchez, I.; Saenz-Morales, D.; Aguado-Fraile, E.; Ponte, B.; Ramos, E.; Saiz, A.; Jimenez, C.; Ordonez, A.; et al. Hypoxia inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1 alpha) is induced during reperfusion after renal ischemia and is critical for proximal tubule cell survival. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Dong, Z. Mouse model of ischemic acute kidney injury: Technical notes and tricks. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2012, 303, F1487–F1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basile, D.P.; Yoder, M.C. Renal endothelial dysfunction in acute kidney ischemia reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. Drug Targets. 2014, 14, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trevisan, G.; Benemei, S.; Materazzi, S.; De Logu, F.; De Siena, G.; Fusi, C.; Fortes Rossato, M.; Coppi, E.; Marone, I.M.; Ferreira, J.; et al. TRPA1 mediates trigeminal neuropathic pain in mice downstream of monocytes/macrophages and oxidative stress. Brain 2016, 139, 1361–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Logu, F.; Li Puma, S.; Landini, L.; Portelli, F.; Innocenti, A.; de Araujo, D.S.M.; Janal, M.N.; Patacchini, R.; Bunnett, N.W.; Geppetti, P.; et al. Schwann cells expressing nociceptive channel TRPA1 orchestrate ethanol-evoked neuropathic pain in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 5424–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Logu, F.; Nassini, R.; Materazzi, S.; Goncalves, M.C.; Nosi, D.; Degl’Innocenti, D.R.; Marone, I.M.; Ferreira, J.; Li Puma, S.; Benemei, S.; et al. Schwann cell TRPA1 mediates neuroinflammation that sustains macrophage-dependent neuropathic pain in mice. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conklin, D.J.; Guo, Y.; Nystoriak, M.A.; Jagatheesan, G.; Obal, D.; Kilfoil, P.J.; Hoetker, J.D.; Guo, L.; Bolli, R.; Bhatnagar, A. TRPA1 channel contributes to myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2019, 316, H889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Piplani, H.; McAllister, S.L.; Hurt, C.M.; Gross, E.R. Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 Activation within the Cardiac Myocyte Limits Ischemia-reperfusion Injury in Rodents. Anesthesiology 2016, 125, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, N.; Mizuno, Y.; Kozai, D.; Yamamoto, S.; Kiyonaka, S.; Shibata, T.; Uchida, K.; Mori, Y. Molecular characterization of TRPA1 channel activation by cysteine-reactive inflammatory mediators. Channels 2008, 2, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, M.Y.; Makino, A.; Yuan, J.X. Role of reactive oxygen species and redox in regulating the function of transient receptor potential channels. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1549–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ates, B.; Abraham, L.; Ercal, N. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging properties of N-acetylcysteine amide (NACA) and comparison with N-acetylcysteine (NAC). Free Radic. Res. 2008, 42, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, A.S.; Reese, S.R.; Wilson, N.A.; Jacobson, L.M.; Zhong, W.; Djamali, A. Nox2 is a mediator of ischemia reperfusion injury. Am. J. Transpl. 2015, 15, 2888–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, E.; Egido, J.; Rubio-Navarro, A.; Buendia, I.; Colio, L.M.B.; Toldos, O.; Manzarbeitia, F.; de Lorenzo, A.; Sanchez, R.; Ortiz, A.; et al. Oxidative stress, macrophage infiltration and CD163 expression are determinants of long-term renal outcome in macrohematuria-induced acute kidney injury of IgA nephropathy. Nephron. Clin. Pract. 2012, 121, c42–c53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Dusting, G.J. NADPH oxidase-mediated redox signaling: Roles in cellular stress response, stress tolerance, and tissue repair. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 218–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.B.; Tan, B.; Li, T.B.; Lou, Z.; Jiang, J.L.; Zhou, Y.J.; Yang, J.; Luo, X.J.; Peng, J. Protective effect of vitexin compound B-1 against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury in differentiated PC12 cells via NADPH oxidase inhibition. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2014, 387, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, C.; Donoso, P. Crosstalk between calcium and redox signaling: From molecular mechanisms to health implications. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 1275–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, E.M.; Lamont, J.D.; Xue, A.; Wylam, M.; Limper, A.H. Pneumocystis cell wall beta-glucan stimulates calcium-dependent signaling of IL-8 secretion by human airway epithelial cells. Respir. Res. 2010, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, R.; Chaudhari, S.; Li, W. Canonical Transient Receptor Potential 6 Channel: A New Target of Reactive Oxygen Species in Renal Physiology and Pathology. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 25, 732–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.L.; Xie, J.; An, S.W.; Oliver, N.; Barrezueta, N.X.; Lin, M.H.; Birnbaumer, L.; Huang, C.L. Inhibition of TRPC6 channels ameliorates renal fibrosis and contributes to renal protection by soluble klotho. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, G.; Wang, W.; Tadagavadi, R.K.; Briley, N.E.; Love, M.I.; Miller, B.A.; Reeves, W.B. TRPM2 mediates ischemic kidney injury and oxidant stress through RAC1. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4989–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yanarates, O.; Guven, A.; Sizlan, A.; Uysal, B.; Akgul, O.; Atim, A.; Ozcan, A.; Korkmaz, A.; Kurt, E. Ameliorative effects of proanthocyanidin on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Ren. Fail. 2008, 30, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Marko, L.; Kassmann, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, K.; Gollasch, M. Role of TRPV1 channels in ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, R.L.; Kellum, J.A.; Shah, S.V.; Molitoris, B.A.; Ronco, C.; Warnock, D.G.; Levin, A. Acute Kidney Injury, N., Acute Kidney Injury Network: Report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit. Care 2007, 11, R31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beg, A.A.; Finco, T.S.; Nantermet, P.V.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 lead to phosphorylation and loss of I kappa B alpha: A mechanism for NF-kappa B activation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 3301–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.-K.; Wu, C.-L.; Lee, T.-S.; Kou, Y.R.; Tarng, D.-C. Renal Tubular Epithelial TRPA1 Acts as An Oxidative Stress Sensor to Mediate Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Kidney Injury through MAPKs/NF-κB Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052309
Wu C-K, Wu C-L, Lee T-S, Kou YR, Tarng D-C. Renal Tubular Epithelial TRPA1 Acts as An Oxidative Stress Sensor to Mediate Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Kidney Injury through MAPKs/NF-κB Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(5):2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052309
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chung-Kuan, Chia-Lin Wu, Tzong-Shyuan Lee, Yu Ru Kou, and Der-Cherng Tarng. 2021. "Renal Tubular Epithelial TRPA1 Acts as An Oxidative Stress Sensor to Mediate Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Kidney Injury through MAPKs/NF-κB Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 5: 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052309
APA StyleWu, C.-K., Wu, C.-L., Lee, T.-S., Kou, Y. R., & Tarng, D.-C. (2021). Renal Tubular Epithelial TRPA1 Acts as An Oxidative Stress Sensor to Mediate Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Kidney Injury through MAPKs/NF-κB Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(5), 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052309







