Applications of Biomaterials in 3D Cell Culture and Contributions of 3D Cell Culture to Drug Development and Basic Biomedical Research
Abstract
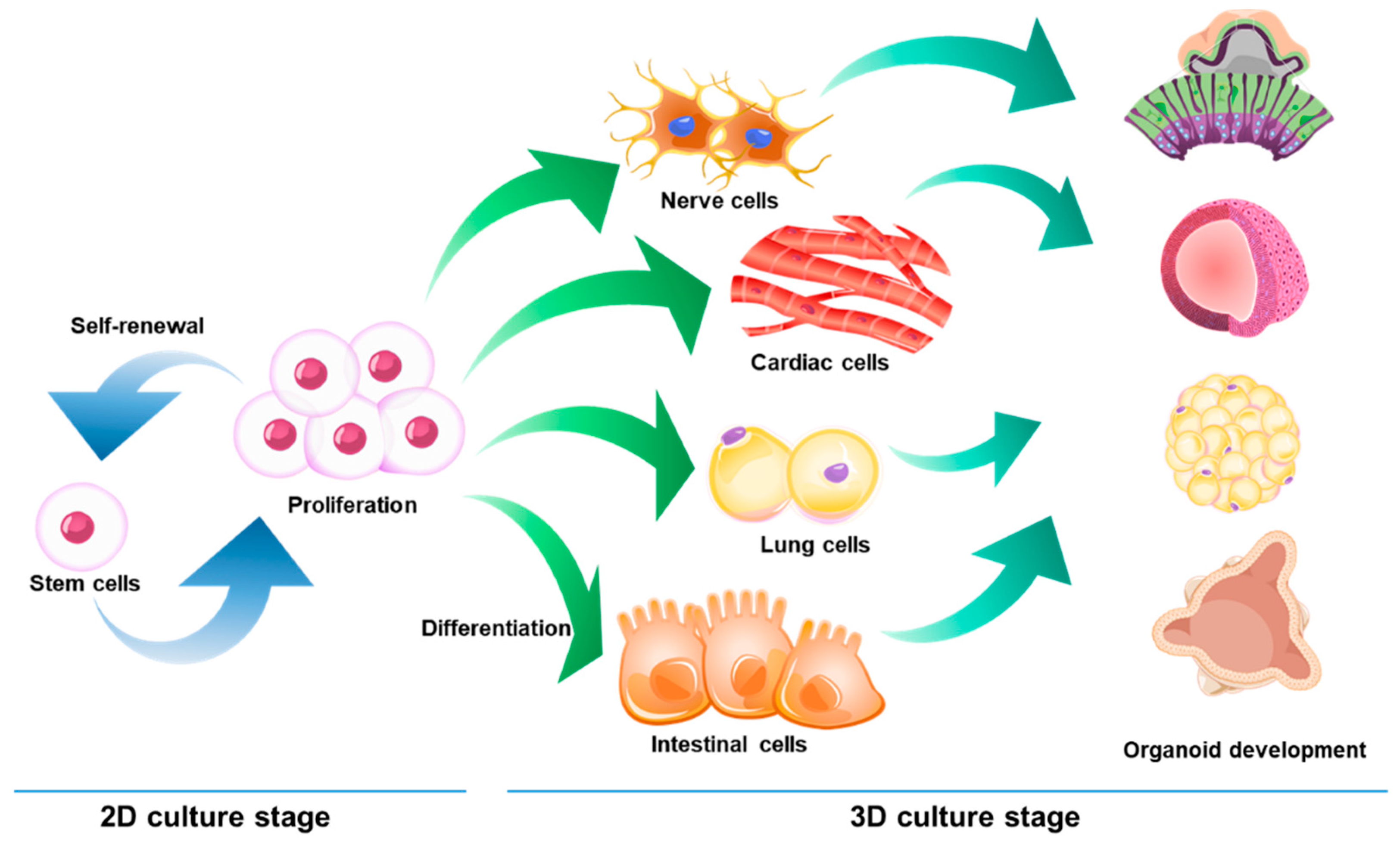
1. Introduction
2. Applications of Biomaterials in 3D Cell Culture
2.1. Hydrogels
2.2. Porous and Fibrous Scaffolds
2.3. Decellularized Native Tissue
2.4. Ultra-Low Attachment Surface
3. Applications of Three-Dimensional Cell Culture
3.1. Cancer Research and Drug Screening
3.2. Stem Cell Research and Drug Screening
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
| 2D | Two-dimensional |
| PHHs | Primary human hepatocytes |
| CYP450 | cytochrome P-450 |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| ULA | Ultra-low attachment |
| PVA | Poly (vinyl alcohol) |
| PLGA | Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) |
| pHEMA | Poly-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate |
| PEG | Poly ethylene glycol |
| RGD | Arginine-glycine-aspartic acid |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| PEG-SG | Four-arm succinimidyl glutarate polyethylene glycol |
| hMSC | Human mesenchymal stem cell |
| HUVEC | Human umbilical vein endothelial cell |
| hASC | Human adipose-derived stem cell |
| hiPSC-NPC | Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural progenitor cell |
| HA | Hyaluronic acid |
| bFGF | Basic fibroblast growth factor |
| AcHA | Acetylated HA |
| PGA | Poly (glycolic acid) |
| PLA | Poly (lactic acid) |
| PCL | Polycarprolactone |
| SCPL | Solvent casting & particulate leaching |
| TPZ | Tirapazamine |
| EB | Embryoid body |
| PSC | Pluripotent stem cell |
| ESC | Embryonic stem cell |
| iPSC | Induced pluripotent stem cell |
References
- Acosta, D.; Anuforo, D.C.; Smith, R.V. Cytotoxicity of acetaminophen and papaverine in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1980, 53, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharvand, H.; Hashemi, S.M.; Ashtiani, S.K.; Farrokhi, A. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into hepatocytes in 2D and 3D culture systems in vitro. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2006, 50, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, E.; Przyborski, S. Advances in 3D cell culture technologies enabling tissue-like structures to be created in vitro. J. Anat. 2015, 227, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.-P.; Li, X.-F.; Yu, F.-S.X. Corneal Organ Culture Model for Assessing Epithelial Responses to Surfactants. Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 58, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliari, S.R.; Burdick, J.A. A practical guide to hydrogels for cell culture. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepantafar, M.; Maheronnaghsh, R.; Mohammadi, H.; Radmanesh, F.; Hasani-Sadrabadi, M.M.; Ebrahimi, M.; Baharvand, H. Engineered Hydrogels in Cancer Therapy and Diagnosis. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, T.; Ghosh, S.; Potlapuvu, U.S.; Kona, L.; Kamaraju, S.R.; Sarkar, S.; Gaddam, S.; Chelluri, L.K. Proliferation and differentiation potential of human adipose-derived stem cells grown on chitosan hydrogel. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, B.R.; Durham, M.J.; Monckton, C.P.; Khetani, S.R. A Cell Culture Platform to Maintain Long-term Phenotype of Primary Human Hepatocytes and Endothelial Cells. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 5, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hira, V.V.V.; Breznik, B.; van Noorden, C.J.F.; Lah, T.; Molenaar, R.J. 2D and 3D in vitro assays to quantify the invasive behavior of glioblastoma stem cells in response to SDF-1α. BioTechniques 2020, 69, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noonan, J.; Grassia, G.; MacRitchie, N.; Garside, P.; Guzik, T.J.; Bradshaw, A.C.; Maffia, P. A Novel Triple-Cell Two-Dimensional Model to Study Immune-Vascular Interplay in Atherosclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, D.S.; Schwartz, M.P.; Durney, A.R.; Anseth, K.S. Small functional groups for controlled differentiation of hydrogel-encapsulated human mesenchymal stem cells. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, C.; Stewart, K.M.; Weaver, V.M. The extracellular matrix at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 4195–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbitt, M.W.; Anseth, K.S. Hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics for 3D cell culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 103, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikovsky, D.; Bianco-Peled, H.; Seliktar, D. The effect of structural alterations of PEG-fibrinogen hydrogel scaffolds on 3-D cellular morphology and cellular migration. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Jing, D.; Ding, J. A “room-temperature” injection molding/particulate leaching approach for fabrication of biodegradable three-dimensional porous scaffolds. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikici, B.A.; Claeyssens, F. Basic Principles of Emulsion Templating and Its Use as an Emerging Manufacturing Method of Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, N.C.; Hallam, D.; Karimi, A.; Mellough, C.B.; Chen, J.; Steel, D.H.W.; Lako, M. 3D culture of human pluripotent stem cells in RGD-alginate hydrogel improves retinal tissue development. Acta Biomater. 2017, 49, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, W.J.; Jongpaiboonkit, L.; Murphy, W.L. Influence of FGF2 and PEG hydrogel matrix properties on hMSC viability and spreading. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 93, 1110–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maximova, N.; Österberg, M.; Koljonen, K.; Stenius, P. Lignin adsorption on cellulose fibre surfaces: Effect on surface chemistry, surface morphology and paper strength. Cellulose 2001, 8, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochleitner, G.; Chen, F.; Blum, C.; Dalton, P.D.; Amsden, B.; Groll, J. Melt electrowriting below the critical translation speed to fabricate crimped elastomer scaffolds with non-linear extension behaviour mimicking that of ligaments and tendons. Acta Biomater. 2018, 72, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.E.; Azevedo, H.S.; Moreira, A.R.; Ellä, V.; Kellomäki, M.; Reis, R.L. Starch–poly(ε-caprolactone) and starch–poly(lactic acid) fibre-mesh scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applications: Structure, mechanical properties and degradation behaviour. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2008, 2, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Peng, G.; Lei, X.; Zhang, G.; Gao, Y. Decellularized liver matrix-modified chitosan fibrous scaffold as a substrate for C3A hepatocyte culture. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 1041–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Wang, Z.; Wan, X.; Weng, J.; Tu, M.; Mei, J.; Wang, Z.; Du, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, C. Crosslinking effects of branched PEG on decellularized lungs of rats for tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Appl. 2019, 34, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.A.; Lee, P.-F.; Barac, Y.; Hochman-Mendez, C.; Sampaio, L.C. Decellularization of whole hearts for cardiac regeneration. Emerg. Technol. Heart Dis. 2020, 1, 291–310. [Google Scholar]
- DeQuach, J.A.; Yuan, S.H.; Goldstein, L.S.B.; Christman, K.L. Decellularized Porcine Brain Matrix for Cell Culture and Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Part A 2011, 17, 2583–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.; Jung, Y.; Kim, S.H. Decellularized heart ECM hydrogel using supercritical carbon dioxide for improved angiogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2018, 67, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomomi, G.; Otsuji, J.; Bin, A.; Yoshimura, M.; Tomura, D.; Tateyama, I.; Minami, Y.; Yoshikawa, K.; Aiba, J.E.; Heuser, T.; et al. A 3D Sphere Culture System Containing Functional Polymers for Large-Scale Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Production. Stem Cell Rep. 2014, 2, 734–745. [Google Scholar]
- Howes, L.; Richardson, R.D.; Finlay, D.; Vuori, K. 3-Dimensional culture systems for anti-cancer compound profiling and high-throughput screening reveal increases in EGFR inhibitor-mediated cytotoxicity compared to monolayer culture systems. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesarz, Z.; Tamama, K. Spheroid Culture of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 9176357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.S.; Zhou, X.; Han, J.; Huang, C.Y.; Nashed, A.; Khatri, S.; Mattson, G.; Fukunishi, T.; Zhang, H.; Hibino, N. In vivo therapeutic applications of cell spheroids. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, C.; Davidson, M.D.; Burdick, J.A. 3D bioprinting of high cell-density heterogeneous tissue models through spheroid fusion within self-healing hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caló, E.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Biomedical applications of hydrogels: A review of patents and commercial products. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 65, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.J.; Rowley, J.; Kong, H.J. Hydrogels used for cell-based drug delivery. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 87, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senol, S.; Akyol, E. Preparation and characterization of pH-sensitive hydrogels from photo-crosslinked poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate incorporating titanium dioxide. Mater. Sci. Pol. 2020, 38, 443–449. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, S.; Stowers, R.; Lou, J.; Xia, Y.; Chaudhuri, O. Varying PEG density to control stress relaxation in alginate-PEG hydrogels for 3D cell culture studies. Biomaterials 2019, 200, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampe, K.J.; Mooney, R.G.; Bjugstad, K.B.; Mahoney, M.J. Effect of macromer weight percent on neural cell growth in 2D and 3D nondegradable PEG hydrogel culture. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 94A, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, B.; Xiang, J.; Cui, Z.; Qu, X.; Qiu, D.; Tian, Y.; Yang, Z. Ultra-tough injectable cytocompatible hydrogel for 3D cell culture and cartilage repair. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muduli, S.; Chen, L.-H.; Li, M.-P.; Heish, Z.-w.; Liu, C.-H.; Kumar, S.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Munusamy, M.A.; Benelli, G.; Murugan, K.; et al. Stem cell culture on polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels having different elasticity and immobilized with ECM-derived oligopeptides. J. Polym. Eng. 2017, 37, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, M.F.; Carvalho, N.M.S.; Rodrigues, A.A.; Bavaresco, V.P.; Jardini, A.L.; Maciel, M.R.W.; Filho, R.M. PHEMA Hydrogels Obtained by Infrared Radiation for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 2019, 4249581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, U.; Zhou, H.; Shikanov, A. Synthetic PEG Hydrogel for Engineering the Environment of Ovarian Follicles. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1758, 115–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Yu, L.; Ding, J. Enzymatically cross-linked hydrogels based on a linear poly(ethylene glycol) analogue for controlled protein release and 3D cell culture. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 6067–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrée, B.; Ichanti, H.; Kalies, S.; Heisterkamp, A.; Strauß, S.; Vogt, P.-M.; Haverich, A.; Hilfiker, A. Formation of three-dimensional tubular endothelial cell networks under defined serum-free cell culture conditions in human collagen hydrogels. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hached, F.; Vinatier, C.; Pinta, P.-G.; Hulin, P.; le Visage, C.; Weiss, P.; Guicheux, J.; Billon-Chabaud, A.; Grimandi, G. Polysaccharide Hydrogels Support the Long-Term Viability of Encapsulated Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Ability to Secrete Immunomodulatory Factors. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 9303598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, J.P.; Hynd, M.R.; Shuler, M.L.; Shain, W. Fabrication and optimization of alginate hydrogel constructs for use in 3D neural cell culture. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 6, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Xu, R.; Duan, B.; Jiang, P. Three-dimensional hyaluronic acid hydrogel-based models for in vitro human iPSC-derived NPC culture and differentiation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3870–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, A.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, T.; Ji, L.; Qian, J. Dual-degradable and injectable hyaluronic acid hydrogel mimicking extracellular matrix for 3D culture of breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 211, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Z.; Xian, C.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, G.; Wu, J. Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogels with Enhanced Mechanical Performances: Preparation, Structure, and Property. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-B.; Polio, S.; Lee, W.; Dai, G.; Menon, L.; Carroll, R.S.; Yoo, S.-S. Bio-printing of collagen and VEGF-releasing fibrin gel scaffolds for neural stem cell culture. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 223, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Stowers, R.; Nam, S.; Xia, Y.; Chaudhuri, O. Stress relaxing hyaluronic acid-collagen hydrogels promote cell spreading, fiber remodeling, and focal adhesion formation in 3D cell culture. Biomaterials 2018, 154, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, K.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, S.J. Selective lithium and magnesium adsorption by phosphonate metal-organic framework-incorporated alginate hydrogel inspired from lithium adsorption characteristics of brown algae. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Javed, F.; Zakaria, M.R.; Jamila, D.N.; Khattak, R.; Khan, A.; Akil, H.M. Determining the Molecular-weight and interfacial properties of chitosan built nanohydrogel for controlled drug delivery applications. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2019, 9, 4452–4457. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, F.; Javed, F.; Khan, A.; Kudus, M.; Jamila, N.; Minhaz, A.; Akil, H. Synthesis and surface modification of chitosan built nanohydrogel with antiviral and antimicrobial agent for controlled drug delivery. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2019, 9, 4439–4445. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-S.; Kim, T.H.; Kang, D.L.; Baek, S.Y.; Lee, Y.; Koh, Y.-G.; Kim, Y.I. Chondrogenic differentiation of human ASCs by stiffness control in 3D fibrin hydrogel. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 522, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraj, K.A.; van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Daamen, W.F. Construction of Collagen Scaffolds That Mimic the Three-Dimensional Architecture of Specific Tissues. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 2387–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.-K.; Li, S.-Y.; Liao, K.; Wang, Z.-J.; Guo, Y.-L.; Tang, L.-S.; Tang, S.-B.; Ma, J.; Chen, J.-S. Characteristics of neural growth and cryopreservation of the dorsal root ganglion using three-dimensional collagen hydrogel culture vs. conventional culture. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 1856–1864. [Google Scholar]
- Smeriglio, P.; Dhulipala, L.; Lai, J.H.; Goodman, S.B.; Dragoo, J.L.; Smith, R.L.; Maloney, W.J.; Yang, F.; Bhutani, N. Collagen VI Enhances Cartilage Tissue Generation by Stimulating Chondrocyte Proliferation. Tissue Eng. Part A 2014, 21, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachence, J.M. Collagen-based devices for soft tissue repair. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1996, 33, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benea, H.; Tomoaia, G.; Soritau, O.; Pasca, R.D. A Review on the Reconstruction of Articular Cartilage Using Collagen Scaffolds. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 21, 11735–11743. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, G.-Z.; Kim, H.-W. Effects of Type I Collagen Concentration in Hydrogel on the Growth and Phenotypic Expression of Rat Chondrocytes. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 14, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaddon, M.; Burrows, M.; Ferreira, S.A.; Dazzi, F.; Apperley, J.F.; Bradshaw, A.; Brand, D.D.; Czernuszka, J.; Gentleman, E. Monomeric, porous type II collagen scaffolds promote chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilmer, C.E.; Battistoni, C.M.; Cox, A.; Breur, G.J.; Panitch, A.; Liu, J.C. Collagen Type I and II Blend Hydrogel with Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cells as a Scaffold for Articular Cartilage Defect Repair. Acs Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 3464–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irawan, V.; Sung, T.-C.; Higuchi, A.; Ikoma, T. Collagen Scaffolds in Cartilage Tissue Engineering and Relevant Approaches for Future Development. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 15, 673–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Puyana, V.; Romero, A.; Guerrero, A. Influence of collagen concentration and glutaraldehyde on collagen-based scaffold properties. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2016, 104, 1462–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, L.-M.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, D.; Jiang, Y.-Q.; Xu, N.-W.; Zhao, G.-Y.; Wei, H.; Zhou, S.-Y.; Han, H.; Han, L. The effect of different cross-linking conditions of EDC/NHS on type II collagen scaffolds: An in vitro evaluation. Cell Tissue Bank. 2019, 20, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotz, C.; Schmid, F.F.; Oechsle, E.; Monaghan, M.G.; Walles, H.; Groeber-Becker, F. Cross-linked Collagen Hydrogel Matrix Resisting Contraction To Facilitate Full-Thickness Skin Equivalents. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 20417–20425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Koenig, A.M.; Sloan, P.; Leipzig, N.D. In vivo assessment of guided neural stem cell differentiation in growth factor immobilized chitosan-based hydrogel scaffolds. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 9049–9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.-J.; Liu, X.-Y.; Yang, X.-P.; An, X.-W.; Liang, J.; Dong, H.-J.; Jiang, W.; et al. 3D printing collagen/chitosan scaffold ameliorated axon regeneration and neurological recovery after spinal cord injury. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107, 1898–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, M.; Su, D.; Ma, Q.; Lv, G.; Chen, J. In situ formed collagen-hyaluronic acid hydrogel as biomimetic dressing for promoting spontaneous wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 101, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodney, M.S.; Wysolmerski, R.B. Isometric contraction by fibroblasts and endothelial cells in tissue culture: A quantitative study. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 117, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, R.D.; Berry, M.G.; Navsaria, H.A. Hyaluronic acid: The scientific and clinical evidence. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2007, 60, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Du, G.; Chen, J. Microbial production of hyaluronic acid: Current state, challenges, and perspectives. Microb. Cell Factories 2011, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Gojgini, S.; Lam, J.; Segura, T. The spreading, migration and proliferation of mouse mesenchymal stem cells cultured inside hyaluronic acid hydrogels. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidlits, S.K.; Khaing, Z.Z.; Petersen, R.R.; Nickels, J.D.; Vanscoy, J.E.; Shear, J.B.; Schmidt, C.E. The effects of hyaluronic acid hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties on neural progenitor cell differentiation. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3930–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Katakami, C. The effect of hyaluronic acid on corneal epithelial cell proliferation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1993, 34, 2313–2315. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.-W.E.; Pedron, S.; Shyu, P.; Hu, Y.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Harley, B.A.C. Influence of Hyaluronic Acid Transitions in Tumor Microenvironment on Glioblastoma Malignancy and Invasive Behavior. Front. Mater. 2018, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boregowda, R.K.; Appaiah, H.N.; Siddaiah, M.; Kumarswamy, S.B.; Sunila, S.; Thimmaiah, K.N.; Mortha, K.; Toole, B.; Banerjee, S.D. Expression of hyaluronan in human tumor progression. J. Carcinog. 2006, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmann, V.; Fieber, C.; Herrlich, P.; Hofmann, M.; Termeer, C.C.; Ahrens, T.; Simon, J.C. CD44 is the Principal Mediator of Hyaluronic-Acid-Induced Melanoma Cell Proliferation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucatariu, S.-M.; Constantin, M.; Varganici, C.-D.; Rusu, D.; Nicolescu, A.; Prisacaru, I.; Carnuta, M.; Anghelache, M.; Calin, M.; Ascenzi, P.; et al. A new sponge-type hydrogel based on hyaluronic acid and poly(methylvinylether-alt-maleic acid) as a 3D platform for tumor cell growth. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2528–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häckel, S.; Zolfaghar, M.; Du, J.; Hoppe, S.; Benneker, L.M.; Garstka, N.; Peroglio, M.; Alini, M.; Grad, S.; Yayon, A.; et al. Fibrin-Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel (RegenoGel) with Fibroblast Growth Factor-18 for In Vitro 3D Culture of Human and Bovine Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Kang, E.; Kang, S.-W.; Huh, K.M. Thermo-irreversible glycol chitosan/hyaluronic acid blend hydrogel for injectable tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 244, 116432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Zhu, N.; Mohabatpour, F.; Sarker, M.D.; Schreyer, D.J.; Chen, X. Bioprinting Schwann cell-laden scaffolds from low-viscosity hydrogel compositions. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 4538–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, O.; Gu, L.; Klumpers, D.; Darnell, M.; Bencherif, S.A.; Weaver, J.C.; Huebsch, N.; Lee, H.-P.; Lippens, E.; Duda, G.N.; et al. Hydrogels with tunable stress relaxation regulate stem cell fate and activity. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huebsch, N.; Arany, P.R.; Mao, A.S.; Shvartsman, D.; Ali, O.A.; Bencherif, S.A.; Rivera-Feliciano, J.; Mooney, D.J. Harnessing traction-mediated manipulation of the cell/matrix interface to control stem-cell fate. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Iwanaga, S.; Henmi, C.; Arai, K.; Nishiyama, Y. Biomatrices and biomaterials for future developments of bioprinting and biofabrication. Biofabrication 2010, 2, 014110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, T.; Gillispie, G.J.; Copus, J.S.; Pr, A.K.; Seol, Y.-J.; Atala, A.; Yoo, J.J.; Lee, S.J. Optimization of gelatin–alginate composite bioink printability using rheological parameters: A systematic approach. Biofabrication 2018, 10, 034106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Richards, D.J.; Pollard, S.; Tan, Y.; Rodriguez, J.; Visconti, R.P.; Trusk, T.C.; Yost, M.J.; Yao, H.; Markwald, R.R.; et al. Engineering alginate as bioink for bioprinting. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4323–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagpulinsa, D.A.; Cao, J.J.L.; Driscoll, R.K.; Sîrbulescu, R.F.; Penson, M.F.E.; Sremac, M.; Engquist, E.N.; Brauns, T.A.; Markmann, J.F.; Melton, D.A.; et al. Alginate-microencapsulation of human stem cell–derived β cells with CXCL12 prolongs their survival and function in immunocompetent mice without systemic immunosuppression. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19, 1930–1940. [Google Scholar]
- De Vos, P.; Faas, M.M.; Strand, B.; Calafiore, R. Alginate-based microcapsules for immunoisolation of pancreatic islets. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5603–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, A.; Manzoli, V.; de Toni, T.; Abreu, M.M.; Poh, Y.-C.; Ye, L.; Roose, A.; Pagliuca, F.W.; Thanos, C.; Ricordi, C.; et al. Conformal Coating of Stem Cell-Derived Islets for β Cell Replacement in Type 1 Diabetes. Stem Cell Rep. 2020, 14, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Kisaalita, W.S. Exploring cellular adhesion and differentiation in a micro-/nano-hybrid polymer scaffold. Biotechnol. Prog. 2010, 26, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, T.; Schinkel, G.; Lendlein, A. Design and preparation of polymeric scaffolds for tissue engineering. Expert Rev. Med Devices 2006, 3, 835–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Nguyen, T.P.; Pham, V.H.; Hoang, G.; Manivasagan, P.; Kim, M.H.; Nam, S.Y.; Oh, J. Hydroxyapatite nano bioceramics optimized 3D printed poly lactic acid scaffold for bone tissue engineering application. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 3443–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, H.; Lisar, H.A.; Kashi, T.S.J.; Tahriri, M.; Ansari, M.; Rafiei, T.; Bastami, F.; Shahin-Shamsabadi, A.; Abbas, F.M.; Tayebi, L. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)(PLGA)/TiO2 nanotube bioactive composite as a novel scaffold for bone tissue engineering: In vitro and in vivo studies. Biologicals 2018, 53, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.M.T.; Monajjemi, M.; Mollaamin, F.; Dang, C. Simulation & modelling of dilute solutions in drop-on-demand inkjet printing: A review. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2019, 9, 4474–4484. [Google Scholar]
- Trakoolwannachai, V.; Kheolamai, P.; Ummartyotin, S. Characterization of hydroxyapatite from eggshell waste and polycaprolactone (PCL) composite for scaffold material. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2019, 173, 106974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri-Hosseinabadi, Z.; Mesbah-Namin, S.A.; Salehinejad, P.; Seyedi, F. Fibrin scaffold could promote survival of the human adipose-derived stem cells during differentiation into cardiomyocyte-like cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 372, 571–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Chen, Y.; Gu, Y.; Tang, C.; Huang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Ran, J.; Heng, B.; Chen, X.; et al. A collagen-coated sponge silk scaffold for functional meniscus regeneration. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 13, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thadavirul, N.; Pavasant, P.; Supaphol, P. Development of polycaprolactone porous scaffolds by combining solvent casting, particulate leaching, and polymer leaching techniques for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2014, 102, 3379–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, D.; Miao, X.; Liu, G.; Wei, F.; Chadwick, G.; Yan, C.; Friis, T. Polyurethane (PU) scaffolds prepared by solvent casting/particulate leaching (SCPL) combined with centrifugation. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 30, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Bismarck, A.; Steinke, J.H.G. Ion-responsive alginate based macroporous injectable hydrogel scaffolds prepared by emulsion templating. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 4736–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.; Pal, J.; Nandan, B.; Srivastava, R.K. Macroporous scaffolds of cross-linked Poly(ɛ-caprolactone) via high internal phase emulsion templating. Polymer 2019, 176, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, A.; Oliviero, M.; Di Maio, E.; Iannace, S.; Netti, P.A. Design of porous polymeric scaffolds by gas foaming of heterogeneous blends. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 20, 2043–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, T.-Y.; Kook, M.-S.; Jung, S.-C.; Kim, B.-H. Biological Effect of Gas Plasma Treatment on CO2 Gas Foaming/Salt Leaching Fabricated Porous Polycaprolactone Scaffolds in Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 657542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Annabi, N.; Khademhosseini, A.; Dehghani, F. Fabrication of porous chitosan scaffolds for soft tissue engineering using dense gas CO2. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.E.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Malafaya, P.B.; Reis, R.L.; Cunha, A.M. A new approach based on injection moulding to produce biodegradable starch-based polymeric scaffolds: Morphology, mechanical and degradation behaviour. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ayoubi, R.; Eliopoulos, N.; Diraddo, R.; Galipeau, J.; Yousefi, A.-M. Design and Fabrication of 3D Porous Scaffolds to Facilitate Cell-Based Gene Therapy. Tissue Eng. Part A 2008, 14, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfield, W. Designing porous scaffolds for tissue engineering. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2006, 364, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, M.; Sankar, R.; Katiyar, V. State of Art on Solvent Casting Particulate Leaching Method for Orthopedic ScaffoldsFabrication. Mater. Today 2017, 4, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Pu, X.; Liao, X.; Huang, Z.; Yin, G. A novel akermanite/poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) porous composite scaffold fabricated via a solvent casting-particulate leaching method improved by solvent self-proliferating process. Regen. Biomater. 2017, 4, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Lang, M. Hepatocyte culture on 3D porous scaffolds of PCL/PMCL. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 173, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.-H.; Kim, A.J.; Park, J.Y.; Yi, N.; Kang, I.; Park, J.; Rhie, J.-W.; Cho, D.-W. Effect of solid freeform fabrication-based polycaprolactone/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/collagen scaffolds on cellular activities of human adipose-derived stem cells and rat primary hepatocytes. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 24, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Riesco, R.; Boyer, L.; Blosse, S.; Lefebvre, P.M.; Assemat, P.; Leichle, T.; Accardo, A.; Malaquin, L. Water-in-PDMS Emulsion Templating of Highly Interconnected Porous Architectures for 3D Cell Culture. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 28631–28640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, X.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Liu, C.; Yang, X. Biomimetic porous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 80, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemon, G.; Waters, S.L.; Rose, F.R.A.J.; King, J.R. Mathematical modelling of human mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and differentiation inside artificial porous scaffolds. J. Theor. Biol. 2007, 249, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Boughton, P.; Rose, B.; Lee, C.S.; Hong, A.M. The Use of Porous Scaffold as a Tumor Model. Int. J. Biomater. 2013, 2013, 396056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dar, A.; Shachar, M.; Leor, J.; Cohen, S. Optimization of cardiac cell seeding and distribution in 3D porous alginate scaffolds. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2002, 80, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardila, D.C.; Tamimi, E.; Doetschman, T.; Wagner, W.R.; Geest, J.P.V. Modulating smooth muscle cell response by the release of TGFβ2 from tubular scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2019, 299, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, T.; Ren, J.; Jia, X.; Pan, K. The bone formation in vitro and mandibular defect repair using PLGA porous scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2005, 74A, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.J.; Lam, C.F.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, W.L.; Li, C.F.; Lin, Y.T.; Yeh, M.L. Transplantation of autologous endothelial progenitor cells in porous PLGA scaffolds create a microenvironment for the regeneration of hyaline cartilage in rabbits. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloise, N.; Berardi, E.; Gualandi, C.; Zaghi, E.; Gigli, M.; Duelen, R.; Ceccarelli, G.; Cortesi, E.E.; Costamagna, D.; Bruni, G.; et al. Ether-Oxygen Containing Electrospun Microfibrous and Sub-Microfibrous Scaffolds Based on Poly(butylene 1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylate) for Skeletal Muscle Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacQueen, L.A.; Alver, C.G.; Chantre, C.O.; Ahn, S.; Cera, L.; Gonzalez, G.M.; O’Connor, B.B.; Drennan, D.J.; Peters, M.M.; Motta, S.E.; et al. Muscle tissue engineering in fibrous gelatin: Implications for meat analogs. NPJ Sci. Food 2019, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.R.; Kim, J.I.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. The controlled design of electrospun PCL/silk/quercetin fibrous tubular scaffold using a modified wound coil collector and L-shaped ground design for neural repair. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, A.; Huang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Li, P.; Liu, M.; Fan, Y. Aligned graphene/silk fibroin conductive fibrous scaffolds for guiding neurite outgrowth in rat spinal cord neurons. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, J.; Brennan, D.; Beachley, V.; Kothapalli, C.R. Cardiomyogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell spheroids within electrospun collagen nanofiber mats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2018, 106, 3303–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damaraju, S.M.; Shen, Y.; Elele, E.; Khusid, B.; Eshghinejad, A.; Li, J.; Jaffe, M.; Arinzeh, T.L. Three-dimensional piezoelectric fibrous scaffolds selectively promote mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Biomaterials 2017, 149, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, A.; Nadri, S.; Kazemi, H.S.; Mortazavi, Y.; Sojoodi, M. Conductive electrospun scaffolds with electrical stimulation for neural differentiation of conjunctiva mesenchymal stem cells. Artif. Organs 2019, 43, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, M.; Eichholz, K.F.; Hoey, D.A. The effect of pore size within fibrous scaffolds fabricated using melt electrowriting on human bone marrow stem cell osteogenesis. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 14, 065016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birhanu, G.; Javar, H.A.; Seyedjafari, E.; Zandi-Karimi, A.; Telgerd, M.D. An improved surface for enhanced stem cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation using electrospun composite PLLA/P123 scaffold. Artif. CellsNanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, E.D.; Wnek, G.E.; Simpson, D.G.; Pawlowski, K.J.; Bowlin, G.L. Tailoring tissue engineering scaffolds using electrostatic processing techniques: A study of poly(glycolic acid) electrospinning. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2001, 38, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberli, D.; Filho, L.F.; Atala, A.; Yoo, J.J. Composite scaffolds for the engineering of hollow organs and tissues. Methods 2009, 47, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartuqui, J.; D’Elía, N.L.; Ercoli, D.; de Alcazar, D.S.; Cortajarena, A.L.; Messina, P.V. Mechanical performance of gelatin fiber mesh scaffolds reinforced with nano-hydroxyapatite under bone damage mechanisms. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 19, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Oh, S.H.; Liu, J.; Soker, S.; Atala, A.; Yoo, J.J. The use of thermal treatments to enhance the mechanical properties of electrospun poly(ɛ-caprolactone) scaffolds. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1422–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, V.; Evrova, O.; Hoerstrup, S.P.; Vogel, V. A Simple Modification Method to Obtain Anisotropic and Porous 3D Microfibrillar Scaffolds for Surgical and Biomedical Applications. Small 2018, 14, 1702650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Nagata, F.; Kato, K.; Nakano, T. Bone apatite anisotropic structure control via designing fibrous scaffolds. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 13500–13506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.S.; Park, T.G. Porous biodegradable polymeric scaffolds prepared by thermally induced phase separation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 47, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Cai, Q.; Yang, J.; Wan, Y.; Bei, J.; Wang, S. The fabrication and characterization of poly(lactic acid) scaffolds for tissue engineering by improved solid–liquid phase separation. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2003, 14, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gelain, F.; Zhao, X. Designer self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffolds for 3D tissue cell cultures. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2005, 15, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Ma, J.; Zhu, L.; Morsi, Y.; Ei-Hamshary, H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Mo, X. Superelastic, superabsorbent and 3D nanofiber-assembled scaffold for tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 142, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Nagrath, D.; Chen, P.C.; Berthiaume, F.; Yarmush, M.L. Three-Dimensional Primary Hepatocyte Culture in Synthetic Self-Assembling Peptide Hydrogel. Tissue Eng. Part A 2008, 14, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galler, K.M.; Cavender, A.; Yuwono, V.; Dong, H.; Shi, S.; Schmalz, G.; Hartgerink, J.D.; D’Souza, R.N. Self-Assembling Peptide Amphiphile Nanofibers as a Scaffold for Dental Stem Cells. Tissue Eng. Part A 2008, 14, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorvaldsson, A.; Stenhamre, H.; Gatenholm, P.; Walkenström, P. Electrospinning of Highly Porous Scaffolds for Cartilage Regeneration. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Lim, C.T.; Ramakrishna, S.; Huang, Z.-M. Electrospinning of gelatin fibers and gelatin/PCL composite fibrous scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2005, 72B, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannutti, J.; Reneker, D.; Ma, T.; Tomasko, D.; Farson, D. Electrospinning for tissue engineering scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Yang, J.; Bei, J.; Wang, S. A novel porous cells scaffold made of polylactide–dextran blend by combining phase-separation and particle-leaching techniques. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4483–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, S.; Soto, C.M.; Wilson, C.D.; Brower, T.L.; Pollack, S.K.; Schull, T.L.; Chatterji, A.; Lin, T.; Johnson, J.E.; Amsinck, C.; et al. An Engineered Virus as a Scaffold for Three-Dimensional Self-Assembly on the Nanoscale. Small 2005, 1, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Lee, J.W.; Kotov, N.A. A Floating Self-Assembly Route to Colloidal Crystal Templates for 3D Cell Scaffolds. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 4918–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Morits, M.; Jonkergouw, C.; Ora, A.; Valle-Delgado, J.J.; Farooq, M.; Ajdary, R.; Huan, S.; Linder, M.; Rojas, O.; et al. Three-Dimensional Printed Cell Culture Model Based on Spherical Colloidal Lignin Particles and Cellulose Nanofibril-Alginate Hydrogel. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1875–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasayama, S.; Hara, T.; Tanaka, T.; Honda, Y.; Baba, S. Osteogenesis of Multipotent Progenitor Cells using the Epigallocatechin Gallate-Modified Gelatin Sponge Scaffold in the Rat Congenital Cleft-Jaw Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wang, S.J.; Zhao, X.R.; Zhu, Y.F.; Yu, J.K. 3D- Printed Poly(epsilon-caprolactone) Scaffold Integrated with Cell-laden Chitosan Hydrogels for Bone Tissue Engineering. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyette, J.P.; Gilpin, S.E.; Charest, J.M.; Tapias, L.F.; Ren, X.; Ott, H.C. Perfusion decellularization of whole organs. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1451–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daryabari, S.S.; Kajbafzadeh, A.-M.; Fendereski, K.; Ghorbani, F.; Dehnavi, M.; Rostami, M.; Garajegayeh, B.A.; Tavangar, S.M. Development of an efficient perfusion-based protocol for whole-organ decellularization of the ovine uterus as a human-sized model and in vivo application of the bioscaffolds. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2019, 36, 1211–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishtul, S.; Baruch, L.; Machluf, M. Processed Tissue–Derived Extracellular Matrices: Tailored Platforms Empowering Diverse Therapeutic Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1900386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierad, L.N.; Shaw, E.L.; Bina, A.; Brazile, B.; Rierson, N.; Patnaik, S.S.; Kennamer, A.; Odum, R.; Cotoi, O.; Terezia, P.; et al. Functional Heart Valve Scaffolds Obtained by Complete Decellularization of Porcine Aortic Roots in a Novel Differential Pressure Gradient Perfusion System. Tissue Eng. Part C 2015, 21, 1284–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, O.; Walters, N.J.; Day, R.M.; Kim, H.-W.; Knowles, J.C. Evaluation of decellularization protocols for production of tubular small intestine submucosa scaffolds for use in oesophageal tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 5043–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casali, D.M.; Handleton, R.M.; Shazly, T.; Matthews, M.A. A novel supercritical CO2-based decellularization method for maintaining scaffold hydration and mechanical properties. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 131, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.S.; Saubaméa, B.; Susen, S.; Kindo, M.; Bruneval, P.; van Belle, E.; Jansen, P.; Roussel, J.-C.; Latrémouille, C.; Carpentier, A. Bioprosthetic Total Artificial Heart Induces a Profile of Acquired Hemocompatibility with Membranes Recellularization. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 404–406. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya, T.; Sivarapatna, A.; Rocco, K.; Nanashima, A.; Nagayasu, T.; Niklason, L.E. Future prospects for tissue engineered lung transplantation. Organogenesis 2014, 10, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caires-Júnior, L.C.; Goulart, E.; Telles-Silva, K.A.; Araujo, B.H.S.; Musso, C.M.; Kobayashi, G.; Oliveira, D.; Assoni, A.; Carvalho, V.M.; Ribeiro, A.F., Jr.; et al. Pre-coating decellularized liver with HepG2-conditioned medium improves hepatic recellularization. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 121, 111862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Gutierrez, A.; Zhang, L.; Medberry, C.; Fukumitsu, K.; Faulk, D.; Jiang, H.; Reing, J.; Gramignoli, R.; Komori, J.; Ross, M.; et al. A Whole-Organ Regenerative Medicine Approach for Liver Replacement. Tissue Eng. Part C 2011, 17, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillebrandt, K.H.; Everwien, H.; Haep, N.; Keshi, E.; Pratschke, J.; Sauer, I.M. Strategies based on organ decellularization and recellularization. Transpl. Int. 2019, 32, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, H.; Yagi, H.; Higashi, H.; Tajima, K.; Kuroda, K.; Abe, Y.; Kitago, M.; Shinoda, M.; Kitagawa, Y. Decellularized liver scaffolds promote liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, M.J.; Knutson, C.C.; Momtahan, N.; Cook, A.D. Extracellular Matrix from Whole Porcine Heart Decellularization for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. In Decellularized Scaffolds and Organogenesis; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Ohata, K.; Ott, H.C. Human-scale lung regeneration based on decellularized matrix scaffolds as a biologic platform. Surg. Today 2020, 50, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, A.; Niu, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, K.; Xiao, Z.; Luan, Y.; Sun, C.; Xie, X.; Zhang, D.; Du, X.; et al. Recellularization of well-preserved decellularized kidney scaffold using adipose tissue-derived stem cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2018, 106, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damodaran, R.G.; Vermette, P. Decellularized pancreas as a native extracellular matrix scaffold for pancreatic islet seeding and culture. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acikgöz, A.; Giri, S.; Cho, M.G.; Bader, A. Morphological and Functional Analysis of Hepatocyte Spheroids Generated on Poly-HEMA-Treated Surfaces under the Influence of Fetal Calf Serum and Nonparenchymal Cells. Biomolecules 2013, 3, 242–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaninezhad, M.; Hill, L.; Kolar, G.; Vogt, K.; Zustiak, S.P. Templated Macroporous Polyethylene Glycol Hydrogels for Spheroid and Aggregate Cell Culture. Bioconjugate Chem. 2019, 30, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Wang, I.J.; Young, T.-H. Formation of Keratocyte Spheroids on Chitosan-Coated Surface Can Maintain Keratocyte Phenotypes. Tissue Eng. Part A 2009, 15, 2001–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, M.; Gowan, S.; Boxall, F.; Patterson, L.; Zimmermann, M.; Court, W.; Lomas, C.; Mendiola, M.; Hardisson, D.; Eccles, S.A. Advances in establishment and analysis of three-dimensional tumor spheroid-based functional assays for target validation and drug evaluation. BMC Biol. 2012, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasebe, Y.; Okumura, N.; Koh, T.; Kazama, H.; Watanabe, G.; Seki, T.; Ariga, T. Formation of rat hepatocyte spheroids on agarose. Hepatol. Res. 2005, 32, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, W.; Ma, N.; Lendlein, A. Spheroid formation of human keratinocyte: Balancing between cell-substrate and cell-cell interaction. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2020, 76, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goričan, L.; Gole, B.; Potočnik, U. Head and Neck Cancer Stem Cell-Enriched Spheroid Model for Anticancer Compound Screening. Cells 2020, 9, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baze, A.; Parmentier, C.; Hendriks, D.F.G.; Hurrell, T.; Heyd, B.; Bachellier, P.; Schuster, C.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Richert, L. Three-Dimensional Spheroid Primary Human Hepatocytes in Monoculture and Coculture with Nonparenchymal Cells. Tissue Eng. Part C 2018, 24, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagemann, J.A.N.; Jacobi, C.; Hahn, M.; Schmid, V.; Welz, C.; Schwenk-Zieger, S.; Stauber, R.; Baumeister, P.; Becker, S. Spheroid-based 3D Cell Cultures Enable Personalized Therapy Testing and Drug Discovery in Head and Neck Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaiahgari, S.C.; Waidyanatha, S.; Dixon, D.; DeVito, M.J.; Paules, R.S.; Ferguson, S.S. From the Cover: Three-Dimensional (3D) HepaRG Spheroid Model with Physiologically Relevant Xenobiotic Metabolism Competence and Hepatocyte Functionality for Liver Toxicity Screening. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 159, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducker, M.; Millar, V.; Ebner, D.; Szele, F.G. A Semi-automated and Scalable 3D Spheroid Assay to Study Neuroblast Migration. Stem Cell Rep. 2020, 15, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessel, S.; Cribbes, S.; Déry, O.; Kuksin, D.; Sincoff, E.; Qiu, J.; Chan, L.L.-Y. High-Throughput 3D Tumor Spheroid Screening Method for Cancer Drug Discovery Using Celigo Image Cytometry. Slas Technol. 2016, 22, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.O.; Li, Z.; Shim, H.-E.; Cho, I.-S.; Nurunnabi, M.; Park, H.; Lee, K.Y.; Moon, S.-H.; Kim, K.-S.; Kang, S.-W.; et al. Bioinspired tuning of glycol chitosan for 3D cell culture. NPG Asia Mater. 2016, 8, e309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loessner, D.; Rockstroh, A.; Shokoohmand, A.; Holzapfel, B.M.; Wagner, F.; Baldwin, J.; Boxberg, M.; Schmalfeldt, B.; Lengyel, E.; Clements, J.A.; et al. A 3D tumor microenvironment regulates cell proliferation, peritoneal growth and expression patterns. Biomaterials 2019, 190–191, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, M.; Soon, R.H.; Lim, C.T.; Khoo, B.L.; Han, J. Microfluidic modelling of the tumor microenvironment for anti-cancer drug development. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoarau-Véchot, J.; Rafii, A.; Touboul, C.; Pasquier, J. Halfway between 2D and Animal Models: Are 3D Cultures the Ideal Tool to Study Cancer-Microenvironment Interactions? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thippabhotla, S.; Zhong, C.; He, M. 3D cell culture stimulates the secretion of in vivo like extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groebe, K.; Mueller-Klieser, W. On the relation between size of necrosis and diameter of tumor spheroids. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1996, 34, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anada, T.; Fukuda, J.; Sai, Y.; Suzuki, O. An oxygen-permeable spheroid culture system for the prevention of central hypoxia and necrosis of spheroids. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8430–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, S.; Costa, E.C.; Nunes, A.S.; de Melo-Diogo, D.; Correia, I.J. Comparative study of the therapeutic effect of Doxorubicin and Resveratrol combination on 2D and 3D (spheroids) cell culture models. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 551, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paškevičiūtė, M.; Petrikaitė, V. Differences of statin activity in 2D and 3D pancreatic cancer cell cultures. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 3273–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aline, G.S.; Beatriz, B.S.I.; Esther, C.-F.; Leticia, S.B.; Brito, S.J.; Karina, M.; Luiz, R.G.; Vivian, A.-G. Comparative Assay of 2D and 3D Cell Culture Models: Proliferation, Gene Expression and Anticancer Drug Response. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 1689–1694. [Google Scholar]
- Riedl, A.; Schlederer, M.; Pudelko, K.; Stadler, M.; Walter, S.; Unterleuthner, D.; Unger, C.; Kramer, N.; Hengstschläger, M.; Kenner, L.; et al. Comparison of cancer cells in 2D vs. 3D culture reveals differences in AKT–mTOR–S6K signaling and drug responses. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, C.; Mersch, S.; Deenen, R.; Schmidt, S.; Messner, I.; Schäfer, K.-L.; Baldus, S.E.; Huckenbeck, W.; Piekorz, R.P.; Knoefel, W.T.; et al. Impact of the 3D Microenvironment on Phenotype, Gene Expression, and EGFR Inhibition of Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimlin, L.C.; Casagrande, G.; Virador, V.M. In vitro three-dimensional (3D) models in cancer research: An update. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietarska, M.; Maugard, C.M.; Filali-Mouhim, A.; Alam-Fahmy, M.; Tonin, P.N.; Provencher, D.M.; Mes-Masson, A.-M. Molecular description of a 3D in vitro model for the study of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). Mol. Carcinog. 2007, 46, 872–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loessner, D.; Stok, K.S.; Lutolf, M.P.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Clements, J.A.; Rizzi, S.C. Bioengineered 3D platform to explore cell–ECM interactions and drug resistance of epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8494–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Mhawech-Fauceglia, P.; Lee, N.; Parsanian, L.C.; Lin, Y.G.; Gayther, S.A.; Lawrenson, K. A three-dimensional microenvironment alters protein expression and chemosensitivity of epithelial ovarian cancer cells in vitro. Lab. Investig. 2013, 93, 528–542. [Google Scholar]
- Bielecka, Z.F.; Maliszewska-Olejniczak, K.; Safir, I.J.; Szczylik, C.; Czarnecka, A.M. Three-dimensional cell culture model utilization in cancer stem cell research. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 1505–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiew, G.G.Y.; Wei, N.; Sultania, S.; Lim, S.; Luo, K.Q. Bioengineered three-dimensional co-culture of cancer cells and endothelial cells: A model system for dual analysis of tumor growth and angiogenesis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 1865–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuen, J.; Darowski, D.; Kluge, T.; Majety, M. Pancreatic cancer cell/fibroblast co-culture induces M2 like macrophages that influence therapeutic response in a 3D model. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182039. [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa, H. Methods for inducing embryoid body formation: In vitro differentiation system of embryonic stem cells. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2007, 103, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giobbe, G.G.; Zagallo, M.; Riello, M.; Serena, E.; Masi, G.; Barzon, L.; di Camillo, B.; Elvassore, N. Confined 3D microenvironment regulates early differentiation in human pluripotent stem cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 3119–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettinato, G.; Wen, X.; Zhang, N. Engineering Strategies for the Formation of Embryoid Bodies from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2015, 24, 1595–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, T.E.; Levenstein, M.E.; Jones, J.M.; Berggren, W.T.; Mitchen, E.R.; Frane, J.L.; Crandall, L.J.; Daigh, C.A.; Conard, K.R.; Piekarczyk, M.S.; et al. Derivation of human embryonic stem cells in defined conditions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.; Yoo, S.J.; Lee, J.E.; You, S.; Lee, H.T.; Yoon, H.S. Enhanced differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into cardiomyocytes by combining hanging drop culture and 5-azacytidine treatment. Differentiation 2006, 74, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, J.C.; de Pablo, J.J.; Palecek, S.P. 3-D microwell culture of human embryonic stem cells. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 6032–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungrin, M.D.; Joshi, C.; Nica, A.; Bauwens, C.; Zandstra, P.W. Reproducible, Ultra High-Throughput Formation of Multicellular Organization from Single Cell Suspension-Derived Human Embryonic Stem Cell Aggregates. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Leslie, P.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J. Stem cells in a three-dimensional scaffold environment. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regmi, S.; Pathak, S.; Thanh, T.P.; Nguyen, T.T.; Sung, J.-H.; Yook, S.; Kim, J.O.; Yong, C.S.; Choi, I.; Doh, K.-O.; et al. Intraportally delivered stem cell spheroids localize in the liver and protect hepatocytes against GalN/LPS-induced fulminant hepatic toxicity. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasai, Y. Next-Generation Regenerative Medicine: Organogenesis from Stem Cells in 3D Culture. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Saunders, L.; Schipani, E.; Chen, Q.; Ma, P.X. Suppressing mesenchymal stem cell hypertrophy and endochondral ossification in 3D cartilage regeneration with nanofibrous poly(l-lactic acid) scaffold and matrilin-3. Acta Biomater. 2018, 76, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Ma, B.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; et al. 3D Culture of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (BMSCs) Could Improve Bone Regeneration in 3D-Printed Porous Ti6Al4V Scaffolds. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 2074021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, S.; Sui, X.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Q.; Du, H.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Seeded Regenerated Silk Fibroin Complex Matrices for Liver Regeneration in an Animal Model of Acute Liver Failure. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 14716–14723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-L.; Xue, Q.; Xu, X.-H.; Hu, F.; Shao, H. Recent progress in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived 3D cultures for cardiac regeneration. Cell Tissue Res. 2021, 164, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Yuan, X.; Jones, Z.; Griffin, K.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, T.; Li, Y. Assembly of Human Stem Cell-Derived Cortical Spheroids and Vascular Spheroids to Model 3-D Brain-like Tissues. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizaw, M.; Faglie, A.; Pieper, M.; Poudel, S.; Chou, S.F. The Role of Electrospun Fiber Scaffolds in Stem Cell Therapy for Skin Tissue Regeneration. Med. ONE 2019, 4, e190002. [Google Scholar]
- Jeena, K.; Manju, C.A.; Sajesh, K.M.; Gowd, G.S.; Sivanarayanan, T.B.; Mol, C.D.; Manohar, M.; Nambiar, A.; Nair, S.V.; Koyakutty, M. Brain-Tumor-Regenerating 3D Scaffold-Based Primary Xenograft Models for Glioma Stem Cell Targeted Drug Screening. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengwimol, D.; Rojanaporn, D.; Chaitankar, V.; Chittavanich, P.; Aroonroch, R.; Boontawon, T.; Thammachote, W.; Jinawath, N.; Hongeng, S.; Kaewkhaw, R. A three-dimensional organoid model recapitulates tumorigenic aspects and drug responses of advanced human retinoblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranga, A.; Gjorevski, N.; Lutolf, M.P. Drug discovery through stem cell-based organoid models. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 69–70, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, P.M.; Siddiqui, M.M.; Lozier, G.; Rodriguez, S.R.; Atala, A.; Soker, S. The use of whole organ decellularization for the generation of a vascularized liver organoid. Hepatology 2011, 53, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Ju, J.H. Generation of 3D Skin Organoid from Cord Blood-derived Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. JoVE 2019, 146, e59297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Uchimura, K.; Donnelly, E.L.; Kirita, Y.; Morris, S.A.; Humphreys, B.D. Comparative Analysis and Refinement of Human PSC-Derived Kidney Organoid Differentiation with Single-Cell Transcriptomics. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 23, 869–881.e868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Völkner, M.; Zschätzsch, M.; Rostovskaya, M.; Overall, R.W.; Busskamp, V.; Anastassiadis, K.; Karl, M.O. Retinal Organoids from Pluripotent Stem Cells Efficiently Recapitulate Retinogenesis. Stem Cell Rep. 2016, 6, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelava, I.; Lancaster, M.A. Dishing out mini-brains: Current progress and future prospects in brain organoid research. Dev. Biol. 2016, 420, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Heo, I.; Clevers, H. Disease Modeling in Stem Cell-Derived 3D Organoid Systems. Trends Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonekamp, E.; Kretzschmar, K.; Wiener, D.J.; Asra, P.; Derakhshan, S.; Puschhof, J.; López-Iglesias, C.; Peters, P.J.; Basak, O.; Clevers, H. Long-term expansion and differentiation of adult murine epidermal stem cells in 3D organoid cultures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 14630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, P.; Wang, J.; Conklin, B.R.; Healy, K.E.; Ma, Z. Generation of spatial-patterned early-developing cardiac organoids using human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchieu, J.; Zimmer, B.; Fattahi, F.; Amin, S.; Zeltner, N.; Chen, S.; Studer, L. A Modular Platform for Differentiation of Human PSCs into All Major Ectodermal Lineages. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 21, 399–410.e397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.R.; Hay, M.P. Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchinton, I.; Tannock, I.F. Drug penetration in solid tumours. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraili, A.; Jafari, P.; Hassani, M.S.; Araghi, B.H.; Mohammadi, M.H.; Ghafari, A.M.; Tamrin, S.H.; Modarres, H.P.; Kolahchi, A.R.; Ahadian, S.; et al. Controlling Differentiation of Stem Cells for Developing Personalized Organ-on-Chip Platforms. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1700426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, A.A.; Albers, H.J.; Passier, R.; Mummery, C.L.; van den Berg, A.; Orlova, V.V.; van der Meer, A.D. Advanced in vitro models of vascular biology: Human induced pluripotent stem cells and organ-on-chip technology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 140, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type | Advantage | Disadvantage | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogel | Tissue like flexibility Easily supplies water-soluble factors to cells | Low mechanical resistance | [5,11,13,17,18] |
| Solid scaffold | Various materials can be used Physical strength is easily adjusted | Difficulty in homogeneous dispersion of cells | [15,16,19,20,21] |
| Decellularized native tissue | Provides complex biochemistry, biomechanics and 3D tissues of tissue-specific extracellular matrix (ECM) | Decrease of mechanical properties (roughness, elasticity, and tension strength) of the tissues as compared to the native group | [22,23,24,25,26] |
| Ultra-low attachment surface | Provides an environment similar to in vivo conditions | Difficulty in mass production Lack of uniformity between spheroids | [27,28,29,30,31] |
| Properties | Materials | Cells | Applications | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic | Provide structural support to various cell types | PVA | Mouse 129 teratocarcinoma AT805 derived cells (ATDC5) [37], Human iPS cells (HPS0077) [38] | Repair cartilage [37], promote differentiation [38] |
| pHEMA | Bovine ear chondrocytes [39] | Proliferate chondrocytes [39] | ||
| PEG | Ovarian Follicle cell [40], human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) [41] | Promote cell survival, growth [40], and viability by encapsulation [41] | ||
| Natural | Support cellular activities and are biocompatible and biodegradable | Collagen | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) [42] | Form stable EC networks [42] |
| Alginate | Human adipose-derived stem cells (hASCs) [43], rat astroglioma (LRM55) [44] | Maintain their ability to secrete therapeutic factors [43], maintain the viability and function [44] | ||
| Hyaluronic acid | Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural progenitor cells (hiPSC-NPCs) [45], human breast cancer MCF-7 cells [46] | Promote neural differentiation [45], higher tumorigenic capability of MCF-7 cells [46] |
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particulate Leaching | Modulate pore size and porosity | Limited pore shape and size | [15] |
| Solvent Casting | Modulate pore size and porosity Easy incorporation of drugs within the scaffold | Low pore interconnectivity | [100,101] |
| Emulsion Templating | Modulate particle size, high porosity, interconnectivity | Difficulty in obtaining emulsions with sufficient monodispersity for crystallization | [16,102,103] |
| Gas Foaming | Modulate pore size and porosity Free of toxic organic solvents | Unexpected pore interconnectivity | [104,105,106] |
| Melt Molding | Modulate pore size and porosity | High temperature required when molding | [107] |
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Mesh | High surface area for cell attachment | Low structural stability | [21] |
| Fiber Bonding | High surface to volume ratio, high porosity | Limited applications to other polymers | [132] |
| Electrospinning | Induces cell alignment and directionality | Limited by cell seeding | [143,144,145] |
| Phase Separation | No reduction in the activity of molecules | Difficult to control the scaffold morphology | [138,146] |
| Self-Assembly | Form extremely stable scaffolds, less use of organic solvent | Expensive material, complicated and elaborate process | [147,148] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, Y.; Huh, K.M.; Kang, S.-W. Applications of Biomaterials in 3D Cell Culture and Contributions of 3D Cell Culture to Drug Development and Basic Biomedical Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052491
Park Y, Huh KM, Kang S-W. Applications of Biomaterials in 3D Cell Culture and Contributions of 3D Cell Culture to Drug Development and Basic Biomedical Research. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(5):2491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052491
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Yujin, Kang Moo Huh, and Sun-Woong Kang. 2021. "Applications of Biomaterials in 3D Cell Culture and Contributions of 3D Cell Culture to Drug Development and Basic Biomedical Research" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 5: 2491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052491
APA StylePark, Y., Huh, K. M., & Kang, S.-W. (2021). Applications of Biomaterials in 3D Cell Culture and Contributions of 3D Cell Culture to Drug Development and Basic Biomedical Research. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(5), 2491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052491







