Non-Coding RNA Signatures of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
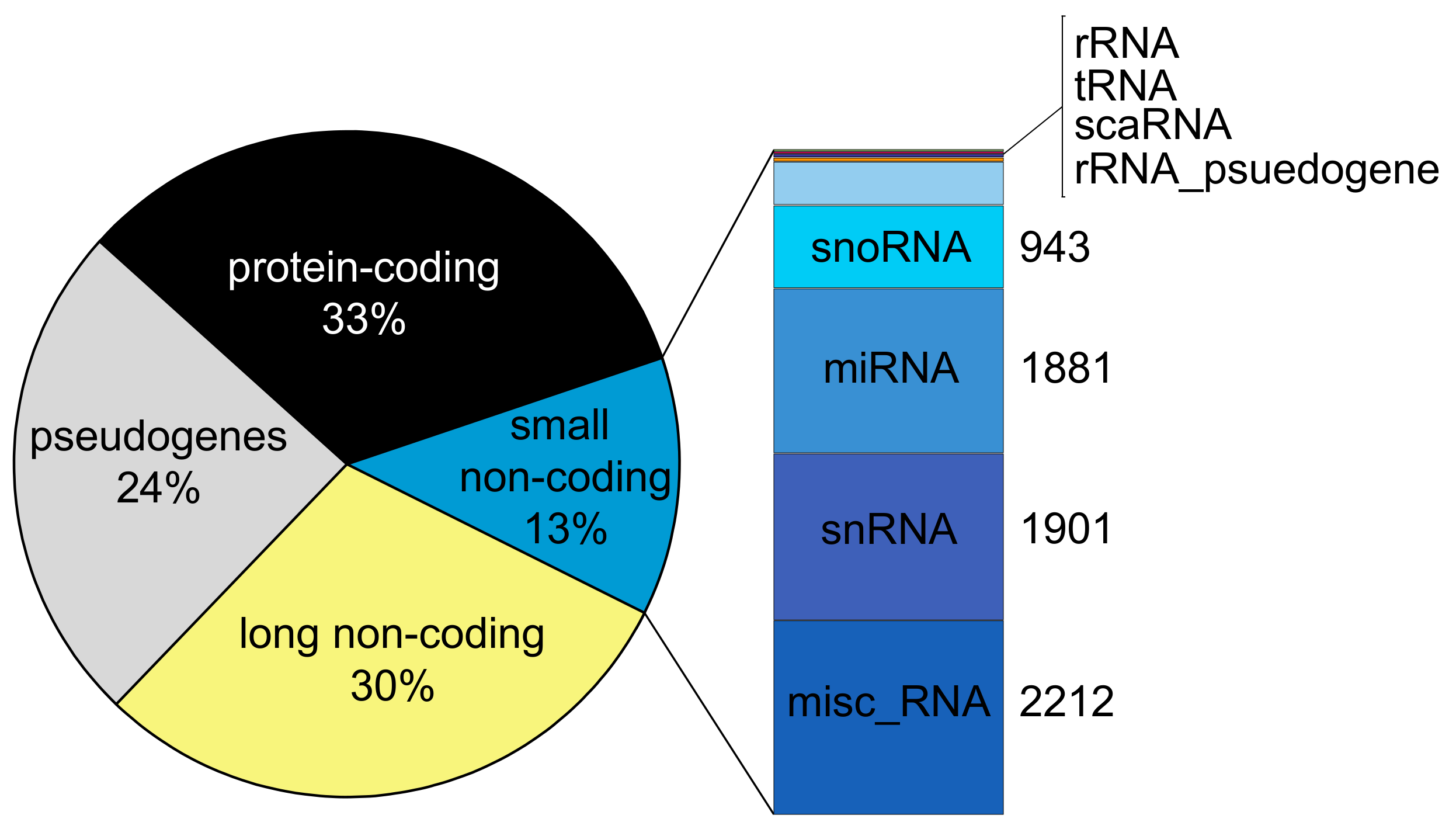
2. A Compendium of Human Non-Coding RNA Genes
2.1. miRNAs Are Regulatory Small Non-Coding RNAs
2.2. Regulatory Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA)
3. Profiling Non-Coding RNAs
4. Long Non-Coding RNAs in Progenitor B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Notable Case: LncRNA GAS5 and Its Connection to Glucocorticoid Resistance
5. MicroRNA and Progenitor B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
6. Other Classes of Non-Coding RNAs and Their Role in Progenitor B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
7. Emerging Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2′OMe | 2′-O-methyl |
| ALL | acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| AML | acute myeloid leukemia |
| B-ALL | B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| BM | bone marrow |
| ceRNA | competing endogenous RNA |
| circRNA | circular RNA |
| GAS5 | growth arrest-specific transcript 5 |
| GR | glucocorticoid receptor |
| GRE | glucocorticoid response element |
| HdH | high hyperdiploidy |
| ID | initial diagnosis |
| lncRNA | long non-coding RNA |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| miscRNA | miscellaneous RNA |
| MRE | miRNA response element |
| ncRNA | non-coding RNA |
| NGS | Next Generation Sequencing |
| NH-HeH | near-haploid and high hyperdiploid |
| nt | nucleotide |
| PB | peripheral blood |
| PCA3 | Prostate Cancer gene 3 |
| Ph+ | Philadelphia chromosome-positive |
| pri-miRNA | primary miRNA |
| pre-miRNA | precursor miRNA |
| REL | relapse |
| RNA-Seq | RNA-sequencing |
| RNP | ribonucleoprotein |
| rRNA | ribosomal RNA |
| scaRNA | Small Cajal body-specific RNA |
| smRNA-Seq | small RNA-sequencing |
| SNP | single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| snoRNA | small nucleolar RNA |
| snRNA | small nuclear RNA |
| T-ALL | T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| TARGET | Therapeutically Applicable Research to Generate Effective Treatments |
| TKI | tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| tRNA | transfer RNA |
| WGS | whole-genome sequencing |
| WES | whole-exome sequencing |
References
- Ward, E.; DeSantis, C.; Robbins, A.; Kohler, B.; Jemal, A. Childhood and adolescent cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.G.; Mullighan, C.G. Genomics in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: Insights and treatment implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, H.; Mullighan, C.G. Pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2524–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.G. Genetics and prognosis of ALL in children vs adults. Hematologica 2018, 2018, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Diebold, J.; Flandrin, G.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Vardiman, J.; Lister, T.A.; Bloomfield, C.D. World Health Organization Classification of Neoplastic Diseases of the Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues: Report of the Clinical Advisory Committee Meeting—Airlie House, Virginia, November 1997. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 3835–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terwilliger, T.; Abdul-Hay, M. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A comprehensive review and 2017 update. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iacobucci, I.; Mullighan, C.G. Genetic Basis of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, A.V.; Richards, S.M.; Martineau, M.; Cheung, K.L.; Robinson, H.M.; Jalali, G.R.; Broadfield, Z.J.; Harris, R.L.; Taylor, K.E.; Gibson, B.E.S.; et al. Outcome heterogeneity in childhood high-hyperdiploid acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2003, 102, 2756–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandemer, V.; Chevret, S.; Petit, A.; Vermylen, C.; Leblanc, T.; Michel, G.; Schmitt, C.; Lejars, O.; Schneider, P.; Demeocq, F.; et al. Excellent prognosis of late relapses of ETV6/RUNX1-positive childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Lessons from the FRALLE 93 protocol. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalle, I.A.; Jabbour, E.; Short, N.J.; Ravandi, F. Treatment of Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2019, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.; Thomas, D.; Yin, C.C.; O’Brien, S.; Cortes, J.E.; Jabbour, E.; Breeden, M.; Giles, F.J.; Zhao, W.; Kantarjian, H.M. Kinase domain point mutations in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia emerge after therapy with BCR-ABL kinase inhibitors. Cancer 2008, 113, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-F.; Dai, Y.-T.; Lilljebjörn, H.; Shen, S.-H.; Cui, B.-W.; Bai, L.; Liu, Y.-F.; Qian, M.-X.; Kubota, Y.; Kiyoi, H.; et al. Transcriptional landscape of B cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia based on an international study of 1,223 cases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11711–E11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, K.G.; Morin, R.D.; Zhang, J.; Hirst, M.; Zhao, Y.; Su, X.; Chen, S.-C.; Payne-Turner, D.; Churchman, M.L.; Harvey, R.C.; et al. Genetic Alterations Activating Kinase and Cytokine Receptor Signaling in High-Risk Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasool, M.; Malik, A.; Zahid, S.; Ashraf, M.A.B.; Qazi, M.H.; Asif, M.; Zaheer, A.; Arshad, M.; Raza, A.; Jamal, M.S. Non-coding RNAs in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Non Coding RNA Res. 2016, 1, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitt, A.M.; Chang, H.Y. Long Noncoding RNAs in Cancer Pathways. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frankish, A.; Diekhans, M.; Ferreira, A.-M.; Johnson, R.; Jungreis, I.; Loveland, J.; Mudge, J.M.; Sisu, C.; Wright, J.; Armstrong, J.; et al. GENCODE reference annotation for the human and mouse genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D766–D773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Leary, N.A.; Wright, M.W.; Brister, J.R.; Ciufo, S.; Haddad, D.; McVeigh, R.; Rajput, B.; Robbertse, B.; Smith-White, B.; Ako-Adjei, D.; et al. Reference sequence (RefSeq) database at NCBI: Current status, taxonomic expansion, and functional annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D733–D745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uszczynska-Ratajczak, B.; Lagarde, J.; Frankish, A.; Guigó, R.; Johnson, R. Towards a complete map of the human long non-coding RNA transcriptome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarde, J.; Uszczynska-Ratajczak, B.; Carbonell, S.; Pérez-Lluch, S.; Abad, A.; Davis, C.; Gingeras, T.R.; Frankish, A.; Harrow, J.; Guigo, R.; et al. High-throughput annotation of full-length long noncoding RNAs with capture long-read sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seal, R.L.; Chen, L.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Lowe, T.M.; Mathews, M.B.; O’Reilly, D.; Pierce, A.J.; Stadler, P.F.; Ulitsky, I.; Wolin, S.L.; et al. A guide to naming human non-coding RNA genes. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e103777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Zhang, L.; Guo, J.; Niu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Teng, X.; Sun, X.; et al. NONCODEV5: A comprehensive annotation database for long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D308–D314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volders, P.-J.; Anckaert, J.; Verheggen, K.; Nuytens, J.; Martens, L.; Mestdagh, P.; Vandesompele, J. LNCipedia 5: Towards a reference set of human long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D135–D139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godoy, P.M.; Bhakta, N.R.; Barczak, A.J.; Cakmak, H.; Fisher, S.; MacKenzie, T.C.; Patel, T.; Price, R.W.; Smith, J.F.; Woodruff, P.G.; et al. Large Differences in Small RNA Composition Between Human Biofluids. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.-H.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2008, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartel, D.P. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell 2018, 173, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szell, M.; Bata-Csorgo, Z.; Kemeny, L. The enigmatic world of mRNA-like ncRNAs: Their role in human evolution and in human diseases. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2008, 18, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsson, P.; Lipovich, L.; Grandér, D.; Morris, K.V. Evolutionary conservation of long non-coding RNAs; sequence, structure, function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laurent, G.S.; Wahlestedt, C.; Kapranov, P. The Landscape of long noncoding RNA classification. Trends Genet. 2015, 31, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kazimierczyk, M.; Kasprowicz, M.K.; Kasprzyk, M.E.; Wrzesinski, J. Human Long Noncoding RNA Interactome: Detection, Characterization and Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boque-Sastre, R.; Soler, M.; Oliveira-Mateos, C.; Portela, A.; Moutinho, C.; Sayols, S.; Villanueva, A.; Esteller, M.; Guil, S. Head-to-head antisense transcription and R-loop formation promotes transcriptional activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5785–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beckedorff, F.C.; Ayupe, A.C.; Crocci-Souza, R.; Amaral, M.S.; Nakaya, H.I.; Soltys, D.T.; Menck, C.F.M.; Reis, E.M.; Verjovski-Almeida, S. The Intronic Long Noncoding RNA ANRASSF1 Recruits PRC2 to the RASSF1A Promoter, Reducing the Expression of RASSF1A and Increasing Cell Proliferation. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, H.R.; Shaginurova, G.; Kim, L.C.; Chapman, N.; Spurlock, C.F.I.; Aune, T.M. Divergent lncRNA GATA3-AS1 Regulates GATA3 Transcription in T-Helper 2 Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arab, K.; Karaulanov, E.; Musheev, M.; Trnka, P.; Schäfer, A.; Grummt, I.; Niehrs, C. GADD45A binds R-loops and recruits TET1 to CpG island promoters. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan-Wong, S.M.; Dhir, S.; Proudfoot, N.J. R-Loops Promote Antisense Transcription across the Mammalian Genome. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 600–616.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holdt, L.M.; Hoffmann, S.; Sass, K.; Langenberger, D.; Scholz, M.; Krohn, K.; Finstermeier, K.; Stahringer, A.; Wilfert, W.; Beutner, F.; et al. Alu Elements in ANRIL Non-Coding RNA at Chromosome 9p21 Modulate Atherogenic Cell Functions through Trans-Regulation of Gene Networks. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Hwang, T.; Gooding, A.R.; Goodrich, K.J.; Rinn, J.L.; Cech, T.R. RNA is essential for PRC2 chromatin occupancy and function in human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.J.; Chen, L.L.; Huarte, M. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichon, A.; Gil, N.; Lubelsky, Y.; Solomon, T.H.; Lemze, D.; Itzkovitz, D.L.S.; Stern-Ginossar, T.H.S.N.; Ulitsky, A.T.N.G.Y.L.I. A conserved abundant cytoplasmic long noncoding RNA modulates repression by Pumilio proteins in human cells. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Kopp, F.; Chang, T.-C.; Sataluri, A.; Chen, B.; Sivakumar, S.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Mendell, J.T. Noncoding RNA NORAD Regulates Genomic Stability by Sequestering PUMILIO Proteins. Cell 2016, 164, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. Functional interactions among microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 34, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, B.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Luo, G.; Liang, S. Research progress on the interactions between long non-coding RNAs and microRNAs in human cancer (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2019, 19, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Wan, J. Competing Endogenous RNA Regulations in Neurodegenerative Disorders: Current Challenges and Emerging Insights. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, T.J.; Spriggs, R.V.; Burgoyne, N.J.; Jones, C.; Willis, A.E. Evaluating bias-reducing protocols for RNA sequencing library preparation. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raabe, C.A.; Tang, T.-H.; Brosius, J.; Rozhdestvensky, T.S. Biases in small RNA deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 1414–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munafó, D.B.; Robb, G.B. Optimization of enzymatic reaction conditions for generating representative pools of cDNA from small RNA. RNA 2010, 16, 2537–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dijk, E.L.; Eleftheriou, E.; Thermes, C. Improving Small RNA-seq: Less Bias and Better Detection of 2′-O-Methyl RNAs. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 2019, e60056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; He, X.; Hoadley, K.A.; Parker, J.S.; Hayes, D.N.; Perou, C.M. Comparison of RNA-Seq by poly (A) capture, ribosomal RNA depletion, and DNA microarray for expression profiling. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, P.; Lin, Q.; Ding, F.; Xin, C.; Gong, W.; Zhang, L.; Geng, J.; Zhang, B.; Yu, X.; Yang, J.; et al. A comparison between ribo-minus RNA-sequencing and polyA-selected RNA-sequencing. Genomics 2010, 96, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Zhao, S.; Sheng, Q.; Guo, M.; Lehmann, B.; Pietenpol, J.; Samuels, D.C.; Shyr, Y. RNAseq by Total RNA Library Identifies Additional RNAs Compared to Poly(A) RNA Library. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gordon, W.; Quan, J.; Xi, H.; Du, S.; Von Schack, D.; Zhang, B. Comparison of stranded and non-stranded RNA-seq transcriptome profiling and investigation of gene overlap. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giraldez, M.D.; Spengler, R.M.; Etheridge, A.; Goicochea, A.J.; Tuck, M.; Choi, S.W.; Galas, D.J.; Tewari, M. Phospho-RNA-seq: A modified small RNA-seq method that reveals circulating mRNA and lncRNA fragments as potential biomarkers in human plasma. EMBO J. 2019, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Ren, Y.; Si, Y.; Wang, F.; Yu, J. Long non-coding RNAs in hematopoietic regulation. Cell Regen. 2018, 7, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, L.; Ronchetti, D.; Taiana, E.; Neri, A. Long non-coding RNAs in B-cell malignancies: A comprehensive overview. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 60605–60623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarzer, A.; Emmrich, S.; Schmidt, F.; Beck, D.; Ng, M.; Reimer, C.; Adams, F.F.; Grasedieck, S.; Witte, D.; Käbler, S.; et al. The non-coding RNA landscape of human hematopoiesis and leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, T.S.; Painter, M.W.; Elpek, K.; Lukacs-Kornek, V.; Mauermann, N.; Turley, S.J.; Koller, D.; Kim, F.S.; Wagers, A.J.; Asinovski, N.; et al. The Immunological Genome Project: Networks of gene ex-pression in immune cells. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1091–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Baldwin, T.M.; Wong, M.; Bolden, J.E.; Fairfax, K.A.; Lucas, E.C.; Cole, R.; Biben, C.; Morgan, C.; Ramsay, K.A.; et al. Haemopedia RNA-seq: A database of gene expression during haematopoiesis in mice and humans. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D780–D785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagger, F.O.; Kinalis, S.; Rapin, N. BloodSpot: A database of healthy and malignant haematopoiesis updated with purified and single cell mRNA sequencing profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D881–D885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonnal, R.J.; Ranzani, V.; Arrigoni, A.; Curti, S.; Panzeri, I.; Gruarin, P.; Abrignani, S.; Rossetti, G.; Pagani, M. De novo transcriptome profiling of highly purified human lymphocytes primary cells. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petri, A.; Dybkær, K.; Bøgsted, M.; Thrue, C.A.; Hagedorn, P.H.; Schmitz, A.; Bødker, J.S.; Johnsen, H.E.; Kauppinen, S. Long Noncoding RNA Expression during Human B-Cell Development. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casero, D.; Sandoval, S.; Seet, C.S.; Scholes, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ha, V.L.; Luong, A.; Parekh, C.; Crooks, G.M. Long non-coding RNA profiling of human lymphoid progenitor cells reveals transcriptional divergence of B cell and T cell lineages. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayari, M.M.; Winkle, M.; Kortman, G.; Sietzema, J.; de Jong, D.; Terpstra, M.; Mestdagh, P.; Kroese, F.G.; Visser, L.; Diepstra, A.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA Expression Profiling in Normal B-Cell Subsets and Hodgkin Lymphoma Reveals Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg Cell–Specific Long Noncoding RNAs. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 2462–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winkle, M.; Kluiver, J.; Diepstra, A.; Berg, A.V.D. Emerging roles for long noncoding RNAs in B-cell development and malignancy. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2017, 120, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Han, B.-W.; Chen, Z.-H.; Lin, K.-Y.; Zeng, C.-W.; Li, X.-J.; Li, J.-H.; Luo, X.-Q.; Chen, Y.-Q. A distinct set of long non-coding RNAs in childhood MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Biology and epigenetic target. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 3278–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernando, T.R.; Rodriguez-Malave, N.I.; Waters, E.V.; Yan, W.; Casero, D.; Basso, G.; Pigazzi, M.; Rao, D.S. LncRNA Expression Discriminates Karyotype and Predicts Survival in B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Affinito, O.; Pane, K.; Smaldone, G.; Orlandella, F.M.; Mirabelli, P.; Beneduce, G.; Parasole, R.; Ripaldi, M.; Salvatore, M.; Franzese, M. lncRNAs-mRNAs Co-Expression Network Underlying Childhood B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: A Pilot Study. Cancers 2020, 12, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajoie, M.; Drouin, S.; Caron, M.; St-Onge, P.; Ouimet, M.; Gioia, R.; Lafond, M.-H.; Vidal, R.; Richer, C.; Oualkacha, K.; et al. Specific expression of novel long non-coding RNAs in high-hyperdiploid childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Malavé, N.I.; Fernando, T.R.; Patel, P.C.; Contreras, J.R.; Palanichamy, J.K.; Tran, T.M.; Anguiano, J.; Davoren, M.J.; Alberti, M.O.; Pioli, K.T.; et al. BALR-6 regulates cell growth and cell survival in B-lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Chen, J.-Z.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Chen, H.-X.; Qiu, F.-N.; Yan, M.-L.; Tian, Y.-F.; Peng, C.-H.; Shen, B.-Y.; Chen, Y.-L.; et al. Silencing of long noncoding RNA LINC00958 prevents tumor initiation of pancreatic cancer by acting as a sponge of microRNA-330-5p to down-regulate PAX8. Cancer Lett. 2019, 446, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Liu, M.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, W.; Wang, X.; Tong, D. LINC00958 regulated miR-627-5p/YBX2 axis to facilitate cell proliferation and migration in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1270–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Han, P.; Wang, R.; Cao, L.; He, S. Downregulation of LINC00958 inhibits proliferation, invasion and migration, and promotes apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by targeting miR-3619-5p. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuadros, M.; Andrades, Á.; Coira, I.F.; Baliñas, C.; Rodríguez, M.I.; Álvarez-Pérez, J.C.; Peinado, P.; Arenas, A.M.; García, D.J.; Jiménez, P.; et al. Expression of the long non-coding RNA TCL6 is associated with clinical outcome in pediatric B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bárcenas-López, D.A.; Núñez-Enríquez, J.C.; Hidalgo-Miranda, A.; Beltrán-Anaya, F.O.; May-Hau, D.I.; Jiménez-Hernández, E.; Bekker-Méndez, V.C.; Flores-Lujano, J.; Medina-Sansón, A.; Tamez-Gómez, E.L.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis Identifies LINC00152 as a Biomarker of Early Relapse and Mortality in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Genes 2020, 11, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.-T.; Chen, T.-Q.; Zeng, Z.-C.; Pan, Q.; Huang, W.; Han, C.; Fang, K.; Sun, L.-Y.; Yang, Q.-Q.; Wang, D.; et al. The lncRNA LAMP5-AS1 drives leukemia cell stemness by directly modulating DOT1L methyltransferase activity in MLL leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, T.R.; Contreras, J.R.; Zampini, M.; Rodriguez-Malave, N.I.; Alberti, M.O.; Anguiano, J.; Tran, T.M.; Palanichamy, J.K.; Gajeton, J.; Ung, N.M.; et al. The lncRNA CASC15 regulates SOX4 expression in RUNX1-rearranged acute leukemia. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazavi, F.; De Moerloose, B.; Van Loocke, W.; Wallaert, A.; Helsmoortel, H.H.; Ferster, A.; Bakkus, M.; Plat, G.; Delabesse, E.; Uyttebroeck, A.; et al. Unique long non-coding RNA expression signature in ETV6/RUNX1-driven B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 73769–73780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ouimet, M.; Drouin, S.; Lajoie, M.; Caron, M.; St-Onge, P.; Gioia, R.; Richer, C.; Sinnett, D. A childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia-specific lncRNA implicated in prednisolone resistance, cell proliferation, and migration. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 7477–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucafò, M.; Bravin, V.; Tommasini, A.; Martelossi, S.; Rabach, I.; Ventura, A.; Decorti, G.; De Iudicibus, S. Differential expression of GAS5 in rapamycin-induced reversion of glucocorticoid resistance. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2016, 43, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasic, V.; Stankovic, B.; Zukic, B.; Janic, D.; Dokmanovic, L.; Krstovski, N.; Lazic, J.; Milosevic, G.; Lucafò, M.; Stocco, G.; et al. Expression pattern of long non-coding RNA growth arrest-specific 5 in the remission induction therapy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Med. Biochem. 2019, 38, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioia, R.; Drouin, S.; Ouimet, M.; Caron, M.; St-Onge, P.; Richer, C.; Sinnett, D. LncRNAs downregulated in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia modulate apoptosis, cell migration, and DNA damage response. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 80645–80650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.X.; Zhang, N.; Fu, X.F.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, M.Y. LncRNA DBH-AS1 facilitates the tumorigenesis of melanoma by targeting miR-233-3p via IGF-1R/Akt signaling. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 7698–7708. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Gao, F.; Peng, Y.; Yang, X. Long non-coding RNA DBH-AS1 promotes cancer progression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by targeting FN1 via RNA-binding protein BUD13. Cell Biol. Int. 2020, 44, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-B.; Wang, J.-A.; Lv, R.-Q. Downregulation of long non-coding RNA DBH-AS1 inhibits osteosarcoma progression by PI3K-AKT signaling pathways and indicates good prognosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J.; Chen, X.; Hou, Y.; Kang, G.; Li, Q.; Xu, Y. LncRNA DBH-AS1 facilitates the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting miR-138 via FAK/Src/ERK pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.-L.; Ren, T.-Y.; Cao, S.-W.; Zheng, S.-H.; Hu, X.-M.; Hu, Y.-W.; Lin, L.; Chen, J.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Q. HBx-related long non-coding RNA DBH-AS1 promotes cell proliferation and survival by activating MAPK signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 33791–33804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aberuyi, N.; Rahgozar, S.; Ghodousi, E.S.; Ghaedi, K. Drug Resistance Biomarkers and Their Clinical Applications in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2020, 9, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouyanrad, S.; Rahgozar, S.; Ghodousi, E.S. Dysregulation of miR-335-3p, targeted by NEAT1 and MALAT1 long non-coding RNAs, is associated with poor prognosis in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Gene 2019, 692, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.R.; Schroeder, M.P.; Neumann, M.; Bastian, L.; Eckert, C.; Gökbuget, N.; Tanchez, J.O.; Schlee, C.; Isaakidis, K.; Schwartz, S.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs defining major subtypes of B cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, B.; Cai, D.; Liu, C.; Fang, C.; Yan, D. Linc00152 Functions as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Confer Oxaliplatin Resistance and Holds Prognostic Values in Colon Cancer. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 2064–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.-L.; Wang, J.; He, W.; Zhao, P.; Wu, W.-Q. Down-regulation of lncRNA Linc00152 suppressed cell viability, invasion, migration, and epithelial to mesenchymal transition, and reversed chemo-resistance in breast cancer cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 3074–3084. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.-J.; Yu, C.; Hu, X.-F.; He, Y.; Chen, P.; Ouyang, S.-X. LINC00152 promotes pancreatic cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via targeting miR-150. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 2241–2256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Su, H. Long non-coding RNA LINC00152/miR-613/CD164 axis regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion in glioma via PI3K/AKT pathway. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yang, S.; Zhao, W. Long Non-Coding RNA NRAD1 and LINC00152 are Highly Expressed and Associated with Prognosis in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 10409–10416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Weng, W.; Chen, T.; Xu, M.; Wei, P.; Li, J.; Lu, L.; Wang, Y. LINC00152 Promotes Tumor Progression and Predicts Poor Prognosis by Stabilizing BCL6 From Degradation in the Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 555132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.-T.; Hatami, R.; Rahimi, Z. Circulating CYTOR as a Potential Biomarker in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Cell Med. 2020, 9, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xiao, X.; Liu, C.; Lin, J.; Zheng, S.; Yang, B.; Ou, Q. A Circulating Long Noncoding RNA Panel Serves as a Diagnostic Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pufall, M.A. Glucocorticoids and Cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 872, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larson, R.A.; Dodge, R.K.; Burns, C.P.; Lee, E.J.; Stone, R.M.; Schulman, P.; Duggan, D.; Davey, F.R.; Sobol, R.E.; Frankel, S.R. A five-drug remission induction regimen with intensive consolidation for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Cancer and leukemia group B study 8811. Blood 1995, 85, 2025–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dördelmann, M.; Reiter, A.; Borkhardt, A.; Ludwig, W.D.; Götz, N.; Viehmann, S.; Gadner, H.; Riehm, H.; Schrappe, M. Prednisone response is the strongest predictor of treatment outcome in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 1999, 94, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möricke, A.; Lauten, M.; Beier, R.; Odenwald, E.; Stanulla, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Attarbaschi, A.; Niggli, F.; Schrappe, M. Prediction of Outcome by Early Response in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Klin. Padiatr. 2013, 225, S50–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bill, M.; Papaioannou, D.; Karunasiri, M.; Kohlschmidt, J.; Pepe, F.; Walker, C.J.; Walker, A.E.; Brannan, Z.; Pathmanathan, A.; Zhang, X.; et al. Expression and functional relevance of long non-coding RNAs in acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2169–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Xie, Z.; Lei, X.; Gan, R. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 in human cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickard, M.R.; Williams, G.T. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Action of Tumour Suppressor GAS5 LncRNA. Genes 2015, 6, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frank, F.; Kavousi, N.; Bountali, A.; Dammer, E.B.; Mourtada-Maarabouni, M.; Ortlund, E.A. The lncRNA Growth Arrest Specific 5 Regulates Cell Survival via Distinct Structural Modules with Independent Functions. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 107933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayama, T.; Marr, A.K.; Kino, T. Differential Expression of Glucocorticoid Receptor Noncoding RNA Repressor Gas5 in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases. Horm. Metab. Res. 2016, 48, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, W.H.; Pickard, M.R.; De Vera, I.M.; Kuiper, E.G.; Mourtada-Maarabouni, M.; Conn, G.L.; Kojetin, D.J.; Williams, G.T.; Ortlund, E.A. Conserved sequence-specific lincRNA-steroid receptor interactions drive transcriptional repression and direct cell fate. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kino, T.; Hurt, D.E.; Ichijo, T.; Nader, N.; Chrousos, G.P. Noncoding RNA Gas5 Is a Growth Arrest- and Starvation-Associated Repressor of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mourtada-Maarabouni, M.; Hasan, A.M.; Farzaneh, F.; Williams, G.T. Inhibition of Human T-Cell Proliferation by Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Antagonists Requires Noncoding RNA Growth-Arrest-Specific Transcript 5 (GAS5). Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 78, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacqub-Usman, K.; Pickard, M.R.; Williams, G.T. Reciprocal regulation of GAS5 lncRNA levels and mTOR inhibitor action in prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2015, 75, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Sun, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, H. Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) Growth Arrest Specific 5 (GAS5) Suppresses Esophageal Squamous Cell Car-cinoma Cell Proliferation and Migration by Inactivating Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Signaling Pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 7689–7696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simioni, C.; Martelli, A.M.; Zauli, G.; Melloni, E.; Neri, L.M. Targeting mTOR in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cells 2019, 8, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambrou, G.I.; Hatziagapiou, K.; Zaravinos, A. The Non-Coding RNA GAS5 and Its Role in Tumor Therapy-Induced Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Z.; Gao, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Nie, B.; Hong, Q. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 regulates human B lymphocytic leukaemia tumourigenesis and metastasis by sponging miR-222. Cancer Biomark. 2019, 26, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffre, M.; Koralov, S.B. miRNAs in B Cell Development and Lymphomagenesis. Trends Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Z.; Li, L.; Lodish, H.F.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs Modulate Hematopoietic Lineage Differentiation. Science 2004, 303, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawoof, A.; Swaminathan, G.; Tiwari, S.; Nair, R.A.; Kumar, L.D. LeukmiR: A database for miRNAs and their targets in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Database 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, S.; Mayr, C.; Bartel, D.P.; Lodish, H.F. miR-150, a microRNA expressed in mature B and T cells, blocks early B cell development when expressed prema-turely. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7080–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, C.; Calado, D.P.; Galler, G.; Thai, T.-H.; Patterson, H.C.; Wang, J.; Rajewsky, N.; Bender, T.P. MiR-150 Controls B Cell Differentiation by Targeting the Transcription Factor c-Myb. Cell 2007, 131, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kluiver, J.; Chen, C.-Z. MicroRNAs regulate B-cell receptor signaling-induced apoptosis. Genes Immun. 2012, 13, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Luo, X.-Q.; Zhang, P.; Huang, L.-B.; Zheng, Y.-S.; Wu, J.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.-H.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.-Q. MicroRNA Patterns Associated with Clinical Prognostic Parameters and CNS Relapse Prediction in Pediatric Acute Leukemia. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schotte, D.; Pieters, R.; Boer, M.L.D. MicroRNAs in acute leukemia: From biological players to clinical contributors. Leukemia 2011, 26, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umerez, M.; Garcia-Obregon, S.; Martin-Guerrero, I.; Astigarraga, I.; Gutierrez-Camino, A.; Garcia-Orad, A. Role of miRNAs in treatment response and toxicity of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pharmacogenomics 2018, 19, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, S.; Lu, J.; Sun, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Neilly, M.B.; Wang, Y.; Qian, Z.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. MicroRNA expression signatures accurately discriminate acute lymphoblastic leukemia from acute myeloid leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19971–19976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, R.D.S.; Silva, M.C.E.; Coutinho, L.L.; Gomes, R.G.; Pedrosa, F.; Massaro, J.D.; Donadi, E.A.; Lucena-Silva, N. MicroRNA expression profiles discriminate childhood T- from B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fulci, V.; Colombo, T.; Chiaretti, S.; Messina, M.; Citarella, F.; Tavolaro, S.; Guarini, A.; Foà, R.; Macino, G. Characterization of B- and T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia by integrated analysis of MicroRNA and mRNA expression profiles. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2009, 48, 1069–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schotte, D.; De Menezes, R.X.; Moqadam, F.A.; Khankahdani, L.M.; Lange-Turenhout, E.; Chen, C.; Pieters, R.; Boer, M.L.D. MicroRNA characterize genetic diversity and drug resistance in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2011, 96, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nucera, S.; Giustacchini, A.; Boccalatte, F.; Calabria, A.; Fanciullo, C.; Plati, T.; Ranghetti, A.; Garcia-Manteiga, J.; Cittaro, D.; Benedicenti, F.; et al. miRNA-126 Orchestrates an Oncogenic Program in B Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 905–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, B.; Theng, P.Y.; Le, M.T.N. Essential functions of miR-125b in cancer. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e12913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapiro, E.; Russell, L.J.; Struski, S.; Cavé, H.; Radfordweiss, I.; Della Valle, V.; Lachenaud, J.; Brousset, P.; Bernard, O.A.; Harrison, C.J.; et al. A new recurrent translocation t(11;14)(q24;q32) involving IGH@ and miR-125b-1 in B-cell progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2010, 24, 1362–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bousquet, M.; Harris, M.H.; Zhou, B.; Lodish, H.F. MicroRNA miR-125b causes leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21558–21563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moqadam, F.A.; Lange-Turenhout, E.; Ariës, I.; Pieters, R.; Boer, M.D. MiR-125b, miR-100 and miR-99a co-regulate vincristine resistance in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.-W.; Feng, D.-D.; Li, Z.-G.; Luo, X.-Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.-J.; Zhang, X.-J.; Zheng, L.-L.; Zeng, C.-W.; Lin, K.-Y.; et al. A set of miRNAs that involve in the pathways of drug resistance and leukemic stem-cell differentiation is associated with the risk of relapse and glucocorticoid response in childhood ALL. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 4903–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avigad, S.; Verly, I.R.; Lebel, A.; Kordi, O.; Shichrur, K.; Ohali, A.; Hameiri-Grossman, M.; Kaspers, G.J.; Cloos, J.; Froňková, E.; et al. miR expression profiling at diagnosis predicts relapse in pediatric precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2015, 55, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, J.; Tang, Y.; Tian, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Yang, D.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Circular RNAs in Cancer: Emerging functions in hallmarks, stemness, resistance and roles as potential biomarkers. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maass, P.G.; Glažar, P.; Memczak, S.; Dittmar, G.; Hollfinger, I.; Schreyer, L.; Sauer, A.V.; Toka, O.; Aiuti, A.; Luft, F.C.; et al. A map of human circular RNAs in clinically relevant tissues. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, G.; Lorenzen, J.M. Biogenesis and Function of Circular RNAs in Health and in Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Li, S.; Guo, W.; Zhao, J.; Chen, D.; Gu, J.; He, X.; Huang, S. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: A promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bahn, J.H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, F.; Chan, T.-M.; Lin, X.; Kim, Y.; Wong, D.T.; Xiao, X. The Landscape of MicroRNA, Piwi-Interacting RNA, and Circular RNA in Human Saliva. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Preußer, C.; Hung, L.H.; Schneider, T.; Schreiner, S.; Hardt, M.; Moebus, A.; Santoso, S.; Bindereif, A. Selective release of circRNAs in platelet-derived extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1424473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, J.R.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. The Potential of Circular RNAS as Cancer Biomarkers. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2020, 29, 2541–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffo, E.; Boldrin, E.; Molin, A.D.; Bresolin, S.; Bonizzato, A.; Trentin, L.; Frasson, C.; Debatin, K.-M.; Meyer, L.H.; Kronnie, G.T.; et al. Circular RNA differential expression in blood cell populations and exploration of circRNA deregulation in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; Fang, K.; Chen, T.-Q.; Zeng, Z.-C.; Sun, Y.-M.; Han, C.; Sun, L.-Y.; Chen, Z.-H.; Yang, Q.-Q.; Pan, Q.; et al. circRNA circAF4 functions as an oncogene to regulate MLL-AF4 fusion protein expression and inhibit MLL leukemia progression. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonizzato, A.; Gaffo, E.; Kronnie, G.T.; Bortoluzzi, S. CircRNAs in hematopoiesis and hematological malignancies. Blood Cancer J. 2016, 6, e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Acha, O.P.; Rossi, M.; Gorospe, M. Circular RNAs in Blood Malignancies. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal, M.; Song, T.; Chen, B.; Faisal, M.; Hong, Z.; Xie, T.; Wu, Y.; Pan, S.; Yin, Q.; Shao, L.; et al. Recent Progress on Circular RNA Research in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronchetti, D.; Todoerti, K.; Tuana, G.; Agnelli, L.; Mosca, L.; Lionetti, M.; Fabris, S.; Colapietro, P.; Miozzo, M.; Ferrarini, M.; et al. The expression pattern of small nucleolar and small Cajal body-specific RNAs characterizes distinct molecular subtypes of multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2012, 2, e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchetti, D.; Mosca, L.; Cutrona, G.; Tuana, G.; Gentile, M.; Fabris, S.; Agnelli, L.; Ciceri, G.; Matis, S.; Massucco, C.; et al. Small nucleolar RNAs as new biomarkers in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. BMC Med. Genom. 2013, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warner, W.A.; Spencer, D.H.; Trissal, M.; White, B.S.; Helton, N.; Ley, T.J.; Link, D.C. Expression profiling of snoRNAs in normal hematopoiesis and AML. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.; Wen, J.; Huang, Z.; Chen, X.-P.; Zhang, B.-X.; Chu, L. Small Nucleolar RNAs: Insight Into Their Function in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiss, T. Small nucleolar RNAs: An abundant group of noncoding RNAs with diverse cellular functions. Cell 2002, 109, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valleron, W.; Laprevotte, E.; Gautier, E.-F.; Quelen, C.; Demur, C.; Delabesse, E.; Agirre, X.; Prosper, F.; Kiss, T.; Brousset, P. Specific small nucleolar RNA expression profiles in acute leukemia. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2052–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, Z.; Churchman, M.L.; Roberts, K.G.; Moore, I.; Zhou, X.; Nakitandwe, J.; Hagiwara, K.; Pelletier, S.; Gingras, S.; Berns, H.; et al. PAX5-driven subtypes of B-progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wang, X.; Lv, L.; Liu, J.; Xing, H.; Song, Y.; Xie, M.; Lei, T.; Zhang, N.; Yang, M. The emerging role of microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, C.-Y.; Liew, S.-M.; Price, A.; Gan, G.-G.; Ong, D.B.-L.; Tan, S.-Y.; Bee, P.-C. Clinical significance of aberrant microRNAs expression in predicting disease relapse/refractoriness to treatment in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2019, 144, 102818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelatos, G.; Fragoulis, G.E.; Koulouri, V.; Lambrou, G.I. MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: From pathogenesis to clinical impact. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.-L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, K.-H. MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for diagnosis, therapy and prognosis of gastric cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 3891–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bussemakers, M.J.; Van Bokhoven, A.; Verhaegh, G.W.; Smit, F.P.; Karthaus, H.F.; Schalken, J.A.; Debruyne, F.M.; Ru, N.; Isaacs, W.B. DD3: A new prostate-specific gene, highly overexpressed in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5975–5979. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deras, I.L.; Aubin, S.M.; Blase, A.; Day, J.R.; Koo, S.; Partin, A.W.; Ellis, W.J.; Marks, L.S.; Fradet, Y.; Rittenhouse, H.; et al. PCA3: A Molecular Urine Assay for Predicting Prostate Biopsy Outcome. J. Urol. 2008, 179, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, L.S.; Bostwick, D.G. Prostate Cancer Specificity of PCA3 Gene Testing: Examples from Clinical Practice. Rev. Urol. 2008, 10, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- De la Taille, A.; Irani, J.; Graefen, M.; Chun, F.; de Reijke, T.; Kil, P.; Gontero, P.; Mottaz, A.; Haese, A. Clinical evaluation of the PCA3 assay in guiding initial biopsy decisions. J. Urol. 2011, 185, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.L.; Dobi, A.; Srivastava, S. Prostate cancer: Diagnostic performance of the PCA3 urine test. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2011, 8, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velonas, V.M.; Woo, H.H.; Dos Remedios, C.G.; Assinder, S.J. Current Status of Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 11034–11060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prensner, J.R.; Rubin, M.A.; Wei, J.T.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Beyond PSA: The Next Generation of Prostate Cancer Biomarkers. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 127rv3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toraih, E.A.; El-Wazir, A.; Al Ageeli, E.; Hussein, M.H.; Eltoukhy, M.M.; Killackey, M.T.; Kandil, E.; Fawzy, M.S. Unleash multifunctional role of long noncoding RNAs biomarker panel in breast cancer: A predictor classification model. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 1215–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lv, Y.; Shao, C.; Chen, C.; Zhang, T.; Wei, Y.; Fan, H.; Lv, T.; Liu, H.; Song, Y. Tumor-derived exosomal lncRNA GAS5 as a biomarker for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer diagnosis. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 20721–20727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisey, C.L.; Tomek, P.; Nursalim, Y.N.; Chamley, L.W.; Leung, E. Towards establishing extracellular vesicle-associated RNAs as biomarkers for HER2+ breast cancer. F1000Res 2020, 9, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, X.-Q.; Yang, Y.-L.; Zhu, K.-W.; Zeng, H.; Li, X.-L.; Cao, S.; Zhou, H.-H.; et al. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 polymorphism predicts a poor prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia in Chinese patients via affecting hematopoietic reconstitution. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 58, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| LncRNA | Neighboring Genes | B-ALL Subtype Expression | Clinical or Functional Implications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BALR-1 | C14orf132 | upregulated in ETV6-RUNX1 and High hyperdiploid subtypes | Unknown | [68,70] |
| BALR-2/CDK6-AS1 | CDK6 | ETV6-RUNX1, TCF3-PBX1 and MLL-rearranged subtypes | High expression correlated with poor overall survival and reduced response to prednisone treatment | [68,70] |
| BALR-6 | SATB1, TBC1D5 | highest expression in MLL-rearranged subtypes | Promotes cell survival in vitro | [68,71] |
| LINC00958 | TEAD1, RASSF10 | upregulated in ETV6-RUNX1 | miRNA sponge | [68,70,72,73,74] |
| TCL6 | TCL1B | ETV6-RUNX1 | Low expression associated with poor disease-free survival | [75] |
| AL133346.1 | CCN2 | unknown | High AL133346.1/CCN2 expression associated with greater disease-free survival | [69] |
| LINC00152/CYTOR | intergenic; resides in a cluster of lncRNAs on 2p11.2 | unknown | High expression associated with risk of early relapse | [76] |
| LINC01013 | intergenic; resides in a cluster of lncRNAs on 6q23.2 | unknown | Low expression associated with risk of early relapse | [76] |
| LAMP5-AS1 | LAMP5 | MLL-rearranged | High expression associated with reduced disease-free survival | [67,77] |
| CASC15/LINC00340 | SOX4 | ETV6-RUNX1 | Regulates expression of SOX4 | [68,78] |
| DBH-AS1 | DBH | unknown | Promotes cell survival through activation of MAPK signaling | [79] |
| lnc-NKX2-3-1 | NKX2-3 | upregulated in ETV6-RUNX1 | Unknown | [79] |
| lnc-TIMM21-5 | NETO1 | upregulated in ETV6-RUNX1 | Unknown | [79] |
| lnc-ASTN1-1 | ASTN1 | upregulated in ETV6-RUNX1 | Unknown | [79] |
| lnc-RTN4R-1 | RTN4R, CCDC188 | upregulated in ETV6-RUNX1 | Unknown | [79] |
| RP11-137H2.4/lnc-DYDC1-1 | TSPAN14, SH2D4B | upregulated in B-ALL compared to control pre-B cells isolated from human cord blood | Associated with cell survival and glucocorticoid resistance in vitro | [70,80] |
| GAS5 | High hyperdiploid and TCF3-PBX1 | Associated with glucocorticoid treatment sensitivity | [81,82] |
| miRNA | B-ALL Expression | Cohort Description | Clinical or Functional Implications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-125b | Upregulated in TEL-AML1-positive compared to non-TEL-AML1 precursor B-ALL | Mononuclear cells were isolated from BM and PB from 81 ALL patients, of which 70 were of the B-ALL subtype and 11 were T-ALL. 17 control samples were also includeda | Highly expressed (along with miR-100and miR-99a) in patients resistant to vincristinea,d | [130]a, [135]b, [133]c, [134]d |
| Upregulated in patients with t(11;14)(q24;q32) compared to B-ALL patients without t(11;14) | Total RNA was extracted from samples taken from 2 patients with t(11;14)(q24;q32) translocations and 28 B-ALL patients without t(11;14) for qPCRb Mononuclear cells were isolated from BM and PB from patients diagnosed with ETV6-RUNX1, TCF3 (E2A)-rearrangement, MLL-rearrangement or BCR-ABL1. Validation experiments was performed on Reh cellsd | When co-expressed with BCR-ABL, was shown to accelerate the development of leukemia in micec | ||
| miR-425-5p | Upregulated in B-ALL compared to T-ALL patients | See abovea BM or PB was obtained from 8 patients with ALL. Of these, 4 patients had T-ALL and 4 had B-ALLe BM or PB was obtained from 20 patients with ALL and analyzed by miRNA array. Of these, 4 had T-ALL and 16 had B-ALL. In the B-ALL cohort, 4 patients had a BCR/ABL rearrangement, 3 had an E2A/PBX1, 3 had an MLL/AF4 rearrangement, and 6 patients had no molecular abnormalitiesf | Unknown | [130]a, [128]e [129]f |
| miR-126 | Upregulated in TEL-AML1-positive compared to non-TEL-AML1 precursor B-ALL | See abovea,f | Higher expression correlated with chemotherapy resistancea | [130]a, [129]f [131]g, [124]h |
| Higher expression in BCR/ABLcohort compared to T-ALL patients | BM aspirates were collected from 17 B-ALL samples; 16 samples were further studied. 11 were of the Ph+ B-ALL subtype and 5 were of the B-ALL ‘other’ subtypeg | In xenotransplant murine model, knockdown induced apoptosis of B-ALL blast cellsg | ||
| Upregulated in B-ALL compared to healthy controls | BM samples from 43 patients were analyzed by microarray. These included 18 ALL, 18 AML, and 7 normal samples. Among the ALL samples, 17 were of the B-cell lineageh | |||
| miR-34a | Upregulated in B-ALL compared to healthy controls | See aboveh | Unknown | [124]h |
| miR-130b | Upregulated in B-ALL compared to healthy controls | See aboveh | Unknown | [124]h |
| miR-146a | Upregulated in B-ALL compared to healthy controls | See aboveh | Unknown | [124]h |
| miR-213 | Upregulated in B-ALL compared to healthy controls | See aboveh | Highly expressed in high-risk and intermediate risk groups; not abnormally expressed in standard-risk group. | [124]h |
| miR-210 | Upregulated in B-ALL compared to healthy controls | See aboveh | Highly expressed in high-risk and intermediate risk groups; not abnormally expressed in standard-risk group. | [124]h |
| miR-128a | Upregulated in B-ALL compared to AML samples and when compared to healthy controls. | See aboveh BM samples were collected from 58 patients for miRNA expression analysis. Of these, 11 were B-ALL and 47 were AML. All B-ALL samples had MLL-rearrangements. 14 cell lines were also included (7 ALL and 7 AML). In addition, 3 BM samples were collected from healthy controlsi | Highly expressed in ALL; can be used in miRNA expression signature to discriminate ALL from AML | [124]h, [127]i |
| miR-128b | Upregulated in B-ALL compared to AML samples and when compared to healthy controls. | See aboveh,i | Highly expressed in ALL; can be used in miRNA expression signature to discriminate ALL from AML | [124]h, [127]i |
| miR-708 | Upregulated at relapse compared to complete remission in matched-paired ALL samples | Matched-paired samples were collected from 18 ALL patients at diagnosis and at relapse or complete remission for microarray studies. Of these, 11 patients had B-ALL. 5 healthy control samples were also includedj | Higher expression correlated with higher relapse free survival in newly diagnosed ALL patients | [136]j |
| miR-1290 | Upregulated in ALL patients with adverse clinical parameters compared to those with good clinical parameters | BM samples from 48 patients were analyzed by microarray of which 35 were of the B-cell lineage and 13 were of the T-cell lineage. 32 of the B-ALL samples from the initial cohort, in addition to, 106 added B-ALL samples (n=132) were used for confirmation studiesk | High expression was associated with increased risk of relapse | [137]k |
| miR-151-5p | Downregulated in ALL patients with adverse clinical parameters compared to those with good clinical parameters | See abovek | Low expression was associated with increased risk of relapse | [137]k |
| miR-451 | Downregulated in ALL patients with adverse clinical parameters compared to those with good clinical parameters | See abovek | Low expression was associated with increased risk of relapse | [137]k |
| miR-150 | Downregulated in relapsed B-ALL patients compared to complete remission | See aboveh | Low expression was associated with poorer response to prednisone and is a part of a miRNA signature used to discriminate between relapse and complete remission | [124]h |
| Let-7b | Downregulated in MLL-rearranged compared to compared to MLL-negative patients | See abovea,i | Target analysis identified c-MYC and RAS as downstream targets of the let-7 family. mRNA levels of c-MYC and RAS were upregulated in MLL-rearranged ALL compared to non-MLL B-ALL patientsa | [130]a, [127]i |
| Downregulated in B-ALL compared to AML samples | Lowly expressed in ALL; can be used in miRNA expression signature to discriminate ALL from AMLi | |||
| miR-223 | Downregulated in B-ALL compared to AML samples | See above i, j | Lowly expressed in ALL; can be used in miRNA expression signature to discriminate ALL from AMLi | [127]i, [136]j |
| Downregulated at relapse compared to complete remission in matched-paired ALL samples | Higher expression correlated with higher relapse free survival in newly diagnosed ALL patients | |||
| miR-27a | Downregulated at relapse compared to complete remission in matched-paired ALL samples | See above j | Higher expression correlated with higher relapse free survival in newly diagnosed ALL patients | [136]j |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodriguez, P.D.; Paculova, H.; Kogut, S.; Heath, J.; Schjerven, H.; Frietze, S. Non-Coding RNA Signatures of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052683
Rodriguez PD, Paculova H, Kogut S, Heath J, Schjerven H, Frietze S. Non-Coding RNA Signatures of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(5):2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052683
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodriguez, Princess D., Hana Paculova, Sophie Kogut, Jessica Heath, Hilde Schjerven, and Seth Frietze. 2021. "Non-Coding RNA Signatures of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 5: 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052683
APA StyleRodriguez, P. D., Paculova, H., Kogut, S., Heath, J., Schjerven, H., & Frietze, S. (2021). Non-Coding RNA Signatures of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(5), 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052683







