Fecal Microbiota Transplantation during and Post-COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
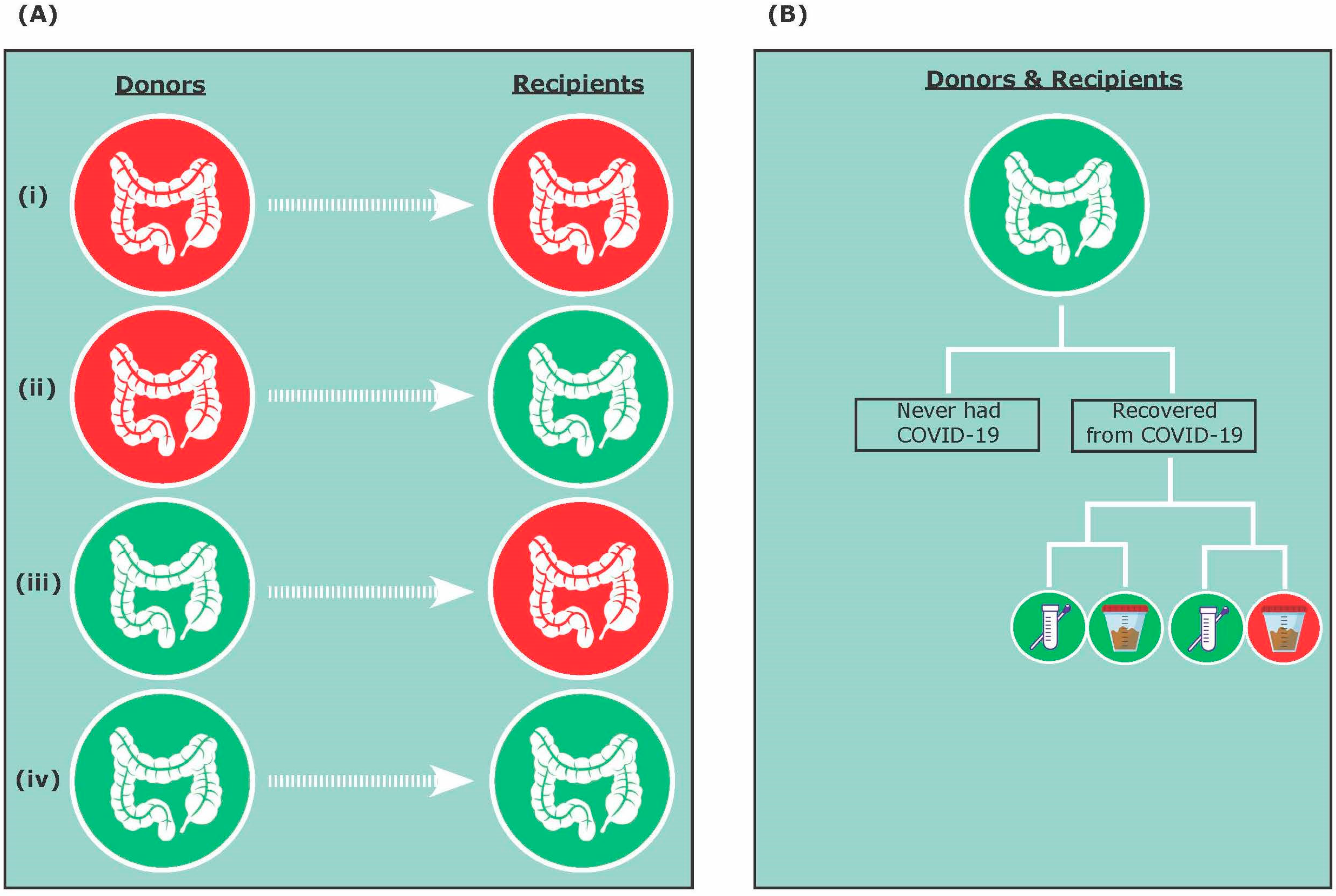
:1. Introduction
2. COVID-19 and FMT Safety
3. COVID-19 and FMT Efficacy
3.1. A Donor Perspective
3.2. A Patient Perspective
4. Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moayyedi, P.; Surette, M.G.; Kim, P.T.; Libertucci, J.; Wolfe, M.; Onischi, C.; Armstrong, D.; Marshall, J.K.; Kassam, Z.; Reinisch, W.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation induces remission in patients with active ulcerative colitis in a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnsen, P.H.; Hilpusch, F.; Cavanagh, J.P.; Leikanger, I.S.; Kolstad, C.; Valle, P.C.; Goll, R. Faecal microbiota transplantation versus placebo for moderate-to-severe irritable bowel syndrome: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, single-centre trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. 2018, 3, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Kassam, Z.; Fagan, A.; Gavis, E.A.; Liu, E.; Cox, I.J.; Kheradman, R.; Heuman, D.; Wang, J.; Gurry, T.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplant from a rational stool donor improves hepatic encephalopathy: A randomized clinical trial. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1727–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Nood, E.; Vrieze, A.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Fuentes, S.; Zoetendal, E.G.; de Vos, W.M.; Visser, C.E.; Kuijper, E.J.; Bartelsman, J.; Tijssen, J.G.P.; et al. Duodenal infusion of donor feces for recurrent Clostridium difficile. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drekonja, D.; Reich, J.; Gezahegn, S.; Greer, N.; Shaukat, A.; MacDonald, R.; Rutks, I.; Wilt, T. Fecal microbiota transplantation for clostridium difficile infection A systematic review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G.; Kelly, C.R.; Mullish, B.H.; Allegretti, J.R.; Kassam, Z.; Putignani, L.; Fischer, M.; Keller, J.J.; Castello, S.P.; et al. International consensus conference on stool banking for faecal microbiota transplantation in clinical practice. Gut 2019, 68, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bakken, J.S.; Polgreen, P.M.; Beekmann, S.E.; Riedo, F.X.; Streit, J.A. Treatment approaches including fecal microbiota transplantation for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection (RCDI) among infectious disease physicians. Anaerobe 2013, 24, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossarizza, A.; De Biasi, S.; Guaraldi, G.; Girardis, M.; Mussini, C. SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19: Cytometry and the new challenge for global health. Cytom. A 2020, 97, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/?gclid=Cj0KCQjwpNr4BRDYARIsAADIx9xT2a_zqbYI9teKhc_7FzirCyXpz556A1zTx_Elu4xHSEVCEnf3w4oaAjNlEALw_wcB (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- Hu, Z.; Song, C.; Xu, C.; Jin, G.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Ma, H.; Chen, W.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Clinical characteristics of 24 asymptomatic infections with COVID-19 screened among close contacts in Nanjing, China. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mizumoto, K.; Kagaya, K.; Zarebski, A.; Chowell, G. Estimating the asymptomatic proportion of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases on board the diamond princess cruise ship, Yokohama, Japan, 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krajicek, E.; Fischer, M.; Allegretti, J.R.; Kelly, C.R. Nuts and bolts of fecal microbiota transplantation. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcilroy, J.R.; Segal, J.P.; Mullish, B.H.; Nabil Quraishi, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G. Current and future targets for faecal microbiota transplantation. Hum. Microbiome J. 2018, 11, 10045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFilipp, Z.; Bloom, P.P.; Torres Soto, M.; Mansour, M.K.; Sater, M.R.A.; Huntley, M.H.; Turbett, S.; Chung, R.T.; Chen, Y.B.; Hohmann, E.L. Drug-resistant E. coli bacteremia transmitted by fecal microbiota transplant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alang, N.; Kelly, C. Weight gain after fecal microbiota transplantation. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2015, 2, ofv004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.; Gluck, M.; Koon, S. Norovirus gastroenteritis after fecal microbiota transplantation for treatment of Clostridium difficile infection despite asymptomatic donors and lack of sick contacts. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.R.; Kahn, S.; Kashyap, P.; Laine, L.; Rubin, D.; Atreja, A.; Moore, T.; Wu, G. Update on fecal microbiota transplantation 2015: Indications, methodologies, mechanisms, and outlook. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G.; Tilg, H.; Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; Kump, P.; Satokari, R.; Sokol, H.; Arkkila, P.; Pintus, C.; Hart, A.; et al. European consensus conference on faecal microbiota transplantation in clinical practice. Gut 2017, 66, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendrik, K.E.W.; Terveer, E.M.; Kuijper, E.J.; Nooij, S.; Boeije-Koppenol, E.; Sanders, I.M.J.G.; van Lingen, E.; Verspaget, H.W.; Berssenbrugge, E.K.L.; Keller, J.J.; et al. Periodic screening of donor faeces with a quarantine period to prevent transmission of multidrug-resistant organisms during faecal microbiota transplantation: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 30473–30474. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Shi, Z. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shang, J.; Ye, G.; Shi, K.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Aihara, H.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 581, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gheblawi, M.; Wang, K.; Viveiros, A.; Nguyen, Q.; Zhong, J.; Turner, A.J.; Raizada, M.K.; Grant, M.; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 receptor and regulator of the renin-angiotensin system: Celebrating the 20th anniversary of the discovery of ACE2. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1456–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.C.; Tilg, H. COVID-19 and the gastrointestinal tract: More than meets the eye. Gut 2020, 69, 973–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.; Chen, Q.; Gu, H.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, S.S.; Zhang, N.N.; Li, X.F.; Xiong, R.; et al. A mouse model of SARS-CoV-2 infection and pathogenesis. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 124–133.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, D.; Mohanty, A. Gut microbiota and covid-19- possible link and implications. Virus Res. 2020, 285, 198018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Tang, M.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Shan, H. Evidence for gastrointestinal infection of SARS-CoV-2. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1831–1833.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Tong, Z.; Wang, H.; Dai, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, J.; Wu, W.; Yuan, C.; Yu, M.L.; Li, P.; et al. Detection of novel coronavirus by RT-PCR in stool specimen from asymptomatic child, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1337–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuba, K.; Imai, Y.; Rao, S.; Gao, H.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Huan, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; et al. A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Y. Main clinical features of COVID-19 and potential prognostic and therapeutic value of the microbiota in SARS-CoV-2 infections. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Safety Alert Regarding Use of Fecal Microbiota for Transplantation and Additional Safety Protections Pertaining to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/safety-availability-biologics/safety-alert-regarding-use-fecal-microbiota-transplantation-and-additional-safety-protections (accessed on 3 December 2020).
- OpenBiome. OpenBiome Updates on COVID-19. Available online: https://www.openbiome.org/covid19 (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Ng, S.C.; Chan, F.K.L.; Chan, P.K.S. Screening FMT donors during the COVID-19 pandemic: A protocol for stool SARS-CoV-2 viral quantification. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 642–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianiro, G.; Mullish, B.H.; Kelly, C.R.; Kassam, Z.; Kuijper, E.J.; Ng, S.C.; Iqbal, T.H.; Allegretti, J.R.; Bibbo, S.; Sokol, H.; et al. Reorganisation of faecal microbiota transplant services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Gut 2020, 69, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianiro, G.; Mullish, B.H.; Kelly, C.R.; Sokol, H.; Kassam, Z.; Ng, S.C.; Fischer, M.; Allegretti, J.R.; Masucci, L.; Zhang, F.; et al. Screening of faecal microbiota transplant donors during the COVID-19 outbreak: Suggestions for urgent updates from an international expert panel. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, N. The Coronavirus Is Here to Stay—Here’s What That Means. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-00396-2 (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Craven, L.J.; Paravathy, S.N.; Tat-Ko, J.; Burton, J.P.; Silverman, M.S. Extended screening costs associated with selecting donors for fecal microbiota transplantation for treatment of metabolic syndrome-associated diseases. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2017, 4, ofx243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tariq, R.; Weatheraly, R.; Kammer, P.; Sardi, D.S.; Khanna, S. Donor screening experience for fecal microbiota transplantation in patients with recurrent C. difficile infection. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 52, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, S.J.; Waetzig, G.H.; Rehman, A.; Moltzau-Anderson, J.; Bharti, R.; Grasis, J.A.; Cassidy, L.; Schreiber, S. Efficacy of sterile fecal filtrate transfer for treating patients with Clostridium difficile infection. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGovern, B.H.; Ford, C.B.; Henn, M.R.; Pardi, D.S.; Khanna, S.; Hohmann, E.L.; O’Brien, E.J.; Desjardins, C.A.; Bernardo, P.; Wortman, J.R.; et al. SER-109, an investigational microbiome drug to reduce recurrence after Clostridioides difficile infection: Lessons learned from a phase 2 trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, ciaa387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kao, D.; Wong, K.; Franz, R.; Cochrane, K.; Sherriff, K.; Chui, L.; Lloyd, C.; Roach, B.; Bai, A.D.; Petrof, E.O.; et al. The effect of a microbial ecosystem therapeutic (MET-2) on recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection: A phase 1, open-label, single-group trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 158, S15. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, T.; Wong, S.; Cheung, C.; Lam, K.; Lui, R.; Cheung, K.; Zhang, F.; Tang, W.; Ching, J.Y.L.; Wu, J.C.Y.; et al. Gut fungal dysbiosis correlates with reduced efficacy of fecal microbiota transplantation in Clostridium difficile infection. Nature 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, A.; Bernard, L.; Poquet, Y.; Lugo-Villarino, G.; Neyrolles, O. The role of the lung microbiota and the gut–lung axis in respiratory infectious diseases. Cell. Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Budden, K.F.; Gellatly, S.L.; Wood, D.L.A.; Cooper, M.A.; Morrison, M.; Hugenholtz, P.; Hansbro, P.M. Emerging pathogenic links between microbiota and the gut-lung axis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuijt, T.J.; Lankelma, J.M.; Scicluna, B.P.; de Sousa e Melo, F.; Roelofs, J.J.; de Boer, J.D.; Hoogendijk, A.J.; de Beer, R.; de Vos, A.; Belzer, C.; et al. The gut microbiota plays a protective role in the host defence against pneumococcal pneumonia. Gut 2016, 65, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Chen, P.; Hsu, C. Commensal microflora contribute to host defense against Escherichia coli pneumonia through toll-like receptors. Shock 2011, 36, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinohe, T.; Pang, I.K.; Kumamoto, Y.; Peaper, D.R.; Ho, J.H.; Murray, T.S.; Iwasaki, A.; Littman, D.R. Microbiota regulates immune defense against respiratory tract influenza A virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5354–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Wang, N.; Tan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y. The cross-talk between gut microbiota and lungs in common lung diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, H.T.; Cuthbertson, L.; James, P.; Moffatt, M.F.; Cox, M.J.; Tregoning, J.S. Respiratory disease following viral lung infection alters the murine gut microbiota. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Oliveira, G.L.V.; Oliveira, C.N.S.; Pinzan, C.F.; de Salis, L.V.V.; de Barros Cardoso, C.R. Microbiota modulation of the gut-lung axis in COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 635471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, Z.; Gu, Z.; Gao, L.; Sihi, H.; Mai, L.; et al. Gastrointestinal symptoms of 95 cases with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Gut 2020, 69, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, T.; Algharawi, A.A.; Idrees, M.; Alzaidy, R.H.; Faris, K.; Cullingford, G.; Rasheed, J. The prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms among patients with COVID-19 and the effect on the severity of the disease. JGH Open 2020, 4, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, T.; Zhang, F.; Lui, G.C.Y.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Li, A.Y.L.; Zhan, H.; Wan, Y.; Chung, A.C.K.; Cheung, C.P.; Chen, N.; et al. Alterations in gut microbiota of patients with COVID-19 during time of hospitalization. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Lv, L.; Guo, F.; Zhang, X.; Luo, R.; Huang, C.; et al. Alterations of the gut microbiota in patients with COVID-19 or H1N1 influenza. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, ciaa709. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, T.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Liu, G.C.; Tso, E.Y.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Chen, Z.; Boon, S.S.; Chan, F.K.L.; Chan, P.K.S.; et al. Depicting SARS-CoV-2 faecal viral activity in association with gut microbiota composition in patients with COVID-19. Gut 2020, 70, 276–284. [Google Scholar]
- Yeoh, Y.K.; Zuo, T.; Lui, G.C.Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Q.; Li, A.Y.L.; Chung, A.C.K.; Cheung, C.P.; Tso, E.Y.K.; Fung, K.S.C.; et al. Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19. Gut 2020, 70, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sokol, H.; Pigneur, B.; Watterlot, L.; Lakhdari, O.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Gratadoux, J.; Blugeon, S.; Bridonneau, C.; Furet, J.P.; Corthier, G.; et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of crohn disease patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16731–16736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Musso, G.; Gambino, R.; Cassader, M. Interactions between gut microbiota and host metabolism predisposing to obesity and diabetes. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011, 62, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, G.T.; Macfarlane, S. Fermentation in the human large intestine: Its physiologic consequences and the potential contribution of prebiotics. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 45, S120–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trompette, A.; Gollwitzer, E.S.; Yadava, K.; Sichelstiel, A.K.; Sprenger, N.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Blacnchard, C.; Junt, T.; Nicod, L.P.; Harris, N.L.; et al. Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrell, J.M.; Boehme, S.; Li, F.; Chiang, J.Y. Cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase-deficient mice are protected from high-fat/high-cholesterol diet-induced metabolic disorders. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, P.S.; Mason, M.R.; Brooker, M.R.; O’Brien, K. Pyrosequencing reveals unique microbial signatures associated with healthy and failing dental implants. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2012, 39, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullish, B.H.; McDonald, J.A.K.; Pechlivanis, A.; Allegretti, J.R.; Kao, D.; Barker, G.F.; Kapila, D.; Petrof, E.O.; Joyce, S.A.; Gahan, C.G.M.; et al. Microbial bile salt hydrolases mediate the efficacy of faecal microbiota transplant in the treatment of recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection. Gut 2019, 68, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorg, J.A.; Sonenshein, A.L. Inhibiting the initiation of Clostridium difficile spore germination using analogs of chenodeoxycholic acid, a bile acid. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 4983–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Xu, R.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Tian, M.; Lu, H.; et al. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) inhibits influenza A viral infection by disrupting viral proton channel M2. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, L.; Han, W.; Du, J.; Yang, X.; Duan, M.; Xu, C.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, W.; Chen, J. Chenodeoxycholic acid from bile inhibits influenza A virus replication via blocking nuclear export of viral ribonucleoprotein complexes. Molecules 2018, 23, 3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Chang, K. Inhibitory effects of bile acids and synthetic farnesoid x receptor agonists on rotavirus replication. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 12570–12577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Peng, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Ren, B.; Jing, Z.; Sui, J.; Li, W. Viral entry of hepatitis b and d viruses and bile salts transportation share common molecular determinants on sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3273–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van den Munckhof, I.C.L.; Kurilshikov, A.; Horst, R.T.; Riksen, N.P.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Zhernakova, A.; Keating, S.T.; Netea, M.G.; de Graaf, J.; Rutten, J.H.W. Role of gut microbiota in chronic low-grade inflammation as potential driver for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A systematic review of human studies. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 1719–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, W.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.J.; Jo, M.; Kumar, H.; Han, I.; Sohn, S. Anti-inflammatory effects of ursodeoxycholic acid by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 macrophages. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ko, W.; Kim, S.J.; Jo, M.; Choi, H.; Lee, D.; Kwon, I.K.; Lee, S.; Han, I.; Sohn, S. Ursodeoxycholic acid inhibits inflammatory responses and promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury in rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, F.; Xu, X.; Zhang, R.; Sun, L.; Gan, N.; Wang, A. Ursodeoxycholic acid stimulates alveolar fluid clearance in LPS-induced pulmonary edema via ALX/cAMP/PI3K pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 20057–20065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cao, B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, M.; Gao, Y.; Wang, G.; Song, G.; Liu, S.; Sun, D.; Xu, Y.; Tian, Z. Functional exhaustion of antiviral lymphocytes in COVID-19 patients. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 533–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Ward, S.A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; El-Omar, E.M. Considering the effects of microbiome and diet on SARS-CoV-2 infection: Nanotechnology roles. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5179–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, M.; Osborne, L.; Monticelli, L.; Doering, T.; Alenghat, T.; Sonnenberg, G.; Paley, M.; Antenus, M.; Williams, K.; Erikson, J.; et al. Commensal bacteria calibrate the activation threshold of innate antiviral immunity. Immunity 2012, 37, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gou, W.; Fu, Y.; Yue, L.; Chen, G.-D.; Cai, X.; Shuai, M.; Xu, F.; Yi, X.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Gut microbiota may underlie the predisposition of healthy individuals to COVID-19. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullish, B.H.; Williams, H.R. Clostridium difficile infection and anti-biotic-associated diarrhoea. Clin. Med. 2018, 8, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schäffler, H.; Breitrück, A. Clostridium difficile—From colonization to infection. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Gu, L.; Zhang, X.; Pu, Z.; Yang, G.; Liu, B.; Nie, Q.; et al. Disease severity and clinical outcomes of community-acquired pneumonia caused by non-influenza respiratory viruses in adults: A multicentre prospective registry study from the CAP-china network. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1802406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, T.; Perlot, T.; Rehman, A.; Trichereau, J.; Ishiguro, H.; Paolino, M.; Sigl, V.; Hanada, T.; Hanada, R.; Lipinski, S.; et al. ACE2 links amino acid malnutrition to microbial ecology and intestinal inflammation. Nature 2012, 487, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briguglio, M.; Pregliasco, F.E.; Lombardi, G.; Perazzo, P.; Banfi, G. The malnutritional status of the host as a virulence factor for new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; He, T.; Becker, S.; Zhang, G.; Li, D.; Ma, X. Butyrate: A double-edged sword for health? Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dang, A.T.; Marsland, B.J. Microbes, metabolites, and the gut-lung axis. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, S. Are Significant False Negatives in the Usually Sensitive RT-PCR Detection of SARS-CoV2 Happening as the Usually RNA-Stranded Bacteria is now DNA within a Bacteria (Prevotella?) Genome—And Won’t be Detected in the Lysogenic State. OSF Prepr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.F.; Yuan, S.; Kok, K.; To, K.K.; Chu, H.; Yang, J.; Xing, F.; Liu, J.; Yip, C.; Poon, R.W.; et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: A study of a family cluster. Lancet 2020, 395, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, K.; Cai, H.; Shen, Y.; Ni, Q.; Chen, Y.; Hu, S.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, L.; Huang, H.; et al. Management of corona virus disease-19 (COVID-19): The Zhejiang experience. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2020, 49, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Gao, R.; Lu, R.; Han, K.; Wu, G.; Tan, W. Detection of SARS- CoV-2 in different types of clinical specimen. JAMA 2020, 323, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taur, Y.; Coyte, K.; Schluter, J.; Robilotti, E.; Figueroa, C.; Gjonbalaj, M.; Littmann, E.R.; Ling, L.; Miller, L.; Gyaltshen, J.; et al. Reconstitution of the gut microbiota of antibiotic-treated patients by autologous fecal microbiota transplant. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaap9489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buffie, C.G.; Bucci, V.; Stein, R.R.; McKenney, P.T.; Ling, L.; Gobourne, A.; No, D.; Liu, H.; Kinnebrew, M.; Viale, A.; et al. Precision microbiome restoration of bile acid-mediated resistance to Clostridium difficile. Nature 2015, 517, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Kakiyama, G.; Savidge, T.; Takei, H.; Kassam, Z.A.; Fagan, A.; Gavis, E.A.; Pandak, W.M.; Nittono, H.; Hylemon, P.B.; et al. Antibiotic-associated disruption of microbiota composition and function in cirrhosis is restored by fecal transplant. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seekatz, A.M.; Theriot, C.M.; Rao, K.; Chang, Y.; Freeman, A.E.; Kao, J.Y.; Young, V.B. Restoration of short chain fatty acid and bile acid metabolism following fecal microbiota transplantation in patients with recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. Anaerobe 2018, 53, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ye, S.; Zhu, X.; He, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Ren, X.; et al. Gastrointestinal disturbance and effect of fecal microbiota transplantation in discharged COVID-19 patients. J. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 15, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Daxini, A.; Baniya, R.; Nandi, N.; Ahmad, A.S. Tu1877—Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, S1156–S1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Atucha, A.; Izagirre, A.; Fraile-Bermúdez, A.B.; Kortajarena, M.; Larrinaga, G.; Martinez-Lage, P.; Echevarria, E.; Gil, J. Sex differences in the aging pattern of renin-angiotensin system serum peptidases. Biol. Sex. Differ. 2017, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaki, A.M. Brief report: Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 394. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, S.L.; Flanagan, K.L. Sex differences in immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, R.; Zheng, Y. The influence of age and sex on the cell counts of peripheral blood leukocyte subpopulations in chinese rhesus macaques. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 6, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgert, B.N.; Oriss, T.B.; Qi, Z.; Dixon-McCarthy, B.; Geerlings, M.; Hylkema, M.N.; Ray, A. Macrophages regulators of sex differences in asthma? Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 42, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisitkun, P.; Deane, J.A.; Difilippantonio, M.J.; Tarasenko, T.; Satterthwaite, A.B.; Bolland, S. Autoreactive B cell responses to RNA-related antigens due to TLR7 gene duplication. Science 2006, 312, 1669–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souyris, M.; Cenac, C.; Azar, P.; Daviaud, D.; Canivet, A.; Grunenwald, S.; Xian, J.; Guéry, J. TLR7 escapes X chromosome inactivation in immune cells. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villacres, M.C.; Longmate, J.; Auge, C.; Diamond, D.J. Predominant type 1 CMV-specific memory T-helper response in humans: Evidence for gender differences in cytokine secretion. Hum. Immunol. 2004, 65, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, B.R.; Bhanushali, A.A.; Khadapkar, R.; Jeswani, K.D.; Bhavsar, M.; Dasgupta, A. Reference ranges for lymphocyte subsets in adults from western india: Influence of sex, age and method of enumeration. Indian J. Med. Sci. 2008, 62, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Ryu, E.; Hathcock, M.; Ballman, K.; Chia, N.; Olson, J.E.; Nelson, H. Impact of demographics on human gut microbial diversity in a US Midwest population. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takagi, T.; Naito, Y.; Inoue, R.; Kashiwagi, S.; Uchiyama, K.; Mizushima, K.; Tsuchiya, S.; Dohi, O.; Yoshida, N.; Kamada, K.; et al. Differences in gut microbiota associated with age, sex, and stool consistency in healthy Japanese subjects. Gastroenterology 2019, 54, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancy, C.W. COVID-19 and African Americans. JAMA 2020, 323, 1891–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agyemang, C.; van den Born, B. Non-communicable diseases in migrants: An expert review. J. Travel Med. 2019, 26, tay107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy-Walls, P.; Long, J.G. African Americans and heart disease. Health Soc. Work 2017, 42, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barfield, W.L.; Boyce, C.A. Sex, ethnicity, and CVD among women of African Descent: An approach for the new era of genomic research. Glob. Heart 2017, 12, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.W.; Priya, S.; Blekhman, R.; Bordenstein, S.R. Gut microbiota diversity across ethnicities in the United States. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2006842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kazemian, N.; Ramezankhani, M.; Sehgal, A.; Khalid, F.M.; Kalkhoran, A.H.Z.; Narayan, A.; Wong, G.K.S.; Kao, D.; Pakpour, S. The trans-kingdom battle between donor and recipient gut microbiome influences fecal microbiota transplantation outcome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smillie, C.S.; Sauk, J.; Gevers, D.; Friedman, J.; Sung, J.; Youngster, I.; Hohmann, E.L.; Staley, C.; Khoruts, A.; Sadowsky, M.J.; et al. Strain tracking reveals the determinants of bacterial engraftment in the human gut following fecal microbiota transplantation. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staley, C.; Kaiser, T.; Vaughn, B.P.; Graiziger, C.T.; Hamilton, M.J.; Rehman, T.U.; Song, K.; Khoruts, A.; Sadowsky, M.J. Predicting recurrence of Clostridium difficile infection following encapsulated fecal microbiota transplantation. Microbiome 2018, 6, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, M.; Kao, D.; Mehta, S.; Martin, T.; Dimitry, J.; Keshteli, A.; Cook, G.K.; Phelps, E.; Sipe, B.W.; Xu, H.; et al. Predictors of early failure after fecal microbiota transplantation for the therapy of Clostridium difficile infection: A multicenter study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, K.; Ye, Z.-W.; Fung, S.; Chan, C.; Jin, D. SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: The most important research questions. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grasselli, G.; Zangrillo, A.; Zanella, A.; Antonelli, M.; Cabrini, L.; Castelli, A.; Cereda, D.; Coluccello, A.; Foti, G.; Fumagalli, R.; et al. Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the lombardy region, Italy. JAMA 2020, 323, 574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avni, T.; Babitch, T.; Ben-Zvi, H.; Hijazi, R.; Ayada, G.; Atamna, A.; Bishara, J. Clostridioides difficile infection in immunocompromised hospitalized patients is associated with a high recurrence rate. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 90, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chitnis, A.S.; Holzbauer, S.M.; Belflower, R.M.; Winston, L.G.; Bamberg, W.M.; Lyons, C.; Farley, M.M.; Dumyati, G.K.; Wilson, L.E.; Beldavs, Z.G.; et al. Epidemiology of community-associated Clostridium difficile infection, 2009 through 2011. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, B.; Li, Q.; Wen, L.; Zhang, R. Clinical features of 69 cases with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chmielewski, P. Leukocyte count, systemic inflammation, and health status in older adults: A narrative review. Anthropol. Rev. 2018, 81, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazemian, N.; Kao, D.; Pakpour, S. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation during and Post-COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063004
Kazemian N, Kao D, Pakpour S. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation during and Post-COVID-19 Pandemic. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(6):3004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063004
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazemian, Negin, Dina Kao, and Sepideh Pakpour. 2021. "Fecal Microbiota Transplantation during and Post-COVID-19 Pandemic" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 6: 3004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063004
APA StyleKazemian, N., Kao, D., & Pakpour, S. (2021). Fecal Microbiota Transplantation during and Post-COVID-19 Pandemic. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(6), 3004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063004





