Differential Disrupting Effects of Prolonged Low-Dose Exposure to Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane on Androgen and Estrogen Production in Males
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
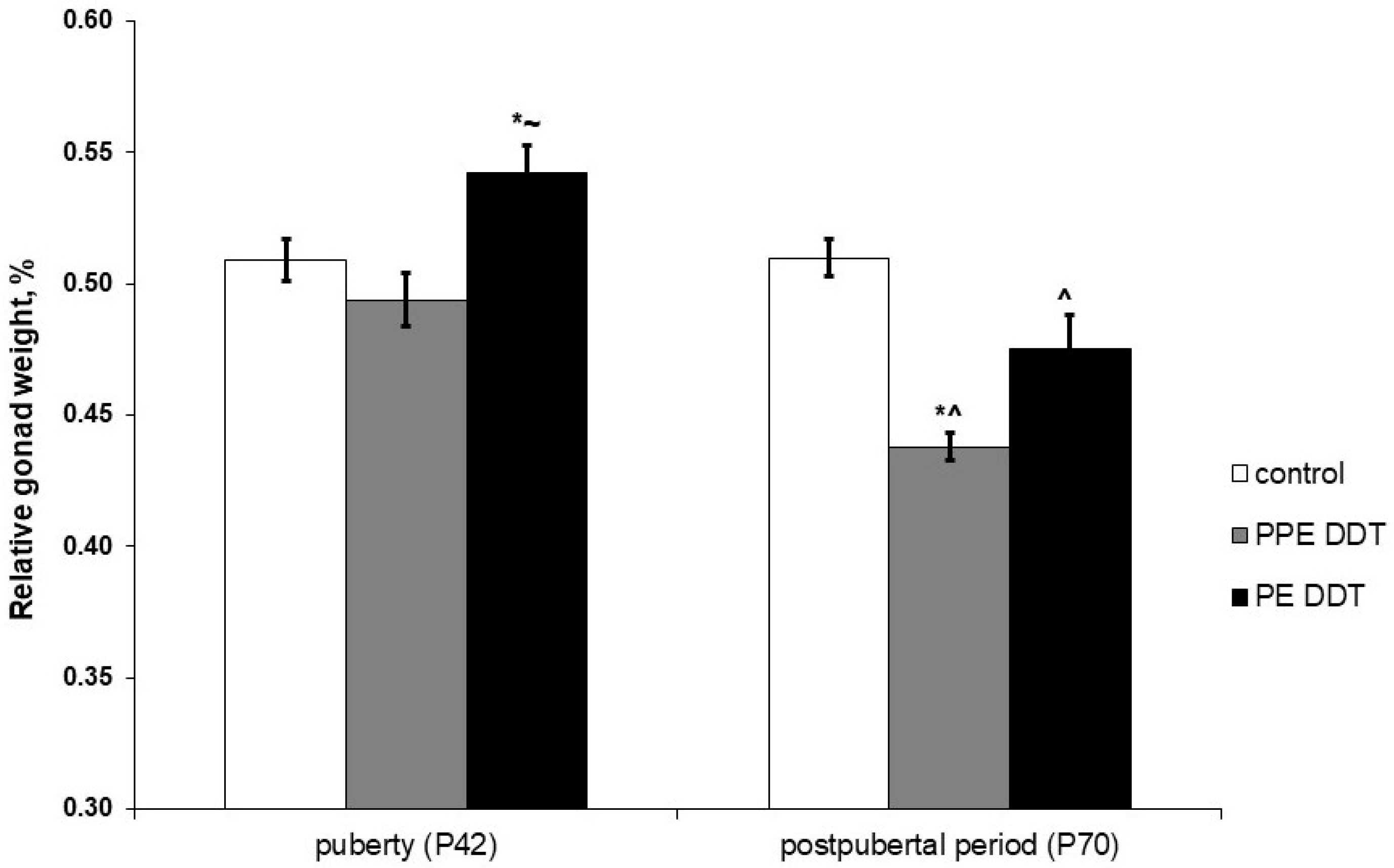
2.1. Changes in Gonadal Development
2.2. Changes in Sex Steroid Precursors’ Secretion
2.3. Changes in Androgen Hormones’ Production
2.4. Changes in Estrogen Hormones’ Production
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. Experimental Design
4.4. Determination of Gonad Weight
4.5. Hormone Assays
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. State of the Science of Evidence for Endocrine Disruption in Humans and Wildlife; Bergman, A., Heindel, J., Jobling, S., Kidd, K., Zoeller, R.T., Eds.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; 260p. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Qin, L.; Xie, X.; Gao, B.; Sun, J.; Li, A. Distribution of endocrine disrupting chemicals in colloidal and soluble phases in municipal secondary effluents and their removal by different advanced treatment processes. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullivier-Hot, V.; Lenoir, A. Invertebrates facing environmental contamination by endocrine disruptors: Novel evidences and recent insights. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 504, 110712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, G.R.; Mourikes, V.E.; Neff, A.M.; Brehm, E.; Flaws, J.A. Mechanisms of action of agrochemicals acting as endocrine disrupting chemicals. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 502, 110680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, A.; Cregut, M.; Abbes, C.; Durand, M.-J.; Landoulsi, A.; Thouand, G. The environmental issues of DDT pollution and bioremediation: A multidisciplinary review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 309–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Pesticide Residues in Food–2018. Toxicological Evaluations; World Health Organization and Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; 780p. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. The Use of DDT in Malaria Vector Control; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; 16p. [Google Scholar]
- Deribe, E.; Rosseland, B.O.; Borgstrom, R.; Salbu, B.; Gebremariam, Z.; Dadebo, E.; Skipperud, L.; Eklo, O.M. Biomagnification of DDT and its metabolites in four fish species of a tropical lake. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 95, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.; Riqing, Y.; Xuan, H.; Qin, T.; Laiguo, C.; Yuping, W. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification of persistent organic pollutants in Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins (Sousa chinensis) from the Pearl River Estuary, China. Chemosphere 2014, 114, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalou, O.; Kandaraki, E.; Papadakis, G.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E. Endocrine disrupting chemicals: An occult mediator of metabolic disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salgueiro-Gonzalez, N.; Turnes-Carou, I.; Besada, V.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S.; Lopez-Mahia, P.; Prada-Rodriguez, D. Occurrence, distribution and bioaccumulation of endocrine disrupting compounds in water, sediment and biota samples from a European river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 529, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylander, C.; Sandanger, T.M.; Brustad, M. Associations between marine food consumption and plasma concentrations of POPs in a Norwegian coastal population. J. Environ. Monit. 2009, 11, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, R.; Smit, N.J.; Van Vuren, J.H.; Nakayama, S.M.; Yohannes, Y.B.; Ikenaka, Y.; Ishizuka, M.; Wepener, V. Bioaccumulation and human health risk assessment of DDT and other organochlorine pesticides in an apex aquatic predator from a premier conservation area. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demeneix, B.; Slama, R. Endocrine Disruptors: From Scientific Evidence to Human Health Protection; Petitions; PE 608.866; Policy Department for Citizens’ Rights and Constitutional Affairs, Directorate General for Internal Policies of the Union, European Parliament: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; 132p. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Maldonado, I.N.; Trejo-Acevedo, A.; Orta-Garcia, S.T.; Ochoa-Martinez, A.C.; Varela-Silva, J.A.; Perez-Vazquez, F.J. DDT and DDE concentrations in the blood of Mexican children residing in the southeastern region of Mexico. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2014, 49, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teeyapant, P.; Ramchiun, S.; Polputpisatkul, D.; Uttawichai, C.; Parnmen, S. Serum concentrations of organochlorine pesticides p,p′-DDE in adult Thai residents with background levels of exposure. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 39, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gore, A.C.; Chappell, V.A.; Fenton, S.E.; Flaws, J.A.; Nadal, A.; Prins, G.S.; Toppari, J.; Zoeller, R.T. EDC-2, The Endocrine Society’s Second Scientific Statement on Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals. Endocr. Rev. 2015, 36, E1–E150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoeller, R.T.; Brown, T.R.; Doan, L.L.; Gore, A.C.; Skakkebaek, N.E.; Soto, A.M.; Woodruff, T.J.; Vom Saal, F.S. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals and public health protection: A statement of principles from The Endocrine Society. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 4097–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Falco, M.; Forte, M.; Laforgia, V. Estrogenic and anti-androgenic disrupting chemicals and their impact on the male reproductive system. Front. Environ. Sci. 2015, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelce, W.R.; Stone, C.R.; Laws, S.C.; Gray, L.E.; Kemppainen, J.A.; Wilson, E.M. Persistent DDT metabolite p,p’-DDE is a potent androgen receptor antagonist. Nature 1995, 375, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maness, S.C.; McDonnell, D.P.; Gaido, K.W. Inhibition of androgen receptor-dependent transcriptional activity by DDT isomers and methoxychlor in HepG2 human hepatoma cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1998, 151, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Endocrine Disrupters and Child Health-Possible Developmental Early Effects of Endocrine Disrupters on Child Health; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; 93p. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, K.A.; Park, S.H.; Yi, B.R.; Choi, K.C. Gene alterations of ovarian cancer cells expressing estrogen receptors by estrogen and bisphenol a using microarray analysis. Lab. Anim. Res. 2011, 27, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwang, K.A.; Kang, N.H.; Yi, B.R.; Lee, H.R.; Park, M.A.; Choi, K.C. Genistein, a soy phytoestrogen, prevents the growth of BG-1 ovarian cancer cells induced by 17betaestradiol or bisphenol A via the inhibition of cell cycle progression. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabaravdic, M. Xenoestrogen effects of chemical compounds: Influence on the breast cancer. Med. Arh. 2006, 60, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Darbre, P.D. Environmental oestrogens, cosmetics and breast cancer. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 20, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, L.S.; Fenton, S.E. Cancer and developmental exposure to endocrine disruptors. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaglova, N.V.; Tsomartova, D.A.; Yaglov, V.V. Differences in production of adrenal steroid hormones in pubertal rats exposed to low doses of the endocrine disruptor DDT during prenatal and postnatal development. Biochem. (Moscow) Suppl. Ser. B Biomed. Chem. 2018, 12, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaglova, N.V.; Yaglov, V.V. Mechanisms of disruptive action of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) on the function of thyroid follicular epitheliocytes. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 160, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acconcia, F.; Marino, M. Principles of endocrinology and hormone action. In Principles of Endocrinology and Hormone Action; Belfiore, A., Le Roith, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 43–72. [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier, G.; Li, S.; Luu-The, V.; Tremblay, Y.; Belanger, A.; Labrie, F. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of three key steroidogenic enzymes (cytochrome P450(scc), 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and cytochrome P450(c17) in rat adrenal cortex and gonads. J. Endocrinol. 2001, 171, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.-M.; Ge, R.-S.; Latif, S.A.; Morris, D.J.; Hardy, M.P. Expression of 11β-Hydroxylase in Rat Leydig Cells. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignatelli, D.; Xiao, F.; Gouvtia, A.; Ferreira, J.; Vinson, G. Adrenarche in the rat. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 191, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaglova, N.V.; Tsomartova, D.A.; Obernikhin, S.S.; Nazimova, S.V. The Role of the Canonical Wnt-Signaling Pathway in Morphogenesis and Regeneration of the Adrenal Cortex in Rats Exposed to the Endocrine Disruptor Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane during Prenatal and Postnatal Development. Biol. Bull. 2019, 46, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemsell, D.L.; Grodin, J.M.; Brenner, P.F.; Siiteri, P.K.; MacDonald, P.C. Plasma precursors of estrogen. II. Correlation of the extent of conversion of plasma androstenedione to estrone with age. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1974, 38, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, R.; Oakley, O.; Kim, H.; Jin, J.; Ko, C.-M. Extra-gonadal sites of estrogen biosynthesis and function. BMB Rep. 2016, 49, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.L.; Auchus, R.J. The molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology of human steroidogenesis and its disorders. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 81–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lappano, R.; Rosano, C.; De Marco, P.; De Francesco, E.M.; Pezzi, V.; Maggiolini, M. Estriol acts as a GPR30 antagonist in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 320, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S.M.; Tang, W.Y.; Belmonte de Frausto, J.; Prins, G.S. Developmental exposure to estradiol and bisphenol A increases susceptibility to prostate carcinogenesis and epigenetically regulates phosphodiesterase type 4 variant 4. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5624–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parthasarathy, C.; Renuka, V.N.; Balasubramanian, K. Sex steroids enhance insulin receptors and glucose oxidation in Chang liver cells. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2009, 399, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, S.V.; Russo, J. Estrogen and xenoestrogens in breast cancer. Toxicol. Pathol. 2010, 38, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soto, A.M.; Sonnenschein, C. Environmental causes of cancer: Endocrine disruptors as carcinogens. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duan, B.; Hu, X.; Zhao, H.; Qin, J.; Luo, J. The relationship between urinary bisphenol A levels and meningioma in Chinese adults. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 18, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.-Y.; Li, Y.; Dai, W.; Wei, C.-D.; Sun, K.-S.; Tong, Y.-Q. Imbalance of testosterone/estradiol promotes male CHD development. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2012, 22, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.X.; Knuiman, M.W.; Hung, J.; Divitini, M.L.; Beilby, J.P.; Handelsman, D.J.; Beilin, J.; McQuillan, B.; Yeap, B.B. Neutral associations of testosterone, dihydrotestosterone and estradiol with fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events, and mortality in men aged 17–97 years. Clin. Endocrinol. 2016, 85, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mela, V.; Vargas, A.; Meza, C.; Kachani, M.; Wagner, E.J. Modulatory influences of estradiol and other anorexigenic hormones on metabotropic, Gi/o-coupled receptor function in the hypothalamic control of energy homeostasis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 160, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Koeverden, I.D.; de Bakker, M.; Haitjema, S.; van der Laan, S.W.; de Vries, J.-P.; Hoefer, I.E.; de Borst, G.J.; Pasterkamp, G.; den Ruijter, H.M. Testosterone to estradiol ratio reflects systemic and plaque inflammation and predicts future cardiovascular events in men with severe atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, L.; Sar, M. Androgen receptor expression in the testes and epididymides of prenatal and postnatal Sprague-Dawley rats. Endocrine 1998, 9, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habert, R.; Lejeune, H.; Saez, J.M. Origin, differentiation and regulation of fetal and adult Leydig cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2001, 179, 47–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtaut, M.I.; Kurilo, L.F. Chronology and dynamics of sex gonadal differentiation and gametogenesis in humans. Clin. Exp. Morphol. 2019, 3, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.; Colborn, T.; Hayes, T.; Heindel, J.; Jacobs, D.; Lee, D.-H.; Shioda, T.; Soto, A.; vom Saal, F.; Welshons, W.; et al. Hormones and endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Low-dose effects and nonmonotonic dose responses. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 378–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parent, A.S.; Franssen, D.; Fudvoye, J.; Pinson, A.; Bourguignon, J.P. Current changes in pubertal timing: Revised vision in relation with environmental factors including endocrine disruptors. Endocr. Dev. 2016, 29, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, A.; Cofini, M.; Rigante, D.; Lucchetti, L.; Cipolla, C.; Penta, L.; Esposito, S. The effect of bisphenol A on puberty: A critical review of the medical literature. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological Profile for DDT, DDE and DDD; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019; 486p. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yaglova, N.V.; Tsomartova, D.A.; Obernikhin, S.S.; Yaglov, V.V.; Nazimova, S.V.; Tsomartova, E.S.; Chereshneva, E.V.; Ivanova, M.Y.; Lomanovskaya, T.A. Differential Disrupting Effects of Prolonged Low-Dose Exposure to Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane on Androgen and Estrogen Production in Males. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063155
Yaglova NV, Tsomartova DA, Obernikhin SS, Yaglov VV, Nazimova SV, Tsomartova ES, Chereshneva EV, Ivanova MY, Lomanovskaya TA. Differential Disrupting Effects of Prolonged Low-Dose Exposure to Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane on Androgen and Estrogen Production in Males. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(6):3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063155
Chicago/Turabian StyleYaglova, Nataliya V., Dibakhan A. Tsomartova, Sergey S. Obernikhin, Valentin V. Yaglov, Svetlana V. Nazimova, Elina S. Tsomartova, Elizaveta V. Chereshneva, Marina Y. Ivanova, and Tatiana A. Lomanovskaya. 2021. "Differential Disrupting Effects of Prolonged Low-Dose Exposure to Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane on Androgen and Estrogen Production in Males" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 6: 3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063155
APA StyleYaglova, N. V., Tsomartova, D. A., Obernikhin, S. S., Yaglov, V. V., Nazimova, S. V., Tsomartova, E. S., Chereshneva, E. V., Ivanova, M. Y., & Lomanovskaya, T. A. (2021). Differential Disrupting Effects of Prolonged Low-Dose Exposure to Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane on Androgen and Estrogen Production in Males. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(6), 3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063155






