Recent Highlights of Research on miRNAs as Early Potential Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
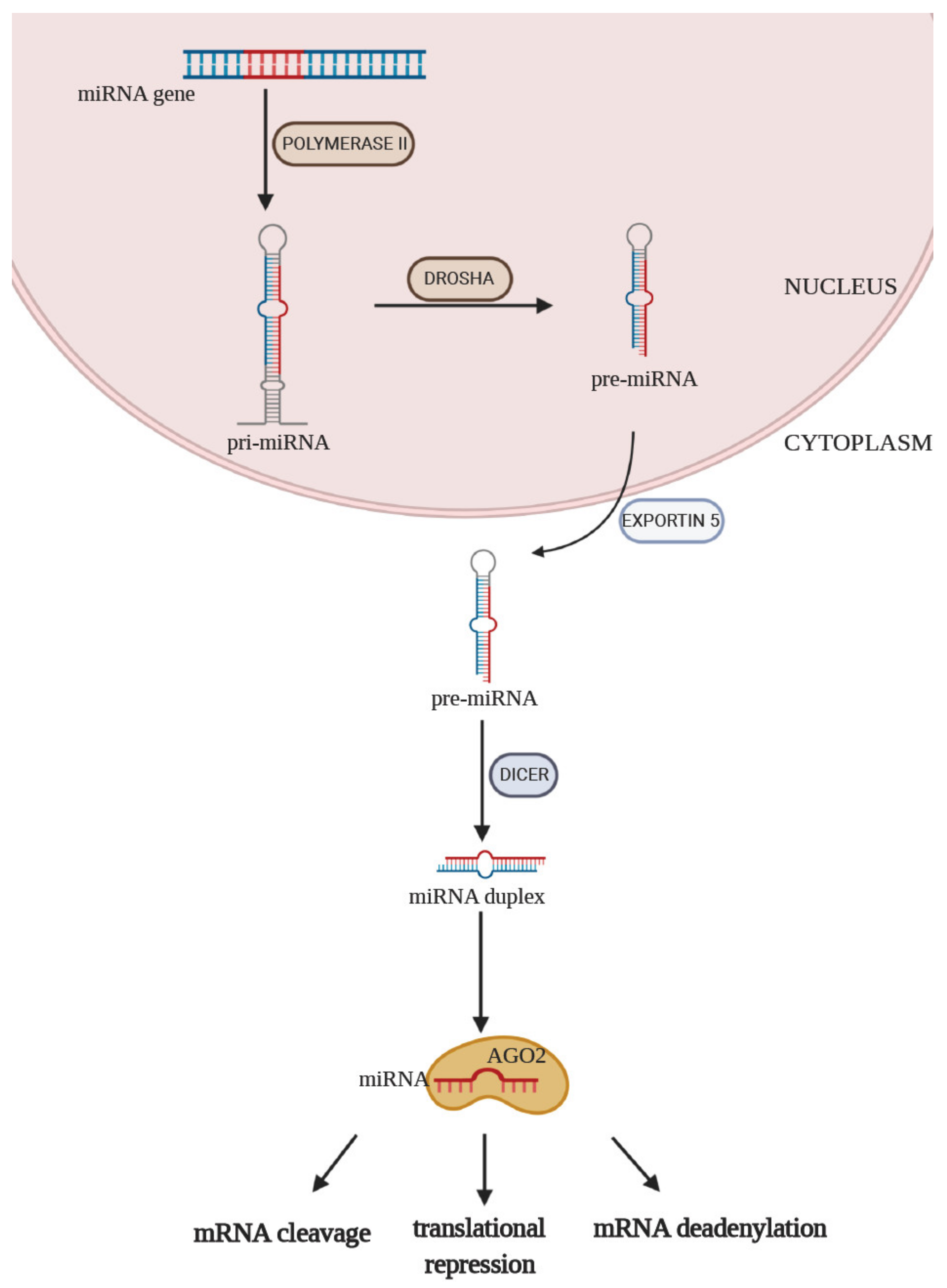
1. Introduction
2. Vascular Complications of T2DM
2.1. Microvascular Complications
2.1.1. Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
2.1.2. Diabetic Nephropathy (DNP)
2.1.3. Diabetic Neuropathy (DN)
2.2. Macrovascular Complications
2.2.1. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) and Myocardial Infarction (MI)
2.2.2. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
2.2.3. Cerebral Vascular Disease and Stroke
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, S14–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogurtsova, K.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Huang, Y.; Linnenkamp, U.; Guariguata, L.; Cho, N.H.; Cavan, D.; Shaw, J.E.; Makaroff, L.E. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 128, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, P.; Salpea, P.; Karuranga, S.; Petersohn, I.; Malanda, B.; Gregg, E.W.; Unwin, N.; Wild, S.H.; Williams, R. Mortality attributable to diabetes in 20–79 years old adults, 2019 estimates: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 108086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes, A. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, S81–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Venegas, C.; Schneider, D.C.; Myrskyla, M.; Mehta, N.K. Life expectancy with and without cognitive impairment by diabetes status among older Americans. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0190488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, A.; Chawla, R.; Jaggi, S. Microvasular and macrovascular complications in diabetes mellitus: Distinct or continuum? Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 20, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhamb, S.; Vangaveti, V.N.; Malabu, U.H. Genetic and molecular basis of diabetic foot ulcers: Clinical review. J. Tissue Viability 2016, 25, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Rooney, M.T.; Tuttle, K.R. Diabetic Kidney Disease: Challenges, Progress, and Possibilities. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 2032–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonneveld, T.P.; Nederkoorn, P.J.; Westendorp, W.F.; Brouwer, M.C.; van de Beek, D.; Kruyt, N.D.; Investigators, P. Hyperglycemia predicts poststroke infections in acute ischemic stroke. Neurology 2017, 88, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, R.; Miyauchi, K. Coronary Artery Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. Heart J. 2017, 58, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartz, J.C.; de Ferranti, S.; Gidding, S. Hypertriglyceridemia in Diabetes Mellitus: Implications for Pediatric Care. J. Endocr. Soc. 2018, 2, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; D’Amato, A.; Netti, L.; Pucci, M.; De Marchis, M.; Palmirotta, R.; Volterrani, M.; Mancone, M.; Fedele, F. Diabetes Mellitus and Ischemic Heart Disease: The Role of Ion Channels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmero, E.I.; de Campos, S.G.; Campos, M.; de Souza, N.C.; Guerreiro, I.D.; Carvalho, A.L.; Marques, M.M. Mechanisms and role of microRNA deregulation in cancer onset and progression. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2011, 34, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W. MicroRNAs: Biomarkers, Diagnostics, and Therapeutics. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1617, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.S.; Saha, I.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Genovese, L.M.; Geraci, F. Genome-wide analysis of NGS data to compile cancer-specific panels of miRNA biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felekkis, K.; Touvana, E.; Stefanou, C.; Deltas, C. microRNAs: A newly described class of encoded molecules that play a role in health and disease. Hippokratia 2010, 14, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ha, M.; Kim, V.N. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preusse, M.; Theis, F.J.; Mueller, N.S. miTALOS v2: Analyzing Tissue Specific microRNA Function. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Leidinger, P.; Becker, K.; Backes, C.; Fehlmann, T.; Pallasch, C.; Rheinheimer, S.; Meder, B.; Stahler, C.; Meese, E.; et al. Distribution of miRNA expression across human tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 3865–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J., Jr.; Batty, J.A.; Sinclair, H.; Kunadian, V. MicroRNAs in Ischemic Heart Disease: From Pathophysiology to Potential Clinical Applications. Cardiol. Rev. 2017, 25, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.X.; Rothenberg, M.E. MicroRNA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliminejad, K.; Khorram Khorshid, H.R.; Ghaffari, S.H. Why have microRNA biomarkers not been translated from bench to clinic? Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 801–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaudewitz, D.; Zampetaki, A.; Mayr, M. MicroRNA Biomarkers for Coronary Artery Disease? Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2015, 17, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condrat, C.E.; Thompson, D.C.; Barbu, M.G.; Bugnar, O.L.; Boboc, A.; Cretoiu, D.; Suciu, N.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Voinea, S.C. miRNAs as Biomarkers in Disease: Latest Findings Regarding Their Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guay, C.; Regazzi, R. Circulating microRNAs as novel biomarkers for diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.M.; Micolucci, L.; Islam, M.S.; Olivieri, F.; Procopio, A.D. Bioinformatic tools for microRNA dissection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellis, D.; Caporali, A. MicroRNA-based therapeutics in cardiovascular disease: Screening and delivery to the target. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, S.M. An overview of microRNAs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 87, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavarretta, E.; Frati, G. MicroRNAs in Coronary Heart Disease: Ready to Enter the Clinical Arena? Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2150763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattikota, S.G.; Rathjen, T.; Hausser, J.; Khedkar, A.; Kabra, U.D.; Pandey, V.; Sury, M.; Wessels, H.H.; Mollet, I.G.; Eliasson, L.; et al. miR-184 Regulates Pancreatic beta-Cell Function According to Glucose Metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 20284–20294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Liang, Y.; Liu, S.; Xiao, H.; Li, F.; Cheng, H.; Fu, Z. miR-375 enhances palmitate-induced lipoapoptosis in insulin-secreting NIT-1 cells by repressing myotrophin (V1) protein expression. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2010, 3, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Naji, A.; Stoffers, D.A. MicroRNA-7 regulates the mTOR pathway and proliferation in adult pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 2013, 62, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, G.; Yang, C.; Zhou, K.; Shen, B.; Liang, H.; Jiang, X. The role of circulating microRNA-126 (miR-126): A novel biomarker for screening prediabetes and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 10567–10577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidorkiewicz, I.; Niemira, M.; Maliszewska, K.; Erol, A.; Bielska, A.; Szalkowska, A.; Adamska-Patruno, E.; Szczerbinski, L.; Gorska, M.; Kretowski, A. Circulating miRNAs as a Predictive Biomarker of the Progression from Prediabetes to Diabetes: Outcomes of a 5-Year Prospective Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, H.; Si, H.; Li, X.; Ding, X.; Sheng, Q.; Chen, P.; Zhang, H. Serum miR-23a, a potential biomarker for diagnosis of pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2014, 51, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescador, N.; Perez-Barba, M.; Ibarra, J.M.; Corbaton, A.; Martinez-Larrad, M.T.; Serrano-Rios, M. Serum circulating microRNA profiling for identification of potential type 2 diabetes and obesity biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oerlemans, M.I.; Mosterd, A.; Dekker, M.S.; de Vrey, E.A.; van Mil, A.; Pasterkamp, G.; Doevendans, P.A.; Hoes, A.W.; Sluijter, J.P. Early assessment of acute coronary syndromes in the emergency department: The potential diagnostic value of circulating microRNAs. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, K.C.; Rye, K.A.; Tabet, F. MicroRNAs in the onset and development of cardiovascular disease. Clin. Sci. 2014, 126, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojciechowska, A.; Braniewska, A.; Kozar-Kaminska, K. MicroRNA in cardiovascular biology and disease. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 26, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckman, J.A.; Creager, M.A. Vascular Complications of Diabetes. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1771–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Zhang, W. Risk factors contributing to type 2 diabetes and recent advances in the treatment and prevention. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 1185–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, A.N.; Ulbig, M.W. Diabetic retinopathy: Early diagnosis and effective treatment. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2010, 107, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, J.; Borsheim, E.; Carvalho, E. The Role of MicroRNAs in Diabetic Complications-Special Emphasis on Wound Healing. Genes 2014, 5, 926–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rask-Madsen, C.; King, G.L. Vascular complications of diabetes: Mechanisms of injury and protective factors. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saaddine, J.B.; Honeycutt, A.A.; Narayan, K.M.; Zhang, X.; Klein, R.; Boyle, J.P. Projection of diabetic retinopathy and other major eye diseases among people with diabetes mellitus: United States, 2005–2050. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2008, 126, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, A.J.; Joglekar, M.V.; Hardikar, A.A.; Keech, A.C.; O’Neal, D.N.; Januszewski, A.S. Biomarkers in Diabetic Retinopathy. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2015, 12, 159–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, D.S.; Aiello, L.P.; Ferris, F.L., 3rd; Klein, R. Diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2540–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezk, N.A.; Sabbah, N.A.; Saad, M.S. Role of MicroRNA 126 in screening, diagnosis, and prognosis of diabetic patients in Egypt. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.L.; An, M.X.; Liu, Y.L.; Xu, H.C.; Lu, Z.Q. MicroRNA-126: A promising novel biomarker in peripheral blood for diabetic retinopathy. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 10, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.H.; Huang, Q.Z.; Li, G.C.; Xiang, Z.Y.; Zhang, X. Effects of miRNA-200b on the development of diabetic retinopathy by targeting VEGFA gene. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.L.; Wang, Y.; Gang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y. Plasma level of miR-93 is associated with higher risk to develop type 2 diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2017, 255, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Lyu, X.M.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, L. Plasma miR-21 expression: An indicator for the severity of Type 2 diabetes with diabetic retinopathy. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.N.; Li, X.; Wu, N.; Tong, M.M.; Chen, S.; Zhu, S.S.; Qian, W.; Chen, X.L. Serum microRNA-221 as a biomarker for diabetic retinopathy in patients associated with type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 11, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Gao, K.P.; Wang, Y.X.; Liu, Z.C.; Tian, L.; Yang, X.Z.; Ding, J.Y.; Wu, W.T.; Yang, W.H.; Li, Y.L.; et al. RNA sequencing identified specific circulating miRNA biomarkers for early detection of diabetes retinopathy. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 315, E374–E385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, A.; Meerson, A.; Rohana, H.; Jabaly, H.; Nahul, N.; Celesh, D.; Romanenko, O.; Tamir, S. MicroRNA-423 may regulate diabetic vasculopathy. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 19, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastukh, N.; Meerson, A.; Kalish, D.; Jabaly, H.; Blum, A. Serum miR-122 levels correlate with diabetic retinopathy. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 19, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas da Costa, E.S.M.E.; Polina, E.R.; Crispim, D.; Sbruzzi, R.C.; Lavinsky, D.; Mallmann, F.; Martinelli, N.C.; Canani, L.H.; Dos Santos, K.G. Plasma levels of miR-29b and miR-200b in type 2 diabetic retinopathy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; He, C.; Pan, X.; Liu, D.; Yang, J.; Sun, L.; Chen, P.; Wang, Q. RNA-Seq Revealed Novel Non-proliferative Retinopathy Specific Circulating MiRNAs in T2DM Patients. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Yi, Q.; Chen, L.; Wong, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhao, J.; Huang, T.; Li, B.; Yang, Y.; et al. Circulating miR-3197 and miR-2116-5p as novel biomarkers for diabetic retinopathy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 501, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, M.S.G.; de Jesus, M.L.; de Goes, T.C.; Mendonca, L.S.O.; Kaneto, C.M. Downregulation of circulating miR-320a and target gene prediction in patients with diabetic retinopathy. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit-McBride, Z.; Nguyen, A.T.; Yu, A.K.; Modjtahedi, S.P.; Hunter, A.A.; Rashid, S.; Moisseiev, E.; Morse, L.S. Unique molecular signatures of microRNAs in ocular fluids and plasma in diabetic retinopathy. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, S.; Zou, C.; Levine, E.M. Retinal pigment epithelium development, plasticity, and tissue homeostasis. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 123, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Dong, L.J.; Takahashi, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Ma, J.X.; Li, X.R. miRNA-451a regulates RPE function through promoting mitochondrial function in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 316, E443–E452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Li, X. miR-142-5p regulates the progression of diabetic retinopathy by targeting IGF1. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2020, 34, 2058738420909041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannou, K. Diabetic nephropathy: Is it always there? Assumptions, weaknesses and pitfalls in the diagnosis. Hormones 2017, 16, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidy, K.; Kang, H.M.; Hostetter, T.; Susztak, K. Molecular mechanisms of diabetic kidney disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Ma, S.X.; Shang, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.Q.; Su, W. microRNAs in chronic kidney disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 491, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossing, K.; Christensen, P.K.; Hovind, P.; Tarnow, L.; Rossing, P.; Parving, H.H. Progression of nephropathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campion, C.G.; Sanchez-Ferras, O.; Batchu, S.N. Potential Role of Serum and Urinary Biomarkers in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Diabetic Nephropathy. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2017, 4, 2054358117705371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Zhong, M.; Zhao, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Paudel, S.D.; Wang, Q.; Lou, T. Urinary miR-29 correlates with albuminuria and carotid intima-media thickness in type 2 diabetes patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Guan, M.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, C.; Xu, W.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, L.; Xue, Y. miRNAs in Urine Extracellular Vesicles as Predictors of Early-Stage Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 7932765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Lu, C.; Lv, C.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q. The Expression of miR-192 and Its Significance in Diabetic Nephropathy Patients with Different Urine Albumin Creatinine Ratio. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 6789402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, F.; Li, W.; Zeng, C.; Xie, L.; Liu, Z. Increased urinary miR-196a level predicts the progression of renal injury in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kafaji, G.; Al-Muhtaresh, H.A. Expression of microRNA377 and microRNA192 and their potential as bloodbased biomarkers for early detection of type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Bae, Y.U.; Jeon, J.S.; Noh, H.; Park, H.K.; Byun, D.W.; Han, D.C.; Ryu, S.; Kwon, S.H. The circulating exosomal microRNAs related to albuminuria in patients with diabetic nephropathy. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawzy, M.S.; Abu AlSel, B.T.; Al Ageeli, E.; Al-Qahtani, S.A.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Toraih, E.A. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 and microRNA-499a expression profiles in diabetic ESRD patients undergoing dialysis: A preliminary cross-sectional analysis. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 126, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmann, T.S.; Recamonde-Mendoza, M.; de Souza, B.M.; Bauer, A.C.; Crispim, D. MicroRNAs and diabetic kidney disease: Systematic review and bioinformatic analysis. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2018, 477, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Cui, Z.; Deng, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Yuan, L. Identification of miRNAs-genes regulatory network in diabetic nephropathy based on bioinformatics analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e16225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholaminejad, A.; Abdul Tehrani, H.; Gholami Fesharaki, M. Identification of candidate microRNA biomarkers in diabetic nephropathy: A meta-analysis of profiling studies. J. Nephrol. 2018, 31, 813–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, G. Diabetic neuropathy. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 115, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelkar, P. Diabetic neuropathy. Semin. Neurol. 2005, 25, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, D.; Gudala, K.; Muthyala, H.; Esam, H.P.; Nayakallu, R.; Bhansali, A. Prevalence and risk factors of development of peripheral diabetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus in a tertiary care setting. J. Diabetes Investig. 2014, 5, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosik, K.S. The neuronal microRNA system. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, J.S.; Michlewski, G. miRNAs in development and pathogenesis of the nervous system. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, L.; Luo, Q.; Wu, M.; Chen, Y.; Shi, X. Involvement of microRNA-146a in diabetic peripheral neuropathy through the regulation of inflammation. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.S.; Fan, B.; Szalad, A.; Jia, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Pan, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Hu, J.; et al. MicroRNA-146a Mimics Reduce the Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Diabetes 2017, 66, 3111–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yang, Q.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Ma, D.; Li, J.; Wan, Y.; Luo, Y. The role of miR-190a-5p contributes to diabetic neuropathic pain via targeting SLC17A6. J. Pain Res. 2017, 10, 2395–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, C.; Liu, J.; Bi, Y.; Li, H. Inhibition of miR-25 aggravates diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Neuroreport 2018, 29, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccacci, C.; Morganti, R.; Di Fusco, D.; D’Amato, C.; Cacciotti, L.; Greco, C.; Rufini, S.; Novelli, G.; Sangiuolo, F.; Marfia, G.A.; et al. Common polymorphisms in MIR146a, MIR128a and MIR27a genes contribute to neuropathy susceptibility in type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2014, 51, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinders, M.; Uceyler, N.; Thomann, A.; Sommer, C. Aberrant microRNA expression in patients with painful peripheral neuropathies. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 380, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccacci, C.; Latini, A.; Greco, C.; Politi, C.; D’Amato, C.; Lauro, D.; Novelli, G.; Borgiani, P.; Spallone, V. Association between a MIR499A polymorphism and diabetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2018, 32, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriegel, A.J.; Baker, M.A.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P.; Cowley, A.W., Jr.; Liang, M. Endogenous microRNAs in human microvascular endothelial cells regulate mRNAs encoded by hypertension-related genes. Hypertension 2015, 66, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Wu, Q.; Liu, J.; Fan, Y.Z.; Yu, K.F.; Cai, Y. miR199a3p is involved in the pathogenesis and progression of diabetic neuropathy through downregulation of SerpinE2. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 2417–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepien, E.L.; Durak-Kozica, M.; Kaminska, A.; Targosz-Korecka, M.; Libera, M.; Tylko, G.; Opalinska, A.; Kapusta, M.; Solnica, B.; Georgescu, A.; et al. Circulating ectosomes: Determination of angiogenic microRNAs in type 2 diabetes. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3874–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, W.; Xie, C.; Zhang, M.; Yin, X.; Wang, F.; Xu, J.; Shi, B. Identification of genes and signaling pathways associated with diabetic neuropathy using a weighted correlation network analysis: A consort study. Medicine 2016, 95, e5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecilazich, F.; Dinh, T.; Pradhan-Nabzdyk, L.; Leal, E.; Tellechea, A.; Kafanas, A.; Gnardellis, C.; Magargee, M.L.; Dejam, A.; Toxavidis, V.; et al. Role of endothelial progenitor cells and inflammatory cytokines in healing of diabetic foot ulcers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zhao, G.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Che, Y.; Song, M.; Gao, S.; Zeng, B.; Wang, Y. MiR-155 targets PTCH1 to mediate endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction caused by high glucose. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 366, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Shu, B.; Wang, P.; Tang, J.; Chen, L.; Qi, S.; Liu, X.; Xie, J. Quantification of the differential expression levels of microRNA-203 in different degrees of diabetic foot. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 13416–13420. [Google Scholar]
- Gujjar, A.R. Diabetes and Stroke: More than just accelerated atherosclerosis? Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2018, 18, e261–e263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low Wang, C.C.; Hess, C.N.; Hiatt, W.R.; Goldfine, A.B. Clinical Update: Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Mellitus: Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease and Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—Mechanisms, Management, and Clinical Considerations. Circulation 2016, 133, 2459–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronson, D.; Edelman, E.R. Coronary artery disease and diabetes mellitus. Cardiol. Clin. 2014, 32, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausenloy, D.J.; Yellon, D.M. Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: A neglected therapeutic target. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Li, G. MicroRNA expression and function in cardiac ischemic injury. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2010, 3, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, R.A.; Dimmeler, S. MicroRNAs in myocardial infarction. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, J.; Jazbutyte, V.; Kirchmaier, B.C.; Gupta, S.K.; Lorenzen, J.; Hartmann, D.; Galuppo, P.; Kneitz, S.; Pena, J.T.; Sohn-Lee, C.; et al. MicroRNA-24 regulates vascularity after myocardial infarction. Circulation 2011, 124, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thum, T.; Gross, C.; Fiedler, J.; Fischer, T.; Kissler, S.; Bussen, M.; Galuppo, P.; Just, S.; Rottbauer, W.; Frantz, S.; et al. MicroRNA-21 contributes to myocardial disease by stimulating MAP kinase signalling in fibroblasts. Nature 2008, 456, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Narang, R.; Sreenivas, V.; Rastogi, V.; Bhatia, J.; Saluja, D.; Srivastava, K. Circulatory miR-133b and miR-21 as Novel Biomarkers in Early Prediction and Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease. Genes 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Wang, G.; Xu, C.; Zeng, M.; Lin, F.; Wu, J.; Wan, Q. Circulating miR-30c as a predictive biomarker of type 2 diabetes mellitus with coronary heart disease by regulating PAI-1/VN interactions. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 117092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleem, M.; Shabayek, M.; Ewida, H.A. MicroRNAs 342 and 450 together with NOX-4 activity and their association with coronary artery disease in diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2019, 35, e3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hayali, M.A.; Sozer, V.; Durmus, S.; Erdenen, F.; Altunoglu, E.; Gelisgen, R.; Atukeren, P.; Atak, P.G.; Uzun, H. Clinical Value of Circulating Microribonucleic Acids miR-1 and miR-21 in Evaluating the Diagnosis of Acute Heart Failure in Asymptomatic Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Biomolecules 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontaraki, J.E.; Marketou, M.E.; Parthenakis, F.I.; Maragkoudakis, S.; Zacharis, E.A.; Petousis, S.; Kochiadakis, G.E.; Vardas, P.E. Hypertrophic and antihypertrophic microRNA levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and their relationship to left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with essential hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2015, 9, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amr, K.S.; Abdelmawgoud, H.; Ali, Z.Y.; Shehata, S.; Raslan, H.M. Potential value of circulating microRNA-126 and microRNA-210 as biomarkers for type 2 diabetes with coronary artery disease. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 75, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, F.; Wang, H.; Przybilla, D.; Franklin, B.S.; Dolf, A.; Pfeifer, P.; Schmitz, T.; Flender, A.; Endl, E.; Nickenig, G.; et al. Vascular endothelial microparticles-incorporated microRNAs are altered in patients with diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gonzalo-Calvo, D.; van der Meer, R.W.; Rijzewijk, L.J.; Smit, J.W.; Revuelta-Lopez, E.; Nasarre, L.; Escola-Gil, J.C.; Lamb, H.J.; Llorente-Cortes, V. Serum microRNA-1 and microRNA-133a levels reflect myocardial steatosis in uncomplicated type 2 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuschnerus, K.; Straessler, E.T.; Muller, M.F.; Luscher, T.F.; Landmesser, U.; Krankel, N. Increased Expression of miR-483-3p Impairs the Vascular Response to Injury in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2019, 68, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, R.S.; Rajagopalan, S.; Natarajan, R.; Deiuliis, J.A. Noncoding RNAs in Cardiovascular Disease: Pathological Relevance and Emerging Role as Biomarkers and Therapeutics. Am. J. Hypertens. 2018, 31, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.F.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Q.X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.H.; Cui, L.M. Association between elevated plasma microRNA-223 content and severity of coronary heart disease. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2018, 78, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez Lopez, Y.O.; Garufi, G.; Seyhan, A.A. Altered levels of circulating cytokines and microRNAs in lean and obese individuals with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 13, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Wu, L.J.; Li, J.J.; Xiao, H.B.; He, Y.; Yan, Y.X. A meta-analysis of dysregulated miRNAs in coronary heart disease. Life Sci. 2018, 215, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Long, G.; Zhao, C.; Li, H.; Chaugai, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, D.W. Plasma microRNA-133a is a new marker for both acute myocardial infarction and underlying coronary artery stenosis. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, J.; Olejnickova, V.; Tkacova, N.; Santulli, G. Mechanistic Role of MicroRNAs in Coupling Lipid Metabolism and Atherosclerosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 887, 79–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; He, H.W.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhao, H.; Lian, X.Q.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhu, J.; Yan, J.J.; Zhang, D.G.; Yang, Z.J.; et al. Plasma levels of lipometabolism-related miR-122 and miR-370 are increased in patients with hyperlipidemia and associated with coronary artery disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Li, J.; Yu, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ji, L.; et al. Exosomal miRNAs as potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 384–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanlialp, M.; Dodurga, Y.; Uludag, B.; Alihanoglu, Y.I.; Enli, Y.; Secme, M.; Bostanci, H.E.; Cetin Sanlialp, S.; Tok, O.O.; Kaftan, A.; et al. Peripheral blood mononuclear cell microRNAs in coronary artery disease. J. Cell Biochem. 2020, 121, 3005–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekar, D.; Venugopal, B.; Sekar, P.; Ramalingam, K. Role of microRNA 21 in diabetes and associated/related diseases. Gene 2016, 582, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostahfezian, M.; Azhir, Z.; Dehghanian, F.; Hojati, Z. Expression Pattern of microRNAs, miR-21, miR-155 and miR-338 in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Arch. Med. Res. 2019, 50, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coban, N.; Pirim, D.; Erkan, A.F.; Dogan, B.; Ekici, B. Hsa-miR-584-5p as a novel candidate biomarker in Turkish men with severe coronary artery disease. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, H.; Zhu, M.; Qian, Y.; Lin, S.; Li, X. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for severe coronary artery disease. Medicine 2020, 99, e19971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, R.L.; Sharma, A.; Horsch, A.D.; Hinchliffe, R.J. Peripheral artery disease. BMJ 2018, 360, j5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criqui, M.H.; Aboyans, V. Epidemiology of peripheral artery disease. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1509–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankey, G.J.; Norman, P.E.; Eikelboom, J.W. Medical treatment of peripheral arterial disease. JAMA 2006, 295, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, W.T.; Hoes, A.W.; Rutgers, D.; Bots, M.L.; Hofman, A.; Grobbee, D.E. Peripheral arterial disease in the elderly: The Rotterdam Study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golledge, J.; Biros, E.; Bingley, J.; Iyer, V.; Krishna, S.M. Epigenetics and Peripheral Artery Disease. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2016, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloos, W.; Vogel, B.; Blessing, E. MiRNAs in peripheral artery disease—Something gripping this way comes. Vasa 2014, 43, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stather, P.W.; Sylvius, N.; Wild, J.B.; Choke, E.; Sayers, R.D.; Bown, M.J. Differential microRNA expression profiles in peripheral arterial disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2013, 6, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamburg, N.M.; Leeper, N.J. Therapeutic Potential of Modulating MicroRNA in Peripheral Artery Disease. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 13, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signorelli, S.S.; Volsi, G.L.; Pitruzzella, A.; Fiore, V.; Mangiafico, M.; Vanella, L.; Parenti, R.; Rizzo, M.; Volti, G.L. Circulating miR-130a, miR-27b, and miR-210 in Patients With Peripheral Artery Disease and Their Potential Relationship With Oxidative Stress. Angiology 2016, 67, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Y.; Cheng, B.; Wang, X.F.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhang, H.M.; Liu, S.F.; Chen, L.S.; Huang, W.J.; Liu, J.; Deng, A.P. Circulating MicroRNA-4739 May Be a Potential Biomarker of Critical Limb Ischemia in Patients with Diabetes. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4232794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, B.; Li, J.Y.; Li, X.C.; Wang, X.F.; Wang, Z.J.; Liu, J.; Deng, A.P. MiR-323b-5p acts as a novel diagnostic biomarker for critical limb ischemia in type 2 diabetic patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiatzi, G.; Oikonomou, E.; Deftereos, S.; Siasos, G.; Tousoulis, D. Peripheral artery disease: A micro-RNA-related condition? Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2018, 39, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergul, A.; Kelly-Cobbs, A.; Abdalla, M.; Fagan, S.C. Cerebrovascular complications of diabetes: Focus on stroke. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2012, 12, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.; Lu, J. Progress on diabetic cerebrovascular diseases. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2014, 14, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Expert Panel on Neurologic, I.; Salmela, M.B.; Mortazavi, S.; Jagadeesan, B.D.; Broderick, D.F.; Burns, J.; Deshmukh, T.K.; Harvey, H.B.; Hoang, J.; Hunt, C.H.; et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria((R)) Cerebrovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2017, 14, S34–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortality, G.B.D.; Causes of Death, C. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1459–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, B.; Peplow, P.V. Immunomodulators and microRNAs as neurorestorative therapy for ischemic stroke. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grysiewicz, R.A.; Thomas, K.; Pandey, D.K. Epidemiology of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke: Incidence, prevalence, mortality, and risk factors. Neurol. Clin. 2008, 26, 871–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haratz, S.; Tanne, D. Diabetes, hyperglycemia and the management of cerebrovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2011, 24, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.D. Stroke and diabetes mellitus. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 126, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsis, G.; Siasos, G.; Spengos, K. The emerging role of microRNA in stroke. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1573–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Ovbiagele, B.; Feng, W. Diabetes and Stroke: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Pharmaceuticals and Outcomes. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 351, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.S.; Armugam, A.; Sepramaniam, S.; Lim, K.Y.; Setyowati, K.D.; Wang, C.W.; Jeyaseelan, K. Expression profile of MicroRNAs in young stroke patients. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Zhang, X.; Peng, S.; Sun, J.; Chen, X.; Deng, Y.; Yi, L. Identification of novel biomarkers in ischemic stroke: A genome-wide integrated analysis. BMC Med. Genet. 2020, 21, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wang, T.; Huang, S.; Di, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Luo, Z.; Han, W.; An, B. Differential expression of microRNAs in plasma of patients with prediabetes and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2016, 53, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Ai, D.; Wu, R.; Zhang, T.; Jing, L.; Lu, J.; Zhong, L. Identification of the differential expression of serum microRNA in type 2 diabetes. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, G.; Li, Y.; Xue, J. Low serum miR-320b expression as a novel indicator of carotid atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 33, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Huang, X.; Xu, M.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, F.; Hua, F.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y. Value of circulating miRNA-21 in the diagnosis of subclinical diabetic cardiomyopathy. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 110944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Zhan, Q.; Song, B.; Zeng, S.; Zhou, J.; Long, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, Z.; Yuan, M.; Chen, X.; et al. Detection of platelet microRNA expression in patients with diabetes mellitus with or without ischemic stroke. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2014, 28, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Gu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Yang, G.Y. Increase of circulating miR-223 and insulin-like growth factor-1 is associated with the pathogenesis of acute ischemic stroke in patients. BMC Neurol. 2014, 14, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Zhan, Q.; Yuan, M.; Duan, X.; Zhou, J.; Lu, J.; Li, Z.; Yu, F.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Q.; et al. The Expression of microRNA-223 and FAM5C in Cerebral Infarction Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2017, 17, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Lei, M. Biomarkers Associated with Ischemic Stroke in Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2016, 16, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikhbahaei, S.; Manizheh, D.; Mohammad, S.; Hasan, T.M.; Saman, N.; Laleh, R.; Mahsa, M.; Sanaz, A.K.; Shaghayegh, H.J. Can MiR-503 be used as a marker in diabetic patients with ischemic stroke? BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Complication of Diabetes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute | Chronic | ||
| diabetic ketoacidosis | Vascular | Nonvascular | |
| nonketotic hyperosmolar coma | Microvascular | Macrovascular | sexual dysfunctions |
| hypoglycemia | retinopathy | coronary artery disease | skin complications |
| diabetic coma | nephropathy | peripheral artery disease | |
| neuropathy | cerebrovascular disease including ischemic stroke | ||
| miRNA | Sample Type | Expression in Research Group vs. Controls | Number of Cases | Method | Significant Findings | Year of Publication | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-126 | serum | down in T2DM patients compared with control group | n = 186; 100 T2DM (14 without complications, 26 with macrovascular complications, 17 DN, 24 DNP, 19 DR), 86 IGT | qPCR | serum miR-126 expression might serve as a potential biomarker for DR | 2016 | [50] |
| serum | down | n = 184; 125 DM (44 NDR, 42 NPDR, 39 PDR) and 59 HC | qPCR | high values of AUC in ROC analysis determine miR-126 as a good diagnostic biomarker that differentiates PDR patients from HC | 2017 | [51] | |
| miR-200b | serum | down | n = 508; 255 DR, 253 HC | qPCR | miR-200b targets VEGFA gene | 2017 | [52] |
| miR-93 | plasma | up | n = 267; 140 T2DM (75 DR, 65 NDR) 127 HC | qPCR | levels of plasma miR-122 might serve as DR biomarkers | 2017 | [53] |
| miR-21 | plasma | up | n = 304; 65 NDR, 73 NPDR, 51 PDR, 115 HC | qPCR | elevated miR-21 expression can be used to identify occurrence and stage of DR | 2017 | [54] |
| miR-221 | serum | up (progressively upregulated in NDR, NPDR, and PDR) | n = 134; (33 HC, 37 NDR, 34 NPDR, 30 PDR) | qPCR | miR-221 might serve as a biomarker for progression and occurrence of DR | 2018 | [55] |
| let-7a- 5p miR-28-3p miR-novel-chr5_15976 | serum | up | screening phase: 9 (3 T2DM NDR, 3 T2DM DR, 3 HC); training phase: 20 (10 T2DM NDR, 10 T2DM DR); validation phase: 79 (29 T2DM-DR, 50 T2DM NDR) | RNASeq, qPCR | this miRNA signature may serve as a biomarker for DR; better than single miRNA | 2018 | [56] |
| miR-423 | serum | down in PDR | n = 69; (22 HC, 10 T2DM NDR, 22 NPDR, 15PDR) | qPCR | miR-423 may serve as a biomarker for DR; is correlated with VEGF, NO, and eNOS expression | 2019 | [57] |
| miR-122 | serum | up in T2DM NDR and T2DM with NPDRdown in T2DM PDR | n = 40; (10 of HC, 10 of T2DM NDR, 10 of T2DM with NPDR, 10 of T2DM with PDR | qPCR | levels of miR-122 in serum of T2DM patients might determine occurrence and progression of DR | 2019 | [58] |
| miR-29b, miR-200b | plasma | down | n = 206; 186 T2DM (91 NDR, 46 NPDR, 49PDR), 20 HC | qPCR | downregulation of miR-29b is associated with progression of DR | 2019 | [59] |
| miR-4448, miR-338-3p, miR-190a-5p, miR-485-5p, miR-9-5p | serum | down: miR-4448, miR-338-3p, miR-485-5p, and miR-9-5pup: miR-190a-5p | n = 21; 10 NPDR, 11 NDR | RNASeq | these miRNAs might serve as good potential biomarkers for DR with high AUC value (0.909) | 2019 | [60] |
| miR-3197, miR-2116-5p | serum | up | n = 90; 42 NPDR, 3 PDR, 45 NDR | microarray, qPCR | high diagnostic value of these 2 miRNAs can indicate patients with DR; NOTCH2 as a possible target gene of miR-2116-5p | 2020 | [61] |
| miR-320a | plasma | down | n = 170; 60 HC, 48 DM without DR, 62 DR | qPCR | DR can be identified by plasma miR-320a measurement; TSC1 and CDK6 are possible target genes for this miRNA | 2020 | [62] |
| let-7b, miR320b, miR-762, miR-4488 | aqueous humor, plasma, vitreous | miRNA let-7b—up in aqueous and vitreous, down—plasma miR-320b—up in aqueous, vitreous, and plasma miR-762 and miR-4488—up in vitreous; up in PDR, down in NPDR in aqueous; down in PDR and up in NPDR in plasma | n = 27; 11 HC, 16 DM: 5 T1DM PDR, 7 T2DM PDR and 4T2DM NPDR | microarray, qPCR | this miRNA signature may contribute to the diagnostic tests or therapeutic approaches for the DR | 2020 | [63] |
| miRNA | Sample Type | Expression in Research Group vs. Controls | Number of Cases | Method | Significant Findings | Year of Publication | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-192, miR-194, miR-215 | urinary EVs | up in microalbuminuria patients | n = 90; 80 T2DM (30 normoalbuminuric, 30 microalbuminuric, 20 macroalbuminuric) 10 HC | qPCR | miR-192 has the highest diagnostic value (AUC = 0.802); miR-192 and miR-215 levels are positively correlated with TGF-β1 levels | 2016 | [73] |
| miR-192 | serum | down | n = 591; 464 T2DM (157 normal albuminuria, 159 microalbuminuria, 148 large albuminuria), 127 HC | qPCR | lower level of miR-192 is connected with the decrease in urine albumin ratio; miR-192 has potential for DNP diagnosis | 2016 | [74] |
| miR-196a | urine | up | n = 209 T2DM DNP | qPCR | miR-196a is a good candidate for a noninvasive marker for the progression of renal fibrosis in DN patients | 2018 | [75] |
| miR-192, miR-377 | whole blood | miR-377—up, miR-192—down | n = 85; 55 T2DM (30 without DN, 15 microalbuminuric, 10 macroalbuminuric), 30 HC | qPCR | both miRNAs can serve as a potential biomarker for DNP and are correlated with DNP risk factors | 2018 | [76] |
| miR-1246, miR-642a-3p, let-7c-5p, miR-1255b-5p, let-7i-3p, miR-5010-5p, miR-150-3p, miR-4449 | serum exosomes | up | n = 74; 18 HC, 33 DM without DNP, 23 DNP | RNASeq | presented miRNAs are correlated with the albuminuria degree and might be helpful for diagnosis of DNP | 2019 | [77] |
| miR-499a | serum | down | n = 180; 90 T2DM with ESRD; 90 T2DM without ESRD | qPCR | altered expressions of miR-499a are possibly involved in DNP, and its level is correlated with serum MALAT1 | 2018 | [78] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bielska, A.; Niemira, M.; Kretowski, A. Recent Highlights of Research on miRNAs as Early Potential Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063153
Bielska A, Niemira M, Kretowski A. Recent Highlights of Research on miRNAs as Early Potential Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(6):3153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063153
Chicago/Turabian StyleBielska, Agnieszka, Magdalena Niemira, and Adam Kretowski. 2021. "Recent Highlights of Research on miRNAs as Early Potential Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 6: 3153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063153
APA StyleBielska, A., Niemira, M., & Kretowski, A. (2021). Recent Highlights of Research on miRNAs as Early Potential Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(6), 3153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063153







