Comparative Genomics Reveals 13 Different Isoforms of Mytimycins (A-M) in Mytilus galloprovincialis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Searching, Screening, and Identifying M. galloprovincialis Mytimycins
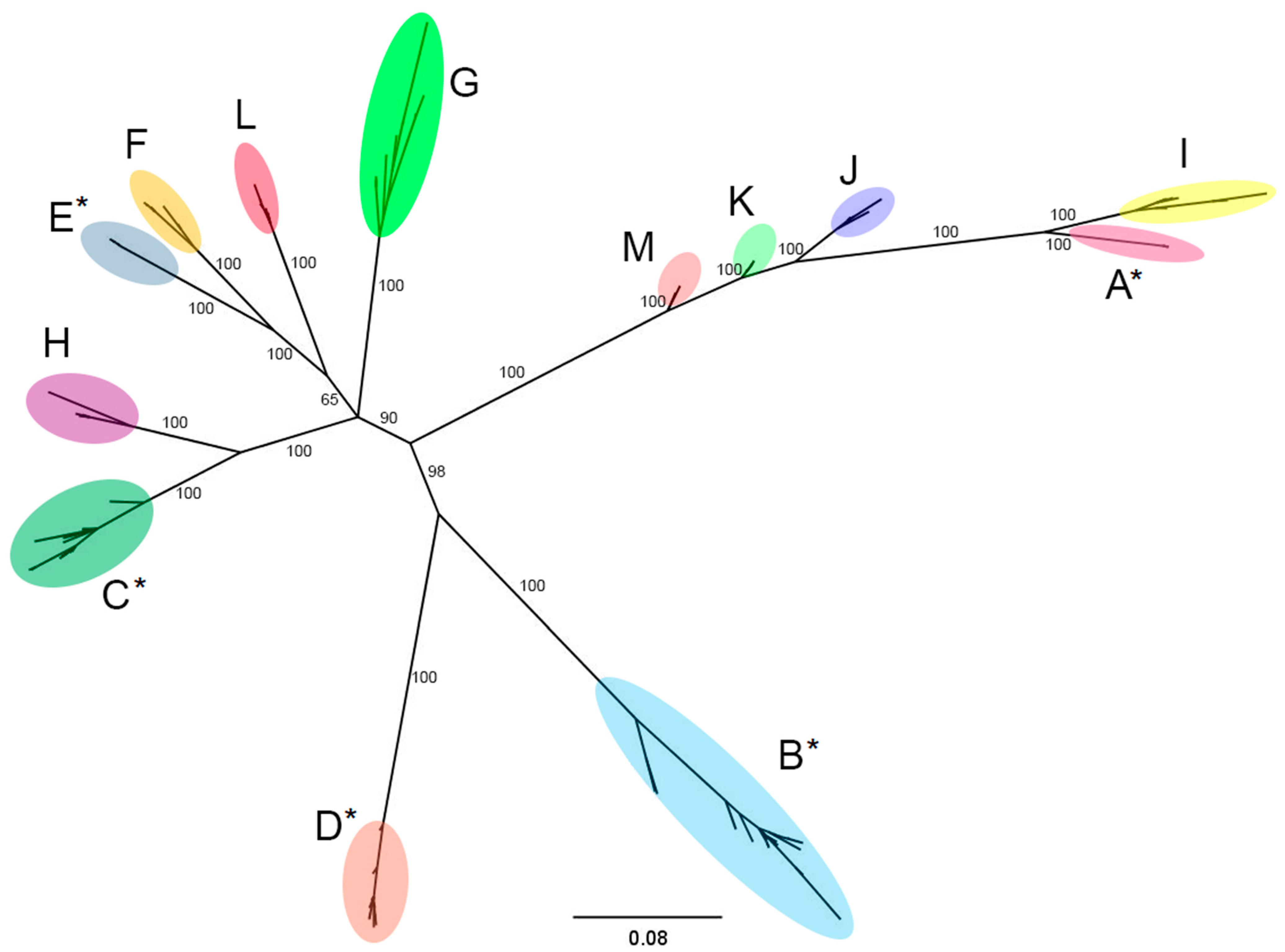
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Presence/Absence Variation
2.4. Isoelectric Point
2.5. Positive and Negative Selection Analysis
2.6. Promoter Analysis
2.7. Genomic vs. Transcriptomic Data
2.8. Expression Analysis
2.9. Taxonomical Distribution of Mytimycins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Searching, Screening, and Identifying M. galloprovincialis Mytimycins
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.3. Isoelectrical Point
4.4. Positive and Negative Selection Analysis
4.5. Promoter Analysis
4.6. Genomic vs. Transcriptomic Data
4.7. Expression Analysis
4.8. Taxonomical Distribution of Mytimycins
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charlet, M.; Chernysh, S.; Philippe, H.; Hetru, C.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Bulet, P. Innate Immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 21808–21813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitta, G.; Vandenbulcke, F.; Noël, T.; Romestand, B.; Beauvillain, J.C.; Salzet, M.; Roch, P. Differential distribution and de-fence involvement of antimicrobial peptides in mussel. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 15, 2759–2769. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sonthi, M.; Toubiana, M.; Pallavicini, A.; Venier, P.; Roch, P. Diversity of Coding Sequences and Gene Structures of the Antifungal Peptide Mytimycin (MytM) from the Mediterranean Mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venier, P.; Varotto, L.; Rosani, U.; Millino, C.; Celegato, B.; Bernante, F.; Lanfranchi, G.; Novoa, B.; Roch, P.; Figueras, A.; et al. Insights into the innate immunity of the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonthi, M.; Cantet, F.; Toubiana, M.; Trapani, M.-R.; Parisi, M.-G.; Cammarata, M.; Roch, P. Gene expression specificity of the mussel antifungal mytimycin (MytM). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2012, 32, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey-Campos, M.; Moreira, R.; Valenzuela-Muñoz, V.; Gallardo-Escárate, C.; Novoa, B.; Figueras, A. High individual variability in the transcriptomic response of Mediterranean mussels to Vibrio reveals the involvement of myticins in tissue injury. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantet, F.; Toubiana, M.; Parisi, M.-G.; Sonthi, M.; Cammarata, M.; Roch, P. Individual variability of mytimycin gene expression in mussel. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2012, 33, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, F.; Noël, T.; Roch, P. A Member of the Arthropod Defensin Family from Edible Mediterranean Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis). JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 240, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitta, G.; Hubert, F.; Noel, T.; Roch, P. Myticin, a novel cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptide isolated from haemocytes and plasma of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 265, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitta, G.; Vandenbulcke, F.; Hubert, F.; Salzet, M.; Roch, P. Involvement of Mytilins in Mussel Antimicrobial Defense. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 12954–12962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero, A.; Costa, M.; Forn-Cuní, G.; Balseiro, P.; Chamorro, R.; Dios, S.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B. Occurrence, seasonality and infectivity of Vibrio strains in natural populations of mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2014, 108, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabdelmouna, A.; Garcia, C.; Ledu, C.; Lamy, P.; Maurouard, E.; Degremont, L. Mortality investigation of Mytilus edulis and Mytilus galloprovincialis in France: An experimental survey under laboratory conditions. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerdol, M.; Moreira, R.; Cruz, F.; Gómez-Garrido, J.; Vlasova, A.; Rosani, U.; Venier, P.; Naranjo-Ortiz, M.A.; Murgarella, M.; Greco, S.; et al. Massive gene presence-absence variation shapes an open pan-genome in the Mediterranean mussel. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Campos, M.; Novoa, B.; Pallavicini, A.; Gerdol, M.; Figueras, A. Comparative Genomics Reveals a Significant Sequence Variability of Myticin Genes in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, P.T.Y.; Ip, J.C.H.; Mak, S.S.; Qiu, J.-W.; Lam, P.K.S.; Wong, C.K.C.; Chan, L.L.; Leung, K.M.Y. De novo transcriptome analysis of Perna viridis highlights tissue-specific patterns for environmental studies. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uliano-Silva, M.; Dondero, F.; Otto, T.D.; Costa, I.; Lima, N.C.B.; Americo, J.A.; Mazzoni, C.J.; Prosdocimi, F.; Rebelo, M.D.F. A hybrid-hierarchical genome assembly strategy to sequence the invasive golden mussel, Limnoperna fortunei. GigaScience 2018, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, Y.; Fields, C.J.; Hui, J.H.L.; Zhang, W.; et al. Adaptation to deep-sea chemosynthetic environments as revealed by mussel genomes. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Briones, C.; Nuñez, J.J.; Pérez, M.; Espinoza-Rojas, D.; Molina-Quiroz, C.; Guiñez, R. De novo male gonad transcriptome draft for the marine mussel Perumytilus purpuratus with a focus on its reproductive-related proteins. Int. J. Genom. 2018, 6, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greco, S.; Gerdol, M.; Edomi, P.; Pallavicini, A. Molecular Diversity of Mytilin-Like Defense Peptides in Mytilidae (Mollusca, Bivalvia). Antibiotics 2020, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerdol, M.; Schmitt, P.; Venier, P.; Rocha, G.; Rosa, R.D.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D. Functional Insights from the Evolutionary Diversification of Big Defensins. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdol, M.; De Moro, G.; Manfrin, C.; Venier, P.; Pallavicini, A. Big defensins and mytimacins, new AMP families of the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 36, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.R.; Thulin, E.; Fagan, P.A.; Forsén, S.; Chazin, W.J. The EF-hand domain: A globally cooperative structural unit. Protein Sci. 2009, 11, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capozzi, F.; Casadei, F.; Luchinat, C. EF-hand protein dynamics and evolution of calcium signal transduction: An NMR view. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 11, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisner, D.A.; Caldwell, J.L.; Kistamás, K.; Trafford, A.W. Calcium and Excitation-Contraction Coupling in the Heart. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambardella, J.; Trimarco, B.; Iaccarino, G.; Santulli, G. New Insights in Cardiac Calcium Handling and Excitation-Contraction Coupling. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1067, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peled, M.; Dragovich, M.A.; Adam, K.; Strazza, M.; Tocheva, A.S.; Vega, I.E.; Mor, A. EF Hand Domain Family Member D2 Is Required for T Cell Cytotoxicity. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2824–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Sheng, C.; Yao, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, S. The EF-Hand Protein CALML6 Suppresses Antiviral Innate Immunity by Impairing IRF3 Dimerization. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 1273–1285.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozlyuk, N.; Monteith, A.J.; Garcia, V.; Damo, S.M.; Skaar, E.P.; Chazin, W.J. S100 Proteins in the Innate Immune Response to Pathogens. Adv. Struct. Saf. Stud. 2019, 1929, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A Simple, Fast, and Accurate Algorithm to Estimate Large Phylogenies by Maximum Likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kishino, H.; Yano, T.-A. Dating of the human-ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. J. Mol. Evol. 1985, 22, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree, A Graphical Viewer of Phylogenetic Trees; University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bendtsen, J.D.; Nielsen, H.; von Heijne, G.; Brunak, S. Improved Prediction of Signal Peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 340, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, L.P. IPC—Isoelectric Point Calculator. Biol. Direct 2016, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weaver, S.; Shank, S.D.; Spielman, S.J.; Li, M.; Muse, S.V.; Pond, S.L.K. Datamonkey 2.0: A Modern Web Application for Characterizing Selective and Other Evolutionary Processes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murrell, B.; Wertheim, J.O.; Moola, S.; Weighill, T.; Scheffler, K.; Pond, S.L.K. Detecting Individual Sites Subject to Episodic Diversifying Selection. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pond, S.L.K.; Frost, S.D.W. Not So Different After All: A Comparison of Methods for Detecting Amino Acid Sites Under Selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1208–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murrell, B.; Moola, S.; Mabona, A.; Weighill, T.; Sheward, D.; Pond, S.L.K.; Scheffler, K. FUBAR: A Fast, Unconstrained Bayesian AppRoximation for Inferring Selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reese, M.G.; Eeckman, F.H.; Kulp, D.; Haussler, D. Improved Splice Site Detection in Genie. J. Comput. Biol. 1997, 4, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, w202–w208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, S.; Goldman, N. A General Empirical Model of Protein Evolution Derived from Multiple Protein Families Using a Maximum-Likelihood Approach. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








| Cys Array | Details | Cys Residues | M. galloprovincialis | Mytilus spp | P. viridis | Modiolus spp | L. fortunei | P. purpuratus | B. platifrons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| type I | CC- C-C-CC-C-CC-C-C-C-C-C | 14 | √ (B, D, E, F, G, L, M) | √ | × | × | × | × | × |
| type II | CC- C-C- C-C- C-C-C-C-C-C | 12 | √ (A, I, J, K) | √ | √ | √ | × | √ | × |
| type III | CC- C-C-CC-C-CC-C-C-C | 12 | √ (C, H) | √ | × | × | √ | × | × |
| type IV | CC- C-C- C-C- C-C-C-C | 10 | × | × | √ | √ | × | √ | × |
| type V | CC-C-C-C-C-CC-C-CC-C-C-C | 14 | × | × | × | × | √ | × | × |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rey-Campos, M.; Novoa, B.; Pallavicini, A.; Gerdol, M.; Figueras, A. Comparative Genomics Reveals 13 Different Isoforms of Mytimycins (A-M) in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063235
Rey-Campos M, Novoa B, Pallavicini A, Gerdol M, Figueras A. Comparative Genomics Reveals 13 Different Isoforms of Mytimycins (A-M) in Mytilus galloprovincialis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(6):3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063235
Chicago/Turabian StyleRey-Campos, Magalí, Beatriz Novoa, Alberto Pallavicini, Marco Gerdol, and Antonio Figueras. 2021. "Comparative Genomics Reveals 13 Different Isoforms of Mytimycins (A-M) in Mytilus galloprovincialis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 6: 3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063235
APA StyleRey-Campos, M., Novoa, B., Pallavicini, A., Gerdol, M., & Figueras, A. (2021). Comparative Genomics Reveals 13 Different Isoforms of Mytimycins (A-M) in Mytilus galloprovincialis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(6), 3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063235








