Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 (TRPA1)—An Inflammation-Induced Factor in Human HaCaT Keratinocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
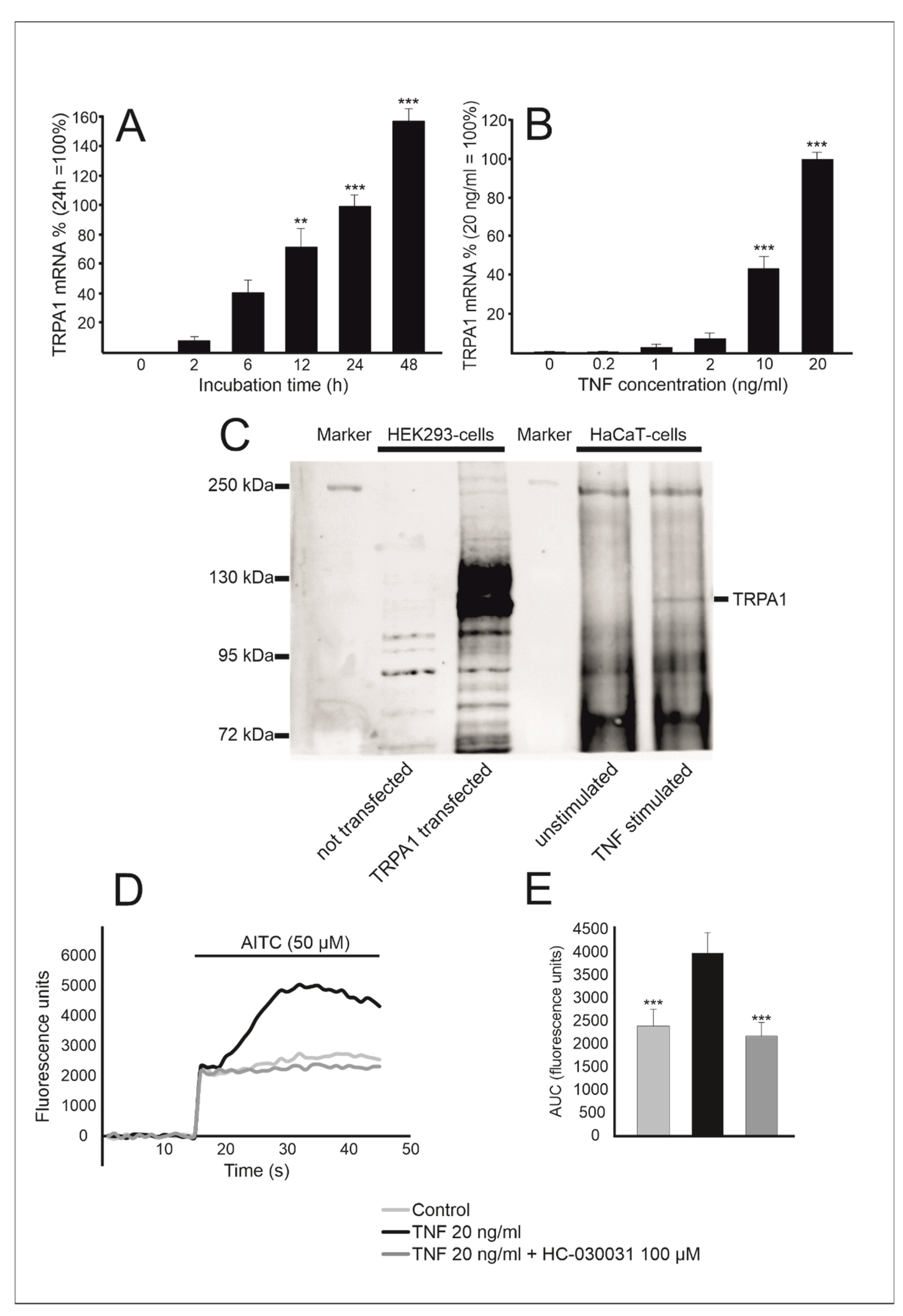
2.1. TRPA1 Expression Is Enhanced by TNF in Human HaCaT Keratinocytes
2.2. TRPA1 Expression Is Upregulated by NF-κB and MAP Kinase Pathways
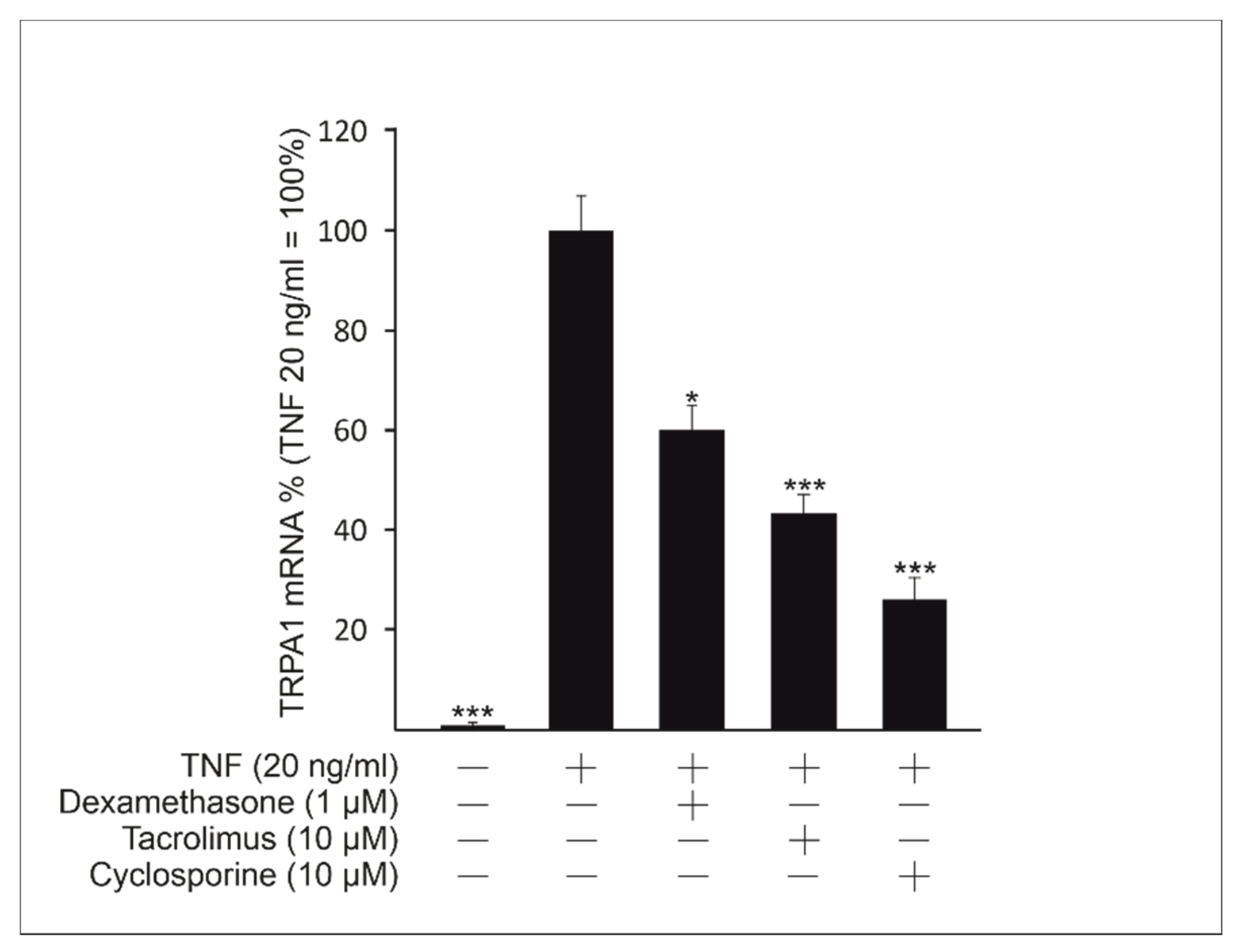
2.3. The Immunosuppressive Drugs Dexamethasone, Cyclosporine and Tacrolimus Inhibit TNF-Induced TRPA1 Expression
2.4. TRPA1 Mediates the Production of the Chemokine MCP-1 in TNF-Stimulated HaCaT Cells and in Mouse Skin Ex Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Animals
4.3. Mouse Skin Sample Culture
4.4. Western Blot Measurements
4.5. Fluo 3-AM Measurements
4.6. Immunoassay
4.7. RNA Extraction and Quantitative RT-PCR
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zygmunt, P.M.; Högestätt, E.D. Trpa1. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2014, 222, 583–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Joshi, S.K.; di Domenico, S.; Perner, R.J.; Mikusa, J.P.; Gauvin, D.M.; Segreti, J.A.; Han, P.; Zhang, X.-F.; Niforatos, W.; et al. Selective blockade of TRPA1 channel attenuates pathological pain without altering noxious cold sensation or body temperature regulation. Pain 2011, 152, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista, D.M.; Jordt, S.-E.; Nikai, T.; Tsuruda, P.R.; Read, A.J.; Poblete, J.; Yamoah, E.N.; Basbaum, A.I.; Julius, D. TRPA1 Mediates the Inflammatory Actions of Environmental Irritants and Proalgesic Agents. Cell 2006, 124, 1269–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouin, O.; l’Herondelle, K.; Lebonvallet, N.; le Gall-Ianotto, C.; Sakka, M.; Buhé, V.; Plée-Gautier, E.; Carré, J.-L.; Lefeuvre, L.; Misery, L.; et al. TRPV1 and TRPA1 in cutaneous neurogenic and chronic inflammation: Pro-inflammatory response induced by their activation and their sensitization. Protein Cell 2017, 8, 644–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, N.; Itoh, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Muraki, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Onozaki, K.; Wood, I.C.; Beech, D.J.; Muraki, K. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1alpha (HIF1alpha) Switches on Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin Repeat 1 (TRPA1) Gene Expression Via a Hypoxia Response Element-Like Motif to Modulate Cytokine Release. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 31962–31972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nummenmaa, E.; Hämäläinen, M.; Moilanen, L.J.; Paukkeri, E.L.; Nieminen, R.M.; Moilanen, T.; Vuolteenaho, K.; Moilanen, E. Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) is Functionally Expressed in Primary Human Osteo-arthritic Chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hackos, D.H. TRPA1 as a Drug Target—Promise and Challenges. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2015, 388, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordt, S.; Bautista, D.M.; Chuang, H.; McKemy, D.D.; Zygmunt, P.M.; Högestätt, E.D.; Meng, I.D.; Julius, D. Mustard Oils and Cannabinoids Excite Sensory Nerve fibres through the TRP Channel ANKTM1. Nature 2004, 427, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macpherson, L.J.; Geierstanger, B.H.; Viswanath, V.; Bandell, M.; Eid, S.R.; Hwang, S.; Patapoutian, A. The Pungency of Garlic: Activation of TRPA1 and TRPV1 in Response to Allicin. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessac, B.F.; Sivula, M.; von Hehn, C.A.; Escalera, J.; Cohn, L.; Jordt, S. TRPA1 is a Major Oxidant Sensor in Murine Airway Sensory Neurons. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.A.; Gentry, C.; Moss, S.; Bevan, S. Transient Receptor Potential A1 is a Sensory Receptor for Multiple Products of Oxidative Stress. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 2485–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor-Clark, T.E.; Ghatta, S.; Bettner, W.; Undem, B.J. Nitrooleic Acid, an Endogenous Product of Nitrative Stress, Activates Nociceptive Sensory Nerves via the Direct Activation of TRPA1. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Mori, Y. TRP Channels as Sensors and Signal Integrators of Redox Status Changes. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandell, M.; Story, G.M.; Hwang, S.W.; Viswanath, V.; Eid, S.R.; Petrus, M.J.; Earley, T.J.; Patapoutian, A. Noxious Cold Ion Channel TRPA1 is Activated by Pungent Compounds and Bradykinin. Neuron 2004, 41, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wang, S.; Tominaga, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Fukuoka, T.; Higashi, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Obata, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Noguchi, K. Sensitization of TRPA1 by PAR2 contributes to the sensation of inflammatory pain. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Dai, Y.; Fukuoka, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Obata, K.; Cui, X.; Tominaga, M.; Noguchi, K. Phospholipase C and protein kinase A mediate bradykinin sensitization of TRPA1: A molecular mechanism of inflammatory pain. Brain 2008, 131, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meents, J.E.; Fischer, M.J.M.; McNaughton, P.A. Sensitization of TRPA1 by Protein Kinase A. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moilanen, L.J.; Hämäläinen, M.; Lehtimaki, L.; Nieminen, R.M.; Muraki, K.; Moilanen, E. Pinosylvin Inhibits TRPA1-Induced Calcium Influx in Vitro and TRPA1-Mediated Acute Paw Inflammation in Vivo. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 118, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moilanen, L.J.; Laavola, M.; Kukkonen, M.; Korhonen, R.; Leppanen, T.; Högestätt, E.D.; Zygmunt, P.M.; Nieminen, R.M.; Moilanen, E. TRPA1 Contributes to the Acute Inflammatory Response and Mediates Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema in the Mouse. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moilanen, L.J.; Hämäläinen, M.; Lehtimaki, L.; Nieminen, R.M.; Moilanen, E. Urate Crystal Induced Inflammation and Joint Pain are Reduced in Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 Deficient Mice—Potential Role for Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 in Gout. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevisan, G.; Hoffmeister, C.; Rossato, M.F.; Oliveira, S.M.; Silva, M.A.; Silva, C.R.; Fusi, C.; Tonello, R.; Minocci, D.; Guerra, G.P. TRPA1 Receptor Stimulation by Hydrogen Peroxide is Critical to Trigger Hyperalgesia and Inflammation in a Model of Acute Gout. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 72, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moilanen, L.J.; Hämäläinen, M.; Nummenmaa, E.; Ilmarinen, P.; Vuolteenaho, K.; Nieminen, R.M.; Lehtimaki, L.; Moilanen, E. Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Inflammation and Joint Pain are Reduced in TRPA1 Deficient Mice—Potential Role of TRPA1 in Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 2017–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Escalera, J.; Balakrishna, S.; Fan, L.; Caceres, A.I.; Robinson, E.; Sui, A.; McKay, M.C.; McAlexander, M.A.; Herrick, C.A.; et al. TRPA1 controls inflammation and pruritogen responses in allergic contact dermatitis. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 3549–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Ding, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, M. TRPA1 Mediated Aggravation of Allergic Contact Dermatitis Induced by DINP and Regulated by NF-κB Activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.-H.; Oh, S.Y.; Lu, J.; Lou, H.; Myers, A.C.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, T. TRPA1-Dependent Pruritus in IL-13–Induced Chronic Atopic Dermatitis. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 5371–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevikbas, F.; Wang, X.; Akiyama, T.; Kempkes, C.; Savinko, T.; Antal, A.; Kukova, G.; Buhl, T.; Ikoma, A.; Buddenkotte, J.; et al. A sensory neuron–expressed IL-31 receptor mediates T helper cell–dependent itch: Involvement of TRPV1 and TRPA1. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 448–460.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.R.; Nelson, A.M.; Batia, L.; Morita, T.; Estandian, D.; Owens, D.M.; Lumpkin, E.A.; Bautista, D.M. The Ion Channel TRPA1 Is Required for Chronic Itch. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 9283–9294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemény, Á.; Kodji, X.; Horváth, S.; Komlódi, R.; Szőke, É.; Sándor, Z.; Perkecz, A.; Gyömörei, C.; Sétáló, G.; Kelemen, B. TRPA1 Acts in a Protective Manner in Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasiform Dermatitis in Mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1774–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Brnneke, S.; Kolbe, L.; Stb, F.; Wenck, H.; Neufang, G. TRP-Channel-Specific Cutaneous Eicosanoid Release Patterns. Pain 2011, 152, 2765–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atoyan, R.; Shander, D.; Botchkareva, N.V. Non-Neuronal Expression of Transient Receptor Potential Type A1 (TRPA1) in Human Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 2312–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaquemar, D.; Schenker, T.; Trueb, B. An Ankyrin-like Protein with Transmembrane Domains Is Specifically Lost after Oncogenic Transformation of Human Fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 7325–7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Story, G.M.; Peier, A.M.; Reeve, A.J.; Eid, S.R.; Mosbacher, J.; Hricik, T.R.; Earley, T.J.; Hergarden, A.C.; Andersson, D.A.; Hwang, S.W.; et al. ANKTM1, a TRP-like Channel Expressed in Nociceptive Neurons, Is Activated by Cold Temperatures. Cell 2003, 112, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilius, B.; Appendino, G.; Owsianik, G. The Transient Receptor Potential Channel TRPA1: From Gene to Pathophysiology. Pflgers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2012, 464, 425–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellono, N.W.; Kammel, L.G.; Zimmerman, A.L.; Oancea, E. UV light phototransduction activates transient receptor potential A1 ion channels in human melanocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2383–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, I.; Gomes, P.; Aranake, S.; Shetty, M.; Karnik, P.; Damle, M.; Kuruganti, S.; Thorat, S.; Khairatkar-Joshi, N. Expression of functional TRPA1 receptor on human lung fibroblast and epithelial cells. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2011, 31, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moilanen, L.J.; Hämäläinen, M.; Ilmarinen, P.; Kankaanranta, H.; Nieminen, R.M.; Moilanen, E.; Lehtimäki, L. Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 Enhances Ovalbumin-Induced Acute Allergic Inflammation in Murine Models. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 178, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, M.A.; Leffler, A.; Niedermirtl, F.; Babes, A.; Zimmermann, K.; Filipović, M.R.; Izydorczyk, I.; Eberhardt, M.; Kichko, T.I.; Mueller–Tribbensee, S.M. TRPA1 and Substance P Mediate Colitis in Mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sbidian, E.; Chaimani, A.; Garcia-Doval, I.; Do, G.; Hua, C.; Mazaud, C.; Droitcourt, C.; Hughes, C.; Ingram, J.R.; Naldi, L. Systemic Pharmacological Treatments for Chronic Plaque Psoriasis: A Network Meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 12, CD011535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lenardo, M.J.; Baltimore, D. 30 Years of NF-κB: A Blossoming of Relevance to Human Pathobiology. Cell 2017, 168, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, J.S.C.; Ley, S.C. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutfreund, K.; Bienias, W.; Szewczyk, A.; Kaszuba, A. Topical calcineurin inhibitors in dermatology. Part I: Properties, method and effectiveness of drug use. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2013, 3, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Daraji, W.I.; Grant, K.R.; Ryan, K.; Saxton, A.; Reynolds, N.J. Localization of Calcineurin/NFAT in Human Skin and Psoriasis and Inhibition of Calcineurin/NFAT Activation in Human Keratinocytes by Cyclosporin A. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 118, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammucari, C.; di Vignano, A.T.; Sharov, A.A.; Neilson, J.; Havrda, M.C.; Roop, D.R.; Botchkarev, V.A.; Crabtree, G.R.; Dotto, G.P. Integration of Notch 1 and Calcineurin/NFAT Signaling Pathways in Keratinocyte Growth and Differentiation Control. Dev. Cell 2005, 8, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jans, R.; Mottram, L.; Johnson, D.L.; Brown, A.M.; Sikkink, S.; Ross, K.; Reynolds, N.J. Lysophosphatidic Acid Promotes Cell Migration through STIM1- and Orai1-Mediated Ca2+ i Mobilization and NFAT2 Activation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.B.; Nadkarni, N.J.; Patil, S.P.; Godse, K.V.; Gautam, M.; Agarwal, S. Topical Corticosteroids in Dermatology. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2016, 82, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nummenmaa, E.; Hämäläinen, M.; Moilanen, L.J.; Moilanen, T.; Vuolteenaho, K.; Moilanen, E. TRPA1 Expression is Downregulated by Dexamethasone and Aurothiomalate in Human Chondrocytes: TRPA1 as a Novel Factor and Drug Target in Arthritis. RMD Open 2017, 3, e000556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bootman, M.D. Calcium Signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a011171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1): An Over-view. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behfar, S.; Hassanshahi, G.; Nazari, A.; Khorramdelazad, H. A Brief Look at the Role of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (CCL2) in the Pathophysiology of Psoriasis. Cytokine 2018, 110, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, V.G. Growth and Differentiation of HaCaT Keratinocytes. Adv. Struct. Saf. Stud. 2013, 1195, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luostarinen, S.; Hämäläinen, M.; Moilanen, E. Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 (TRPA1)—An Inflammation-Induced Factor in Human HaCaT Keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073322
Luostarinen S, Hämäläinen M, Moilanen E. Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 (TRPA1)—An Inflammation-Induced Factor in Human HaCaT Keratinocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(7):3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073322
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuostarinen, Samu, Mari Hämäläinen, and Eeva Moilanen. 2021. "Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 (TRPA1)—An Inflammation-Induced Factor in Human HaCaT Keratinocytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 7: 3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073322
APA StyleLuostarinen, S., Hämäläinen, M., & Moilanen, E. (2021). Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 (TRPA1)—An Inflammation-Induced Factor in Human HaCaT Keratinocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(7), 3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073322





