Manmade Electromagnetic Fields and Oxidative Stress—Biological Effects and Consequences for Health
Abstract
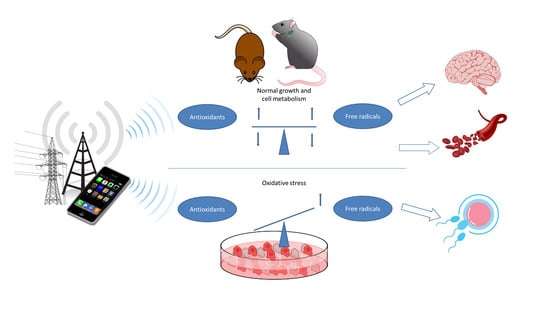
:1. Introduction
2. Background Information on Oxidative Stress
2.1. Origin of ROS and Oxidative Stress
2.2. Protective Mechanisms
2.3. Detection of Oxidative Stress
3. Impact of EMF on the Nervous System
3.1. Observations in EMF-Exposed Animals
3.2. Observations in EMF-Exposed Cultured Neuronal Cells
3.3. Assessment of EMF-Induced Oxidative Stress in the Nervous System
4. EMF Effects on the Blood and Immune System
4.1. Oxidative Stress in EMF-Exposed Animals
4.2. Radical Formation in EMF-Exposed Cells of the Blood and Immune System
4.3. Assessment of EMF Effects on Blood and Immune Organs
5. EMF Exposure and Oxidative Stress: Effects on Reproduction
5.1. In Animals
5.2. In Cultured Cells
5.3. Assessment of EMF Effects on Reproduction and Fertility
6. Further Observations of Oxidative Stress Induced by EMF
6.1. Oxidative Influences on Other Organs
6.2. Experimental Data on the Effect of EMF on Skin, Epithelial, and Cancer Cells
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 8-OHdG | 8-Oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine, 8-oxo-G |
| AC | Alternating current |
| ATRA | All-trans retinoic acid |
| CAT | Catalase |
| ELF-MF | Extremely-low-frequency magnetic field |
| EMF | Electromagnetic field |
| eNOS | Endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| ERK | External signal-regulated kinase |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| GSM | Global system for mobile communications, 2G |
| GSSG | Glutathione disulfide |
| GST | Glutathione S-transferase |
| GR | Glutathione reductase |
| HSC | Hematopoietic stem cell |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| LTE | Long-term evolution, 4G |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| NADPH | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| nNOS | Neuronal nitric oxide synthase |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NOS | Nitric oxide synthase |
| NOX | NADPH oxidase |
| PMA | Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate |
| PRDx | Peroxiredoxin |
| RF-EMF | Radiofrequency magnetic field |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SAR | Specific absorption rate |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| TRPV1 | Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 |
| UMTS | Universal mobile telecommunications system, 3G |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| WiFi | Wireless Fidelity, WLAN standard |
References
- Brieger, K.; Schiavone, S.; Miller, F.J., Jr.; Krause, K.H. Reactive oxygen species: From health to disease. Swiss. Med. Wkly. 2012, 142, w13659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Droge, W. Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 47–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Berndt, C.; Jones, D.P. Oxidative Stress. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 715–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M.C. Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; p. 944. [Google Scholar]
- Marnett, L.J. Oxyradicals and DNA damage. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cadet, J.; Davies, K.J.A.; Medeiros, M.H.; Di Mascio, P.; Wagner, J.R. Formation and repair of oxidatively generated damage in cellular DNA. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2017, 107, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakymenko, I.; Tsybulin, O.; Sidorik, E.; Henshel, D.; Kyrylenko, O.; Kyrylenko, S. Oxidative mechanisms of biological activity of low-intensity radiofrequency radiation. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2016, 35, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X. Magnetic Fields and Reactive Oxygen Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamrin, S.H.; Majedi, F.S.; Tondar, M.; Sanati-Nezhad, A.; Hasani-Sadrabadi, M.M. Electromagnetic Fields and Stem Cell Fate: When Physics Meets Biology. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 171, 63–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, S.J.; Cordone, V.; Falone, S.; Mijit, M.; Tatone, C.; Amicarelli, F.; Di Emidio, G. Role of Mitochondria in the Oxidative Stress Induced by Electromagnetic Fields: Focus on Reproductive Systems. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longevity 2018, 2018, 5076271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosado, M.M.; Simko, M.; Mattsson, M.O.; Pioli, C. Immune-Modulating Perspectives for Low Frequency Electromagnetic Fields in Innate Immunity. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manna, D.; Ghosh, R. Effect of radiofrequency radiation in cultured mammalian cells: A review. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2016, 35, 265–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H. Exposure to Static and Extremely-Low Frequency Electromagnetic Fields and Cellular Free Radicals. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2019, 38, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falone, S.; Santini, S., Jr.; Cordone, V.; Di Emidio, G.; Tatone, C.; Cacchio, M.; Amicarelli, F. Extremely Low-Frequency Magnetic Fields and Redox-Responsive Pathways Linked to Cancer Drug Resistance: Insights from Co-Exposure-Based In Vitro Studies. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dasdag, S.; Akdag, M.Z. The link between radiofrequencies emitted from wireless technologies and oxidative stress. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2016, 75, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, C.D. Oxidative stress-induced biological damage by low-level EMFs: Mechanism of free radical pair electron spin-polarization and biochemical amplification. In In Non-thermal Effects and Mechanisms of Interaction Between Electromagnetic Fields and Living Matter; Giuliani, L., Soffritti, M., Eds.; European Journal of Oncology—Library: Bologna, Italy, 2010; Volume 5, pp. 63–113. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, L.; Yamamoto, M. The Molecular Mechanisms Regulating the KEAP1-NRF2 Pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, C.; Chio, I.I.C.; Tuveson, D.A. Transcriptional Regulation by Nrf2. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 1727–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sies, H.; Jones, D.P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard, K.; Krause, K.H. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: Physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bazhin, A.V.; Werner, J.; Karakhanova, S. Reactive oxygen species in the immune system. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 32, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Branicky, R.; Noe, A.; Hekimi, S. Superoxide dismutases: Dual roles in controlling ROS damage and regulating ROS signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, M.C.W.; Garnham, N.; Sweeney, S.T.; Landgraf, M. Regulation of neuronal development and function by ROS. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.G.; Kil, I.S. Multiple Functions and Regulation of Mammalian Peroxiredoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 749–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigelius-Flohe, R.; Maiorino, M. Glutathione peroxidases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3289–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Dai, M.H.; Yuan, Z.H. Methods for the detection of reactive oxygen species. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 4625–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 524, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.; Munoz-Palma, E.; Gonzalez-Billault, C. From birth to death: A role for reactive oxygen species in neuronal development. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 80, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkis, M.E.; Bilgin, H.M.; Akpolat, V.; Dasdag, S.; Yegin, K.; Yavas, M.C.; Akdag, M.Z. Effect of 900-, 1800-, and 2100-MHz radiofrequency radiation on DNA and oxidative stress in brain. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2019, 38, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, S.; El-Saba, A.A.; Galal, M.K. Biochemical and histological studies on adverse effects of mobile phone radiation on rat’s brain. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2016, 78, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesari, K.K.; Meena, R.; Nirala, J.; Kumar, J.; Verma, H.N. Effect of 3G cell phone exposure with computer controlled 2-D stepper motor on non-thermal activation of the hsp27/p38MAPK stress pathway in rat brain. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 68, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megha, K.; Deshmukh, P.S.; Banerjee, B.D.; Tripathi, A.K.; Ahmed, R.; Abegaonkar, M.P. Low intensity microwave radiation induced oxidative stress, inflammatory response and DNA damage in rat brain. Neurotoxicology 2015, 51, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, D.; Ozgur, E.; Guler, G.; Tomruk, A.; Unlu, I.; Sepici-Dinçel, A.; Seyhan, N. The 2100MHz radiofrequency radiation of a 3G-mobile phone and the DNA oxidative damage in brain. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2016, 75, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Shukla, S. Effect of electromagnetic radiation on redox status, acetylcholine esterase activity and cellular damage contributing to the diminution of the brain working memory in rats. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2020, 106, 101784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragy, M.M. Effect of exposure and withdrawal of 900-MHz-electromagnetic waves on brain, kidney and liver oxidative stress and some biochemical parameters in male rats. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2015, 34, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motawi, T.K.; Darwish, H.A.; Moustafa, Y.M.; Labib, M.M. Biochemical modifications and neuronal damage in brain of young and adult rats after long-term exposure to mobile phone radiations. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 70, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.J.; Son, Y.; Han, N.K.; Choi, H.D.; Pack, J.K.; Kim, N.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, H.J. Impact of Long-Term RF-EMF on Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Aging Brains of C57BL/6 Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zong, C.; Ji, Y.; He, Q.; Zhu, S.; Qin, F.; Tong, J.; Cao, Y. Adaptive response in mice exposed to 900 MHZ radiofrequency fields: Bleomycin-induced DNA and oxidative damage/repair. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2015, 91, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado-Filho, O.V.; Borba, J.B.; Maraschin, T.; Souza, L.M.; Henriques, J.A.; Moreira, J.C.; Saffi, J. Effects of chronic exposure to 950 MHz ultra-high-frequency electromagnetic radiation on reactive oxygen species metabolism in the right and left cerebral cortex of young rats of different ages. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2015, 91, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Jelodar, G.; Nazifi, S. Vitamin C protects rat cerebellum and encephalon from oxidative stress following exposure to radiofrequency wave generated by a BTS antenna model. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2014, 24, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, B.; Akar, A.; Bilgici, B.; Tunçel, Ö.K. Oxidative stress induced by 1.8 GHz radio frequency electromagnetic radiation and effects of garlic extract in rats. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2012, 88, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodera, P.; Makarova, K.; Zawada, K.; Antkowiak, B.; Paluch, M.; Sobiczewska, E.; Sirav, B.; Siwicki, A.K.; Stankiewicz, W. The effect of 1800MHz radio-frequency radiation on NMDA receptor subunit NR1 expression and peroxidation in the rat brain in healthy and inflammatory states. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertilav, K.; Uslusoy, F.; Ataizi, S.; Nazıroğlu, M. Long term exposure to cell phone frequencies (900 and 1800 MHz) induces apoptosis, mitochondrial oxidative stress and TRPV1 channel activation in the hippocampus and dorsal root ganglion of rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürler, H.; Bilgici, B.; Akar, A.K.; Tomak, L.; Bedir, A. Increased DNA oxidation (8-OHdG) and protein oxidation (AOPP) by low level electromagnetic field (2.45 GHz) in rat brain and protective effect of garlic. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2014, 90, 892–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naziroğlu, M.; Çelik, Ö.; Özgül, C.; Çiğ, B.; Doğan, S.; Bal, R.; Gümral, N.; Rodríguez, A.B.; Pariente, J.A. Melatonin modulates wireless (2.45 GHz)-induced oxidative injury through TRPM2 and voltage gated Ca(2+) channels in brain and dorsal root ganglion in rat. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 105, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, R.; Majumdar, A.; Kumar, G.; Shukla, A. Rats exposed to 2.45GHz of non-ionizing radiation exhibit behavioral changes with increased brain expression of apoptotic caspase 3. Pathophysiology 2018, 25, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerimoğlu, G.; Hanci, H.; Bas, O.; Aslan, A.; Erol, H.S.; Turgut, A.; Kaya, H.; Cankaya, S.; Sönmez, O.F.; Odaci, E. Pernicious effects of long-term, continuous 900-MHz electromagnetic field throughout adolescence on hippocampus morphology, biochemistry and pyramidal neuron numbers in 60-day-old Sprague Dawley male rats. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2016, 77, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.; Verma, H.N.; Sisodia, R.; Kesari, K.K. Microwave radiation (2.45 GHz)-induced oxidative stress: Whole-body exposure effect on histopathology of Wistar rats. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2017, 36, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesari, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Behari, J. 900-MHz microwave radiation promotes oxidation in rat brain. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2011, 30, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asl, J.F.; Goudarzi, M.; Shoghi, H. The radio-protective effect of rosmarinic acid against mobile phone and Wi-Fi radiation-induced oxidative stress in the brains of rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, S.; Singh, S.P.; Chaturvedi, C.M. Mobile phone (1800MHz) radiation impairs female reproduction in mice, Mus musculus, through stress induced inhibition of ovarian and uterine activity. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 73, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, S.; Banerjee, S.; Swarup, V.; Singh, S.P.; Chaturvedi, C.M. From the Cover: 2.45-GHz Microwave Radiation Impairs Hippocampal Learning and Spatial Memory: Involvement of Local Stress Mechanism-Induced Suppression of iGluR/ERK/CREB Signaling. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 161, 349–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikinci, A.; Mercantepe, T.; Unal, D.; Erol, H.S.; Sahin, A.; Aslan, A.; Bas, O.; Erdem, H.; Sönmez, O.F.; Kaya, H.; et al. Morphological and antioxidant impairments in the spinal cord of male offspring rats following exposure to a continuous 900MHz electromagnetic field during early and mid-adolescence. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2016, 75, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgici, B.; Akar, A.; Avci, B.; Tuncel, O.K. Effect of 900 MHz radiofrequency radiation on oxidative stress in rat brain and serum. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2013, 32, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, S.; Mishra, V.; Singh, S.P.; Chaturvedi, C.M. 2.45-GHz microwave irradiation adversely affects reproductive function in male mouse, Mus musculus by inducing oxidative and nitrosative stress. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megha, K.; Deshmukh, P.S.; Banerjee, B.D.; Tripathi, A.K.; Abegaonkar, M.P. Microwave radiation induced oxidative stress, cognitive impairment and inflammation in brain of Fischer rats. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 50, 889–896. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, Q.; Tan, L.; Zuo, S.; Feng, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, G. Exposure to 900 MHz electromagnetic fields activates the mkp-1/ERK pathway and causes blood-brain barrier damage and cognitive impairment in rats. Brain Res. 2015, 1601, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Dong, J.; Yao, B.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Gao, Y.; et al. Study on dose-dependent, frequency-dependent, and accumulative effects of 1.5 GHz and 2.856 GHz microwave on cognitive functions in Wistar rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Othman, H.; Ammari, M.; Sakly, M.; Abdelmelek, H. Effects of repeated restraint stress and WiFi signal exposure on behavior and oxidative stress in rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, H.; Ammari, M.; Sakly, M.; Abdelmelek, H. Effects of prenatal exposure to WIFI signal (2.45GHz) on postnatal development and behavior in rat: Influence of maternal restraint. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 326, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, H.; Ammari, M.; Rtibi, K.; Bensaid, N.; Sakly, M.; Abdelmelek, H. Postnatal development and behavior effects of in-utero exposure of rats to radiofrequency waves emitted from conventional WiFi devices. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 52, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmekaya, M.A.; Tuysuz, M.Z.; Tomruk, A.; Canseven, A.G.; Yücel, E.; Aktuna, Z.; Keskil, S.; Seyhan, N. Effects of cell phone radiation on lipid peroxidation, glutathione and nitric oxide levels in mouse brain during epileptic seizure. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2016, 75, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouji, M.; Lecomte, A.; Gamez, C.; Blazy, K.; Villégier, A.S. Impact of Cerebral Radiofrequency Exposures on Oxidative Stress and Corticosterone in a Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer Dis. JAD 2020, 73, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikonda, P.K.; Rajendra, P.; Devendranath, D.; Gunasekaran, B.; Channakeshava; Aradhya, S.R.; Sashidhar, R.B.; Subramanyam, C. Extremely low frequency magnetic fields induce oxidative stress in rat brain. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2014, 33, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akdag, M.Z.; Dasdag, S.; Ulukaya, E.; Uzunlar, A.K.; Kurt, M.A.; Taşkin, A. Effects of extremely low-frequency magnetic field on caspase activities and oxidative stress values in rat brain. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2010, 138, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelenković, A.; Janać, B.; Pesić, V.; Jovanović, D.M.; Vasiljević, I.; Prolić, Z. Effects of extremely low-frequency magnetic field in the brain of rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 68, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, L.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Nam, Y.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, W.H.; Lee, B.C.; Kim, D.; Chung, Y.H.; Jeong, J.H. Extremely low frequency magnetic field induces oxidative stress in mouse cerebellum. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2011, 30, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ciejka, E.; Kleniewska, P.; Skibska, B.; Goraca, A. Effects of extremely low frequency magnetic field on oxidative balance in brain of rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2011, 62, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Sámano, J.; Torres-Durán, P.V.; Juárez-Oropeza, M.A.; Verdugo-Díaz, L. Effect of acute extremely low frequency electromagnetic field exposure on the antioxidant status and lipid levels in rat brain. Arch. Med. Res. 2012, 43, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.I.; Nam, Y.S.; Chu, L.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Bang, J.S.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, H.D.; Sul, J.D.; et al. Extremely low-frequency magnetic fields modulate nitric oxide signaling in rat brain. Bioelectromagnetics 2012, 33, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, M.L.; Van Remmen, H.; Drake, J.A.; Yang, H.; Guo, Z.M.; Kewitt, K.; Walter, C.A.; Richardson, A. Does oxidative damage to DNA increase with age? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10469–10474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falone, S.; Mirabilio, A.; Carbone, M.C.; Zimmitti, V.; Di Loreto, S.; Mariggiò, M.A.; Mancinelli, R.; Di Ilio, C.; Amicarelli, F. Chronic exposure to 50Hz magnetic fields causes a significant weakening of antioxidant defence systems in aged rat brain. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 2762–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bediz, C.S.; Baltaci, A.K.; Mogulkoc, R.; Öztekin, E. Zinc supplementation ameliorates electromagnetic field-induced lipid peroxidation in the rat brain. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2006, 208, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, L. Effects of aluminum and extremely low frequency electromagnetic radiation on oxidative stress and memory in brain of mice. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 156, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Shen, Y.; Hong, L.; Chen, Y.; Shi, X.; Zeng, Q.; Yu, P. Effects of Single and Repeated Exposure to a 50-Hz 2-mT Electromagnetic Field on Primary Cultured Hippocampal Neurons. Neurosci. Bull. 2017, 33, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benassi, B.; Filomeni, G.; Montagna, C.; Merla, C.; Lopresto, V.; Pinto, R.; Marino, C.; Consales, C. Extremely Low Frequency Magnetic Field (ELF-MF) Exposure Sensitizes SH-SY5Y Cells to the Pro-Parkinson’s Disease Toxin MPP+. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 4247–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consales, C.; Cirotti, C.; Filomeni, G.; Panatta, M.; Butera, A.; Merla, C.; Lopresto, V.; Pinto, R.; Marino, C.; Benassi, B. Fifty-Hertz Magnetic Field Affects the Epigenetic Modulation of the miR-34b/c in Neuronal Cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 5698–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, M.; Kamal, M.A.; Patruno, A.; Costantini, E.; D’Angelo, C.; Pesce, M.; Greig, N.H. Neuronal cellular responses to extremely low frequency electromagnetic field exposure: Implications regarding oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consales, C.; Panatta, M.; Butera, A.; Filomeni, G.; Merla, C.; Carrì, M.T.; Marino, C.; Benassi, B. 50-Hz magnetic field impairs the expression of iron-related genes in the in vitro SOD1(G93A) model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2019, 95, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, M.; D’Angelo, C.; Costantini, E.; Tata, A.M.; Regen, F.; Hellmann-Regen, J. Effect of Environmental Extremely Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Fields Exposure on Inflammatory Mediators and Serotonin Metabolism in a Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2016, 15, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.A.; Úbeda, A.; Moreno, J.; Trillo, M.A. Power Frequency Magnetic Fields Affect the p38 MAPK-Mediated Regulation of NB69 Cell Proliferation Implication of Free Radicals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, C.; Guarnieri, S.; Fano, G.; Mariggio, M.A. Effects of acute and chronic low frequency electromagnetic field exposure on PC12 cells during neuronal differentiation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 26, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, M.W.; Kock, M.D.; Westerink, R.H. Assessment of the neurotoxic potential of exposure to 50Hz extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields (ELF-EMF) in naive and chemically stressed PC12 cells. Neurotoxicology 2014, 44, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.E.; Seo, Y.K.; Yoon, H.H.; Kim, C.W.; Park, J.K.; Jeon, S. Electromagnetic fields induce neural differentiation of human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells via ROS mediated EGFR activation. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, W.Y.; Kim, J.B.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, C.W. Extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field promotes astrocytic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by modulating SIRT1 expression. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villarini, M.; Gambelunghe, A.; Giustarini, D.; Ambrosini, M.V.; Fatigoni, C.; Rossi, R.; Dominici, L.; Levorato, S.; Muzi, G.; Piobbico, D.; et al. No evidence of DNA damage by co-exposure to extremely low frequency magnetic fields and aluminum on neuroblastoma cell lines. Mutat. Res. 2017, 823, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falone, S.; Santini, S., Jr.; Cordone, V.; Cesare, P.; Bonfigli, A.; Grannonico, M.; Di Emidio, G.; Tatone, C.; Cacchio, M.; Amicarelli, F. Power frequency magnetic field promotes a more malignant phenotype in neuroblastoma cells via redox-related mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Höytö, A.; Herrala, M.; Luukkonen, J.; Juutilainen, J.; Naarala, J. Cellular detection of 50 Hz magnetic fields and weak blue light: Effects on superoxide levels and genotoxicity. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2017, 93, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesari, K.K.; Juutilainen, J.; Luukkonen, J.; Naarala, J. Induction of micronuclei and superoxide production in neuroblastoma and glioma cell lines exposed to weak 50 Hz magnetic fields. J. R. Soc. Interface 2016, 13, 20150995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kesari, K.K.; Luukkonen, J.; Juutilainen, J.; Naarala, J. Genomic instability induced by 50Hz magnetic fields is a dynamically evolving process not blocked by antioxidant treatment. Mutat. Res. 2015, 794, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, J.; Liimatainen, A.; Juutilainen, J.; Naarala, J. Induction of genomic instability, oxidative processes, and mitochondrial activity by 50Hz magnetic fields in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Mutat. Res. 2014, 760, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; et al. Exposure to 1800 MHz radiofrequency radiation induces oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA in primary cultured neurons. Brain Res. 2010, 1311, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.Q.; Hu, Y.J.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Kong, W.; Kong, W.J. Sensitivity of spiral ganglion neurons to damage caused by mobile phone electromagnetic radiation will increase in lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in vitro model. J. Neuroinflammation 2015, 12, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsoy, A.; Saliev, T.; Abzhanova, E.; Turgambayeva, A.; Kaiyrlykyzy, A.; Akishev, M.; Saparbayev, S.; Umbayev, B.; Askarova, S. The Effects of Mobile Phone Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields on beta-Amyloid-Induced Oxidative Stress in Human and Rat Primary Astrocytes. Neuroscience 2019, 408, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; He, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, C.; Pi, H.; Yu, Z.; et al. Differential pro-inflammatory responses of astrocytes and microglia involve STAT3 activation in response to 1800 MHz radiofrequency fields. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, A.; Gulino, M.; Acquaviva, R.; Bellia, P.; Raciti, G.; Grasso, R.; Musumeci, F.; Vanella, A.; Triglia, A. Reactive oxygen species levels and DNA fragmentation on astrocytes in primary culture after acute exposure to low intensity microwave electromagnetic field. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 473, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, N.; Kwon, J.H.; Park, M.J. Effects of radiofrequency field exposure on glutamate-induced oxidative stress in mouse hippocampal HT22 cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2017, 93, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.C.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, N.; Park, M.J. Effects of combined radiofrequency field exposure on amyloid-beta-induced cytotoxicity in HT22 mouse hippocampal neurones. J. Radiat. Res. 2016, 57, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, J.; Hakulinen, P.; Mäki-Paakkanen, J.; Juutilainen, J.; Naarala, J. Enhancement of chemically induced reactive oxygen species production and DNA damage in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells by 872 MHz radiofrequency radiation. Mutat. Res. 2009, 662, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, J.; Juutilainen, J.; Naarala, J. Combined effects of 872 MHz radiofrequency radiation and ferrous chloride on reactive oxygen species production and DNA damage in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Bioelectromagnetics 2010, 31, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, J.; Ducray, A.D.; Moeller, A.M.; Murbach, M.; Kuster, N.; Mevissen, M. Effects of pulse-modulated radiofrequency magnetic field (RF-EMF) exposure on apoptosis, autophagy, oxidative stress and electron chain transport function in human neuroblastoma and murine microglial cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2020, 68, 104963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.A.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, J.J.; Hong, M.N.; Park, M.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Choi, H.D.; Kim, N.; Ko, Y.G.; Lee, J.S. Effects of combined radiofrequency radiation exposure on levels of reactive oxygen species in neuronal cells. J. Radiat. Res. 2014, 55, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poulletier de Gannes, F.; Haro, E.; Hurtier, A.; Taxile, M.; Ruffié, G.; Billaudel, B.; Veyret, B.; Lagroye, I. Effect of exposure to the edge signal on oxidative stress in brain cell models. Radiat. Res. 2011, 175, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanovic Cermak, A.M.; Pavicic, I.; Trosic, I. Oxidative stress response in SH-SY5Y cells exposed to short-term 1800 MHz radiofrequency radiation. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2018, 53, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.; Zhan, Q.; He, Y.; Cui, J.; He, S.; Wang, G. 1800 MHz Microwave Induces p53 and p53-Mediated Caspase-3 Activation Leading to Cell Apoptosis In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Niederhäusern, N.; Ducray, A.; Zielinski, J.; Murbach, M.; Mevissen, M. Effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic field exposure on neuronal differentiation and mitochondrial function in SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2019, 61, 104609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Ma, Q.; Feng, W.; Yang, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, L. 8-oxoG DNA glycosylase-1 inhibition sensitizes Neuro-2a cells to oxidative DNA base damage induced by 900 MHz radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, A.A. Electromagnetic fields instantaneously modulate nitric oxide signaling in challenged biological systems. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 426, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duitama, M.; Vargas-Lopez, V.; Casas, Z.; Albarracin, S.L.; Sutachan, J.J.; Torres, Y.P. TRP Channels Role in Pain Associated With Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Shimizu, S. Significance of TRP channels in oxidative stress. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 793, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiğ, B.; Naziroğlu, M. Investigation of the effects of distance from sources on apoptosis, oxidative stress and cytosolic calcium accumulation via TRPV1 channels induced by mobile phones and Wi-Fi in breast cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1848, 2756–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yüksel, M.; Nazıroğlu, M.; Ozkaya, M.O. Long-term exposure to electromagnetic radiation from mobile phones and Wi-Fi devices decreases plasma prolactin, progesterone, and estrogen levels but increases uterine oxidative stress in pregnant rats and their offspring. Endocrine 2016, 52, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Chen, G.; Chen, C.; Sun, C.; Zhang, D.; Murbach, M.; Kuster, N.; Zeng, Q.; Xu, Z. Cell type-dependent induction of DNA damage by 1800 MHz radiofrequency electromagnetic fields does not result in significant cellular dysfunctions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simkó, M.; Remondini, D.; Zeni, O.; Scarfi, M.R. Quality matters: Systematic analysis of endpoints related to “cellular life” in vitro data of radiofrequency electromagnetic field exposure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayalaxmi; Prihoda, T.J. Comprehensive Review of Quality of Publications and Meta-analysis of Genetic Damage in Mammalian Cells Exposed to Non-Ionizing Radiofrequency Fields. Radiat. Res. 2019, 191, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, B.; Akar, A. Effects of a 900-MHz electromagnetic field on oxidative stress parameters in rat lymphoid organs, polymorphonuclear leukocytes and plasma. Arch. Med. Res. 2011, 42, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumral, N.; Nazıroğlu, M.; Koyu, A.; Ongel, K.; Celik, O.; Saygin, M.; Kahriman, M.; Caliskan, S.; Kayan, M.; Gencel, O.; et al. Effects of selenium and L-carnitine on oxidative stress in blood of rat induced by 2.45-GHz radiation from wireless devices. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2009, 132, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahin, S.; Singh, V.P.; Shukla, R.K.; Dhawan, A.; Gangwar, R.K.; Singh, S.P.; Chaturvedi, C.M. 2.45 GHz microwave irradiation-induced oxidative stress affects implantation or pregnancy in mice, Mus musculus. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 169, 1727–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirel, S.; Doganay, S.; Turkoz, Y.; Dogan, Z.; Turan, B.; Firat, P.G. Effects of third generation mobile phone-emitted electromagnetic radiation on oxidative stress parameters in eye tissue and blood of rats. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokus, B.; Akdag, M.Z.; Dasdag, S.; Cakir, D.U.; Kizil, M. Extremely low frequency magnetic fields cause oxidative DNA damage in rats. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2008, 84, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokus, B.; Cakir, D.U.; Akdag, M.Z.; Sert, C.; Mete, N. Oxidative DNA damage in rats exposed to extremely low frequency electro magnetic fields. Free Radical Res. 2005, 39, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannerling, A.C.; Simkó, M.; Mild, K.H.; Mattsson, M.O. Effects of 50-Hz magnetic field exposure on superoxide radical anion formation and HSP70 induction in human K562 cells. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2010, 49, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patruno, A.; Tabrez, S.; Pesce, M.; Shakil, S.; Kamal, M.A.; Reale, M. Effects of extremely low frequency electromagnetic field (ELF-EMF) on catalase, cytochrome P450 and nitric oxide synthase in erythro-leukemic cells. Life Sci. 2015, 121, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AyŞe, I.G.; Zafer, A.; Şule, O.; IŞil, I.T.; Kalkan, T. Differentiation of K562 cells under ELF-EMF applied at different time courses. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2010, 29, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisdelli, F.; Bennato, F.; Bozzi, A.; Cinque, B.; Mancini, F.; Iorio, R. ELF-MF attenuates quercetin-induced apoptosis in K562 cells through modulating the expression of Bcl-2 family proteins. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 397, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, A.E.; Amatori, S.; Nasoni, M.G.; Persico, G.; Russo, S.; Mastrogiacomo, A.R.; Gambarara, A.; Fanelli, M. Effects of Fifty-Hertz Electromagnetic Fields on Granulocytic Differentiation of ATRA-Treated Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia NB4 Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akan, Z.; Aksu, B.; Tulunay, A.; Bilsel, S.; Inhan-Garip, A. Extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields affect the immune response of monocyte-derived macrophages to pathogens. Bioelectromagnetics 2010, 31, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patruno, A.; Pesce, M.; Marrone, A.; Speranza, L.; Grilli, A.; De Lutiis, M.A.; Felaco, M.; Reale, M. Activity of matrix metallo proteinases (MMPs) and the tissue inhibitor of MMP (TIMP)-1 in electromagnetic field-exposed THP-1 cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 2767–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patruno, A.; Costantini, E.; Ferrone, A.; Pesce, M.; Diomede, F.; Trubiani, O.; Reale, M. Short ELF-EMF Exposure Targets SIRT1/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling in THP-1 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Jang, Y.W.; Hyung, K.E.; Lee, D.K.; Hyun, K.H.; Jeong, S.H.; Min, K.H.; Kang, W.; Jeong, J.H.; Park, S.Y.; et al. Extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field exposure enhances inflammatory response and inhibits effect of antioxidant in RAW 264.7 cells. Bioelectromagnetics 2017, 38, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Nakamura, A.; Hondou, T.; Miyata, H. Evaluation of cell viability, DNA single-strand breaks, and nitric oxide production in LPS-stimulated macrophage RAW264 exposed to a 50-Hz magnetic field. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2016, 92, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frahm, J.; Mattsson, M.O.; Simkó, M. Exposure to ELF magnetic fields modulate redox related protein expression in mouse macrophages. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 192, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, C.N.; Kim, J.Y. Exposure to electromagnetic field attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced microglial cell death by reducing intracellular Ca(2+) and ROS. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2016, 92, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.L.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, C.H.; Gao, P.; Yu, Z.P.; Yang, X.S. The amelioration of phagocytic ability in microglial cells by curcumin through the inhibition of EMF-induced pro-inflammatory responses. J. Neuroinflammation 2014, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, G.L.; Luo, Z.; Shen, T.T.; Li, P.; Yang, J.; Luo, X.; Chen, C.H.; Gao, P.; Yang, X.S. Inhibition of STAT3- and MAPK-dependent PGE2 synthesis ameliorates phagocytosis of fibrillar beta-amyloid peptide (1-42) via EP2 receptor in EMF-stimulated N9 microglial cells. J. Neuroinflammation 2016, 13, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López-Furelos, A.; Salas-Sánchez, A.A.; Ares-Pena, F.J.; Leiro-Vidal, J.M.; López-Martín, E. Exposure to radiation from single or combined radio frequencies provokes macrophage dysfunction in the RAW 264.7 cell line. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2018, 94, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueiro-Benavides, R.A.; Leiro-Vidal, J.M.; Salas-Sánchez, A.A.; Rodríguez-González, J.A.; Ares-Pena, F.J.; López-Martín, M.E. Radiofrequency at 2.45 GHz increases toxicity, pro-inflammatory and pre-apoptotic activity caused by black carbon in the RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 142681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, E.; Mortazavi, S.M.; Ali-Ghanbari, A.; Sharifzadeh, S.; Ranjbaran, R.; Mostafavi-Pour, Z.; Zal, F.; Haghani, M. Effect of 900 MHz Electromagnetic Radiation on the Induction of ROS in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2015, 5, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Lasalvia, M.; Scrima, R.; Perna, G.; Piccoli, C.; Capitanio, N.; Biagi, P.F.; Schiavulli, L.; Ligonzo, T.; Centra, M.; Casamassima, G.; et al. Exposure to 1.8 GHz electromagnetic fields affects morphology, DNA-related Raman spectra and mitochondrial functions in human lympho-monocytes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.S.; Huang, B.T.; Huang, Y.X. Reactive oxygen species formation and apoptosis in human peripheral blood mononuclear cell induced by 900 MHz mobile phone radiation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longevity 2012, 2012, 740280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gläser, K.; Rohland, M.; Kleine-Ostmann, T.; Schrader, T.; Stopper, H.; Hintzsche, H. Effect of Radiofrequency Radiation on Human Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Radiat. Res. 2016, 186, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durdik, M.; Kosik, P.; Markova, E.; Somsedikova, A.; Gajdosechova, B.; Nikitina, E.; Horvathova, E.; Kozics, K.; Davis, D.; Belyaev, I. Microwaves from mobile phone induce reactive oxygen species but not DNA damage, preleukemic fusion genes and apoptosis in hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Zong, L.; Gao, Z.; Zhu, S.; Tong, J.; Cao, Y. Mitochondrial DNA damage and oxidative damage in HL-60 cells exposed to 900MHz radiofrequency fields. Mutat. Res. 2017, 797–799, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naziroğlu, M.; Çiğ, B.; Doğan, S.; Uğuz, A.C.; Dilek, S.; Faouzi, D. 2.45-Gz wireless devices induce oxidative stress and proliferation through cytosolic Ca(2)(+) influx in human leukemia cancer cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2012, 88, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanci, H.; Kerimoğlu, G.; Mercantepe, T.; Odaci, E. Changes in testicular morphology and oxidative stress biomarkers in 60-day-old Sprague Dawley rats following exposure to continuous 900-MHz electromagnetic field for 1 h a day throughout adolescence. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 81, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.; Singh, K.V.; Nirala, J.; Murmu, N.N.; Meena, R.; Rajamani, P. Oxidative stress-mediated alterations on sperm parameters in male Wistar rats exposed to 3G mobile phone radiation. Andrologia 2019, 51, e13201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Si, T.; Xu, X.; Liang, F.; Wang, L.; Pan, S. Electromagnetic radiation at 900 MHz induces sperm apoptosis through bcl-2, bax and caspase-3 signaling pathways in rats. Reprod. Health 2015, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, N.; Giri, S. Melatonin attenuates radiofrequency radiation (900 MHz)-induced oxidative stress, DNA damage and cell cycle arrest in germ cells of male Swiss albino mice. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2018, 34, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksay, T.; Naziroğlu, M.; Doğan, S.; Güzel, A.; Gümral, N.; Koşar, P.A. Protective effects of melatonin against oxidative injury in rat testis induced by wireless (2.45 GHz) devices. Andrologia 2014, 46, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmekaya, M.A.; Ozer, C.; Seyhan, N. 900 MHz pulse-modulated radiofrequency radiation induces oxidative stress on heart, lung, testis and liver tissues. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2011, 30, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, N.; Giri, S.; Das, S.; Upadhaya, P. Radiofrequency radiation (900 MHz)-induced DNA damage and cell cycle arrest in testicular germ cells in swiss albino mice. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2017, 33, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, N.N.; El-Nabarawy, N.A.; Gouda, A.S.; Megarbane, B. The protective role of spermine against male reproductive aberrations induced by exposure to electromagnetic field—An experimental investigation in the rat. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 370, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, S.; Singh, S.P.; Chaturvedi, C.M. 1800 MHz mobile phone irradiation induced oxidative and nitrosative stress leads to p53 dependent Bax mediated testicular apoptosis in mice, Mus musculus. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 7253–7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesari, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Behari, J. Effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic wave exposure from cellular phones on the reproductive pattern in male Wistar rats. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 164, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolovic, D.; Djordjevic, B.; Kocic, G.; Stoimenov, T.J.; Stanojkovic, Z.; Sokolovic, D.M.; Veljkovic, A.; Ristic, G.; Despotovic, M.; Milisavljevic, D.; et al. The Effects of Melatonin on Oxidative Stress Parameters and DNA Fragmentation in Testicular Tissue of Rats Exposed to Microwave Radiation. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 24, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oyewopo, A.O.; Olaniyi, S.K.; Oyewopo, C.I.; Jimoh, A.T. Radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation from cell phone causes defective testicular function in male Wistar rats. Andrologia 2017, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Damegh, M.A. Rat testicular impairment induced by electromagnetic radiation from a conventional cellular telephone and the protective effects of the antioxidants vitamins C and E. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 2012, 67, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzay, D.; Ozer, C.; Sirav, B.; Canseven, A.G.; Seyhan, N. Oxidative effects of extremely low frequency magnetic field and radio frequency radiation on testes tissues of diabetic and healthy rats. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2017, 118, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guney, M.; Ozguner, F.; Oral, B.; Karahan, N.; Mungan, T. 900 MHz radiofrequency-induced histopathologic changes and oxidative stress in rat endometrium: Protection by vitamins E and C. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2007, 23, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özorak, A.; Nazıroğlu, M.; Çelik, Ö.; Yüksel, M.; Özçelik, D.; Özkaya, M.O.; Çetin, H.; Kahya, M.C.; Kose, S.A. Wi-Fi (2.45 GHz)- and mobile phone (900 and 1800 MHz)-induced risks on oxidative stress and elements in kidney and testis of rats during pregnancy and the development of offspring. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 156, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangun, O.; Dundar, B.; Darici, H.; Comlekci, S.; Doguc, D.K.; Celik, S. The effects of long-term exposure to a 2450 MHz electromagnetic field on growth and pubertal development in female Wistar rats. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2015, 34, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solek, P.; Majchrowicz, L.; Koziorowski, M. Aloe arborescens juice prevents EMF-induced oxidative stress and thus protects from pathophysiology in the male reproductive system in vitro. Environ. Res. 2018, 166, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solek, P.; Majchrowicz, L.; Bloniarz, D.; Krotoszynska, E.; Koziorowski, M. Pulsed or continuous electromagnetic field induce p53/p21-mediated apoptotic signaling pathway in mouse spermatogenic cells in vitro and thus may affect male fertility. Toxicology 2017, 382, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; He, M.; Xu, S.; Chen, C.; Pi, H.; Gao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, M.; et al. Comparison of the genotoxic effects induced by 50 Hz extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields and 1800 MHz radiofrequency electromagnetic fields in GC-2 cells. Radiat. Res. 2015, 183, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasan, S.S.; Veerachari, S.B. Mobile Phone Electromagnetic Waves and Its Effect on Human Ejaculated Semen: An in vitro Study. Int. J. Infertil. Fetal Med. 2012, 3, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani-Enomoto, S.; Okutsu, M.; Suzuki, S.; Suganuma, R.; Groiss, S.J.; Kadowaki, S.; Enomoto, H.; Fujimori, K.; Ugawa, Y. Effects of 1950 MHz W-CDMA-like signal on human spermatozoa. Bioelectromagnetics 2016, 37, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzone, N.; Huyser, C.; Franken, D.R.; Leszczynski, D. Mobile phone radiation does not induce pro-apoptosis effects in human spermatozoa. Radiat. Res. 2010, 174, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.S.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Tian, H.; Huo, Y.W.; Wang, L.R.; Han, Y.; Xing, J.P. Moderate Dose of Trolox Preventing the Deleterious Effects of Wi-Fi Radiation on Spermatozoa In vitro through Reduction of Oxidative Stress Damage. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2018, 131, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ma, M.; Li, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, T.; Gao, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, Q.; Luo, X.; et al. The Protective Effect of Autophagy on DNA Damage in Mouse Spermatocyte-Derived Cells Exposed to 1800 MHz Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Dong, J.; Dong, X.; Liu, J.; Cao, J.; Ao, L.; Zhang, S. The protective effect of autophagy on mouse spermatocyte derived cells exposure to 1800MHz radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 228, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Duan, W.; Xu, S.; Chen, C.; He, M.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, Z. Exposure to 1800 MHz radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation induces oxidative DNA base damage in a mouse spermatocyte-derived cell line. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 218, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, B.J.; Nixon, B.; King, B.V.; Aitken, R.J.; De Iuliis, G.N. Probing the Origins of 1,800 MHz Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Radiation Induced Damage in Mouse Immortalized Germ Cells and Spermatozoa in vitro. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, F.; Shen, T.; Cao, H.; Qian, J.; Zou, D.; Ye, M.; Pei, H. CeO2NPs relieve radiofrequency radiation, improve testosterone synthesis, and clock gene expression in Leydig cells by enhancing antioxidation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4601–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Wu, T.; Liu, J.Y.; Gao, P.; Li, K.C.; Guo, Q.Y.; Yuan, M.; Lang, H.Y.; Zeng, L.H.; Guo, G.Z. 1950MHz Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Radiation Inhibits Testosterone Secretion of Mouse Leydig Cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koohestani, N.V.; Zavareh, S.; Lashkarbolouki, T.; Azimipour, F. Exposure to cell phone induce oxidative stress in mice preantral follicles during in vitro cultivation: An experimental study. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. (Yazd) 2019, 17, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okatan, D.O.; Kulaber, A.; Kerimoğlu, G.; Odaci, E. Altered morphology and biochemistry of the female rat liver following 900 megahertz electromagnetic field exposure during mid to late adolescence. Biotech. Histochem. 2019, 94, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumkaya, L.; Yilmaz, A.; Akyildiz, K.; Mercantepe, T.; Yazici, Z.A.; Yilmaz, H. Prenatal Effects of a 1,800-MHz Electromagnetic Field on Rat Livers. Cells Tissues Organs 2019, 207, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado-Filho, O.V.; Borba, J.B.; Dallegrave, A.; Pizzolato, T.M.; Henriques, J.A.; Moreira, J.C.; Saffi, J. Effect of 950 MHz UHF electromagnetic radiation on biomarkers of oxidative damage, metabolism of UFA and antioxidants in the livers of young rats of different ages. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2014, 90, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaiil, L.A.; Joumaa, W.H.; Moustafa, M.E. The impact of exposure of diabetic rats to 900 MHz electromagnetic radiation emitted from mobile phone antenna on hepatic oxidative stress. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2019, 38, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuybulu, A.E.; Öktem, F.; Çiriş, I.M.; Sutcu, R.; Örmeci, A.R.; Çömlekçi, S.; Uz, E. Effects of long-term pre- and post-natal exposure to 2.45 GHz wireless devices on developing male rat kidney. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bodera, P.; Stankiewicz, W.; Antkowiak, B.; Paluch, M.; Kieliszek, J.; Sobiech, J.; Niemcewicz, M. Influence of electromagnetic field (1800 MHz) on lipid peroxidation in brain, blood, liver and kidney in rats. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2015, 28, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odaci, E.; Ünal, D.; Mercantepe, T.; Topal, Z.; Hanci, H.; Türedi, S.; Erol, H.S.; Mungan, S.; Kaya, H.; Çolakoğlu, S. Pathological effects of prenatal exposure to a 900 MHz electromagnetic field on the 21-day-old male rat kidney. Biotech. Histochem. 2015, 90, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türedi, S.; Kerimoğlu, G.; Mercantepe, T.; Odaci, E. Biochemical and pathological changes in the male rat kidney and bladder following exposure to continuous 900-MHz electromagnetic field on postnatal days 22-59. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2017, 93, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okatan, D.O.; Okatan, A.E.; Hanci, H.; Demir, S.; Yaman, S.O.; Colakoğlu, S.; Odaci, E. Effects of 900-MHz electromagnetic fields exposure throughout middle/late adolescence on the kidney morphology and biochemistry of the female rat. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2018, 34, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedir, R.; Tumkaya, L.; Mercantepe, T.; Yilmaz, A. Pathological Findings Observed in the Kidneys of Postnatal Male Rats Exposed to the 2100 MHz Electromagnetic Field. Arch. Med. Res. 2018, 49, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Cui, Y.; Feng, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Lv, S. The apoptotic effect and the plausible mechanism of microwave radiation on rat myocardial cells. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 94, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gumral, N.; Saygin, M.; Asci, H.; Uguz, A.C.; Celik, O.; Doguc, D.K.; Savas, H.B.; Comlekci, S. The effects of electromagnetic radiation (2450 MHz wireless devices) on the heart and blood tissue: Role of melatonin. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2016, 117, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Türedi, S.; Hanci, H.; Topal, Z.; Ünal, D.; Mercantepe, T.; Bozkurt, I.; Kaya, H.; Odaci, E. The effects of prenatal exposure to a 900-MHz electromagnetic field on the 21-day-old male rat heart. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2015, 34, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerimoğlu, G.; Mercantepe, T.; Erol, H.S.; Turgut, A.; Kaya, H.; Çolakoğlu, S.; Odaci, E. Effects of long-term exposure to 900 megahertz electromagnetic field on heart morphology and biochemistry of male adolescent rats. Biotech. Histochem. 2016, 91, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aynali, G.; Nazıroğlu, M.; Çelik, Ö.; Doğan, M.; Yarıktaş, M.; Yasan, H. Modulation of wireless (2.45 GHz)-induced oxidative toxicity in laryngotracheal mucosa of rat by melatonin. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol 2013, 270, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tök, L.; Naziroğlu, M.; Doğan, S.; Kahya, M.C.; Tök, O. Effects of melatonin on Wi-Fi-induced oxidative stress in lens of rats. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 62, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdal, N.; Gürgül, S.; Tamer, L.; Ayaz, L. Effects of long-term exposure of extremely low frequency magnetic field on oxidative/nitrosative stress in rat liver. J. Radiat. Res. 2008, 49, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Sámano, J.; Torres-Durán, P.V.; Juárez-Oropeza, M.A.; Elías-Viñas, D.; Verdugo-Díaz, L. Effects of acute electromagnetic field exposure and movement restraint on antioxidant system in liver, heart, kidney and plasma of Wistar rats: A preliminary report. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2010, 86, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcabrini, C.; Mancini, U.; De Bellis, R.; Diaz, A.R.; Martinelli, M.; Cucchiarini, L.; Sestili, P.; Stocchi, V.; Potenza, L. Effect of extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields on antioxidant activity in the human keratinocyte cell line NCTC 2544. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2017, 64, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Hong, L.; Zeng, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zeng, Q. Power frequency magnetic fields induced reactive oxygen species-related autophagy in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 57, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Im, S.H.; Yoon, Y.J.; Kim, H.M.; Lee, H.J.; Park, G.S. A 60 Hz uniform electromagnetic field promotes human cell proliferation by decreasing intracellular reactive oxygen species levels. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekovic, M.H.; Drekovic, N.E.; Granica, N.D.; Mahmutovic, E.H.; Djordjevic, N.Z. Extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field induces a change in proliferative capacity and redox homeostasis of human lung fibroblast cell line MRC-5. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 39466–39473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, E.; Sinjari, B.; D’Angelo, C.; Murmura, G.; Reale, M.; Caputi, S. Human Gingival Fibroblasts Exposed to Extremely Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Fields: In Vitro Model of Wound-Healing Improvement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patruno, A.; Amerio, P.; Pesce, M.; Vianale, G.; Di Luzio, S.; Tulli, A.; Franceschelli, S.; Grilli, A.; Muraro, R.; Reale, M. Extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields modulate expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase, endothelial nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in the human keratinocyte cell line HaCat: Potential therapeutic effects in wound healing. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 162, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.N.; Han, N.K.; Lee, H.C.; Ko, Y.K.; Chi, S.G.; Lee, Y.S.; Gimm, Y.M.; Myung, S.H.; Lee, J.S. Extremely low frequency magnetic fields do not elicit oxidative stress in MCF10A cells. J. Radiat. Res. 2012, 53, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, L.; Shao, G.; Yang, S.; Tao, S.; Fang, K.; Zhang, X. 6-mT 0-120-Hz magnetic fields differentially affect cellular ATP levels. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 28237–28247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Dai, A.; Chen, L.; Qiu, L.; Fu, Y.; Sun, W. NADPH oxidase-produced superoxide mediated a 50-Hz magnetic field-induced epidermal growth factor receptor clustering. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2016, 92, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Qiu, L.; Ye, C.; Chen, L.; Fu, Y.; Sun, W. Exposure to a 50-Hz magnetic field induced mitochondrial permeability transition through the ROS/GSK-3beta signaling pathway. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2016, 92, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Ye, C.; Qiu, L.; Chen, L.; Fu, Y.; Sun, W. Mitochondrial ROS Release and Subsequent Akt Activation Potentially Mediated the Anti-Apoptotic Effect of a 50-Hz Magnetic Field on FL Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 2489–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Chen, L.; Bai, L.; Xia, Y.; Yang, X.; Jiang, W.; Sun, W. Reactive oxygen species mediates 50-Hz magnetic field-induced EGF receptor clustering via acid sphingomyelinase activation. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2018, 94, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Kraus, S.; Hauptman, Y.; Schiff, Y.; Seger, R. Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies. Biochem. J. 2007, 405, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Wang, M.; Wu, S.; Ma, X.; An, G.; Liu, H.; Xie, F. Oxidative changes and apoptosis induced by 1800-MHz electromagnetic radiation in NIH/3T3 cells. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2015, 34, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.N.; Kim, B.C.; Ko, Y.G.; Lee, Y.S.; Hong, S.C.; Kim, T.; Pack, J.K.; Choi, H.D.; Kim, N.; Lee, J.S. Effects of 837 and 1950 MHz radiofrequency radiation exposure alone or combined on oxidative stress in MCF10A cells. Bioelectromagnetics 2012, 33, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jooyan, N.; Goliaei, B.; Bigdeli, B.; Faraji-Dana, R.; Zamani, A.; Entezami, M.; Mortazavi, S.M.J. Direct and indirect effects of exposure to 900MHz GSM radiofrequency electromagnetic fields on CHO cell line: Evidence of bystander effect by non-ionizing radiation. Environ. Res. 2019, 174, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanovic Cermak, A.M.; Pavicic, I.; Tariba Lovakovic, B.; Pizent, A.; Trosic, I. In vitro non-thermal oxidative stress response after 1800 MHz radiofrequency radiation. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2017, 36, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanovic, A.M.; Pavicic, I.; Trosic, I. Cell oxidation-reduction imbalance after modulated radiofrequency radiation. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2015, 34, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuermann, D.; Ziemann, C.; Barekati, Z.; Capstick, M.; Oertel, A.; Focke, F.; Murbach, M.; Kuster, N.; Dasenbrock, C.; Schar, P. Assessment of Genotoxicity in Human Cells Exposed to Modulated Electromagnetic Fields of Wireless Communication Devices. Genes 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Lai, K.; Yao, K. Study of oxidative stress in human lens epithelial cells exposed to 1.8 GHz radiofrequency fields. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, B.; Zhang, J.; He, W.; Hu, D.; Yang, Y.; Lai, J.; He, M.; et al. Exposure to a 50 Hz magnetic field at 100 microT exerts no DNA damage in cardiomyocytes. Biol. Open 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buldak, R.J.; Polaniak, R.; Buldak, L.; Zwirska-Korczala, K.; Skonieczna, M.; Monsiol, A.; Kukla, M.; Dulawa-Buldak, A.; Birkner, E. Short-term exposure to 50 Hz ELF-EMF alters the cisplatin-induced oxidative response in AT478 murine squamous cell carcinoma cells. Bioelectromagnetics 2012, 33, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Wang, Q.; Lin, T. Low-Frequency Magnetic Fields (LF-MFs) Inhibit Proliferation by Triggering Apoptosis and Altering Cell Cycle Distribution in Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahya, M.C.; Naziroğlu, M.; Çiğ, B. Selenium reduces mobile phone (900 MHz)-induced oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, and apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 160, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefidbakht, Y.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A.; Hosseinkhani, S.; Khodagholi, F.; Torkzadeh-Mahani, M.; Foolad, F.; Faraji-Dana, R. Effects of 940 MHz EMF on bioluminescence and oxidative response of stable luciferase producing HEK cells. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2014, 13, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsobaci, N.P.; Ergün, D.D.; Tunçdemir, M.; Özçelik, D. Protective Effects of Zinc on 2.45 GHz Electromagnetic Radiation-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in HEK293 Cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 194, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastaci Özsobaci, N.; Düzgün Ergün, D.; Durmus, S.; Tunçdemir, M.; Uzun, H.; Gelisgen, R.; Özçelik, D. Selenium supplementation ameliorates electromagnetic field-induced oxidative stress in the HEK293 cells. J. Trace Elem. Exp. Med. 2018, 50, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, G.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y. Protective Role of Vitamin C in Wi-Fi Induced Oxidative Stress in MC3T3-E1 Cells in Vitro. Appl. Comput. Electromagn. Soc. J. 2020, 35, 587–594. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Min, K.; Jeon, S.; Kim, N.; Pack, J.K.; Song, K. Continuous Exposure to 1.7 GHz LTE Electromagnetic Fields Increases Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species to Decrease Human Cell Proliferation and Induce Senescence. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Hilly, O.; Strenov, Y.; Tzabari, C.; Hauptman, Y.; Feinmesser, R. Effect of cell phone-like electromagnetic radiation on primary human thyroid cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2016, 92, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schuermann, D.; Mevissen, M. Manmade Electromagnetic Fields and Oxidative Stress—Biological Effects and Consequences for Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073772
Schuermann D, Mevissen M. Manmade Electromagnetic Fields and Oxidative Stress—Biological Effects and Consequences for Health. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(7):3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073772
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchuermann, David, and Meike Mevissen. 2021. "Manmade Electromagnetic Fields and Oxidative Stress—Biological Effects and Consequences for Health" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 7: 3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073772
APA StyleSchuermann, D., & Mevissen, M. (2021). Manmade Electromagnetic Fields and Oxidative Stress—Biological Effects and Consequences for Health. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(7), 3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073772