Hypophosphatasia: A Unique Disorder of Bone Mineralization
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Background
2. Prevalence of HPP
3. The Enzyme
4. Genetics of HPP
5. TNSALP Structure
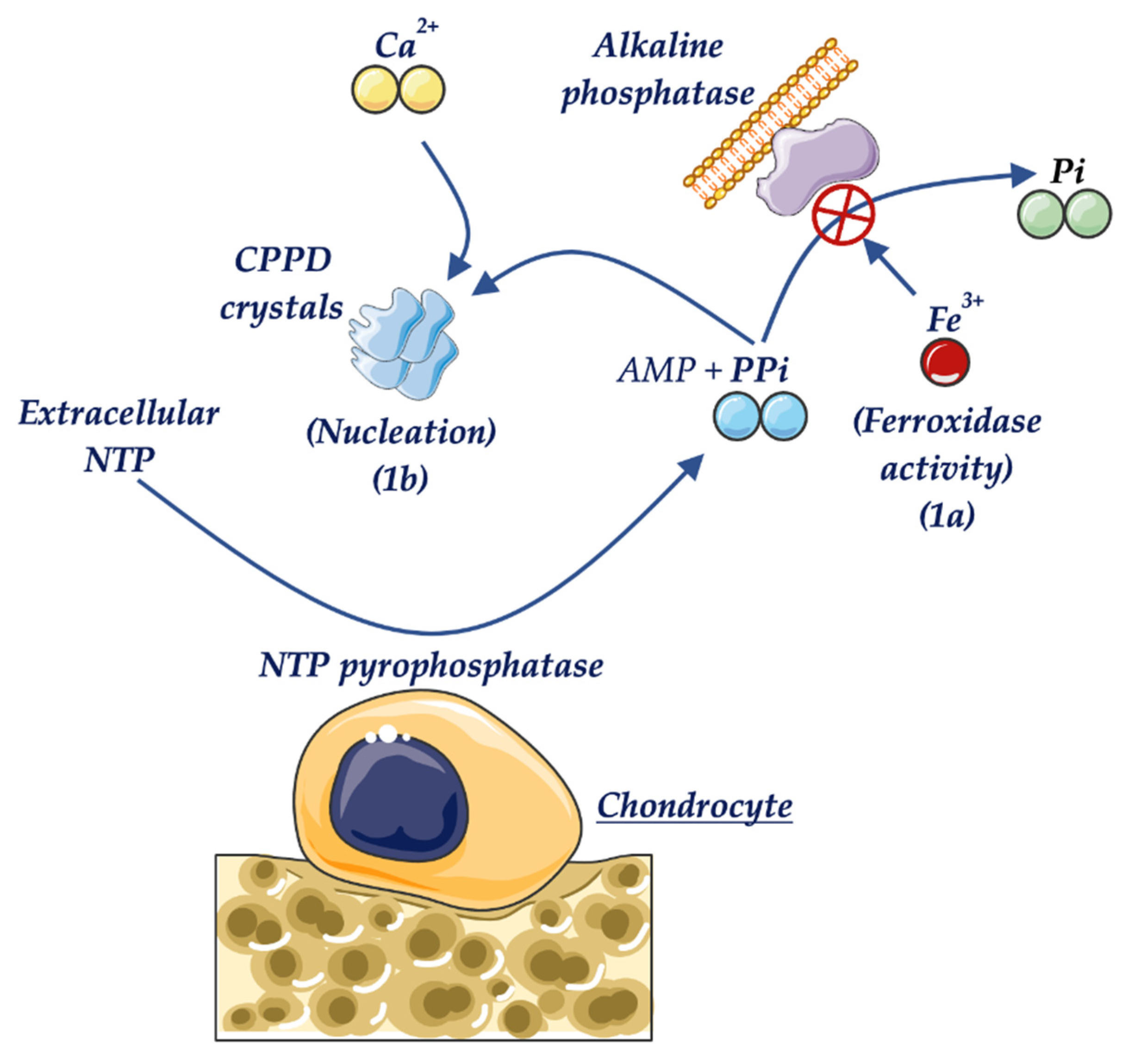
6. Clinical Manifestations
7. Subtypes of HPP
7.1. Perinatal Lethal Hypophosphatasia
7.2. ”Benign Prenatal” Hypophosphatasia
7.3. Infantile Hypophosphatasia
7.4. Childhood-Onset Hypophosphatasia
7.5. Adult Hypophosphatasia
7.6. Odontohypophosphatasia
8. Diagnosis of HPP
9. Genotype–Phenotype Correlations
10. Treatment of HPP
11. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mornet, E. Hypophosphatasia. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2007, 2, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whyte, M.P. Hypophosphatasia—Aetiology, nosology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linglart, A.; Biosse-Duplan, M. Hypophosphatasia. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2016, 14, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, M.L. Hypophosphatasia: An overview of the disease and its treatment. Osteoporos. Int. 2015, 26, 2743–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinan-Vega, M.N.; Abate, E.G. Hypophosphatasia: Clinical Assessment and Management in the Adult Patient–A Narrative Review. Endocr. Practice 2018, 24, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araci, M.B.; Akgun, B.; Atik, T.; Isik, E.; Ak, G.; Barutcuoglu, B.; Ozkinay, F. Clinical and molecular findings in children and young adults with persistent low alkaline phosphatase concentrations. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2021, 45632211000102. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33601892/ (accessed on 18 March 2021). [CrossRef]
- García-Fontana, C.; Villa-Suárez, J.M.; Andújar-Vera, F.; González-Salvatierra, S.; Martínez-Navajas, G.; Real, P.J.; Vida, J.M.G.; De Haro, T.; García-Fontana, B.; Muñoz-Torres, M. Epidemiological, Clinical and Genetic Study of Hypophosphatasia in A Spanish Population: Identification of Two Novel Mutations in The Alpl Gene. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fraser, D. Hypophosphatasia. Am. J. Med. 1957, 22, 730–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mornet, E.; Yvard, A.; Taillandier, A.; Fauvert, D.; Simon-Bouy, B. A Molecular-Based Estimation of the Prevalence of Hypophosphatasia in the European Population. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2011, 75, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodirker, B.N.; Evans, J.A.; Seargeant, L.E.; Cheang, M.S.; Greenberg, C.R. Hyperphosphatemia in infantile hypophosphatasia: Implications for carrier diagnosis and screening. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1990, 46, 280–285. [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson, R.I.; Kroeker, M.; Houston, C.S. Hypophosphatasia. J. Can. Assoc. Radiol. 1972, 23, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mornet, E. Hypophosphatasia. Metab. 2018, 82, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mornet, E.; Taillandier, A.; Domingues, C.; Dufour, A.; Benaloun, E.; Lavaud, N.; Wallon, F.; Rousseau, N.; Charle, C.; Guberto, M.; et al. Hypophosphatasia: A genetic-based nosology and new insights in genotype-phenotype correlation. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 29, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mornet, E.; Stura, E.; Lia-Baldini, A.-S.; Stigbrand, T.; Ménez, A.; Le Du, M.-H. Structural Evidence for a Functional Role of Human Tissue Nonspecific Alkaline Phosphatase in Bone Mineralization. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 31171–31178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwartz, J.H.; Lipmann, F. Phosphate incorporation into alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1961, 47, 1996–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, U.; Pal, D.; Prasad, R. Alkaline Phosphatase: An Overview. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 29, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millán, J.L.; Fishman, W.H.; Stinson, R. Biology of Human Alkaline Phosphatases with Special Reference to Cancer. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1995, 32, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millán, J. Alkaline phosphatase as a reporter of cancerous transformation. Clin. Chim. Acta 1992, 209, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, J.L. Oncodevelopmental expression and structure of alkaline phosphatase genes. Anticancer Res. 1988, 8, 995–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg, C.R.; Evans, J.A.; McKendry-Smith, S.; Redekopp, S.; Haworth, J.C.; Mulivor, R.; Chodirker, B.N. Infantile hypophosphatasia: Localization within chromosome region 1p36.1-34 and prenatal diagnosis using linked DNA markers. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1990, 46, 286–292. [Google Scholar]
- Millan, J.L. Mammalian Alkaline Phosphatases: From Biology to Applications in Medicine and Biotechnology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; p. 337. [Google Scholar]
- Millán, J.L.; Plotkin, H. Hypophosphatasia—pathophysiology and treatment. Actual. Osteol. 2012, 8, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Millán, J.L.; Whyte, M.P. Alkaline Phosphatase and Hypophosphatasia. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2016, 98, 398–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narisawa, S.; Yadav, M.C.; Millán, J.L. In Vivo Overexpression of Tissue-Nonspecific Alkaline Phosphatase Increases Skeletal Mineralization and Affects the Phosphorylation Status of Osteopontin. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 1587–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pettengill, M.; Matute, J.D.; Tresenriter, M.; Hibbert, J.; Burgner, D.; Richmond, P.; Millán, J.L.; Ozonoff, A.; Strunk, T.; Currie, A.; et al. Human alkaline phosphatase dephosphorylates microbial products and is elevated in preterm neonates with a history of late-onset sepsis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, M.P.; Zhang, F.; Wenkert, D.; McAlister, W.H.; Mack, K.E.; Benigno, M.C.; Coburn, S.P.; Wagy, S.; Griffin, D.M.; Ericson, K.L.; et al. Hypophosphatasia: Validation and expansion of the clinical nosology for children from 25years experience with 173 pediatric patients. Bone 2015, 75, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauvert, D.; Brun-Heath, I.; Lia-Baldini, A.-S.; Bellazi, L.; Taillandier, A.; Serre, J.-L.; De Mazancourt, P.; Mornet, E. Mild forms of hypophosphatasia mostly result from dominant negative effect of severe alleles or from compound heterozygosity for severe and moderate alleles. BMC Med. Genet. 2009, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Du, M.H.; Stigbrand, T.; Taussig, M.J.; Ménez, A.; Stura, E.A. Crystal Structure of Alkaline Phosphatase from Human Placenta at 1.8 Å Resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 9158–9165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoylaerts, M.F.; Manes, T.; Millan, J.L. Molecular mechanism of uncompetitive inhibition of human placental and germ-cell alkaline phosphatase. Biochem. J. 1992, 286, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hummer, C.; Millan, J.L. Gly429 is the major determinant of uncompetitive inhibition of human germ cell alkaline phosphatase by l-leucine. Biochem. J. 1991, 274, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vittur, F.; Stagni, N.; Moro, L.; De Bernard, B. Alkaline phosphatase binds to collagen; a hypothesis on the mechanism of extravesicular mineralization in epiphyseal cartilage. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1984, 40, 836–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.N.; Genge, B.R.; Lloyd, G.C.; Wuthier, R.E. Collagen-binding proteins in collagenase-released matrix vesi-cles from cartilage. interaction between matrix vesicle proteins and different types of collagen. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, C.H.; Enander, K.; Magnusson, P. Glycation Contributes to Interaction Between Human Bone Alkaline Phosphatase and Collagen Type I. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 98, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoylaerts, M.F.; Van Kerckhoven, S.; Kiffer-Moreira, T.; Sheen, C.; Narisawa, S.; Millán, J.L. Functional Significance of Calcium Binding to Tissue-Nonspecific Alkaline Phosphatase. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoylaerts, M.F.; Ding, L.; Narisawa, S.; Van Kerckhoven, S.; Millan, J.L. Mammalian Alkaline Phosphatase Catalysis Requires Active Site Structure Stabilization via the N-Terminal Amino Acid Microenvironment†. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 9756–9766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mornet, E. Molecular Genetics of Hypophosphatasia and Phenotype-Genotype Correlations. Prokaryotic Cytoskelet. 2015, 76, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurutuza, L.; Muller, F.; Gibrat, J.; Taillandier, A.; Simon-Bouy, B.; Serre, J.L.; Mornet, E. Correlations of genotype and phenotype in hypophosphatasia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999, 8, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orimo, H. Pathophysiology of hypophosphatasia and the potential role of asfotase alfa. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2016, 12, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whyte, M.P. Hypophosphatasia and the Role of Alkaline Phosphatase in Skeletal Mineralization*. Endocr. Rev. 1994, 15, 439–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkseth, K.E.; Tebben, P.J.; Drake, M.T.; Hefferan, T.E.; Jewison, D.E.; Wermers, R.A. Clinical spectrum of hypophosphatasia diagnosed in adults. Bone 2013, 54, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKiernan, F.E.; Berg, R.L.; Fuehrer, J. Clinical and radiographic findings in adults with persistent hypophosphatasemia. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Delgado, L.; Riancho-Zarrabeitia, L.; García-Unzueta, M.T.; Tenorio, J.A.; García-Hoyos, M.; Lapunzina, P.; Valero, C.; Riancho, J.A. Abnormal bone turnover in individuals with low serum alkaline phosphatase. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 2147–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Genest, F.; Claußen, L.; Rak, D.; Seefried, L. Bone mineral density and fracture risk in adult patients with hypophosphatasia. Osteoporos. Int. 2021, 32, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.; Mussawy, H.; Rolvien, T.; Hawellek, T.; Hubert, J.; Rüther, W.; Amling, M.; Barvencik, F. Clinical, radiographic and biochemical characteristics of adult hypophosphatasia. Osteoporos. Int. 2017, 28, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castells, L.; Cassanello, P.; Muñiz, F.; de Castro, M.-J.; Couce, M.L. Neonatal lethal hypophosphatasia. Medicine 2018, 97, e13269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millán, J.L. Mammalian Alkaline Phosphatases: From Biology to Applications in Medicine and Biotechnology; WILEY-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; ISBN 3527310797. [Google Scholar]
- Colazo, J.; Hu, J.; Dahir, K.; Simmons, J. Neurological symptoms in Hypophosphatasia. Osteoporos. Int. 2019, 30, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collmann, H.; Mornet, E.; Gattenlöhner, S.; Beck, C.; Girschick, H. Neurosurgical aspects of childhood hypophosphatasia. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2008, 25, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketani, T. Neurological Symptoms of Hypophosphatasia. In Subcellular Biochemistry; J.B. Metzler: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 76, pp. 309–322. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, M.L.; On behalf of the Rare Bone Disease Action Group of the European Calcified Tissue Society; Bishop, N.J.; Guañabens, N.; Hofmann, C.; Jakob, F.; Roux, C.; Zillikens, M.C. Hypophosphatasia in adolescents and adults: Overview of diagnosis and treatment. Osteoporos. Int. 2020, 31, 1445–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Nam, H.; Crouch, S.; Hatch, N. Tissue Nonspecific Alkaline Phosphatase Function in Bone and Muscle Progenitor Cells: Control of Mitochondrial Respiration and ATP Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenkert, D.; McAlister, W.H.; Coburn, S.P.; Zerega, J.A.; Ryan, L.M.; Ericson, K.L.; Hersh, J.H.; Mumm, S.; Whyte, M.P. Hypophosphatasia: Nonlethal disease despite skeletal presentation in utero (17 new cases and literature review). J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 2389–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinico, M.; Levaillant, J.M.; Vergnaud, A.; Blondeau, J.R.; Encha-Razavi, F.; Mornet, E.; Le Merrer, M.; Gerard-Blanluet, M. Specific osseous spurs in a lethal form of hypophosphatasia correlated with 3D prenatal ultrasonographic images. Prenat. Diagn. 2007, 27, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaruratanasirikul, S.; Chanvitan, P. Hypophosphatasia: The Importance of Alkaline Phosphatase in Bone Miner-alization. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 1999, 82, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Martos-Moreno, G.A.; Calzada, J.; Couce, M.L.; Argente, J. Hypophosphatasia: Clinical manifestations, diagnostic recommendations and therapeutic options. Anales de Pediatría 2018, 88, 356.e1–356.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Wang, J.; Xu, X. Lethal perinatal hypophosphatasia caused by a novel compound heterozygous mutation: A case report. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, M.P.; Leung, E.; Wilcox, W.R.; Liese, J.; Argente, J.; Martos-Moreno, G.Á.; Reeves, A.; Fujita, K.P.; Moseley, S.; Hofmann, C.; et al. Natural History of Perinatal and Infantile Hypophosphatasia: A Retrospective Study. J. Pediatr. 2019, 209, 116–124.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokoi, K.; Nakajima, Y.; Shinkai, Y.; Sano, Y.; Imamura, M.; Akiyama, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Ito, T.; Kurahashi, H. Clinical and genetic aspects of mild hypophosphatasia in Japanese patients. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2019, 21, 100515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, M.; Kitoh, H.; Michigami, T.; Tachikawa, K.; Ishiguro, N. Benign prenatal hypophosphatasia: A treatable disease not to be missed. Pediatr. Radiol. 2013, 44, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, R.M.; Modaff, P.; Sipes, S.L.; Whyte, M.P. Mild hypophosphatasia mimicking severe osteogenesis imper-fecta in utero: Bent but not broken. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1999, 86, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genetics of Bone Biology and Skeletal Disease–1st Edition. Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/books/genetics-of-bone-biology-and-skeletal-disease/thakker/978-0-12-387829-8 (accessed on 9 March 2021).
- Bloch-Zupan, A. Hypophosphatasia: Diagnosis and clinical signs—A dental surgeon perspective. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2016, 26, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whyte, M.P.; Greenberg, C.R.; Salman, N.J.; Bober, M.B.; McAlister, W.H.; Wenkert, D.; Van Sickle, B.J.; Simmons, J.H.; Edgar, T.S.; Bauer, M.L.; et al. Enzyme-Replacement Therapy in Life-Threatening Hypophosphatasia. New Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baumgartner-Sigl, S.; Haberlandt, E.; Mumm, S.; Scholl-Bürgi, S.; Sergi, C.; Ryan, L.; Ericson, K.L.; Whyte, M.P.; Högler, W. Pyridoxine-responsive seizures as the first symptom of infantile hypophosphatasia caused by two novel missense mutations (c.677T>C, p.M226T; c.1112C>T, p.T371I) of the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase gene. Bone 2007, 40, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reibel, A.; Manière, M.-C.; Clauss, F.; Droz, D.; Alembik, Y.; Mornet, E.; Bloch-Zupan, A. Orodental phenotype and genotype findings in all subtypes of hypophosphatasia. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2009, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bos, T.V.D.; Handoko, G.; Niehof, A.; Ryan, L.; Coburn, S.; Whyte, M.; Beertsen, W. Cementum and Dentin in Hypophosphatasia. J. Dent. Res. 2005, 84, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, M.P.; Wenkert, D.; Zhang, F. Hypophosphatasia: Natural history study of 101 affected children investigated at one research center. Bone 2016, 93, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girschick, H.J.; Mornet, E.; Beer, M.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Schneider, P. Chronic multifocal non-bacterial osteomyelitis in hypophosphatasia mimicking malignancy. BMC Pediatr. 2007, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, M.P.; Wenkert, D.; McAlister, W.H.; Mughal, M.Z.; Freemont, A.J.; Whitehouse, R.; Baildam, E.M.; Coburn, S.P.; Ryan, L.M.; Mumm, S. Chronic Recurrent Multifocal Osteomyelitis Mimicked in Childhood Hypophosphatasia*. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2009, 24, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graser, S.; Liedtke, D.; Jakob, F. TNAP as a New Player in Chronic Inflammatory Conditions and Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessueille, L.; Briolay, A.; Como, J.; Mebarek, S.; Mansouri, C.; Gleizes, M.; El Jamal, A.; Buchet, R.; Dumontet, C.; Matera, E.; et al. Tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase is an anti-inflammatory nucleotidase. Bone 2020, 133, 115262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girschick, H.J.; Schneider, P.; Haubitz, I.; Hiort, O.; Collmann, H.; Beer, M.; Shin, Y.S.; Seyberth, H.W. Effective NSAID treatment indicates that hyperprostaglandinism is affecting the clinical severity of childhood hypophosphatasia. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2006, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whyte, M.P.; Teitelbaum, S.L.; Murphy, W.A.; Bergfeld, M.A.; Avioli, L.V. Adult hypophosphatasia. Clinical, laboratory, and genetic investigation of a large kindred with review of the literature. Med. Baltim. 1979, 58, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.A.L.; Mumm, S.; Coburn, S.P.; Ericson, K.L.; Whyte, M.P. “Atypical femoral fractures” during bisphosphonate exposure in adult hypophosphatasia. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2012, 27, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, M.P.; Murphy, W.A.; Fallon, M.D. Adult hypophosphatasia with chondrocalcinosis and arthropathy. Am. J. Med. 1982, 72, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guañabens, N.; Mumm, S.; Möller, I.; González-Roca, E.; Peris, P.; Demertzis, J.L.; Whyte, M.P. Calcific Periarthritis as the Only Clinical Manifestation of Hypophosphatasia in Middle-Aged Sisters. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, J.D.; Murphy, W.A.; Whyte, M.P. Management of femoral fractures and pseudofractures in adult hypophosphatasia. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1986, 68, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, M.P. Atypical Femoral Fractures, Bisphosphonates, and Adult Hypophosphatasia. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2009, 24, 1132–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, M.P.; Leelawattana, R.; Reinus, W.R.; Yang, C.; Mumm, S.; Veis, D. Acute Severe Hypercalcemia After Traumatic Fractures and Immobilization in Hypophosphatasia Complicated by Chronic Renal Failure. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4606–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynch, C.D.; Ziada, H.M.; Buckley, L.A.; O’Sullivan, V.R.; Aherne, T.; Aherne, S. Prosthodontic rehabilitation of hypophosphatasia using dental implants: A review of the literature and two case reports. J. Oral Rehabil. 2009, 36, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, B.L.; Nagatomo, K.J.; Nociti, F.H.; Fong, H.; Dunn, D.; Tran, A.B.; Wang, W.; Narisawa, S.; Millan, J.L.; Somerman, M.J. Central Role of Pyrophosphate in Acellular Cementum Formation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lundgren, T.; Westphal, O.; Bolme, P.; Modéer, T.; Norén, J.G. Retrospective study of children with hypophosphatasia with reference to dental changes. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 1991, 99, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.; Resch, H.; Klaushofer, K.; Roschger, P.; Zwerina, J.; Kocijan, R. Hypophosphatasia: From Diagnosis to Treatment. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guañabens, N.; Blanch, J.; Martínez-Díaz-Guerra, G.; Muñoz-Torres, M. Identificación de hipofosfatasia en la práctica clínica: Manifestaciones clínicas y recomendaciones diagnósticas en pacientes adultos. Med. Clínica 2018, 150, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martos-moreno, G.A.; Calzada, J.; Couce, M.L.; Argente, J. Hipofosfatasia: Manifestaciones clínicas, recomendaciones diagnósticas y opciones terapéuticas. Anales Pediatría 2018, 88, e1–e356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, M.P. Hypophosphatasia: An overview for 2017. Bone 2017, 102, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarjou, A.; Jeney, V.; Arosio, P.; Poli, M.; Zavaczki, E.; Balla, G.; Balla, J. Ferritin ferroxidase activity: A potent inhibitor of osteogenesis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2009, 25, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.D.; Doherty, M. Calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition is not always ‘wear and tear’ or aging. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1997, 56, 586–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unger, S.; Mornet, E.; Mundlos, S.; Blaser, S.; Cole, D. Severe cleidocranial dysplasia can mimic hypophosphatasia. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2002, 161, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Thornell, A.P.; Crompton, T.; Denzel, A.; Gilmour, K.C.; Rosewell, I.R.; Stamp, G.W.; Beddington, R.S.; Mundlos, S.; Olsen, B.R.; et al. Cbfa1, a Candidate Gene for Cleidocranial Dysplasia Syndrome, Is Essential for Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Development. Cell 1997, 89, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mammalian Alkaline Phosphatases: From Biology to Applications in Medicine and Biotechnology; Wiley. Available online: https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Mammalian+Alkaline+Phosphatases%3A+From+Biology+to+Applications+in+Medicine+and+Biotechnology-p-9783527607471 (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- Scriver, C.R.; Cameron, D. Pseudohypophosphatasia. New Engl. J. Med. 1969, 281, 604–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, B.W.; McClendon, J.L. Childhood pseudohypophosphatasia. Clinical and laboratory study of two cases. Tex. Dent. J. 1986, 103, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, A.K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Mitra, P.; Mandal, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Mathew, J. Pseudohypophosphatasia. Indian J. Pediatr. 1997, 64, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.C.; Simão, A.M.S.; Narisawa, S.; Huesa, C.; McKee, M.D.; Farquharson, C.; Millán, J.L. Loss of skeletal mineralization by the simultaneous ablation of PHOSPHO1 and alkaline phosphatase function: A unified model of the mechanisms of initiation of skeletal calcification. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2010, 26, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mentrup, B.; Girschick, H.; Jakob, F.; Hofmann, C. A homozygous intronic branch-point deletion in the ALPL gene causes infantile hypophosphatasia. Bone 2017, 94, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandl, N.M.; Schmidt, T.; Rolvien, T.; Stürznickel, J.; Chrysostomou, K.; von Vopelius, E.; Volk, A.E.; Schinke, T.; Kubisch, C.; Amling, M.; et al. Genotype–Phenotype Associations in 72 Adults with Suspected ALPL-Associated Hypophosphatasia. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2021, 108, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lia-Baldini, A.; Muller, F.; Taillandier, A.; Gibrat, J.; Mouchard, M.; Robin, B.; Simon-Bouy, B.; Serre, J.; Aylsworth, A.; Bieth, E.; et al. A molecular approach to dominance in hypophosphatasia. Qual. Life Res. 2001, 109, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedde, K.N.; Michell, M.P.; Henthorn, P.S.; Whyte, M.P. Aberrant properties of alkaline phosphatase in patient fibroblasts correlate with clinical expressivity in severe forms of hypophosphatasia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Mauro, S.; Manes, T.; Hessle, L.; Kozlenkov, A.; Pizauro, J.M.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Millán, J.L. Kinetic characterization of hypophosphatasia mutations with physiological substrates. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2002, 17, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lefever, E.; Witters, P.; Gielen, E.; Vanclooster, A.; Meersseman, W.; Morava, E.; Cassiman, D.; Laurent, M.R. Hypophosphatasia in adults: Clinical spectrum and its association with genetics and metabolic substrates. J. Clin. Densitom. 2020, 23, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henthorn, P.S.; Raducha, M.; Fedde, K.N.; Lafferty, M.A.; Whyte, M.P. Different missense mutations at the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase gene locus in autosomal recessively inherited forms of mild and severe hypophosphatasia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 9924–9928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cahill, R.A.; Wenkert, D.; Perlman, S.A.; Steele, A.; Coburn, S.P.; McAlister, W.H.; Mumm, S.; Whyte, M.P. Infantile Hypophosphatasia: Transplantation Therapy Trial Using Bone Fragments and Cultured Osteoblasts. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 2923–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taketani, T.; Oyama, C.; Mihara, A.; Tanabe, Y.; Abe, M.; Hirade, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Bo, R.; Kanai, R.; Tadenuma, T.; et al. Ex Vivo expanded allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells with bone marrow transplantation improved osteogene-sis in infants with severe hypophosphatasia. Cell Transpl. 2015, 24, 1931–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moulin, P.; de Gauzy, J.S.; Vaysse, Y.; Mornet, E.; Salles, J.P. Growth hormone increases growth velocity and alkaline phosphatase level in children with hypophosphatasia. Bull. Group. Int. Rech. Sci-entifique en Stomatol. Odontol. 2012, 51, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpal-Szczyrska, M.; Balcerska, A. The Effect of Growth Hormone Treatment on Serum Bone Alkaline Phospha-tase in Growth Hormone Deficient Children. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2008, 14, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Girschick, H.J.; Seyberth, H.W.; Huppertz, H.I. Treatment of childhood hypophosphatasia with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Bone 1999, 25, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, G.; Varsavsky, M.; Muñoz-Torres, M. Hipofosfatasia: Nuevas perspectivas terapéuticas. Med. Clínica. 2009, 132, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalin-Jäntti, C.; Mornet, E.; Lamminen, A.; Välimäki, M.J. Parathyroid Hormone Treatment Improves Pain and Fracture Healing in Adult Hypophosphatasia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 5174–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, K.B.; Hamrahian, A.H.; Licata, A.A. Teriparatide Treatment in Adult Hypophosphatasia in a Patient Ex-posed to Bisphosphonate: A Case Report. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2009, 6, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whyte, M.P.; Mumm, S.; Deal, C. Adult Hypophosphatasia Treated with Teriparatide. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camacho, P.M.; Painter, S.; Kadanoff, R. Treatment of Adult Hypophosphatasia with Teriparatide. Endocr. Pract. 2008, 14, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Rolvien, T.; Linke, C.; Jandl, N.M.; Oheim, R.; Amling, M.; Barvencik, F. Outcome of teriparatide treatment on fracture healing complications and symptomatic bone marrow edema in four adult patients with hypophosphatasia. JBMR Plus 2019, 3, e10215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laroche, M. Failure of Teriparatide in Treatment of Bone Complications of Adult Hypophosphatasia. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2012, 90, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gagnon, C.; Sims, N.A.; Mumm, S.; McAuley, S.A.; Jung, C.; Poulton, I.J.; Ng, K.W.; Ebeling, P.R. Lack of Sustained Response to Teriparatide in a Patient with Adult Hypophosphatasia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seefried, L.; Baumann, J.; Hemsley, S.; Hofmann, C.; Kunstmann, E.; Kiese, B.; Huang, Y.; Chivers, S.; Valentin, M.-A.; Borah, B.; et al. Efficacy of anti-sclerostin monoclonal antibody BPS804 in adult patients with hypophosphatasia. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 2148–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Genest, F.; Seefried, L. Subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures in hypophosphatasia—not atypical at all. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 1815–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peris, P.; González-Roca, E.; Rodríguez-García, S.C.; López-Cobo, M.D.M.; Monegal, A.; Guañabens, N. Incidence of mutations in the ALPL, GGPS1, and CYP1A1 genes in patients with atypical femoral fractures. JBMR Plus 2019, 3, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stürznickel, J.; Schmidt, F.N.; von Vopelius, E.; Delsmann, M.M.; Schmidt, C.; Jandl, N.M.; Oheim, R.; Barvencik, F. Bone healing and reactivation of remodeling under asfotase alfa therapy in adult patients with pediatric-onset hypophosphatasia. Bone 2021, 143, 115794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genest, F.; Rak, D.; Petryk, A.; Seefried, L. Physical function and health-related quality of life in adults treated with asfotase alfa for pediatric-onset hypophosphatasia. JBMR Plus 2020, 4, 10395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishnani, P.S.; Rockman-Greenberg, C.; Rauch, F.; Bhatti, M.T.; Moseley, S.; Denker, A.E.; Watsky, E.; Whyte, M.P. Five-year efficacy and safety of asfotase alfa therapy for adults and adolescents with hypophosphatasia. Bone 2019, 121, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, M.P. Hypophosphatasia: Enzyme Replacement Therapy Brings New Opportunities and New Challenges. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villa-Suárez, J.M.; García-Fontana, C.; Andújar-Vera, F.; González-Salvatierra, S.; de Haro-Muñoz, T.; Contreras-Bolívar, V.; García-Fontana, B.; Muñoz-Torres, M. Hypophosphatasia: A Unique Disorder of Bone Mineralization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094303
Villa-Suárez JM, García-Fontana C, Andújar-Vera F, González-Salvatierra S, de Haro-Muñoz T, Contreras-Bolívar V, García-Fontana B, Muñoz-Torres M. Hypophosphatasia: A Unique Disorder of Bone Mineralization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(9):4303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094303
Chicago/Turabian StyleVilla-Suárez, Juan Miguel, Cristina García-Fontana, Francisco Andújar-Vera, Sheila González-Salvatierra, Tomás de Haro-Muñoz, Victoria Contreras-Bolívar, Beatriz García-Fontana, and Manuel Muñoz-Torres. 2021. "Hypophosphatasia: A Unique Disorder of Bone Mineralization" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 9: 4303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094303
APA StyleVilla-Suárez, J. M., García-Fontana, C., Andújar-Vera, F., González-Salvatierra, S., de Haro-Muñoz, T., Contreras-Bolívar, V., García-Fontana, B., & Muñoz-Torres, M. (2021). Hypophosphatasia: A Unique Disorder of Bone Mineralization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(9), 4303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094303






