Alpha-Helical Protein KfrC Acts as a Switch between the Lateral and Vertical Modes of Dissemination of Broad-Host-Range RA3 Plasmid from IncU (IncP-6) Incompatibility Group
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
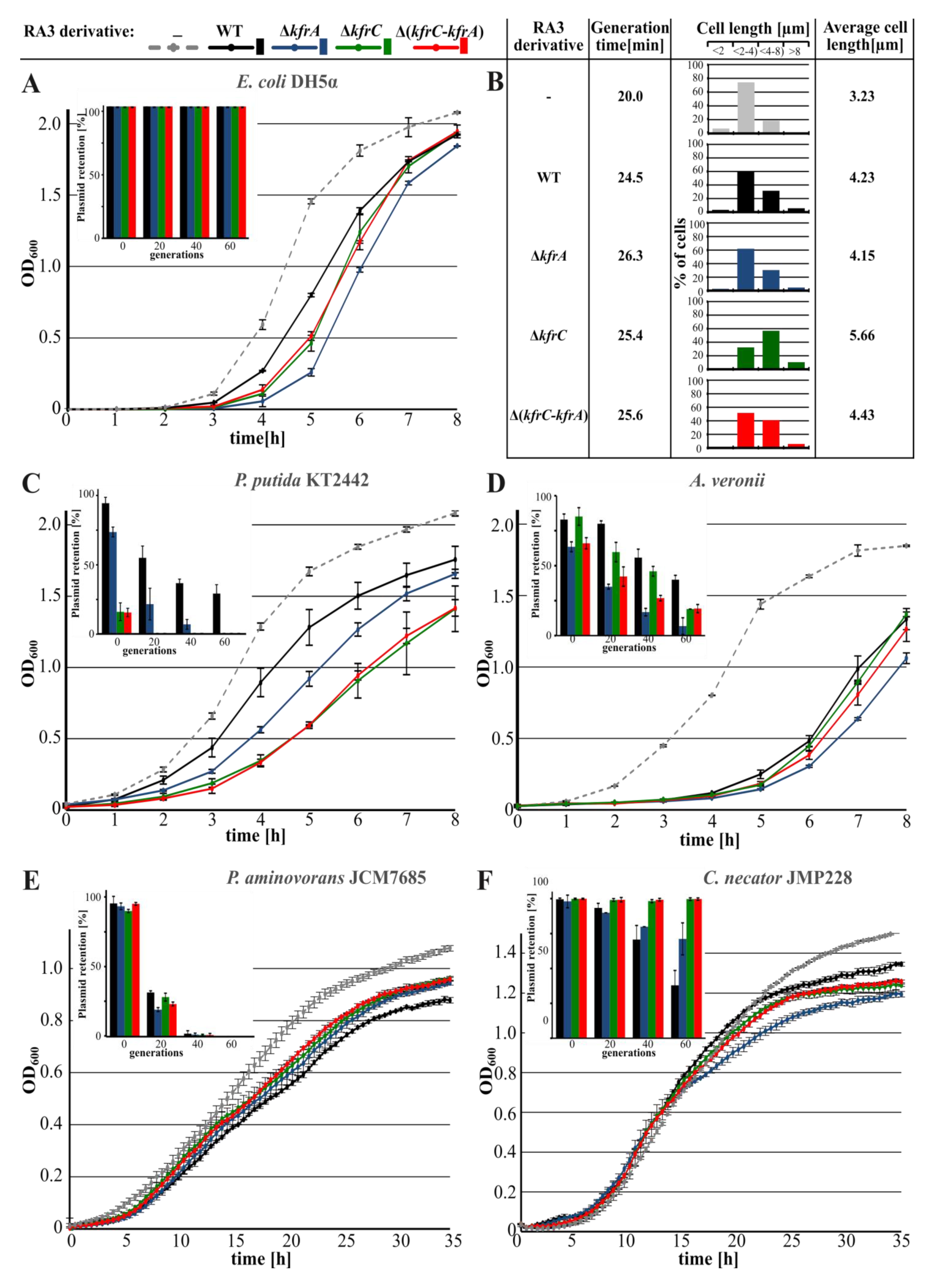
2.1. Role of KfrA and KfrC in the Stable Maintenance of RA3 Derivatives in Various Hosts
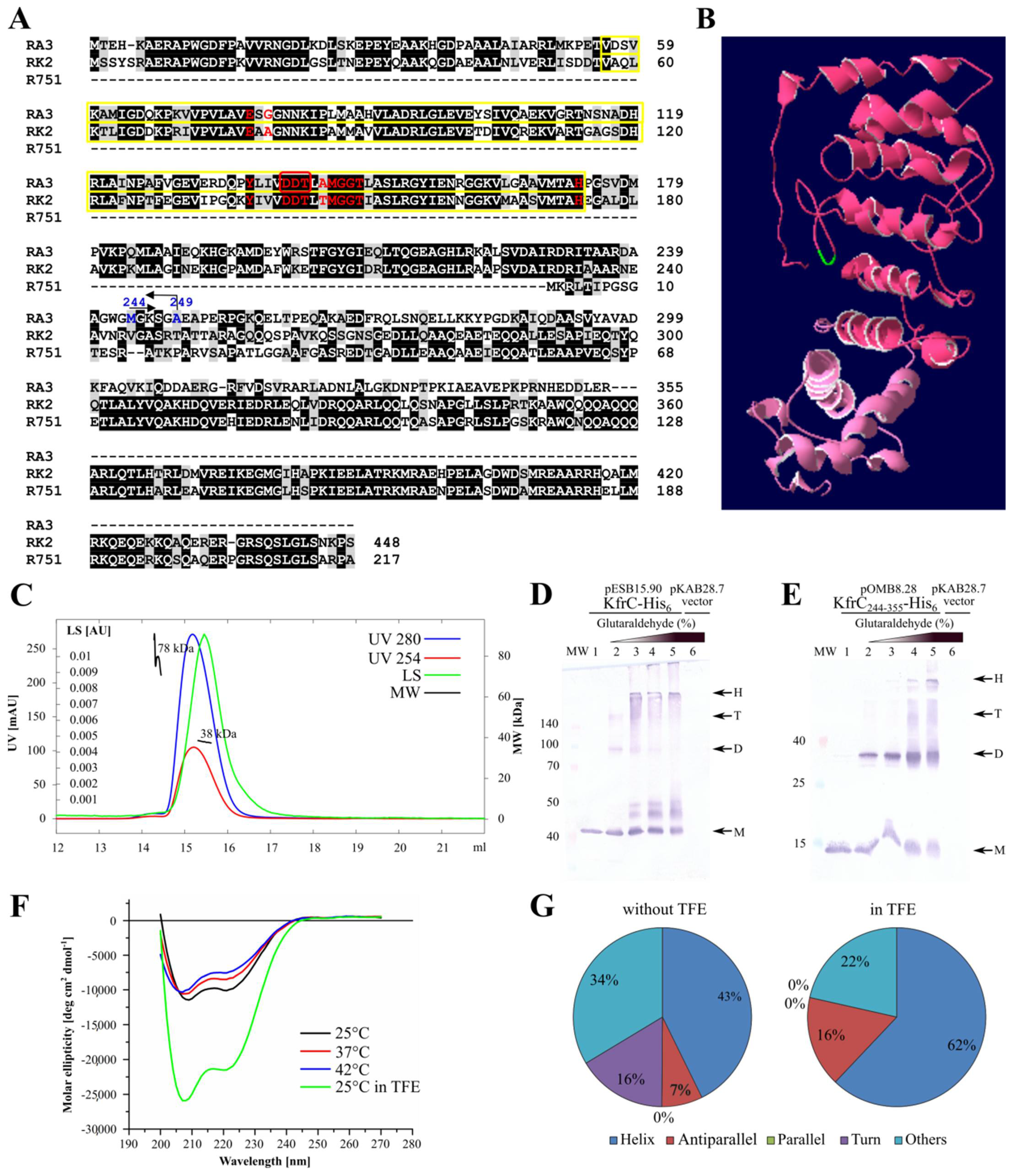
2.2. KfrCRA3 Structure
2.3. Inhibition of Hosts’ Growth by the Abundance of Kfr Proteins
2.4. Mapping of the KfrC Domain of Self-Interactions and Interactions with KfrA and KorB
2.5. Search for the KfrCRA3 Partners
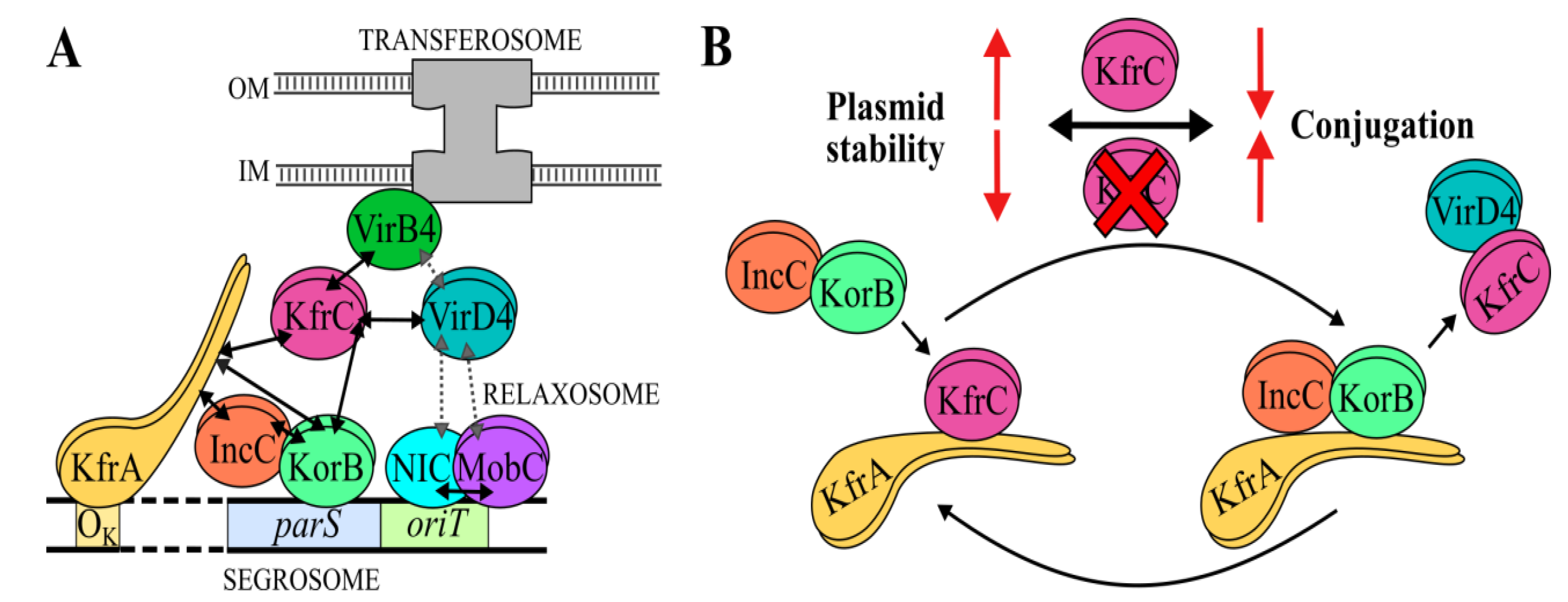
2.6. The Interactions between the KfrCRA3 Partners Involved in Two Modes of Plasmid Spreading
2.7. The Interplay between the Active Partitioning and the Conjugative Transfer Processes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. Plasmid DNA Isolation, Analysis, DNA Amplification, and Manipulation
4.2.1. Construction of KfrC Alanine Substitution Mutant
4.2.2. Construction of the translational fusions of FLAG with VirD434–641 via N-terminus and KfrC with His6-tag via C-terminus
4.2.3. Construction of RA3# Derivative with parSP1-Kmr Cassette
4.3. Bacterial Transformation and Conjugation
4.4. Bacterial Adenylate Cyclase Two-Hybrid (BACTH) System
4.5. Genome-Wide Library Construction of E. coli, A. veronii, and RA3 Plasmid Using BACTH System
4.6. High-Throughput Screening of Interaction Partners for a Bait Protein
4.7. Overexpression and Purification of His6-tagged Proteins by Affinity Chromatography
4.8. Determination of Protein Oligomeric States by Size-Exclusion Chromatography Coupled to Multiangle Light Scattering (SEC-MALS)
4.9. Crosslinking with Glutaraldehyde
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Determination of the Protein Secondary Structure by Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy
4.12. Construction of RA3 Mutants Using Site-Directed Mutagenesis Based on λ Red-Mediated Recombination
4.13. Co-Immunoprecipitation
4.14. Determination of Growth Rate of Strains Overproducing Proteins
4.15. Observations of the Nucleoids after DAPI Staining
4.16. Plasmid Stability Assays
4.17. Fluorescence Microscopy
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Boer, P.; Crossley, R.; Rothfield, L. The Essential Bacterial Cell-Division Protein FtsZ Is a GTPase. Nature 1992, 359, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagstaff, J.; Löwe, J. Prokaryotic Cytoskeletons: Protein Filaments Organizing Small Cells. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celler, K.; Koning, R.I.; Koster, A.J.; Wezel, G.P. van Multidimensional View of the Bacterial Cytoskeleton. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amos, L.A.; Löwe, J. Overview of the Diverse Roles of Bacterial and Archaeal Cytoskeletons. Subcell. Biochem. 2017, 84, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, G.H. Intermediate Filaments Supporting Cell Shape and Growth in Bacteria. In Prokaryotic Cytoskeletons: Filamentous Protein Polymers Active in the Cytoplasm of Bacterial and Archaeal Cells; Löwe, J., Amos, L.A., Eds.; Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 161–211. ISBN 978-3-319-53047-5. [Google Scholar]
- Pollard, T.D.; Goldman, R.D. Overview of the Cytoskeleton from an Evolutionary Perspective. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdes, K.; Howard, M.; Szardenings, F. Pushing and Pulling in Prokaryotic DNA Segregation. Cell 2010, 141, 927–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michie, K.A.; Löwe, J. Dynamic Filaments of the Bacterial Cytoskeleton. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006, 75, 467–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Thanbichler, M. Nucleotide-Independent Cytoskeletal Scaffolds in Bacteria. Cytoskeleton 2013, 70, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.L.; Rothfield, L. The Bacterial Cytoskeleton. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 70, 729–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaikeeratisak, V.; Khanna, K.; Nguyen, K.T.; Sugie, J.; Egan, M.E.; Erb, M.L.; Vavilina, A.; Nonejuie, P.; Nieweglowska, E.; Pogliano, K.; et al. Viral Capsid Trafficking along Treadmilling Tubulin Filaments in Bacteria. Cell 2019, 177, 1771–1780.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, J.A.; Erb, M.L.; Waddling, C.A.; Montabana, E.A.; Zehr, E.A.; Wang, H.; Nguyen, K.; Pham, D.S.L.; Agard, D.A.; Pogliano, J. A Phage Tubulin Assembles Dynamic Filaments by a Novel Mechanism to Center Viral DNA within the Host Cell. Cell 2012, 149, 1488–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, M.; Dolowy, P.; Jonczyk, M.; Thomas, C.M.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. The KfrA Gene Is the First in a Tricistronic Operon Required for Survival of IncP-1 Plasmid R751. Microbiol. Read. Engl. 2006, 152, 1621–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-López, R.; Garcillán-Barcia, M.P.; Revilla, C.; Lázaro, M.; Vielva, L.; de la Cruz, F. Dynamics of the IncW Genetic Backbone Imply General Trends in Conjugative Plasmid Evolution. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 942–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iiyama, K.; Mon, H.; Mori, K.; Mitsudome, T.; Lee, J.M.; Kusakabe, T.; Tashiro, K.; Asano, S.; Yasunaga-Aoki, C. Characterization of KfrA Proteins Encoded by a Plasmid of Paenibacillus Popilliae ATCC 14706T. Meta Gene 2015, 4, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagura-Burdzy, G.; Thomas, C.M. KfrA Gene of Broad Host Range Plasmid RK2 Encodes a Novel DNA-Binding Protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 225, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulinska, A.; Godziszewska, J.; Wojciechowska, A.; Ludwiczak, M.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. Global Transcriptional Regulation of Backbone Genes in Broad-Host-Range Plasmid RA3 from the IncU Group Involves Segregation Protein KorB (ParB Family). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 2320–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewicka, E.; Mitura, M.; Steczkiewicz, K.; Kieracinska, J.; Skrzynska, K.; Adamczyk, M.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. Unique Properties of the Alpha-Helical DNA-Binding Protein KfrA Encoded by the IncU Incompatibility Group Plasmid RA3 and Its Host-Dependent Role in Plasmid Maintenance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Top, E.M.; Wang, Y.; Brown, C.J.; Yao, F.; Yang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H. The Broad-Host-Range Plasmid PSFA231 Isolated from Petroleum-Contaminated Sediment Represents a New Member of the PromA Plasmid Family. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Auwera, G.A.; Król, J.E.; Suzuki, H.; Foster, B.; Van Houdt, R.; Brown, C.J.; Mergeay, M.; Top, E.M. Plasmids Captured in C. Metallidurans CH34: Defining the PromA Family of Broad-Host-Range Plasmids. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2009, 96, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolowy, P. The Regulatory Network of RA3 Plasmid from IncU Group. The Role of Kfr Proteins in Stable Maintenance. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Biochemistry and Biophysics, PAS, Warsaw, Poland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kulinska, A.; Czeredys, M.; Hayes, F.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. Genomic and Functional Characterization of the Modular Broad-Host-Range RA3 Plasmid, the Archetype of the IncU Group. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 4119–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godziszewska, J.; Kulinska, A.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. MobC of Conjugative RA3 Plasmid from IncU Group Autoregulates the Expression of Bicistronic MobC-Nic Operon and Stimulates Conjugative Transfer. BMC Microbiol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulinska, A.; Cao, Y.; Macioszek, M.; Hayes, F.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. The Centromere Site of the Segregation Cassette of Broad-Host-Range Plasmid RA3 Is Located at the Border of the Maintenance and Conjugative Transfer Modules. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2414–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ludwiczak, M.; Dolowy, P.; Markowska, A.; Szarlak, J.; Kulinska, A.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. Global Transcriptional Regulator KorC Coordinates Expression of Three Backbone Modules of the Broad-Host-Range RA3 Plasmid from IncU Incompatibility Group. Plasmid 2013, 70, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewicka, E.; Dolowy, P.; Godziszewska, J.; Litwin, E.; Ludwiczak, M.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. Transcriptional Organization of Stability Module of Broad-Host-Range RA3 Plasmid from IncU Group. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godziszewska, J.; Moncalián, G.; Cabezas, M.; Bartosik, A.A.; de la Cruz, F.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. Concerted Action of NIC Relaxase and Auxiliary Protein MobC in RA3 Plasmid Conjugation. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 101, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Egusa, S.; Kimura, T.; Watanabe, T. Detection of R Factors in Naturally Occurring Aeromonas Salmonicida Strains. Appl. Microbiol. 1971, 22, 716–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczyk, M.; Lewicka, E.; Szatkowska, R.; Nieznanska, H.; Ludwiczak, J.; Jasiński, M.; Dunin-Horkawicz, S.; Sitkiewicz, E.; Swiderska, B.; Goch, G.; et al. Revealing Biophysical Properties of KfrA-Type Proteins as a Novel Class of Cytoskeletal, Coiled-Coil Plasmid-Encoded Proteins. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L. One-Step Inactivation of Chromosomal Genes in Escherichia Coli K-12 Using PCR Products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccatano, D.; Colombo, G.; Fioroni, M.; Mark, A.E. Mechanism by Which 2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol/Water Mixtures Stabilize Secondary-Structure Formation in Peptides: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12179–12184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: A Unified Platform for Automated Protein Structure and Function Prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micsonai, A.; Wien, F.; Bulyáki, É.; Kun, J.; Moussong, É.; Lee, Y.-H.; Goto, Y.; Réfrégiers, M.; Kardos, J. BeStSel: A Web Server for Accurate Protein Secondary Structure Prediction and Fold Recognition from the Circular Dichroism Spectra. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W315–W322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimova, G.; Pidoux, J.; Ullmann, A.; Ladant, D. A Bacterial Two-Hybrid System Based on a Reconstituted Signal Transduction Pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5752–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowska, M.; Popowska, M. Insight into the Mobilome of Aeromonas Strains. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmakuri, K.; Cascales, E.; Christie, P.J. Energetic Components VirD4, VirB11 and VirB4 Mediate Early DNA Transfer Reactions Required for Bacterial Type IV Secretion. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansegrau, W.; Lanka, E.; Barth, P.T.; Figurski, D.H.; Guiney, D.G.; Haas, D.; Helinski, D.R.; Schwab, H.; Stanisich, V.A.; Thomas, C.M. Complete Nucleotide Sequence of Birmingham IncPα Plasmids: Compilation and Comparative Analysis. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 239, 623–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsted, P.B.; Macartney, D.P.; Akhtar, P.; Haines, A.S.; Ali, N.; Davidson, P.; Stafford, T.; Pocklington, M.J.; Pansegrau, W.; Wilkins, B.M.; et al. Complete Sequence of the IncPβ Plasmid R751: Implications for Evolution and Organisation of the IncP Backbone11Edited by J. Karn. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 282, 969–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.; Christie, P.J. The Agrobacterium VirB/VirD4 T4SS: Mechanism and Architecture Defined Through In Vivo Mutagenesis and Chimeric Systems. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 418, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Frost, L.S. Mutations in the C-Terminal Region of TraM Provide Evidence for in Vivo TraM-TraD Interactions during F-Plasmid Conjugation. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 4767–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Moncalián, G.; de la Cruz, F. DNA Binding Properties of Protein TrwA, a Possible Structural Variant of the Arc Repressor Superfamily. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Proteins Proteom. 2004, 1701, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Martinez, C.E.; Christie, P.J. Biological Diversity of Prokaryotic Type IV Secretion Systems. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2009, 73, 775–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, M.-J.; Kim, J.D.; Kim, H.; Kim, C.; Bowman, J.W.; Kim, S.; Joo, K.; Lee, J.; Jin, K.S.; Kim, Y.-G.; et al. Architecture of the Type IV Coupling Protein Complex of Legionella Pneumophila. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guynet, C.; Cuevas, A.; Moncalián, G.; de la Cruz, F. The Stb Operon Balances the Requirements for Vegetative Stability and Conjugative Transfer of Plasmid R388. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, C.J.; Lang, S.; Rajendra, V.K.H.; Nuk, M.; Raffl, S.; Schildbach, J.F.; Zechner, E.L. Conjugative DNA Transfer Is Enhanced by Plasmid R1 Partitioning Proteins. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, R.; Priefer, U.; Pühler, A.; Preifer, U. A Broad Host Range Mobilization System for In Vivo Genetic Engineering: Transposon Mutagenesis in Gram Negative Bacteria. Nature Biotechnol. 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koekman, B.P.; Hooykaas, P.J.J.; Schilperoort, R.A. A Functional Map of the Replicator Region of the Octopine Ti Plasmid. Plasmid 1982, 7, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecki, J.; Dziewit, L.; Puzyna, M.; Prochwicz, E.; Tudek, A.; Wibberg, D.; Schlüter, A.; Pühler, A.; Bartosik, D. Lifestyle-Determining Extrachromosomal Replicon PAMV1 and Its Contribution to the Carbon Metabolism of the Methylotrophic Bacterium Paracoccus Aminovorans JCM 7685. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 4536–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, M.; Kolter, R.; Thomas, C.; Figurski, D.; Meyer, R.; Remaut, E.; Helinski, D.R. [17] Plasmid cloning vehicles derived from plasmids ColE1, F, R6K, and RK2. In Methods in Enzymology; Recombinant DNA; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1979; Volume 68, pp. 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bartosik, A.A.; Markowska, A.; Szarlak, J.; Kulińska, A.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. Novel Broad-Host-Range Vehicles for Cloning and Shuffling of Gene Cassettes. J. Microbiol. Methods 2012, 88, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawalek, A.; Glabski, K.; Bartosik, A.A.; Fogtman, A.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. Increased ParB Level Affects Expression of Stress Response, Adaptation and Virulence Operons and Potentiates Repression of Promoters Adjacent to the High Affinity Binding Sites ParS3 and ParS4 in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovach, M.E.; Phillips, R.W.; Elzer, P.H.; Roop, R.M.; Peterson, K.M. PBBR1MCS: A Broad-Host-Range Cloning Vector. BioTechniques 1994, 16, 800–802. [Google Scholar]
- Kovach, M.E.; Elzer, P.H.; Hill, D.S.; Robertson, G.T.; Farris, M.A.; Roop, R.M.; Peterson, K.M. Four New Derivatives of the Broad-Host-Range Cloning Vector PBBR1MCS, Carrying Different Antibiotic-Resistance Cassettes. Gene 1995, 166, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spratt, B.G.; Hedge, P.J.; te Heesen, S.; Edelman, A.; Broome-Smith, J.K. Kanamycin-Resistant Vectors That Are Analogues of Plasmids PUC8, PUC9, PEMBL8 and PEMBL9. Gene 1986, 41, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaszewicz, M.; Kostelidou, K.; Bartosik, A.A.; Cooke, G.D.; Thomas, C.M.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. Functional Dissection of the ParB Homologue (KorB) from IncP-1 Plasmid RK2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagura-Burdzy, G.; Ibbotson, J.P.; Thomas, C.M. The KorF Region of Broad-Host-Range Plasmid RK2 Encodes Two Polypeptides with Transcriptional Repressor Activity. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kawalek, A.; Modrzejewska, M.; Zieniuk, B.; Bartosik, A.A.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. Interaction of ArmZ with the DNA-Binding Domain of MexZ Induces Expression of MexXY Multidrug Efflux Pump Genes and Antimicrobial Resistance in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mierzejewska, J.; Bartosik, A.A.; Macioszek, M.; Płochocka, D.; Thomas, C.M.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. Identification of C-Terminal Hydrophobic Residues Important for Dimerization and All Known Functions of ParB of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Microbiol. Read. Engl. 2012, 158, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanisch-Perron, C.; Vieira, J.; Messing, J. Improved M13 Phage Cloning Vectors and Host Strains: Nucleotide Sequences of the M13mp18 and PUC19 Vectors. Gene 1985, 33, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.H. Experiments in Molecular Genetics; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1972; ISBN 978-0-87969-106-6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.P.; Kuo, T.T. A Simple and Rapid Method for the Preparation of Gram-Negative Bacterial Genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenney, K.; Shimatake, H.; Court, D.; Schmeissner, U.; Brady, C.; Rosenberg, M. A System to Study Promoter and Terminator Signals Recognized by Escherichia Coli RNA Polymerase. Gene Amplif. Anal. 1981, 2, 383–415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clarke, L.; Carbon, J. A Colony Bank Containing Synthetic Col El Hybrid Plasmids Representative of the Entire E. Coli Genome. Cell 1976, 9, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagura-Burdzy, G.; Thomas, C.M. Purification of KorA Protein from Broad Host Range Plasmid RK2: Definition of a Hierarchy of KorA Operators. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 253, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenfield, N.J. Using Circular Dichroism Spectra to Estimate Protein Secondary Structure. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2876–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosik, A.A.; Glabski, K.; Jecz, P.; Lasocki, K.; Mikosa, M.; Plochocka, D.; Thomas, C.M.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. Dissection of the Region of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa ParA That Is Important for Dimerization and Interactions with Its Partner ParB. Microbiology 2014, 160, 2406–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Library | DNA Coordinates (Peptide) * | Gene | Predicted Function ** | NCBI Accession Number | Number of Clones |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli DH5α | 792619 (209–332) | edd | phosphogluconate dehydratase | WP_001069467.1 | 1 |
| 1321046 (266–446) | fadL | long-chain fatty acid transporter | WP_001295701.1 | 1 | |
| 2535141 (76–228) | yhjJ | Zn-dependent peptidase | WP_001163141.1 | 1 | |
| 3019820 (475–614) | btuB | vitamin B12 transporter | WP_000591359.1 | 1 | |
| 3869607 (138–272) | cof | HMP-PP phosphatase | WP_001336137.1 | 1 | |
| 4142310 (494–648) | ybgQ | outer membrane usher protein | WP_001350492.1 | 1 | |
| 4242142 (25–171) | ompX | outer membrane protein OmpX | WP_001295296.1 | 1 | |
| Most similar Protein (BLASTP) | Number of Clones | ||||
| A. veronii | Protein Length (Peptide) § | Predicted Function ** | NCBI Accession Number | ||
| 354 (103–354) | 3-deoxy-7-phosphoheptulonate synthase | WP_113739212.1 | 1 | ||
| 403 (184–403) | EAL domain-containing protein | WP_064340963.1 | 1 | ||
| 385 (187–327) | acyl-CoA dehydrogenase | WP_129504156.1 | 1 | ||
| Bait | Coordinates * | Prey | Number of Clones | Cloned Fragment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KfrC-T25 | 16,448 | VirD4 | 1 |  |
| 16,451 | 8 |  | ||
| 16,511 | 1 |  | ||
| 16,931 | 3 |  | ||
| 17,633 | 1 |  | ||
| T25-KfrC | 17,501 | VirD4 | 2 |  |
| 17,549 | 1 |  | ||
| 24,447 | VirB4 | 2 |  | |
| 4307 | KfrC | 3 |  |
| Plasmids Provided by Others | |
|---|---|
| Designation | Relevant Features or Description |
| pABB19 | oriMB1, Apr, transcriptional terminator Tpro/Tlyz P1 [51] |
| pABB28.2 | pET28a with his-tag replaced by flag-tag [52] |
| pAKB2.55 | pGBT30 with kfrC without a stop codon (IBB) a |
| pAKB2.70 | pGBT30 with kfrCRA3-yfp (IBB) a |
| pAKB7.5 | oriMB1, Kmr, parS-oriTRA3 (RA3 coordinates 9397–9854 nt) [24] |
| pAKB16.50 | pLKB4 cyaT18-korBRA3 [17] |
| pAKB16.50N | pKGB4 korBRA3-cyaT18 [17] |
| pAMB8 | pBBR1MCS-3 modified in tetM to remove EcoRI site (IBB) a |
| pBBR1MCS | IncA/C, Cmr, BHR cloning vector [53] |
| pBBR1MCS-2 | IncA/C, Kmr BHR cloning vector [54] |
| pBGS18 | oriMB1, Kmr, cloning vector [55] |
| pESB5.58 | pGBT30 with tacp-kfrA [18] |
| pET28a | oriMB1, Kmr, T7p, lacO, His6-tag, T7 tag (Novagen) |
| pET28mod | pET28a derivative, T7 tag removed [56] |
| pGBT30 | oriVMB1, Apr, lacIq, tacp expression vector [57] |
| pJSB8.5.2 | pLKB4 cyaT18-virD4 (IBB) a |
| pJSB9.5.1 | pKGB4 virD4-cyaT18 (IBB) a |
| pJSB10.5.2 | pLKB2 cyaT25-virD4 (IBB) a |
| pJSB11.5.1 | pKGB5 virD4-cyaT25 (IBB) a |
| pKAB20 | pUC19 derivative with flag-mcsb-his6; allows in-frame attachment of flag to 5′ and/or his6 to the 3′ of a gene [58] |
| pKAB28 | pET28mod with deletion of his6-tag and EcoRI site adjacent to RBS [57] |
| pKAB28.7 | pET28mod derivative with his6- mcsb [58] |
| pKD13 | template plasmid for gene disruption [30] |
| pKD46 | oriR101, araBp-gam-bet-exo, repA101(ts), Apr, lambda Red recombinase expression plasmid [30] |
| pKGB4 | oriColE1, pUT18 with modified mcs, lacp- mcsb -cyaT18, Apr (IBB) a |
| pKGB5 | orip15, pKNT25 with modified mcs, lacp- mcsb -cyaT25, Kmr (IBB) a |
| pKT25-zip | pKT25 derivative encoding CyaT25 in translational fusion with leucine zipper of GCN4 [34] |
| pLKB2 | orip15, pKT25 with modified mcs, lacp-cyaT25- mcsb, Kmr [59] |
| pLKB4 | oriColE1, pUT18C with modified mcs, lacp-cyaT18- mcsb, Apr [59] |
| pMRA1.3 | pLKB4 with cyaT18-kfrCR751 (IBB) a |
| pMRB2.3 | pKGB4 with kfrCR751-cyaT18 (IBB) a |
| pMRB3.3 | pLKB2 with cyaT25-kfrCR751 (IBB) a |
| pMRB4.3 | pKGB5 with kfrCR751-cyaT25 (IBB) a |
| pOMB3.104 | pUC18 derivative with parS P1 prophage (IBB) a |
| pOMB4.13 | pLKB4 with cyaAT18-kfrA [18] |
| pOMB4.15 | pLKB4 with cyaAT18-kfrC [18] |
| pOMB5.13 | pLKB2 with cyaAT25-kfA [18] |
| pOMB5.15 | pLKB2 with cyaAT25-kfrC [18] |
| pOMB6.14 | pKGB4 with kfrA-cyaAT18 [18] |
| pOMB6.16.1 | pKGB4 with kfrC-cyaAT18 [18] |
| pOMB7.14 | pKGB5 with kfrA-cyaAT25 [18] |
| pOMB7.16.1 | pKGB5 with kfrC-cyaAT25 [18] |
| pOMB9.80 | pGBT30 with kfrARA3-cfp (IBB) a |
| pUC18 | oriMB1, Apr, cloning vector [60] |
| pUT18C-zip | pUT18C derivative encoding CyaT18 in translational fusion with leucine zipper of GCN4 [34] |
| R751TcR | IncPβ (IncP-1β) c, Tcr-derivative of R751 [38] |
| RA3 | IncU (IncP-6) c, Cmr, Smr, Sur (F. Hayes) |
| RK2 | IncPα (IncP-1α) c, Apr, Kmr, Tcr (C.M. Thomas) |
| Plasmids Constructed during This Work | |
| Designation | Relevant Features or Description |
| pESB5.88 | pGBT30 with tacp-kfrC; annealed oligonucleotides 28 and 29 inserted between Xba-SalI of pAKB2.55 |
| pESB5.90 | pGBT30 with tacp-kfrC without a stop codon; annealed oligonucleotides 6 and 7 inserted between Xba-SalI of pAKB2.55 |
| pESB10 | pBBR1MCS-2 lacIq tacp with transcriptional terminator T1/T2rrnB; PCR product obtained with primers 36 and 37 on E. coli genomic DNA inserted as XhoI-KpnI fragment between SalI-KpnI sites |
| pESB11 | pOMB12.0 derivative with transcriptional terminator T1/T2rrnB; PCR fragment obtained with primers 36 and 37 on E. coli genomic DNA inserted between XhoI-KpnI sites |
| pESB11.58 | pESB11 with tacp-kfrA; EcoRI-SalI fragment from pESB5.58 inserted between EcoRI-XhoI sites |
| pESB15 | pET28a with annealed oligonucleotides 30 and 31 inserted between NcoI and BamHI sites |
| pESB15.90 | pESB15 with kfrC-his6; EcoRI-HindIII fragment from pESB5.90 |
| pJSB1.4 | pBGS18 with the mobCp-mobC-nic; PCR fragment obtained with primers 26 and 5 on RA3 template inserted between EcoR-SalI sites (RA3 coordinates 9437–11355 nt) |
| pJSB1.5.2 | pBGS18 with virD4; PCR fragment obtained with primers 44 and 45 on RA3 template cloned between the BamHI-KpnI sites (RA3 coordinates 18230–16305 nt) |
| pJSB1.8 | pBGS18 with TraRA3; pJSB1.4 with SmaI-SalI fragment of RA3 plasmid (RA3 coordinates 10733–22925 nt) |
| pJSB1.24 | pBGS18 with TraRA3-korCp-korC; PCR fragment korCp-korC obtained with primers 2 and 3 (RA3 coordinates 3093–3705) inserted into pJSB1.8 |
| pJSB8.1 | pLKB4 with cyaT18-mobC; PCR fragment obtained with primers 22 and 23, cloned between the EcoRI-HincII sites (RA3 coordinates 9837–10455 nt) |
| pJSB8.3 | pLKB4 with cyaT18-nic; PCR fragment obtained with primers 25 and 26 cloned between the EcoRI-HincII sites (RA3 coordinates 10360–11355 nt) |
| pJSB8.5.2 | pLKB4 with cyaT18-virD4; fragment BamHI-KpnI from pJSB1.5.2 cloned into pLKB4 |
| pJSB8.35 | pLKB4 with cyaT18-mobC-oriTRA3; SmaI-HincII fragment of pAKB7.5 carrying parS-oriT cloned into PvuII site of pJSB8.1 |
| pJSB9.1.1 | pKGB4 with mobC-cyaT18; PCR fragment obtained with primers 22 and 24 cloned between EcoRI-SacI sites, (RA3 coordinates 9837–10364 nt) |
| pJSB9.5.1 | pKGB4 with virD4-cyaT18; PCR fragment obtained with primers 44 and 46 cloned between BamHI-SacI sites (RA3 coordinates 18230–16308 nt) |
| pJSB10.1 | pLKB2 with cyaT25-mobC; PCR fragment EcoRI-HincII obtained with primers 22 and 23, cloned between the EcoRI-SmaI sites (RA3 coordinates 9837–10455 nt) |
| pJSB10.3 | pLKB2 with cyaT25-nic; PCR fragment EcoRI-HincII obtained with primers 25 and 26 cloned between EcoRI-SmaI sites (RA3 coordinates10360–11355 nt) |
| pJSB10.5.2 | pLKB2 with cyaT25-virD4; PCR fragment obtained with primers 44 and 45 cloned between BamHI-KpnI sites (RA3 coordinates18230–16305 nt) |
| pJSB11.1 | pKGB5 with mobC-cyaT25; PCR fragment obtained with primers 22 and 24 cloned between EcoRI-SacI sites (RA3 coordinates 9837–10364 nt) |
| pJSB11.3 | pKGB5 with nic-cyaT25; PCR fragment obtained with primers 25 and 27 cloned between EcoRI-SacI sites (RA3 coordinates 10360–11352 nt) |
| pJSB11.5.1 | pKGB5 with virD4-cyaT25; PCR fragment obtained with primers 44 and 46 cloned between BamHI-SacI sites (RA3 coordinates 18230–16308 nt) |
| pOMB1.17 | pBGS18 with kfrC1–249; PCR product amplified on RA3 template with primers 8 and 9 inserted between EcoRI-SalI sites (RA3 coordinates: 3692–4438) |
| pOMB1.18 | pBGS18 with kfrC244–355; PCR product amplified on RA3 template with primers 10 and 11 inserted between EcoRI-SalI sites (RA3 coordinates: 4421–4756) |
| pOMB1.42 | pBGS18 with virD4434–641; EcoRI-BamHI fragment from pOMB4.42 |
| pOMB1.51 | pBGS18 with virD4434–641 kfrC; PCR product amplified on RA3 template with primers 14 and 18 inserted as BglII-SalI fragment between BamHI-SalI sites of pOMB1.42 (RA3 coordinates: 3686–4756) |
| pOMB1.74 | pBGS18 virD4-cfp; BamHI-HindIII fragment from pOMB9.80 with overhangs filled in using Klenow fragment of PolI inserted within EcoICRI site of pJSB1.5.2 |
| pOMB2.0 | pKAB20 derivative with Ecl136II restriction site inserted between MunI and HindIII sites (annealed oligonucleotides 33 and 34) |
| pOMB2.0.28 | pUC19 with kfrC244–355-his6; EcoRI-SmaI fragment from pOMB1.18 inserted in EcoRI-Ecl136II sites of pOMB2.0 |
| pOMB2.49 | pUC19 with flag-virD4; PCR product amplified on RA3 template with primers 4 and 49 inserted between MunI-HindIII sites of pKAB20 (RA3 coordinates: 18230–16305) |
| pOMB2.50 | pUC19 with flag-vird4434–641; EcoRI-SalI fragment from pOMB1.42 inserted between MunI-SalI sites of pKAB20 |
| pOMB2.52 | pUC19 with flag-virD4434–641 kfrC-his6; EcoRI-SalI fragment from pOMB1.51 inserted between MunI-XhoI sites of pKAB20 |
| pOMB2.74 | pUC19 virD4-cfp; PCR product amplified on pOMB1.74 template with primers 1 and 49 inserted as MunI-SmaI sites of pOMB2.0 |
| pOMB4.0 | pLKB4 derivative with I-SceI restriction site inserted into KpnI site (annealed oligonucleotides 20 and 21) |
| pOMB4.17 | pLKB4 with cyaT18-kfrC1–249; EcoRI-SmaI fragment from pOMB1.17 |
| pOMB4.18 | pLKB4 with cyaT18-kfrC244–355; EcoRI-SmaI fragment from pOMB1.18 |
| pOMB4.34 | pLKB4 with cyaT18-traGR751; PCR product amplified on R751 template with primers 38 and 39 inserted as EcoRI-KpnI fragment (R751 coordinates: 48800–46887) |
| pOMB4.36 | pLKB4 with cyaT18-kfrCRK2; PCR product amplified on RK2 template with primers 15 and 16 inserted as EcoRI-KpnI fragment (RK2 coordinates: 54424–53079) |
| pOMB4.38 | pLKB4 with cyaT18-traGRK2; PCR product amplified on RK2 template with primers 40 and 41 inserted as EcoRI-KpnI fragment (RK2 coordinates: 48495–46588) |
| pOMB4.42 | pLKB4 with cyaT18-virD4434–641; PCR product amplified on RA3 template with primers 47 and 48 inserted between EcoRI-BamHI sites (RA3 coordinates: 16931–16305) |
| pOMB5.17 | pLKB2 with cyaT25-kfrC1–249; EcoRI-SmaI fragment from pOMB1.17 |
| pOMB5.18 | pLKB2 with cyaT25-kfrC244–355; EcoRI-SmaI fragment from pOMB1.18 |
| pOMB5.34 | pLKB2 with cyaT25-traGR751; EcoRI-KpnI fragment from pOMB4.34 |
| pOMB5.36 | pLKB2 with cyaT25-kfrCRK2; EcoRI-KpnI fragment from pOMB4.36 |
| pOMB5.38 | pLKB2 with cyaT25-traGRK2; EcoRI-KpnI fragment from pOMB4.38 |
| pOMB6.17 | pKGB4 with kfrC1–249-cyaT18; EcoRI-SmaI fragment from pOMB1.17 |
| pOMB6.18 | pKGB4 with kfrC244–355-cyaT18; EcoRI-SmaI fragment from pOMB1.18 |
| pOMB6.35 | pKGB4 with traGR751-cyaT18; PCR product amplified on R751 template with primers 38 and 43 inserted as EcoRI-SmaI fragment (R751 coordinates: 48800–46890) |
| pOMB6.37 | pKGB4 with kfrCRK2-cyaT18; PCR product amplified on RK2 template with primers 15 and 17 inserted as EcoRI-SmaI fragment (RK2 coordinates: 54424–53082) |
| pOMB6.39 | pKGB4 with traGRK2-cyaT18; PCR product amplified on RK2 template with primers 40 and 42 inserted as EcoRI-SmaI fragment (RK2 coordinates: 48495–46591) |
| pOMB7.17 | pKGB5 with kfrC1–249-cyaT25; EcoRI-SmaI fragment from pOMB1.17 |
| pOMB7.18 | pKGB5 with kfrC244–355-cyaT25; EcoRI-SmaI fragment from pOMB1.18 |
| pOMB7.35 | pKGB5 with traGR751-cyaT25; EcoRI-SmaI fragment from pOMB6.35 |
| pOMB7.37 | pKGB5 with kfrCRK2-cyaT25; EcoRI-SmaI fragment from pOMB6.37 |
| pOMB7.39 | pKGB5 with traGRK2-cyaT25; EcoRI-SmaI fragment from pOMB6.39 |
| pOMB8.28 | pET28mod with kfrC244–355-his6; pKAB28 derivative with EcoRI-SalI fragment from pOMB2.0.28 |
| pOMB8.49 | pET28mod with flag-virD4; MunI-HindIII fragment from pOMB2.49 inserted between EcoRI-HindIII sites of pKAB28 |
| pOMB8.50 | pET28mod with flag-virD4434–641; pKAB28 derivative with EcoRI-SalI fragment from pOMB2.50 |
| pOMB8.52 | pET28mod with flag-virD4434–641 kfrC-his6; pKAB28 derivative with EcoRI-SalI fragment from pOMB2.52 |
| pOMB9.18 | pGBT30 with tacp-kfrC244–355; EcoRI-SalI fragment from pOMB1.18 |
| pOMB9.29 | pGBT30 with tacp-kfrC-his6; PCR product amplified on the pESB15.90 template with primers 19 and 35 inserted between XbaI-SalI sites of pESB5.88 |
| pOMB9.31 | pGBT30 with tacp-kfrC*; two-stage PCR was used for KfrC site-directed mutagenesis, described in detail in Metods, PCR final product was inserted between XbaI-SalI sites |
| pOMB12.0 | pOMB12.30 derivative with transcriptional terminator Tpro/Tlyz P1; PCR product amplified on pABB19 as a template with primers 50 and 51 inserted as EcoRI-SalI fragment between EcoRI-XhoI sites |
| pOMB12.15 | pESB11 with tacp-kfrC; EcoRI-SalI fragment from pESB5.88 inserted between EcoRI-XhoI sites |
| pOMB12.30 | pBBR1MCS-3 lacIq tacp; pAMB8 derivative with EcoRI-PstI fragment from pGBT30 |
| pOMB12.74 | pBBR1MCS-2 virD4-cfp; pESB10 derivative with MunI-SmaI fragment from pOMB2.74 inserted between EcoRI-SmaI sites |
| RA3ΔincC | incC gene replaced by Kmr cassette amplified on pKD13 template with primers 52 and 53 (coordinates of deletion: 6356–7080) |
| RA3Δnic | nic gene replaced by Kmr cassette amplified on pKD13 template with primers 54 and 55 (coordinates of deletion: 10380–11352) |
| RA3ΔvirD4 | virD4 replaced by Kmr cassette amplified on pKD13 template with primers 56 and 57 (coordinates of deletion: 18195–16314) |
| RA3ΔparS | parS site replaced by Kmr cassette amplified on pKD13 template with primers 58 and 59 (coordinates of deletion: 9707–9722) |
| RA3ΔoriT | oriT site replaced by Kmr cassette amplified on pKD13 template with primers 60 and 61 (coordinates of deletion: 9747–9756) |
| RA3parS▼oriT | Kmr cassette amplified on pKD13 template with primers 59 and 62 and inserted between parS and oriT sites (coordinates of insertion: 9722/9723) |
| RA3ΔkfrA | kfrA replaced by Kmr cassette amplified on pKD13 template with primers 63 and 64 (coordinates of deletion: 4892–5935) |
| RA3ΔkfrC | kfrC replaced by Kmr cassette amplified on pKD13 template with primers 65 and 66 (coordinates of deletion: 3695–4738) |
| RA3Δ(kfrC-A) | kfrC-kfrA replaced by Kmr cassette amplified on pKD13 template with primers 65 and 64 (coordinates of deletion: 3695–5935) |
| RA3# | parSP1-Kmr cassette inserted within integron at position 38,663 of RA3 genome |
| No | Designation | Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CFPSmSaP | gccccggGGTCGACTTACTTGTACAGCTCG |
| 2 | CkorCD | cgacatgtTTATGTTCGGTCATGGTTTC |
| 3 | CkorCG | gcgcatgcCTTAAAGGAGGTGCATAGGT |
| 4 | FLAGVirDR | ccaagcttTTATGCCGCTTCAGCCAAGC |
| 5 | kasmob1 | cggaattcacatgtTTCTCGTTGGAGGGTGATCA |
| 6 | KFRCBSD | tcgacaagcttCCGCT |
| 7 | KFRCBSG | CTAGAGCGGaagcttg |
| 8 | kfrCFL | gcaagctttggaattCATGACCGAACATAAGGCCGA |
| 9 | kfrCIR | cggtcgacttacccgggAGCTCCGCTTTTGCCCATTC |
| 10 | kfrCIIF | cggaattcATGGGCAAAAGCGGAGCTGA |
| 11 | kfrCIIR | cggtcgacTTAcccgggCCGCTCTAGATCGTCTTCAT |
| 12 | kfrCmutF | TGTCGcgGccgCGCTGGCGATGGGCG |
| 13 | kfrCmutR | CCAGCGcggCcgCGACAATCAGATAAGGCTGGTCA |
| 14 | kfrCrbsF | cggaattcagatctaaggagGAAACCATGACCGAACATAA |
| 15 | KfrCRK2N | gcgaattcaTGAGCAGCTACAGCAGAG |
| 16 | KfrCRK2R | gcggtaccTTAGCTGGGCTTGTTTGAC |
| 17 | KfrCRKst | cgcccgggGCTGGGCTTGTTTGACAGG |
| 18 | KfrCstop | cggtcgacCCGCTCTAGATCGTCTTCAT |
| 19 | KfrCXbaF | cgTCTAGAGCGGAAGCTTGCGG |
| 20 | LinkSceF | tagggataacagggtaatgtac |
| 21 | LinkSceR | attaccctgttatccctagtac |
| 22 | mobC1 | cggaattcATGGCAAAGAGCTATCGGATCG |
| 23 | mobC2 | cggtcGACTCGCTTAACTCGGCCTTTCA |
| 24 | mobCT | gcgagctccTTCATCGATCCCCCACTTG |
| 25 | nic1 | cggaattcATGAATAAGGGCTATGACACTCTAGCCGGG |
| 26 | nic2 | cggtcgacTTATCTCTCGTCTTCGTCCC |
| 27 | Nic2k | gcgagctcgTCTCTCGTCTTCGTCCCTCTCTGATTTTGC |
| 28 | OKFRCD2 | tcgacggtaccagcggcttcaCCGCT |
| 29 | OKFRCG2 | CTAGAGCGGtgaagccgctggtaccg |
| 30 | OPETD | GATCGTGCAGC |
| 31 | OPETG | CATGGCTGCAC |
| 32 | pGBT30R | CTCTTCCGCATAAACGCTTC |
| 33 | podst4F | aattggggctcc |
| 34 | podst4R | agctggagctcc |
| 35 | T7TERR | gcgtcgacCAAAAAACCCCTCAAGACCC |
| 36 | TerpKKKF | cgcggtaccctcgagcccgggATCAGAACGCAGAAGCGGTC |
| 37 | TerpKKR | cgcggtaccagtactGGCTTGTAGATATGACGACAG |
| 38 | TraGEcoF | gcgaattcATGAAGATCAAGATGAACAAC |
| 39 | TraGKpnR | gcggtacCTCATATCGTGATGCCCTCCC |
| 40 | TraGRK2F | gcgaattcATGAAGAACCGAAACAACGCC |
| 41 | TraGRK2R | gcggtacCTCATATCGTGATCCCCTCC |
| 42 | TraGRKst | cgcccgggTATCGTGATCCCCTCCCCTTC |
| 43 | TraGSmaR | cgcccgggTATCGTGATGCCCTCCC |
| 44 | virD4Gm | gcggattcATGACCCAGAATTCAAACGGACAC |
| 45 | virD4Kpn | cgggtaCCTTATGCCGCTTCAGCCAAGCCATT |
| 46 | virD4N | cggagctcCTGCCGCTTCAGCCAAGCCATTAA |
| 47 | VirDfr2F | gcgaattcTTGCGTGAAACATATGGG |
| 48 | VirDfrBR | gcggaTCCTTATGCCGCTTCAGCCAAG |
| 49 | VirDMunF | cgcaattgATGACCCAGAATTCAAACG |
| 50 | TProLyzF | gcgaattctacgtactcgagagatctACATGTGGTACCAACCACC |
| 51 | TProLyzR | gcgtcgacCCATGGATAATAGTTAACGAG |
| 52 | delincF | CGAGGATGAGGCATATAAACAGGCTAATAAACCAAAGGGTTGAGCATATGATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGACC |
| 53 | delincR | CCGCTGAGGTCTGCCCCTTTACCACTCATTCAGCCACCCCCATTTTTTCATGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTCG |
| 54 | delnicF | TCGCCGGTTTGCTTCAACGCAACTTAAACAAGTGGGGGATCGATGAATAAATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGACC |
| 55 | delnicR | GAACGCTAAATACCTGAAAACAAAAACCGGCCAACAGGCCGGTTTTTTTATGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTCG |
| 56 | delvirF | TAACGGAGATTTACTATGACCCAGAATTCAAACGGACACAAATGGCGTAAATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGACC |
| 57 | delvirR | TATGTTTTTTCCTGTGCAATATTTGCCATTTCAATTATTCCTTATGCCGCTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTCG |
| 58 | delparF | CGACCTGGTGAGCCTGGCCGAAGGCCAAAAGCCACTGCAAAACCGAAAAAATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGACC |
| 59 | delparR | AGACGCTAGCAAATTGCGAATCCTGCCCTAGTTCTAACCCCCCCATGTTTTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTCG |
| 60 | deloriF | AACCGAAAAATTTCGTACGTACGAAAAAACATGGGGGGGTTAGAACTAGGATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGACC |
| 61 | deloriR | GGGGGACAGGTGCAATTTTAGCACAAGCGGCGGCAGACGCTAGCAAATTGTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTCG |
| 62 | oriparF | GCCGAAGGCCAAAAGCCACTGCAAAACCGAAAAATTTCGTACGTACGAAAATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGACC |
| 63 | delkfrAF | ATGTATTGTATTAAAATACAATACATACAATACAGGGAGCCGAAGCCATGTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTCG |
| 64 | delkfrAR | CACTTTATCTGTTTACGTCAATAGATAGGGGTTACTCTTTGGTGTCGGCTGCATGGGAATTAGCCATGG |
| 65 | delkfrCF | CCTGGCAGGTTTCGGGGCTATATGGGACGCTGACCGGGATTGAAACCATGTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTCG |
| 66 | delkfrCR | AATGGCCGGGGTCGGTGACAGGGTAGCGGCTTCACCGCTCTAGATCGTCTTCATGGGAATTAGCCATGG |
| 67 | Kmpar1F | GGTGCAAAGACGCCGTGGAAGCGTGTGAGGTTGACTCGCGGCTTAGGTACATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGACC |
| 68 | Kmpar2R | TGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTCG |
| 69 | Kmpar3F | cgaacgagctccagcctacaCTTGCATGCCTGCAGGGTAC |
| 70 | Kmpar4R | CCCATGTGATCTTCGAGCCGCTGGACTTCATCGCCAAACTCGCTGCGTTGGGTACCCTGCCGGGGTTCTC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mitura, M.; Lewicka, E.; Godziszewska, J.; Adamczyk, M.; Jagura-Burdzy, G. Alpha-Helical Protein KfrC Acts as a Switch between the Lateral and Vertical Modes of Dissemination of Broad-Host-Range RA3 Plasmid from IncU (IncP-6) Incompatibility Group. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094880
Mitura M, Lewicka E, Godziszewska J, Adamczyk M, Jagura-Burdzy G. Alpha-Helical Protein KfrC Acts as a Switch between the Lateral and Vertical Modes of Dissemination of Broad-Host-Range RA3 Plasmid from IncU (IncP-6) Incompatibility Group. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(9):4880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094880
Chicago/Turabian StyleMitura, Monika, Ewa Lewicka, Jolanta Godziszewska, Malgorzata Adamczyk, and Grazyna Jagura-Burdzy. 2021. "Alpha-Helical Protein KfrC Acts as a Switch between the Lateral and Vertical Modes of Dissemination of Broad-Host-Range RA3 Plasmid from IncU (IncP-6) Incompatibility Group" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 9: 4880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094880
APA StyleMitura, M., Lewicka, E., Godziszewska, J., Adamczyk, M., & Jagura-Burdzy, G. (2021). Alpha-Helical Protein KfrC Acts as a Switch between the Lateral and Vertical Modes of Dissemination of Broad-Host-Range RA3 Plasmid from IncU (IncP-6) Incompatibility Group. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(9), 4880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094880






