Circulating Monocyte Subsets and Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Physiopathology of Aortic Valve Stenosis
3. Impact of Aortic Valve Stenosis on Hemodynamic Features of Blood Flow
4. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement and Complications
5. Markers for Predicting Post-TAVR Complications
6. Human Monocyte Heterogeneity
7. Monocyte Subsets and Cardiovascular Diseases
8. Monocyte Subsets and Aortic Valve Stenosis
9. Monocyte Subsets and Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
10. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement, Monocytes and Clonal Hematopoiesis of Indeterminate Potential
11. Preventive Therapy to Reduce Inflammation in Context of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goody, P.R.; Hosen, M.R.; Christmann, D.; Niepmann, S.T.; Zietzer, A.; Adam, M.; Bönner, F.; Zimmer, S.; Nickenig, G.; Jansen, F. Aortic Valve Stenosis: From Basic Mechanisms to Novel Therapeutic Targets. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, L.S.A.; Lupieri, A.; Becker-Greene, D.; Aikawa, E. Innate and adaptive immunity in cardiovascular calcification. Atherosclerosis 2020, 306, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grim, J.C.; Aguado, B.A.; Vogt, B.J.; Batan, D.; Andrichik, C.L.; Schroeder, M.E.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, A.; Yavitt, F.M.; Weiss, R.M.; Anseth, K.S. Secreted Factors from Proinflammatory Macrophages Promote an Osteoblast-Like Phenotype in Valvular Interstitial Cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, e296–e308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, C.M.; Kuusisto, J.; Reichenbach, D.D.; Gown, A.M.; O’Brien, K.D. Characterization of the early lesion of “degenerative” valvular aortic stenosis. Histological and immunohistochemical studies. Circulation 1994, 90, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, R.V.; Otto, C.M. Spectrum of Calcific Aortic Valve Disease. Circulation 2005, 111, 3316–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zebhi, B.; Lazkani, M.; Bark, D. Calcific Aortic Stenosis—A Review on Acquired Mechanisms of the Disease and Treatments. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 734175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, W.; Wang, Z.; Sun, C.; Zhang, D.-M. Pathogenesis and Molecular Immune Mechanism of Calcified Aortic Valve Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 765419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahanian, A.; Beyersdorf, F.; Praz, F.; Milojevic, M.; Baldus, S.; Bauersachs, J.; Capodanno, D.; Conradi, L.; De Bonis, M.; De Paulis, R.; et al. 2021 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 561–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, C.M.; Nishimura, R.A.; Bonow, R.O.; Carabello, B.A.; Erwin, J.P.; Gentile, F.; Jneid, H.; Krieger, E.V.; Mack, M.; McLeod, C.; et al. 2020 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Management of Patients with Valvular Heart Disease: Executive Summary. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 450–500. [Google Scholar]
- Rouleau, S.G.; Brady, W.J.; Koyfman, A.; Long, B. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement complications: A narrative review for emergency clinicians. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 56, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieniak, K.; Jędrzejczyk, S.; Domaszk, O.; Grodecki, K.; Rymuza, B.; Huczek, Z.; Kochman, J.; Filipiak, K.J.; Gąsecka, A. Predictors and Biomarkers of Subclinical Leaflet Thrombosis after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, H.; Mack, C.D.; Li, S.C.H.; Fletcher, J.P.; Medbury, H.J. Nature versus Number: Monocytes in Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Vorst, E.P.C.; Weber, C. Novel Features of Monocytes and Macrophages in Cardiovascular Biology and Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, e30–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ożańska, A.; Szymczak, D.; Rybka, J. Pattern of human monocyte subpopulations in health and disease. Scand. J. Immunol. 2020, 92, e12883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idzkowska, E.; Eljaszewicz, A.; Miklasz, P.; Musial, W.J.; Tycinska, A.M.; Moniuszko, M. The Role of Different Monocyte Subsets in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis and Acute Coronary Syndromes. Scand. J. Immunol. 2015, 82, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehu, M.; Narasimhulu, C.A.; Singla, D.K. Inflammatory Cells in Atherosclerosis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, B.F.; Siscovick, D.; Lind, B.K.; Gardin, J.M.; Gottdiener, J.S.; Smith, V.E.; Kitzman, D.W.; Otto, C.M. Clinical Factors Associated with Calcific Aortic Valve Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1997, 29, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindman, B.R.; Clavel, M.-A.; Mathieu, P.; Iung, B.; Lancellotti, P.; Otto, C.M.; Pibarot, P. Calcific aortic stenosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2016, 2, 16006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, S.; Cox, B.; Williams, M.J.A. The Prevalence, Incidence, Progression, and Risks of Aortic Valve Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2852–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, G.K. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Song, Z.; Han, L.; He, Y.; Xu, Z. MicroRNA-30b is a multifunctional regulator of aortic valve interstitial cells. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 1073–1080.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajamannan, N.M. Calcific Aortic Stenosis: A Disease Ready for Prime Time. Circulation 2006, 114, 2007–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Weston, M.W.; LaBorde, D.V.; Yoganathan, A.P. Estimation of the Shear Stress on the Surface of an Aortic Valve Leaflet. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1999, 27, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balachandran, K.; Sucosky, P.; Yoganathan, A.P. Hemodynamics and Mechanobiology of Aortic Valve Inflammation and Calcification. Int. J. Inflamm. 2011, 2011, 263870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäck, M.; Gasser, T.C.; Michel, J.-B.; Caligiuri, G. Biomechanical factors in the biology of aortic wall and aortic valve diseases. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 99, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ooij, P.; Markl, M.; Collins, J.D.; Carr, J.C.; Rigsby, C.; Bonow, R.O.; Malaisrie, S.C.; McCarthy, P.M.; Fedak, P.W.M.; Barker, A.J. Aortic Valve Stenosis Alters Expression of Regional Aortic Wall Shear Stress: New Insights from a 4-Dimensional Flow Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study of 571 Subjects. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareti, F.I.; Lattuada, A.; Bressi, C.; Zanobini, M.; Sala, A.; Steffan, A.; Ruggeri, Z.M. Proteolysis of Von Willebrand Factor and Shear Stress–Induced Platelet Aggregation in Patients with Aortic Valve Stenosis. Circulation 2000, 102, 1290–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Belle, E.; Vincent, F.; Rauch, A.; Casari, C.; Jeanpierre, E.; Loobuyck, V.; Rosa, M.; Delhaye, C.; Spillemaeker, H.; Paris, C.; et al. Von Willebrand Factor and Management of Heart Valve Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siediecki, C.; Lestini, B.; Kottke-Marchant, K.; Eppell, S.; Wilson, D.; Marchant, R. Shear-dependent changes in the three-dimensional structure of human von Willebrand factor. Blood 1996, 88, 2939–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.; Sussman, I.; Nagel, R. Shear stress enhances the proteolysis of von Willebrand factor in normal plasma. Blood 1994, 83, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincentelli, A.; Susen, S.; Le Tourneau, T.; Six, I.; Fabre, O.; Juthier, F.; Bauters, A.; Decoene, C.; Goudemand, J.; Prat, A.; et al. Acquired von Willebrand syndrome in aortic stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warkentin, T.E.; Moore, J.C.; Morgan, D.G. Aortic stenosis and bleeding gastrointestinal angiodysplasia: Is acquired von Willebrand’s disease the link? Lancet Lond. Engl. 1992, 340, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyde, E. Gastrointestinal Bleeding in Aortic Stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1958, 259, 196. [Google Scholar]
- Love, J.; Jahnke, E.; Zacharias, D.; Davidson, W.; Kidder, W.; Luan, L. Calcific Aortic Stenosis and Gastrointestinal Bleeding. N. Engl. J. Med. 1980, 302, 968. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Godino, C.; Lauretta, L.; Pavon, A.G.; Mangieri, A.; Viani, G.; Chieffo, A.; Galaverna, S.; Latib, A.; Montorfano, M.; Cappelletti, A.; et al. Heyde’s Syndrome Incidence and Outcome in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 687–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, R.A.; Lwaleed, B.A.; Kazmi, R.S. Gastrointestinal Bleeding and Aortic Stenosis (Heyde Syndrome): The Role of Aortic Valve Replacement: Gastrointestinal Bleeding and Aortic Stenosis. J. Card. Surg. 2013, 28, 414–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, M.B.; Smith, C.R.; Mack, M.; Miller, D.C.; Moses, J.W.; Svensson, L.G.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Webb, J.G.; Fontana, G.P.; Makkar, R.R.; et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve implantation for aortic stenosis in patients who cannot undergo surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Belle, E.; Rauch, A.; Vincent, F.; Robin, E.; Kibler, M.; Labreuche, J.; Jeanpierre, E.; Levade, M.; Hurt, C.; Rousse, N.; et al. Von Willebrand Factor Multimers during Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Replacement. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodés-Cabau, J.; Dauerman, H.L.; Cohen, M.G.; Mehran, R.; Small, E.M.; Smyth, S.S.; Costa, M.A.; Mega, J.L.; O’Donoghue, M.L.; Ohman, E.M.; et al. Antithrombotic Treatment in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Insights for Cerebrovascular and Bleeding Events. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 2349–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Belle, E.; Hengstenberg, C.; Lefevre, T.; Kupatt, C.; Debry, N.; Husser, O.; Pontana, F.; Kuchcinski, G.; Deliargyris, E.N.; Mehran, R.; et al. Cerebral Embolism during Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: The BRAVO-3 MRI Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedeney, P.; Mehran, R.; Collet, J.-P.; Claessen, B.E.; ten Berg, J.; Dangas, G.D. Antithrombotic Therapy after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 12, e007411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapadia, S.; Agarwal, S.; Miller, D.C.; Webb, J.G.; Mack, M.; Ellis, S.; Herrmann, H.C.; Pichard, A.D.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Svensson, L.G.; et al. Insights into Timing, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in the PARTNER Trial. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2016, 9, e002981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlert, P.; Knipp, S.C.; Schlamann, M.; Thielmann, M.; Al-Rashid, F.; Weber, M.; Johansson, U.; Wendt, D.; Jakob, H.G.; Forsting, M.; et al. Silent and Apparent Cerebral Ischemia after Percutaneous Transfemoral Aortic Valve Implantation: A Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Circulation 2010, 121, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uriel, N.; Pak, S.-W.; Jorde, U.P.; Jude, B.; Susen, S.; Vincentelli, A.; Ennezat, P.-V.; Cappleman, S.; Naka, Y.; Mancini, D. Acquired von Willebrand syndrome after continuous-flow mechanical device support contributes to a high prevalence of bleeding during long-term support and at the time of transplantation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Belle, E.; Rauch, A.; Vincentelli, A.; Jeanpierre, E.; Legendre, P.; Juthier, F.; Hurt, C.; Banfi, C.; Rousse, N.; Godier, A.; et al. Von Willebrand Factor as a Biological Sensor of Blood Flow to Monitor Percutaneous Aortic Valve Interventions. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawaya, F.; Jørgensen, T.H.; Søndergaard, L.; De Backer, O. Transcatheter Bioprosthetic Aortic Valve Dysfunction: What We Know So Far. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 6, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbe, A.C.; Pislaru, S.V.; Pellikka, P.A.; Poterucha, J.T.; Schaff, H.V.; Maleszewski, J.J.; Connolly, H.M. Bioprosthetic Valve Thrombosis Versus Structural Failure: Clinical and Echocardiographic Predictors. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 2285–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, R.R.; Thourani, V.H.; Mack, M.J.; Kodali, S.K.; Kapadia, S.; Webb, J.G.; Yoon, S.-H.; Trento, A.; Svensson, L.G.; Herrmann, H.C.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes of Transcatheter or Surgical Aortic-Valve Replacement. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, G.; Shamekhi, J.; Al-Kassou, B.; Tabata, N.; Parco, C.; Klein, K.; Maier, O.; Sedaghat, A.; Polzin, A.; Sugiura, A.; et al. Risk modeling in transcatheter aortic valve replacement remains unsolved: An external validation study in 2946 German patients. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2021, 110, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockburn, J.; Dooley, M.; de Belder, A.; Trivedi, U.; Hildick-Smith, D. A comparison between surgical risk scores for predicting outcome in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 58, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindman, B.R.; Breyley, J.G.; Schilling, J.D.; Vatterott, A.M.; Zajarias, A.; Maniar, H.S.; Damiano, R.J.; Moon, M.R.; Lawton, J.S.; Gage, B.F.; et al. Prognostic utility of novel biomarkers of cardiovascular stress in patients with aortic stenosis undergoing valve replacement. Heart Br. Card. Soc. 2015, 101, 1382–1388. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, K.; Okura, H.; Kume, T.; Yamada, R.; Miyamoto, Y.; Kawamoto, T.; Watanabe, N.; Neishi, Y.; Toyota, E.; Yoshida, K. C-Reactive protein predicts severity, progression, and prognosis of asymptomatic aortic valve stenosis. Am. Heart J. 2008, 156, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahraman, S.; Can Dogan, A.; Demirci, G.; Riza Demir, A.; Yilmaz, E.; Zencirkiran Agus, H.; Kemal Kalkan, A.; Uzun, F.; Erturk, M. The Prognostic Value of C-reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio in Patients with Isolated Degenerative Aortic Valve Stenosis Undergoing Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement. Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 35, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, H.; Kuno, T.; Hari, Y.; Nakashima, K.; Yokoyama, Y.; Ueyama, H.; Ando, T.; ALICE (All-Literature Investigation of Cardiovascular Evidence) Group. Prognostic impact of baseline C-reactive protein levels on mortality after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. J. Card. Surg. 2020, 35, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hioki, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Kozuma, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Naganuma, T.; Araki, M.; Tada, N.; Shirai, S.; Yamanaka, F.; Higashimori, A.; et al. Effect of Serum C-Reactive Protein Level on Admission to Predict Mortality after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2018, 122, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navani, R.V.; Quine, E.J.; Duffy, S.J.; Htun, N.M.; Nanayakkara, S.; Walton, A.S.; Stub, D. Relation of Preprocedure Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation for Aortic Stenosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2022, 163, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Han, S.; Zhou, L. The prognostic value of the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in acute coronary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Kardiol. Pol. 2017, 75, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condado, J.F.; Junpaparp, P.; Binongo, J.N.; Lasanajak, Y.; Witzke-Sanz, C.F.; Devireddy, C.; Leshnower, B.; Mavromatis, K.; Stewart, J.; Guyton, R.; et al. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) can risk stratify patients in transcatheter aortic-valve replacement (TAVR). Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 223, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosu, A.; Cinar, T.; Guler, A.; Kahraman, S.; Gurbak, I. The predictive value of platelet to lymphocyte ratio for procedural complications and mid-term mortality in aortic stenosis patients who underwent a transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Ann. Med. Res. 2019, 26, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, C.; Pham, M.; Sawant, A.C.; Sinibaldi, E.; Bhardwaj, A.; Ramanan, T.; Qureshi, R.; Khan, S.; Ibrahim, A.; Gowda, S.N.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts heart failure readmissions and outcomes in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Indian Heart J. 2018, 70, S313–S318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinas, K.C.; O’Sullivan, C.J.; Heg, D.; Praz, F.; Stortecky, S.; Pilgrim, T.; Buellesfeld, L.; Jüni, P.; Windecker, S.; Wenaweser, P. Effect of B-Type Natriuretic Peptides on Long-Term Outcomes after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 116, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krau, N.-C.; Lünstedt, N.-S.; Freitag-Wolf, S.; Brehm, D.; Petzina, R.; Lutter, G.; Bramlage, P.; Dempfle, A.; Frey, N.; Frank, D. Elevated growth differentiation factor 15 levels predict outcome in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation: GDF15 predicts outcome in TAVI patients. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinning, J.-M.; Wollert, K.C.; Sedaghat, A.; Widera, C.; Radermacher, M.-C.; Descoups, C.; Hammerstingl, C.; Weber, M.; Stundl, A.; Ghanem, A.; et al. Risk scores and biomarkers for the prediction of 1-year outcome after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Am. Heart J. 2015, 170, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oury, C.; Nchimi, A.; Lancellotti, P.; Bergler-Klein, J. Can Blood Biomarkers Help Predicting Outcome in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation? Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingersoll, M.A.; Platt, A.M.; Potteaux, S.; Randolph, G.J. Monocyte trafficking in acute and chronic inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock, L.; Hofer, T.P. Toward a Refined Definition of Monocyte Subsets. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyette, L.B.; Macedo, C.; Hadi, K.; Elinoff, B.D.; Walters, J.T.; Ramaswami, B.; Chalasani, G.; Taboas, J.M.; Lakkis, F.G.; Metes, D.M. Phenotype, function, and differentiation potential of human monocyte subsets. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connaughton, E.P.; Naicker, S.; Hanley, S.A.; Slevin, S.M.; Eykelenboom, J.K.; Lowndes, N.F.; O’Brien, T.; Ceredig, R.; Griffin, M.D.; Dennedy, M.C. Phenotypic and functional heterogeneity of human intermediate monocytes based on HLA-DR expression. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 742–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.; Tacke, R.; Hedrick, C.C.; Hanna, R.N. Nonclassical Patrolling Monocyte Function in the Vasculature. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormican, S.; Griffin, M.D. Human Monocyte Subset Distinctions and Function: Insights from Gene Expression Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cros, J.; Cagnard, N.; Woollard, K.; Patey, N.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Senechal, B.; Puel, A.; Biswas, S.K.; Moshous, D.; Picard, C.; et al. Human CD14dim Monocytes Patrol and Sense Nucleic Acids and Viruses via TLR7 and TLR8 Receptors. Immunity 2010, 33, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.L.; Tai, J.J.-Y.; Wong, W.-C.; Han, H.; Sem, X.; Yeap, W.-H.; Kourilsky, P.; Wong, S.-C. Gene expression profiling reveals the defining features of the classical, intermediate, and nonclassical human monocyte subsets. Blood 2011, 118, e16–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawada, A.M.; Rogacev, K.S.; Rotter, B.; Winter, P.; Marell, R.-R.; Fliser, D.; Heine, G.H. SuperSAGE evidence for CD14++ CD16+ monocytes as a third monocyte subset. Blood 2011, 118, e50–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugeri, N.; Brambilla, M.; Camera, M.; Carbone, A.; Tremoli, E.; Donati, M.B.; Gaetano, G.D.; Cerletti, C. Human polymorphonuclear leukocytes produce and express functional tissue factor upon stimulation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, F.S.M.; Whyte, C.S.; Tuncay, A.; Williams, M.-L.; Wilson, H.M.; Mutch, N.J. Monocytes Expose Factor XIII-A and Stabilize Thrombi against Fibrinolytic Degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seillier, C.; Hélie, P.; Petit, G.; Vivien, D.; Clemente, D.; Le Mauff, B.; Docagne, F.; Toutirais, O. Roles of the tissue-type plasminogen activator in immune response. Cell. Immunol. 2022, 371, 104451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaertner, F.; Massberg, S. Blood coagulation in immunothrombosis—At the frontline of intravascular immunity. Semin. Immunol. 2016, 28, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbousset, R.; Thomas, G.M.; Mezouar, S.; Frère, C.; Bonier, R.; Mackman, N.; Renné, T.; Dignat-George, F.; Dubois, C.; Panicot-Dubois, L. Tissue factor–positive neutrophils bind to injured endothelial wall and initiate thrombus formation. Blood 2012, 120, 2133–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, I.; Klocke, A.; Alex, M.; Kotzsch, M.; Luther, T.; Morgenstern, E.; Zieseniss, S.; Zahler, S.; Preissner, K.; Engelmann, B. Intravascular tissue factor initiates coagulation via circulating microvesicles and platelets. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Simon, D.I. Inflammation and Thrombosis. Circulation 2001, 103, 1718–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.S.; Na, M.; Rogers, C.J. The Association between Monocyte Subsets and Cardiometabolic Disorders/Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 640124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeynalova, S.; Bucksch, K.; Scholz, M.; Yahiaoui-Doktor, M.; Gross, M.; Löffler, M.; Melzer, S.; Tárnok, A. Monocyte subtype counts are associated with 10-year cardiovascular disease risk as determined by the Framingham Risk Score among subjects of the LIFE-Adult study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wildgruber, M.; Aschenbrenner, T.; Wendorff, H.; Czubba, M.; Glinzer, A.; Haller, B.; Schiemann, M.; Zimmermann, A.; Berger, H.; Eckstein, H.-H.; et al. The “Intermediate” CD14++ CD16+ monocyte subset increases in severe peripheral artery disease in humans. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elchinova, E.; Teubel, I.; Roura, S.; Fernández, M.A.; Lupón, J.; Gálvez-Montón, C.; de Antonio, M.; Moliner, P.; Domingo, M.; Zamora, E.; et al. Circulating monocyte subsets and heart failure prognosis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogacev, K.S.; Cremers, B.; Zawada, A.M.; Seiler, S.; Binder, N.; Ege, P.; Große-Dunker, G.; Heisel, I.; Hornof, F.; Jeken, J.; et al. CD14++ CD16+ Monocytes Independently Predict Cardiovascular Events. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, Y.; Imanishi, T.; Hosokawa, S.; Nishiguchi, T.; Taruya, A.; Tanimoto, T.; Kuroi, A.; Yamano, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Ino, Y.; et al. Association of Toll-Like Receptor 4 on Human Monocyte Subsets and Vulnerability Characteristics of Coronary Plaque as Assessed by 64-Slice Multidetector Computed Tomography. Circ. J. 2017, 81, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, T.; Ikejima, H.; Tsujioka, H.; Kuroi, A.; Ishibashi, K.; Komukai, K.; Tanimoto, T.; Ino, Y.; Takeshita, T.; Akasaka, T. Association of monocyte subset counts with coronary fibrous cap thickness in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Atherosclerosis 2010, 212, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoni, S.; Meledin, V.; Bar, I.; Fabricant, J.; Gandelman, G.; George, J. Circulating CD14(+) monocytes in patients with aortic stenosis. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. JGC 2016, 13, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Efe, T.H.; Gayretli Yayla, K.; Yayla, C.; Ertem, A.G.; Cimen, T.; Erken Pamukcu, H.; Bilgin, M.; Erat, M.; Dogan, M.; Yeter, E. Calcific aortic stenosis and its correlation with a novel inflammatory marker, the lymphocyte/monocyte ratio. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2016, 35, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewing, B.; Au, S.C.-D.; Ludwig, A.; Ellerbroek, R.; van Dijck, P.; Hartmann, L.; Grubitzsch, H.; Giannini, C.; Laule, M.; Stangl, V.; et al. Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis in Adults is Associated with Increased Levels of Circulating Intermediate Monocytes. J Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2017, 10, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewing, B.; Ellerbroek, R.; Au, S.; Stangl, V.; Dreger, H.; Laule, M.; Grubitzsch, H.; Knebel, F.; Baumann, G.; Ludwig, A.; et al. Levels of Circulating Intermediate Monocytes Decrease after Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients with Severe Aortic Stenosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 2346–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuser, J.; Galuppo, P.; Fraccarollo, D.; Willig, J.; Kempf, T.; Berliner, D.; Bauersachs, J.; Widder, J.D. Intermediate CD14++ CD16+ monocytes decline after transcatheter aortic valve replacement and correlate with functional capacity and left ventricular systolic function. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfluecke, C.; Wydra, S.; Berndt, K.; Tarnowski, D.; Cybularz, M.; Jellinghaus, S.; Mierke, J.; Ende, G.; Poitz, D.M.; Barthel, P.; et al. Mon2-monocytes and increased CD-11b expression before transcatheter aortic valve implantation are associated with earlier death. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 318, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybularz, M.; Wydra, S.; Berndt, K.; Poitz, D.M.; Barthel, P.; Alkouri, A.; Heidrich, F.M.; Ibrahim, K.; Jellinghaus, S.; Speiser, U.; et al. Frailty is associated with chronic inflammation and pro-inflammatory monocyte subpopulations. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 149, 111317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Mas-Peiro, S.; Berkowitsch, A.; Boeckling, F.; Rasper, T.; Pieszko, K.; De Rosa, R.; Hiczkiewicz, J.; Burchardt, P.; Fichtlscherer, S.; et al. Inflammatory signatures are associated with increased mortality after transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve implantation. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 2597–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baratchi, S.; Zaldivia, M.T.K.; Wallert, M.; Loseff-Silver, J.; Al-Aryahi, S.; Zamani, J.; Thurgood, P.; Salim, A.; Htun, N.M.; Stub, D.; et al. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Represents an Anti-Inflammatory Therapy via Reduction of Shear Stress–Induced, Piezo-1–Mediated Monocyte Activation. Circulation 2020, 142, 1092–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amancherla, K.; Wells, J.A.; Bick, A.G. Clonal hematopoiesis and vascular disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 2022, 44, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimlich, J.B.; Bick, A.G. Somatic Mutations in Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2022, 130, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, S.; Natarajan, P.; Silver, A.J.; Gibson, C.J.; Bick, A.G.; Shvartz, E.; McConkey, M.; Gupta, N.; Gabriel, S.; Ardissino, D.; et al. Clonal Hematopoiesis and Risk of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, I.; Tanaka, T.; Glass, C.K.; Yeang, C. Clonal hematopoiesis driven by DNMT3A and TET2 mutations: Role in monocyte and macrophage biology and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2022, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, J.J.; MacLauchlan, S.; Zuriaga, M.A.; Polackal, M.N.; Ostriker, A.C.; Chakraborty, R.; Wu, C.-L.; Sano, S.; Muralidharan, S.; Rius, C.; et al. Clonal hematopoiesis associated with TET2 deficiency accelerates atherosclerosis development in mice. Science 2017, 355, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscarlet, M.; Provost, S.; Zada, Y.F.; Bourgoin, V.; Mollica, L.; Dubé, M.-P.; Busque, L. Lineage restriction analyses in CHIP indicate myeloid bias for TET2 and multipotent stem cell origin for DNMT3A. Blood 2018, 132, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, S.; Oshima, K.; Wang, Y.; MacLauchlan, S.; Katanasaka, Y.; Sano, M.; Zuriaga, M.A.; Yoshiyama, M.; Goukassian, D.; Cooper, M.A.; et al. Tet2-Mediated Clonal Hematopoiesis Accelerates Heart Failure through a Mechanism Involving the IL-1β/NLRP3 Inflammasome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Peiro, S.; Hoffmann, J.; Fichtlscherer, S.; Dorsheimer, L.; Rieger, M.A.; Dimmeler, S.; Vasa-Nicotera, M.; Zeiher, A.M. Clonal haematopoiesis in patients with degenerative aortic valve stenosis undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, R.; Kanti Barman, P.; Kumar Thatoi, P.; Tripathy, R.; Kumar Das, B.; Ravindran, B. Non-Classical Monocytes Display Inflammatory Features: Validation in Sepsis and Systemic Lupus Erythematous. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abplanalp, W.T.; Mas-Peiro, S.; Cremer, S.; John, D.; Dimmeler, S.; Zeiher, A.M. Association of Clonal Hematopoiesis of Indeterminate Potential with Inflammatory Gene Expression in Patients with Severe Degenerative Aortic Valve Stenosis or Chronic Postischemic Heart Failure. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluba-Brzózka, A.; Franczyk, B.; Rysz-Górzyńska, M.; Ławiński, J.; Rysz, J. Emerging Anti-Atherosclerotic Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiane, A.; Daskalopoulou, S.S. Targeting the residual cardiovascular risk by specific anti-inflammatory interventions as a therapeutic strategy in atherosclerosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 178, 106157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P. Interleukin-1 Beta as a Target for Atherosclerosis Therapy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 2278–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Everett, B.M.; Thuren, T.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Chang, W.H.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Nicolau, J.; Koenig, W.; Anker, S.D.; et al. Antiinflammatory Therapy with Canakinumab for Atherosclerotic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, C.; Soehnlein, O. The potential of chronopharmacology for treatment of atherosclerosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2018, 29, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, T.; Mao, C.; Wang, Y.; Han, Z.; Chen, K.; Zhang, J.; Fan, Y.; Gu, J.; et al. MicroRNA-21 deficiency attenuated atherogenesis and decreased macrophage infiltration by targeting Dusp-8. Atherosclerosis 2019, 291, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Bungau, S.; Kumar, K.; Zengin, G.; Khan, F.; Kumar, A.; Kaur, R.; Venkatachalam, T.; Tit, D.M.; Vesa, C.M.; et al. Pleotropic Effects of Polyphenols in Cardiovascular System. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naruszewicz, M.; Łaniewska, I.; Millo, B.; Dłużniewski, M. Combination therapy of statin with flavonoids rich extract from chokeberry fruits enhanced reduction in cardiovascular risk markers in patients after myocardial infraction (MI). Atherosclerosis 2007, 194, e179–e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, F.; Barani, M.; Mukhtar, M.; Rahdar, A.; Cucchiarini, M.; Zafar, M.N.; Behl, T.; Bungau, S. Nanodiagnosis and Nanotreatment of Cardiovascular Diseases: An Overview. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashiro, S.; Matoba, T.; Umezu, R.; Koga, J.; Tokutome, M.; Katsuki, S.; Nakano, K.; Sunagawa, K.; Egashira, K. Pioglitazone-Incorporated Nanoparticles Prevent Plaque Destabilization and Rupture by Regulating Monocyte/Macrophage Differentiation in ApoE−/− Mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Long-Term Intervention with Pravastatin in Ischaemic Disease (LIPID) Study Group. Prevention of Cardiovascular Events and Death with Pravastatin in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease and a Broad Range of Initial Cholesterol Levels. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, G.; Toth, P.P.; Bungau, S.; Behl, T.; Ilie, M.; Pantea Stoian, A.; Bratu, O.G.; Bacalbasa, N.; Rus, M.; Diaconu, C.C. Cardiovascular Risk and Statin Therapy Considerations in Women. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossebø, A.B.; Pedersen, T.R.; Boman, K.; Brudi, P.; Chambers, J.B.; Egstrup, K.; Gerdts, E.; Gohlke-Bärwolf, C.; Holme, I.; Kesäniemi, Y.A.; et al. Intensive Lipid Lowering with Simvastatin and Ezetimibe in Aortic Stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1343–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefieva, T.I.; Filatova, A.Y.; Potekhina, A.V.; Shchinova, A.M. Immunotropic Effects and Proposed Mechanism of Action for 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A Reductase Inhibitors (Statins). Biochem. Biokhimiia 2018, 83, 874–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peri-Okonny, P.A.; Liu, Y.; Malaisrie, S.C.; Huded, C.P.; Kapadia, S.; Thourani, V.H.; Kodali, S.K.; Webb, J.; McAndrew, T.C.; Leon, M.B.; et al. Association of Statin Use and Mortality after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huded, C.P.; Benck, L.R.; Stone, N.J.; Sweis, R.N.; Ricciardi, M.J.; Malaisrie, S.C.; Davidson, C.J.; Flaherty, J.D. Relation of Intensity of Statin Therapy and Outcomes after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 119, 1832–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Kozuma, K.; Kataoka, A.; Hioki, H.; Nagura, F.; Fumiaki, Y.; Shirai, S.; Tada, N.; Yamawaki, M.; et al. Comparison of long-term mortality in patients who underwent transcatheter aortic valve replacement with or without anti-atherosclerotic therapy. Heart Vessels 2021, 36, 1892–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Dargham, S.; Al Suwaidi, J.; Jneid, H.; Abi Khalil, C. Trends and Outcomes of Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients with Diabetes in the US. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 844068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Ohno, Y.; Miyamoto, J.; Ikari, Y.; Tada, N.; Naganuma, T.; Yamawaki, M.; Yamanaka, F.; Shirai, S.; Mizutani, K.; et al. Impact of diabetes mellitus on outcome after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: Identifying high-risk diabetic population from the OCEAN-TAVI registry. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 98, E1058–E1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Monocyte Subsets | Classical Monocytes | Intermediate MONOCYTES | Non-Classical Monocytes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Schematic representation | 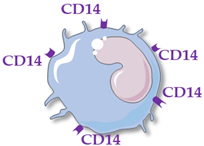 |  | 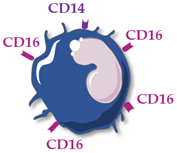 |
| Surface receptors | CD14++ CD16− | CD14++ CD16+ | CD14+ CD16++ |
| Proportion of total monocytes | 85–90% | 5–10% | 5–10% |
| Main functions | Phagocytosis, tissue repair, inflammation, reactive oxygen species production | Antigen presentation, T-cell proliferation and stimulation, reactive oxygen species production, phagocytosis | Patrolling of endothelial cell integrity, clearance of dying endothelial cells, wound healing |
| Cytokine production | IL-10, IL-6 | TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6 | TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6 |
| Number; Origin of Patients | Age; Gender Proportion | STS Score (%) EuroSCORE II (%) | Time of Blood Sampling | Classical Monocytes | Intermediate Monocytes | Non-Classical Monocytes | Association with Outcomes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 44; Germany, single center | 80.2 ± 6.1; 50% male | 2.5 (1.4–3.9); 3.6 (2.3–5.7) | Pre-TAVR | Not available | Hewing [91] | |||
| 3 months * | = | ↘ | = | |||||
| 6 months * | = | ↘ | = | |||||
| 57; Germany, single center | 83.3 ± 0.79; 47% male | 5.97 ± 0.39; 6.71 ± 0.65 | Pre-TAVR | High levels of intermediate monocytes pre-procedure associated with worse cardiac function and lower probability to reach an improvement in NYHA 3 months after TAVR | Neuser [92] | |||
| Day 4 to 7 * | = | ↘ | = | |||||
| 120; Germany, single center | 81; 33% male | >4 | Pre-TAVR | No comparison between times | High levels of intermediate monocytes pre-procedure associated with 3-month mortality | Pfluecke [93] Cybularz [94] | ||
| 24 h * | ||||||||
| Day 7 * | ||||||||
| 129; Germany, single center | 83 (79–86); 76% male | 3.41 (2.45–4.94) 3.31 (2.31–6.04) | Pre-TAVR | High levels of intermediate monocytes pre-procedure trended to be predictive of 12-month mortality and high levels of non-classical monocytes post-procedure associated with 12-month mortality | Hoffmann [95] | |||
| 24 h * | ↗ | ↗ | ↗ | |||||
| Day 3 * | ↗ | ↗ | ↗ | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lassalle, F.; Rosa, M.; Staels, B.; Van Belle, E.; Susen, S.; Dupont, A. Circulating Monocyte Subsets and Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105303
Lassalle F, Rosa M, Staels B, Van Belle E, Susen S, Dupont A. Circulating Monocyte Subsets and Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(10):5303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105303
Chicago/Turabian StyleLassalle, Fanny, Mickael Rosa, Bart Staels, Eric Van Belle, Sophie Susen, and Annabelle Dupont. 2022. "Circulating Monocyte Subsets and Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 10: 5303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105303
APA StyleLassalle, F., Rosa, M., Staels, B., Van Belle, E., Susen, S., & Dupont, A. (2022). Circulating Monocyte Subsets and Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(10), 5303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105303






