Maternal and Fetal Bile Acid Homeostasis Regulated by Sulfated Progesterone Metabolites through FXR Signaling Pathway in a Pregnant Sow Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
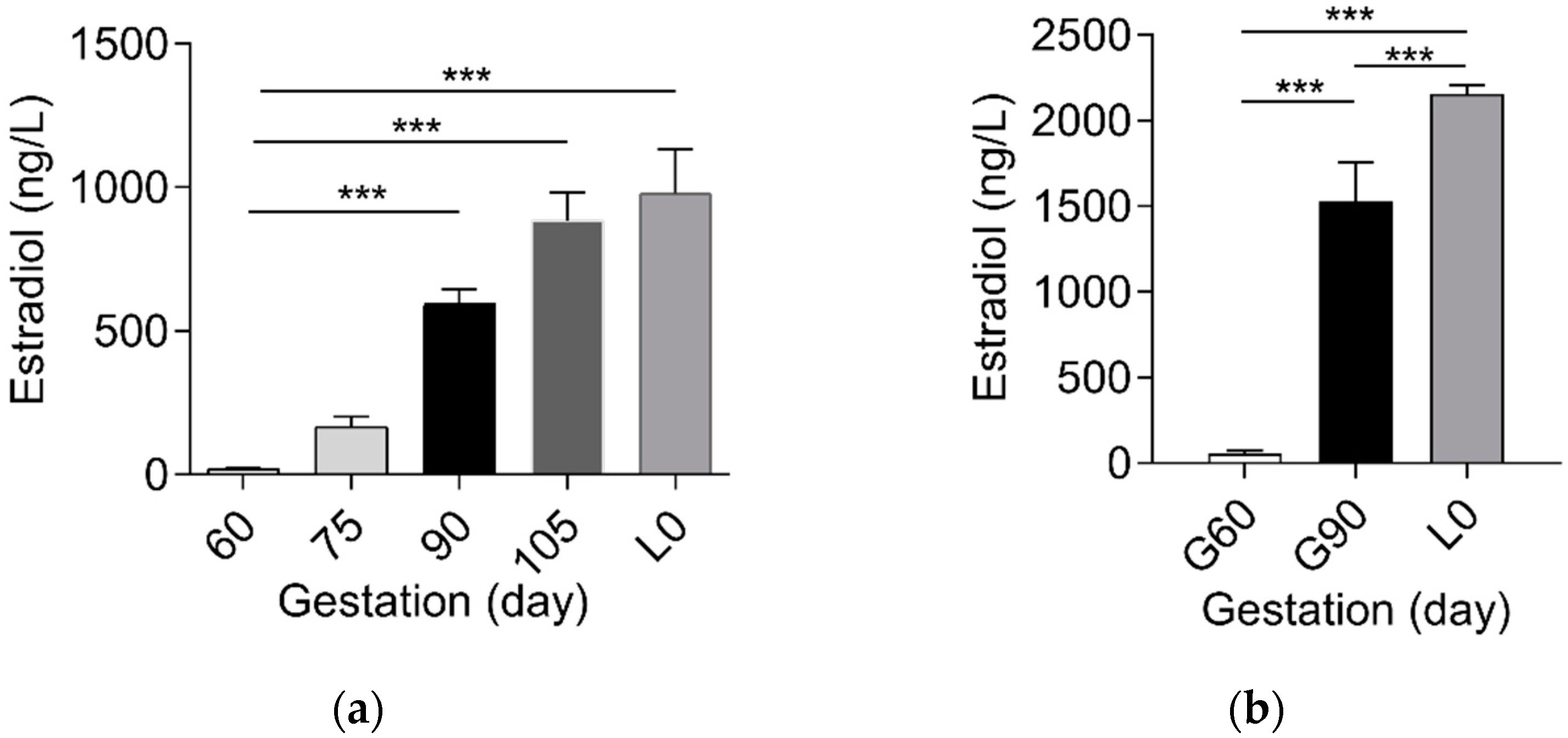
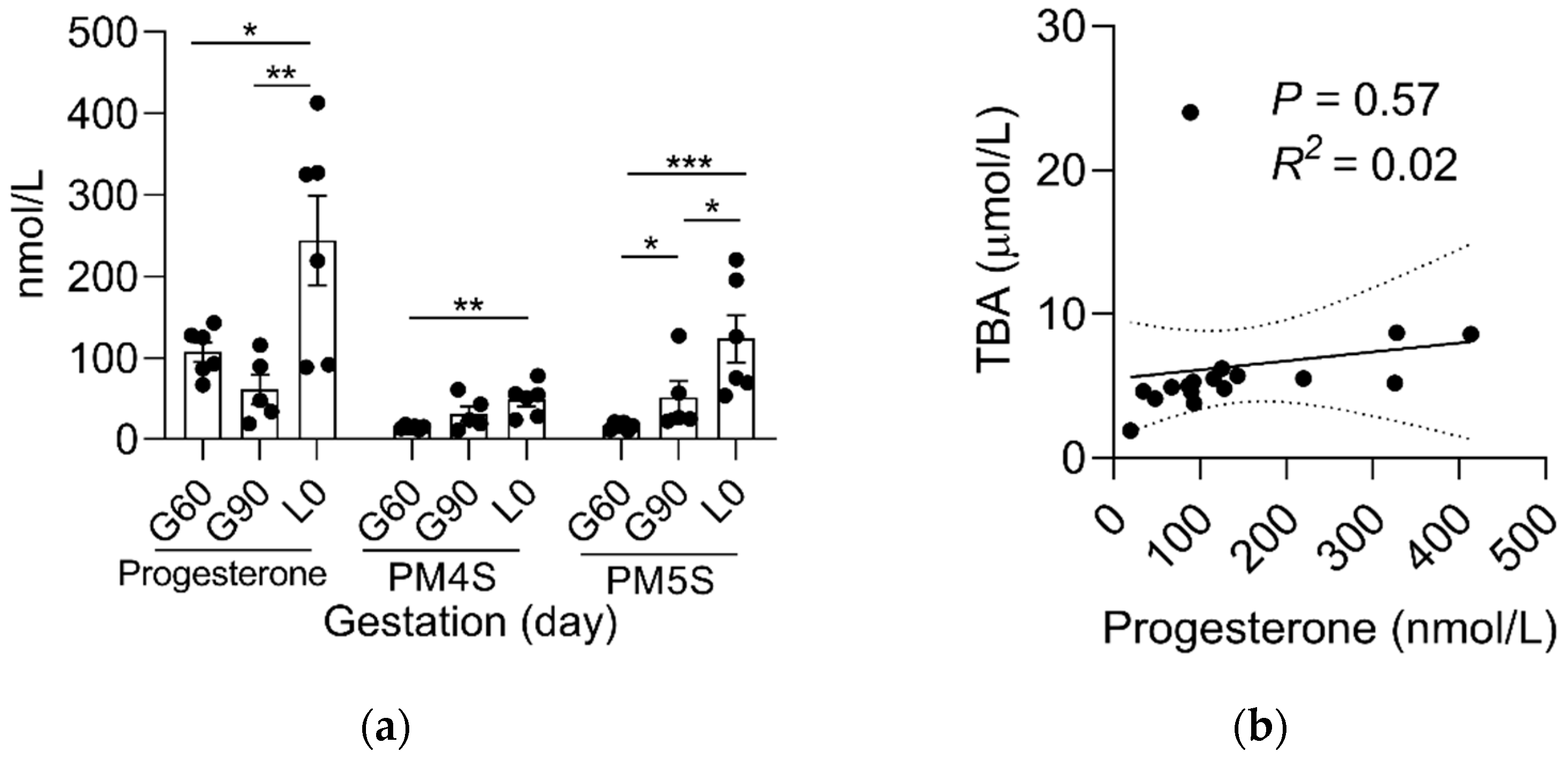
2.1. Sulfated Progesterone Metabolism in Mother during Pregnancy
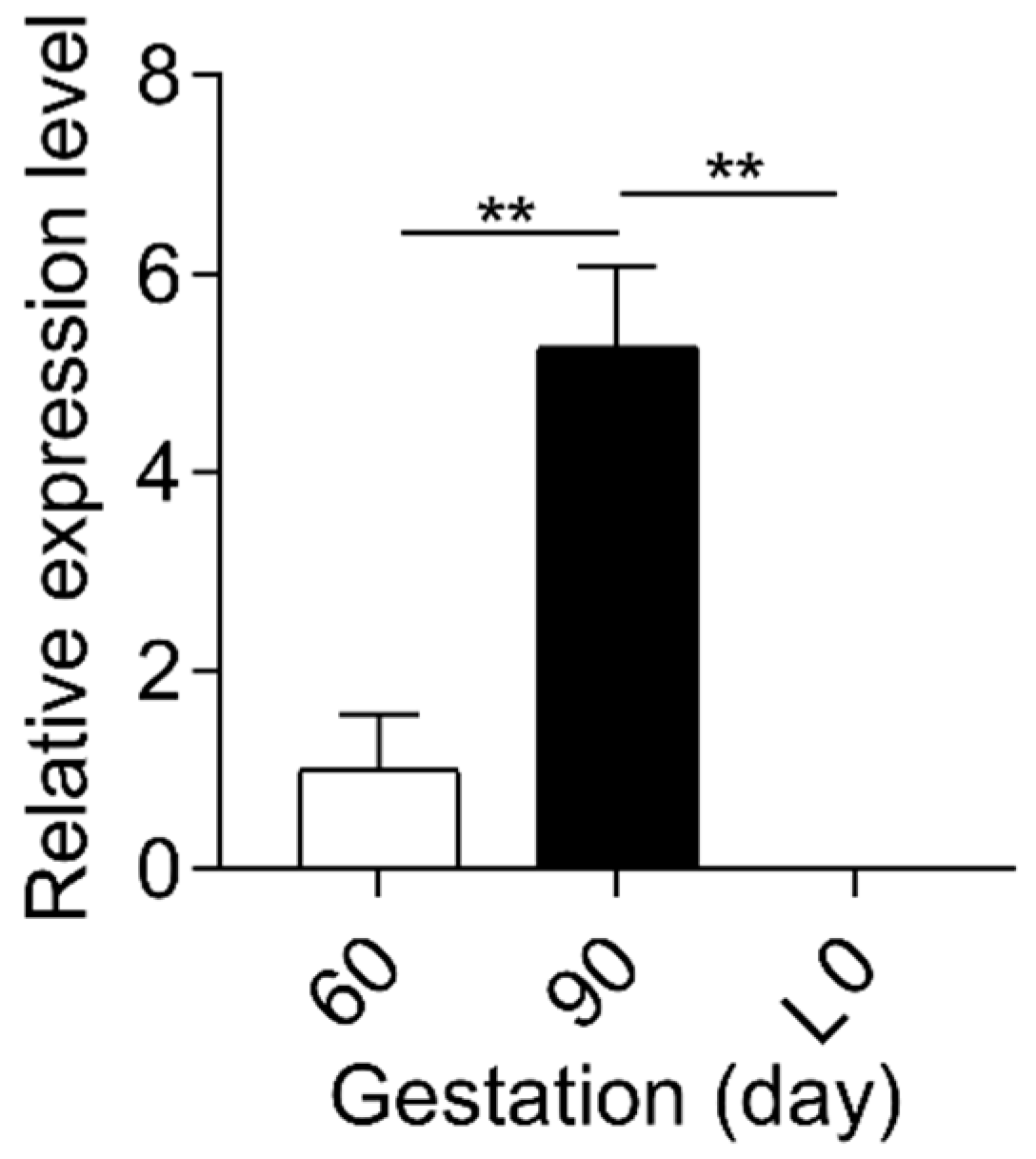
2.2. Sulfated Progesterone Metabolism in Fetuses during Pregnancy
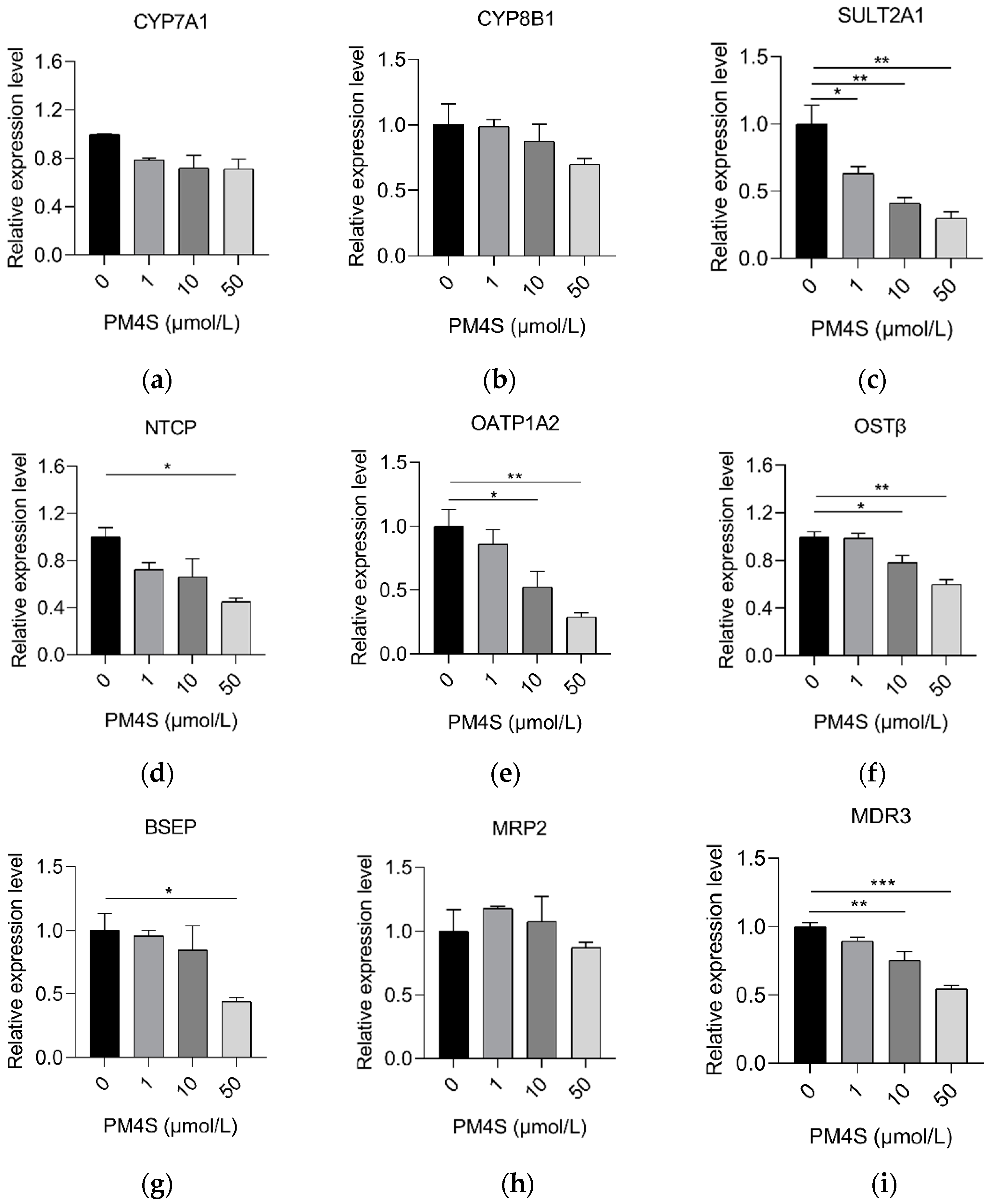
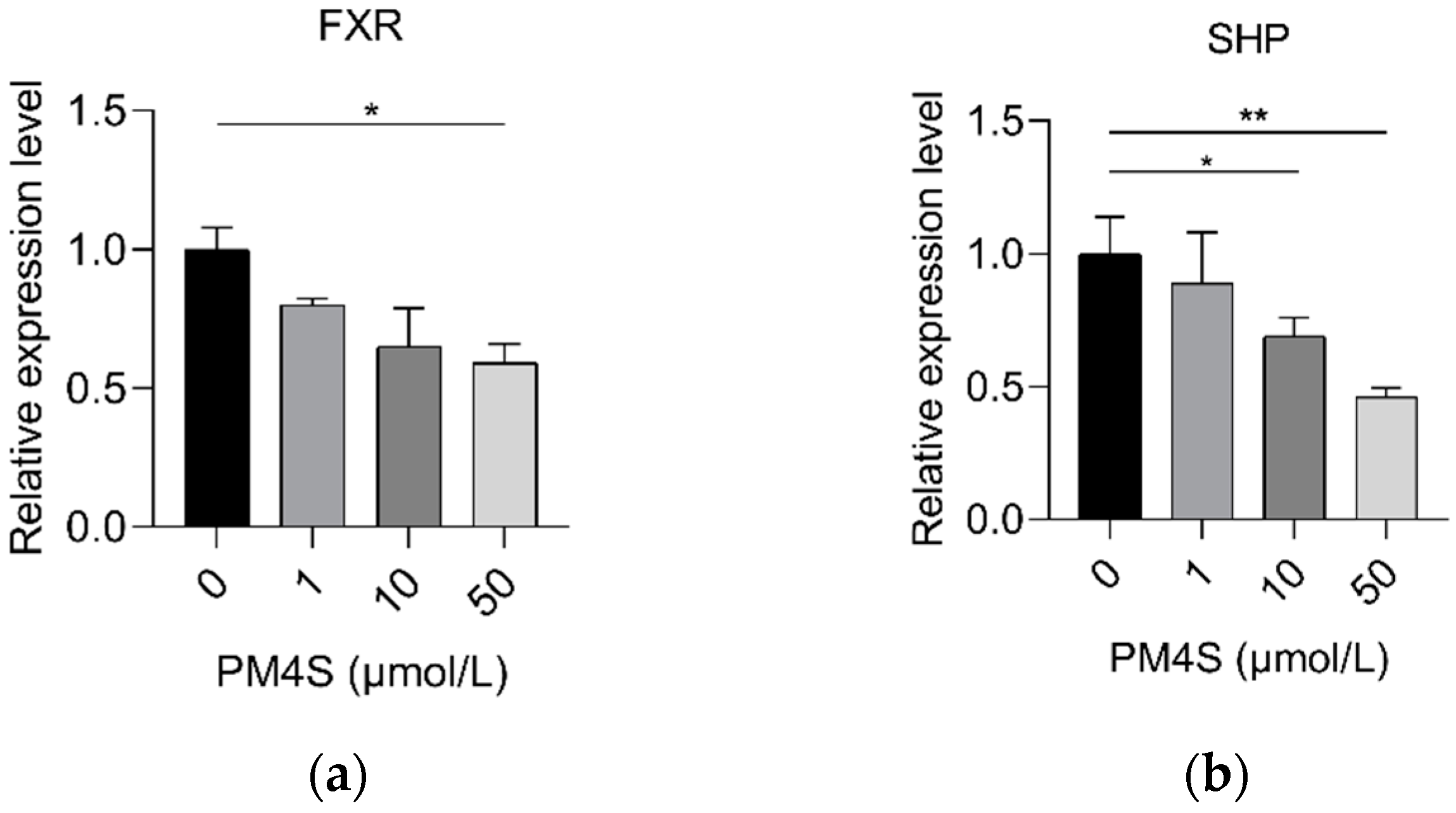
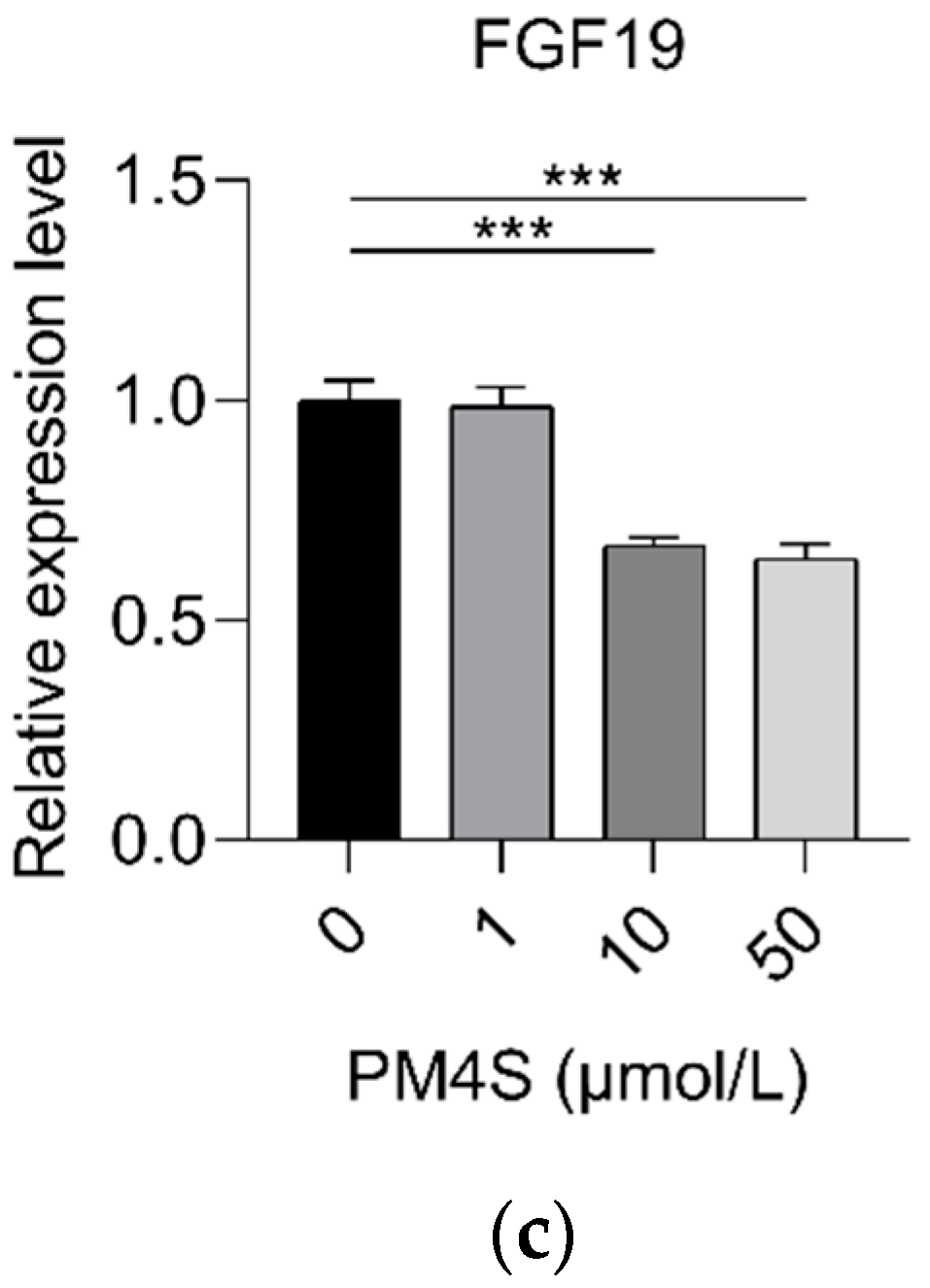
2.3. PM4S Inhibits FXR-Mediated BA Metabolism
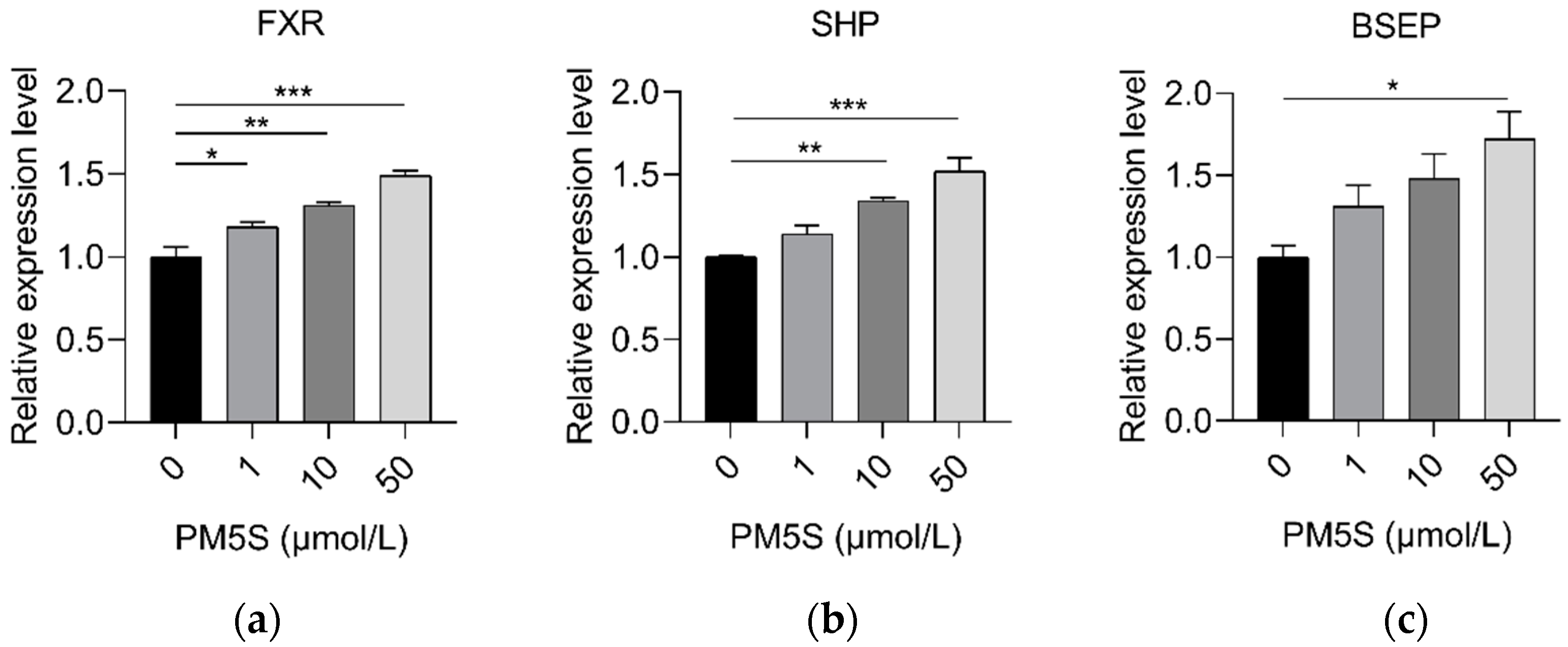
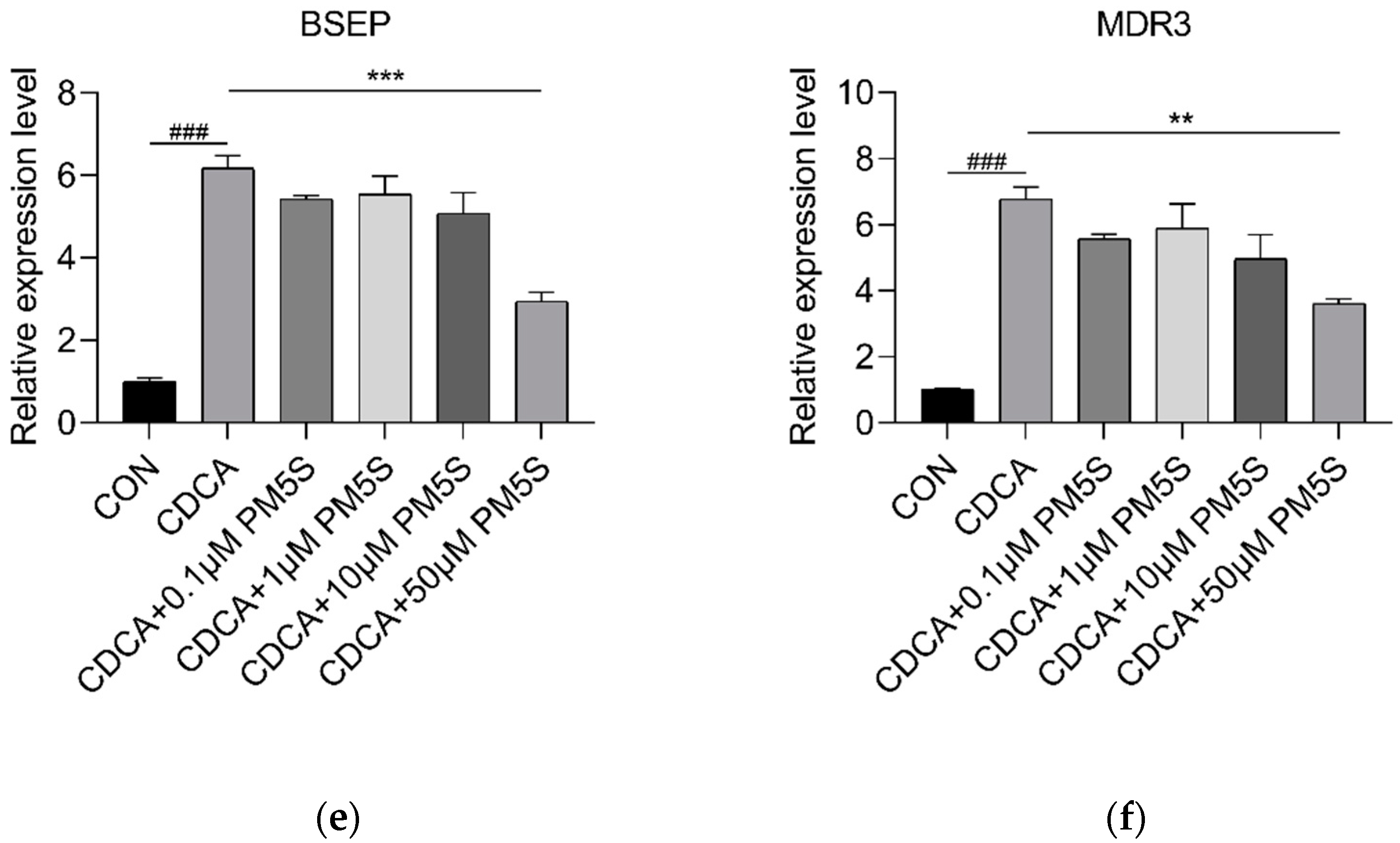
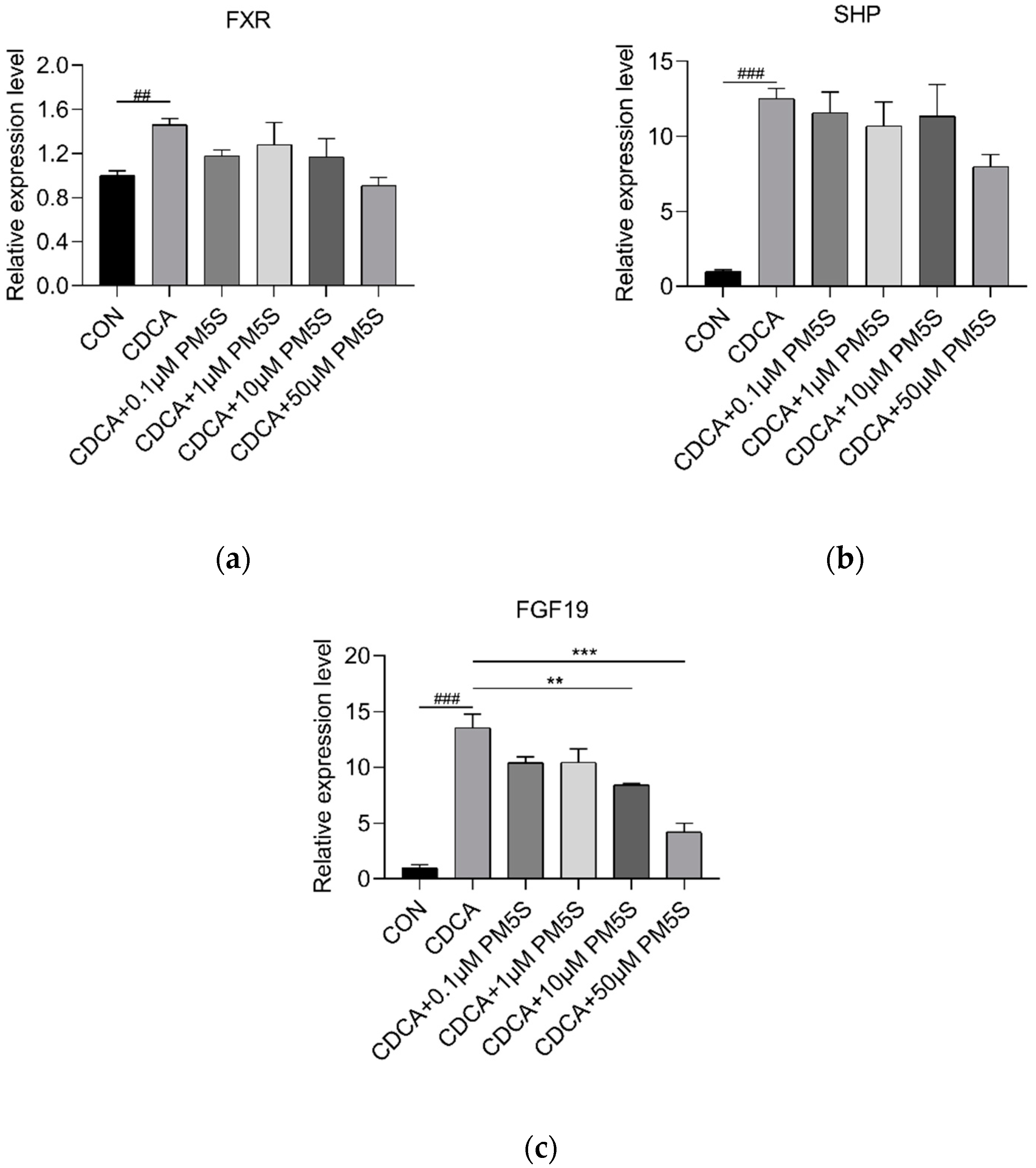
2.4. PM5S Function as Antagonist of FXR Signaling Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animals and Samples
4.3. Cell Culture and Treatments
4.4. TBA Analysis
4.5. Estradiol, Progesterone and Sulfated Progesterone Metabolites
4.6. Real-Time RT-PCR
5. Data Analysis
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milona, A.; Owen, B.M.; Cobbold, J.F.L.; Willemsen, E.C.L.; Cox, I.J.; Boudjelal, M.; Cairns, W.; Schoonjans, K.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Klomp, L.W.J.; et al. Raised Hepatic Bile Acid Concentrations During Pregnancy in Mice Are Associated with Reduced Farnesoid X Receptor Function. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brites, D.; Rodrigues, C.l.M.; van-Zeller, H.; Brito, A.; Silva, R. Relevance of serum bile acid profile in the diagnosis of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy in a high incidence area: Portugal. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 1998, 80, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glantz, A.; Marschall, H.U.; Mattsson, L.A. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: Relationships between bile acid levels and fetal complication rates. Hepatology 2004, 40, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, M.C.; Reyes, H.; Arrese, M.; Figueroa, D.; Lorca, B.; Andresen, M.; Segovia, N.; Molina, C.; Arce, S. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy in twin pregnancies. J. Hepatol. 1989, 9, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Landon, M.B.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, W. Perinatal outcomes with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy in twin pregnancies. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 29, 2176–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Pitre, A.; Fang, Z.Z.; Frank, M.W.; Calabrese, C.; Krausz, K.W.; Neale, G.; Frase, S.; et al. Maternal bile acid transporter deficiency promotes neonatal demise. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williamson, C.; Miragoli, M.; Kadir, S.S.A.; Abuhayyeh, S.; Papacleovoulou, G.; Geenes, V.; Gorelik, J. Bile Acid Signaling in Fetal Tissues: Implications for Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy. Dig. Dis. 2011, 29, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geenes, V.; Williamson, C. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 2049–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desai, M.; Mathur, B.; Eblimit, Z.; Vasquez, H.; Taegtmeyer, H.; Karpen, S.; Penny, D.J.; Moore, D.D.; Anakk, S. Bile acid excess induces cardiomyopathy and metabolic dysfunctions in the heart. Hepatology 2016, 65, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glantz, A.; Marschall, H.U.; Lammert, F.; Mattsson, L.Å. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: A randomized controlled trial comparing dexamethasone and ursodeoxycholic acid. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geenes, V.; Lovgren-Sandblom, A.; Benthin, L.; Lawrance, D.; Chambers, J.; Gurung, V.; Thornton, J.; Chappell, L.; Khan, E.; Dixon, P.; et al. The Reversed Feto-Maternal Bile Acid Gradient in Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy Is Corrected by Ursodeoxycholic Acid. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e83828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stieger, B.; Fattinger, K.; Madon, J.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Meier, P.J. Drug- and estrogen-induced cholestasis through inhibition of the hepatocellular bile salt export pump (Bsep) of rat liver. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Hayyeh, S.; Papacleovoulou, G.; Lovgren-Sandblom, A.; Tahir, M.; Oduwole, O.; Jamaludin, N.A.; Ravat, S.; Nikolova, V.; Chambers, J.; Selden, C.; et al. Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy Levels of Sulfated Progesterone Metabolites Inhibit Farnesoid X Receptor Resulting in a Cholestatic Phenotype. Hepatology 2013, 57, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Estiu, M.C.; Monte, M.J.; Rivas, L.; Moiron, M.; Gomez-Rodriguez, L.; Rodriguez-Bravo, T.; Marin, J.J.G.; Macias, R.I.R. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid treatment on the altered progesterone and bile acid homeostasis in the mother-placenta-foetus trio during cholestasis of pregnancy. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 79, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenen, M.A.M.; Archibald, A.; Uenishi, H.; Tuggle, C.K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Rothschild, M.F.; Rogelgaillard, C.; Park, C.; Milan, D.; Megens, H.; et al. Analyses of pig genomes provide insight into porcine demography and evolution. Nature 2012, 491, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, D.; Avila, E.; Hernández, G.; Halhali, A.; Biruete, B.; Larrea, F.; Díaz, L. Estradiol and progesterone synthesis in human placenta is stimulated by calcitriol. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 103, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.W.; Kukoly, C.A. In vitro release of progesterone and estrone by the porcine placenta throughout gestation. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 1990, 7, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, M.J.; Serrano, M.A.; Elmir, M.Y.; Macias, R.I.R.; Jimenez, F.; Marin, J.J.G. Relationship between asymptomatic hypercholanaemia of pregnancy and progesterone metabolism. Clin. Sci. 2002, 102, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhong, H.J.; Song, Y.M.; Yuan, P.Q.; Li, Y.X.; Lin, S.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, J.; Che, L.Q.; Feng, B.; et al. Targeted metabolomics analysis of maternal-placental-fetal metabolism in pregnant sows reveals links in fetal bile acid homeostasis and sulfation capacity. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 317, G8–G16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrin, D.; Stoll, B.; Moore, D. Digestive physiology of the pig symposium: Intestinal bile acid sensing is linked to key endocrine and metabolic signaling pathways. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 1991–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Vasilenko, A.; Song, X.; Valanejad, L.; Verma, R.; You, S.; Yan, B.; Shiffka, S.; Hargreaves, L.; Nadolny, C. Estrogen and Estrogen Receptor-α-Mediated Transrepression of Bile Salt Export Pump. Mol. Endocrinol 2015, 29, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, X.; Vasilenko, A.; Chen, Y.; Valanejad, L.; Verma, R.; Yan, B.; Deng, R. Transcriptional Dynamics of Bile Salt Export Pump during Pregnancy: Mechanisms and Implications in Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1993–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tuckey, R.C. Progesterone synthesis by the human placenta. Placenta 2005, 26, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abunnaja, M.S.; Alherz, F.A.; El Daibani, A.A.; Bairam, A.F.; Rasool, M.I.; Gohal, S.A.; Kurogi, K.; Suiko, M.; Sakakibara, Y.; Liu, M.-C. Effects of genetic polymorphisms on the sulfation of dehydroepiandrosterone and pregnenolone by human cytosolic sulfotransferase SULT2A1. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vree, J.M.L.; Jacquemin, E.; Sturm, E.; Cresteil, D.; Bosma, P.J.; Aten, J.; Deleuze, J.-F.; Desrochers, M.; Burdelski, M.; Bernard, O.; et al. Mutations in the MDR3 gene cause progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Smit, J.W.; Meijer, D.K.; Vore, M. Mrp2 is essential for estradiol-17β (β-D-glucuronide)–induced cholestasis in rats. Hepatology 2000, 32, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakare, R.; Alamoudi, J.A.; Gautam, N.; Rodrigues, A.D.; Alnouti, Y. Species differences in bile acids I. Plasma and urine bile acid composition. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Song, Y.; Zhong, H.; Lin, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Che, L.; Feng, B.; Lin, Y.; Xu, S.; et al. Transcriptome Profiling of Placenta through Pregnancy Reveals Dysregulation of Bile Acids Transport and Detoxification Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McIlvride, S.; Dixon, P.H.; Williamson, C. Bile acids and gestation. Mol. Asp. Med. 2017, 56, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribe, R.M.; Dann, A.T.; Kenyon, A.P.; Seed, P.; Shennan, A.H.; Mallet, A. Longitudinal profiles of 15 serum bile acids in patients with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, H.; Sjövall, J. Bile acids and progesterone metabolites intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Ann. Med. 2000, 32, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuhayyeh, S.; Martinezbecerra, P.; Kadir, S.H.S.A.; Selden, C.; Romero, M.R.; Rees, M.; Marschall, H.U.; Marin, J.J.G.; Williamson, C. Inhibition of Na+-Taurocholate Co-transporting Polypeptide-mediated Bile Acid Transport by Cholestatic Sulfated Progesterone Metabolites. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 16504–16512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vallejo, M.; Briz, O.; Serrano, M.A.; Monte, M.J.; Marin, J.J.G. Potential role of trans-inhibition of the bile salt export pump by progesterone metabolites in the etiopathogenesis of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, T.; Choi, M.; Moschetta, A.; Peng, L.; Cummins, C.L.; McDonald, J.G.; Luo, G.; Jones, S.A.; Goodwin, B.; Richardson, J.A.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 15 functions as an enterohepatic signal to regulate bile acid homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2005, 2, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, W.; Xie, G.; Jia, W. Bile acid-microbiota crosstalk in gastrointestinal inflammation and carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, K.; Li, T.; Owsley, E.; Strom, S.C.; Chiang, J.Y.L. Bile acids activate fibroblast growth factor 19 signaling in human hepatocytes to inhibit cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase gene expression. Hepatology 2009, 49, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, L.-J.; Reyes, H.; Palma, J.; Hernandez, I.; Ribalta, J.; Sjövall, J. Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid on conjugated bile acids and progesterone metabolites in serum and urine of patients with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. J. Hepatol. 1997, 27, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Reyes, H.; Axelson, M.; Palma, J.; Hernandez, I.; Ribalta, J.; Sjovall, J. Progesterone metabolites and bile acids in serum of patients with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid therapy. Hepatology 1997, 26, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyssen, H.; Van Eldere, J.; Parmentier, G.; Huijghebaert, S.; Mertens, J. Influence of microbial bile salt desulfation upon the fecal excretion of bile salts in gnotobiotic rats. J. Steroid Biochem. 1985, 22, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eldere, J.R.; De Pauw, G.; Eyssen, H.J. Steroid sulfatase activity in a Peptococcus niger strain from the human intestinal microflora. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Eldere, J.; Robben, J.; De Pauw, G.; Merckx, R.; Eyssen, H. Isolation and identification of intestinal steroid-desulfating bacteria from rats and humans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 2112–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robben, J.; Caenepeel, P.; Van Eldere, J.; Eyssen, H. Effects of intestinal microbial bile salt sulfatase activity on bile salt kinetics in gnotobiotic rats. Gastroenterology 1988, 94, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Q.; Qi, X.; Weng, R.; Xi, F.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhao, B.; Luo, Q. Alterations of the Human Gut Microbiota in Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 635680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Song, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hao, Z.; Feng, W. Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG prevents progesterone metabolite epiallaopregnanolone sulfate-induced hepatic bile acid accumulation and liver injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 520, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, L.; Zhuo, Y.; Jiang, D.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Yan, L.; Jin, C.; Jiang, X. Identification of hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 as a mediator in 17β-estradiol-induced white adipose tissue browning. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 5602–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlaardingerbroek, H.; Kenneth, N.; Stoll, B.; Benight, N.; Chacko, S.; Kluijtmans, L.A.J.; Kulik, W.; Squires, E.J.; Olutoye, O.; Schady, D.; et al. New generation lipid emulsions prevent PNALD in chronic parenterally fed preterm pigs. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Yuan, P.; Lin, S.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhuo, Y.; Li, J.; Che, L.; Feng, B.; Lin, Y.; et al. Maternal and Fetal Bile Acid Homeostasis Regulated by Sulfated Progesterone Metabolites through FXR Signaling Pathway in a Pregnant Sow Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126496
Wang P, Yuan P, Lin S, Zhong H, Zhang X, Zhuo Y, Li J, Che L, Feng B, Lin Y, et al. Maternal and Fetal Bile Acid Homeostasis Regulated by Sulfated Progesterone Metabolites through FXR Signaling Pathway in a Pregnant Sow Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(12):6496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126496
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Peng, Peiqiang Yuan, Sen Lin, Heju Zhong, Xiaoling Zhang, Yong Zhuo, Jian Li, Lianqiang Che, Bin Feng, Yan Lin, and et al. 2022. "Maternal and Fetal Bile Acid Homeostasis Regulated by Sulfated Progesterone Metabolites through FXR Signaling Pathway in a Pregnant Sow Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 12: 6496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126496
APA StyleWang, P., Yuan, P., Lin, S., Zhong, H., Zhang, X., Zhuo, Y., Li, J., Che, L., Feng, B., Lin, Y., Xu, S., Wu, D., Burrin, D. G., & Fang, Z. (2022). Maternal and Fetal Bile Acid Homeostasis Regulated by Sulfated Progesterone Metabolites through FXR Signaling Pathway in a Pregnant Sow Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(12), 6496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126496







