Modafinil Administration to Preadolescent Rat Impairs Non-Selective Attention, Frontal Cortex D2 Expression and Mesolimbic GABA Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. GLU and GABA Tissue Content Levels in NAc and VTA
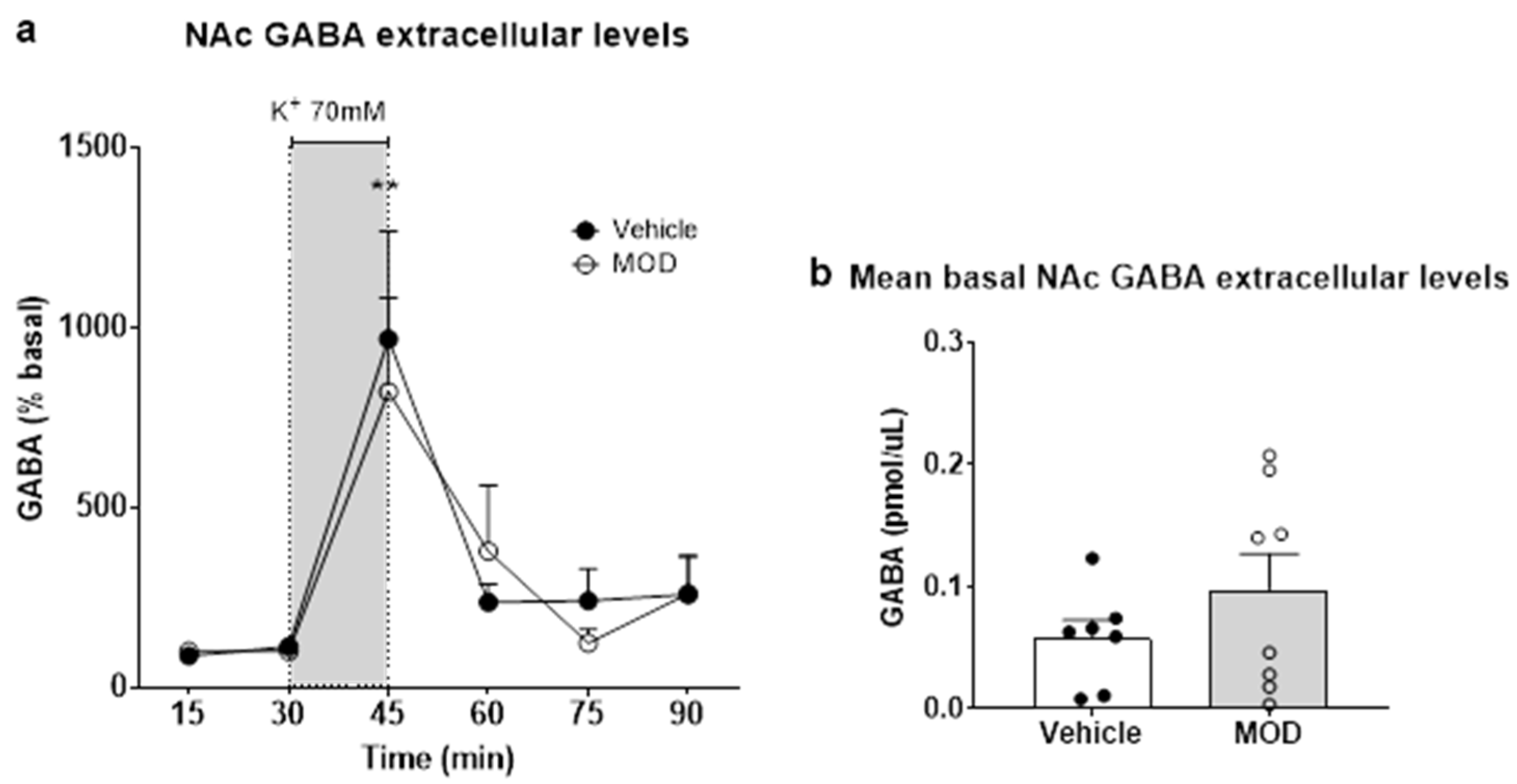
2.2. Extracellular GLU and GABA Levels in NAc
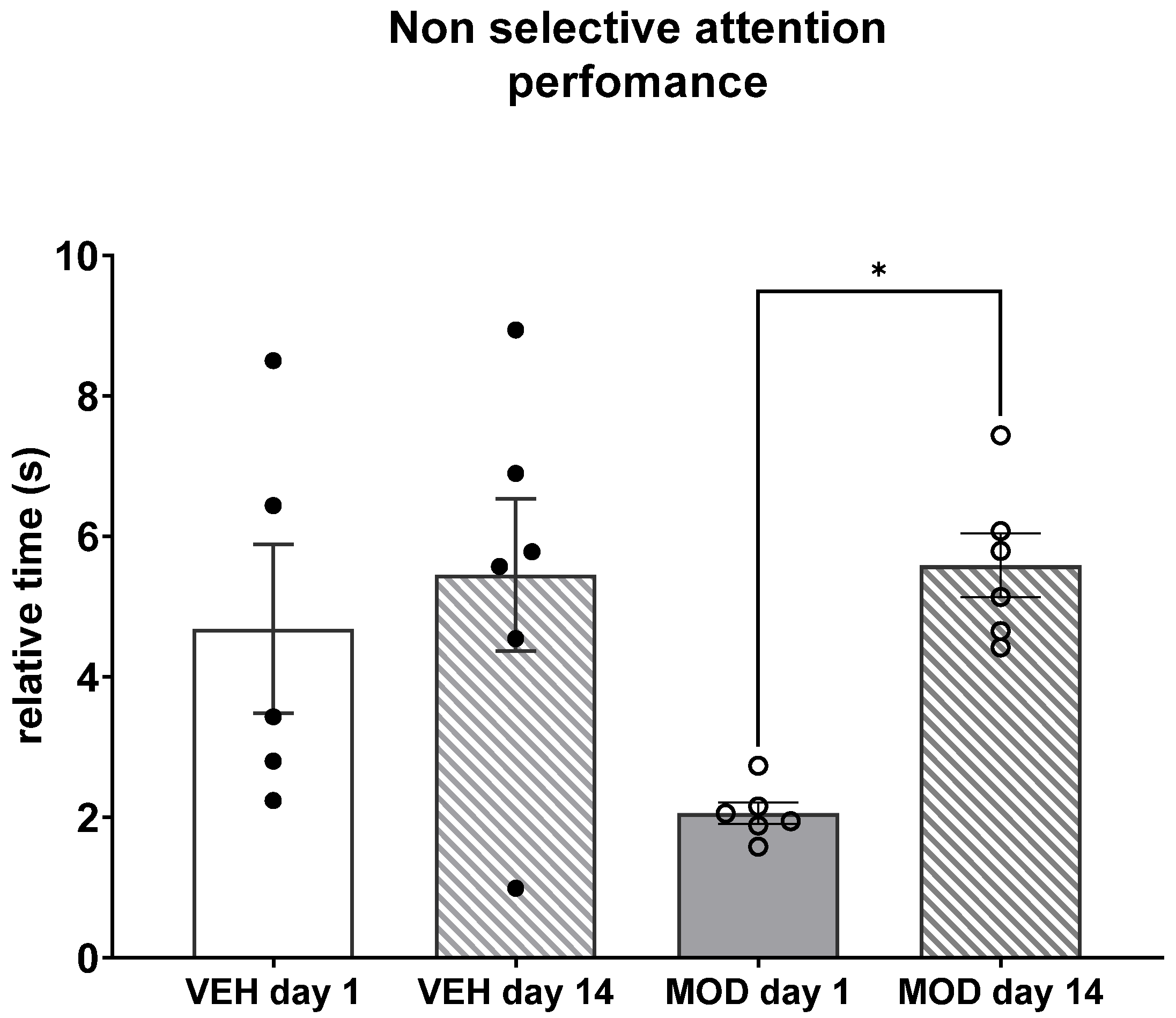
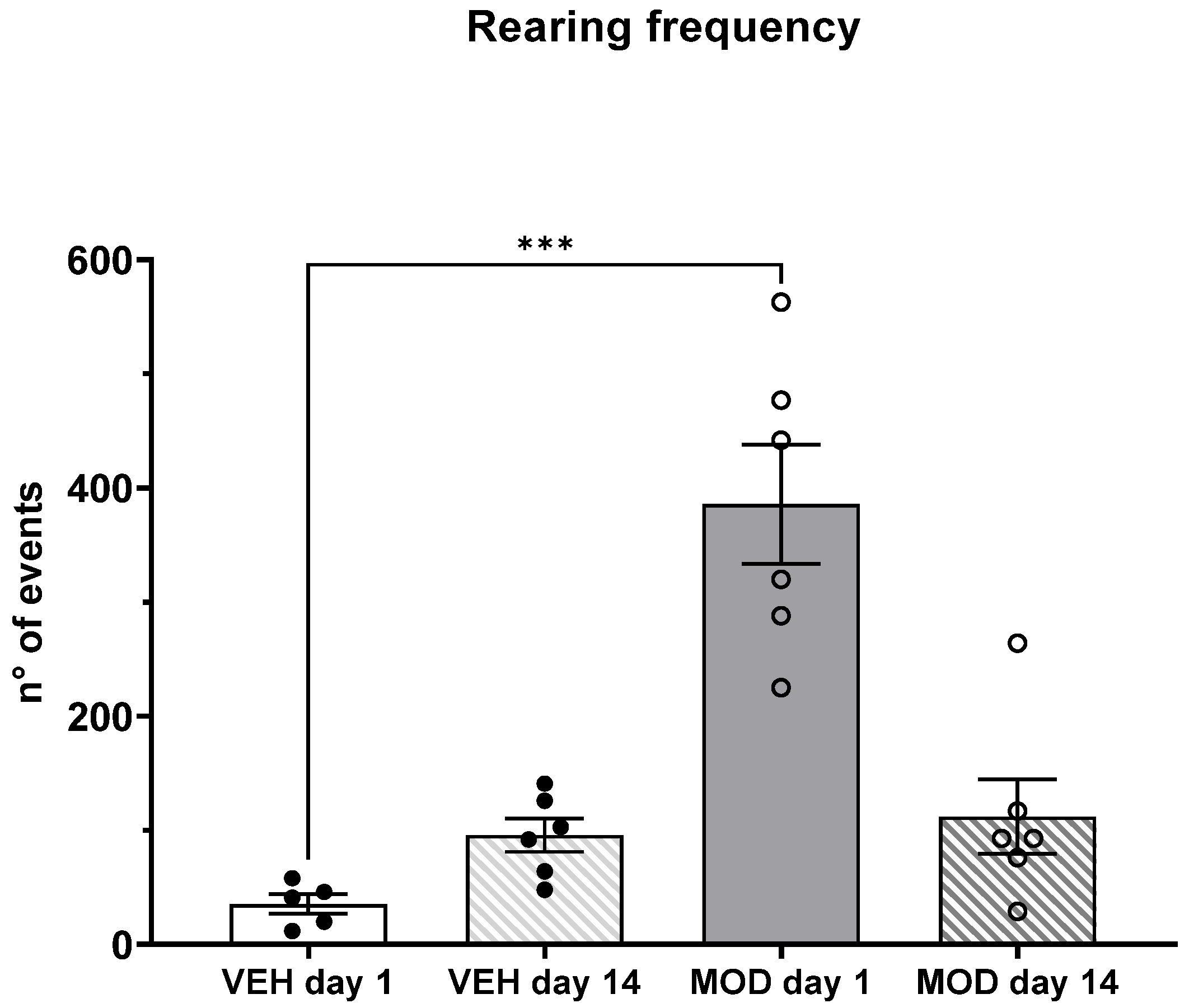
2.3. Non-Selective Attention (NSA) and Rearing Frequency
2.4. D2 Expression in PFC
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Neurochemistry in NAc and VTA
4.3.1. GABA and GLU Tissue Content Levels
4.3.2. In Vivo Microdialysis in NAc
4.3.3. GLU and GABA Analysis
4.4. Cognitive-Behavioral Test
4.4.1. Non-Selective Attention (NSA) Test
4.4.2. D2 Expression in PFC
5. Statistical Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ballon, J.S.; Feifel, D. A systematic review of modafinil: Potential clinical uses and mechanisms of action. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2006, 67, 554–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R. Approved and investigational uses of modafinil: An evidence-based review. Drugs 2008, 68, 1803–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dance, A. Smart drugs: A dose of intelligence. Nature 2016, 531, S2–S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polanczyk, G.V.; Willcutt, E.G.; Salum, G.A.; Kieling, C.; Rohde, L.A. ADHD prevalence estimates across three decades: An updated systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, S.; Mohammadi, M.R.; Mohammadi, M.; Nouroozinejad, G.H.; Kahbazi, M.; Akhondzadeh, S. Modafinil as a treatment for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in children and adolescents: A double blind, randomized clinical trial. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, V.K.; Feifel, D.; Earl, C.Q.; Yang, R.; Adler, L.A. A 9-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, dose-finding study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of modafinil as treatment for adults with ADHD. J. Atten. Disord. 2014, 18, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Han, C.; Lee, S.J.; Jun, T.Y.; Patkar, A.A.; Masand, P.S.; Pae, C.U. Modafinil for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A meta-analysis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2017, 84, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnsten, A.F.; Pliszka, S.R. Catecholamine influences on prefrontal cortical function: Relevance to treatment of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and related disorders. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 99, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, C.W.; Devilbiss, D.M. Psychostimulants as cognitive enhancers: The prefrontal cortex, catecholamines, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 69, e101–e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeichel, B.E.; Zemlan, F.P.; Berridge, C.W. A selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor improves prefrontal cortex-dependent cognitive function: Potential relevance to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Neuropharmacology 2013, 64, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, M.; Latagliata, E.C.; Rizzo, F.R.; Ledonne, A.; Gu, H.H.; Romigi, A.; Nistico, R.; Puglisi-Allegra, S.; Mercuri, N.B. Electrophysiological and amperometric evidence that modafinil blocks the dopamine uptake transporter to induce behavioral activation. Neuroscience 2013, 252, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Fowler, J.S.; Logan, J.; Alexoff, D.; Zhu, W.; Telang, F.; Wang, G.J.; Jayne, M.; Hooker, J.M.; Wong, C.; et al. Effects of modafinil on dopamine and dopamine transporters in the male human brain: Clinical implications. JAMA 2009, 301, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mereu, M.; Bonci, A.; Newman, A.H.; Tanda, G. The neurobiology of modafinil as an enhancer of cognitive performance and a potential treatment for substance use disorders. Psychopharmacology 2013, 229, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignot, E.; Nishino, S.; Guilleminault, C.; Dement, W.C. Modafinil binds to the dopamine uptake carrier site with low affinity. Sleep 1994, 17, 436–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, W.; Ma, Y.; Tossell, K.; Harris, J.J.; Harding, E.C.; Ba, W.; Miracca, G.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; et al. GABA and glutamate neurons in the VTA regulate sleep and wakefulness. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemelli, R.M.; Willie, J.T.; Sinton, C.M.; Elmquist, J.K.; Scammell, T.; Lee, C.; Richardson, J.A.; Williams, S.C.; Xiong, Y.; Kisanuki, Y.; et al. Narcolepsy in orexin knockout mice: Molecular genetics of sleep regulation. Cell 1999, 98, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, L.; Tanganelli, S.; O’Connor, W.T.; Antonelli, T.; Rambert, F.; Fuxe, K. The vigilance promoting drug modafinil increases dopamine release in the rat nucleus accumbens via the involvement of a local GABAergic mechanism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 306, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, L.; Antonelli, T.; O’Connor, W.T.; Tanganelli, S.; Rambert, F.A.; Fuxe, K. Modafinil: An antinarcoleptic drug with a different neurochemical profile to d-amphetamine and dopamine uptake blockers. Biol. Psychiatry 1997, 42, 1181–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, L.; Antonelli, T.; O’Connor, W.T.; Tanganelli, S.; Rambert, F.A.; Fuxe, K. The effects of modafinil on striatal, pallidal and nigral GABA and glutamate release in the conscious rat: Evidence for a preferential inhibition of striato-pallidal GABA transmission. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 253, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, N.; Floren, S.; Kharas, N.; Thomas, M.; Dafny, N. Glutaminergic signaling in the caudate nucleus is required for behavioral sensitization to methylphenidate. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2019, 184, 172737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floren, S.; King, N.; Carrasco, A.; Dafny, N. Glutamate and dopamine in the VTA participate differently in the acute and chronic effect of methylphenidate. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 380, 112390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cid-Jofre, V.; Garate-Perez, M.; Clark, P.J.; Valero-Jara, V.; Espana, R.A.; Sotomayor-Zarate, R.; Cruz, G.; Renard, G.M. Chronic modafinil administration to preadolescent rats impairs social play behavior and dopaminergic system. Neuropharmacology 2021, 183, 108404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuster, J.M. The prefrontal cortex–An update: Time is of the essence. Neuron 2001, 30, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennerley, S.W.; Walton, M.E. Decision making and reward in frontal cortex: Complementary evidence from neurophysiological and neuropsychological studies. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 125, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushworth, M.F.; Noonan, M.P.; Boorman, E.D.; Walton, M.E.; Behrens, T.E. Frontal cortex and reward-guided learning and decision-making. Neuron 2011, 70, 1054–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnasko, T.S.; Hjelmstad, G.O.; Fields, H.L.; Edwards, R.H. Ventral tegmental area glutamate neurons: Electrophysiological properties and projections. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 15076–15085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koob, G.F.; Volkow, N.D. Neurocircuitry of addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, S.; Derst, C.; Veh, R.W.; Zahm, D.S. Glutamatergic afferents of the ventral tegmental area in the rat. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 5730–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboni, E.; Imperato, A.; Perezzani, L.; Di Chiara, G. Amphetamine, cocaine, phencyclidine and nomifensine increase extracellular dopamine concentrations preferentially in the nucleus accumbens of freely moving rats. Neuroscience 1989, 28, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carelli, R.M.; King, V.C.; Hampson, R.E.; Deadwyler, S.A. Firing patterns of nucleus accumbens neurons during cocaine self-administration in rats. Brain Res. 1993, 626, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalivas, P.W.; Volkow, N.; Seamans, J. Unmanageable motivation in addiction: A pathology in prefrontal-accumbens glutamate transmission. Neuron 2005, 45, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, K.; Davidge, S.B.; Lapish, C.C.; Kalivas, P.W. Limbic and motor circuitry underlying footshock-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias Montano, J.A.; Martinez-Fong, D.; Aceves, J. GABAB receptor activation partially inhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate-mediated tyrosine hydroxylase stimulation in rat striatal slices. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 218, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrada, C.; Sotomayor-Zarate, R.; Abarca, J.; Gysling, K. The activation of metabotropic glutamate 5 receptors in the rat ventral tegmental area increases dopamine extracellular levels. Neuroreport 2017, 28, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalivas, P.W. Neurotransmitter regulation of dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area. Brain Res. Rev. 1993, 18, 75–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalivas, P.W.; Duffy, P. A comparison of axonal and somatodendritic dopamine release using in vivo dialysis. J. Neurochem. 1991, 56, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzschentke, T.M. Pharmacology and behavioral pharmacology of the mesocortical dopamine system. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 63, 241–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulaer, B.; Kunisawa, K.; Tanabe, M.; Yanagawa, A.; Saito, K.; Mouri, A.; Nabeshima, T. Pharmacological blockade of dopamine D1-or D2-receptor in the prefrontal cortex induces attentional impairment in the object-based attention test through different neuronal circuits in mice. Mol. Brain 2021, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Ordonez, D.; Juarez, J. Differential effect of modafinil on impulsivity, attention and motor activity in preadolescent rats prenatally treated with alcohol. Brain Res. 2019, 1722, 146395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspide, R.; Gironi Carnevale, U.A.; Sergeant, J.A.; Sadile, A.G. Non-selective attention and nitric oxide in putative animal models of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Behav. Brain Res. 1998, 95, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspide, R.; Fresiello, A.; de Filippis, G.; Gironi Carnevale, U.A.; Sadile, A.G. Non-selective attention in a rat model of hyperactivity and attention deficit: Subchronic methylphenydate and nitric oxide synthesis inhibitor treatment. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffensen, S.C.; Svingos, A.L.; Pickel, V.M.; Henriksen, S.J. Electrophysiological characterization of GABAergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 8003–8015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez de la Mora, M.; Aguilar-Garcia, A.; Ramon-Frias, T.; Ramirez-Ramirez, R.; Mendez-Franco, J.; Rambert, F.; Fuxe, K. Effects of the vigilance promoting drug modafinil on the synthesis of GABA and glutamate in slices of rat hypothalamus. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 259, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, T.A.; Swedlow, N.; Swetschinski, L. Decreasing GABA function within the medial prefrontal cortex or basolateral amygdala decreases sociability. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 317, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannenhoffer, C.A.; Varlinskaya, E.I.; Spear, L.P. Effects of AMPA receptor antagonist, NBQX, and extrasynaptic GABAA agonist, THIP, on social behavior of adolescent and adult rats. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 194, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, W.; Dayan, P.; Montague, P.R. A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 1997, 275, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, L.; Schultz, W. Relative reward preference in primate orbitofrontal cortex. Nature 1999, 398, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, M.A.; Jackson, W.J.; Terry, A.V., Jr.; Kille, N.J.; Arneric, S.P.; Decker, M.W.; Buccafusco, J.J. Age-related differences in distractibility and response to methylphenidate in monkeys. Cereb. Cortex 1998, 8, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gomes, K.M.; Comim, C.M.; Valvassori, S.S.; Reus, G.Z.; Inacio, C.G.; Martins, M.R.; Souza, R.P.; Quevedo, J. Diurnal differences in memory and learning in young and adult rats treated with methylphenidate. J. Neural Transm. 2010, 117, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadyen, M.P.; Brown, R.E.; Carrey, N. Subchronic methylphenidate administration has no effect on locomotion, emotional behavior, or water maze learning in prepubertal mice. Dev. Psychobiol. 2002, 41, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, F. Dopamine vs noradrenaline: Inverted-U effects and ADHD theories. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2009, 43, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgos, H.; Castillo, A.; Flores, O.; Puentes, G.; Morgan, C.; Gatica, A.; Cofre, C.; Hernandez, A.; Laurido, C.; Constandil, L. Effect of modafinil on learning performance and neocortical long-term potentiation in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2010, 83, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyberg, F. Structural plasticity of the brain to psychostimulant use. Neuropharmacology 2014, 87, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauchey, V.; Jaber, M.; Caron, M.G.; Bloch, B.; Le Moine, C. Differential regulation of the dopamine D1, D2 and D3 receptor gene expression and changes in the phenotype of the striatal neurons in mice lacking the dopamine transporter. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.R.; Gainetdinov, R.R.; Hu, X.T.; Cooper, D.C.; Wightman, R.M.; White, F.J.; Caron, M.G. Loss of autoreceptor functions in mice lacking the dopamine transporter. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Tian, Y.H.; You, I.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, C.G. Modafinil-induced conditioned place preference via dopaminergic system in mice. Synapse 2011, 65, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.M.; Huang, Z.L.; Xu, X.H.; Matsumoto, N.; Urade, Y. Dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors are essential for the arousal effect of modafinil. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 8462–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotkova, T.M.; Klyuch, B.P.; Ponomarenko, A.A.; Lin, J.S.; Haas, H.L.; Sergeeva, O.A. Modafinil inhibits rat midbrain dopaminergic neurons through D2-like receptors. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, V.A.; Souza de Freitas, B.; Busato, S.B.; D’Avila Portal, B.C.; Piazza, F.C.; Schroder, N. Differential effects of modafinil on memory in naive and memory-impaired rats. Neuropharmacology 2013, 75, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotomayor, R.; Forray, M.I.; Gysling, K. Acute morphine administration increases extracellular DA levels in the rat lateral septum by decreasing the GABAergic inhibitory tone in the ventral tegmental area. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 81, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates: Hard Cover Edition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Garate-Perez, M.F.; Mendez, A.; Bahamondes, C.; Sanhueza, C.; Guzman, F.; Reyes-Parada, M.; Sotomayor-Zarate, R.; Renard, G.M. Vasopressin in the lateral septum decreases conditioned place preference to amphetamine and nucleus accumbens dopamine release. Addict. Biol. 2021, 26, e12851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhang, M.; Pan, X.Q.; Guo, M.; Fei, L.; Tong, M.L.; Chen, R.H.; Guo, X.R.; Chi, X. Increased locomotor activity and non-selective attention and impaired learning ability in SD rats after lentiviral vector-mediated RNA interference of Homer 1a in the brain. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 10, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yang, P.B.; Swann, A.C.; Dafny, N. Chronic administration of methylphenidate produces neurophysiological and behavioral sensitization. Brain Res. 2007, 1145, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosetti, V.; Guerra, M.; Ramirez, L.A.; Reyes, A.; Alvarez, D.; Olguin, S.; Gonzalez-Manan, D.; Fernandois, D.; Sotomayor-Zarate, R.; Cruz, G. Increase in endogenous estradiol in the progeny of obese rats is associated with precocious puberty and altered follicular development in adulthood. Endocrine 2016, 53, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Perez, S.J.; Vergara, P.; Ventura-Valenzuela, J.P.; Urena-Guerrero, M.E.; Segovia, J.; Beas-Zarate, C. Modification of dopaminergic markers expression in the striatum by neonatal exposure to glutamate during development. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2005, 23, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cid-Jofré, V.; Moreno, M.; Sotomayor-Zárate, R.; Cruz, G.; Renard, G.M. Modafinil Administration to Preadolescent Rat Impairs Non-Selective Attention, Frontal Cortex D2 Expression and Mesolimbic GABA Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126602
Cid-Jofré V, Moreno M, Sotomayor-Zárate R, Cruz G, Renard GM. Modafinil Administration to Preadolescent Rat Impairs Non-Selective Attention, Frontal Cortex D2 Expression and Mesolimbic GABA Levels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(12):6602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126602
Chicago/Turabian StyleCid-Jofré, Valeska, Macarena Moreno, Ramón Sotomayor-Zárate, Gonzalo Cruz, and Georgina M. Renard. 2022. "Modafinil Administration to Preadolescent Rat Impairs Non-Selective Attention, Frontal Cortex D2 Expression and Mesolimbic GABA Levels" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 12: 6602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126602
APA StyleCid-Jofré, V., Moreno, M., Sotomayor-Zárate, R., Cruz, G., & Renard, G. M. (2022). Modafinil Administration to Preadolescent Rat Impairs Non-Selective Attention, Frontal Cortex D2 Expression and Mesolimbic GABA Levels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(12), 6602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126602







