Loxin Reduced the Inflammatory Response in the Liver and the Aortic Fatty Streak Formation in Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Result
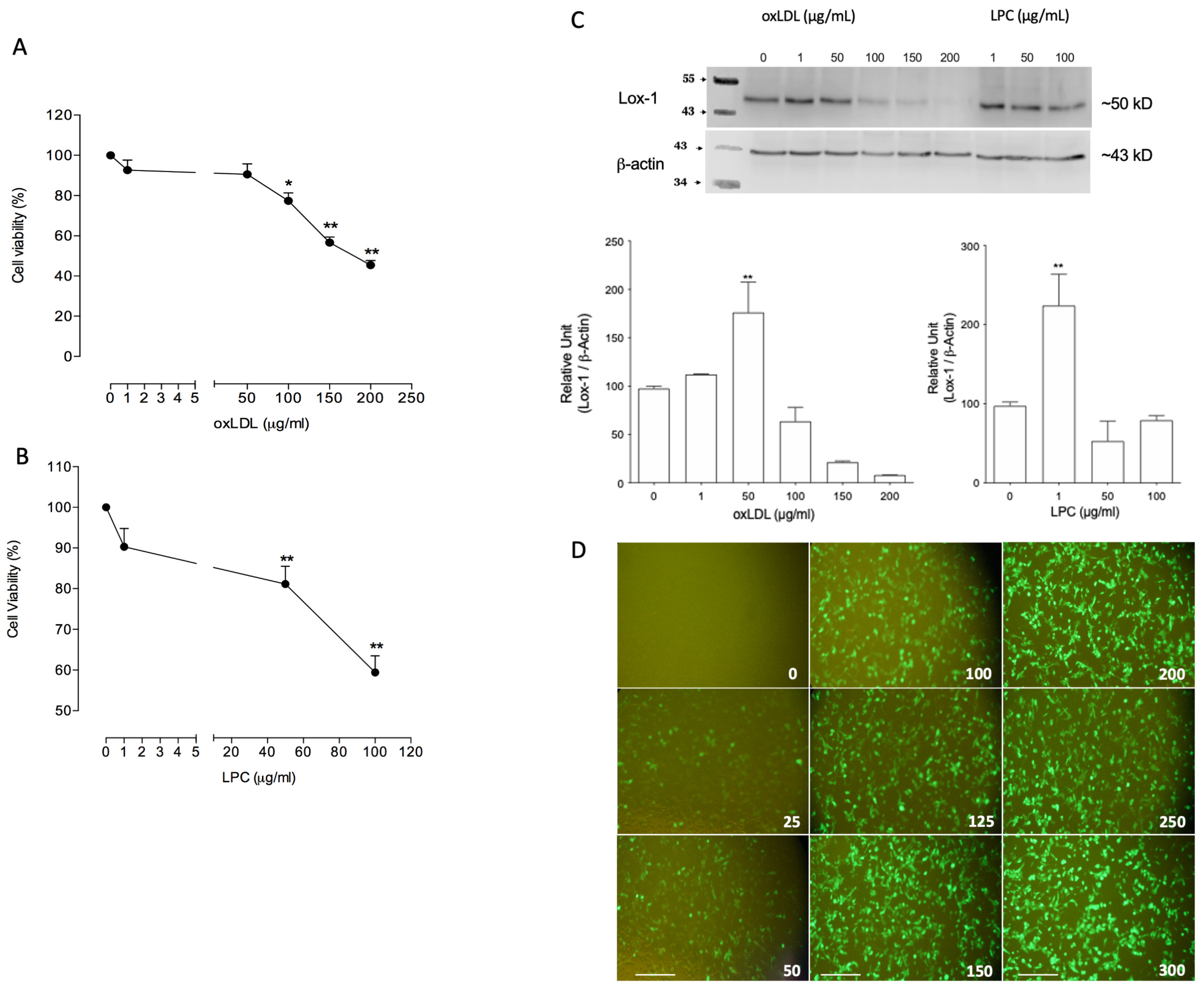
2.1. Ox-LDL and Lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) Reduced Viability and Modulated Lox-1 Expression in H4-II-E-C3 Cells
2.2. Overexpression of Ado-LOXIN in H4-II-E-C3 Cells Reduced the Internalization of Ox-LDL
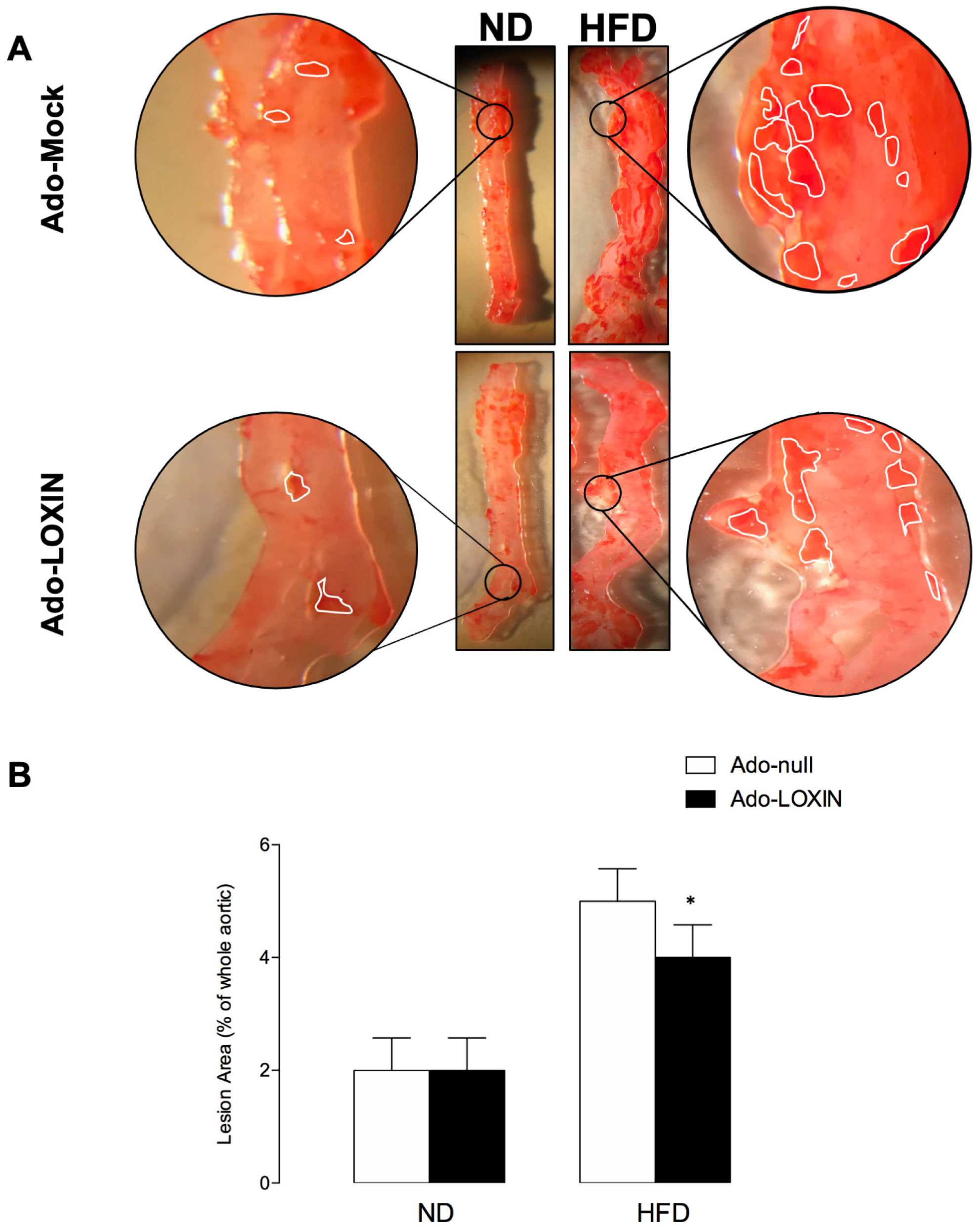
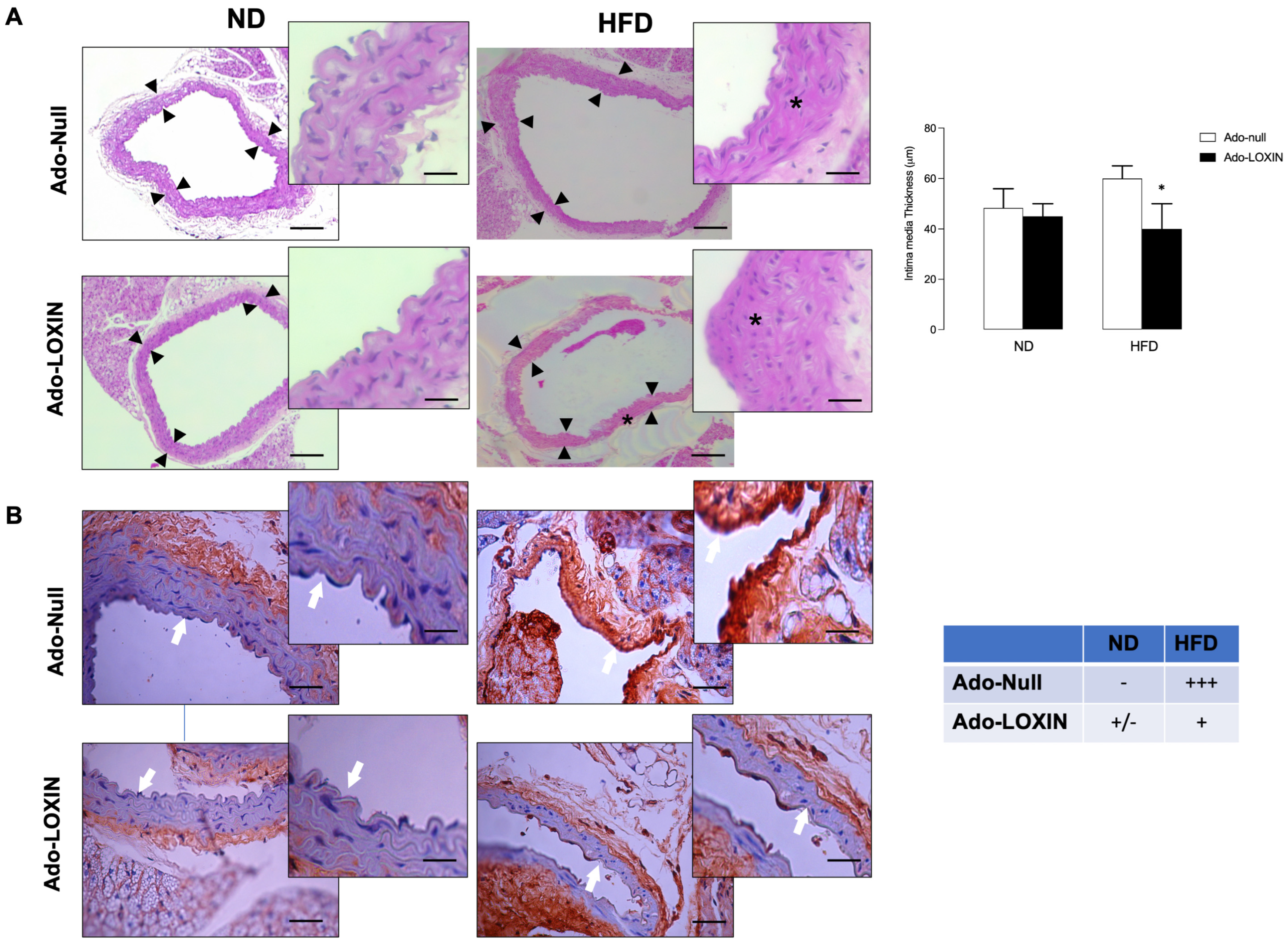
2.3. LOXIN Overexpression Reduced Lipid Deposition in Aortas
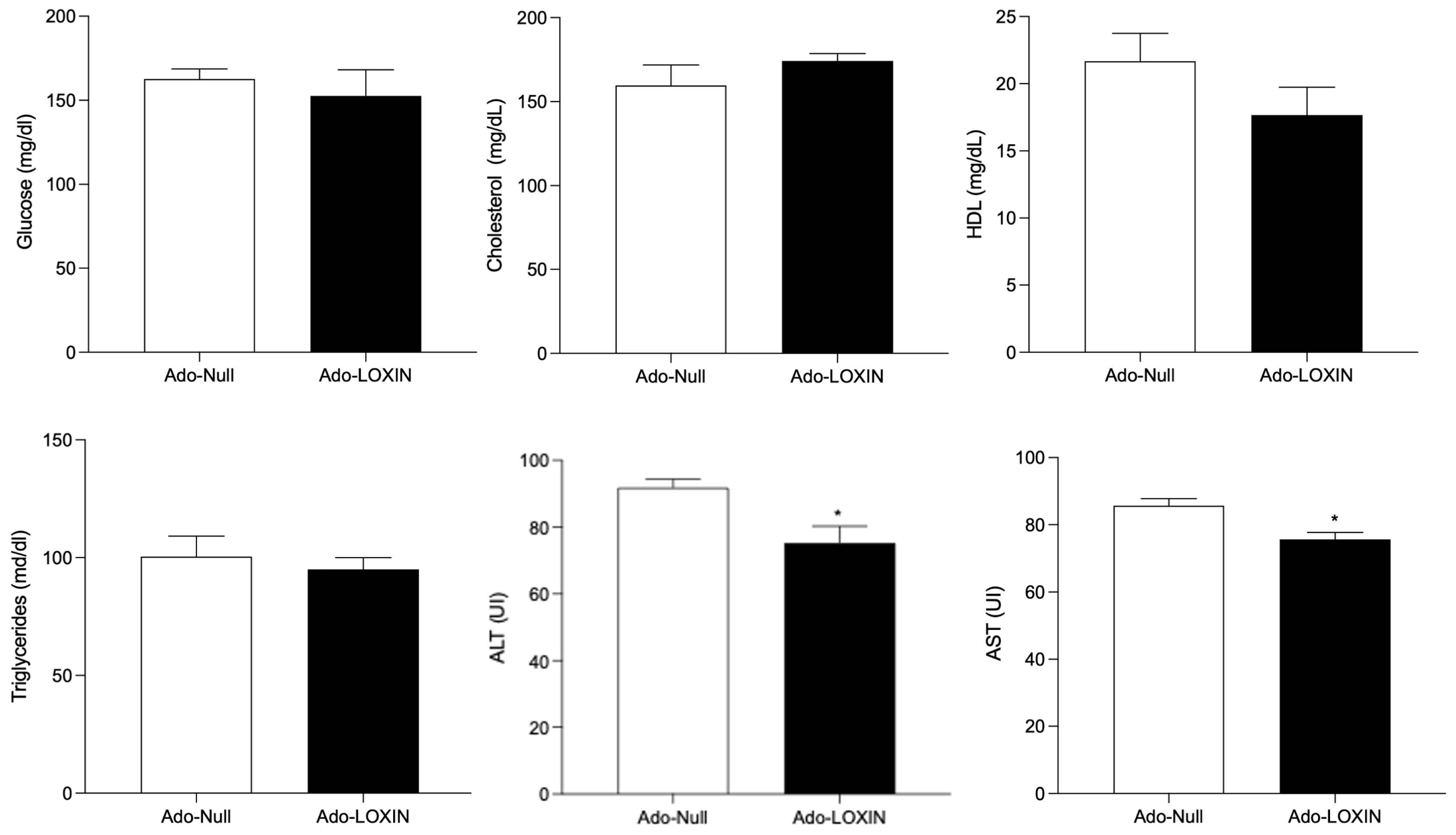
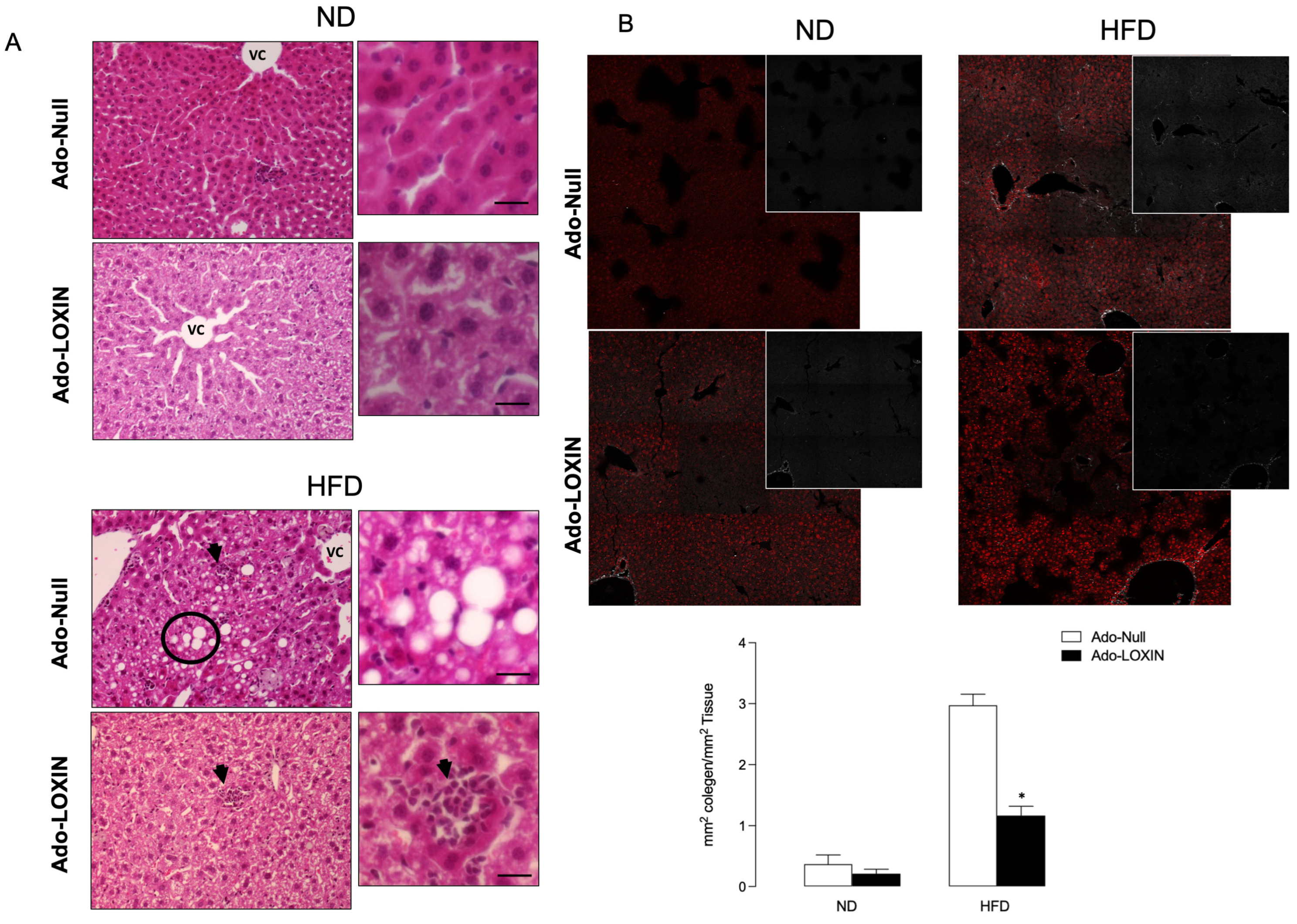
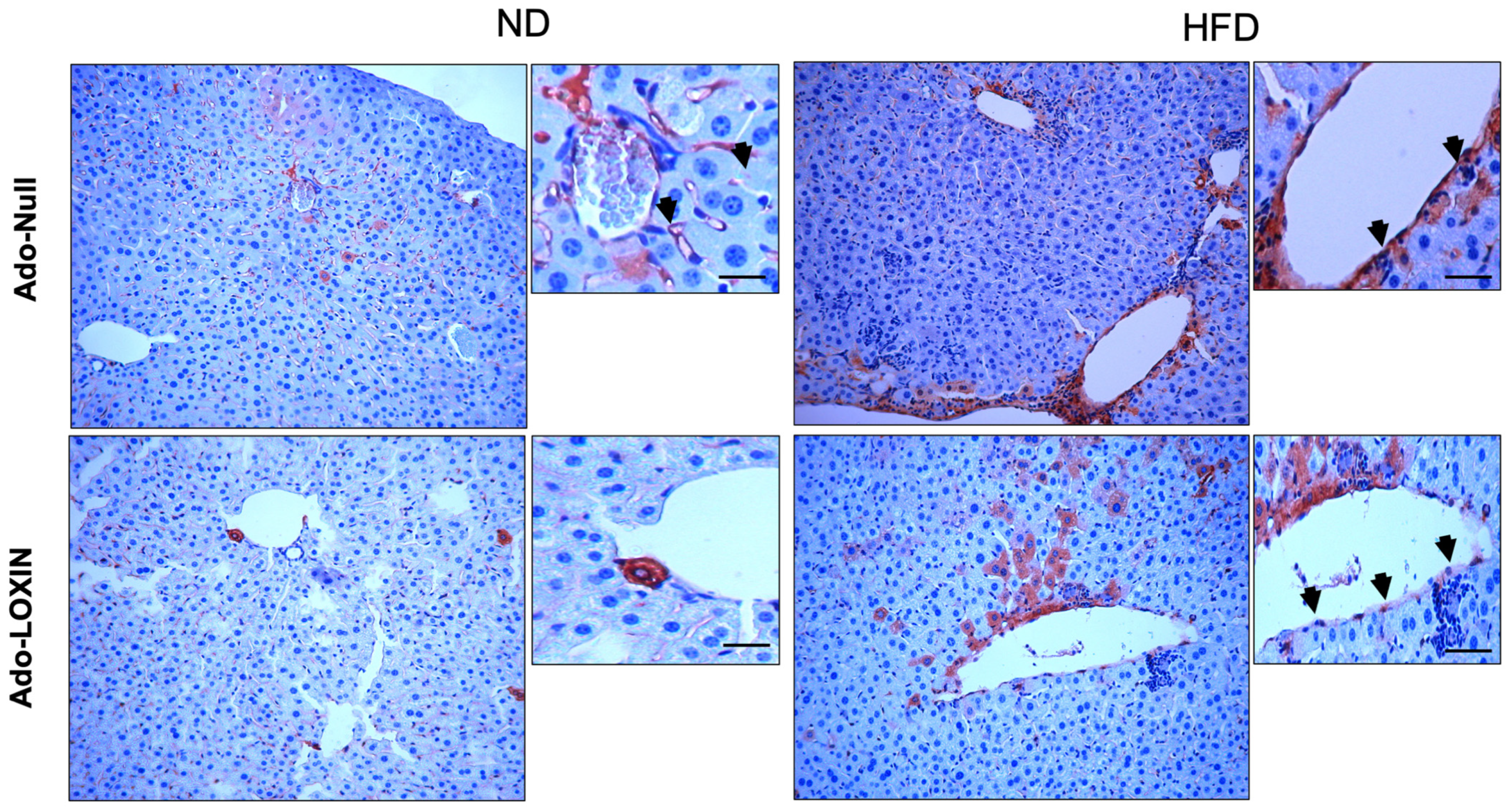
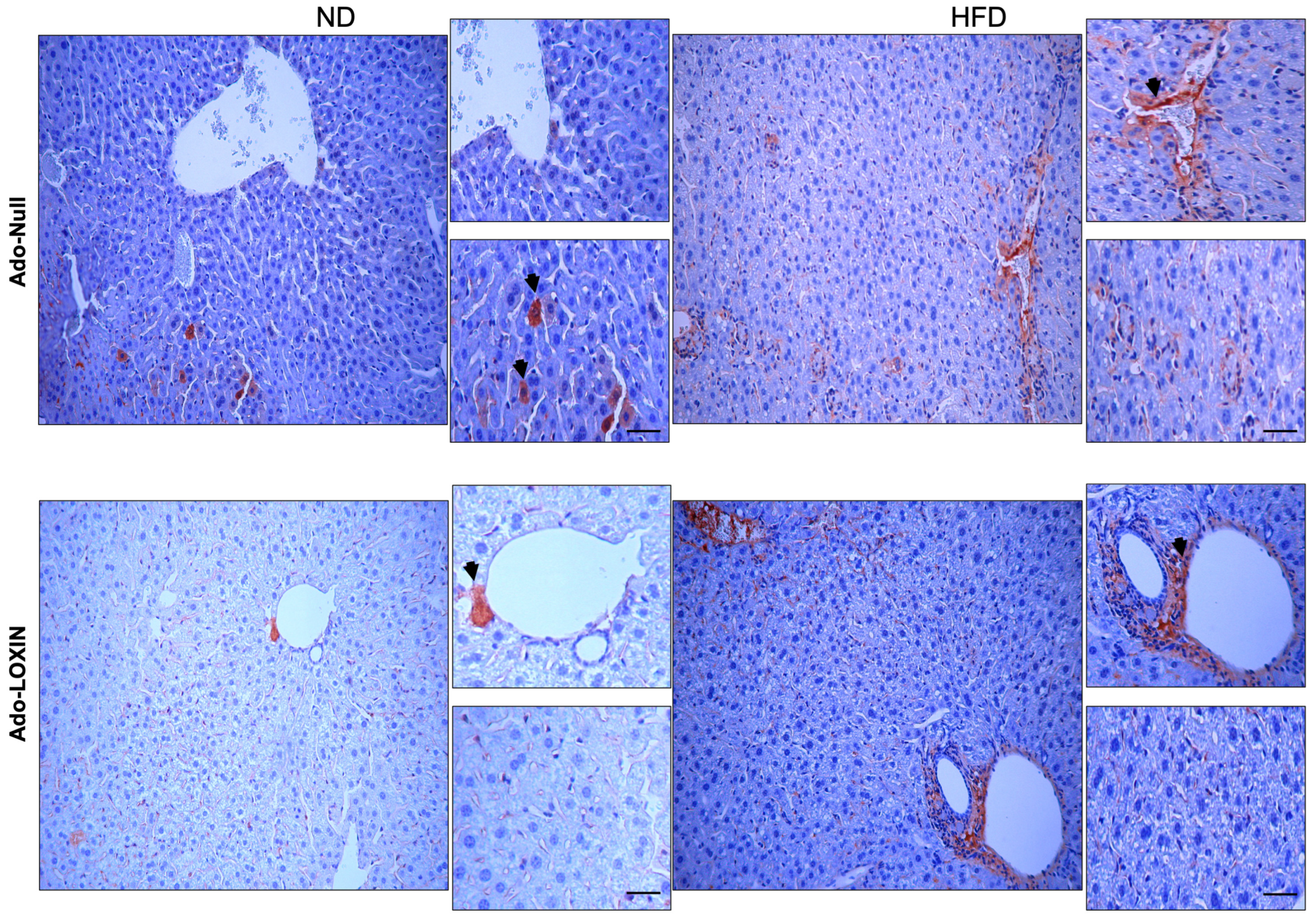
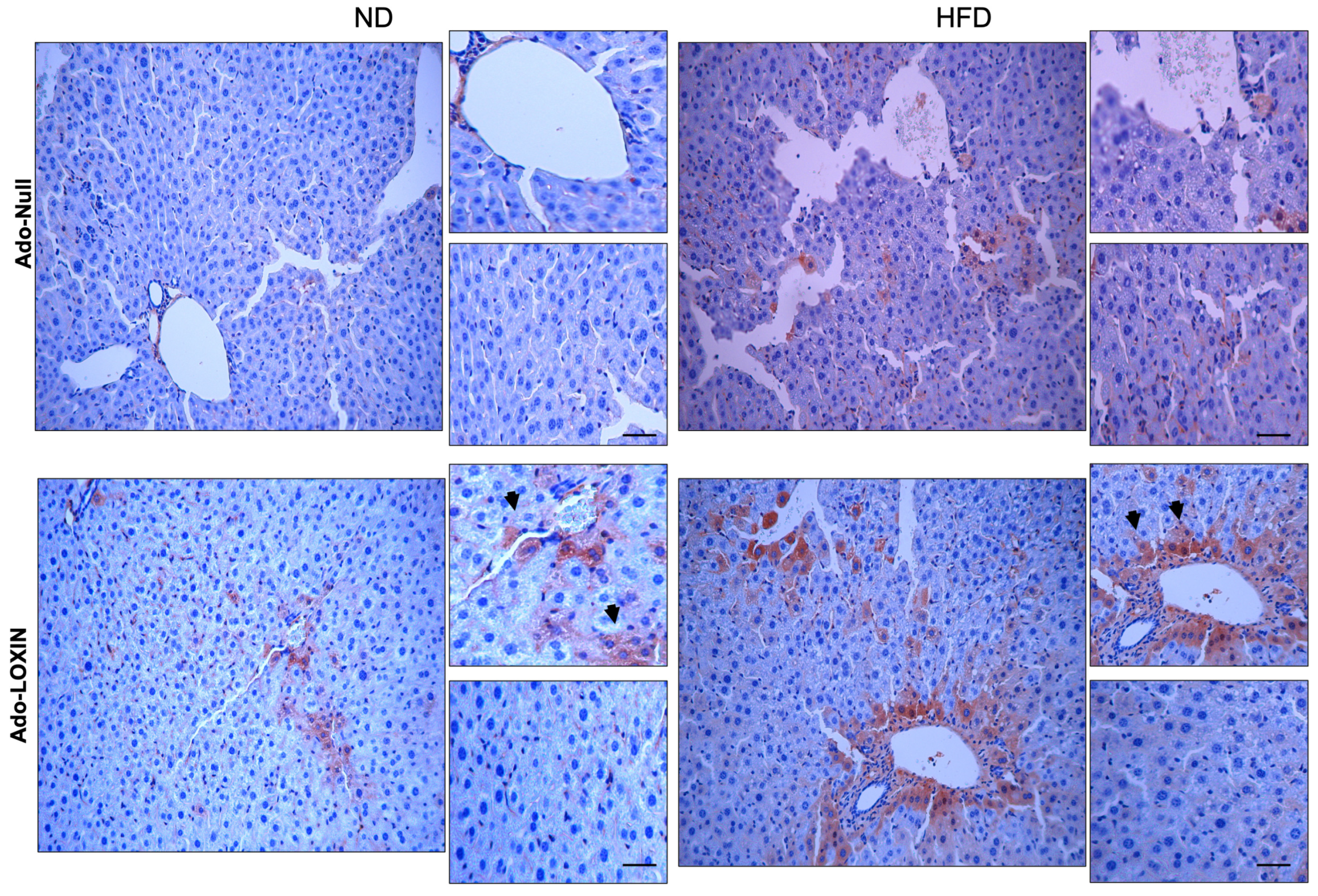
2.4. Effect of LOXIN Overexpression on Hepatic Tissues
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. LDL Isolation and Ox-LDL Preparation
4.2. H4-II-E-C3 and COS Culture
4.3. Western Blotting
4.4. Generation of the Adenoviral Vector for the Overexpression of the Protein LOXIN
4.5. Overexpression of LOXIN in H4-II-E-C3
4.6. Ethidium Homodimer-1 (EthD-1) Incorporation Assay for Adenoviral Transduced H4-II-E-C3 cells
4.7. Metabolic Analysis
4.8. Tissue Harvesting and Quantification of Atherosclerosis
4.9. Microscopic Analysis and Immunohistochemistry
4.10. Second-Harmonic Generation (SHG) Microscopy
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arjuman, A.; Chandra, N.C. LOX-1: A potential target for therapy in atherosclerosis; an in vitro study. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 91, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, G.K.; Robertson, A.K.; Soderberg-Naucler, C. Inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2006, 1, 297–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J. Pathophysiology and biochemistry of cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2004, 14, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzan, S.; Lubrano, V. LOX-1 receptor: A potential link in atherosclerosis and cancer. Life Sci. 2018, 198, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, T.; Mitra, S.; Khaidakov, M.; Wang, X.; Singla, S.; Ding, Z.; Liu, S.; Mehta, J.L. Current Concepts of the Role of Oxidized LDL Receptors in Atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2012, 14, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Orekhov, A.N.; Bobryshev, Y.V. LOX-1-Mediated Effects on Vascular Cells in Atherosclerosis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 1851–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, J.L.; Chen, J.; Hermonat, P.L.; Romeo, F.; Novelli, G. Lectin-like, oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1): A critical player in the development of atherosclerosis and related disorders. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 69, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirillo, A.; Norata, G.D.; Catapano, A.L. LOX-1, OxLDL, and atherosclerosis. Mediators. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 152786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofmann, A.; Brunssen, C.; Morawietz, H. Contribution of lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 and LOX-1 modulating compounds to vascular diseases. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2017, 107, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mango, R.; Biocca, S.; del Vecchio, F.; Clementi, F.; Sangiuolo, F.; Amati, F.; Filareto, A.; Grelli, S.; Spitalieri, P.; Filesi, I.; et al. In vivo and studies support that a new splicing isoform of OLR1 gene is protective against acute myocardial infarction. Circ. Res. 2005, 97, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mango, R.; Predazzi, I.M.; Romeo, F.; Novelli, G. LOX-1/LOXIN: The yin/yang of atheroscleorosis. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2011, 25, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzacasa, B.; Morini, E.; Pucci, S.; Murdocca, M.; Novelli, G.; Amati, F. LOX-1 and Its Splice Variants: A New Challenge for Atherosclerosis and Cancer-Targeted Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biocca, S.; Filesi, I.; Mango, R.; Maggiore, L.; Baldini, F.; Vecchione, L.; Viola, A.; Citro, G.; Federici, G.; Romeo, F.; et al. The splice variant LOXIN inhibits LOX-1 receptor function through hetero-oligomerization. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2008, 44, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biocca, S.; Falconi, M.; Filesi, I.; Baldini, F.; Vecchione, L.; Mango, R.; Romeo, F.; Federici, G.; Desideri, A.; Novelli, G. Functional analysis and molecular dynamics simulation of LOX-1 K167N polymorphism reveal alteration of receptor activity. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cappelletti, A.; Zanussi, M.; Mazzavillani, M.; Magni, V.; Calori, G.; Godino, C.; Ferrari, M.; Margonato, A. Association of LOXIN, a new functional splicing isoform of the OLR1 gene, with severity and prognostic localization of critical coronary artery stenoses. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2014, 15, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmori, R.; Momiyama, Y.; Nagano, M.; Taniguchi, H.; Egashira, T.; Yonemura, A.; Nakamura, H.; Kondo, K.; Ohsuzu, F. An oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor gene variant is inversely associated with the severity of coronary artery disease. Clin. Cardiol. 2004, 27, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veas, C.; Jara, C.; Willis, N.D.; Perez-Contreras, K.; Gutierrez, N.; Toledo, J.; Fernandez, P.; Radojkovic, C.; Zuniga, F.A.; Escudero, C.; et al. Overexpression of LOXIN Protects Endothelial Progenitor Cells From Apoptosis Induced by Oxidized Low Density Lipoprotein. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 67, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, M.; McGivan, J. The rat hepatoma cell line H4-II-E-C3 expresses high activities of the high-affinity glutamate transporter GLT-1A. FEBS Lett. 2000, 484, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, Y.S.; Yang, T.C.; Chang, P.Y.; Chang, S.F.; Ho, S.L.; Chen, H.L.; Lu, S.C. Electronegative LDL is linked to high-fat, high-cholesterol diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in hamsters. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 30, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cominacini, L.; Pasini, A.F.; Garbin, U.; Davoli, A.; Tosetti, M.L.; Campagnola, M.; Rigoni, A.; Pastorino, A.M.; Lo Cascio, V.; Sawamura, T. Oxidized low density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) binding to ox-LDL receptor-1 in endothelial cells induces the activation of NF-kappaB through an increased production of intracellular reactive oxygen species. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 12633–12638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terpstra, V.; van Amersfoort, E.S.; van Velzen, A.G.; Kuiper, J.; van Berkel, T.J. Hepatic and extrahepatic scavenger receptors: Function in relation to disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1860–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nan, J.; Xing, Y.F.; Hu, B.; Tang, J.X.; Dong, H.M.; He, Y.M.; Ruan, D.Y.; Ye, Q.J.; Cai, J.R.; Ma, X.K.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induced LOX-1(+) CD15(+) polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Immunology 2018, 154, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Chavarria, I.; Fernandez, E.; Gutierrez, N.; Gonzalez-Horta, E.E.; Sandoval, F.; Cifuentes, P.; Castillo, C.; Cerro, R.; Sanchez, O.; Toledo, J.R. LOX-1 activation by oxLDL triggers an epithelial mesenchymal transition and promotes tumorigenic potential in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 414, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Li, L.; Yang, C.; Song, S.; Peng, P.; Shao, M.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, J.; et al. Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 facilitates metastasis of gastric cancer through driving epithelial-mesenchymal transition and PI3K/Akt/GSK3beta activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, S.; Sugihara, M.; Yamada, R.; Katayanagi, K.; Tate, S. Structural implication for the impaired binding of W150A mutant LOX-1 to oxidized low density lipoprotein, OxLDL. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1824, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, H.; Adsit, F.G.; Boyington, J.C. The 1.4 angstrom crystal structure of the human oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor lox-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 13593–13599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biocca, S.; Iacovelli, F.; Matarazzo, S.; Vindigni, G.; Oteri, F.; Desideri, A.; Falconi, M. Molecular mechanism of statin-mediated LOX-1 inhibition. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 1583–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weitzel, J.M.; Vernunft, A.; Kruger, B.; Plinski, C.; Viergutz, T. Inactivation of the LOX-1 pathway promotes the Golgi apparatus during cell differentiation of mural granulosa cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 1946–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreyer, S.A.; Wilson, D.L.; LeBoeuf, R.C. C57BL/6 mice fed high fat diets as models for diabetes-accelerated atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 1998, 136, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paigen, B.; Morrow, A.; Brandon, C.; Mitchell, D.; Holmes, P. Variation in susceptibility to atherosclerosis among inbred strains of mice. Atherosclerosis 1985, 57, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishina, P.M.; Lowe, S.; Verstuyft, J.; Naggert, J.K.; Kuypers, F.A.; Paigen, B. Effects of dietary fats from animal and plant sources on diet-induced fatty streak lesions in C57BL/6J mice. J. Lipid Res. 1993, 34, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gilbert, T.R.; Matsumoto, A.H.; Shi, W. Effect of aging on fatty streak formation in a diet-induced mouse model of atherosclerosis. J. Vasc. Res. 2008, 45, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, W.; Wang, X.; Shih, D.M.; Laubach, V.E.; Navab, M.; Lusis, A.J. Paradoxical reduction of fatty streak formation in mice lacking endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circulation 2002, 105, 2078–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Von Der Thusen, J.H.; Kuiper, J.; Fekkes, M.L.; De Vos, P.; Van Berkel, T.J.; Biessen, E.A. Attenuation of atherogenesis by systemic and local adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of interleukin-10 in LDLr-/- mice. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2730–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, S.J.; Sala-Newby, G.B.; Newby, A.C. Overexpression of scavenger receptor LOX-1 in endothelial cells promotes atherogenesis in the ApoE (-/-) mouse model. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2011, 20, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; Robbins, J.S.; Pister, A.; Zafar, M.B.; Zhang, Z.W.; Gupta, J.; Lee, K.J.; Newman, K.; Yun, C.O.; Guise, T.; et al. A modified hTERT promoter-directed oncolytic adenovirus replication with concurrent inhibition of TGFbeta signaling for breast cancer therapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 2010, 17, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.M.; Chung, J.S.; Choi, M.J.; Jin, H.R.; Yin, G.N.; Kwon, M.H.; Park, J.M.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Effectiveness of intracavernous delivery of adenovirus encoding Smad7 gene on erectile function in a mouse model of cavernous nerve injury. J. Sex Med. 2014, 11, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Bañuelos, J.; Siller-Lopez, F.; Miranda, A.; Aguilar, L.K.; Aguilar-Cordova, E.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Cirrhotic rat livers with extensive fibrosis can be safely transduced with clinical-grade adenoviral vectors. Evidence of cirrhosis reversion. Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Rodríguez, A.; Mena-Enriquez, M.; García-Bañuelos, J.; Salazar-Montes, A.; Fafutis-Morris, M.; Vázquez-Del Mercado, M.; Santos-García, A.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Adenovirus Biodistribution is Modified in Sensitive Animals Compared to Naïve Animals. Mol. Biotechnol. 2020, 62, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallone, T.; Malin, S.; Samuelsson, A.; Wilbertz, J.; Miyahara, M.; Okamoto, K.; Poellinger, L.; Philipson, L.; Pettersson, S. A mouse model for adenovirus gene delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7910–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, C.M.; Ho, S.L.; Jeng, Y.M.; Lai, Y.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Lu, S.C.; Chen, H.L.; Chang, P.Y.; Hu, R.H.; Lee, P.H. Accumulation of free cholesterol and oxidized low-density lipoprotein is associated with portal inflammation and fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Inflamm. Lond. 2019, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, W.; Tian, L.; Quan, J.; Wang, Y.; Niu, R. oxLDL induces injury and defenestration of human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells via LOX1. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 53, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oteiza, A.; Li, R.; McCuskey, R.S.; Smedsrod, B.; Sorensen, K.K. Effects of oxidized low-density lipoproteins on the hepatic microvasculature. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 301, G684–G693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dorman, R.B.; Wunder, C.; Saba, H.; Shoemaker, J.L.; MacMillan-Crow, L.A.; Brock, R.W. NAD(P)H oxidase contributes to the progression of remote hepatic parenchymal injury and endothelial dysfunction, but not microvascular perfusion deficits. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G1025–G1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walenbergh, S.M.; Koek, G.H.; Bieghs, V.; Shiri-Sverdlov, R. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: The role of oxidized low-density lipoproteins. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Oteiza, A.; Sorensen, K.K.; McCourt, P.; Olsen, R.; Smedsrod, B.; Svistounov, D. Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and stabilins in elimination of oxidized low-density lipoproteins. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G71–G81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krenkel, O.; Tacke, F. Liver macrophages in tissue homeostasis and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlmark, K.R.; Weiskirchen, R.; Zimmermann, H.W.; Gassler, N.; Ginhoux, F.; Weber, C.; Merad, M.; Luedde, T.; Trautwein, C.; Tacke, F. Hepatic recruitment of the inflammatory Gr1+ monocyte subset upon liver injury promotes hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology 2009, 50, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, C.J.; Chang, M.K.; Shaw, P.X.; Miller, Y.I.; Hartvigsen, K.; Dewan, A.; Witztum, J.L. Innate and acquired immunity in atherogenesis. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.K.; Bergmark, C.; Laurila, A.; Horkko, S.; Han, K.H.; Friedman, P.; Dennis, E.A.; Witztum, J.L. Monoclonal antibodies against oxidized low-density lipoprotein bind to apoptotic cells and inhibit their phagocytosis by elicited macrophages: Evidence that oxidation-specific epitopes mediate macrophage recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6353–6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barreto, J.; Karathanasis, S.K.; Remaley, A.; Sposito, A.C. Role of LOX-1 (Lectin-Like Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor 1) as a Cardiovascular Risk Predictor: Mechanistic Insight and Potential Clinical Use. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, N.; Ishibashi, T.; Sugimoto, K.; Sawamura, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Inoue, N.; Saitoh, S.; Kamioka, M.; Uekita, H.; Ohkawara, H.; et al. Role of LOX-1 in monocyte adhesion-triggered redox, Akt/eNOS and Ca2+ signaling pathways in endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 220, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, J.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Leiva, E.; Guzman, L.; Orrego, R.; Fernandez, P.; Gonzalez, M.; Radojkovic, C.; Zuniga, F.A.; Lamperti, L.; et al. Lemon grass (Cymbopogon citratus (D.C) Stapf) polyphenols protect human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVECs) from oxidative damage induced by high glucose, hydrogen peroxide and oxidised low-density lipoprotein. Food Chem. 2014, 151, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, V.; Briceno, L.; Contreras, H.; Lamperti, L.; Sepulveda, E.; Diaz-Perez, F.; Leon, M.; Veas, C.; Maura, R.; Toledo, J.R.; et al. Endothelium trans differentiated from Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal cells promote tissue regeneration: Potential role of soluble pro-angiogenic factors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nonalcohol. Steatohepatitis Clin. Res. Netw. Hepatol. 2005, 41, 41,113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Chang, S.; Tai, D.C.; Tan, N.; Xiao, G.; Tang, H.; Yu, H. Nonlinear optical microscopy: Use of second harmonic generation and two-photon microscopy for automated quantitative liver fibrosis studies. J. Biomed. Opt. 2008, 13, 064010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reyes, C.; Nova-Lamperti, E.; Duran-Sandoval, D.; Rojas, D.; Gajardo, J.; Guzman-Gutierrez, E.; Bustos-Ruiz, C.; Ormazábal, V.; Zúñiga, F.A.; Escudero, C.; et al. Loxin Reduced the Inflammatory Response in the Liver and the Aortic Fatty Streak Formation in Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23137329
Reyes C, Nova-Lamperti E, Duran-Sandoval D, Rojas D, Gajardo J, Guzman-Gutierrez E, Bustos-Ruiz C, Ormazábal V, Zúñiga FA, Escudero C, et al. Loxin Reduced the Inflammatory Response in the Liver and the Aortic Fatty Streak Formation in Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(13):7329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23137329
Chicago/Turabian StyleReyes, Camila, Estefanía Nova-Lamperti, Daniel Duran-Sandoval, Daniela Rojas, Jorge Gajardo, Enrique Guzman-Gutierrez, Camila Bustos-Ruiz, Valeska Ormazábal, Felipe A. Zúñiga, Carlos Escudero, and et al. 2022. "Loxin Reduced the Inflammatory Response in the Liver and the Aortic Fatty Streak Formation in Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 13: 7329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23137329
APA StyleReyes, C., Nova-Lamperti, E., Duran-Sandoval, D., Rojas, D., Gajardo, J., Guzman-Gutierrez, E., Bustos-Ruiz, C., Ormazábal, V., Zúñiga, F. A., Escudero, C., & Aguayo, C. (2022). Loxin Reduced the Inflammatory Response in the Liver and the Aortic Fatty Streak Formation in Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(13), 7329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23137329







