CALMODULIN1 and WRKY53 Function in Plant Defense by Negatively Regulating the Jasmonic Acid Biosynthesis Pathway in Arabidopsis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CAM1 and WRKY53 Maybe Negatively Regulate the JA Biosynthesis Process When Resistant to Spodoptera Littoralis
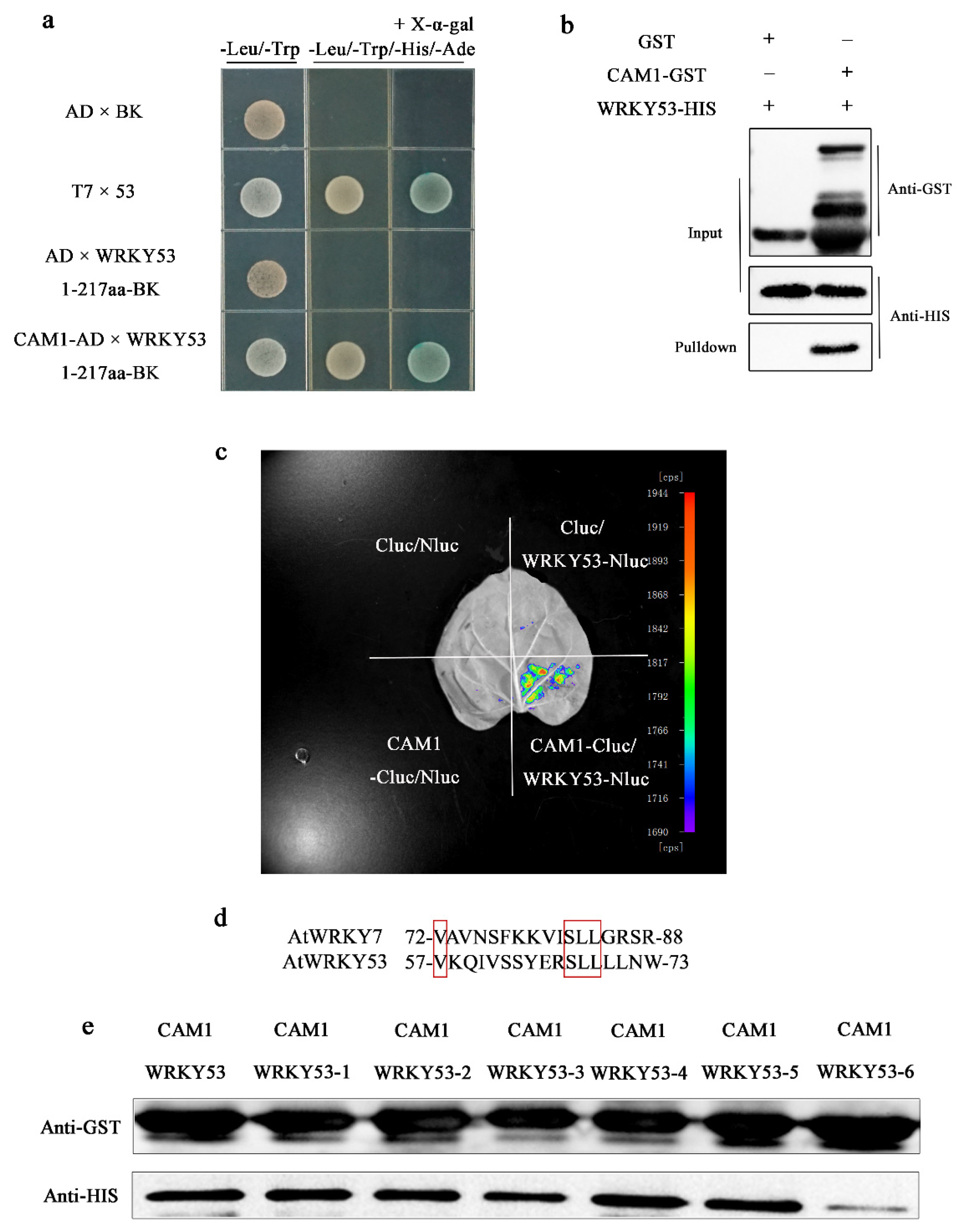
2.2. CAM1 Interacts with WRKY53
2.3. WRKY53 Negatively Regulates LOX3 and LOX4 Expression
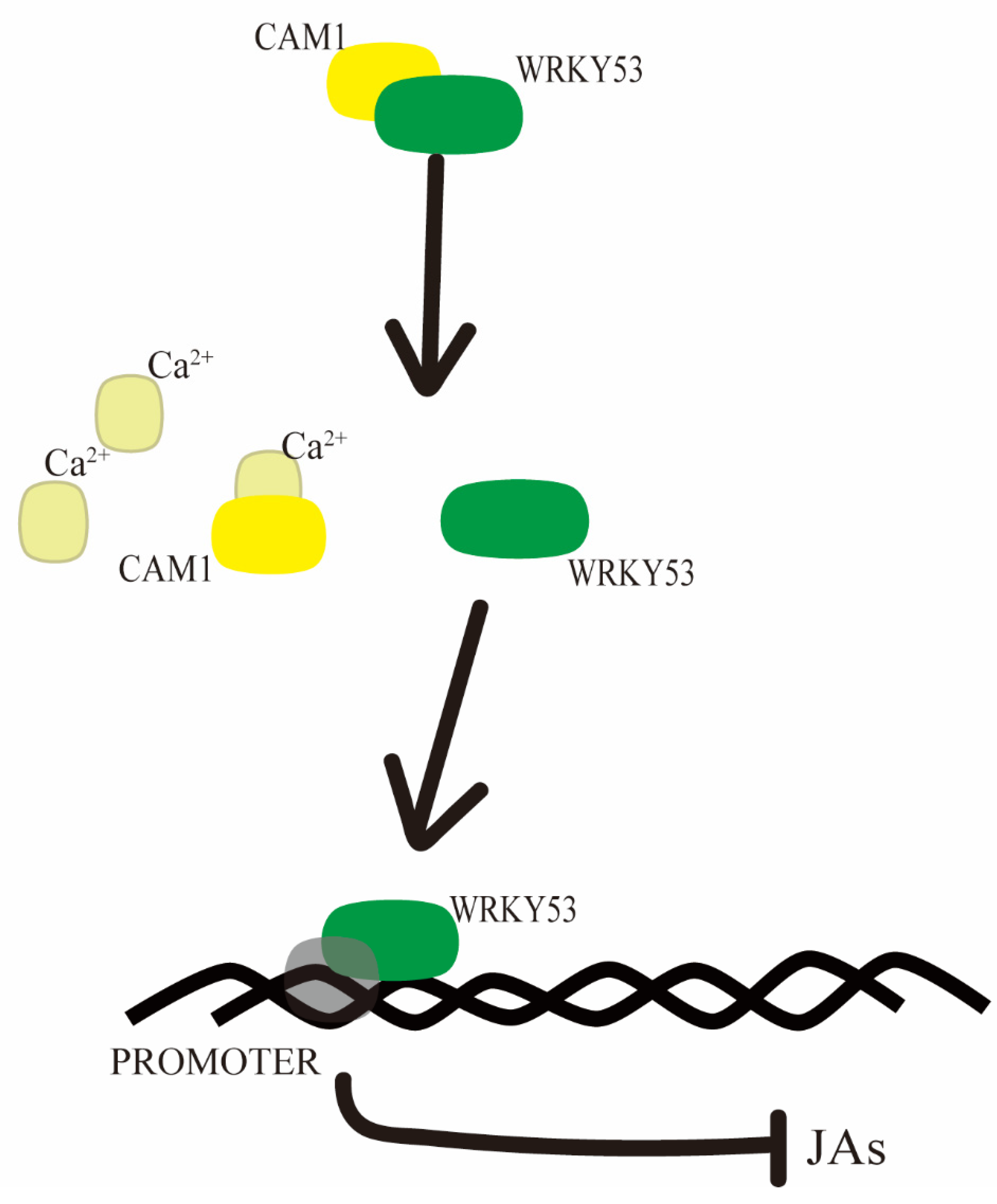
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Culture Conditions
4.2. Spodoptera Littoralis Egg Hatching and Inoculation
4.3. Yeast Two-Hybrid (Y2H) Assay
4.4. Firefly Luciferase Complementation Imaging Assay (LCI)
4.5. In Vitro Pull-Down Assay
4.6. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
4.7. Luciferase Activity Assay
4.8. Measuring JA Levels in Leaves
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ozawa, R.; Bertea, C.M.; Foti, M.; Narayana, R.; Arimura, G.-I.; Muroi, A.; Horiuchi, J.-I.; Nishioka, T.; Maffei, M.; Takabayashi, J. Exogenous Polyamines Elicit Herbivore-Induced Volatiles in Lima Bean Leaves: Involvement of Calcium, H2O2 and Jasmonic Acid. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 2183–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bricchi, I.; Occhipinti, A.; Bertea, C.M.; Zebelo, S.A.; Brillada, C.; Verrillo, F.; De Castro, C.; Molinaro, A.; Faulkner, C.; Maule, A.J.; et al. Separation of early and late responses to herbivory in Arabidopsis by changing plasmodesmal function. Plant J. 2012, 73, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vadassery, J.; Reichelt, M.; Hause, B.; Gershenzon, J.; Boland, W.; Mithöfer, A. CML42-Mediated Calcium Signaling Coordinates Responses to Spodoptera Herbivory and Abiotic Stresses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 1159–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scholz, S.S.; Vadassery, J.; Heyer, M.; Reichelt, M.; Bender, K.W.; Snedden, W.A.; Boland, W.; Mithöfer, A. Mutation of the Ara-bidopsis Calmodulin-Like Protein CML37 Deregulates the Jasmonate Pathway and Enhances Susceptibility to Herbivory. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1712–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCormack, E.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Braam, J. Handling calcium signaling: Arabidopsis CaMs and CMLs. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-T.; Sun, D.-Y.; Zhou, R.-G. Ca2+ and AtCaM3 are involved in the expression of heat shock protein gene in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2005, 28, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, R.-G.; Gao, Y.-J.; Zheng, S.-Z.; Xu, P.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Sun, D.-Y. Molecular and Genetic Evidence for the Key Role of AtCaM3 in Heat-Shock Signal Transduction in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 1773–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.; Jia, L.; Chu, H.; Wu, D.; Peng, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Chen, K.; Zhao, L. Arabidopsis CaM1 and CaM4 Promote Nitric Oxide Production and Salt Resistance by Inhibiting S-Nitroso glutathione Reductase via Direct Binding. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Shen, S.; Li, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S. AtCaM4 interacts with a Sec14-like protein, PATL1, to regulate freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis in a CBF-independent manner. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 5241–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, C.; Xie, D. Jasmonate in plant defence: Sentinel or double agent? Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wasternack, C.; Hause, B. Jasmonates: Biosynthesis, perception, signal transduction and action in plant stress response, growth and development. An update to the 2007 review in Annals of Botany. Ann. Bot. 2013, 111, 1021–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauvin, A.; Caldelari, D.; Wolfender, J.; Farmer, E.E. Four 13-lipoxygenases contribute to rapid jasmonate synthesis in wounded, Arabidopsis thaliana, leaves: A role for lipoxygenase 6 in responses to long-distance wound signals. New Phytol. 2013, 197, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauvin, A.; Lenglet, A.; Wolfender, J.-L.; Farmer, E.E. Paired Hierarchical Organization of 13-Lipoxygenases in Arabidopsis. Plants 2016, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rushton, P.J.; Somssich, I.E.; Ringler, P.; Shen, Q.J. WRKY transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eulgem, T.; Rushton, P.J.; Robatzek, S.; Somssich, I.E. The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Fan, M.; Yang, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Su, Y.; Xiao, L.; Deng, H.; Xie, D. Injury Activates Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Phosphorylation of JAV1-JAZ8-WRKY51 Complex for Jasmonate Biosynthesis. Mol. Cell 2018, 70, 136–149.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Üiker, B.; Somssich, I.E. WRKY transcription factors: From DNA binding towards biological function. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 491–498. [Google Scholar]
- Besseau, S.; Li, J.; Palva, E.T. WRKY54 and WRKY70 co-operate as negative regulators of leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 2667–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Zentgraf, U. The Antagonist Function of Arabidopsis WRKY53 and ESR/ESP in Leaf Senescence Is Modulated by the Jasmonic and Salicylic Acid Equilibrium. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, Y.; Smykowski, A.; Zentgraf, U. A novel upstream regulator ofWRKY53transcription during leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Biol. 2008, 10, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yu, D. Activated expression of AtWRKY53 negatively regulates drought tolerance by mediating stomatal movement. Plant Cell Rep. 2015, 34, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Song, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Zou, C.; Yu, D. The role of WRKY transcription factors in plant abiotic stresses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1819, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Dong, Q.; Yu, D. Arabidopsis WRKY46 coordinates with WRKY70 and WRKY53 in basal resistance against pathogen Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Sci. 2012, 185–186, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astegno, A.; La Verde, V.; Marino, V.; Dell’Orco, D.; Dominici, P. Biochemical and biophysical characterization of a plant calmodulin: Role of the N- and C-lobes in calcium binding, conformational change, and target interaction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1864, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dou, N.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C. The versatile GABA in plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2021, 16, 1862565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Lee, Y.; Lee, I.C.; Nam, H.G.; Kwak, J.M. Calmodulin 1 Regulates Senescence and ABA Response in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landoni, M.; Francesco, A.D.; Galbiati, M.; Tonelli, C. A loss-of-function mutation in Calmodulin2 gene affects pollen ger-mination in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol. Biol. 2010, 74, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mazumder, M.; Gupta, N.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Gourinath, S. Crystal structure of Arabidopsis thaliana calmodulin7 and insight into its mode of DNA binding. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 3029–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, J.H.; Moon, B.C.; Choi, M.S.; Kang, Y.H.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, K.Y.; Chung, W.S.; et al. WRKY group IId transcription factors interact with calmodulin. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, S.C.; Popescu, G.V.; Bachan, S.; Zhang, Z.; Seay, M.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M.; Dinesh-Kumar, S.P. Differential binding of calmodulin-related proteins to their targets revealed through high-density Arabidopsis protein microarrays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4730–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wasternack, C. Jasmonates: An Update on Biosynthesis, Signal Transduction and Action in Plant Stress Response, Growth and Development. Ann. Bot. 2007, 100, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, S.; Jiao, C.; McLamore, E.; Wang, N.; Yao, H.; Shen, Y. Insect Herbivory of Leaves Affects the Auxin Flux Along Root Apices in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2017, 36, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquis, V.; Smirnova, E.; Poirier, L.; Zumsteg, J.; Schweizer, F.; Reymond, P.; Heitz, T. Stress- and pathway-specific impacts of impaired jasmonoylisoleucine (JA-Ile) catabolism on defense signaling and biotic stress resistance. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, C.; Li, K.; Zuo, Y.; Gong, J.; Guo, Z.; Shen, Y. CALMODULIN1 and WRKY53 Function in Plant Defense by Negatively Regulating the Jasmonic Acid Biosynthesis Pathway in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7718. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147718
Jiao C, Li K, Zuo Y, Gong J, Guo Z, Shen Y. CALMODULIN1 and WRKY53 Function in Plant Defense by Negatively Regulating the Jasmonic Acid Biosynthesis Pathway in Arabidopsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(14):7718. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147718
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Chunyang, Kaixiang Li, Yixin Zuo, Junqing Gong, Zhujuan Guo, and Yingbai Shen. 2022. "CALMODULIN1 and WRKY53 Function in Plant Defense by Negatively Regulating the Jasmonic Acid Biosynthesis Pathway in Arabidopsis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 14: 7718. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147718
APA StyleJiao, C., Li, K., Zuo, Y., Gong, J., Guo, Z., & Shen, Y. (2022). CALMODULIN1 and WRKY53 Function in Plant Defense by Negatively Regulating the Jasmonic Acid Biosynthesis Pathway in Arabidopsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(14), 7718. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147718





