Disruption of a Conservative Motif in the C-Terminal Loop of the KCNQ1 Channel Causes LQT Syndrome
Abstract
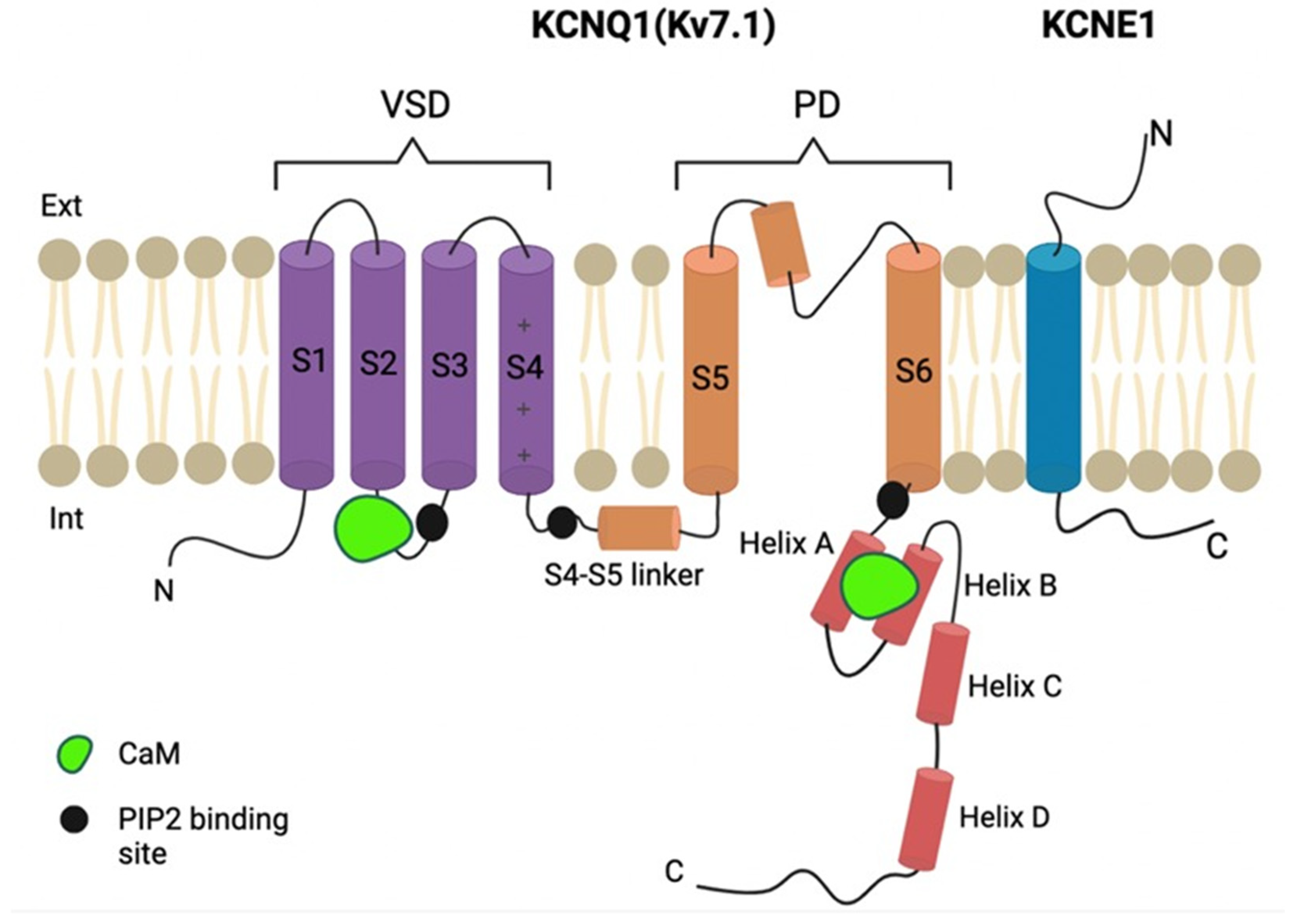
:1. Introduction
2. Results
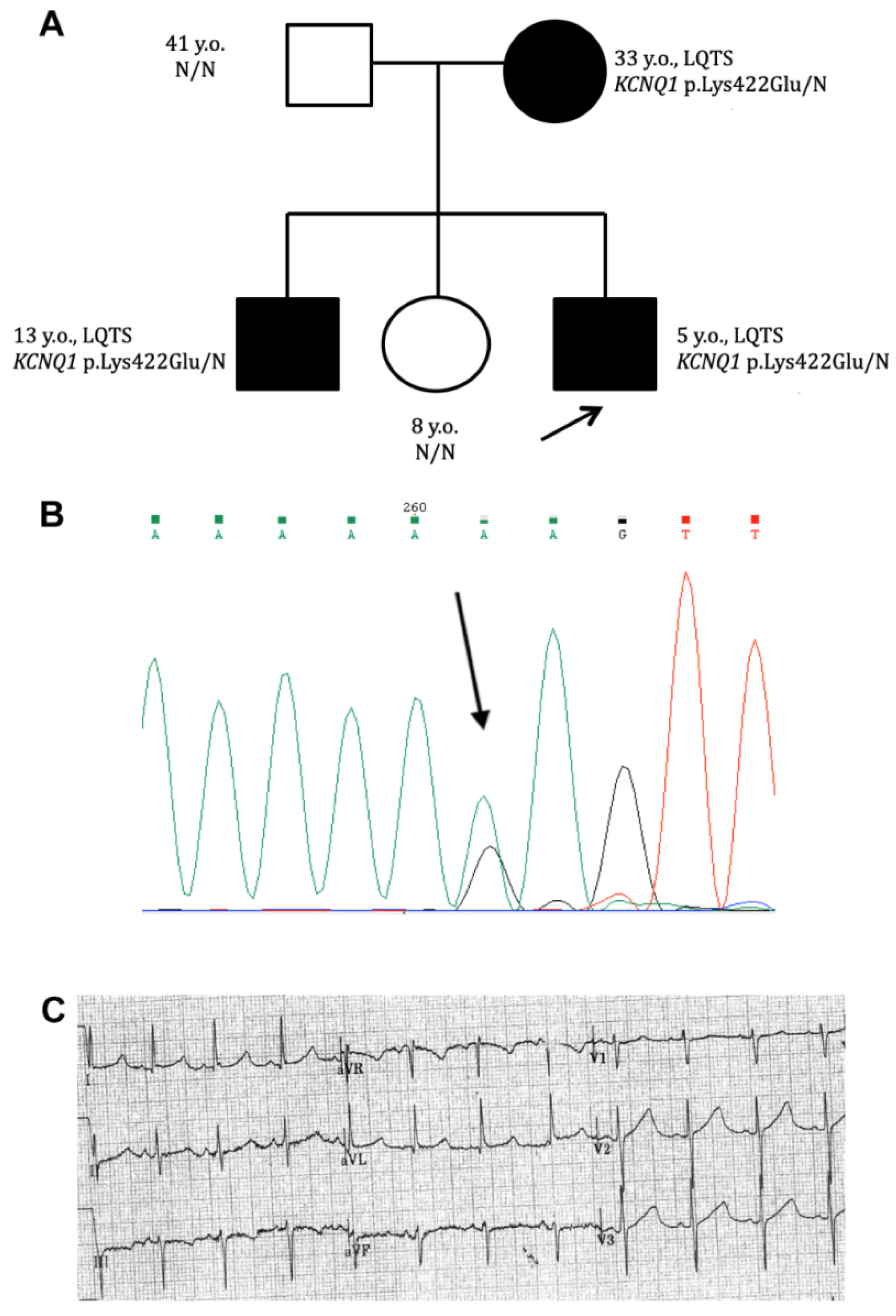
2.1. Clinical Case
2.2. Expression and Subcellular Localization of Wild-Type and Mutant Kv7.1 Channels
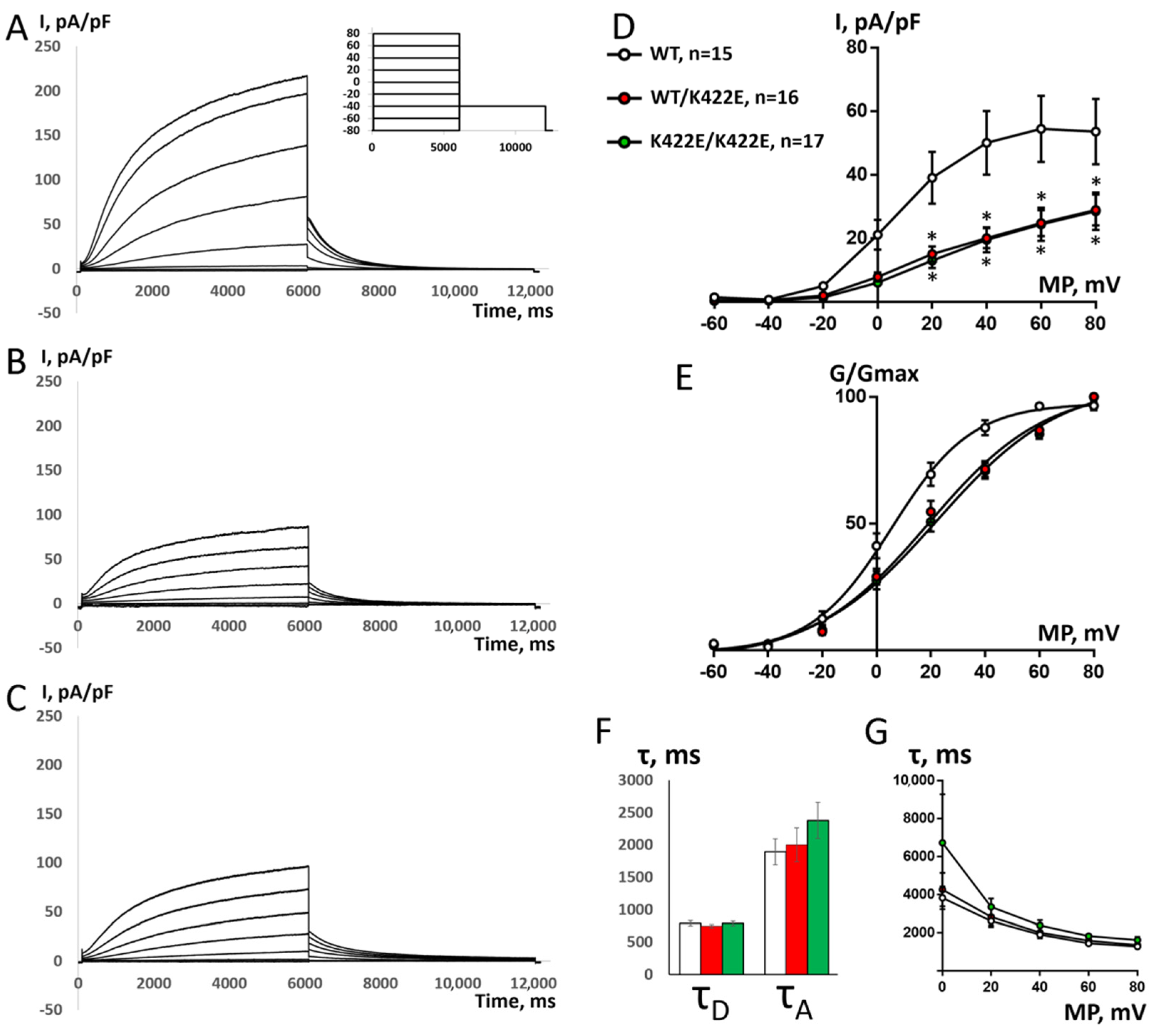
2.3. Electrophysiological Properties of WT and K422E Channel Complexes
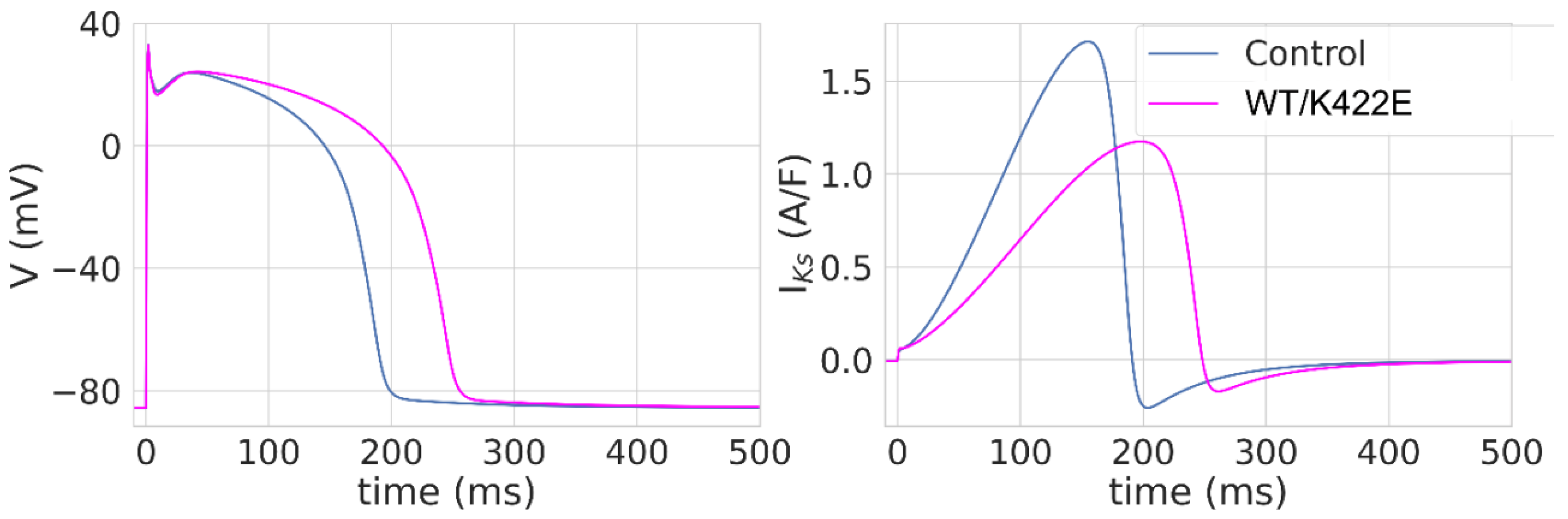
2.4. Modeling of the Influence of the K422E Mutation on Simulated Human Ventricular AP
3. Discussion
3.1. K422E Mutation Analysis
3.2. Proposed Mechanisms of Functional Loss
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Clinical and Genetic Evaluation
4.2. Plasmids
4.3. Introduction of a Point Mutation into a Channel Sequence
4.4. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.5. Fluorescent Microscopy
4.6. Immunoblotting
4.7. Electrophysiology
4.8. Computer Simulations of Human Ventricular Action Potential
4.9. Statistics
4.10. Electrostatics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahm, A.K.; Lugenbiel, P.; Schweizer, P.A.; Katus, H.A.; Thomas, D. Role of ion channels in heart failure and channelopathies. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledford, H.A.; Ren, L.; Thai, P.N.; Park, S.; Timofeyev, V.; Sirish, P.; Xu, W.; Emigh, A.M.; Priest, J.R.; Perez, M.V.; et al. Disruption of protein quality control of the human ether-à-go-go related gene K+ channel results in profound long QT syndrome. Heart Rhythm. 2022, 19, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Larsson, H.P. Insights into Cardiac IKs (KCNQ1/KCNE1) Channels Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, L.; Eckhardt, L.L. Cardiac potassium inward rectifier Kir2: Review of structure, regulation, pharmacology, and arrhythmogenesis. Heart Rhythm. 2021, 18, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros-Domingo, A.; Tan, B.-H.; Crotti, L.; Tester, D.J.; Eckhardt, L.; Cuoretti, A.; Kroboth, S.L.; Song, C.; Zhou, Q.; Kopp, D.; et al. Gain-of-function mutation S422L in the KCNJ8-encoded cardiac K(ATP) channel Kir6.1 as a pathogenic substrate for J-wave syndromes. Heart Rhythm. 2010, 7, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohno, S.; Ozawa, J.; Fukuyama, M.; Makiyama, T.; Horie, M. An NGS-based genotyping in LQTS; minor genes are no longer minor. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 65, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.S.; Tan, H.L.; Wilde, A.A.M. Cardiac Ion Channels in Health and Disease. Heart Rhythm. 2010, 7, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.B.; Campbell, E.B.; Mackinnon, R. Crystal Structure of a Mammalian Voltage-Dependent Shaker Family K+ Channel. Science 2005, 309, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sokolova, O.; Accardi, A.; Gutierrez, D.; Lau, A.; Rigney, M.; Grigorieff, N. Conformational Changes in the C Terminus of Shaker K+ Channel Bound to the Rat Kvbeta2-Subunit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12607–12612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; MacKinnon, R. Structural Basis of Human KCNQ1 Modulation and Gating. Cell 2020, 180, 340–347.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimoto, K.; Kinoshita, K.; Yokoyama, T.; Hata, Y.; Komatsu, T.; Tsushima, T.; Nishide, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Mizumaki, K.; Tabata, T.; et al. Characterization of a Novel Mutant KCNQ1 Channel Subunit Lacking a Large Part of the C-Terminal Domain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 440, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pischalnikova, A.V.; Sokolova, O.S. The Domain and Conformational Organization in Potassium Voltage-Gated Ion Channels. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2009, 4, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, A.; Abderemane-Ali, F.; Hura, G.L.; Rossen, N.D.; Gate, R.E.; Minor, D.L. A Calmodulin C-Lobe Ca2+-Dependent Switch Governs Kv7 Channel Function. Neuron 2018, 97, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haitin, Y.; Wiener, R.; Shaham, D.; Peretz, A.; Ben Tal Cohen, E.; Shamgar, L.; Pongs, O.; Hirsch, J.A.; Attali, B. Intracellular Domains Interactions and Gated Motions of I(KS) Potassium Channel Subunits. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 1994–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aivar, P.; Fernández-Orth, J.; Gomis-Perez, C.; Alberdi, A.; Alaimo, A.; Rodríguez, M.S.; Giraldez, T.; Miranda, P.; Areso, P.; Villarroel, A. Surface Expression and Subunit Specific Control of Steady Protein Levels by the Kv7.2 Helix A-B Linker. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sachyani, D.; Dvir, M.; Strulovich, R.; Tria, G.; Tobelaim, W.; Peretz, A.; Pongs, O.; Svergun, D.; Attali, B.; Hirsch, J.A. Structural Basis of a Kv7.1 Potassium Channel Gating Module: Studies of the Intracellular c-Terminal Domain in Complex with Calmodulin. Structure 2014, 22, 1582–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ten Tusscher, K.H.W.J.; Panfilov, A.V. Alternans and Spiral Breakup in a Human Ventricular Tissue Model. Am. J. Physiol.—Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, 1088–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleckar, M.M.; Myklebust, L.; Uv, J.; Florvaag, P.M.; Strøm, V.; Glinge, C.; Jabbari, R.; Vejlstrup, N.; Engstrøm, T.; Ahtarovski, K.; et al. Combined In-Silico and Machine Learning Approaches Toward Predicting Arrhythmic Risk in Post-Infarction Patients. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 745349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Rasmusson, R.L.; Bett, G.C.; Franks, B.; Zhang, H.; Hancox, J.C. Investigation of the Effects of the Short QT Syndrome D172N Kir2.1 Mutation on Ventricular Action Potential Profile Using Dynamic Clamp. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 794620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.U.; Lee, J.; Lim, K.M. Computational Study to Identify the Effects of the KCNJ2 E299V Mutation in Cardiac Pumping Capacity. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2020, 2020, 7194275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizawa, Y.; Ueda, K.; Wu, L.M.; Inagaki, N.; Hayashi, T.; Takahashi, M.; Ohta, M.; Kawano, S.; Hirano, Y.; Yasunami, M.; et al. Truncated KCNQ1 Mutant, A178fs/105, Forms Hetero-Multimer Channel with Wild-Type Causing a Dominant-Negative Suppression Due to Trafficking Defect. FEBS Lett. 2004, 574, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aromolaran, A.S.; Subramanyam, P.; Chang, D.D.; Kobertz, W.R.; Colecraft, H.M. LQT1 Mutations in KCNQ1 C-Terminus Assembly Domain Suppress IKs Using Different Mechanisms. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 104, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harmer, S.C.; Mohal, J.S.; Royal, A.A.; McKenna, W.J.; Lambiase, P.D.; Tinker, A. Cellular Mechanisms Underlying the Increased Disease Severity Seen for Patients with Long QT Syndrome Caused by Compound Mutations in KCNQ1. Biochem. J. 2014, 462, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Splawski, I.; Shen, J.; Timothy, K.W.; Lehmann, M.H.; Priori, S.; Robinson, J.L.; Moss, A.J.; Schwartz, P.J.; Towbin, J.A.; Vincent, G.M.; et al. Spectrum of Mutations in Long-QT Syndrome Genes. Circulation 2000, 102, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choveau, F.S.; Abderemane-Ali, F.; Coyan, F.C.; Es-Salah-Lamoureux, Z.; Baro, I.; Loussouarn, G. Opposite Effects of the S4-S5 Linker and PIP(2) on Voltage-Gated Channel Function: KCNQ1/KCNE1 and Other Channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choveau, F.S.; Rodriguez, N.; Ali, F.A.; Labro, A.J.; Rose, T.; Dahimène, S.; Boudin, H.; Le Hénaff, C.; Escande, D.; Snyders, D.J.; et al. KCNQ1 Channels Voltage Dependence through a Voltage-Dependent Binding of the S4-S5 Linker to the Pore Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malak, O.A.; Gluhov, G.S.; Grizel, A.V.; Kudryashova, K.S.; Sokolova, O.S.; Loussouarn, G. Voltage-Dependent Activation in EAG Channels Follows a Ligand-Receptor Rather than a Mechanical-Lever Mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malak, O.A.; Es-Salah-Lamoureux, Z.; Loussouarn, G. HERG S4-S5 Linker Acts as a Voltage-Dependent Ligand That Binds to the Activation Gate and Locks It in a Closed State. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 2015, 17, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asada, K.; Kurokawa, J.; Furukawa, T. Redox- and calmodulin-dependent S-nitrosylation of the KCNQ1 channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 6014–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veerman, C.C.; Verkerk, A.O.; Blom, M.T.; Klemens, C.A.; Langendijk, P.N.; Van Ginneken, A.C.; Wilders, R.; Tan, H.L. Slow Delayed Rectifier Potassium Current Blockade Contributes Importantly to Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2013, 6, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vandonselaar, M.; Hickie, R.A.; Quail, J.W.; Delbaere, L.T. Trifluoperazine-induced conformational change in Ca2+-calmodulin. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1994, 11, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics. 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karlova, M.G.; Voskoboynikova, N.; Gluhov, G.S.; Abramochkin, D.; Malak, O.A.; Mulkidzhanyan, A.; Loussouarn, G.; Steinhoff, H.J.; Shaitan, K.V.; Sokolova, O.S. Detergent-Free Solubilization of Human Kv Channels Expressed in Mammalian Cells. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2019, 219, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, C.S.; Park, K.H.; El Harchi, A.; Camonis, J.; Kass, R.S.; Escande, D.; Mérot, J.; Loussouarn, G.; Le Bouffant, F.; Baró, I. IKs Response to Protein Kinase A-Dependent KCNQ1 Phosphorylation Requires Direct Interaction with Microtubules. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 79, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hindmarsh, A.C.; Brown, P.N.; Grant, K.E.; Lee, S.L.; Serban, R.; Shumaker, D.E.; Woodward, C.S. SUNDIALS. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 2005, 31, 363–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerx, M.; Collins, P.; de Lange, E.; Volders, P.G.A. Myokit: A Simple Interface to Cardiac Cellular Electrophysiology. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2016, 120, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksimentiev, A.; Schulten, K. Imaging α-Hemolysin with Molecular Dynamics: Ionic Conductance, Osmotic Permeability, and the Electrostatic Potential Map. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 3745–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jurrus, E.; Engel, D.; Star, K.; Monson, K.; Brandi, J.; Felberg, L.E.; Brookes, D.H.; Wilson, L.; Chen, J.; Liles, K.; et al. Improvements to the APBS Biomolecular Solvation Software Suite. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karlova, M.; Abramochkin, D.V.; Pustovit, K.B.; Nesterova, T.; Novoseletsky, V.; Loussouarn, G.; Zaklyazminskaya, E.; Sokolova, O.S. Disruption of a Conservative Motif in the C-Terminal Loop of the KCNQ1 Channel Causes LQT Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147953
Karlova M, Abramochkin DV, Pustovit KB, Nesterova T, Novoseletsky V, Loussouarn G, Zaklyazminskaya E, Sokolova OS. Disruption of a Conservative Motif in the C-Terminal Loop of the KCNQ1 Channel Causes LQT Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(14):7953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147953
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarlova, Maria, Denis V. Abramochkin, Ksenia B. Pustovit, Tatiana Nesterova, Valery Novoseletsky, Gildas Loussouarn, Elena Zaklyazminskaya, and Olga S. Sokolova. 2022. "Disruption of a Conservative Motif in the C-Terminal Loop of the KCNQ1 Channel Causes LQT Syndrome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 14: 7953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147953
APA StyleKarlova, M., Abramochkin, D. V., Pustovit, K. B., Nesterova, T., Novoseletsky, V., Loussouarn, G., Zaklyazminskaya, E., & Sokolova, O. S. (2022). Disruption of a Conservative Motif in the C-Terminal Loop of the KCNQ1 Channel Causes LQT Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(14), 7953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147953





