Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Understanding the Inflammatory Implications of the Microbiome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Role of Microbiome on Inflammatory Processes in Conditions Which Lead to Chronic Liver Disease
2.1. Alcoholic Liver Disease
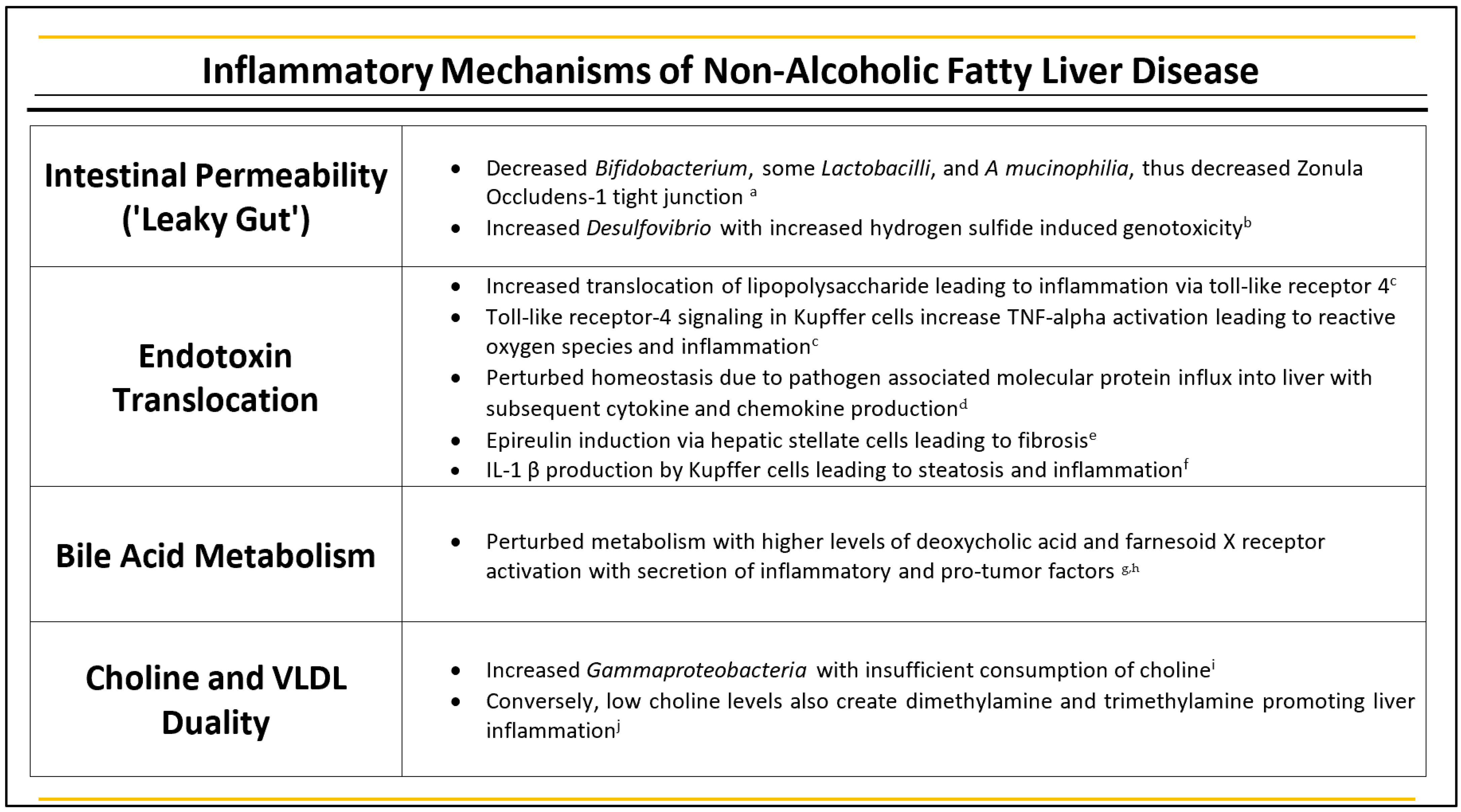
2.2. NAFLD
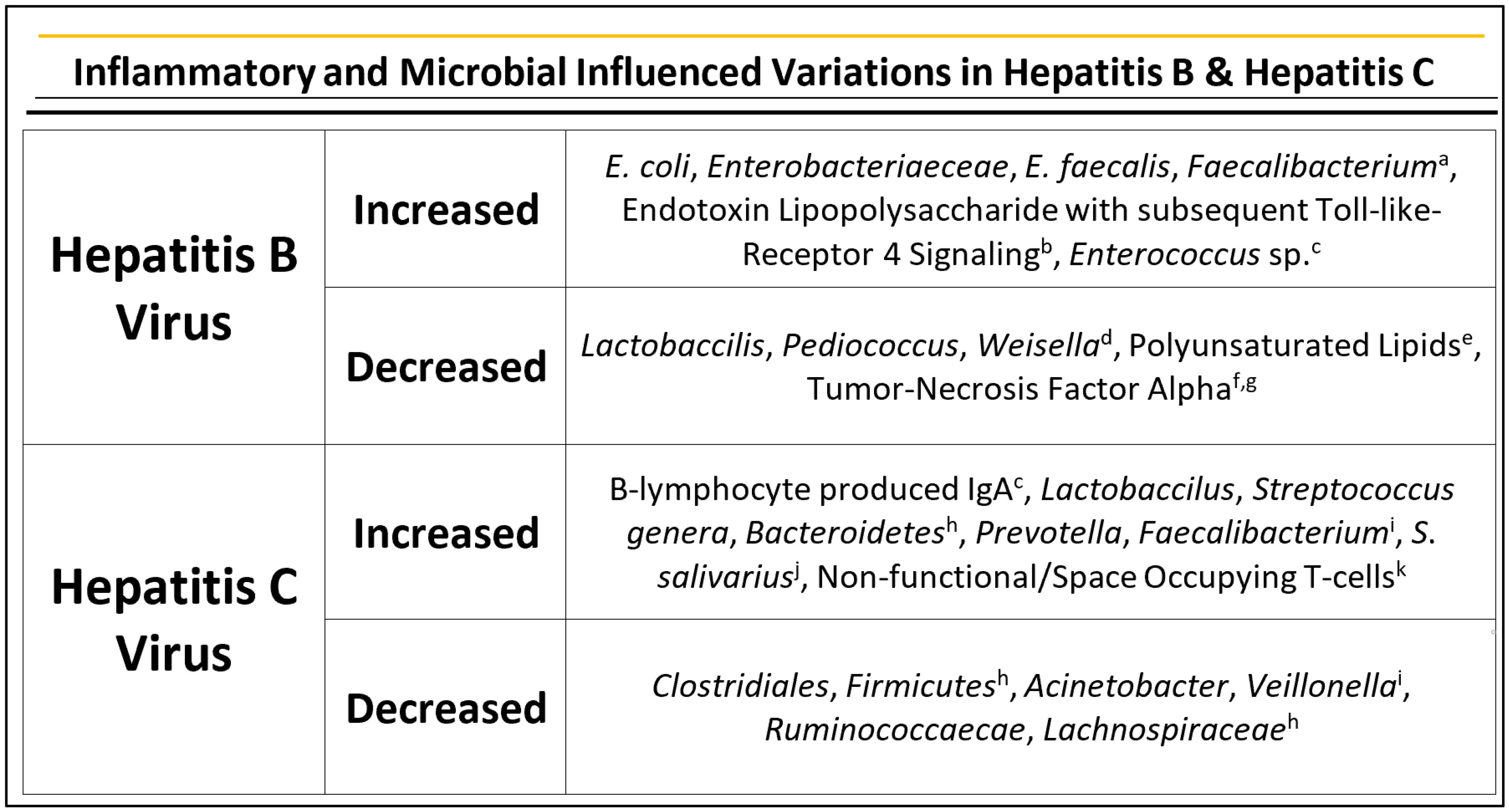
2.3. Hepatitis B
2.4. Hepatitis C
3. Role of the Microbiome on Inflammatory Processes in HCC
4. Role of Microbiome on EMT
5. Microbial Metabolites
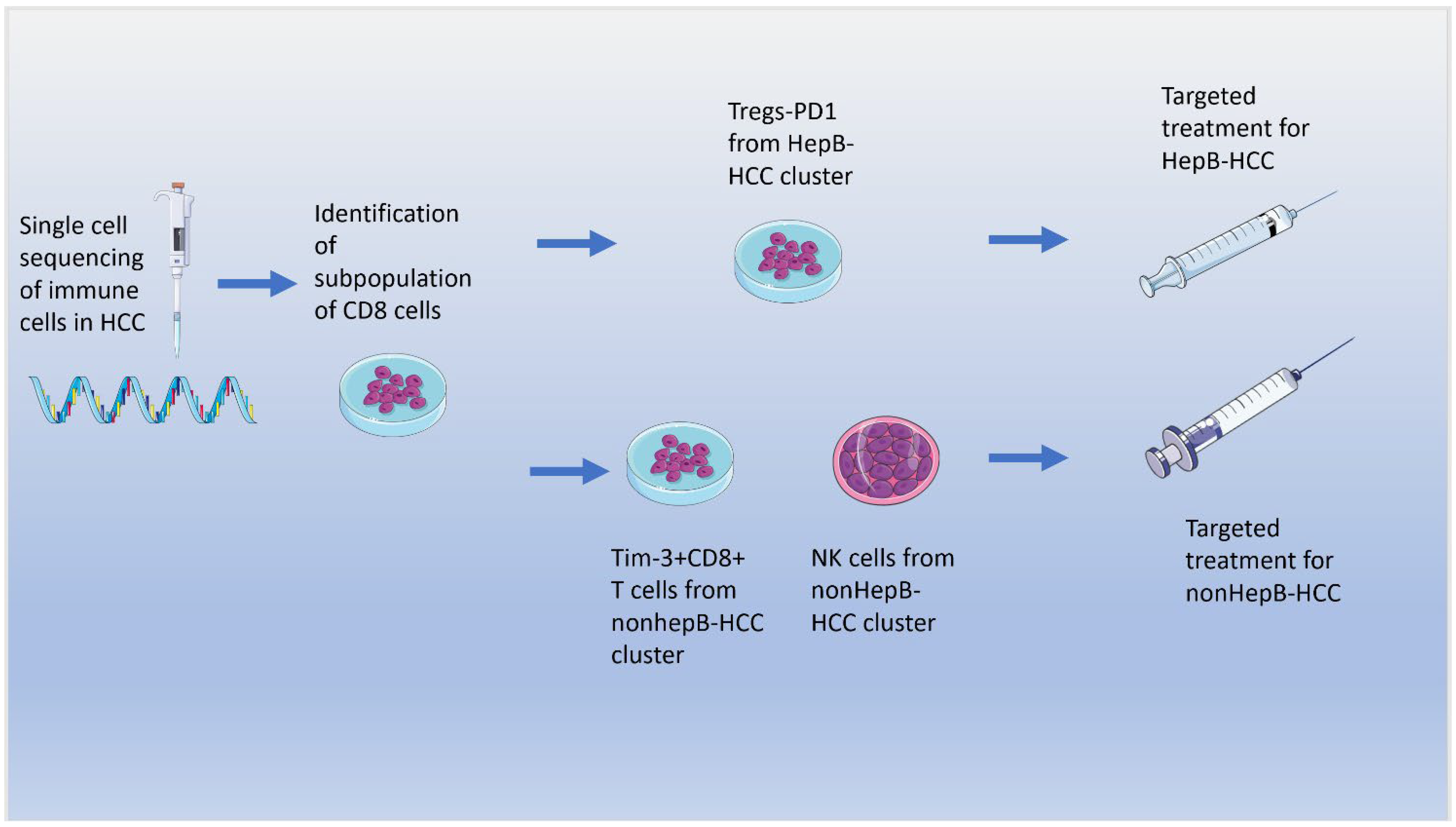
6. Role of the Microbiome on the Immune System and Immunotherapy
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nault, J.C.; Ningarhari, M.; Rebouissou, S.; Zucman-Rossi, J. The Role of Telomeres and Telomerase in Cirrhosis and Liver Cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopala, S.V.; Vashee, S.; Oldfield, L.M.; Suzuki, Y.; Venter, J.C.; Telenti, A.; Nelson, K.E. The Human Microbiome and Cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2017, 10, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschke, R. Alcoholic Liver Disease: Alcohol Metabolism, Cascade of Molecular Mechanisms, Cellular Targets, and Clinical Aspects. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thursz, M.; Gual, A.; Lackner, C.; Mathurin, P.; Moreno, C.; Spahr, L.; Sterneck, M.; Cortez-Pinto, H. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, Stability and Resilience of the Human Gut Microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, M.; Longo, M.; Dongiovanni, P. Alcohol or Gut Microbiota: Who Is the Guilty? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Lemasters, J.J. A Unifying Hypothesis Linking Hepatic Adaptations for Ethanol Metabolism to the Proinflammatory and Profibrotic Events of Alcoholic Liver Disease. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 2072–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull-Otterson, L.; Feng, W.; Kirpich, I.; Wang, Y.; Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Gobejishvili, L.; Joshi-Barve, S.; Ayvaz, T.; Petrosino, J.; et al. Metagenomic Analyses of Alcohol Induced Pathogenic Alterations in the Intestinal Microbiome and the Effect of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG Treatment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Kakiyama, G.; Zhao, D.; Takei, H.; Fagan, A.; Hylemon, P.; Zhou, H.; Pandak, W.M.; Nittono, H.; Fiehn, O.; et al. Continued Alcohol Misuse in Human Cirrhosis Is Associated with an Impaired Gut–Liver Axis. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fouts, D.E.; Stärkel, P.; Hartmann, P.; Chen, P.; Llorente, C.; DePew, J.; Moncera, K.; Ho, S.B.; Brenner, D.A.; et al. Intestinal REG3 Lectins Protect against Alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Reducing Mucosa-Associated Microbiota and Preventing Bacterial Translocation. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Stärkel, P.; Turner, J.R.; Ho, S.B.; Schnabl, B. Dysbiosis-Induced Intestinal Inflammation Activates Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor I and Mediates Alcoholic Liver Disease in Mice. Hepatology 2015, 61, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R. Endotoxemia and Gut Barrier Dysfunction in Alcoholic Liver Disease. Hepatology 2009, 50, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Ahmad, M.F.; Nagy, L.E.; Tsukamoto, H. Inflammatory Pathways in Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temko, J.E.; Bouhlal, S.; Farokhnia, M.; Lee, M.R.; Cryan, J.F.; Leggio, L. The Microbiota, the Gut and the Brain in Eating and Alcohol Use Disorders: A “Ménage à Trois”? Alcohol Alcohol. 2017, 52, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sung, C.Y.J.; Lee, N.; Ni, Y.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Panagiotou, G.; El-Nezami, H. Probiotics Modulated Gut Microbiota Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1306–E1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Wu, W.K.; Wu, M.S. Microbiota-Associated Therapy for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis-Induced Liver Cancer: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luther, J.; Garber, J.J.; Khalili, H.; Dave, M.; Bale, S.S.; Jindal, R.; Motola, D.L.; Luther, S.; Bohr, S.; Jeoung, S.W.; et al. Hepatic Injury in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Contributes to Altered Intestinal Permeability. CMGH 2015, 1, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Y.Y.; Ha, C.W.Y.; Campbell, C.R.; Mitchell, A.J.; Dinudom, A.; Oscarsson, J.; Cook, D.I.; Hunt, N.H.; Caterson, I.D.; Holmes, A.J.; et al. Increased Gut Permeability and Microbiota Change Associate with Mesenteric Fat Inflammation and Metabolic Dysfunction in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Y.Y.; Ha, C.W.Y.; Hoffmann, J.M.A.; Oscarsson, J.; Dinudom, A.; Mather, T.J.; Cook, D.I.; Hunt, N.H.; Caterson, I.D.; Holmes, A.J.; et al. Effects of Dietary Fat Profile on Gut Permeability and Microbiota and Their Relationships with Metabolic Changes in Mice. Obesity 2015, 23, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejczyk, A.A.; Zheng, D.; Shibolet, O.; Elinav, E. The Role of the Microbiome in NAFLD and NASH. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e9302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapito, D.H.; Mencin, A.; Gwak, G.Y.; Pradere, J.P.; Jang, M.K.; Mederacke, I.; Caviglia, J.M.; Khiabanian, H.; Adeyemi, A.; Bataller, R.; et al. Promotion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by the Intestinal Microbiota and TLR4. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Greten, T.F. Gut Microbiome in HCC—Mechanisms, Diagnosis and Therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, S.; Rajak, S.; Anjum, B.; Sinha, R.A. Molecular Links between Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatoma Res. 2019, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Loo, T.M.; Atarashi, K.; Kanda, H.; Sato, S.; Oyadomari, S.; Iwakura, Y.; Oshima, K.; Morita, H.; Hattori, M.; et al. Obesity-Induced Gut Microbial Metabolite Promotes Liver Cancer through Senescence Secretome. Nature 2013, 499, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Tanaka, N.; Fukami, T.; Xie, C.; Yagai, T.; Kim, D.; Velenosi, T.J.; Yan, T.; Krausz, K.W.; Levi, M.; et al. Role of Farnesoid X Receptor and Bile Acids in Hepatic Tumor Development. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Baker, R.D.; Zhu, R.; Baker, S.S. Gut Microbiota Produce Alcohol and Contribute to NAFLD. Gut 2016, 65, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Q.; Li, H. Gut Microbiota and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Insights on Mechanisms and Therapy. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, M.D.; Hamp, T.J.; Reid, R.W.; Fischer, L.M.; Zeisel, S.H.; Fodor, A.A. Association between Composition of the Human Gastrointestinal Microbiome and Development of Fatty Liver with Choline Deficiency. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Williams, B.; Schnabl, B. Gut microbiota, fatty liver disease, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Res. 2018, 2, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wu, Z.; Xu, W.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, L. Intestinal Microbiota Was Assessed in Cirrhotic Patients with Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 61, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, J.; Feng, Q.; Dai, J.; Sun, S.; et al. Gut Microbial Dysbiosis Is Associated with Altered Hepatic Functions and Serum Metabolites in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadkhani, A. On the potential role of intestinal microbial community in hepatocarcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis B. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 3095–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pålsson-McDermott, E.M.; O’Neill, L.A.J. Signal Transduction by the Lipopolysaccharide Receptor, Toll-like Receptor-4. Immunology 2004, 113, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, E.; Yang, D.; Lu, M. Contribution of Toll-like Receptors to the Control of Hepatitis B Virus Infection by Initiating Antiviral Innate Responses and Promoting Specific Adaptive Immune Responses. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 12, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roderburg, C.; Luedde, T. The Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Development and Progression of Liver Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosevic, I.; Vujovic, A.; Barac, A.; Djelic, M.; Korac, M.; Spurnic, A.R.; Gmizic, I.; Stevanovic, O.; Djordjevic, V.; Lekic, N.; et al. Gut-Liver Axis, Gut Microbiota, and Its Modulation in the Management of Liver Diseases: A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, F.; Zhuang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Mao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Alteration in Gut Microbiota Associated with Hepatitis B and Non-Hepatitis Virus Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Yang, H.I.; Yuan, Y.; L’Italien, G.; Chen, C.J. Epidemiology and Natural History of Hepatitis C Virus Infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 9270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mowafy, M.; Elgaml, A.; El-Mesery, M.; Sultan, S.; Ahmed, T.A.E.; Gomaa, A.I.; Aly, M.; Mottawea, W. Changes of Gut-Microbiota-Liver Axis in Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Biology 2021, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.M.; Adel, A.; El-Gendy, A.O.; Essam, T.M.; Aziz, R.K. Gut Microbiome Alterations in Patients with Stage 4 Hepatitis C. Gut Pathog. 2016, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Huo, Z.; Song, X.; Chen, X.; Tian, X.; Wang, X. Mir-106a Regulates Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis of Colon Cancer Cells through Targeting the PTEN/ PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3197–3201. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, N.; Yang, F.; Li, A.; Prifti, E.; Chen, Y.; Shao, L.; Guo, J.; le Chatelier, E.; Yao, J.; Wu, L.; et al. Alterations of the Human Gut Microbiome in Liver Cirrhosis. Nature 2014, 513, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoulis, V.G.; Dubovan, P.; Papoutsi, E.; Kataki, A.; Koskinas, J. Senescence in Hbv-, Hcv-and Nafld- Mediated Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Senotherapeutics: Current Evidence and Future Perspective. Cancers 2021, 13, 4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinati, F.; Cardin, R.; Bortolami, M.; Burra, P.; Russo, F.P.; Rugge, M.; Guido, M.; Sergio, A.; Naccarato, R. Hepatitis C Virus: From Oxygen Free Radicals to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Viral Hepat. 2007, 14, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponziani, F.R.; Bhoori, S.; Castelli, C.; Putignani, L.; Rivoltini, L.; del Chierico, F.; Sanguinetti, M.; Morelli, D.; Paroni Sterbini, F.; Petito, V.; et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is Associated with Gut Microbiota Profile and Inflammation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2019, 69, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Li, A.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, L.; Yu, Z.; Lu, H.; Xie, H.; Chen, X.; Shao, L.; Zhang, R.; et al. Gut Microbiome Analysis as a Tool towards Targeted Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut 2019, 68, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Wang, G.; Pang, Z.; Ran, N.; Gu, Y.; Guan, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zuo, X.; Pan, H.; Zheng, J.; et al. Liver Cirrhosis Contributes to the Disorder of Gut Microbiota in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 4232–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakladar, J.; Wong, L.M.; Kuo, S.Z.; Li, W.T.; Yu, M.A.; Chang, E.Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Ongkeko, W.M. The Liver Microbiome Is Implicated in Cancer Prognosis and Modulated by Alcohol and Hepatitis B. Cancers 2020, 12, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.G.; Feng, Y.; Theve, E.J.; Raczynski, A.R.; Fiala, J.L.A.; Doernte, A.L.; Williams, M.; McFaline, J.L.; Essigmann, J.M.; Schauer, D.B.; et al. Gut Microbes Define Liver Cancer Risk in Mice Exposed to Chemical and Viral Transgenic Hepatocarcinogens. Gut 2010, 59, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behary, J.; Amorim, N.; Jiang, X.T.; Raposo, A.; Gong, L.; McGovern, E.; Ibrahim, R.; Chu, F.; Stephens, C.; Jebeili, H.; et al. Gut Microbiota Impact on the Peripheral Immune Response in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalyfa, A.A.; Punatar, S.; Aslam, R.; Yarbrough, A. Exploring the Inflammatory Pathogenesis of Colorectal Cancer. Diseases 2021, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Yu, L.X.; Yang, W.; Tang, L.; Lin, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhai, B.; Tan, Y.X.; Shan, L.; Liu, Q.; et al. Profound Impact of Gut Homeostasis on Chemically-Induced pro-Tumorigenic Inflammation and Hepatocarcinogenesis in Rats. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern Recognition Receptors and Inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, J.; Cammarota, E.; Wright, J.A.; Cicuta, P.; Gottschalk, R.A.; Li, N.; Fraser, I.D.C.; Bryant, C.E. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced NF-ΚB Nuclear Translocation Is Primarily Dependent on MyD88, but TNFα Expression Requires TRIF and MyD88. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Deng, M.; Loughran, P.A.; Yang, M.; Lin, M.; Yang, C.; Gao, W.; Jin, S.; Li, S.; Cai, J.; et al. LPS Induces Active HMGB1 Release from Hepatocytes into Exosomes Through the Coordinated Activities of TLR4 and Caspase-11/GSDMD Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, J. LPS Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Activation of TLR4/JNK Signaling. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 10429–10435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, M.K.; Celià-Terrassa, T. Dynamics of Phenotypic Heterogeneity during Emt and Stemness in Cancer Progression. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.J.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Development and Disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D.; Tamma, R.; Annese, T. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer: A Historical Overview. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Xu, F.; Dai, C.L. Relationship between Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and the Inflammatory Microenvironment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, Y.; Huang, X.; Westover, K.D.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, B.; Hua, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Intergrated Analysis of ELMO1, Serves as a Link between Tumour Mutation Burden and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2019, 46, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichl, P.; Haider, C.; Grubinger, M.; Mikulits, W. TGF-β in Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis of Liver Carcinoma. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 4135–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honko, A.N.; Mizel, S.B. Effects of Flagellin on Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Immunol. Res. 2005, 33, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, M.R.; Goo, M.J.; Park, J.K.; Hong, I.H.; Ji, A.R.; Han, S.Y.; You, S.Y.; Lee, E.M.; Kim, A.Y.; Park, S.J.; et al. Helicobacter Pylori Accelerates Hepatic Fibrosis by Sensitizing Transforming Growth Factor-Β1-Induced Inflammatory Signaling. Lab. Investig. 2010, 90, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.H.; Parashurama, N.; Park, E.Y.H.; Suganuma, K.; Nahmias, Y.; Park, J.; Tilles, A.W.; Berthiaume, F.; Yarmush, M.L. Homogeneous Differentiation of Hepatocyte-like Cells from Embryonic Stem Cells: Applications for the Treatment of Liver Failure. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 898–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cane, G.; le Moal, V.L.; Pagès, G.; Servin, A.L.; Hofman, P.; Vouret-Craviari, V. Up-Regulation of Intestinal Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor by Afa/Dr Diffusely Adhering Escherichia Coli. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cane, G.; Ginouvès, A.; Marchetti, S.; Buscà, R.; Pouysségur, J.; Berra, E.; Hofman, P.; Vouret-Craviari, V. HIF-1α Mediates the Induction of IL-8 and VEGF Expression on Infection with Afa/Dr Diffusely Adhering E. Coli and Promotes EMT-like Behaviour. Cell. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Z.; da Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, H.L.; Li, X.W.; Dong, J.H. HBx Protein Induces EMT through C-Src Activation in SMMC-7721 Hepatoma Cell Line. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 382, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkari, L.; Grégoire, D.; Floc’H, N.; Moreau, M.; Hernandez, C.; Simonin, Y.; Rosenberg, A.R.; Lassus, P.; Hibner, U. Hepatitis C Viral Protein NS5A Induces EMT and Participates in Oncogenic Transformation of Primary Hepatocyte Precursors. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavio, N.; Battaglia, S.; Boucreux, D.; Arnulf, B.; Sobesky, R.; Hermine, O.; Brechot, C. Hepatitis C Virus Core Variants Isolated from Liver Tumor but Not from Adjacent Non-Tumor Tissue Interact with Smad3 and Inhibit the TGF-β Pathway. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6119–6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, S.; Benzoubir, N.; Nobilet, S.; Charneau, P.; Samuel, D.; Zignego, A.L.; Atfi, A.; Bréchot, C.; Bourgeade, M.F. Liver Cancer-Derived Hepatitis C Virus Core Proteins Shift TGF-Beta Responses from Tumor Suppression to Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makki, K.; Deehan, E.C.; Walter, J.; Bäckhed, F. The Impact of Dietary Fiber on Gut Microbiota in Host Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fu, X.; van Ness, C.; Meng, Z.; Ma, X.; Huang, W. Bile Acid Receptors and Liver Cancer. Current Pathobiology Reports 2013, 1, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Ma, C.; Liu, J.; Li, N.; Gao, M.; Huang, A.; Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Huang, X. Erratum: Downregulation of Nuclear Receptor FXR Is Associated with Multiple Malignant Clinicopathological Characteristics in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver. Physiol. 2012, 303, G1245–G1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ge, X.; Heemstra, L.A.; Chen, W.D.; Xu, J.; Smith, J.L.; Ma, H.; Kasim, N.; Edwards, P.A.; Novak, C.M. Loss of FXR Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Accelerates Liver Carcinogenesis in Ob/Ob Mice. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Takashina, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Nagamine, R.; Saito, Y.; Kamada, N.; Saito, H. Bile Acid Metabolism Regulated by the Gut Microbiota Promotes Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Mice. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 9925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Wang, X.; Zhao, A.; Yan, J.; Chen, W.; Jiang, R.; Ji, J.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, S.; et al. Sex-Dependent Effects on Gut Microbiota Regulate Hepatic Carcinogenic Outcomes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Han, M.; Heinrich, B.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Sandhu, M.; Agdashian, D.; Terabe, M.; Berzofsky, J.A.; Fako, V.; et al. Gut Microbiome–Mediated Bile Acid Metabolism Regulates Liver Cancer via NKT Cells. Science 2018, 360, eaan5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Jiang, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, P.; Zhao, A.; Wu, Y.; Huang, F.; Liu, Z.; Rajani, C.; Zheng, X.; et al. Conjugated Secondary 12α-Hydroxylated Bile Acids Promote Liver Fibrogenesis. EBioMedicine 2021, 66, 103290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bossche, L.; Hindryckx, P.; Devisscher, L.; Devriese, S.; van Welden, S.; Holvoet, T.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Vital, M.; Pieper, D.H.; vanden Bussche, J.; et al. Ursodeoxycholic Acid and Its Taurine- or Glycine-Conjugated Species Reduce Colitogenic Dysbiosis and Equally Suppress Experimental Colitis in Mice. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e02766-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Yeoh, B.S.; Chassaing, B.; Xiao, X.; Saha, P.; Aguilera Olvera, R.; Lapek, J.D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.B.; Hao, S.; et al. Dysregulated Microbial Fermentation of Soluble Fiber Induces Cholestatic Liver Cancer. Cell 2018, 175, 679–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; You, H.J.; Bajaj, J.S.; Joo, S.K.; Yu, J.; Park, S.; Kang, H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Distinct Signatures of Gut Microbiome and Metabolites Associated with Significant Fibrosis in Non-Obese NAFLD. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, A.W.F.; Houben, T.; Katiraei, S.; Dijk, W.; Boutens, L.; van der Bolt, N.; Wang, Z.; Brown, J.M.; Hazen, S.L.; Mandard, S.; et al. Modulation of the Gut Microbiota Impacts Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Potential Role for Bile Acids. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1399–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, H.; Youn, G.S.; Shin, M.J.; Suk, K.T. Role of Gut Microbiota in Hepatocarcinogenesis. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.G.; Huang, X.D.; Shen, P.; Li, L.R.; Xue, H.T.; Ji, G.Z. Anticancer Effects of Sodium Butyrate on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells in Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui-Yuasa, I.; Kojima-Yuasa, A. Abstract 2813: The Synergistic Anticancer Activity of 1’-Acetoxychavicol Acetate and Sodium Butyrate in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Cancer Res. 2016, 76 (Suppl. S14), 2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mola, S.; Pandolfo, C.; Sica, A.; Porta, C. The Macrophages-Microbiota Interplay in Colorectal Cancer (CRC)-Related Inflammation: Prognostic and Therapeutic Significance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.J.; von Felden, J.; Garcia-Lezana, T.; Sarcognato, S.; Villanueva, A. Tumour Evolution in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lou, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Feng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Fu, Q.; Ye, M.; et al. Integrated Multiomic Analysis Reveals Comprehensive Tumour Heterogeneity and Novel Immunophenotypic Classification in Hepatocellular Carcinomas. Gut 2019, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshida, Y.; Nijman, S.M.B.; Kobayashi, M.; Chan, J.A.; Brunet, J.P.; Chiang, D.Y.; Villanueva, A.; Newell, P.; Ikeda, K.; Hashimoto, M.; et al. Integrative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Common Molecular Subclasses of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7385–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zheng, L.; Yoo, J.K.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Kang, B.; Hu, R.; Huang, J.Y.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Landscape of Infiltrating T Cells in Liver Cancer Revealed by Single-Cell Sequencing. Cell 2017, 169, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Pan, L.; Lai, L.; Chua, C.; Wasser, M.; Lim, T.K.H.; Yeong, J.; Toh, H.C.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Multidimensional Analyses Reveal Distinct Immune Microenvironment in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut 2018, 68, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Wang, D.; Long, J.; Yang, X.; Lin, J.; Song, Y.; Xie, F.; Xun, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Gut Microbiome Is Associated with the Clinical Response to Anti-PD-1 Based Immunotherapy in Hepatobiliary Cancers. J. ImmunoTherapy Cancer 2021, 9, e003334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivan, A.; Corrales, L.; Hubert, N.; Williams, J.B.; Aquino-Michaels, K.; Earley, Z.M.; Benyamin, F.W.; Lei, Y.M.; Jabri, B.; Alegre, M.L.; et al. Commensal Bifidobacterium Promotes Antitumor Immunity and Facilitates Anti-PD-L1 Efficacy. Science 2015, 350, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vétizou, M.; Pitt, J.M.; Daillère, R.; Lepage, P.; Waldschmitt, N.; Flament, C.; Rusakiewicz, S.; Routy, B.; Roberti, M.P.; Duong, C.P.M.; et al. Anticancer Immunotherapy by CTLA-4 Blockade Relies on the Gut Microbiota. Science 2015, 350, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.W.H.; Tsui, Y.M.; Chan, L.K.; Sze, K.M.F.; Zhang, X.; Cheu, J.W.S.; Chiu, Y.T.; Lee, J.M.F.; Chan, A.C.Y.; Cheung, E.T.Y.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Shows the Immunosuppressive Landscape and Tumor Heterogeneity of HBV-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur, C.; Ibrahim, Y.; Isaacson, B.; Yamin, R.; Abed, J.; Gamliel, M.; Enk, J.; Bar-On, Y.; Stanietsky-Kaynan, N.; Coppenhagen-Glazer, S.; et al. Binding of the Fap2 Protein of Fusobacterium nucleatum to Human Inhibitory Receptor TIGIT Protects Tumors from Immune Cell Attack. Immunity 2015, 42, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalyfa, A.A.; Punatar, S.; Yarbrough, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Understanding the Inflammatory Implications of the Microbiome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158164
Khalyfa AA, Punatar S, Yarbrough A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Understanding the Inflammatory Implications of the Microbiome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158164
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalyfa, Ahamed A., Shil Punatar, and Alex Yarbrough. 2022. "Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Understanding the Inflammatory Implications of the Microbiome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158164
APA StyleKhalyfa, A. A., Punatar, S., & Yarbrough, A. (2022). Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Understanding the Inflammatory Implications of the Microbiome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158164





