3D Printed Solutions for Spheroid Engineering and Cancer Research
Abstract
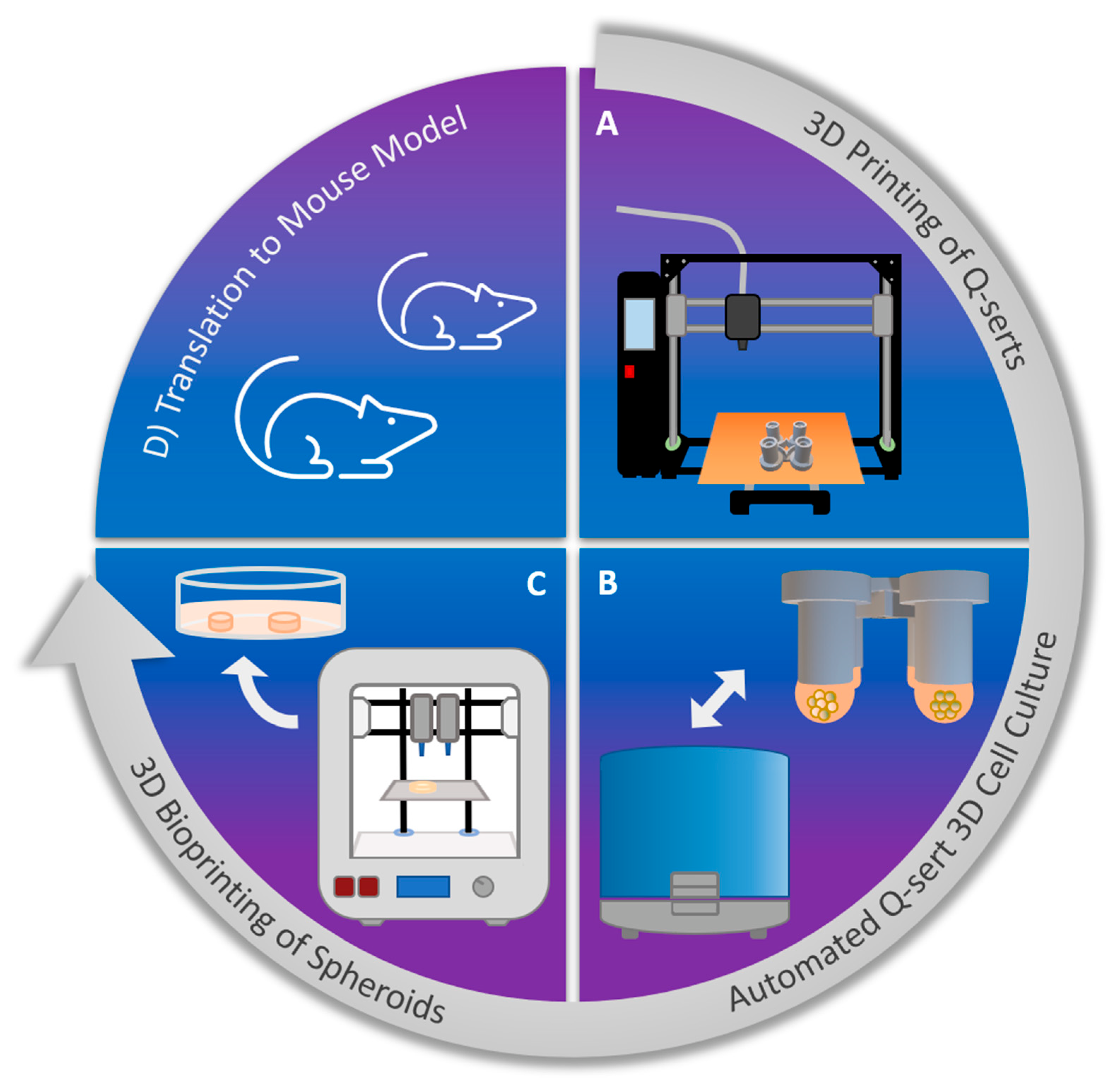
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. 3D Printing and Sterilization of Q-Serts
2.2. Culture of Spheroids in 3D Printed Q-Serts
2.3. Automated Spheroid Culture Handling
2.4. Comparison of the Culture of STEMs in Q-Serts versus Commercial Systems
2.5. Rheology of Tumor-ECM Mimic Bioink
2.6. 3D Bioprinting of Spheroids
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Spheroid Culture
4.3. Printing of Hanging Drop Inserts (Q-Serts)
4.4. Synthesis of Carboxylated Agarose
4.5. Bioink Preparation
4.6. Rheology
4.7. Bioprinting
4.8. Histology and Live-Dead Staining
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Report on Cancer: Setting Priorities, Investing Wisely and Providing Care for All; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, C.; Teng, Y. Is It Time to Start Transitioning From 2D to 3D Cell Culture? Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jong, B.K. Three-dimensional tissue culture models in cancer biology. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2005, 15, 365. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, L.G.; Swartz, M.A. Capturing complex 3D tissue physiology in vitro. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortesi, M.M.; Zamagni, A.; Arienti, C.; Pignatta, S.; Tesei, A. Modeling neoplastic disease with spheroids and organoids. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, R.Z.; Chang, H.Y. Recent advances in three-dimensional multicellular spheroid culture for biomedical research. Biotechnol. J. 2008, 3, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, S.P.; Arya, N.; Kohler, E.; Xiang, S.; Christensen, J.; Shastri, V.P. Recapitulating epithelial tumor microenvironment in vitro using three dimensional tri-culture of human epithelial, endothelial, and mesenchymal cells. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panek, M.; Grabacka, M.; Pierzchalska, M. The formation of intestinal organoids in a hanging drop culture. Cytotechnology 2018, 70, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riede, J.; Wollmann, B.M.; Molden, E.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Primary human hepatocyte spheroids as an in vitro tool for investigating drug compounds with low clearance. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2021, 49, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliari, S.R.; Burdick, J.A. A practical guide to hydrogels for cell culture. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tibbitt, M.W.; Anseth, K.S. Hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics for 3D cell culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 103, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Lewin Mejia, D.; Chiang, B.; Luker, K.E.; Luker, G.D. Hybrid collagen alginate hydrogel as a platform for 3D tumor spheroid invasion. Acta Biomater. 2018, 75, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gurski, L.A.; Zhang, C.; Harrington, D.A.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Jia, X. Recreating the tumor microenvironment in a bilayer, hyaluronic acid hydrogel construct for the growth of prostate cancer spheroids. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 9049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Y.; Schwarz, B.; Forget, A.; Barbero, A.; Martin, I.; Shastri, V.P. Advanced Bioink for 3D Bioprinting of Complex Free-Standing Structures with High Stiffness. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forget, A.; Blaeser, A.; Miessmer, F.; Köpf, M.; Campos, D.F.D.; Voelcker, N.H.; Blencowe, A.; Fischer, H.; Shastri, V.P. Mechanically Tunable Bioink for 3D Bioprinting of Human Cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, G.; Jiang, N.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Y.S. Three-dimensional bioprinting of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA). Bio-Des. Manuf. 2018, 1, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yu, M.; Aazmi, A.; Gao, L.; Xue, Q.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, B.; et al. 3D bioprinted hyaluronic acid-based cell-laden scaffold for brain microenvironment simulation. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2020, 3, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Duchamp, M.; Oklu, R.; Ellisen, L.W.; Langer, R.; Khademhosseini, A. Bioprinting the Cancer Microenvironment. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1710–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Y.; Forget, A.; Shastri, V.P. Biobridge: An Outlook on Translational Bioinks for 3D Bioprinting. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2103469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y. Spatial Heterogeneity in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026583. [Google Scholar]
- LaBarbera, D.V.; Reid, B.G.; Yoo, B.H. The multicellular tumor spheroid model for high-throughput cancer drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongisto, V.; Jernström, S.; Fey, V.; Mpindi, J.P.; Kleivi Sahlberg, K.; Kallioniemi, O.; Perälä, M. High-throughput 3D screening reveals differences in drug sensitivities between culture models of JIMT1 breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77232. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, D.; Kaduri, M.; Poley, M.; Adir, O.; Krinsky, N.; Shainsky-Roitman, J.; Schroeder, A. Biocompatibility, biodegradation and excretion of polylactic acid (PLA) in medical implants and theranostic systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 340, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, T.; Rintoul, R.C.; Moore, S.M.; MacKinnon, A.C.; Salter, D.; Choo, C.; Chilvers, E.R.; Dransfield, I.; Donnelly, S.C.; Strieter, R.; et al. Extracellular matrix proteins protect small cell lung cancer cells against apoptosis: A mechanism for small cell lung cancer growth and drug resistance in vivo. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 662–668. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Sidell, N.; Roman, J. Fibronectin stimulates human lung carcinoma cell proliferation by suppressing p21 gene expression via signals involving Erk and Rho kinase. Cancer Lett. 2005, 219, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.N.; Jin, Y.; Yu, Y.; Bai, J.; Liu, G.Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, F.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Characterisation of fibronectin-mediated FAK signalling pathways in lung cancer cell migration and invasion. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rangel, M.P.; de Sá, V.K.; Martins, V.; Martins, J.; Parra, E.R.; Mendes, A.; Andrade, P.C.; Reis, R.M.; Longatto-Filho, A.; Oliveira, C.Z.; et al. Tissue hyaluronan expression, as reflected in the sputum of lung cancer patients, is an indicator of malignancy. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, R.K.; Baker, A.C.; DeBiasi, R.M.; Winckler, W.; LaFramboise, T.; Lin, W.M.; Wang, M.; Feng, W.; Zander, T.; MacConnaill, L.E.; et al. High-throughput oncogene mutation profiling in human cancer. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 347–351. [Google Scholar]
- Glas, A.M.; Floore, A.; Delahaye, L.J.M.J.; Witteveen, A.T.; Pover, R.C.F.; Bakx, N.; Lahti-Domenici, J.S.T.; Bruinsma, T.J.; Warmoes, M.O.; Bernards, R.; et al. Converting a breast cancer microarray signature into a high-throughput diagnostic test. BMC Genomics 2006, 7, 278. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Luo, J.; Polunas, M.; Bosnjak, N.; Dean Chueng, S.-T.; Chadwick, M.; Sabaawy, H.E.; Chester, S.A.; Lee, K.-B.; Lee, H.; et al. 4D-Printed Transformable Tube Array for High-Throughput 3D Cell Culture and Histology. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e2004285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Xiu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Pan, W.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X. A 3D Printed Hanging Drop Dripper for Tumor Spheroids Analysis without Recovery. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frey, O.; Misun, P.M.; Fluri, D.A.; Hengstler, J.G.; Hierlemann, A. Reconfigurable microfluidic hanging drop network for multi-tissue interaction and analysis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doulgkeroglou, M.-N.; Di Nubila, A.; Niessing, B.; König, N.; Schmitt, R.H.; Damen, J.; Szilvassy, S.J.; Chang, W.; Csontos, L.; Louis, S.; et al. Automation, Monitoring, and Standardization of Cell Product Manufacturing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.J.; Kwon, S.; Kim, K.S. Challenges of applying multicellular tumor spheroids in preclinical phase. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, K.; Gandhi, M.; Khalil, S.; Yan, K.C.; Marcolongo, M.; Barbee, K.; Sun, W. Characterization of cell viability during bioprinting processes. Biotechnol. J. 2009, 4, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boularaoui, S.; Al Hussein, G.; Khan, K.A.; Christoforou, N.; Stefanini, C. An overview of extrusion-based bioprinting with a focus on induced shear stress and its effect on cell viability. Bioprinting 2020, 20, e00093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horder, H.; Guaza Lasheras, M.; Grummel, N.; Nadernezhad, A.; Herbig, J.; Ergün, S.; Teßmar, J.; Groll, J.; Fabry, B.; Bauer-Kreisel, P.; et al. Bioprinting and Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stromal Cell Spheroids for a 3D Breast Cancer-Adipose Tissue Model. Cells 2021, 10, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Hascall, V.C.; Markwald, R.R.; Ghatak, S. Interactions between Hyaluronan and Its Receptors (CD44, RHAMM) Regulate the Activities of Inflammation and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swaminathan, S.; Hamid, Q.; Sun, W.; Clyne, A.M. Bioprinting of 3D breast epithelial spheroids for human cancer models. Biofabrication 2019, 11, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro Carpio, M.; Dabaghi, M.; Ungureanu, J.; Kolb, M.R.; Hirota, J.A.; Moran-Mirabal, J.M. 3D Bioprinting Strategies, Challenges, and Opportunities to Model the Lung Tissue Microenvironment and Its Function. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 773511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polio, S.R.; Kundu, A.N.; Dougan, C.E.; Birch, N.P.; Aurian-Blajeni, D.E.; Schiffman, J.D.; Crosby, A.J.; Peyton, S.R. Cross-platform mechanical characterization of lung tissue. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forget, A.; Christensen, J.; Lüdeke, S.; Kohler, E.; Tobias, S.; Matloubi, M.; Thomann, R.; Prasad, V.S. Polysaccharide hydrogels with tunable stiffness and provasculogenic properties via α-helix to β-sheet switch in secondary structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12887–12892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Cell Line (Label) | Culture Medium | Additive | Nr. of Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hepa1-6 | DMEM | 10% FBS | 5000 |
| MCF7 | DMEM | 10% FBS | 5000 |
| A549 (BFP) | DMEM | 10% FBS | 5/10,000 |
| A549 (BFP), HPMEC (RFP), MSC (GFP) | DMEM, ECGM, alpha-MEM | 10% FBS, 100 U/mL P/S 5% FBS, 50 U/mL P/S 10% FBS, 5 ng/mL FGF2, 1% P/S | 25,000 (5:3:2 cell and medium ratio) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Butelmann, T.; Gu, Y.; Li, A.; Tribukait-Riemenschneider, F.; Hoffmann, J.; Molazem, A.; Jaeger, E.; Pellegrini, D.; Forget, A.; Shastri, V.P. 3D Printed Solutions for Spheroid Engineering and Cancer Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158188
Butelmann T, Gu Y, Li A, Tribukait-Riemenschneider F, Hoffmann J, Molazem A, Jaeger E, Pellegrini D, Forget A, Shastri VP. 3D Printed Solutions for Spheroid Engineering and Cancer Research. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158188
Chicago/Turabian StyleButelmann, Tobias, Yawei Gu, Aijun Li, Fabian Tribukait-Riemenschneider, Julius Hoffmann, Amin Molazem, Ellen Jaeger, Diana Pellegrini, Aurelien Forget, and V. Prasad Shastri. 2022. "3D Printed Solutions for Spheroid Engineering and Cancer Research" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158188
APA StyleButelmann, T., Gu, Y., Li, A., Tribukait-Riemenschneider, F., Hoffmann, J., Molazem, A., Jaeger, E., Pellegrini, D., Forget, A., & Shastri, V. P. (2022). 3D Printed Solutions for Spheroid Engineering and Cancer Research. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158188








