Experiences of Trauma and DNA Methylation Profiles among African American Mothers and Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
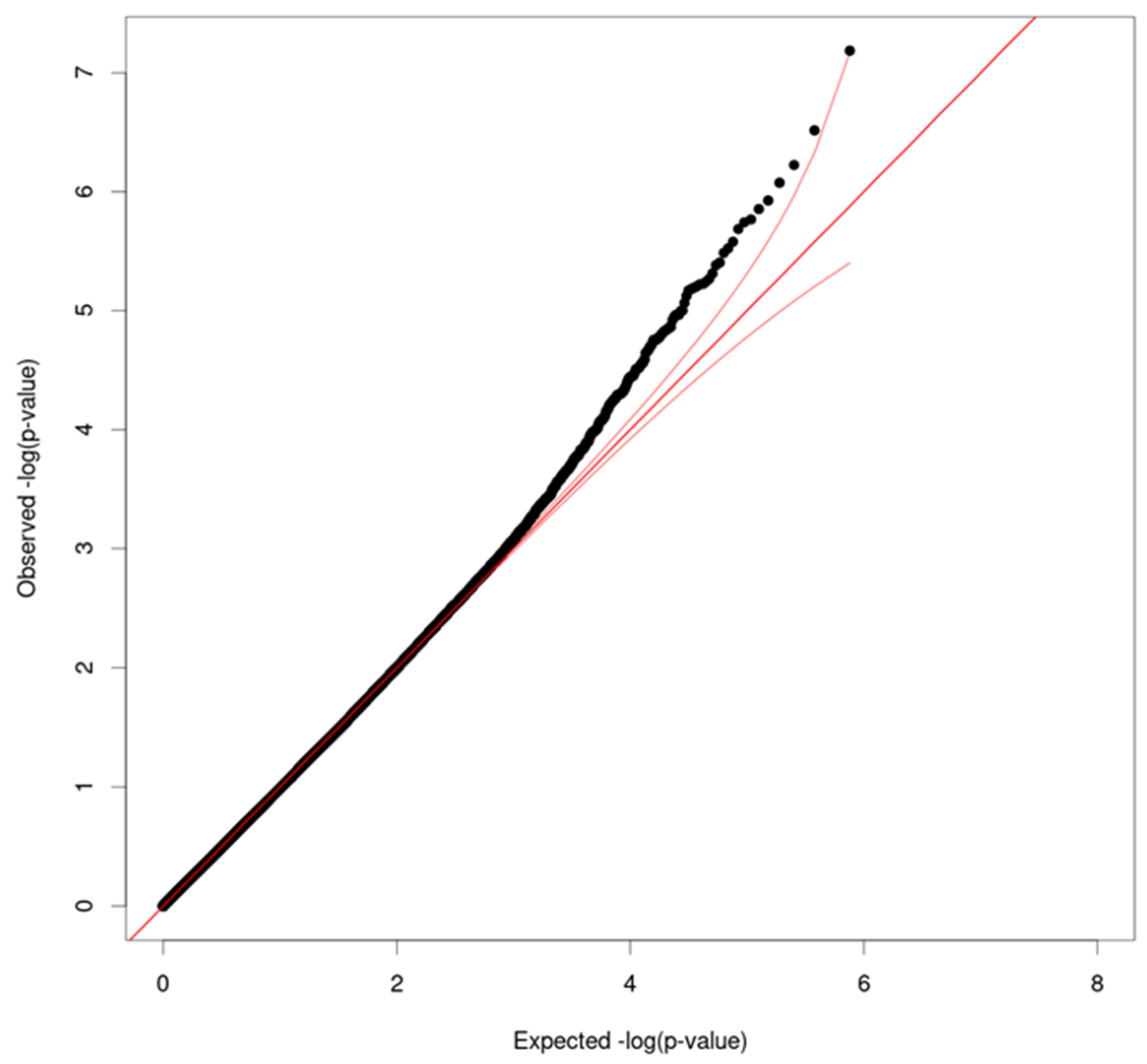
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Sample
4.2. Survey Measures
4.3. Potential Confounders
4.4. DNA and Epigenetic Processing
4.5. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bellis, M.A.; Hughes, K.; Ford, K.; Rodriguez, G.R.; Sethi, D.; Passmore, J. Life course health consequences and associated annual costs of adverse childhood experiences across Europe and North America: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Public Health 2019, 4, e517–e528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, A. Association of Adverse Childhood Experiences with Life Course Health and Development. North Carol. Med. J. 2018, 79, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, J.J.; McLaughlin, K.A.; Saha, S.; Aguilar-Gaxiola, S.; Al-Hamzawi, A.; Alonso, J.; Bruffaerts, R.; de Girolamo, G.; de Jonge, P.; Esan, O.; et al. The association between childhood adversities and subsequent first onset of psychotic experiences: A cross-national analysis of 23 998 respondents from 17 countries. Psychol. Med. 2017, 47, 1230–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, J.I.; Schmahl, C. Adverse Childhood Experiences and the Consequences on Neurobiological, Psychosocial, and Somatic Conditions Across the Lifespan. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mersky, J.; Topitzes, J.; Reynolds, A. Impacts of adverse childhood experiences on health, mental health, and substance use in early adulthood: A cohort study of an urban, minority sample in the U.S. Child Abus. Negl. 2013, 37, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonu, S.; Post, S.; Feinglass, J. Adverse childhood experiences and the onset of chronic disease in young adulthood. Prev. Med. 2019, 123, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, H.; Wright, B.J.; Vartanian, K.; Dulacki, K.; Li, H.-F. Examining the Prevalence of Adverse Childhood Experiences and Associated Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Among Low-Income Uninsured Adults. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2019, 12, e004391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Berk, M.; Maes, M.; Carvalho, A.F.; Puri, B.K. Socioeconomic Deprivation, Adverse Childhood Experiences and Medical Disorders in Adulthood: Mechanisms and Associations. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 5866–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shonkoff, J.P.; Boyce, W.T.; McEwen, B.S. Neuroscience, Molecular Biology, and the Childhood Roots of Health Disparities: Building a new framework for health promotion and disease prevention. JAMA 2009, 301, 2252–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, L.J.H.; Moffitt, T.E.; Arseneault, L.; Danese, A.; Eugen-Olsen, J.; Fisher, H.L.; Harrington, H.; Houts, R.; Matthews, T.; Sugden, K.; et al. Association of Adverse Experiences and Exposure to Violence in Childhood and Adolescence With Inflammatory Burden in Young People. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slopen, N.; Shonkoff, J.P.; Albert, M.A.; Yoshikawa, H.; Jacobs, A.; Stoltz, R.; Williams, D.R. Racial Disparities in Child Adversity in the U.S.: Interactions With Family Immigration History and Income. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 50, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, D.; McCartney, G.; Smith, M.; Armour, G. Relationship between childhood socioeconomic position and adverse childhood experiences (ACEs): A systematic review. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2019, 73, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, N.J.; Hellman, J.L.; Scott, B.G.; Weems, C.; Carrion, V.G. The impact of adverse childhood experiences on an urban pediatric population. Child Abus. Negl. 2011, 35, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saban, K.L.; Mathews, H.L.; Bryant, F.B.; Tell, D.; Joyce, C.; DeVon, H.A.; Janusek, L.W. Perceived discrimination is associated with the inflammatory response to acute laboratory stress in women at risk for cardiovascular disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 73, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, S.M.; Wright, R.J.; Hibert, E.N.; Spiegelman, D.; Forman, J.P.; Rich-Edwards, J.W. Intimate partner violence and incidence of hypertension in women. Ann. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, S.M.; Wright, R.J.; Hibert, E.N.; Spiegelman, D.; Jun, H.-J.; Hu, F.B.; Rich-Edwards, J.W. Intimate Partner Violence and Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in Women. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandan, J.S.; Thomas, T.; Bradbury-Jones, C.; Taylor, J.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Nirantharakumar, K. Risk of Cardiometabolic Disease and All-Cause Mortality in Female Survivors of Domestic Abuse. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deighton, S.; Neville, A.; Pusch, D.; Dobson, K. Biomarkers of adverse childhood experiences: A scoping review. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 269, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensah, G.A.; Jaquish, C.; Srinivas, P.; Papanicolaou, G.J.; Wei, G.S.; Redmond, N.; Roberts, M.C.; Nelson, C.; Aviles-Santa, M.L.; Puggal, M.; et al. Emerging Concepts in Precision Medicine and Cardiovascular Diseases in Racial and Ethnic Minority Populations. Circ. Res. 2019, 125, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Postovit, L.; Cattaneo, A.; Binder, E.B.; Aitchison, K.J. Epigenetic Modifications in Stress Response Genes Associated With Childhood Trauma. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, P.H.; Bird, A.P. Effects of DNA methylation on DNA-binding proteins and gene expression. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1993, 3, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyf, M.; Bick, J. DNA Methylation: A Mechanism for Embedding Early Life Experiences in the Genome. Child Dev. 2013, 84, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massart, R.; Nemoda, Z.; Suderman, M.J.; Sutti, S.; Ruggiero, A.M.; Dettmer, A.M.; Suomi, S.J.; Szyf, M. Early life adversity alters normal sex-dependent developmental dynamics of DNA methylation. Dev. Psychopathol. 2016, 28, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Knaap, L.J.; Riese, H.; Hudziak, J.J.; Verbiest, M.M.; Verhulst, F.C.; Oldehinkel, A.J.; van Oort, F.V. Adverse life events and allele-specific methylation of the serotonin transporter gene (SLC6A4) in adolescents: The TRAILS study. Psychosom. Med. 2015, 77, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiacco, S.; Gardini, E.S.; Mernone, L.; Schick, L.; Ehlert, U. DNA Methylation in Healthy Older Adults With a History of Childhood Adversity—Findings From the Women 40+ Healthy Aging Study. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecil, C.A.; Smith, R.G.; Walton, E.; Mill, J.; McCrory, E.J.; Viding, E. Epigenetic signatures of childhood abuse and neglect: Implications for psychiatric vulnerability. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 83, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, P.-E.; Almeida, D.; Fiori, L.; Turecki, G. Childhood Maltreatment and Stress-Related Psychopathology: The Epigenetic Memory Hypothesis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- O’Donnell, K.J.; Chen, L.; MacIsaac, J.L.; McEwen, L.M.; Nguyen, T.; Beckmann, K.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, L.M.; Brooks-Gunn, J.; Goldman, D.; et al. DNA methylome variation in a perinatal nurse-visitation program that reduces child maltreatment: A 27-year follow-up. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gene Cards. ENOX1 Gene. Available online: https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=ENOX1#function (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Liu, X.; Kelsoe, J.R.; Greenwood, T.A. A genome-wide association study of bipolar disorder with comorbid eating disorder replicates the SOX2-OT region. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 189, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, C.; Leggio, G.M.; Drago, F.; Serretti, A. Imputed expression of schizophrenia-associated genes and cognitive measures in patients with schizophrenia. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2022, 10, e1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, S.; Madigan, S.; Racine, N.; Benzies, K.; Tomfohr, L.; Tough, S. Maternal adverse childhood experiences, mental health, and child behaviour at age 3: The all our families community cohort study. Prev. Med. 2019, 118, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, B.C.L.; Callinan, L.S.; Smith, M.V. Adverse Childhood Experiences and Their Relation to Parenting Stress and Parenting Practices. Community Ment. Health J. 2019, 55, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, J.E.; Racine, N.; Plamondon, A.; Tough, S.; Madigan, S. Maternal adverse childhood experiences, attachment style, and mental health: Pathways of transmission to child behavior problems. Child Abus. Negl. 2019, 93, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouch, E.; Radcliff, E.; Brown, M.J.; Hung, P. Exploring the association between parenting stress and a child’s exposure to adverse childhood experiences (ACEs). Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2019, 102, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, Y.H.; Campbell, C.A.; Ferguson, M.; Crusto, C.A. The Role of Parenting Stress in Young Children’s Mental Health Functioning After Exposure to Family Violence. J. Trauma. Stress 2013, 26, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, M.L.; Huang, Y.; Hui, Q.; Newhall, K.; Crusto, C.; Sun, Y.V.; Taylor, J.Y. Parenting stress and DNA methylation among African Americans in the InterGEN Study. J. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2017, 1, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condon, E.M.; Barcelona, V.; Ibrahim, B.B.; Crusto, C.A.; Taylor, J.Y. Racial Discrimination, Mental Health, and Parenting Among African American Mothers of Preschool-Aged Children. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2021, 61, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, K.J.; Denietolis, B.; Goodwin, B.J.; Dvir, Y. Childhood Trauma and Psychosis. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 29, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avenevoli, S.; Swendsen, J.; He, J.-P.; Burstein, M.; Merikangas, K.R. Major Depression in the National Comorbidity Survey–Adolescent Supplement: Prevalence, Correlates, and Treatment. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2015, 54, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, B.L.; Trinh, N.-H.; Li, Z.; Hou, S.S.-Y.; Progovac, A.M. Trends in Racial-Ethnic Disparities in Access to Mental Health Care, 2004–2012. Psychiatr. Serv. 2017, 68, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montano, C.; Taub, M.A.; Jaffe, A.; Briem, E.; Feinberg, J.I.; Trygvadottir, R.; Idrizi, A.; Runarsson, A.; Berndsen, B.; Gur, R.C.; et al. Association of DNA Methylation Differences With Schizophrenia in an Epigenome-Wide Association Study. JAMA Psychiatry 2016, 73, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.K.; Conneely, K.N.; Kilaru, V.; Mercer, K.B.; Weiss, T.E.; Bradley, B.; Tang, Y.; Gillespie, C.; Cubells, J.F.; Ressler, K.J. Differential immune system DNA methylation and cytokine regulation in post-traumatic stress disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2011, 156, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.K.; Kilaru, V.; Klengel, T.; Mercer, K.B.; Bradley, B.; Conneely, K.N.; Ressler, K.J.; Binder, E.B. DNA extracted from saliva for methylation studies of psychiatric traits: Evidence tissue specificity and relatedness to brain. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2015, 168, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, K.; Bellis, M.A.; Hardcastle, K.A.; Sethi, D.; Butchart, A.; Mikton, C.; Jones, L.; Dunne, M.P. The effect of multiple adverse childhood experiences on health: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Public Health 2017, 2, e356–e366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-C.; Wang, Q.; Chung, W.K.; Andrulis, I.L.; Daly, M.B.; John, E.M.; Keegan, T.H.M.; Knight, J.; Bradbury, A.R.; A Kappil, M.; et al. Correlation of DNA methylation levels in blood and saliva DNA in young girls of the LEGACY Girls study. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crusto, C.A.; de Mendoza, V.B.; Connell, C.M.; Sun, Y.V.; Taylor, J.Y. The Intergenerational Impact of Genetic and Psychological Factors on Blood Pressure Study (InterGEN): Design and Methods for Recruitment and Psychological Measures. Nurs. Res. 2016, 65, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, M.J.; Litz, B.; Hsu, J.L.; Lombardo, T.W. Psychometric Properties of the Life Events Checklist. Assessment 2004, 11, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh-Ippen, C.; Ford, J.; Racusin, R.; Acker, M.; Bosquet, K.; Rogers, C.; Edwards, J. Trauma Events Screening Inventory-Parent Report Revised; The Child Trauma Research Project of Early Trauma Network and The National Center for PTSD Dartmouth Child Trauma Research Group: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pugach, C.P.; Nomamiukor, F.O.; Gay, N.G.; Wisco, B.E. Temporal Stability of Self-Reported Trauma Exposure on the Life Events Checklist for DSM-5. J. Trauma. Stress 2020, 34, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.L.; Jerman, P.; Boparai, S.K.P.; Koita, K.; Briner, S.; Bucci, M.; Harris, N.B. Review of Tools for Measuring Exposure to Adversity in Children and Adolescents. J. Pediatr. Health Care Off. Publ. Natl. Assoc. Pediatr. Nurse Assoc. Pract. 2018, 32, 564–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houseman, E.A.; Kile, M.L.; Christiani, D.C.; Ince, T.A.; Kelsey, K.T.; Marsit, C.J. Reference-free deconvolution of DNA methylation data and mediation by cell composition effects. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahlo, M.; Stankovich, J.; Danoy, P.; Hickey, P.F.; Taylor, B.V.; Browning, S.R.; Brown, M.A.; Rubio, J.P.; The Australian and New Zealand Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium (ANZgene). Saliva-Derived DNA Performs Well in Large-Scale, High-Density Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Microarray Studies. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.Y.; Wright, M.L.; Crusto, C.A.; Sun, Y.V. The Intergenerational Impact of Genetic and Psychological Factors on Blood Pressure (InterGEN) Study: Design and Methods for Complex DNA Analysis. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2016, 18, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barfield, R.T.; Almli, L.M.; Kilaru, V.; Smith, A.K.; Mercer, K.B.; Duncan, R.; Klengel, T.; Mehta, D.; Binder, E.B.; Epstein, M.P.; et al. Accounting for population stratification in DNA methylation studies. Genet. Epidemiol. 2014, 38, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2011. [Google Scholar]

| n * (Mean) | % (S.D.) | |
|---|---|---|
| Maternal characteristics (n = 236) | ||
| Age (mean, S.D.) | 31.2 | 5.6 |
| 20–29 | 99 | 41.9 |
| 30–39 | 118 | 50.0 |
| 40–49 | 19 | 8.0 |
| Current smoker No | 183 | 77.9 |
| Yes | 52 | 22.1 |
| Education <High School | 13 | 5.5 |
| High School graduate | 86 | 36.6 |
| Some college | 78 | 33.1 |
| Associates/College Grad or higher | 58 | 24.6 |
| Annual household income ≤$15,000 | 106 | 46.4 |
| >$15,000–$50,000 | 100 | 43.8 |
| >$50,000 | 22 | 9.6 |
| Health insurance type Private | 32 | 13.6 |
| Medicaid | 148 | 62.9 |
| Government/ACA | 35 | 14.8 |
| None | 13 | 5.5 |
| Hispanic/Latina ethnicity No | 213 | 90.2 |
| Yes | 22 | 9.3 |
| Marital Status | ||
| Married | 56 | 23.8 |
| Single | 154 | 65.5 |
| Divorced/Separated | 13 | 5.4 |
| Living with a partner | 12 | 5.1 |
| LEC scores (Total lifetime trauma events) (mean, S.D.) | 2.0 | 2.1 |
| None reported | 66 | 29.7 |
| At least one event | 156 | 70.2 |
| Child characteristics (n = 232) | ||
| Sex Male | 92 | 39.7 |
| Female | 140 | 60.3 |
| Age (years), mean (S.D.) | 3.7 | 0.7 |
| TESI scores (Total child trauma events), mean (S.D.) | 0.9 | 1.4 |
| None reported | 117 | 50.9 |
| One or more | 113 | 49.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barcelona, V.; Huang, Y.; Caceres, B.A.; Newhall, K.P.; Hui, Q.; Cerdeña, J.P.; Crusto, C.A.; Sun, Y.V.; Taylor, J.Y. Experiences of Trauma and DNA Methylation Profiles among African American Mothers and Children. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168951
Barcelona V, Huang Y, Caceres BA, Newhall KP, Hui Q, Cerdeña JP, Crusto CA, Sun YV, Taylor JY. Experiences of Trauma and DNA Methylation Profiles among African American Mothers and Children. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(16):8951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168951
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarcelona, Veronica, Yunfeng Huang, Billy A. Caceres, Kevin P. Newhall, Qin Hui, Jessica P. Cerdeña, Cindy A. Crusto, Yan V. Sun, and Jacquelyn Y. Taylor. 2022. "Experiences of Trauma and DNA Methylation Profiles among African American Mothers and Children" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 16: 8951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168951
APA StyleBarcelona, V., Huang, Y., Caceres, B. A., Newhall, K. P., Hui, Q., Cerdeña, J. P., Crusto, C. A., Sun, Y. V., & Taylor, J. Y. (2022). Experiences of Trauma and DNA Methylation Profiles among African American Mothers and Children. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(16), 8951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168951






