Mystery(n) Phenotypic Presentation in Europeans: Report of Three Further Novel Missense RNF213 Variants Leading to Severe Syndromic Forms of Moyamoya Angiopathy and Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
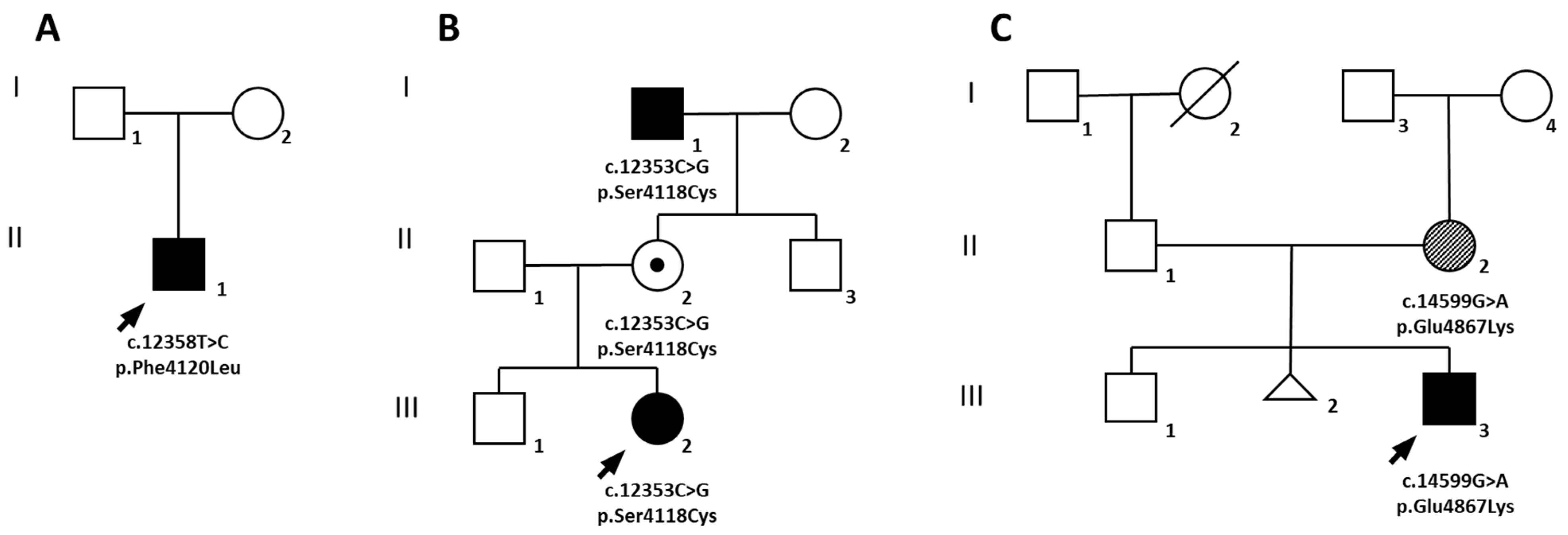
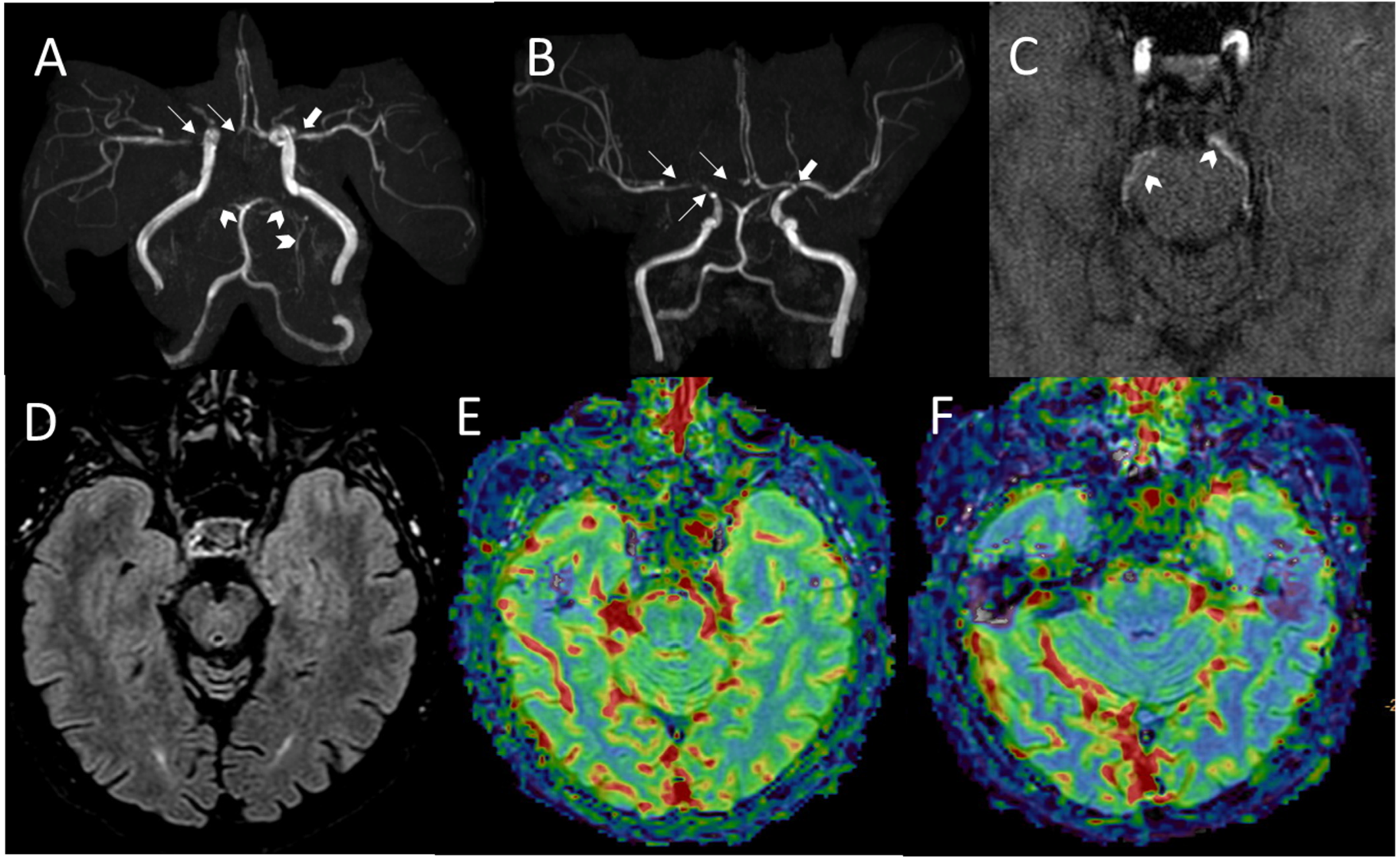
2.1. Family A
2.2. Family B
2.3. Family C
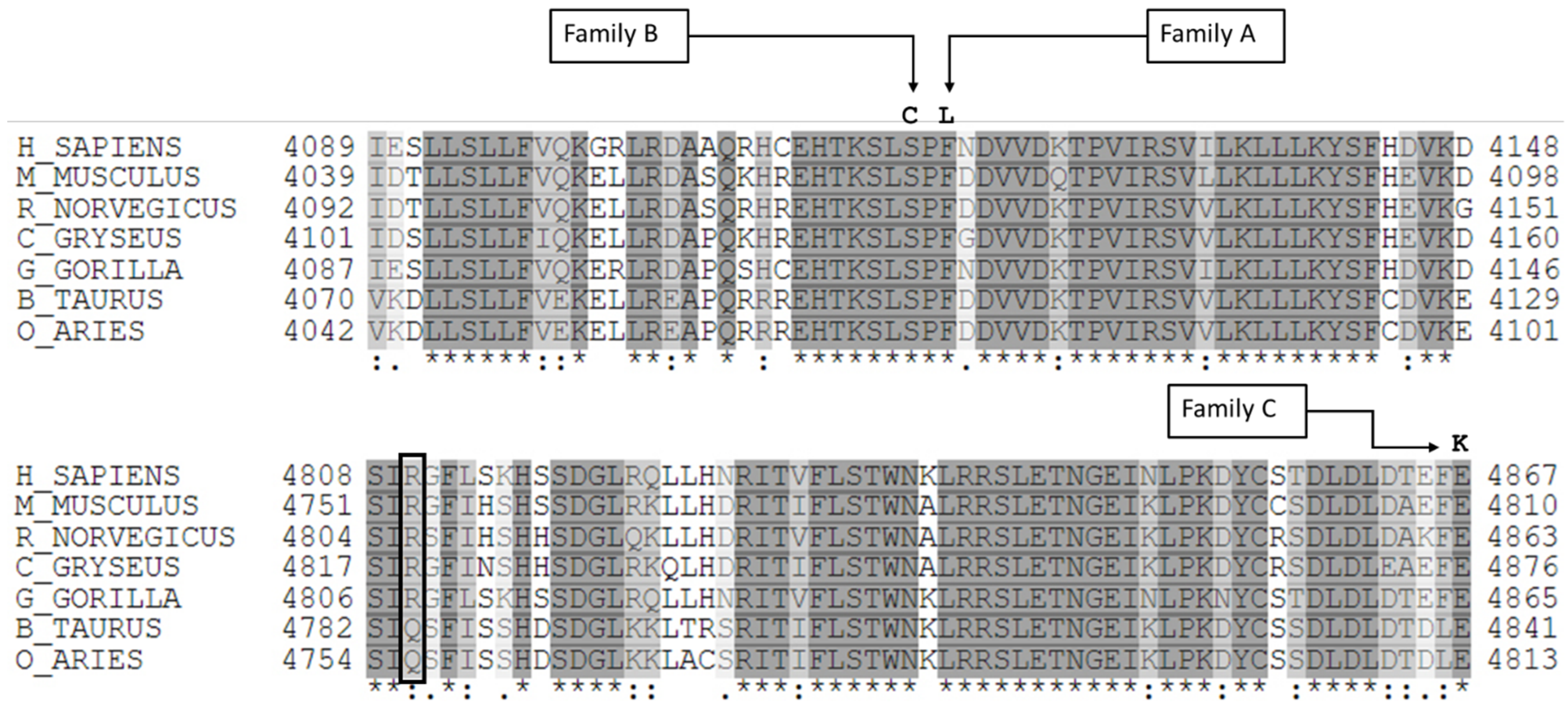
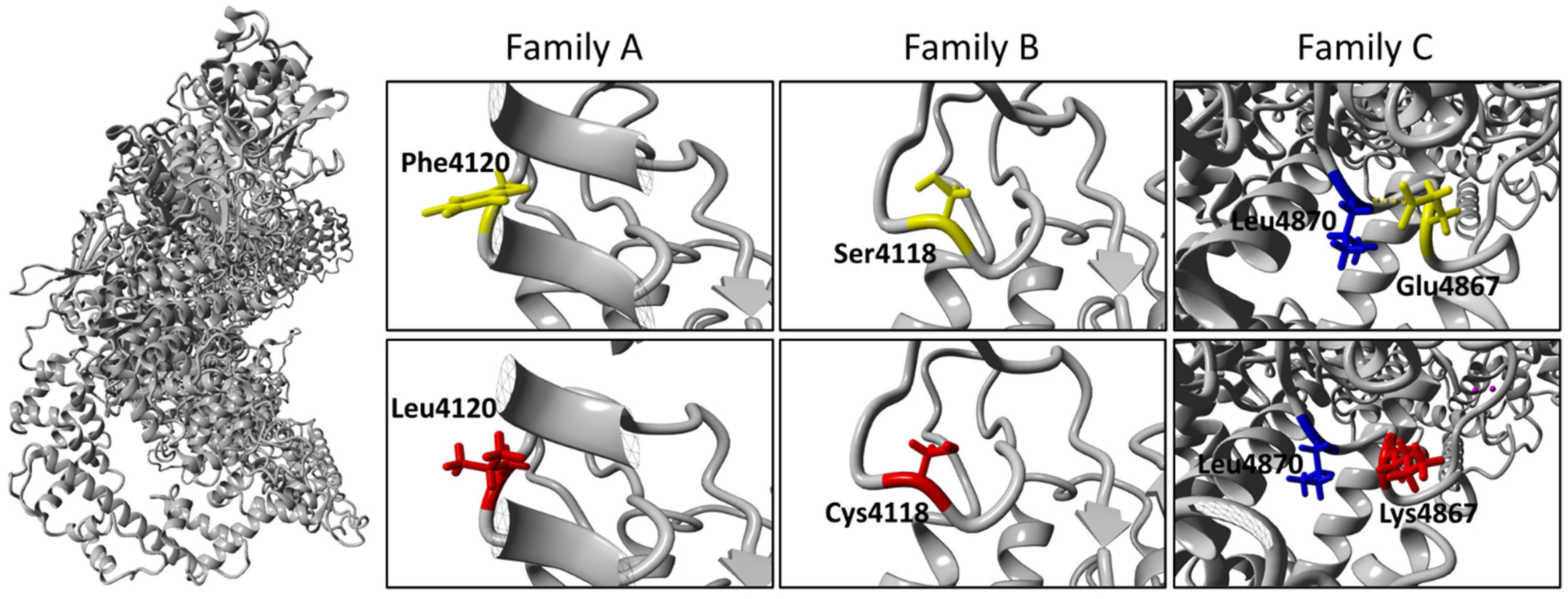
2.4. Molecular Diagnosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Recruitment
4.2. Exome Sequencing
4.3. Variant Validation and Segregation Analysis
4.4. Bioinformatic Tools
4.5. Literature Search Strategy
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scott, R.M.; Smith, E.R. Moyamoya disease and moyamoya syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, M.J.; Dlamini, N.; Bhatia, A.; Jordan, L.C. Neuroimaging Advances in Pediatric Stroke. Stroke 2019, 50, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiaschi, P.; Scala, M.; Piatelli, G.; Tortora, D.; Secci, F.; Cama, A.; Pavanello, M. Limits and pitfalls of indirect revascularization in moyamoya disease and syndrome. Neurosurg. Rev. 2021, 44, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Tyagi, A.; Romo, M.; Amoroso, K.C.; Sonia, F. Moyamoya Disease: A Review of Current Literature. Cureus 2020, 12, e10141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Bao, X.Y.; Yang, W.Z.; Shi, W.C.; Li, D.S.; Zhang, Z.S.; Zong, R.; Han, C.; Zhao, F.; Feng, J. Moyamoya disease in China: Its clinical features and outcomes. Stroke 2012, 43, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Kazumata, K.; Nakatani, E.; Houkin, K.; Kanatani, Y. Characteristics of Moyamoya Disease Based on National Registry Data in Japan. Stroke 2019, 50, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S. Moyamoya Disease: Epidemiology, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis. J. Stroke 2016, 18, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Morito, D.; Takashima, S.; Mineharu, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Hitomi, T.; Hashikata, H.; Matsuura, N.; Yamazaki, S.; Toyoda, A.; et al. Identification of RNF213 as a susceptibility gene for moyamoya disease and its possible role in vascular development. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Wei, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, P.; Wei, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; et al. Novel Susceptibility Loci for Moyamoya Disease Revealed by a Genome-Wide Association Study. Stroke 2018, 49, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Kang, Z.; Song, D.; Zhang, J.; Guan, M.; Gu, Y. Molecular analysis of RNF213 gene for moyamoya disease in the Chinese Han population. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hitomi, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Harada, K.H.; Koizumi, A. Distribution of moyamoya disease susceptibility polymorphism p.R4810K in RNF213 in East and Southeast Asian populations. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2012, 52, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.A.; Shin, S.; Yoon, J.H.; Ki, C.S. Frequency of the moyamoya-related RNF213 p.Arg4810Lys variant in 1516 Korean individuals. BMC Med. Genet. 2015, 16, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, A.C.; Guo, D.; Ren, Z.; Flynn, K.; Santos-Cortez, R.L.; Leal, S.M.; Wang, G.T.; Regalado, E.S.; Steinberg, G.K.; Shendure, J.; et al. RNF213 rare variants in an ethnically diverse population with Moyamoya disease. Stroke 2014, 45, 3200–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Ambalavanan, A.; Rochefort, D.; Xie, P.; Bourassa, C.V.; Hince, P.; Dionne-Laporte, A.; Spiegelman, D.; Gan-Or, Z.; Mirarchi, C.; et al. RNF213 Is Associated with Intracranial Aneurysms in the French-Canadian Population. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 1072–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Brozman, M.; Kyselova, K.; Viszlayova, D.; Morimoto, T.; Roubec, M.; Skoloudik, D.; Petrovicova, A.; Juskanic, D.; Strauss, J.; et al. RNF213 Rare Variants in Slovakian and Czech Moyamoya Disease Patients. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guey, S.; Kraemer, M.; Herve, D.; Ludwig, T.; Kossorotoff, M.; Bergametti, F.; Schwitalla, J.C.; Choi, S.; Broseus, L.; Callebaut, I.; et al. Rare RNF213 variants in the C-terminal region encompassing the RING-finger domain are associated with moyamoya angiopathy in Caucasians. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 25, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grangeon, L.; Guey, S.; Schwitalla, J.C.; Bergametti, F.; Arnould, M.; Corpechot, M.; Hadjadj, J.; Riant, F.; Aloui, C.; Drunat, S.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Features of 5 European Multigenerational Families With Moyamoya Angiopathy. Stroke 2019, 50, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagunashvili, A.N.; Ocaka, L.; Kelberman, D.; Munot, P.; Bacchelli, C.; Beales, P.L.; Ganesan, V. Novel missense variants in the RNF213 gene from a European family with Moyamoya disease. Hum. Genome Var. 2019, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Senevirathna, S.T.; Hitomi, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Roder, C.; Herzig, R.; Kraemer, M.; Voormolen, M.H.; Cahova, P.; Krischek, B.; et al. Genomewide association study identifies no major founder variant in Caucasian moyamoya disease. J. Genet. 2013, 92, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, L.; Westmacott, R.; Friefeld, S.; MacGregor, D.; Curtis, R.; Allen, A.; Yau, I.; Askalan, R.; Moharir, M.; Domi, T.; et al. The pediatric stroke outcome measure: A validation and reliability study. Stroke 2012, 43, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinard, A.; Fiander, M.D.J.; Cecchi, A.C.; Rideout, A.L.; Azouz, M.; Fraser, S.M.; McNeely, P.D.; Walling, S.; Novara, S.C.; Hurst, A.C.E.; et al. Association of De Novo RNF213 Variants With Childhood Onset Moyamoya Disease and Diffuse Occlusive Vasculopathy. Neurology 2021, 96, e1783–e1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harel, T.; Posey, J.E.; Graham, B.H.; Walkiewicz, M.; Yang, Y.; Lalani, S.R.; Belmont, J.W. Atypical presentation of moyamoya disease in an infant with a de novo RNF213 variant. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2015, 167A, 2742–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahel, J.; Lehner, A.; Vogel, A.; Schleiffer, A.; Meinhart, A.; Haselbach, D.; Clausen, T. Moyamoya disease factor RNF213 is a giant E3 ligase with a dynein-like core and a distinct ubiquitin-transfer mechanism. Elife 2020, 9, e56185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ittisoponpisan, S.; Islam, S.A.; Khanna, T.; Alhuzimi, E.; David, A.; Sternberg, M.J.E. Can Predicted Protein 3D Structures Provide Reliable Insights into whether Missense Variants Are Disease Associated? J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 2197–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Shimizu, K. Hypoplasia of bilateral internal carotid arteries. Brain Nerve 1957, 9, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Herve, D.; Philippi, A.; Belbouab, R.; Zerah, M.; Chabrier, S.; Collardeau-Frachon, S.; Bergametti, F.; Essongue, A.; Berrou, E.; Krivosic, V.; et al. Loss of alpha1beta1 soluble guanylate cyclase, the major nitric oxide receptor, leads to moyamoya and achalasia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 94, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, C.; Giugliano, T.; Kraemer, M.; Torella, A.; Schwitalla, J.C.; Cirillo, M.; Melis, D.; Berlit, P.; Nigro, V.; Perrotta, S.; et al. Whole exome sequencing identifies MRVI1 as a susceptibility gene for moyamoya syndrome in neurofibromatosis type 1. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolis, M.; Bond, L.M.; Kampmann, M.; Pulimeno, P.; Chitraju, C.; Jayson, C.B.K.; Vaites, L.P.; Boland, S.; Lai, Z.W.; Gabriel, K.R.; et al. Probing the Global Cellular Responses to Lipotoxicity Caused by Saturated Fatty Acids. Mol. Cell 2019, 74, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banh, R.S.; Iorio, C.; Marcotte, R.; Xu, Y.; Cojocari, D.; Rahman, A.A.; Pawling, J.; Zhang, W.; Sinha, A.; Rose, C.M.; et al. PTP1B controls non-mitochondrial oxygen consumption by regulating RNF213 to promote tumour survival during hypoxia. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Matsuda, Y.; Hitomi, T.; Okuda, H.; Shioi, H.; Matsuda, T.; Imai, H.; Sone, M.; Taura, D.; Harada, K.H.; et al. Biochemical and Functional Characterization of RNF213 (Mysterin) R4810K, a Susceptibility Mutation of Moyamoya Disease, in Angiogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e002146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineharu, Y.; Miyamoto, S. RNF213 and GUCY1A3 in Moyamoya Disease: Key Regulators of Metabolism, Inflammation, and Vascular Stability. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 687088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, O.Y.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, D.H.; Won, H.H.; Yeon, J.Y.; Ki, C.S.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Hong, S.C.; Kim, D.K.; et al. Moyamoya Disease and Spectrums of RNF213 Vasculopathy. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.C.; Papke, C.L.; Tran-Fadulu, V.; Regalado, E.S.; Avidan, N.; Johnson, R.J.; Kim, D.H.; Pannu, H.; Willing, M.C.; Sparks, E.; et al. Mutations in smooth muscle alpha-actin (ACTA2) cause coronary artery disease, stroke, and Moyamoya disease, along with thoracic aortic disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkubo, K.; Sakai, Y.; Inoue, H.; Akamine, S.; Ishizaki, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Sanefuji, M.; Torisu, H.; Ihara, K.; Sardiello, M.; et al. Moyamoya disease susceptibility gene RNF213 links inflammatory and angiogenic signals in endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.A.; Song, J.S.; Park, T.K.; Yang, J.H.; Kwon, W.C.; Kim, S.R.; Kim, S.M.; Cha, J.; Jang, S.Y.; Cho, Y.S.; et al. Nonsyndromic Peripheral Pulmonary Artery Stenosis Is Associated With Homozygosity of RNF213 p.Arg4810Lys Regardless of Co-occurrence of Moyamoya Disease. Chest 2018, 153, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, K.A.; Paller, A.S. Livedo reticularis in a child with moyamoya disease. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2003, 20, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, M.; Strzelczuk-Judka, L.; Ostalska-Nowicka, D.; Jonczyk-Potoczna, K. Phakomatoses and cutaneous manifestations associated with moyamoya disease and syndrome. Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2020, 37, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehner, A.; Neuhauser, R.; Zink, A.; Ring, J. Figurate erythemas—Update and diagnostic approach. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2021, 19, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, A.; O’Grady, G.; Shih, E.; Bishop, J.R.; Loomes, K.; Diamond, T.; Hartung, E.A.; Wong, W.; Cuddapah, S.; Cahill, A.M.; et al. A new syndrome of moyamoya disease, kidney dysplasia, aminotransferase elevation, and skin disease associated with de novo variants in RNF213. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2021, 185, 2168–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, R.; Graupera, M.; Gerhardt, H.; Bersano, A.; Tournier-Lasserve, E.; Mensah, M.A.; Mundlos, S.; Vajkoczy, P. The Genetic Basis of Moyamoya Disease. Transl. Stroke Res. 2022, 13, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, O.Y.; Ryoo, S.; Kim, S.J.; Yoon, C.H.; Cha, J.; Yeon, J.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, G.M.; Chung, C.S.; Lee, K.H.; et al. Adult Moyamoya Disease: A Burden of Intracranial Stenosis in East Asians? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.W.; Kim, S.J.; Bang, O.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Ki, C.S.; Jeon, P.; Yeon, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Hong, S.C.; Shin, H.J. Determinants of Basal Collaterals in Moyamoya Disease: Clinical and Genetic Factors. Eur. Neurol. 2016, 75, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineharu, Y.; Takenaka, K.; Yamakawa, H.; Inoue, K.; Ikeda, H.; Kikuta, K.I.; Takagi, Y.; Nozaki, K.; Hashimoto, N.; Koizumi, A. Inheritance pattern of familial moyamoya disease: Autosomal dominant mode and genomic imprinting. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006, 77, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iascone, M.; Sana, M.E.; Pezzoli, L.; Bianchi, P.; Marchetti, D.; Fasolini, G.; Sadou, Y.; Locatelli, A.; Fabiani, F.; Mangili, G.; et al. Extensive arterial tortuosity and severe aortic dilation in a newborn with an EFEMP2 mutation. Circulation 2012, 126, 2764–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musacchia, F.; Ciolfi, A.; Mutarelli, M.; Bruselles, A.; Castello, R.; Pinelli, M.; Basu, S.; Banfi, S.; Casari, G.; Tartaglia, M.; et al. VarGenius executes cohort-level DNA-seq variant calling and annotation and allows to manage the resulting data through a PostgreSQL database. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukawa, M.; Nariai, T.; Onda, H.; Yoneyama, T.; Aihara, Y.; Hirota, K.; Kudo, T.; Sumita, K.; Maehara, T.; Kawamata, T.; et al. Exome Sequencing Identified CCER2 as a Novel Candidate Gene for Moyamoya Disease. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 26, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Chan, A.P. PROVEAN web server: A tool to predict the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2745–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.C.; Henikoff, S. SIFT: Predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3812–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I.; Jordan, D.M.; Sunyaev, S.R. Predicting functional effect of human missense mutations using PolyPhen-2. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2013, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Rodelsperger, C.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster evaluates disease-causing potential of sequence alterations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentzsch, P.; Schubach, M.; Shendure, J.; Kircher, M. CADD-Splice-improving genome-wide variant effect prediction using deep learning-derived splice scores. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejaver, V.; Urresti, J.; Lugo-Martinez, J.; Pagel, K.A.; Lin, G.N.; Nam, H.J.; Mort, M.; Cooper, D.N.; Sebat, J.; Iakoucheva, L.M.; et al. Inferring the molecular and phenotypic impact of amino acid variants with MutPred2. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega for making accurate alignments of many protein sequences. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Patient ID | Family A | Family B | Family C III.3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II.1 (Index) | III.2 (Index) | II.2 | I.1 | III.3 (Index) | II.2 | |
| Sex | M | F | F | M | M | F |
| Mutation | p.Phe4120Leu | p.Ser4118Cys | p.Glu4867Lys | |||
| MMA/other cerebrovascular condition/bilateral or unilateral | MMA/B | MMA/B | No | MMA/B | MMA/B | No |
| Age at onset (y) | 1.5 | 7 | n.a. | n.r. | 5 | n.r. |
| MMA symptoms | Left facio-brachial weakness associated with focal motor seizures | Persistent headache and seizures characterized by brief motor arrest and loss of consciousness | n.a. | None | Acute onset of right-sided hemiparesis and dysarthria | n.a. |
| Atypical angiographic features | Posterior cerebral arteries P1 and P2 tracts | n.r. | n.r. | Occlusion of the PCAs and thin leptomeningeal collaterals | n.r. | n.r. |
| HBP | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Extracerebral arterial or cardiac anomalies | Pulmonary artery L branch stenosis, hypoplasia of distal abdominal aorta | Generalized thickening of arterial walls | None | Chronic lower limb venous insufficiency, diffuse atherosclerotic disease, myxomatous mitral valve disease | None | Atrial myxoma |
| Hypertransaminasemia/hepatitis | Transitory hypertransaminasemia | No | No | No | Elevated transaminases triggered by Epstein-Barr virus infection | No |
| Other systemic features | None | None | None | None | LR, delayed refill, EAC | LR, EAC (confirmed by pathology), facial fibromata, short stature |
| Patient | Family A | Family B | Family C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II.1 (Index) | III.2 (Index) | II.2 | I.1 | III.3 (Index) | II.2 | |
| Age (yrs) | 4 | 14 | 45 | 68 | 8 | 40 |
| Gender | M | F | F | M | M | F |
| Genomic (Hg19) | chr17-78343600-T-C | chr17-78343595-C-G | chr17-78360109-G-A | |||
| cDNA (NM_001256071.3) | c.12358T>C | c.12353C>G | c.14599G>A | |||
| Exon | 46 of 68 | 46 of 68 | 62 of 68 | |||
| Protein | p.Phe4120Leu | p.Ser4118Cys | p.Glu4867Lys | |||
| Inheritance | de novo | Maternal | Paternal | n.d. | Maternal | de novo |
| ACMG Classification | Pathogenic (PM2;PM1;PS1;PS2) | Likely pathogenic (PM1;PM2;PM5) | Uncertain significance (PM2;BP4) | |||
| MAF (gnomAD) | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| SIFT | Deleterious (score: 0) | Deleterious (score: 0) | Tolerated (0.11) | |||
| Polyphen-2 | Probably damaging (score: 0.976) | Probably damaging (score: 1.000) | Possibly damaging (score: 0.493) | |||
| PROVEAN | Deleterious (score: −5.433) | Deleterious (score: −4.450) | Neutral (score: −2.200) | |||
| MutationTaster | Disease causing (score: 0.98) | Disease causing (score: 0.99) | Polymorphism (score: 0.86) | |||
| CADD | 26.1 | 25.9 | 21.7 | |||
| MUtPred2 (cutoff = 0.5) | 0.697 | 0.735 | 0.607 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santoro, C.; Mirone, G.; Zanobio, M.; Ranucci, G.; D’Amico, A.; Cicala, D.; Iascone, M.; Bernardo, P.; Piccolo, V.; Ronchi, A.; et al. Mystery(n) Phenotypic Presentation in Europeans: Report of Three Further Novel Missense RNF213 Variants Leading to Severe Syndromic Forms of Moyamoya Angiopathy and Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168952
Santoro C, Mirone G, Zanobio M, Ranucci G, D’Amico A, Cicala D, Iascone M, Bernardo P, Piccolo V, Ronchi A, et al. Mystery(n) Phenotypic Presentation in Europeans: Report of Three Further Novel Missense RNF213 Variants Leading to Severe Syndromic Forms of Moyamoya Angiopathy and Literature Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(16):8952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168952
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantoro, Claudia, Giuseppe Mirone, Mariateresa Zanobio, Giusy Ranucci, Alessandra D’Amico, Domenico Cicala, Maria Iascone, Pia Bernardo, Vincenzo Piccolo, Andrea Ronchi, and et al. 2022. "Mystery(n) Phenotypic Presentation in Europeans: Report of Three Further Novel Missense RNF213 Variants Leading to Severe Syndromic Forms of Moyamoya Angiopathy and Literature Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 16: 8952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168952
APA StyleSantoro, C., Mirone, G., Zanobio, M., Ranucci, G., D’Amico, A., Cicala, D., Iascone, M., Bernardo, P., Piccolo, V., Ronchi, A., Limongelli, G., Carotenuto, M., Nigro, V., Cinalli, G., & Piluso, G. (2022). Mystery(n) Phenotypic Presentation in Europeans: Report of Three Further Novel Missense RNF213 Variants Leading to Severe Syndromic Forms of Moyamoya Angiopathy and Literature Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(16), 8952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168952











