Effects of Polymers on the Drug Solubility and Dissolution Enhancement of Poorly Water-Soluble Rivaroxaban
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
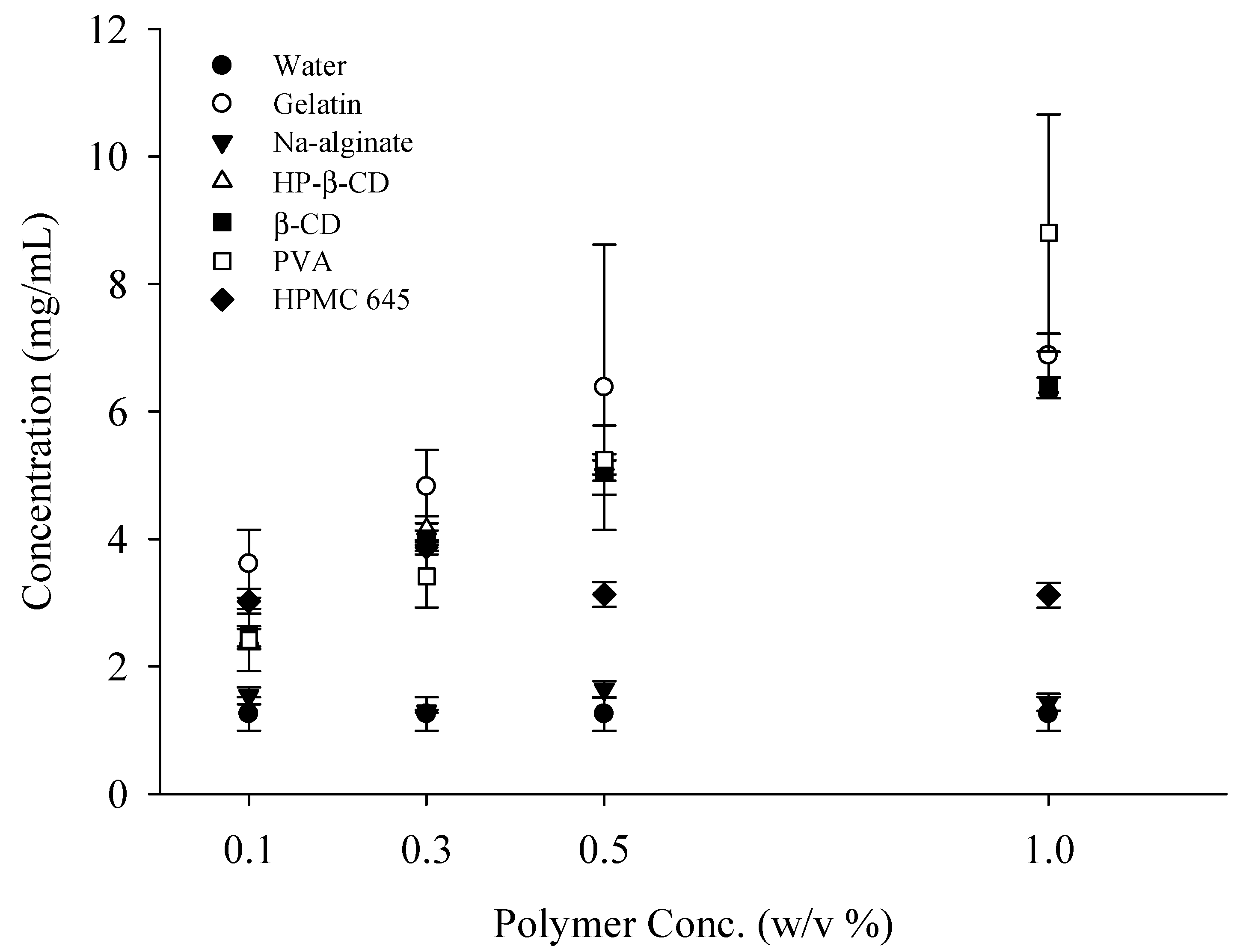
2.1. Effect of Polymer Concentration on the Solubility of RXB
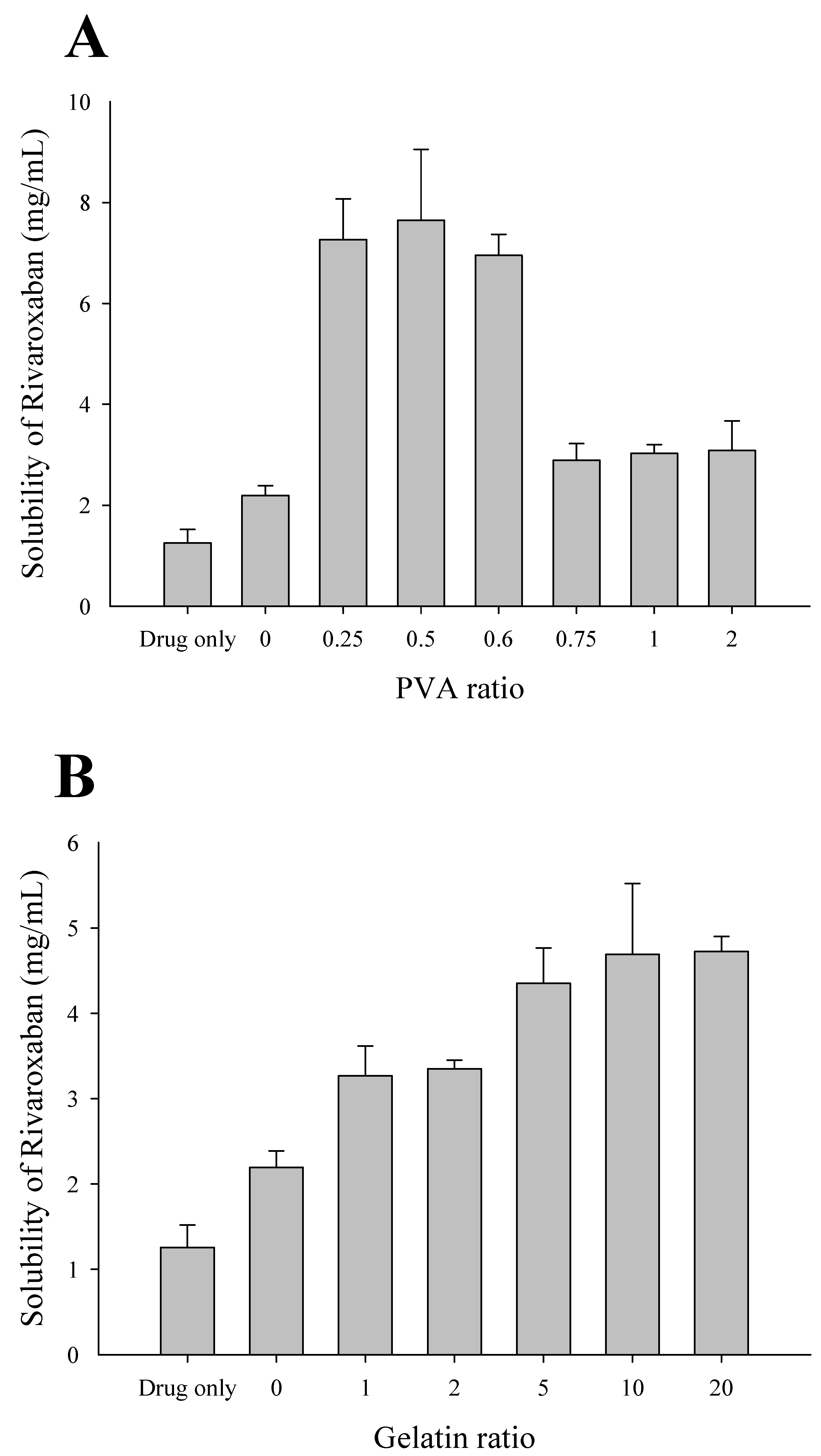
2.2. Effect of Polymer Concentration on the Solubility of RXB-Loaded Solid Dispersions
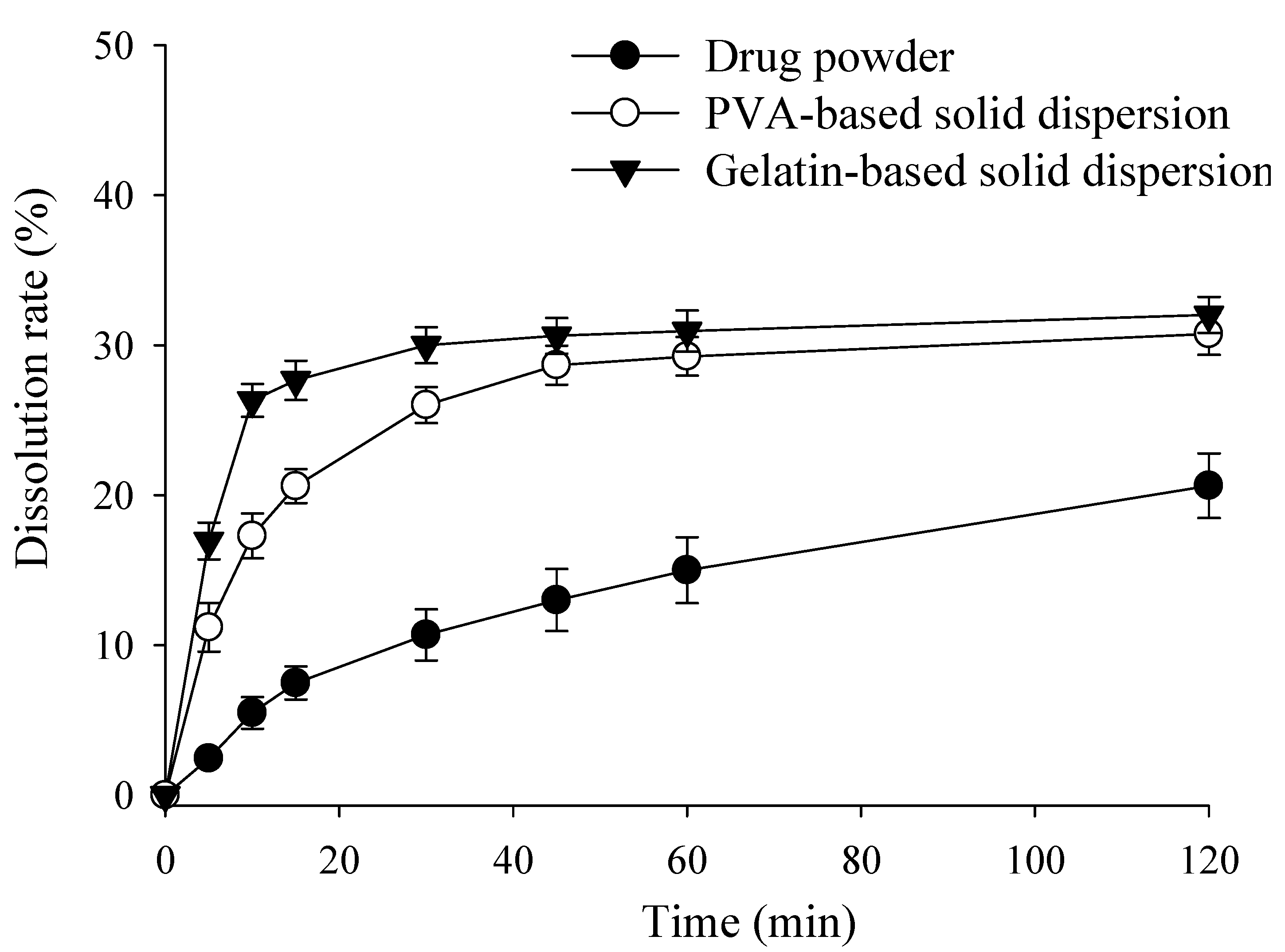
2.3. Effect of Polymer Concentration on Dissolution Rate of RXB-Loaded Solid Dispersions
2.4. Physicochemical Properties of RXB-Loaded Solid Dispersions
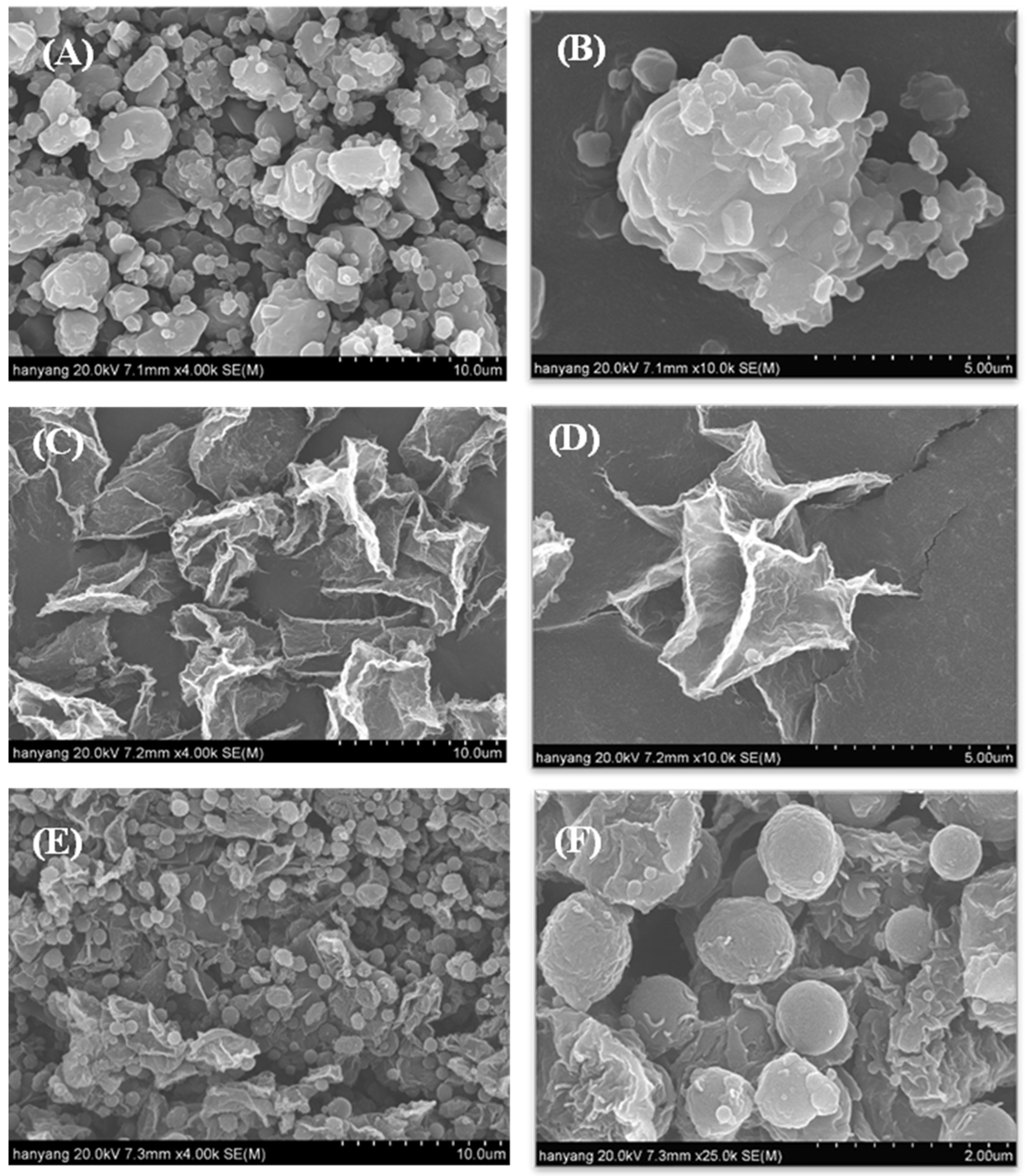
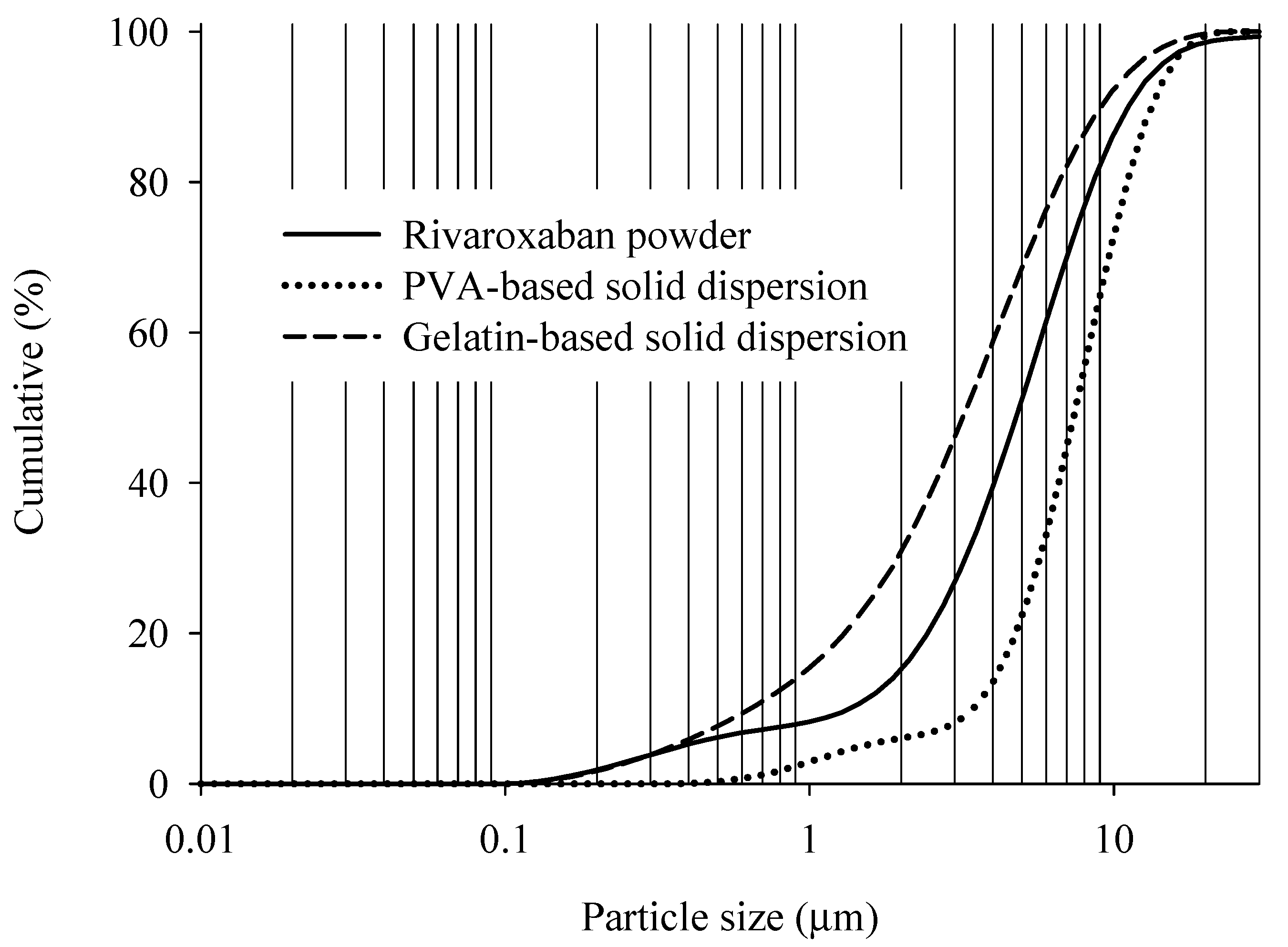
2.4.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Particle Size Distribution Studies
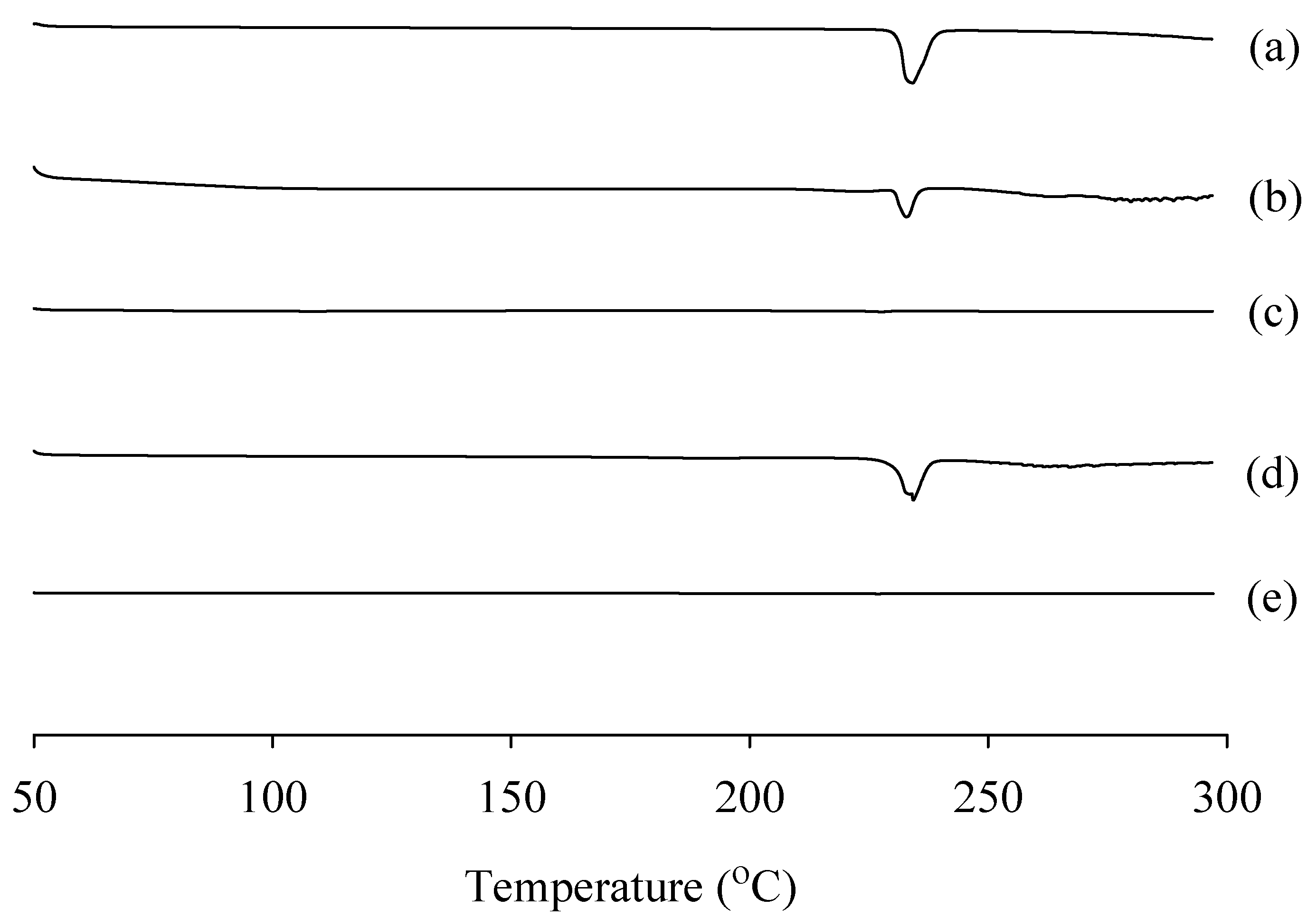
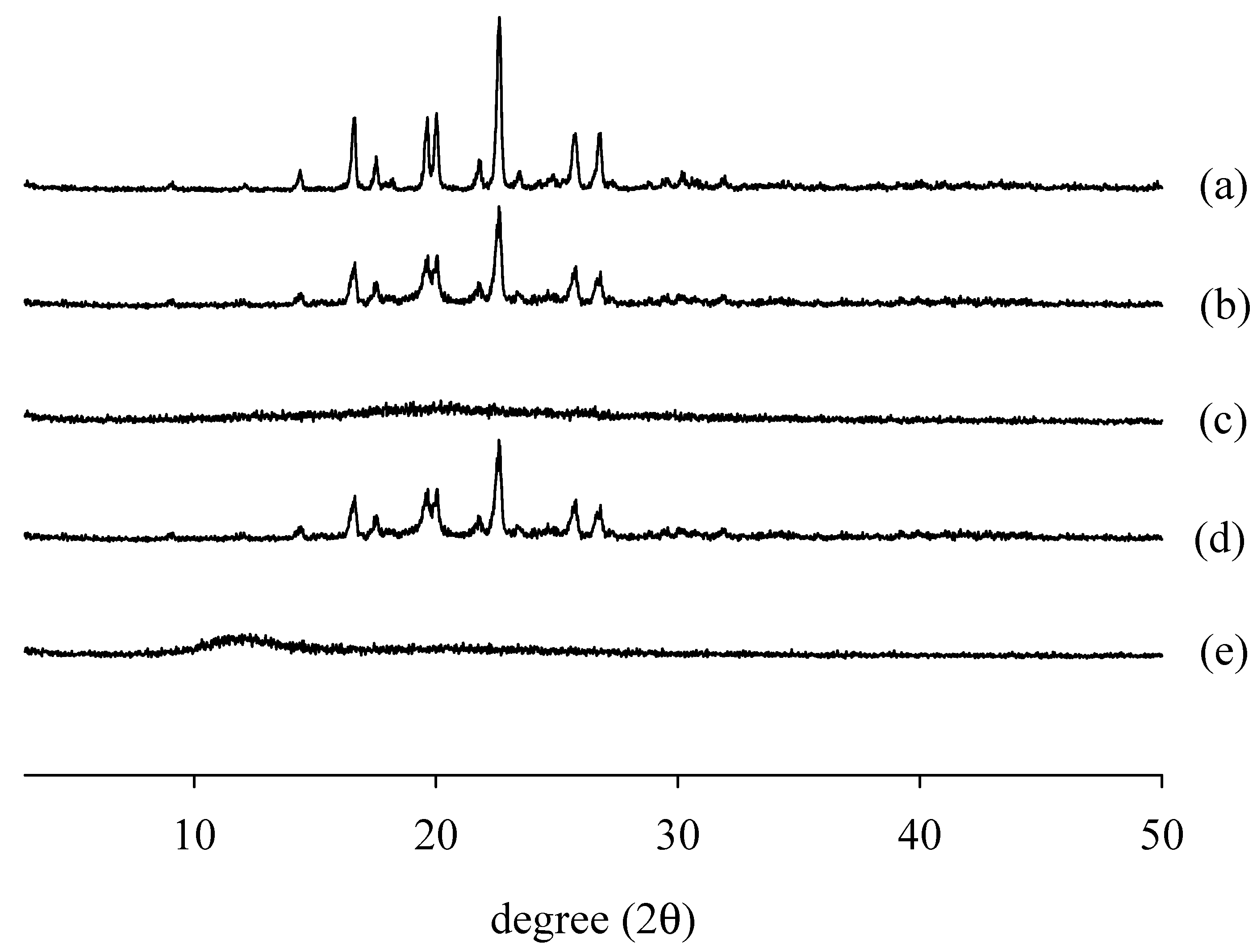
2.4.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of RXB-Loaded Spray-Dried Solid Dispersions
3.3. Effect of Polymer on the Solubility of RXB
3.4. Solubility and Dissolution Study of RXB-Loaded Solid Dispersions
3.5. HPLC
3.6. Physicochemical Properties of RXB-Loaded Solid Dispersions
3.6.1. SEM Studies
3.6.2. DSC Study
3.6.3. PXRD
3.6.4. Particle Size Distribution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, N.; Di, P.; Ning, S.; Jiang, W.; Jing, Q.; Ren, G.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, G.; et al. Modified rivaroxaban microparticles for solid state properties improvement based on drug-protein/polymer supramolecular interactions. Powder. Technol. 2019, 344, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.J.; Kim, J.S.; Yu, H.S.; Woo, M.R.; Choi, J.E.; Baek, K.H.; Kim, J.O.; Choi, Y.S.; Choi, H.G.; Jin, S.G. Comparison of the physicochemical properties, aqueous solubility, and oral bioavailability of rivaroxaban-loaded high-pressure homogenised and Shirasu porous glass membrane emulsified solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 23, 117057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Jin, S.G. Microneedle for transdermal drug delivery: Current trends and fabrication. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Choi, Y.G.; Woo, M.R.; Cheon, S.H.; Ji, S.H.; Im, D.S.; Din, F.U.; Kim, J.O.; Oh, K.T.; Lim, S.J.; et al. New potential application of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin in solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system and solid dispersion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 271, 118433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí Coma-Cros, E.; Biosca, A.; Lantero, E.; Manca, M.L.; Caddeo, C.; Gutiérrez, L.; Ramírez, M.; Borgheti-Cardoso, L.N.; Manconi, M.; Fernàndez-Busquets, X. Antimalarial activity of orally administered curcumin incorporated in Eudragit-containing liposomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sweed, N.M.; Fayez, A.M.; El-Emam, S.Z.; Dawoud, M.H. Response surface optimization of self nano-emulsifying drug delivery system of rosuvastatin calcium for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xing, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Z. Pharmaceutical dispersion techniques for dissolution and bioavailability enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.S.; Choi, H.G.; Jin, S.G. Influence of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose and sodium lauryl sulfate on the solubility and dissolution of sirolimus in solvent-evaporated solid dispersions. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2018, 39, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, K.S.; Seo, Y.G.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, J.O.; Yong, C.S.; Youn, Y.S.; Lim, S.J.; et al. Comparison of solvent-wetted and kneaded l-sulpiride-loaded solid dispersions: Powder characterization and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonsa, N.; Almutairy, B.; Kallakunta, V.R.; Sarabu, S.; Thipsay, P.; Bandari, S.; Repka, M.A. Manufacturing strategies to develop amorphous solid dispersions: An overview. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.S.; Matzger, A.J. Probing the interplay between amorphous solid dispersion stability and polymer functionality. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 2714–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemoto, Y.; Uchida, S.; Yoshida, T.; Shimada, K.; Kojima, H.; Takagi, A.; Tanaka, S.; Kashiwagura, Y.; Namiki, N. An effective polyvinyl alcohol for the solubilization of poorly water-soluble drugs in solid dispersion formulations. J. Drug. Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 101401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Yu, H.; Woo, M.R.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, J.O.; Ku, S.K.; Jin, S.G.; Choi, H.G. Influence of hydrophilic polymers on mechanical property and wound recovery of hybrid bilayer wound dressing system for delivering thermally unstable probiotic. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2022, 135, 112696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, T.; Yoshimura, N.; Kobayashi, A.; Ito, T.; Hara, K.; Tahara, K. Emulsion-electrospun polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers as a solid dispersion system to improve solubility and control the release of probucol, a poorly water-soluble drug. J. Drug. Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 67, 102953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Park, J.H.; Jeong, S.C.; Kim, D.S.; Yousaf, A.M.; Din, F.U.; Kim, J.O.; Yong, C.S.; Youn, Y.S.; Oh, K.T.; et al. Novel revaprazan-loaded gelatin microsphere with enhanced drug solubility and oral bioavailability. J. Microencapsul. 2018, 35, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadpour, S.; Kargozar, S.; Moradi, L.; Ai, A.; Nosrati, H.; Ai, J. Natural biomacromolecule based composite scaffolds from silk fibroin, gelatin and chitosan toward tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pas, T.; Vergauwen, B.; Mooter, G.V. Exploring the feasibility of the use of biopolymers as a carrier in the formulation of amorphous solid dispersions–Part I: Gelatin. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Estaca, J.; Balaguer, M.P.; López-Carballo, G.; Gavara, R.; Hernández-Muñoz, P. Improving antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of curcumin by means of encapsulation in gelatin through electrohydrodynamic atomization. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jeong, H.S.; Jeong, J.W.; Koo, T.S.; Kim, D.K.; Cho, Y.H.; Lee, G.W. The Development and Optimization of Hot-Melt Extruded Amorphous Solid Dispersions Containing Rivaroxaban in Combination with Polymers. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, H.G.; Jin, S.G.; Cho, C.W. Novel ezetimibe-loaded fibrous microparticles for enhanced solubility and oral bioavailability by electrospray technique. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schittny, A.; Huwyler, J.; Puchkov, M. Mechanisms of increased bioavailability through amorphous solid dispersions: A review. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Chen, L.; Müllers, W.; Serno, P.; Qian, F. Water-Resistant Drug–Polymer Interaction Contributes to the Formation of Nano-Species during the Dissolution of Felodipine Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 2888–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Tong, M.; Li, S.; Yu, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, R.; Wang, J. Surfactant-free amorphous solid dispersion with high dissolution for bioavailability enhancement of hydrophobic drugs: A case of quercetin. Drug. Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 47, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Prezotti, F.; Araújo, F.; Lopes, C.; Loureiro, A.; Marques, S.; Sarmento, B. Third-generation solid dispersion combining Soluplus and poloxamer 407 enhances the oral bioavailability of resveratrol. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 595, 120245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, S.B.; Costa Duarte, F.Í.; Heimfarth, L.; Siqueira Quintans, J.D.S.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; Veiga Júnior, V.F.D.; de Neves Lima, Á.A. Cyclodextrin–drug inclusion complexes: In vivo and in vitro approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Metre, S.; Mukesh, S.; Samal, S.K.; Chand, M.; Sangamwar, A.T. Enhanced biopharmaceutical performance of rivaroxaban through polymeric amorphous solid dispersion. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 652–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Din, F.U.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, D.S.; Woo, M.R.; Cheon, S.; Ji, S.H.; Kim, J.O.; Youn, Y.S.; Oh, K.T.; et al. Comparison of three different aqueous microenvironments for enhancing oral bioavailability of sildenafil: Solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system, amorphous microspheres and crystalline microspheres. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 5797–5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, H.; Gulsun, T.; Ozkan, M.H.; Nemutlu, E.; Sahin, S.; Öner, L. Assessment of dose proportionality of rivaroxaban nanocrystals. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Mai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J. Mechanism and improved dissolution of glycyrrhetinic acid solid dispersion by alkalizers. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dedroog, S.; Pas, T.; Vergauwen, B.; Huygens, C.; Van den Mooter, G. Solid-state analysis of amorphous solid dispersions: Why DSC and XRPD may not be regarded as stand-alone techniques. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 178, 112937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Williams, R.O., III. Characterization of amorphous solid dispersions: An update. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 50, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaraj, N.; Pailla, S.R.; Chowta, P.; Sampathi, S. Fabrication of ibrutinib nanosuspension by quality by design approach: Intended for enhanced oral bioavailability and diminished fast fed variability. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Pan, H.; Li, T.; Bu, T.; Zhou, W.; Zang, X. Role of polymers in the physical and chemical stability of amorphous solid dispersion: A case study of carbamazepine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 169, 106086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimento, A.; De Amicis, F.; Sirianni, R.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Puoci, F.; Casaburi, I.; Saturnino, C.; Pezzi, V. Progress to improve oral bioavailability and beneficial effects of resveratrol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Wan, Q.; Xu, X.; Xing, Y.; Ding, J.; Yang, S.; Sun, W.; Lu, M.; Pan, B. A novel oil-based suspension of a micro-environmental, pH-modifying solid dispersion for parenteral delivery: Formulation and stability evaluation. Colloids. Surf. B. Biointerfaces. 2019, 179, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.E.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, M.J.; Baek, K.H.; Woo, M.R.; Kim, J.O.; Choi, H.G.; Jin, S.G. Effects of different physicochemical characteristics and supersaturation principle of solidified SNEDDS and surface-modified microspheres on the bioavailability of carvedilol. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 597, 120377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Din, F.U.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, D.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Woo, M.R.; Kim, J.O.; Youn, Y.S.; Jin, S.G.; Choi, H.G. Comparative study between high-pressure homogenisation and Shirasu porous glass membrane technique in sildenafil base-loaded solid SNEDDS: Effects on physicochemical properties and in vivo characteristics. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 592, 120039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Woo, M.R.; Kim, K.S.; Jin, S.G.; Choi, H.G. Development of novel d-cycloserine tablet with improvement of drug stability and dissolution-equivalence to the d-cycloserine-loaded commercial hard capsule. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2020, 41, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, D.W.; Park, E.S.; Youn, Y.S.; Ud Din, F.; Kim, J.O.; Ku, S.K.; Jin, S.G.; Choi, H.G. Novel composite double-layered dressing with improved mechanical properties and wound recovery for thermosensitive drug, Lactobacillus brevis. Compos. B Eng. 2021, 225, 109276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.S.; Kim, J.; Park, J.W.; Jin, S.G. Novel acyclovir-loaded film-forming gel with enhanced mechanical properties and skin permeability. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 70, 103213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, J.S.; Lim, S.J.; Kim, J.O.; Yong, C.S.; Choi, H.G.; Jin, S.G. Comparison of 1-palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl-3-acetyl-rac-glycerol-loaded self-emulsifying granule and solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system: Powder property, dissolution and oral bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Formulations | PVA-Based Solid Dispersions | Gelatin-Based Solid Dispersions |
|---|---|---|
| Rivaroxaban (g) | 1 | 1 |
| PVA (g) | 0.5 | - |
| Gelatin (g) | - | 5 |
| Acetonitrile (L) | 1 | |
| Ethanol (L) | - | 3 |
| Distilled water (L) | 1.5 | 3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, M.-J.; Woo, M.R.; Choi, H.-G.; Jin, S.G. Effects of Polymers on the Drug Solubility and Dissolution Enhancement of Poorly Water-Soluble Rivaroxaban. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169491
Choi M-J, Woo MR, Choi H-G, Jin SG. Effects of Polymers on the Drug Solubility and Dissolution Enhancement of Poorly Water-Soluble Rivaroxaban. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(16):9491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169491
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Min-Jong, Mi Ran Woo, Han-Gon Choi, and Sung Giu Jin. 2022. "Effects of Polymers on the Drug Solubility and Dissolution Enhancement of Poorly Water-Soluble Rivaroxaban" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 16: 9491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169491
APA StyleChoi, M.-J., Woo, M. R., Choi, H.-G., & Jin, S. G. (2022). Effects of Polymers on the Drug Solubility and Dissolution Enhancement of Poorly Water-Soluble Rivaroxaban. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(16), 9491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169491






