Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer: From Molecular to Clinical Aspects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
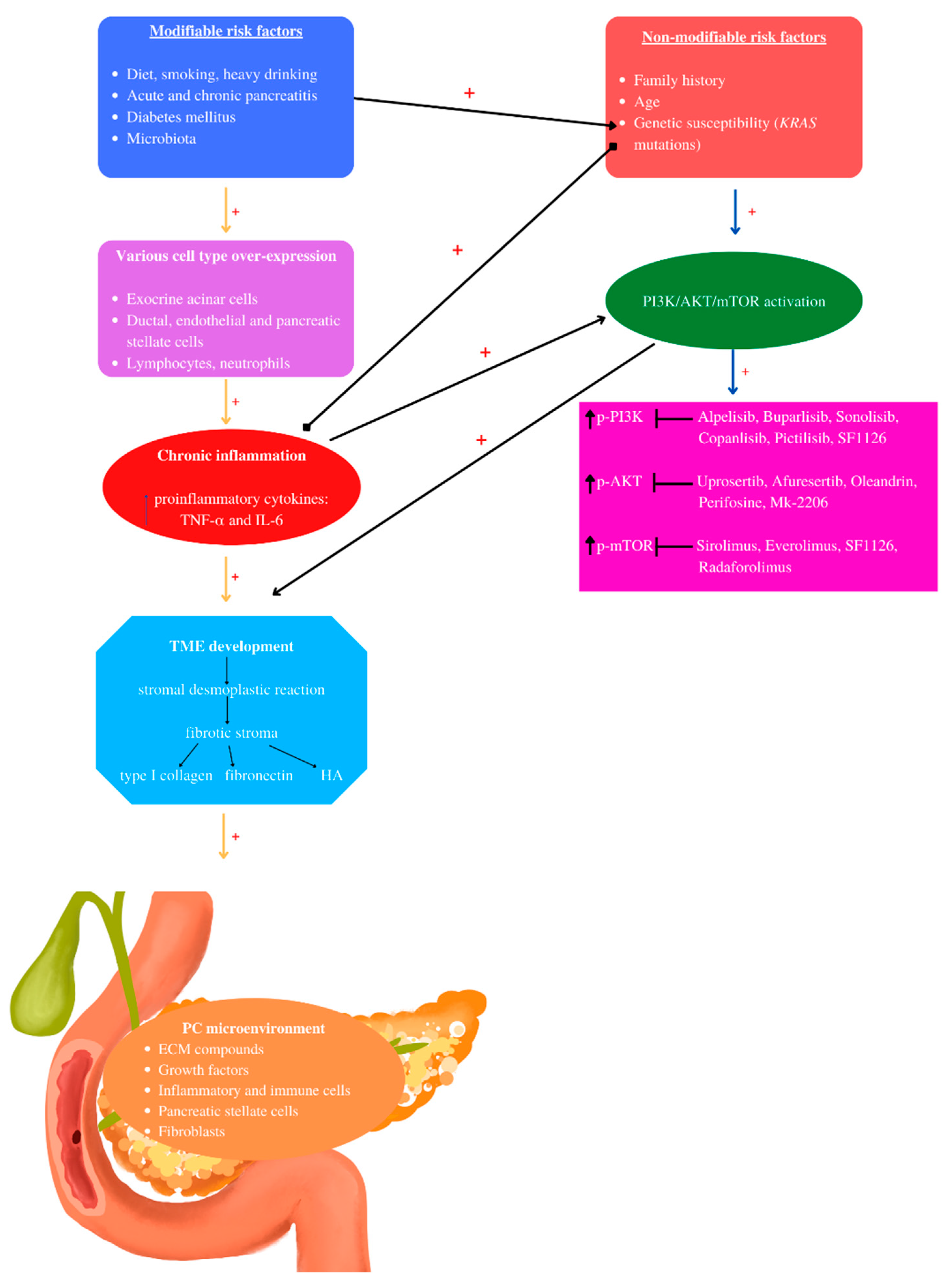
2. Pancreatic Cancer Risk Factors
2.1. Non-Modifiable Pancreatic Cancer Risk Factors: Family History, Genetic Susceptibility, Age
2.2. Modifiable Pancreatic Cancer Risk Factors: Diabetes Mellitus, Diet, Smoking, Alcohol, Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis, Intestinal Microbiota
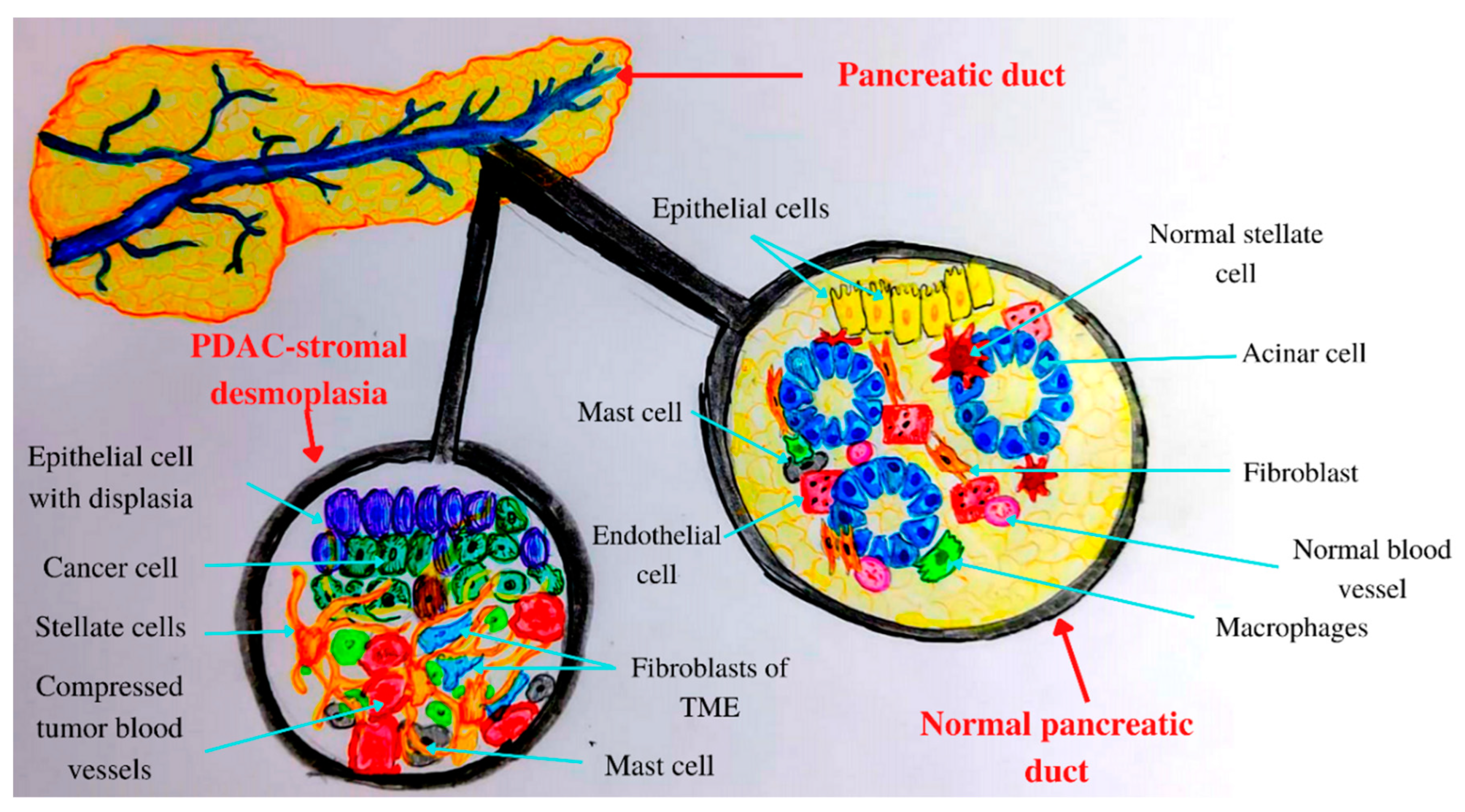
3. Tumor Microenvironment (TME) of Pancreatic Cancer
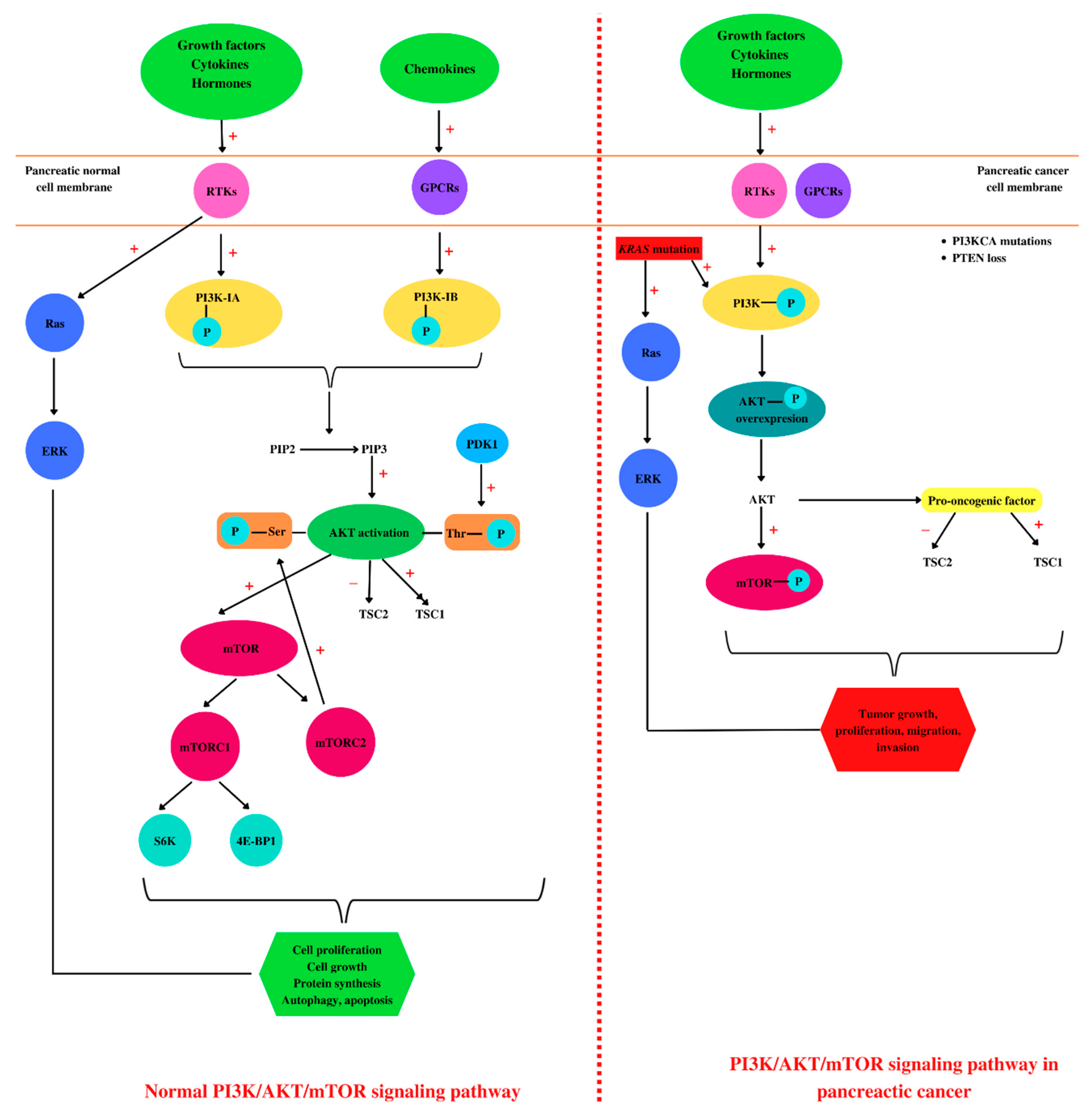
4. PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Pancreatic Cancer
5. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Inhibitors and Pancreatic Cancer
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGuigan, A.; Kelly, P.; Turkington, R.C.; Jones, C.; Coleman, H.G.; McCain, R.S. Pancreatic cancer: A review of clinical diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment and outcomes. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 21, 4846–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuse, J.; Nagashima, F. Emerging protein kinase inhibitors for treating pancreatic cancer. Expert. Opin. Emerg. Drugs. 2017, 22, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowenfels, A.B.; Maisonneuve, P. Epidemiology and risk factors for pancreatic cancer. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 20, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korc, M.; Jeon, C.Y.; Edderkaoui, M.; Pandol, S.J.; Petrov, M.S. Tobacco and alcohol as risk factors for pancreatic cancer. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 31, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilic, M.; Ilic, I. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 28, 9694–9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, A.H.; Byrne, K.T.; Vonderheide, R.H. Immunotherapy and prevention of pancreatic cancer. Trends Cancer 2018, 4, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveday, B.P.T.; Lipton, L.; Thomson, B.N. Pancreatic cancer: An update on diagnosis and management. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2019, 48, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torphy, R.J.; Fujiwara, Y.; Schulick, R.D. Pancreatic cancer treatment: Better, but a long way to go. Surg. Today 2020, 50, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goral, V. Pancreatic cancer: Pathogenesis and Diagnosis. Asian. Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 5619–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfredini, S.; Thapa, A.; O’Neill, E. RAS in pancreatic cancer. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 30, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, R.T.; Berna, M.J.; Bingham, D.B.; Norton, J.A. Inherited pancreatic endocrine tumor syndromes: Advances in molecular pathogenesis, diagnosis, management, and controversies. Cancer 2008, 1, 1807–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakiya, T.; Ishido, K.; Yoshizawa, T.; Kanda, T.; Hakamada, K. Roles of the nervous system in pancreatic cancer. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2021, 29, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clift, A.K.; Kidd, M.; Bodei, L.; Toumpanakis, C.; Baum, R.P.; Oberg, K.; Modlin, I.M.; Frilling, A. neuroendocrine neoplasms of the small bowel and pancreas. Neuroendocrinology 2020, 110, 444–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.L.; Adams, P.D.; Morton, J.P. Ras, PI3K and senescence. Small GTPase 2011, 2, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavoral, M.; Minarikova, P.; Zavada, F.; Salek, C.; Minarik, M. Molecular biology of pancreatic cancer. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 28, 2897–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariston, G.A.N.; Jiao, Q.; Yvette, U.; Yang, X.; Al-Ameri, S.A.; Du, L.; Wang, C. Differences between KC and KPC pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma mice models, in terms of their modeling biology and their clinical relevance. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarantis, P.; Koustas, E.; Papadimitropoulou, A.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Karamouzis, M.V. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Treatment hurdles, tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy. World. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 15, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.P.; Oldfield, L.; Ney, A.; Hart, P.A.; Keane, M.G.; Pandol, S.J.; Li, D.; Greenhalf, W.; Jeon, C.Y.; Koay, E.J.; et al. Early detection of pancreatic cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanini, S.; Renzi, S.; Giovinazzo, F.; Bermano, G. mTOR pathway in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine numor (GEP-NETs). Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 562505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, R.; Schmutz-Kober, K.; Kühnel, J.; Maak, M.; Rosenberg, R. Pancreatic cancer. Ther. Umsch. 2021, 78, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biller, L.H.; Wolpin, B.M.; Goggins, M. Inherited pancreatic cancer syndromes and high-risk screening. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 30, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.K.; Chari, S.T. Early detection of pancreatic cancer. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2020, 36, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, H.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, B.; You, L.; Zhang, T.; Dai, M.; Zhao, Y. Advances in the epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: Trends, risk factors, screening, and prognosis. Cancer Lett. 2021, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, J.; Kanno, A.; Ikeda, E.; Ando, K.; Nagai, H.; Miwata, T.; Kawasaki, Y.; Tada, Y.; Yokoyama, K.; Numao, N.; et al. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Epidemiology and risk factors. Diagnostics 2021, 20, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.U.; Zahid, E.; Khan, M.T.; Naeem, A.; Ali, S.; Rashid, M.U.; Ahmad, S. Familial pancreatic cancer: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2019, 24, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, J.D.; Surana, R.; Valle, J.W.; Shroff, R.T. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2020, 27, 2008–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, E.; Nehoray, B.M. Hereditary pancreatic cancer syndromes: Providing care to at-risk families. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2019, 1, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotný, I. Precancerous conditions and risk factors for pancreatic and bile duct cancer. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 26, S29–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisonneuve, P. Epidemiology and burden of pancreatic cancer. Presse. Med. 2019, 48, e113–e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principe, D.R.; Rana, A. Updated risk factors to inform early pancreatic cancer screening and identify high risk patients. Cancer. Lett. 2020, 10, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleeff, J.; Korc, M.; Apte, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Johnson, C.D.; Biankin, A.V.; Neale, R.E.; Tempero, M.; Tuveson, D.A.; Hruban, R.H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 21, 16022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevala-Plagemann, C.; Hidalgo, M.; Garrido-Laguna, I. From state-of-the-art treatments to novel therapies for advanced-stage pancreatic cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falasca, M.; Selvaggi, F.; Buus, R.; Sulpizio, S.; Edling, C.E. Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathways in pancreatic cancer--from molecular signalling to clinical trials. Anticancer Agent. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.E.; Hernandez, Y.G.; Frucht, H.; Lucas, A.L. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Risk factors, screening, and early detection. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 28, 11182–11198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christenson, E.S.; Jaffee, E.; Azad, N.S. Current and emerging therapies for patients with advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A bright future. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, e135–e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.A.; Pasca di Magliano, M. Kras as a key oncogene and therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer. Front. Physiol. 2014, 21, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J. KRAS mutation in pancreatic cancer. Semin Oncol. 2021, 48, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Li, Y.; Qi, G.; Yuan, S.; Wang, Z.; Yu, S.; Li, B.; He, S. Clinicopathological significance of CDKN2A promoter hypermethylation frequency with pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 13563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, W. Pancreatic Cancer: A review of risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820962117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midha, S.; Chawla, S.; Garg, P.K. Modifiable and non modifiable risk factors for pancreatic cancer: A review. Cancer. Lett. 2016, 10, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, R.; Tian, W.; Hao, X.; Koirala, R. Risk factor, early diagnosis and overall survival on outcome of association between pancreatic cancer and diabetes mellitus: Changes and advances, a review. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 52, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzato, M.; Turati, F.; Rosato, V.; La Vecchia, C. Exploring the link between diabetes and pancreatic cancer. Expert. Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2019, 19, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, M. Pancreatic cancer and diabetes. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 771, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salem, A.A.; Mackenzie, G.G. Pancreatic cancer: A critical review of dietary risk. Nutr. Res. 2018, 52, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, C.; Simon, P.; Weiss, F.U.; Fluhr, G.; Weber, E.; Gärtner, S.; Behn, C.O.; Kraft, M.; Ringel, J.; Aghdassi, A.; et al. Environmental risk factors for chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Dig. Dis. 2011, 29, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M. Possibility of pancreatic cancer chemoprevention by anti-inflammatory/anti-diabetic/anti-dyslipidemic drugs. Cancer Chemother. 2021, 48, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, P.Y.; Shu, L.; Shen, S.S.; Chen, X.J.; Zhang, X.Y. Dietary patterns and pancreatic cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Nutrients 2017, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Kartsonaki, C.; Turnbull, I.; Guo, Y.; Yang, L.; Bian, Z.; Chen, Y.; Millwood, I.Y.; Bragg, F.; Gong, W.; et al. Metabolic and lifestyle risk factors for acute pancreatitis in Chinese adults: A prospective cohort study of 0.5 million people. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.J.; Yang, F.; Jin, C.; Fu, D.L. Current status and progress of pancreatic cancer in China. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 14, 7988–8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preziosi, G.; Oben, J.A.; Fusai, G. Obesity and pancreatic cancer. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 23, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piciucchi, M.; Capurso, G.; Valente, R.; Larghi, A.; Archibugi, L.; Signoretti, M.; Stigliano, S.; Zerboni, G.; Barucca, V.; La Torre, M.; et al. Early onset pancreatic cancer: Risk factors, presentation and outcome. Pancreatology 2015, 15, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aier, I.; Semwal, R.; Sharma, A.; Varadwaj, P.K. A systematic assessment of statistics, risk factors, and underlying features involved in pancreatic cancer. Cancer. Epidemiol. 2019, 58, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Forsmark, C.E. Chronic pancreatitis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 33, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, D.; Lowenfels, A.B. The epidemiology of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkegård, J.; Mortensen, F.V.; Cronin-Fenton, D. Chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, A.; Freelove, R. Pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Prim. Care 2017, 44, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofaru, F.A.; Nica, S.; Fierbinteanu-Braticevici, C. Assessment of severity of acute pancreatitis over time. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 58, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandol, S.; Gukovskaya, A.; Edderkaoui, M.; Dawson, D.; Eibl, G.; Lugea, A. Epidemiology, risk factors, and the promotion of pancreatic cancer: Role of the stellate cell. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zeng, X.P.; Xin, L.; Wang, D.; Pan, J.; Bi, Y.W.; Ji, J.T.; Du, T.T.; Lin, J.H.; Zhang, D.; et al. Incidence of and risk factors for pancreatic cancer in chronic pancreatitis: A cohort of 1656 patients. Dig. Liver. Dis. 2017, 49, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, E.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Montiel, M.; Zoltan, M.; Dong, W.; Quesada, P.; Sahin, I.; Chandra, V.; San Lucas, A.; et al. Tumor microbiome diversity and composition influence pancreatic cancer outcomes. Cell 2019, 8, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.Y.; Shi, S.; Liang, C.; Meng, Q.C.; Hua, J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.; Xu, J.; Yu, X.J. The microbiota and microbiome in pancreatic cancer: More influential than expected. Mol. Cancer 2019, 20, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.X.; Zhao, C.F.; Chen, W.B.; Liu, Q.C.; Li, Q.W.; Lin, Y.Y.; Gao, F. Pancreatic cancer: A review of epidemiology, trend, and risk factors. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 4298–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, X.; Shi, J.; Liu, R.; Geng, S.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Jin, H.; Yang, S.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z. Using the risk factors of pancreatic cancer and their interactions in cancer screening: A case-control study in Shanghai, China. Ann. Glob. Health. 2019, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zheng, R.; He, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, N.; Chen, T.; Chen, W. Risk factors for pancreatic cancer in China: A multicenter case-control study. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licata, A.; Montalto, G.; Soresi, M. Pancreatic cancer: Risk and preventive factors. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2018, 13, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tan, C.; Ke, N.; Du, B.; Liu, X. Risk of pancreatic cancer in patients undergoing surgery for chronic pancreatitis. BMC Surg. 2019, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.A.; Bellin, M.D.; Andersen, D.K.; Bradley, D.; Cruz-Monserrate, Z.; Forsmark, C.E.; Goodarzi, M.O.; Habtezion, A.; Korc, M.; Kudva, Y.C.; et al. Type 3c (pancreatogenic) diabetes mellitus secondary to chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Lancet. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van-Tran, T.; Van Dao, T.; Nguyen, K.D.; Van Ta, T.; Vu, K.T.; Trinh, S.H.; Nguyen, H.C.; Bui, O.T.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Vu, H.D.; et al. Risk factors of pancreatic cancer in Vietnam: A matched case-control hospital-based study. Cancer. Control. 2021, 28, 1073274821989320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettison, T.M.; Nahm, C.B.; Gill, A.J.; Mittal, A.; Malhi, G.S.; Samra, J.S. Understanding the pathophysiology of psychological distress and pancreatic cancer: A systematic review. Pancreas 2018, 47, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, G.; Silverman, D.T. Occupational risk factors and pancreatic cancer: A review of recent findings. Mol Carcinog. 2012, 51, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.S.; Yeo, J.; Hwang, I.C.; Shim, J.Y. Risk of pancreatic cancer in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 3109–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Kunovský, L.; Kala, Z.; Trna, J. Risk factors of pancreatic cancer and their possible uses in diagnostics. Neoplasma 2021, 68, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.S.; Lee, J.M. Imaging diagnosis of pancreatic cancer: A state-of-the-art review. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 28, 7864–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, G. Pancreatic cancer related pain: Review of pathophysiology and intrathecal drug delivery systems for pain management. Pain Physician 2021, 24, E583–E594. [Google Scholar]
- Coveler, A.L.; Mizrahi, J.; Eastman, B.; Apisarnthanarax, S.J.; Dalal, S.; McNearney, T.; Pant, S.; Precision Promise Consortium. Pancreas cancer-associated pain management. Oncologist 2021, 26, e971–e982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, I.; Brothers, S.P. Pathogenesis and treatment of pancreatic cancer related pain. Anticancer. Res. 2020, 40, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.; Donahue, T. Pancreatic Cancer. JAMA 2019, 8, 322, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Amanam, I.; Chung, V. Current and future therapies for advanced pancreatic cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 116, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Kumar, S.; Momi, N.; Sasson, A.R.; Batra, S.K. Mucins in pancreatic cancer and its microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessmann, E.; Buchholz, S.M.; Demir, I.E.; Singh, S.K.; Gress, T.M.; Ellenrieder, V.; Neesse, A. Microenvironmental determinants of pancreatic cancer. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 1, 1707–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neoptolemos, J.P.; Kleeff, J.; Michl, P.; Costello, E.; Greenhalf, W.; Palmer, D.H. Therapeutic developments in pancreatic cancer: Current and future perspectives. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Pothula, S.P.; Wilson, J.S.; Apte, M.V. Pancreatic cancer and its stroma: A conspiracy theory. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 28, 11216–112129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Xue, J. Inflammation and development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamtaji, O.R.; Mirhosseini, N.; Reiter, R.J.; Behnamfar, M.; Asemi, Z. Melatonin and pancreatic cancer: Current knowledge and future perspectives. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 5372–5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlacchio, A.; Mazzone, P. The Role of Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) mediated inflammation in pancreatic cancer pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 25, 12743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Xiang, H.; Pan, Y.; Shang, D.; Guo, J.; Gao, G.; Xiao, G.G. Pancreatitis initiated pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Pathophysiology explaining clinical evidence. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 168, 105595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdek, P.E.; Jakubowska, M.A. Biology of pancreatic stellate cells-more than just pancreatic cancer. Pflugers Arch. 2017, 469, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetan, K.; Baloda, V.; Sahoo, R.K.; Vishnubhathla, S.; Yadav, R.; Saraya, A.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, S.D.; Das, P. SPARC expression in desmoplastic and non desmoplastic pancreatic carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Kim, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, C.J.; Sugimoto, H.; LeBleu, V.S.; Kalluri, R. Type I collagen deletion in αSMA + myofibroblasts augments immune suppression and accelerates progression of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell 2021, 12, 548–565.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaugh, L.C.; Keefe, M.D. Regeneration and repair of the exocrine pancreas. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 2015, 77, 229–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, X.; Kang, R.; Zeh, H.; Klionsky, D.J.; Tang, D. Regulation and function of autophagy in pancreatic cancer. Autophagy 2021, 17, 3275–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiński, T.M. The microbiota and pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterol. Clin. North. Am. 2019, 48, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suklabaidya, S.; Dash, P.; Das, B.; Suresh, V.; Sasmal, P.K.; Senapati, S. Experimental models of pancreatic cancer desmoplasia. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaps, L.; Schuppan, D. Targeting cancer associated fibroblasts in liver fibrosis and liver cancer using nanocarriers. Cells 2020, 3, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Luo, J.; Guo, J.; Yao, X.; Jing, X.; Guo, F. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: A narrative review. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2020, 28, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanian, F.; Azhir, Z.; Khalilian, S.; Grüning, B. Non-coding RNAs underlying the pathophysiological links between type 2 diabetes and pancreatic cancer: A systematic review. J. Diabetes. Investig. 2022, 13, 405–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Maitra, A.; Ying, H. Recent insights into the biology of pancreatic cancer. EBioMedicine 2020, 53, 102655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krantz, S.B.; Shields, M.A.; Dangi-Garimella, S.; Munshi, H.G.; Bentrem, D.J. Contribution of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells to pancreatic cancer progression. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 173, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wu, D.; Zhou, S.; Wan, F.; Liu, H.; Xu, X.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, M. The pancreatic cancer secreted REG4 promotes macrophage polarization to M2 through EGFR/AKT/CREB pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Jung, X.; Hines, O.J.; Eibl, G.; Chen, Y. Obesity and pancreatic cancer: Overview of epidemiology and potential prevention by weight loss. Pancreas 2018, 47, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, I.A.; Melo, S.A. Exosomes and the future of immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 29, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.; Kohlmann, W.; Adler, D.G. Identification and screening of individuals at increased risk for pancreatic cancer with emphasis on known environmental and genetic factors and hereditary syndromes. JOP 2010, 5, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Kurahara, H.; Maemura, K.; Mataki, Y.; Sakoda, M.; Iino, S.; Kawasaki, Y.; Arigami, T.; Mori, S.; Kijima, Y.; Ueno, S.; et al. A therapeutic strategy for resectable pancreatic cancer based on risk factors of early recurrence. Pancreas 2018, 47, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Ni, B. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in pancreatic cancer: Regulatory mechanisms and future direction. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 4, 2323–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepstad, I.; Hatfield, K.J.; Grønningsæter, I.S.; Reikvam, H. The PI3K-Akt-mTOR Signaling Pathway in Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibble, C.C.; Cantley, L.C. Regulation of mTORC1 by PI3K signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noorolyai, S.; Shajari, N.; Baghbani, E.; Sadreddini, S.; Baradaran, B. The relation between PI3K/AKT signalling pathway and cancer. Gene 2019, 25, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Mehan, S. Targeting PI3K-AKT/mTOR signaling in the prevention of autism. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 147, 105067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, G.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. The PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 6, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Shi, X.; Sheng, K.; Han, G.; Li, W.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, B.; Feng, J.; Li, J.; Gu, Y. PI3K/Akt signaling transduction pathway, erythropoiesis and glycolysis in hypoxia (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.C. Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, S.; Deshpande, N.; Nagathihalli, N. Targeting PI3K pathway in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Rationale and progress. Cancers 2021, 2, 4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.W.; Zhang, R.; Tan, Z.; Chung, J.P.W.; Zhang, T.; Wang, C.C. Pharmaceuticals targeting signaling pathways of endometriosis as potential new medical treatment: A review. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 2489–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnero, A.; Blanco-Aparicio, C.; Renner, O.; Link, W.; Leal, J.F. The PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in cancer, therapeutic implications. Curr. Cancer Drug. Targets 2008, 8, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Ghadami, E.; Dadkhah, T.; Akhavan-Niaki, H. PI3k/AKT signaling pathway: Erythropoiesis and beyond. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 2373–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, N.; Jücker, M. Distinct functions of AKT isoforms in breast cancer: A comprehensive review. Cell Commun. Signal 2019, 21, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Aggarwal, R.; Zeng, N.; He, L.; Stiles, E.X.; Debebe, A.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.Y.; Stiles, B.L. AKT1 regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress and mediates the adaptive response of pancreatic β Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 14, e00031-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, M.C.; Sala, V.; Martini, M.; Ferrero, G.B.; Hirsch, E. PI3K Signaling in Tissue hyper-proliferation: From overgrowth syndromes to kidney cysts. Cancers 2017, 29, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoki, K.; Li, Y.; Zhu, T.; Wu, J.; Guan, K.L. TSC2 is phosphorylated and inhibited by Akt and suppresses mTOR signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallela, K.; Kumar, A. Role of TSC1 in physiology and diseases. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 2269–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makker, A.; Goel, M.M.; Mahdi, A.A. PI3K/PTEN/Akt and TSC/mTOR signaling pathways, ovarian dysfunction, and infertility: An update. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 53, R103–R118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Khuri, F.R. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: Biomarkers of success and tribulation. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2013, 33, e395–e401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.H.; Yap, T.A.; Yan, L.; Cunningham, D. Targeting the PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling network in cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2013, 32, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larsen, L.J.; Møller, L.B. Crosstalk of hedgehog and mTORC1 pathways. Cells 2020, 18, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Gámez-Díaz, L.; Proietti, M.; Grimbacher, B. Immune TOR-opathies," a novel disease entity in clinical immunology. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y. Targeting the mTOR-DEPTOR pathway by CRL E3 ubiquitin ligases: Therapeutic application. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Hosseini, M.; Shahidsales, S.; Maftouh, M.; Ferns, G.A.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Hassanian, S.M.; Avan, A. Targeting the Akt/PI3K signaling pathway as a potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of pancreatic Cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, C.; Hu, Y.; Song, G.; Shen, X. The diverse roles of circular RNAs in pancreatic cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 226, 107869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertacchini, J.; Heidari, N.; Mediani, L.; Capitani, S.; Shahjahani, M.; Ahmadzadeh, A.; Saki, N. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR network for treatment of leukemia. Cell. Mol. Life. Sci. 2015, 72, 2337–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polivka, J., Jr.; Janku, F. Molecular targets for cancer therapy in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 142, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaria, J.P.; Campa, C.C.; De Santis, M.C.; Hirsch, E.; Franco, I. The PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in polycystic kidney disease: A complex interaction with polycystins and primary cilium. Cell Signal 2020, 66, 09468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoletti, M.; Broggini, M. PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors in ovarian cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 4433–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duzgun, Z.; Eroglu, Z.; Biray Avci, C. Role of mTOR in glioblastoma. Gene 2016, 10, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, J.A. HER2 in colorectal carcinoma: Are we there yet? Surg. Pathol. Clin. 2020, 13, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Li, X.; Zhen, L.; Chen, W.; Mu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Song, A. Everolimus inhibits breast cancer cell growth through PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 7163–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degan, S.E.; Gelman, I.H. Emerging roles for AKT isoform preference in cancer progression pathways. Mol. Cancer. Res. 2021, 19, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, R.; Cintas, C.; Therville, N.; Guillermet-Guibert, J. Implication of PI3K/Akt pathway in pancreatic cancer: When PI3K isoforms matter? Adv. Biol. Regul. 2015, 59, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, B.; Makhdoomi, U.; Vishwakarma, R.; Malik, F. Protein kinase B: Emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific regulation of cellular signaling in cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2017, 28, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ediriweera, M.K.; Tennekoon, K.H.; Samarakoon, S.R. Role of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in ovarian cancer: Biological and therapeutic significance. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.S. PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in cancer: At the bench and bedside. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asati, V.; Mahapatra, D.K.; Bharti, S.K. PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways inhibitors as anticancer agents: Structural and pharmacological perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 15, 314–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajoo, N.; Stanslas, J.; Islam, M.K.; Sagineedu, S.R.; Ho, K.L.; Lim, J.C.W. Pharmacological modulation of apoptosis and autophagy in the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergadi, E.; Ieronymaki, E.; Lyroni, K.; Vaporidi, K.; Tsatsanis, C. Akt signaling pathway in macrophage activation and M1/M2 polarization. J. Immunol. 2017, 1, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briest, F.; Grabowski, P. PI3K-AKT-mTOR-signaling and beyond: The complex network in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Theranostics 2014, 29, 336–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Lin, N. The effect of ibrutinib on radiosensitivity in pancreatic cancer cells by targeting EGFR/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyens, M.; Vandamme, T.; Peeters, M.; Van Camp, G.; Op de Beeck, K. Resistance to targeted treatment of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2019, 1, R109–R130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, P.A.; Moody, C.L.; Murali, R. Allosteric modulation of Ras and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: Emerging therapeutic opportunities. Front. Physiol. 2014, 16, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, L.; Wu, X.; Li, R.; Wen, J.; Sha, J.; Wen, X. The PI3K/AKT pathway in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer. Front. Biosci. 2016, 1, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Nishiyama, A.; Matsuyama, M.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y. The (pro)renin receptor: A novel biomarker and potential therapeutic target for various cancers. Cell Commun. Signal 2020, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Qian, X.; Shi, M.; Li, H.; Peng, C.; Ding, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, B.; Xu, G.; Lv, Y.; et al. ALDH1A3 accelerates pancreatic cancer metastasis by promoting glucose metabolism. Front. Oncol. 2020, 16, 10–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Ali, S.; Banerjee, S.; Ahmad, A.; Sarkar, F.H. The complexities of obesity and diabetes with the development and progression of pancreatic cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011, 1815, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Hui, Y.; Hua, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, L.; Peng, F.; Tang, C.; Liu, D.; Song, J.; Wang, F. EG-VEGF silencing inhibits cell proliferation and promotes cell apoptosis in pancreatic carcinoma via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.C. Tanshinone IIA can inhibit MiaPaCa2 human pancreatic cancer cells by dual blockade of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3102–3111. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Pan, Y.; Xu, C. Effects of aspirin on pancreatic cancer cells PANC-1 and its potential molecular mechanism. J. Buon. 2020, 25, 2449–2455. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Xu, J.; Guo, J.; Shang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, T. The enhancement of tetrandrine to gemcitabine-resistant PANC-1 cytochemical sensitivity involves the promotion of PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated apoptosis and AMPK-regulated autophagy. Acta. Histochem. 2021, 123, 151769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.N.; Kumar, D.; Shankar, S.; Srivastava, R.K. Rottlerin induces autophagy which leads to apoptotic cell death through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in human pancreatic cancer stem cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 1, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tan, X.; Liu, P.; Wu, Y.; Qian, S.; Zhang, X. Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 (PGAM1) promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) metastasis by acting as a novel downstream target of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncol. Res. 2018, 23, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Xiang, J.; Zhan, C.; Liu, J.; Yan, S. STK33 promotes the growth and progression of human pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour via activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Neuroendocrinology 2020, 110, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, J.R.; Herrmann, D.; Evans, T.J.; Morton, J.P.; Timpson, P. Combating pancreatic cancer with PI3K pathway inhibitors in the era of personalised medicine. Gut 2019, 68, 742–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, D.R.; Karim, S.A.; Sano, M.; Gay, D.M.; Jacob, W.; Yu, J.; Mizukami, Y.; Gopinathan, A.; Jodrell, D.I.; Evans, T.R.; et al. mTORC2 signaling drives the development and progression of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6911–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisawa, T.; Wood, L.D.; Itoi, T.; Takaori, K. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, A.; Herman, J.; Schulick, R.; Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2011, 378, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xie, K.; Wolff, R.; Abbruzzese, J.L. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2004, 363, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, F.; Ciruelos, E.; Rubovszky, G.; Campone, M.; Loibl, S.; Rugo, H.S.; Iwata, H.; Conte, P.; Mayer, I.A.; Kaufman, B.; et al. Alpelisib for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor–positive advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Approves Alpelisib for PIK3CA-Related Overgrowth Spectrum. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-alpelisib-pik3ca-related-overgrowth-spectrum (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Thibault, B.; Ramos-Delgado, F.; Pons-Tostivint, E.; Therville, N.; Cintas, C.; Arcucci, S.; Cassant-Sourdy, C.; Reyes-Castellanos, G.; Tosolini, M.; Villard, A.V.; et al. Pancreatic cancer intrinsic PI3Kα activity accelerates metastasis and rewires macrophage component. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e13502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, H.P.; Al-Toubah, T.E.; Kim, R.D.; Kim, J.; Lewis, N.K.; Mahipal, A. Final report: A phase I trial of BYL719 in Combination with Gemcitabine and (Nab)-Paclitaxel in Locally Advanced and Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 398, NCT02155088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard, P.L.; Tabernero, J.; Janku, F.; Wainberg, Z.A.; Paz-Ares, L.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Perez-Garcia, J.; Stathis, A.; Britten, C.D.; et al. Phase Ib dose-escalation study of the oral Pan-PI3K inhibitor Buparlisib (BKM120) in combination with the oral MEK1/2 inhibitor Trametinib (GSK1120212) in patients with selected advanced solid tumors PI3K inhibitor Buparlisib with MEK inhibitor Trametinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Sender, S.; Sekora, A.; Kong, W.; Bauer, P.; Ameziane, N.; Al-Ali, R.; Krake, S.; Radefeldt, M.; Weiss, F.U.; et al. The inhibitory response to PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitors MK-2206 and Buparlisib is related to genetic differences in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BKM120 + mFOLFOX6 in Advanced Solid Tumors with Expansion Cohort Pancreatic Cancer. NCT01571024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01571024 (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- McRee, A.J.; Sanoff, H.K.; Carlson, C.; Ivanova, A.; O’Neil, B.H. A phase I trial of mFOLFOX6 combined with the oral PI3K inhibitor BKM120 in patients with advanced refractory solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihle, N.T.; Williams, R.; Chow, S.; Chew, W.; Berggren, M.I.; Paine-Murrieta, G.; Minion, D.J.; Halter, R.J.; Wipf, P.; Abraham, R.; et al. Molecular pharmacology and antitumor activity of PX-866, a novel inhibitor of phosphoinositide-3-kinase signaling. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; Bowles, D.W.; Falchook, G.S.; Messersmith, W.A.; George, G.C.; O’Bryant, C.L.; Vo, A.C.H.; Klucher, K.; Herbst, R.S.; Eckhardt, G.; et al. A multicenter phase I trial of PX-866, an oral irreversible phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors first-in-human trial of PX-866. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4173–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BAY80-6946 Open Label, Phase I Study in Patients with Advanced Cancer. NCT00962611. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00962611 (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Patnaik, A.; Appleman, L.J.; Tolcher, A.W.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Beeram, M.; Rasco, D.W.; Weiss, G.J.; Sachdev, J.C.; Chadha, M.; Fulk, M.; et al. First-in-human phase I study of copanlisib (BAY 80-6946), an intravenous pan-class I phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1928–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynaud, F.I.; Eccles, S.A.; Patel, S.; Alix, S.; Baker, S.J.; Box, G.; Chuckowree, I.; Folkes, A.; Gowan, S.; De Haven Brandon, A.; et al. Biological properties of potent inhibitors of class I phosphatidylinositide 3-kinases: From PI-103 through PI-540, PI-620 to the oral agent GDC-0941. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1725–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, D.; Ang, J.E.; Baird, R.; Kristeleit, R.; Shah, K.; Moreno, V.; Clarke, P.A.; Raynaud, F.I.; Levy, G.; Ware, J.A.; et al. First-in-human phase I study of Pictilisib (GDC-0941), a Potent Pan–Class I Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase (PI3K) Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid TumorsFIH Phase I Trial of Potent and Selective Pan–PI3K Inhibitor Pictilisib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Fujiwara, Y.; Tamura, K.; Kondo, S.; Iwasa, S.; Tanabe, Y.; Horiike, A.; Yanagitani, N.; Kitazono, S.; Inatani, M.; et al. Phase Ia/Ib study of the pan-class I PI3K inhibitor pictilisib (GDC-0941) administered as a single agent in Japanese patients with solid tumors and in combination in Japanese patients with non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of Cobimetinib in Combination with Pictilisib in Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors. NCT00996892. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00996892 (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Shapiro, G.I.; LoRusso, P.; Kwak, E.; Pandya, S.; Rudin, C.M.; Kurkjian, C.; Cleary, J.M.; Pilat, M.J.; Jones, S.; de Crespigny, A.; et al. Phase Ib study of the MEK inhibitor cobimetinib (GDC-0973) in combination with the PI3K inhibitor pictilisib (GDC-0941) in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New. Drugs. 2020, 38, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, M.; Moosavi, F.; Martini, M.; Giovannetti, E.; Firuzi, O. Prospects of targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in pancreatic cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022, 176, 103749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Shen, X.D.; Cheng, L.; Hong, D.F.; Chen, B. Perifosine inhibits S6K1–Gli1 signaling and enhances gemcitabine-induced anti-pancreatic cancer efficiency. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 73, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.D.W.; Lima, C.M.R.; Levy, D.E.; Mitchell, E.P.; Rowland Jr, K.M.; Benson, A.B., III. A phase II trial of perifosine in locally advanced, unresectable, or metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 30, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, D.; Moore, M.J.; Hirte, H.; Siu, L.; Vincent, M.; Jonker, D.; Wang, H.M.; Nagai, J.; Dancey, J. A phase II trial of perifosine as second line therapy for advanced pancreatic cancer. A study of the Princess Margaret Hospital [PMH] phase II consortium. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, A.; Man, J.; Timpson, P.; Pajic, M. Targeting the complexity of Src signalling in the tumour microenvironment of pancreatic cancer: From mechanism to therapy. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 3510–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safety, Pharmacokinetics (PK) of AKT and MEK Combination. NCT01138085. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01138085 (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Tolcher, A.W.; Kurzrock, R.; Valero, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Heist, R.S.; Tan, A.R.; Means-Powell, J.; Werner, T.L.; Becerra, C.; Wang, C.; et al. Phase I dose-escalation trial of the oral AKT inhibitor uprosertib in combination with the oral MEK1/MEK2 inhibitor trametinib in patients with solid tumors. Cancer Chemoter. Pharmacol. 2020, 85, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Tang, W.; Zhuo, H.; Zhao, G. Recent advance of Akt inhibitors in clinical trials. Chemistry. Select. 2019, 4, 9040–9044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uko, N.E.; Güner, O.F.; Matesic, D.F.; Bowen, J.P. Akt pathway inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 883–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Study of the Safety and Activity of the MEK Inhibitor Given Together with the AKT Inhibitor to Patients with Multiple Myeloma or Solid Tumor Cancers. NCT01476137. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01476137 (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Continuation Study of the Oral AKT Inhibitor GSK2110183. NCT01531894. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01531894 (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Francischini, C.R.D.; Mendonça, C.R.; Barcelos, K.A.; Silva, M.A.M.; Botelho, A.F.M. Antitumor effects of oleandrin in different types of cancers: Systematic review. Toxicon 2022, 216, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Rhea, P.; Tan, L.; Cartwright, C.; Lee, H.J.; Ravoori, M.K.; Addington, C.; Gagea, M.; Kundra, V.; Kim, S.-J.; et al. PBI-05204, a supercritical CO2 extract of Nerium oleander, inhibits growth of human pancreatic cancer via targeting the PI3K/mTOR pathway. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, R.A.; Kondo, Y.; Yokoyama, T.; Dixon, S.; Cartwright, C.; Chan, D.; Johansen, M.; Yang, P. Autophagic cell death of human pancreatic tumor cells mediated by oleandrin, a lipid-soluble cardiac glycoside. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Menter, D.G.; Cartwright, C.; Chan, D.; Dixon, S.; Suraokar, M.; Mendoza, G.; LLansa, N.; Newman, R.A. Oleandrin-mediated inhibition of human tumor cell proliferation: Importance of Na, K-ATPase α subunits as drug targetsNa, K-ATPase Composition and Oleandrin Cytotoxicity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 2319–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; Henary, H.; Falchook, G.S.; Naing, A.; Fu, S.; Moulder, S.; Wheler, J.J.; Tsimberidou, A.; Durand, J.B.; Khan, R.; et al. First-in-human study of pbi-05204, an oleander-derived inhibitor of akt, fgf-2, nf-κΒ and p70s6k, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2014, 32, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, M.T.; Cardin, D.B.; Borazanci, E.H.; Steinbach, M.; Picozzi, V.J.; Rosemury, A.; Wadlow, R.C.; Newman, R.A.; Berlin, J. A phase II, single-arm, open-label, bayesian adaptive efficacy and safety study of PBI-05204 in patients with stage IV metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Oncologist 2020, 25, e1446–e1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangadhar, T.C.; Cohen, E.E.; Wu, K.; Janisch, L.; Geary, D.; Kocherginsky, M.; House, L.K.; Ramirez, J.; Undevia, S.D.; Maitland, M.L.; et al. Two drug interaction studies of Sirolimus in combination with sorafenib or sunitinib in patients with advanced malignancies two drug interaction studies of Sirolimus. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1956–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Laguna, I.; Tan, A.C.; Uson, M.; Angenendt, M.; Ma, W.W.; Villaroel, M.C.; Zhao, M.; Rajeshkumar, N.V.; Jimeno, A.; Donehower, R.; et al. Integrated preclinical and clinical development of mTOR inhibitors in pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolpin, B.M.; Hezel, A.F.; Abrams, T.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Chan, J.A.; Enzinger, P.C.; Allen, B.; Clark, J.W.; Ryan, D.P.; et al. Oral mTOR inhibitor everolimus in patients with gemcitabine-refractory metastatic pancreatic cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.C.; Lombard-Bohas, C.; Baudin, E.; Kvols, L.K.; Rougier, P.; Ruszniewski, P.; Hoosen, S.; St Peter, J.; Haas, T.; Lebwohl, D.; et al. Daily oral everolimus activity in patients with metastatic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors after failure of cytotoxic chemotherapy: A phase II trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordes, S.; Klümpen, H.J.; Weterman, M.J.; Schellens, J.H.; Richel, D.J.; Wilmink, J.W. Phase II study of capecitabine and the oral mTOR inhibitor everolimus in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2015, 75, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, C.; Yalcin, S. Current and future systemic treatment options in metastatic pancreatic cancer. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2014, 5, 280–295. [Google Scholar]
- Metformin Combined with Chemotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer. NCT01210911. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01210911 (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Kordes, S.; Pollak, M.N.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Mathôt, R.A.; Weterman, M.J.; Beeker, A.; Punt, C.J.; Richel, D.J.; Wilmink, J.W. Metformin in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Study of Metformin with or Without Rapamycin as Maintenance Therapy After Induction Chemotherapy in Subjects with Pancreatic Cancer. NCT02048384. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02048384 (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Bever, K.M.; Borazanci, E.H.; Thompson, E.A.; Durham, J.N.; Pinero, K.; Jameson, G.S.; Vrana, A.; Liu, M.; Wilt, C.; Wu, A.A.; et al. An exploratory study of metformin with or without rapamycin as maintenance therapy after induction chemotherapy in patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanikas, M.; Esempidis, A.; Chasan, Z.T.M.; Deftereou, T.; Antonopoulou, M.; Bozali, F.; Amarantidis, K.; Man, Y.G. Pancreatic cancer from molecular pathways to treatment opinion. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, T.; Yashiro, M. Molecular targets for the treatment of pancreatic cancer: Clinical and experimental studies. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 776–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Safety and Efficacy Study of RX-0201 Plus Gemcitabine in Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. NCT01028495. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01028495 (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Yap, T.A.; Patnaik, A.; Fearen, I.; Olmos, D.; Papadopoulos, K.; Tunariu, N.; Sullivan, D.; Yan, L.; De Bono, J.S.; Tolcher, A.W. First-in-class phase I trial of a selective Akt inhibitor, MK2206 (MK), evaluating alternate day (QOD) and once weekly (QW) doses in advanced cancer patients (pts) with evidence of target modulation and antitumor activity. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, G.; Qiu, Z. Akt inhibitor MK2206 reduces pancreatic cancer cell viability and increases the efficacy of gemcitabine. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1999–2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Dadon, T.; Chenna, V.; Yabuuchi, S.; Bannerji, R.; Booher, R.; Strack, P.; Azad, N.; Nelkin, B.D.; Maitra, A. Combined inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases (Dinaciclib) and AKT (MK-2206) blocks pancreatic tumor growth and metastases in patient-derived xenograft models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.G.; Zahurak, M.; Shah, M.; Weekes, C.D.; Hansen, A.; Siu, L.L.; Spreafico, A.; LeConte, N.; Ander, N.M.; Miles, T.; et al. A Phase I Study of Dinaciclib in Combination With MK-2206 in Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 13, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, C.R.; Coppola, D.; Wenham, R.M.; Cubitt, C.L.; Neuger, A.M.; Frost, T.J.; Lush, R.M.; Sullivan, D.M.; Cheng, J.Q.; Sebti, S.M. Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of triciribine phosphate monohydrate, a small-molecule inhibitor of AKT phosphorylation, in adult subjects with solid tumors containing activated AKT. Investig. New Drugs 2011, 29, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.; Yamauchi, T.; Husain, K.; Sebti, S.; Malafa, M. Triciribine phosphate monohydrate, an AKT inhibitor, enhances gemcitabine activity in pancreatic cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 4599–4604. [Google Scholar]
- Javle, M.M.; Shroff, R.T.; Xiong, H.; Varadhachary, G.A.; Fogelman, D.; Reddy, S.A.; Davis, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wolff, R.A.; Abbruzzese, J.L. Inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in advanced pancreatic cancer: Results of two phase II studies. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavasilis, V.; Samantas, E.; Koliou, G.A.; Kalogera-Fountzila, A.; Pentheroudakis, G.; Varthalitis, I.; Linardou, H.; Rallis, G.; Skondra, M.; Papadopoulos, G.; et al. Gemcitabine combined with the mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus in patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer. A hellenic cooperative oncology group phase i/II study. Target. Oncol. 2018, 13, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemunaitis, J.; Hochster, H.S.; Lustgarten, S.; Rhodes, R.; Ebbinghaus, S.; Turner, C.D.; Dodion, P.F.; Mita, M.M. A phase I trial of oral ridaforolimus (AP23573; MK-8669) in combination with bevacizumab for patients with advanced cancers. Clin Oncol. 2013, 25, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, B.; Dean, E.; Puglisi, M.; Greystoke, A.; Ong, M.; Burke, W.; Cavallin, M.; Bigley, G.; Womack, C.; Harrington, E.A.; et al. First-in-Human Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Study of the Dual m-TORC 1/2 Inhibitor AZD2014Phase I Study of AZD2014. Clin. Cancer. Res 2015, 21, 3412–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaro, A.; Rodon, J.; Calles, A.; Braña, I.; Hidalgo, M.; Lopez-Casas, P.P.; Munoz, M.; Westwood, P.; Miller, J.; Moser, B.A.; et al. A first-in-human phase I trial of LY2780301, a dual p70 S6 kinase and Akt Inhibitor, in patients with advanced or metastatic cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, N.; Yen, P.L.; Schwarz, M.A.; Schwarz, R.E. The efficacy of a novel, dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 to enhance chemotherapy and antiangiogenic response in pancreatic cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, H.P.; Ming, M.; Mellon, M.; Young, S.H.; Han, L.; Sinnet-Smith, J.; Rozengurt, E. Dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors induce rapid overactivation of the MEK/ERK pathway in human pancreatic cancer cells through suppression of mTORC2. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.J.; Pan, W.W.; Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Nanta, R.; Sharma, J.; Gunewardena, S.; Singh, K.P.; Shankar, S.; Srivastava, R.K. PI3K/AKT/mTOR and sonic hedgehog pathways cooperate together to inhibit human pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics and tumor growth. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 32039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Wu, X.; Jiang, J.; Gao, W.; Wan, Y.; Cheng, D.; Han, D.; Liu, J.; Englund, N.P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Discovery of NVP-LDE225, a potent and selective smoothened antagonist. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Borrego, M.; Jimenez, B.; Antolín, S.; García-Saenz, J.A.; Corral, J.; Jerez, Y.; Trigo, J.; Urruticoechea, A.; Colom, H.; Gonzalo, N.; et al. A phase Ib study of sonidegib (LDE225), an oral small molecule inhibitor of smoothened or Hedgehog pathway, in combination with docetaxel in triple negative advanced breast cancer patients: GEICAM/2012–12 (EDALINE) study. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 37, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chan, D.K.; Sen, A.; Ma, W.W.; Straubinger, R.M. Tumor priming by SMO inhibition enhances antibody delivery and efficacy in a pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.Y.; Omuro, A.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Fathallah-Shaykh, H.M.; Mohile, N.; Lager, J.J.; Laird, A.D.; Tang, J.; Jiang, J.; Egile, C.; et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of the PI3K/mTOR inhibitor voxtalisib (SAR245409, XL765) plus temozolomide with or without radiotherapy in patients with high-grade glioma. Neuro-Oncol. 2015, 17, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schram, A.M.; Gandhi, L.; Mita, M.M.; Damstrup, L.; Campana, F.; Hidalgo, M.; Grande, E.; Hyman, D.M.; Heist, R.S. A phase Ib dose-escalation and expansion study of the oral MEK inhibitor pimasertib and PI3K/MTOR inhibitor voxtalisib in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, K.P.; Tabernero, J.; Markman, B.; Patnaik, A.; Tolcher, A.W.; Baselga, J.; Shi, W.; Egile, C.; Ruiz-Soto, R.; Laird, A.D.; et al. Phase I safety, Pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of SAR245409 (XL765), a novel, orally administered PI3K/mTOR inhibitor in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2445–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainberg, Z.A.; Alsina, M.; Soares, H.P.; Braña, I.; Britten, C.D.; Del Conte, G.; Ezeh, P.; Houk, B.; Kern, K.A.; Leong, S.; et al. A multi-arm phase I study of the PI3K/mTOR inhibitors PF-04691502 and gedatolisib (PF-05212384) plus irinotecan or the MEK inhibitor PD-0325901 in advanced cancer. Target Oncol. 2017, 12, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadevan, D.; Chiorean, E.G.; Harris, W.B.; Von Hoff, D.D.; Stejskal-Barnett, A.; Qi, W.; Anthony, S.P.; Younger, A.E.; Rensvold, D.M.; Cordova, F.; et al. Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the pan-PI3K/mTORC vascular targeted pro-drug SF1126 in patients with advanced solid tumours and B-cell malignancies. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 3319–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, C.; Paglino, C.; Mosca, A. Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in cancer. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, M.E.; Hainsworth, J.D.; Baudin, E.; Peeters, M.; Hörsch, D.; Winkler, R.E.; Klimovsky, J.; Lebwohl, D.; Jehl, V.; Wolin, E.M.; et al. Everolimus plus octreotide long-acting repeatable for the treatment of advanced neuroendocrine tumours associated with carcinoid syndrome (RADIANT-2): A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet 2011, 378, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Okusaka, T.; Ikeda, M.; Igarashi, H.; Morizane, C.; Nakachi, K.; Tajima, T.; Kasuga, A.; Fujita, Y.; Furuse, J. Everolimus for advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours: A subgroup analysis evaluating Japanese patients in the RADIANT-3 trial. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 42, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, J.; Pierce, A.; Bye, B.; Walsh, M.; Chalise, P.; VanSaun, M.N. Dual MEK and AKT inhibition suppresses pancreatic cancer growth and migration. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munster, P.N.; Aggarwal, R.; Hong, D.; Schellens, J.H.; Van Der Noll, R.; Specht, J.M.; Witteveen, P.O.; Werner, T.L.; Dees, E.C.; Bergsland, E.K.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I Study of GSK2126458, an Oral Pan-Class I Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumor Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Inhibitor | Target | Mechanism | Study | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpelisib (BY719, NVP-BYL719) | PI3K | ATP competitive | Solar-1 phase III | [164,165] |
| Buparlisib (BKM120, NVP-BKM120) | PI3K | ATP competitive | Phase Ib multicenter | [168] |
| Sonolisib (PX-866) | PI3K | Allosteric | Multicenter phase I | [172,173] |
| Copanlisib (BAY80-6946) | PI3K | ATP competitive | Phase I clinical trial | [174,175] |
| Pictilisib (GDC-0941, RG7621) | PI3K | ATP competitive | Xenograft murine models | [176] |
| Pictilisib (GDC-0941, RG7621) | PI3K | ATP competitive | First-in-human phase I | [177,178,179] |
| Perifosine (KRX041, NSC639966) | AKT | Allosteric | Cell lines | [182] |
| Perifosine (KRX041, NSC639966) | AKT | Allosteric | Phase II, clinical trial | [183,184] |
| Uprosertib (GSK2141795) | AKT | ATP competitive | Non-randomized clinical study | [185,186] |
| Afuresertib (GSK2110183) | AKT | ATP competitive | Phase I/II | [190,191] |
| Oleandrin (PBI-05204) | AKT | Information not available | Pancreatic cells | [193,194,195] |
| Oleandrin (PBI-05204) | AKT | Information not available | First-in-human phase I/II | [196,197] |
| MK-2206 | AKT | Allosteric | Cell lines | [169,215,216] |
| MK-2206 | AKT | Allosteric | Xenograft models | [212,213] |
| MK-2206 | AKT | Allosteric | Phase I clinical trial | [214] |
| Archexin (RX0201) | AKT | Antisense oligonucleotide | Phase II clinical trial | [210] |
| LY2780301 | AKT | ATP competitive | Phase I | [221] |
| Sirolimus (AY-22989, RAPA, SILA, WY090217) | mTOR | Allosteric | Phase II clinical trial/ multi-institutional phase II | [199,200] |
| Everolimus (RAD001) | mTOR | Allosteric | Phase II/clinical trial | [201,202,233,235,236] |
| Metformin | mTOR | Information not available | Phase I/II | [204,205,206,207] |
| Temsirolimus (CCI 779, WAY-CCI779) | mTOR | Allosteric | xenografts | [199] |
| Temsirolimus (CCI 779, WAY-CCI779) | mTOR | Allosteric | Clinical trial/phase I/II | [217,218] |
| Ridaforolimus (AP23573, MK-8669) | mTOR | Allosteric | Phase I clinical trial | [219] |
| Vistusertib (AZD2014) | mTOR | ATP competitive | Clinical trial | [220] |
| Dactolisib (NVP-BEZ235, BEZ235) | PI3K/mTOR | ATP competitive | Cell lines | [222,225] |
| Voxtalisib (SAR245409, XL765) | PI3K/mTOR | ATP competitive | Phase I clinical trial | [230,231] |
| Gedatolisib (PF05212384, PKI-587) | PI3K/mTOR | ATP competitive | Four-arm-clinical trial | [232] |
| PF-04691502 | PI3K/mTOR | ATP competitive | Four-arm-clinical trial | [232] |
| SF1126 | PI3K/mTOR | ATP competitive | Clinical trial | [233] |
| Omipalisib (GSK458, GSK2126458) | PI3K/mTOR | ATP competitive | Clinical trial | [238] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stanciu, S.; Ionita-Radu, F.; Stefani, C.; Miricescu, D.; Stanescu-Spinu, I.-I.; Greabu, M.; Ripszky Totan, A.; Jinga, M. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer: From Molecular to Clinical Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231710132
Stanciu S, Ionita-Radu F, Stefani C, Miricescu D, Stanescu-Spinu I-I, Greabu M, Ripszky Totan A, Jinga M. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer: From Molecular to Clinical Aspects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(17):10132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231710132
Chicago/Turabian StyleStanciu, Silviu, Florentina Ionita-Radu, Constantin Stefani, Daniela Miricescu, Iulia-Ioana Stanescu-Spinu, Maria Greabu, Alexandra Ripszky Totan, and Mariana Jinga. 2022. "Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer: From Molecular to Clinical Aspects" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 17: 10132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231710132
APA StyleStanciu, S., Ionita-Radu, F., Stefani, C., Miricescu, D., Stanescu-Spinu, I. -I., Greabu, M., Ripszky Totan, A., & Jinga, M. (2022). Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer: From Molecular to Clinical Aspects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(17), 10132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231710132








