Retinal Ganglion Cell Survival and Axon Regeneration after Optic Nerve Injury: Role of Inflammation and Other Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. History
3. Intraocular Inflammation Promotes RGC Survival and Axon Regeneration
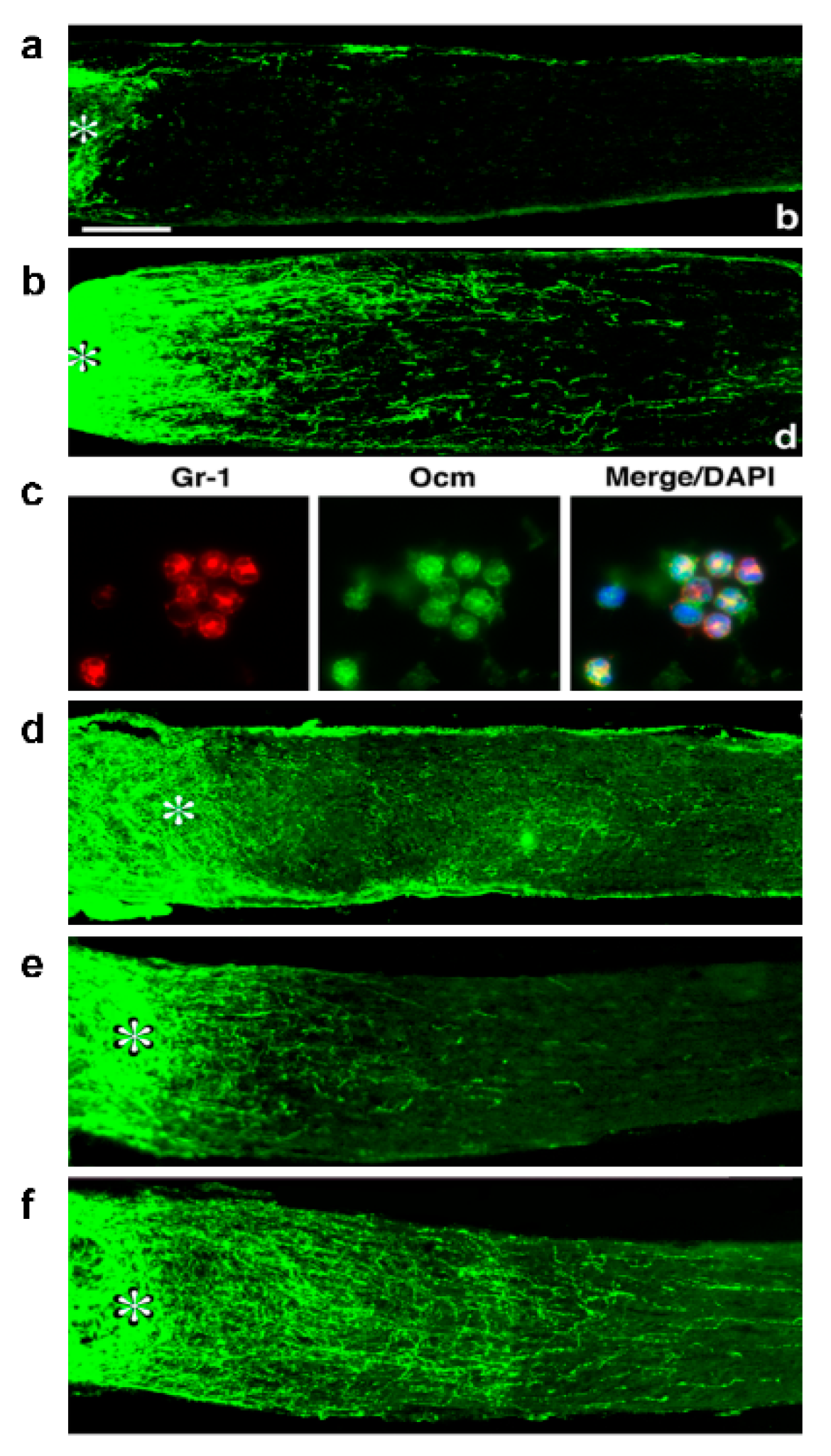
4. Oncomodulin: A Key Mediator of Inflammation-Induced Regeneration
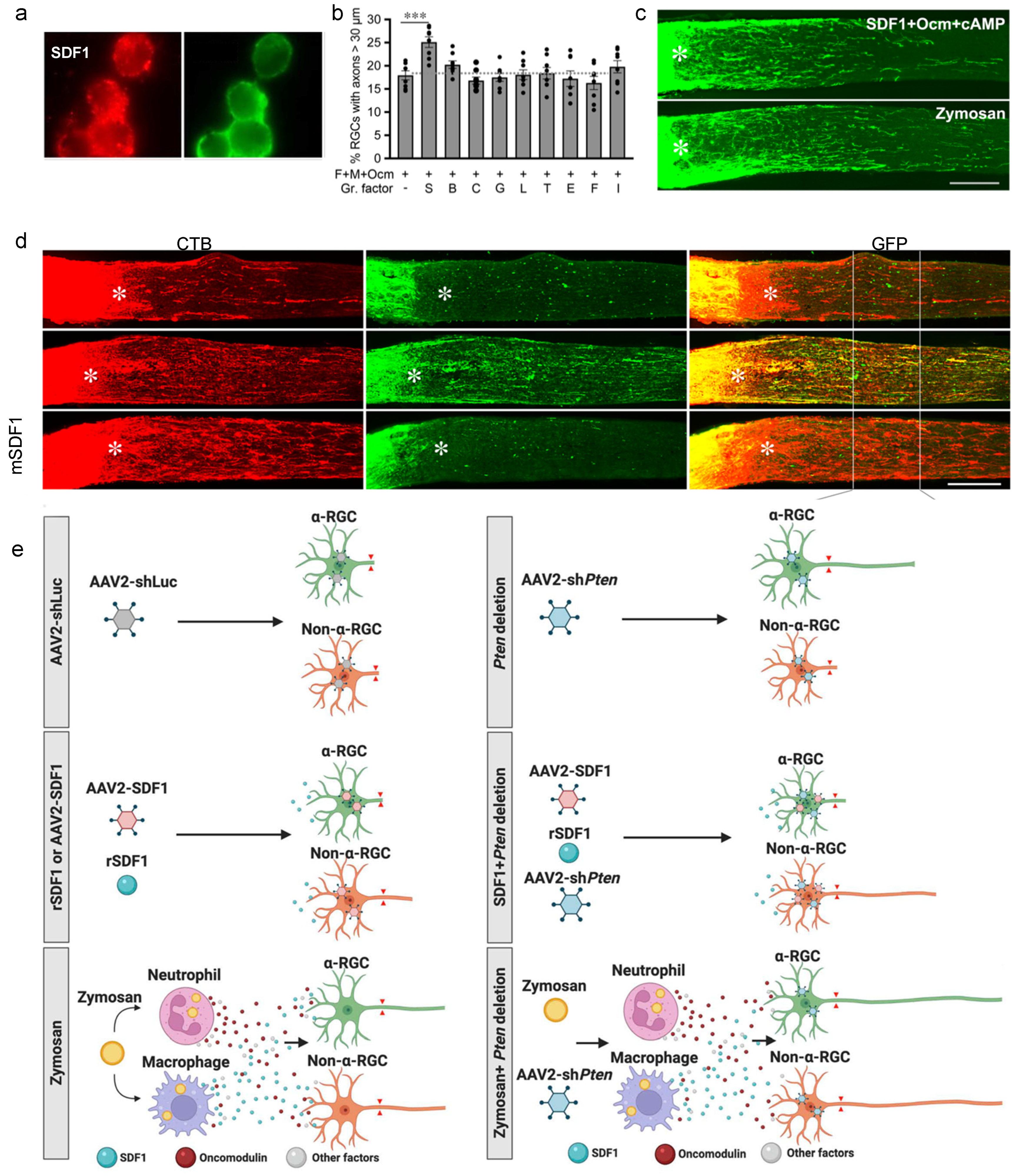
5. Macrophage-Derived SDF1 Complements the Effects of Ocm
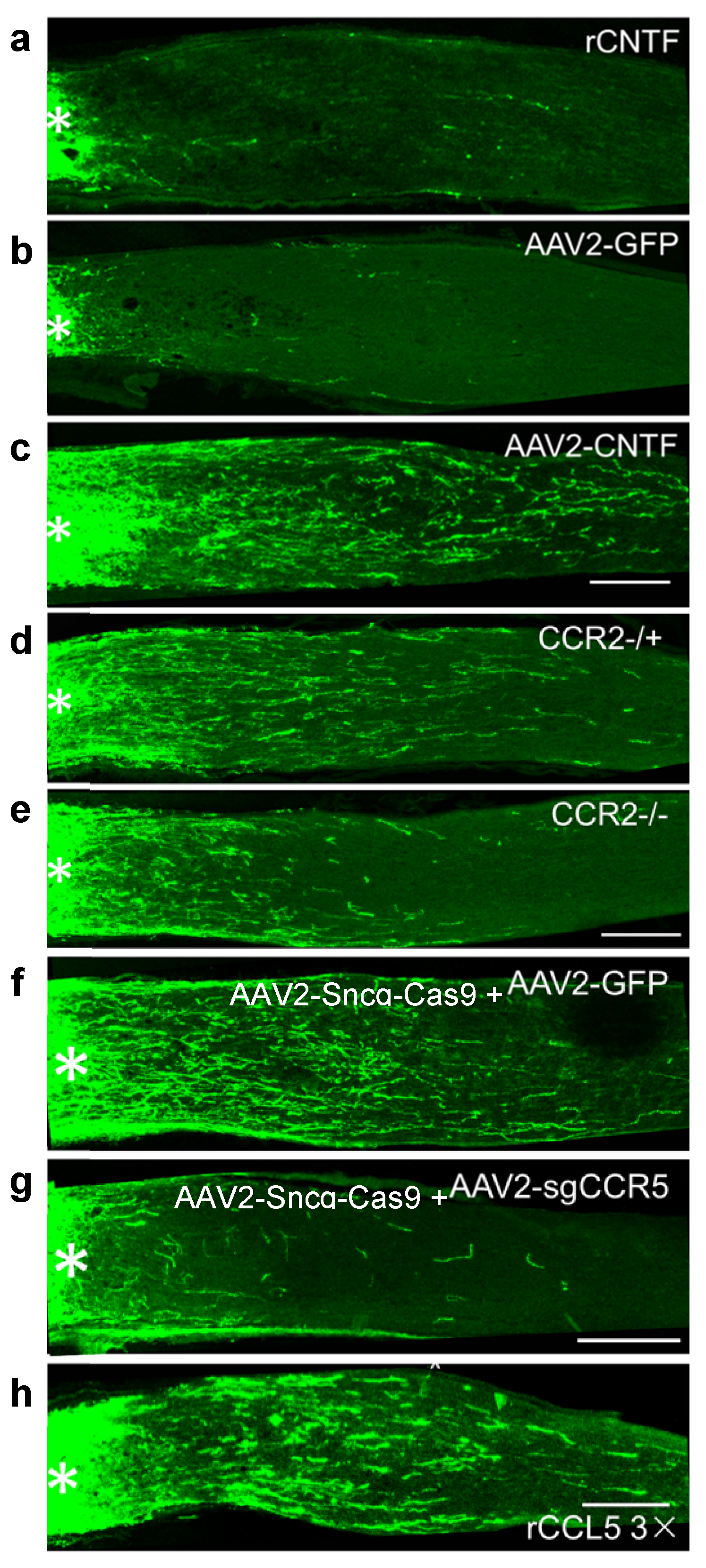
6. CNTF Gene Therapy, like Zymosan and LI, Promotes Regeneration via Neuroinflammation
7. Inflammatory Pre-Conditioning Enables Robust Axon Regeneration
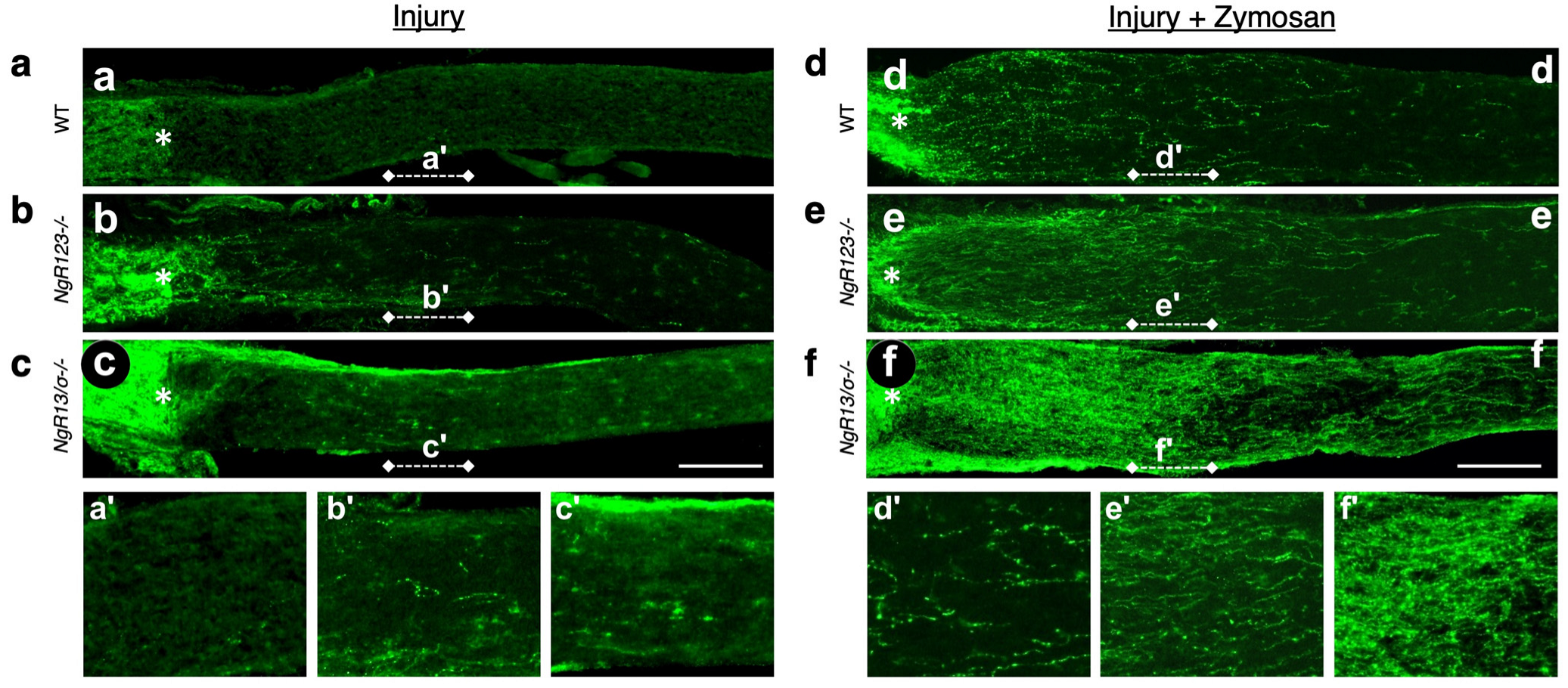
8. Synergy between Intraocular Inflammation and Counteracting Cell-Extrinsic Suppressors of Axon Growth
9. Role of Microglia in RGC Survival and Axon Regeneration
10. Neuroinflammation and RGC-Intrinsic Regulators of Survival and Axon Regeneration: Synergistic Effects
11. Prospectives
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramon y Cajal, S. Degeneration and Regeneration of the Nervous System; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Cho, K.; Vu, T.; Shen, C.; Kaur, M.; Chen, G.; Mathew, R.; McHam, M.; Fazelat, A.; Lashkari, K.; et al. Commensal microflora-induced T cell responses mediate progressive neurodegeneration in glaucoma. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, A.; Fei, F.; Jones, A.; Busto, P.; Marshak-Rothstein, A.; Ksander, B.R.; Gregory-Ksander, M. Overexpression of Soluble Fas Ligand following Adeno-Associated Virus Gene Therapy Prevents Retinal Ganglion Cell Death in Chronic and Acute Murine Models of Glaucoma. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 4626–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, M.; Zhang, Y.; Murakami, Y.; Thanos, A.; Lee, S.C.; Vavvas, D.G.; Benowitz, L.I.; Miller, J.W. Etanercept, a widely used inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), prevents retinal ganglion cell loss in a rat model of glaucoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Cui, Q.; Gilbert, H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Berlinicke, C.; Li, Z.; Zaverucha-do-Valle, C.; He, H.; Petkova, V.; et al. Oncomodulin links inflammation to optic nerve regeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19587–19592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Cui, Q.; Li, Y.; Irwin, N.; Fischer, D.; Harvey, A.R.; Benowitz, L.I. Macrophage-derived factors stimulate optic nerve regeneration. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 2284–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, S.; Yin, Y.; Nguyen, J.; Irwin, N.; Benowitz, L. Lens injury stimulates axon regeneration in the mature rat optic nerve. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 4615–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Cen, L.P.; Li, Y.; Gilbert, H.Y.; Strelko, O.; Berlinicke, C.; Stavarache, M.A.; Ma, M.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Q.; et al. Monocyte-derived SDF1 supports optic nerve regeneration and alters retinal ganglion cells’ response to Pten deletion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113751119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Liang, J.J.; Ng, T.K.; Hu, Z.; Xu, C.; Chen, S.; Chen, S.L.; Xu, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Huang, S.; et al. CXCL5/CXCR2 modulates inflammation-mediated neural repair after optic nerve injury. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 341, 113711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauk, T.G.; Leibinger, M.; Muller, A.; Andreadaki, A.; Knippschild, U.; Fischer, D. Stimulation of axon regeneration in the mature optic nerve by intravitreal application of the toll-like receptor 2 agonist Pam3Cys. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, K.T.; Carbajal, K.S.; Segal, B.M.; Giger, R.J. Neuroinflammation triggered by beta-glucan/dectin-1 signaling enables CNS axon regeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2581–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sas, A.R.; Carbajal, K.S.; Jerome, A.D.; Menon, R.; Yoon, C.; Kalinski, A.L.; Giger, R.J.; Segal, B.M. A new neutrophil subset promotes CNS neuron survival and axon regeneration. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 1496–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Henzl, M.; Lorber, B.; Nakazawa, T.; Thomas, T.; Jiang, F.; Langer, R.; Benowitz, L. Oncomodulin is a macrophage-derived signal for axon regeneration in retinal ganglion cells. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurimoto, T.; Yin, Y.; Habboub, G.; Gilbert, H.; Li, Y.; Nakao, S.; Hafezi-Moghadam, A.; Benowitz, L. Neutrophils express oncomodulin and promote optic nerve regeneration. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 14816–14824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurimoto, T.; Yin, Y.; Omura, K.; Gilbert, H.; Kim, D.; Cen, L.; Moko, L.; Kügler, S.; Benowitz, L. Long-distance axon regeneration in the mature optic nerve: Contributions of oncomodulin, cAMP, and pten gene deletion. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 15654–15663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Yin, Y.; Peterson, S.L.; Jayakar, S.; Shi, C.; Lenfers Turnes, B.; Zhang, Z.; Oses-Prieto, J.; Li, J.; Burlingame, A.; et al. The atypical receptor-ligand pair Ocm-R/oncomodulin enables axon regeneration in the central and peripheral nervous systems. In Proceedings of the Society for Neuroscience, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–16 November2022. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X.; Qiao, M.; Bei, F.; Kim, I.J.; He, Z.; Sanes, J.R. Subtype-specific regeneration of retinal ganglion cells following axotomy: Effects of osteopontin and mTOR signaling. Neuron 2015, 85, 1244–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibinger, M.; Muller, A.; Andreadaki, A.; Hauk, T.G.; Kirsch, M.; Fischer, D. Neuroprotective and axon growth-promoting effects following inflammatory stimulation on mature retinal ganglion cells in mice depend on ciliary neurotrophic factor and leukemia inhibitory factor. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14334–14341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibinger, M.; Andreadaki, A.; Diekmann, H.; Fischer, D. Neuronal STAT3 activation is essential for CNTF- and inflammatory stimulation-induced CNS axon regeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldman, M.B.; Bemben, M.A.; Goldman, D. Tuba1a gene expression is regulated by KLF6/7 and is necessary for CNS development and regeneration in zebrafish. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2010, 43, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernet, V.; Di Polo, A. Synergistic action of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and lens injury promotes retinal ganglion cell survival, but leads to optic nerve dystrophy in vivo. Brain 2006, 129, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Yin, Y.; Benowitz, L. Chemokine CCL5 promotes robust optic nerve regeneration and mediates many of the effects of CNTF gene therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2017282118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.D.; Sun, F.; Park, K.K.; Cai, B.; Wang, C.; Kuwako, K.; Martinez-Carrasco, I.; Connolly, L.; He, Z. SOCS3 deletion promotes optic nerve regeneration in vivo. Neuron 2009, 64, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, E.R.; Yungher, B.J.; Levay, K.; Ribeiro, M.; Dvoryanchikov, G.; Ayupe, A.C.; Thakor, K.; Marks, V.; Randolph, M.; Danzi, M.C.; et al. Thrombospondin-1 Mediates Axon Regeneration in Retinal Ganglion Cells. Neuron 2019, 103, 642–657.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leaver, S.G.; Cui, Q.; Plant, G.W.; Arulpragasam, A.; Hisheh, S.; Verhaagen, J.; Harvey, A.R. AAV-mediated expression of CNTF promotes long-term survival and regeneration of adult rat retinal ganglion cells. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 1328–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernet, V.; Joly, S.; Dalkara, D.; Jordi, N.; Schwarz, O.; Christ, F.; Schaffer, D.V.; Flannery, J.G.; Schwab, M.E. Long-distance axonal regeneration induced by CNTF gene transfer is impaired by axonal misguidance in the injured adult optic nerve. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 51, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yungher, B.J.; Ribeiro, M.; Park, K.K. Regenerative Responses and Axon Pathfinding of Retinal Ganglion Cells in Chronically Injured Mice. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yungher, B.J.; Luo, X.; Salgueiro, Y.; Blackmore, M.G.; Park, K.K. Viral vector-based improvement of optic nerve regeneration: Characterization of individual axons’ growth patterns and synaptogenesis in a visual target. Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Ribeiro, M.; Bray, E.R.; Lee, D.H.; Yungher, B.J.; Mehta, S.T.; Thakor, K.A.; Diaz, F.; Lee, J.K.; Moraes, C.T.; et al. Enhanced Transcriptional Activity and Mitochondrial Localization of STAT3 Co-induce Axon Regrowth in the Adult Central Nervous System. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, F.; Lee, H.H.C.; Liu, X.; Gunner, G.; Jin, H.; Ma, L.; Wang, C.; Hou, L.; Hensch, T.K.; Frank, E.; et al. Restoration of Visual Function by Enhancing Conduction in Regenerated Axons. Cell 2016, 164, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellstrom, M.; Pollett, M.A.; Harvey, A.R. Post-injury delivery of rAAV2-CNTF combined with short-term pharmacotherapy is neuroprotective and promotes extensive axonal regeneration after optic nerve trauma. J. Neurotrauma 2011, 28, 2475–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Huang, S.; Ng, T.K.; Liang, J.J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.L.; Xu, C.; Zhang, M.; Pang, C.P.; Cen, L.P. Longitudinal evaluation of immediate inflammatory responses after intravitreal AAV2 injection in rats by optical coherence tomography. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 193, 107955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, L.P.; Luo, J.M.; Zhang, C.W.; Fan, Y.M.; Song, Y.; So, K.F.; van Rooijen, N.; Pang, C.P.; Lam, D.S.; Cui, Q. Chemotactic effect of ciliary neurotrophic factor on macrophages in retinal ganglion cell survival and axonal regeneration. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 4257–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Mizisin, A.P. CNTFR alpha alone or in combination with CNTF promotes macrophage chemotaxis in vitro. Neuropeptides 2000, 34, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Wong, K.A.; Peterson, S.L.; Benowitz, L. Harnessing neuroinflammation to promote axon regeneration after optic nerve injury. In Proceedings of the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Annual Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 28 April–2 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Schwab, M.E. Nogo and axon regeneration. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2004, 14, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawcett, J.W.; Schwab, M.E.; Montani, L.; Brazda, N.; Muller, H.W. Defeating inhibition of regeneration by scar and myelin components. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2012, 109, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.P.; Warren, P.M.; Silver, J. The Biology of Regeneration Failure and Success After Spinal Cord Injury. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 881–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, D.; He, Z.; Benowitz, L.I. Counteracting the Nogo receptor enhances optic nerve regeneration if retinal ganglion cells are in an active growth state. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 1646–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickendesher, T.L.; Baldwin, K.T.; Mironova, Y.A.; Koriyama, Y.; Raiker, S.J.; Askew, K.L.; Wood, A.; Geoffroy, C.G.; Zheng, B.; Liepmann, C.D.; et al. NgR1 and NgR3 are receptors for chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hasan, O.; Arzeno, A.; Benowitz, L.I.; Cafferty, W.B.; Strittmatter, S.M. Axonal regeneration induced by blockade of glial inhibitors coupled with activation of intrinsic neuronal growth pathways. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 237, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Tenney, A.P.; Busch, S.A.; Horn, K.P.; Cuascut, F.X.; Liu, K.; He, Z.; Silver, J.; Flanagan, J.G. PTPsigma is a receptor for chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan, an inhibitor of neural regeneration. Science 2009, 326, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, C.S.; Mencio, C.P.; Barber, A.C.; Martin, K.R.; Geller, H.M. Identification of a critical sulfation in chondroitin that inhibits axonal regeneration. eLife 2018, 7, e37139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, S.; Li, Y.; Sun, C.; Wong, K.; Leung, K.; de Lima, S.; Hanovice, N.; Yuki, K.; Stevens, B.; Benowitz, L. Retinal Ganglion Cell Axon Regeneration Requires Complement and Myeloid Cell Activity within the Optic Nerve. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 8508–8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, D.; Lehrman, E.; Kautzman, A.; Koyama, R.; Mardinly, A.; Yamasaki, R.; Ransohoff, R.; Greenberg, M.; Barres, B.; Stevens, B. Microglia sculpt postnatal neural circuits in an activity and complement-dependent manner. Neuron 2012, 74, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, B.; Allen, N.; Vazquez, L.; Howell, G.; Christopherson, K.; Nouri, N.; Micheva, K.; Mehalow, A.; Huberman, A.; Stafford, B.; et al. The classical complement cascade mediates CNS synapse elimination. Cell 2007, 131, 1164–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.A.; Marsh-Armstrong, N.; Howell, G.R.; Bosco, A.; Danias, J.; Simon, J.; Di Polo, A.; Kuehn, M.H.; Przedborski, S.; Raff, M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in glaucoma: A new opportunity. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 157, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, A.; Breen, K.; Anderson, S.; Steele, M.; Calkins, D.; Vetter, M. Glial coverage in the optic nerve expands in proportion to optic axon loss in chronic mouse glaucoma. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 150, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, A.; Romero, C.; Breen, K.; Chagovetz, A.; Steele, M.; Ambati, B.; Vetter, M. Neurodegeneration severity can be predicted from early microglia alterations monitored in vivo in a mouse model of chronic glaucoma. Dis. Models Mech. 2015, 8, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, A.; de Hoz, R.; Salobrar-Garcia, E.; Salazar, J.; Rojas, B.; Ajoy, D.; López-Cuenca, I.; Rojas, P.; Triviño, A.; Ramírez, J. The Role of Microglia in Retinal Neurodegeneration: Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson, and Glaucoma. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, M.; Stute, G.; Alzureiqi, M.; Reinhard, J.; Wiemann, S.; Schmid, H.; Faissner, A.; Dick, H.; Joachim, S. Optic Nerve Degeneration after Retinal Ischemia/Reperfusion in a Rodent Model. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2017, 11, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, A.; Inman, D.; Steele, M.; Wu, G.; Soto, I.; Marsh-Armstrong, N.; Hubbard, W.; Calkins, D.; Horner, P.; Vetter, M. Reduced retina microglial activation and improved optic nerve integrity with minocycline treatment in the DBA/2J mouse model of glaucoma. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Singh, B.; Chauhan, A.; Singh, D.; Patel, D.; Singh, C. Minocycline Rescues from Zinc-Induced Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration: Biochemical and Molecular Interventions. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 2761–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, R.; Pham, J.; Lee, R.; Najafi, A.; West, B.; Green, K. Microglial repopulation resolves inflammation and promotes brain recovery after injury. Glia 2017, 65, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, A.; Shinozaki, Y.; Kashiwagi, K.; Ohno, N.; Eto, K.; Wake, H.; Nabekura, J.; Koizumi, S. Microglia mediate non-cell-autonomous cell death of retinal ganglion cells. Glia 2018, 66, 2366–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttenplan, K.A.; Stafford, B.K.; El-Danaf, R.N.; Adler, D.I.; Münch, A.E.; Weigel, M.K.; Huberman, A.D.; Liddelow, S.A. Neurotoxic Reactive Astrocytes Drive Neuronal Death after Retinal Injury. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttenplan, K.A.; Weigel, M.K.; Prakash, P.; Wijewardhane, P.R.; Hasel, P.; Rufen-Blanchette, U.; Münch, A.E.; Blum, J.A.; Fine, J.; Neal, M.C.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes induce cell death via saturated lipids. Nature 2021, 599, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.; Guttenplan, K.; Clarke, L.; Bennett, F.; Bohlen, C.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.; Münch, A.; Chung, W.; Peterson, T.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, J.; Xu, L.; Foo, L.; Nouri, N.; Zhou, L.; Giffard, R.; Barres, B. Genomic analysis of reactive astrogliosis. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 6391–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, F.; Huang, C.; Tong, J.; Qiu, G.; Huang, B.; Wu, Q.; Li, F.; Xu, Z.; Bowser, R.; Xia, X.; et al. Reactive astrocytes secrete lcn2 to promote neuron death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4069–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun-Julien, F.; Duplan, L.; Pernet, V.; Osswald, I.; Sapieha, P.; Bourgeois, P.; Dickson, K.; Bowie, D.; Barker, P.; Di Polo, A. Excitotoxic death of retinal neurons in vivo occurs via a non-cell-autonomous mechanism. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 5536–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew, M. Multiple roles for astrocytes as effectors of cytokines and inflammatory mediators. Neuroscientist 2014, 20, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.A.; Peterson, S.; Benowitz, L. Zinc and microglia regulate retinal ganglion cell survival and axon regeneration after optic nerve injury. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 5176. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Wu, J. TRPV4-induced Müller cell gliosis and TNF-α elevation-mediated retinal ganglion cell apoptosis in glaucomatous rats via JAK2/STAT3/NF-κB pathway. J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, C.; Ackerman, K.; O’Hayer, P.; Bailey, T.; Gorsuch, R.; Hyde, D. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha is produced by dying retinal neurons and is required for Muller glia proliferation during zebrafish retinal regeneration. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 6524–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezel, G.; Wax, M.B. Increased production of tumor necrosis factor-α by glial cells exposed to simulated ischemia or elevated hydrostatic pressure induces apoptosis in cocultured retinal ganglion cells. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 8693–8700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun-Julien, F.; Bertrand, M.J.; De Backer, O.; Stellwagen, D.; Morales, C.R.; Di Polo, A.; Barker, P.A. ProNGF induces TNFalpha-dependent death of retinal ganglion cells through a p75NTR non-cell-autonomous signaling pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3817–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, T.; Nakazawa, C.; Matsubara, A.; Noda, K.; Hisatomi, T.; She, H.; Michaud, N.; Hafezi-Moghadam, A.; Miller, J.; Benowitz, L. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates oligodendrocyte death and delayed retinal ganglion cell loss in a mouse model of glaucoma. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 12633–12641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.; Kocab, A.J.; Zacks, D.N.; Marshak-Rothstein, A.; Gregory-Ksander, M. A small peptide antagonist of the Fas receptor inhibits neuroinflammation and prevents axon degeneration and retinal ganglion cell death in an inducible mouse model of glaucoma. J. Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
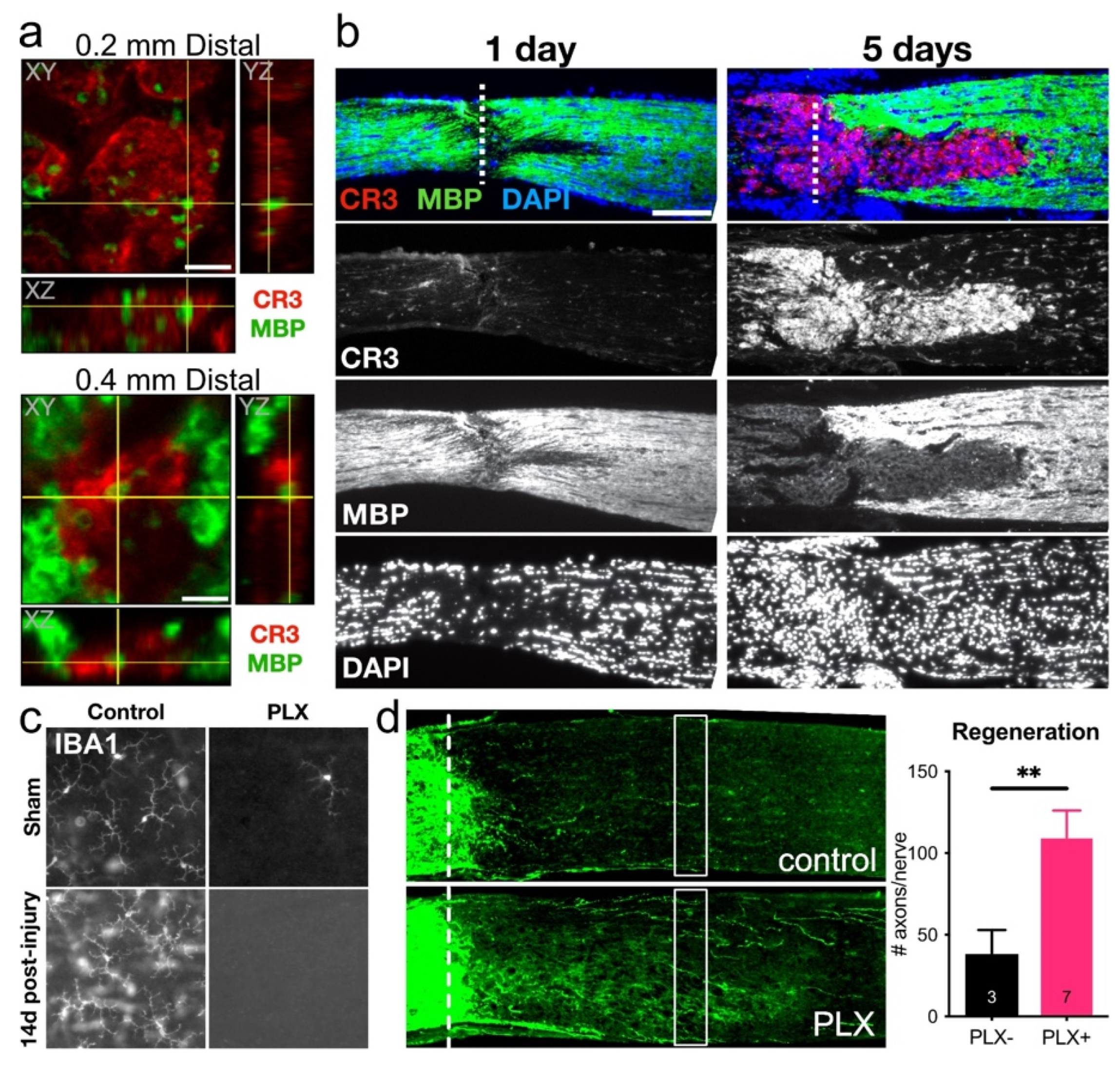
- Hilla, A.; Diekmann, H.; Fischer, D. Microglia Are Irrelevant for Neuronal Degeneration and Axon Regeneration after Acute Injury. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 6113–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
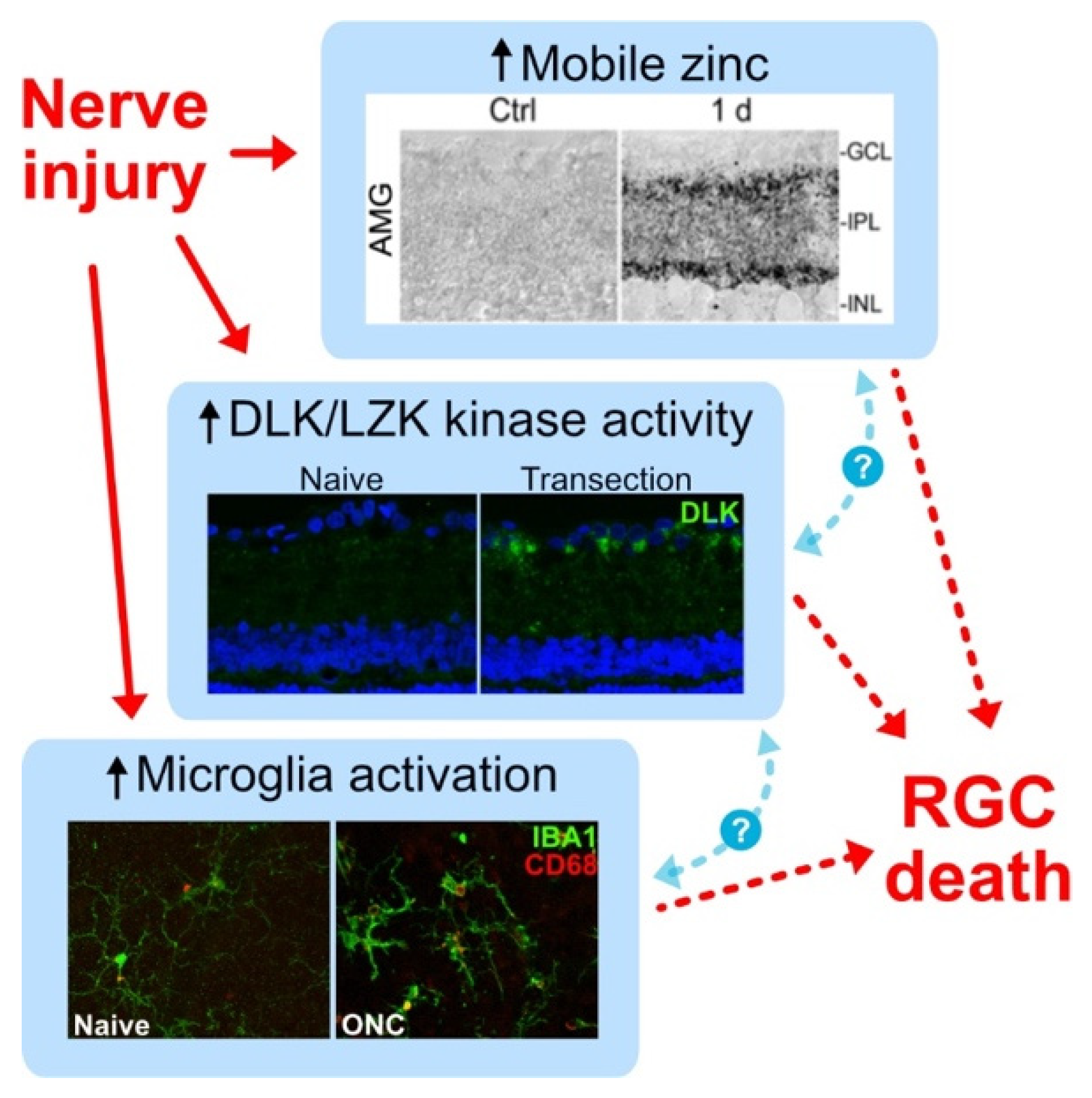
- Li, Y.; Andereggen, L.; Yuki, K.; Omura, K.; Yin, Y.; Gilbert, H.; Erdogan, B.; Asdourian, M.; Shrock, C.; de Lima, S.; et al. Mobile zinc increases rapidly in the retina after optic nerve injury and regulates ganglion cell survival and optic nerve regeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E209–E218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, Y.; Aratake, T.; Shimizu, S.; Shimizu, T.; Nakamura, K.; Tsuda, M.; Yawata, T.; Ueba, T.; Saito, M. Influence of extracellular zinc on M1 microglial activation. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 43778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, Y.; Segawa, S.; Matsuo, T.; Nakamura, S.; Kikkawa, Y.; Nishida, K.; Nagasawa, K. Microglial zinc uptake via zinc transporters induces ATP release and the activation of microglia. Glia 2011, 59, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppinen, T.; Higashi, Y.; Suh, S.; Escartin, C.; Nagasawa, K.; Swanson, R. Zinc triggers microglial activation. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 5827–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueba, Y.; Aratake, T.; Onodera, K.; Higashi, Y.; Hamada, T.; Shimizu, T.; Shimizu, S.; Yawata, T.; Nakamura, R.; Akizawa, T.; et al. Attenuation of zinc-enhanced inflammatory M1 phenotype of microglia by peridinin protects against short-term spatial-memory impairment following cerebral ischemia in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 507, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, W.; Friede, R. The role of complement in myelin phagocytosis during PNS wallerian degeneration. J. Neurol. Sci. 1991, 103, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, H.; Kotter, M.; Franklin, R. Debris clearance by microglia: An essential link between degeneration and regeneration. Brain 2009, 132, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Liu, K.; Hu, Y.; Smith, P.; Wang, C.; Cai, B.; Xu, B.; Connolly, L.; Kramvis, I.; Sahin, M.; et al. Promoting axon regeneration in the adult CNS by modulation of the PTEN/mTOR pathway. Science 2008, 322, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
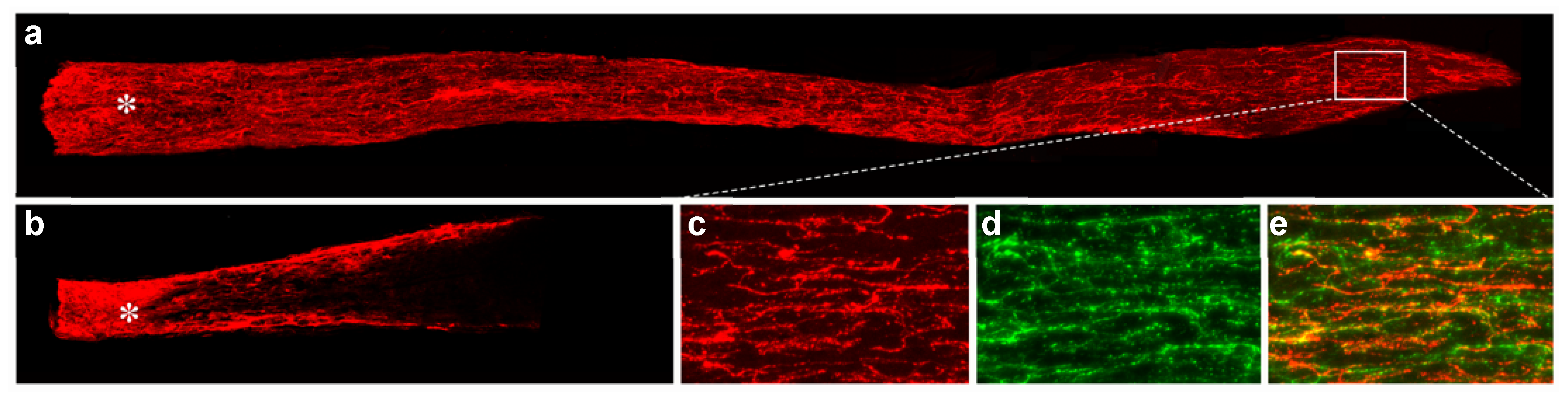
- de Lima, S.; Koriyama, Y.; Kurimoto, T.; Oliveira, J.T.; Yin, Y.; Li, Y.; Gilbert, H.Y.; Fagiolini, M.; Martinez, A.M.; Benowitz, L. Full-length axon regeneration in the adult mouse optic nerve and partial recovery of simple visual behaviors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9149–9154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Stafford, B.K.; Nguyen, P.L.; Lien, B.V.; Wang, C.; Zukor, K.; He, Z.; Huberman, A.D. Neural activity promotes long-distance, target-specific regeneration of adult retinal axons. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Park, K.K.; Belin, S.; Wang, D.; Lu, T.; Chen, G.; Zhang, K.; Yeung, C.; Feng, G.; Yankner, B.A.; et al. Sustained axon regeneration induced by co-deletion of PTEN and SOCS3. Nature 2011, 480, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Salgueiro, Y.; Beckerman, S.R.; Lemmon, V.P.; Tsoulfas, P.; Park, K.K. Three-dimensional evaluation of retinal ganglion cell axon regeneration and pathfinding in whole mouse tissue after injury. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 247, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; He, Q.; Wang, H.; Tang, X.; Ho, K.W.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Cheung, A.; Wong, F.; et al. Injured adult retinal axons with Pten and Socs3 co-deletion reform active synapses with suprachiasmatic neurons. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 73, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.L.; Blackmore, M.G.; Hu, Y.; Kaestner, K.H.; Bixby, J.L.; Lemmon, V.P.; Goldberg, J.L. KLF family members regulate intrinsic axon regeneration ability. Science 2009, 326, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blackmore, M.G.; Wang, Z.; Lerch, J.K.; Motti, D.; Zhang, Y.P.; Shields, C.B.; Lee, J.K.; Goldberg, J.L.; Lemmon, V.P.; Bixby, J.L. Krüppel-like Factor 7 engineered for transcriptional activation promotes axon regeneration in the adult corticospinal tract. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7517–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, C.L. Cross-talk between KLF4 and STAT3 regulates axon regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Brommer, B.; Tian, X.; Krishnan, A.; Meer, M.; Wang, C.; Vera, D.L.; Zeng, Q.; Yu, D.; Bonkowski, M.S.; et al. Reprogramming to recover youthful epigenetic information and restore vision. Nature 2020, 588, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apara, A.; Galvao, J.; Wang, Y.; Blackmore, M.; Trillo, A.; Iwao, K.; Brown, D.; Fernandes, K.; Huang, A.; Nguyen, T.; et al. KLF9 and JNK3 Interact to Suppress Axon Regeneration in the Adult CNS. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 9632–9644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakhtenberg, E.; Li, Y.; Feng, Q.; Tso, J.; Rosenberg, P.; Goldberg, J.; Benowitz, L. Zinc chelation and Klf9 knockdown cooperatively promote axon regeneration after optic nerve injury. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 300, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, A.; Bernstein, A.M.; Kawaguchi, R.; Gao, K.; Potter, K.; Gilbert, H.; Ao, Y.; Ou, J.H.; et al. Transcription factor network analysis identifies REST/NRSF as an intrinsic regulator of CNS regeneration in mice. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, T.A.; Wang, B.; Huntwork-Rodriguez, S.; Yang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Eastham-Anderson, J.; Modrusan, Z.; Kaminker, J.S.; Tessier-Lavigne, M.; Lewcock, J.W. DLK initiates a transcriptional program that couples apoptotic and regenerative responses to axonal injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4039–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsbie, D.; Mitchell, K.; Jaskula-Ranga, V.; Sluch, V.; Yang, Z.; Kim, J.; Buehler, E.; Patel, A.; Martin, S.; Zhang, P.; et al. Enhanced Functional Genomic Screening Identifies Novel Mediators of Dual Leucine Zipper Kinase-Dependent Injury Signaling in Neurons. Neuron 2017, 94, 1142–1154.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsbie, D.; Yang, Z.; Ge, Y.; Mitchell, K.; Zhou, X.; Martin, S.; Berlinicke, C.; Hackler, L.; Fuller, J.; Fu, J.; et al. Functional genomic screening identifies dual leucine zipper kinase as a key mediator of retinal ganglion cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4045–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.A.; Martheswaran, T.; Msaddi, J.; Patel, V.; Li, Y.; Peterson, S.; Benowitz, L. Retinal ganglion cell survival and axon regeneration after optic nerve injury: Crosstalk among early injury signals. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 1661. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, A.K.; Broyer, R.M.; Lee, C.D.; Lu, T.; Louie, M.J.; La Torre, A.; Al-Ali, H.; Vu, M.T.; Mitchell, K.L.; Wahlin, K.J.; et al. Inhibition of GCK-IV kinases dissociates cell death and axon regeneration in CNS neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 33597–33607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, A.; Tran, N.M.; Yan, W.; Benhar, I.; Tian, F.; Schaffer, R.; He, Z.; Sanes, J.R. Overlapping transcriptional programs promote survival and axonal regeneration of injured retinal ganglion cells. Neuron 2022, 110, 2625–2645.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Q.; Monavarfeshani, A.; Gao, K.; Jiang, W.; Kawaguchi, R.; Wang, Q.; Tang, M.; et al. Core transcription programs controlling injury-induced neurodegeneration of retinal ganglion cells. Neuron 2022, 110, 2607–2624.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.Y.; Bian, J.; Davis, A.E.; Liu, P.; Kempton, H.R.; Zhang, X.; Chemparathy, A.; Gu, B.; Lin, X.; Rane, D.A.; et al. Multiplexed genome regulation in vivo with hyper-efficient Cas12a. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, M.A.; de Lima, S.; Gilbert, H.Y.; Giger, R.J.; Benowitz, L.; Rasband, M.N. Reassembly of Excitable Domains after CNS Axon Regeneration. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 9148–9160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, X.; Meng, H.; Li, Y.; Dmitriev, P.; Tian, F.; Page, J.C.; Lu, Q.R.; He, Z. Robust Myelination of Regenerated Axons Induced by Combined Manipulations of GPR17 and Microglia. Neuron 2020, 108, 876–886.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wong, K.A.; Benowitz, L.I. Retinal Ganglion Cell Survival and Axon Regeneration after Optic Nerve Injury: Role of Inflammation and Other Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231710179
Wong KA, Benowitz LI. Retinal Ganglion Cell Survival and Axon Regeneration after Optic Nerve Injury: Role of Inflammation and Other Factors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(17):10179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231710179
Chicago/Turabian StyleWong, Kimberly A., and Larry I. Benowitz. 2022. "Retinal Ganglion Cell Survival and Axon Regeneration after Optic Nerve Injury: Role of Inflammation and Other Factors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 17: 10179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231710179
APA StyleWong, K. A., & Benowitz, L. I. (2022). Retinal Ganglion Cell Survival and Axon Regeneration after Optic Nerve Injury: Role of Inflammation and Other Factors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(17), 10179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231710179






