Quinolizidines as Novel SARS-CoV-2 Entry Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Entry Activity
2.2. Effect of Compound 5 on SARS-CoV-2 Variants
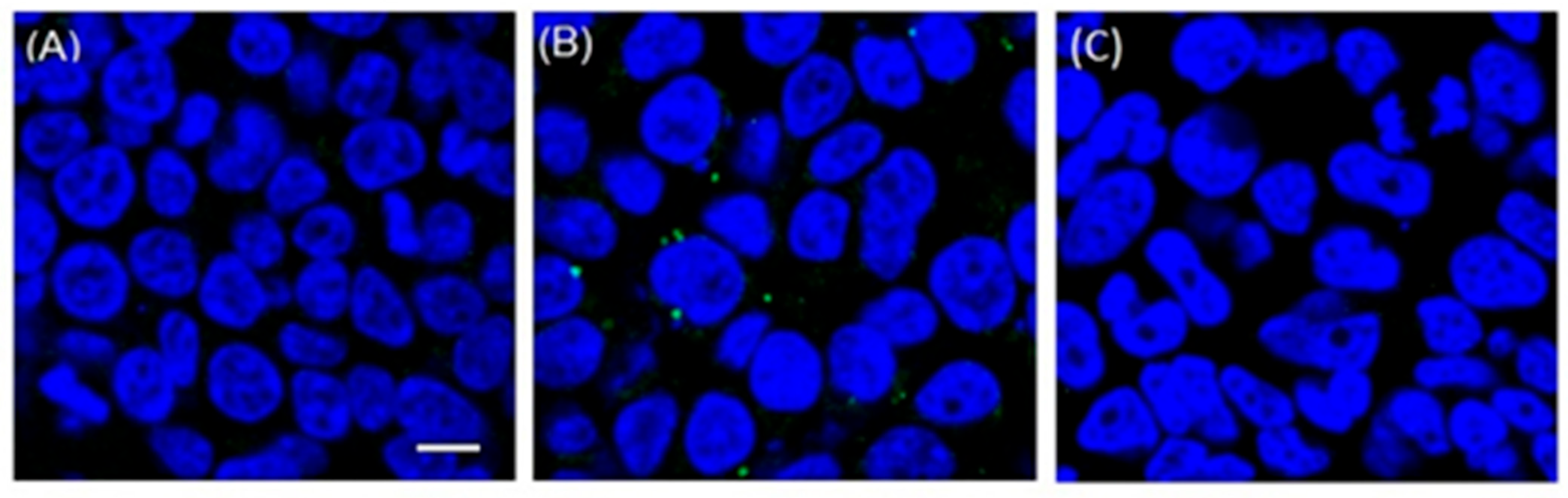
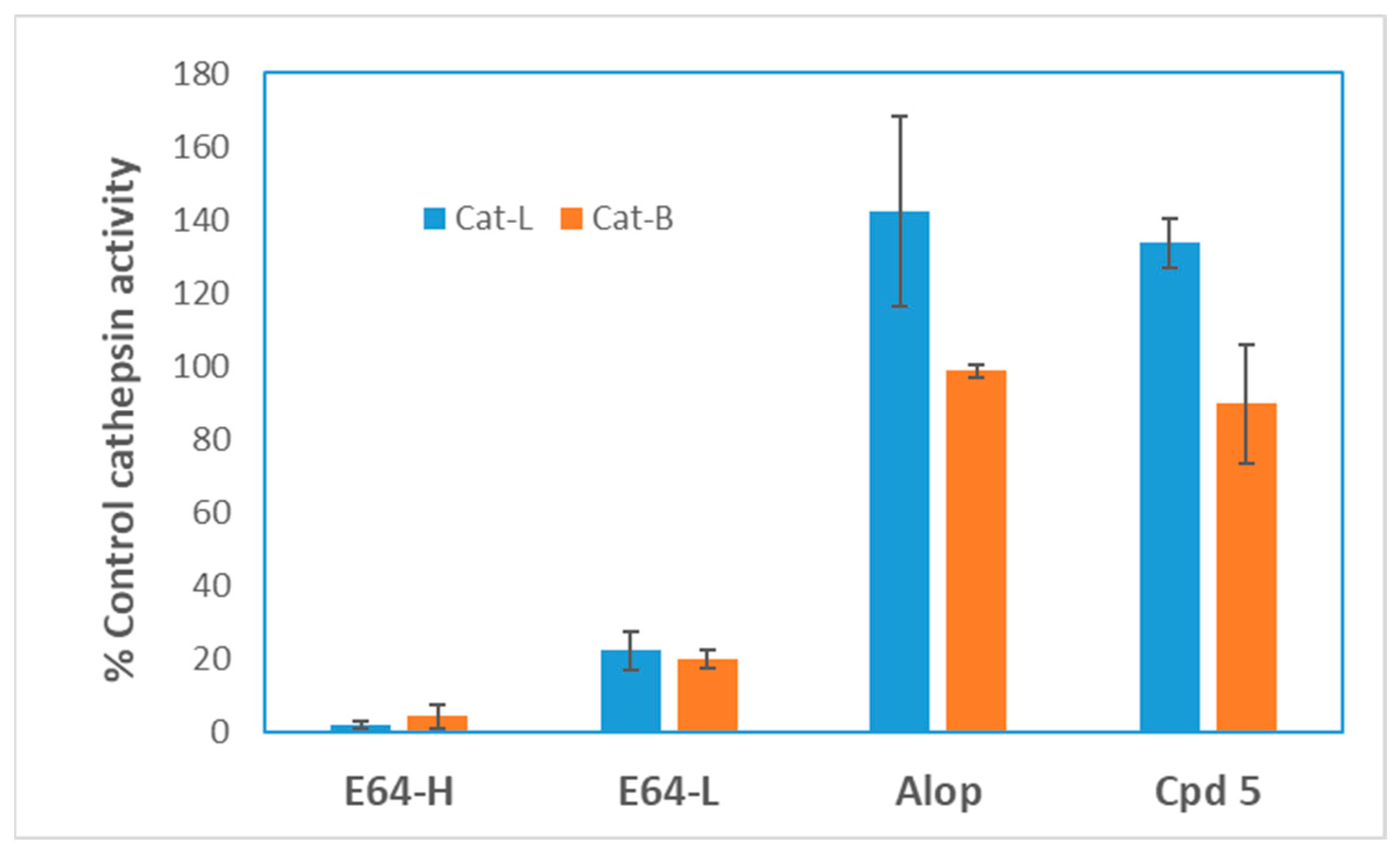
2.3. Mechanism of Action Study
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. SARS-CoV-2 Pseudovirus Inhibition Assay
4.3. Immunofluorescence Staining of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Proteins and Confocal Microscopy
4.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pascarella, G.; Strumia, A.; Piliego, C.; Bruno, F.; Del Buono, R.; Costa, F.; Scarlata, S.; Agrò, F.E. COVID-19 diagnosis and management: A comprehensive review. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 288, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.J.; Shan, J. 2019 novel coronavirus: Where we are and what we know. Infection 2020, 48, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Madhavan, M.V.; Sehgal, K.; Nair, N.; Mahajan, S.; Sehrawat, T.S.; Bikdeli, B.; Ahluwalia, N.; Ausiello, J.C.; Wan, E.Y.; et al. Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, R.; Patankar, P. Emerging pharmacotherapies for COVID-19. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, J.H.; Udy, A.; Peleg, A.Y. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-Preliminary Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 992–993. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, W.; Chen, C.; Tang, J.; Wang, C.; Zhou, M.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Z.; et al. Efficacy and safety of three new oral antiviral treatment (molnupiravir, fluvoxamine and Paxlovid) for COVID-19: A meta-analysis. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahase, E. Covid-19: Pfizer’s paxlovid is 89% effective in patients at risk of serious illness, company reports. BMJ 2021, 375, n2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plante, J.A.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Xia, H.; Johnson, B.A.; Lokugamage, K.G.; Zhang, X.; Muruato, A.E.; Zou, J.; Fontes-Garfias, C.R.; et al. Spike mutation D614G alters SARS-CoV-2 fitness. Nature 2021, 592, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jian, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; An, R.; et al. Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Nature 2022, 602, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandia, R.; Singhal, S.; Alqahtani, T.; Kamal, M.A.; El-Shall, N.A.; Nainu, F.; Desingu, P.A.; Dhama, K. Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant, salient features, high global health concerns and strategies to counter it amid ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyke, K.E.; Atmar, R.L.; Islas, C.D.; Posavad, C.M.; Szydlo, D.; Chourdhury, R.P.; Deming, M.E.; Eaton, A.; Jackson, L.A.; Branche, A.R.; et al. Rapid decline in vaccine-boosted neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, J.; Schelhaas, M.; Helenius, A. Virus entry by endocytosis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 803–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helenius, A. Virus entry: Looking back and moving forward. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, S.; Nao, N.; Shirato, K.; Kawase, M.; Saito, S.; Takayama, I.; Nagata, N.; Sekizuka, T.; Katoh, H.; Kato, F.; et al. Enhanced isolation of SARS-CoV-2 by TMPRSS2-expressing cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 31, 7001–7003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, R.; Gomez Castro, M.F.; McCune, B.T.; Zeng, Q.; Rothlauf, P.W.; Sonnek, N.M.; Liu, Z.; Brulois, K.F.; Wang, X.; Greenberg, H.B.; et al. TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 promote SARS-CoV-2 infection of human small intestinal enterocytes. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabc3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Z.; Jung, K.; Zhu, L.; Lai, W.; Xie, H.; Lee, K.H.; Huang, L.; Chen, C.H. Identification and synthesis of quinolizidines with anti-influenza a virus activity. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Lai, W.; Bogerd, H.; Lee, K.H.; Huang, L.; Chen, C.H. Aloperine and its derivatives as a new class of HIV-1 entry inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Z.; Xie, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Huang, L.; Chen, C.H. Structure optimization of aloperine derivatives as HIV-1 entry inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Xie, L.; Lee, K.H.; Malik, F.; Li, Z.; Huang, L.; Chen, C.H. Design and synthesis of quinolizidine derivatives as influenza virus and HIV-1 inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 4995–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissman, D.; Alameh, M.G.; de Silva, T.; Collini, P.; Hornsby, H.; Brown, R.; LaBranche, C.C.; Edwards, R.J.; Sutherland, L.; Santra, S.; et al. D614G spike mutation increases SARS CoV-2 susceptibility to neutralization. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, D.R.; Schaefer, A.; Gobeil, S.; Li, D.; de la Cruz, G.; Parks, R.; Lu, X.; Barr, M.; Manne, K.; Mansouri, K.; et al. A broadly neutralizing antibody protects against SARS-CoV, pre-emergent bat CoVs, and SARS-CoV-2 variants in mice. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghir, S.A.M.; AlGabri, N.A.; Alagawany, M.M.; A Attia, Y.; Alyileili, S.R.; Elnesr, S.S.; E Shafi, M.; Al-Shargi, O.Y.; Al-Balagi, N.; Alwajeeh, A.S.; et al. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: A fiction, hope or hype? An updated review. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2021, 17, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, J.J.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Q.X.; Zhang, N.; Huang, W.J.; Tang, S.; Wang, Y.X.; Kong, W.J.; Wang, Y.C.; et al. Discovery and evolution of 12N-substituted aloperine derivatives as anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents through targeting late entry stage. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 115, 105196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Maldonado, P.; Alvarenga, N.; Burgos-Edwards, A.; Flores-Giubi, M.E.; Barúa, J.E.; Romero-Rodríguez, M.C.; Soto-Rifo, R.; Valiente-Echeverría, F.; Langjahr, P.; Cantero-González, G.; et al. Screening of natural products inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 entry. Molecules 2022, 27, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Dong, S.; Hou, Y.; Jia, X.; Lan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Xiao, G.; et al. Screening of botanical drugs against SARS-CoV-2 entry reveals novel therapeutic agents to treat COVID-19. Viruses 2022, 14, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Pei, R.J.; Li, H.; Ma, X.N.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, F.H.; He, P.L.; Tang, W.; Zhang, Y.C.; Xiong, J.; et al. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 entry inhibitors among already approved drugs. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Cao, M.A.; Li, W.H.; Shen, C.S.; Yan, S.Q.; Yuan, C.S. Alkaloids from Sophora flavescens Aition. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yi, C.Q.; Yang, X.Q.; Wang, X.R. Liquid chromatography of active principles in Sophora flavescens root. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 812, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X. Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic action of aloperine. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 1989, 10, 360–365. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.Y.; Ma, H.M.; Li, R.Z.; Wang, R.Y.; Liu, W.; Guo, J.Y. Topical application of aloperine improves 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 658, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

 | D614G Spike-Pseudotyped Virus | 293T-ACE2 | PA/Puerto Rico/8/1934 Influenza A Virus (PR8) | HIV-1NL4-3-nanoluc-sec | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cpds | Linker (n) | R | IC50 1 | CC50 2 | IC50 1 | IC50 1 |
| Alop 3–6 | none | none | 11.5 ± 2.3 | >20 | 14.5 | 1.75 |
| 1 (cis) 6,7 | 6 |  | 4.7 ± 0.76 | >20 | 0.091 | >20 |
| 2 3,6 | 2 |  | Inactive 8 | ND 9 | 5.5 | >25 |
| 3 5,6 | 4 |  | 3.8 ± 0.68 | >20 | >20 | 0.12 |
| 4 4 | 5 |  | 0.86 ± 1.5 | >20 | >40 | 0.84 |
| 5 4 | 4 |  | 0.5 ± 0.12 >20 ** | >20 | >40 | 0.96 |
| 6 4,6 | 4 |  | 11.9 ± 2.1 | >20 | >20 | 11.4 |
| 7 6 | 6 |  | 3.7 ± 0.87 | >20 | 0.83 | 0.80 |
| 8 6 |  |  | 17.5 ± 2.3 | >20 | >28.5 | >20 |
| 9 | 4 |  | 0.61 ± 0.18 | >10 | 4.8 ± 1.4 | Inac 8 |
| Chloroquine diphosphate | 2.3 ± 3.6 | ND 9 | ND 9 | ND 9 | ||
| Variants | IC50 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cpd 5 (µM) | E64D (µM) | DH1047 (µg/mL) | |
| D614G | 0.53 ± 0.12 | 0.48 ± 0.11 | 1.2 ± 2.1 |
| Delta | 0.58 ± 0.15 | 0.45 ± 0.082 | 0.72 ± 0.12 |
| Omicron BA.1 | 0.76 ± 0.22 | 0.36 ± 0.076 | >10 |
| Omicron BA.2 | 0.83 ± 0.21 | 0.37 ± 0.066 | >10 |
| Omicron BA.4/BA.5 | 0.86 ± 0.25 | 0.34 ± 0.081 | >10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, L.; Zhu, L.; Xie, H.; Goodwin, J.S.; Rana, T.; Xie, L.; Chen, C.-H. Quinolizidines as Novel SARS-CoV-2 Entry Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179659
Huang L, Zhu L, Xie H, Goodwin JS, Rana T, Xie L, Chen C-H. Quinolizidines as Novel SARS-CoV-2 Entry Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(17):9659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179659
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Li, Lei Zhu, Hua Xie, Jeffery Shawn Goodwin, Tanu Rana, Lan Xie, and Chin-Ho Chen. 2022. "Quinolizidines as Novel SARS-CoV-2 Entry Inhibitors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 17: 9659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179659
APA StyleHuang, L., Zhu, L., Xie, H., Goodwin, J. S., Rana, T., Xie, L., & Chen, C.-H. (2022). Quinolizidines as Novel SARS-CoV-2 Entry Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(17), 9659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179659






