NEXGB: A Network Embedding Framework for Anticancer Drug Combination Prediction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
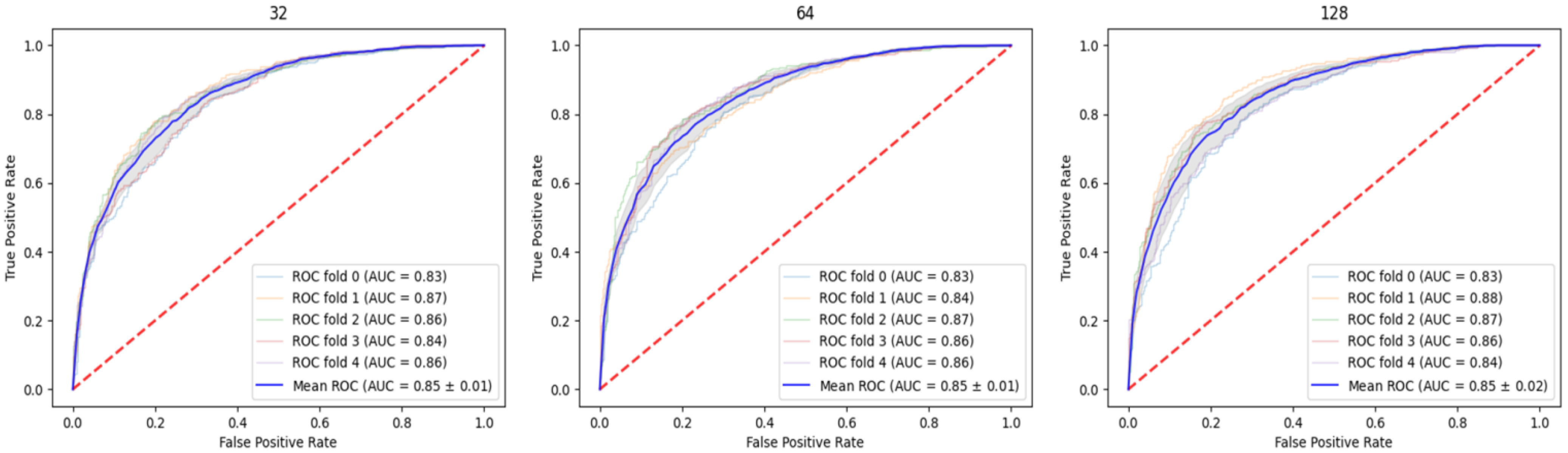
2.1. Parameter Relation
2.2. Comparison Study of Existing Methods
2.3. Discussion on Feature Dimension
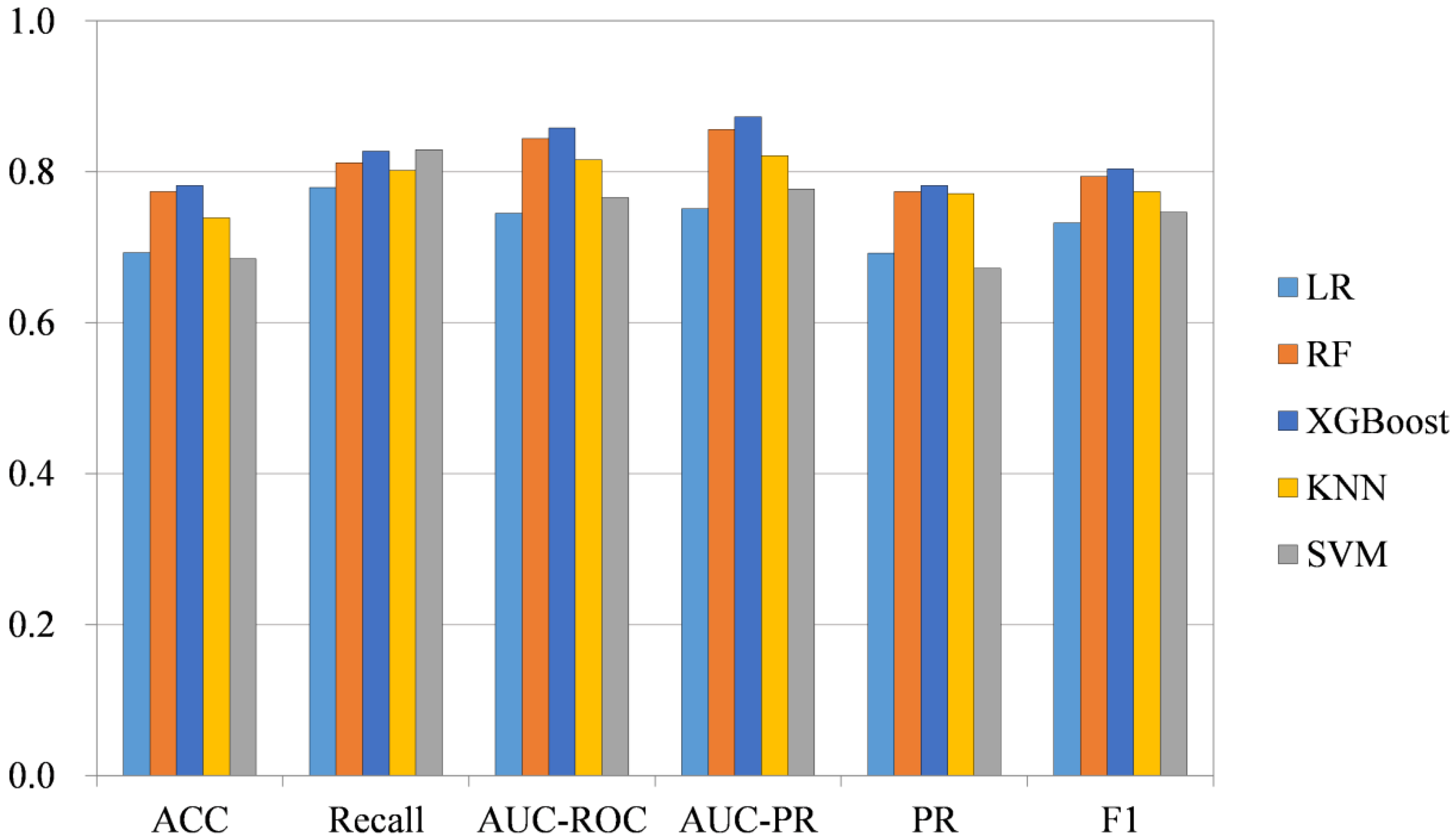
2.4. Classification Method
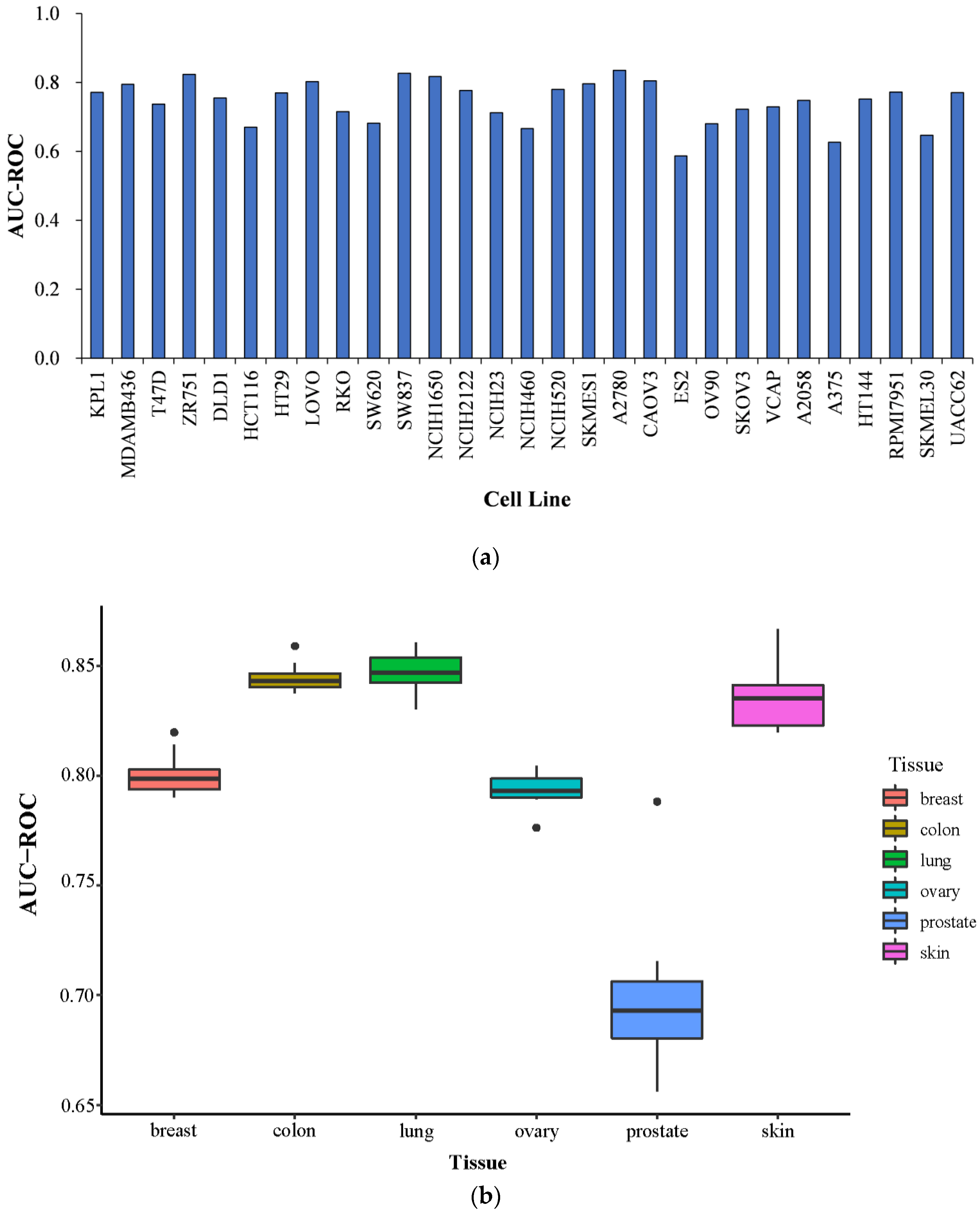
2.5. Prediction Performance on Specific Tissues and Specific Cell Lines
3. Discussion
4. Datasets and Methods
4.1. Datasets
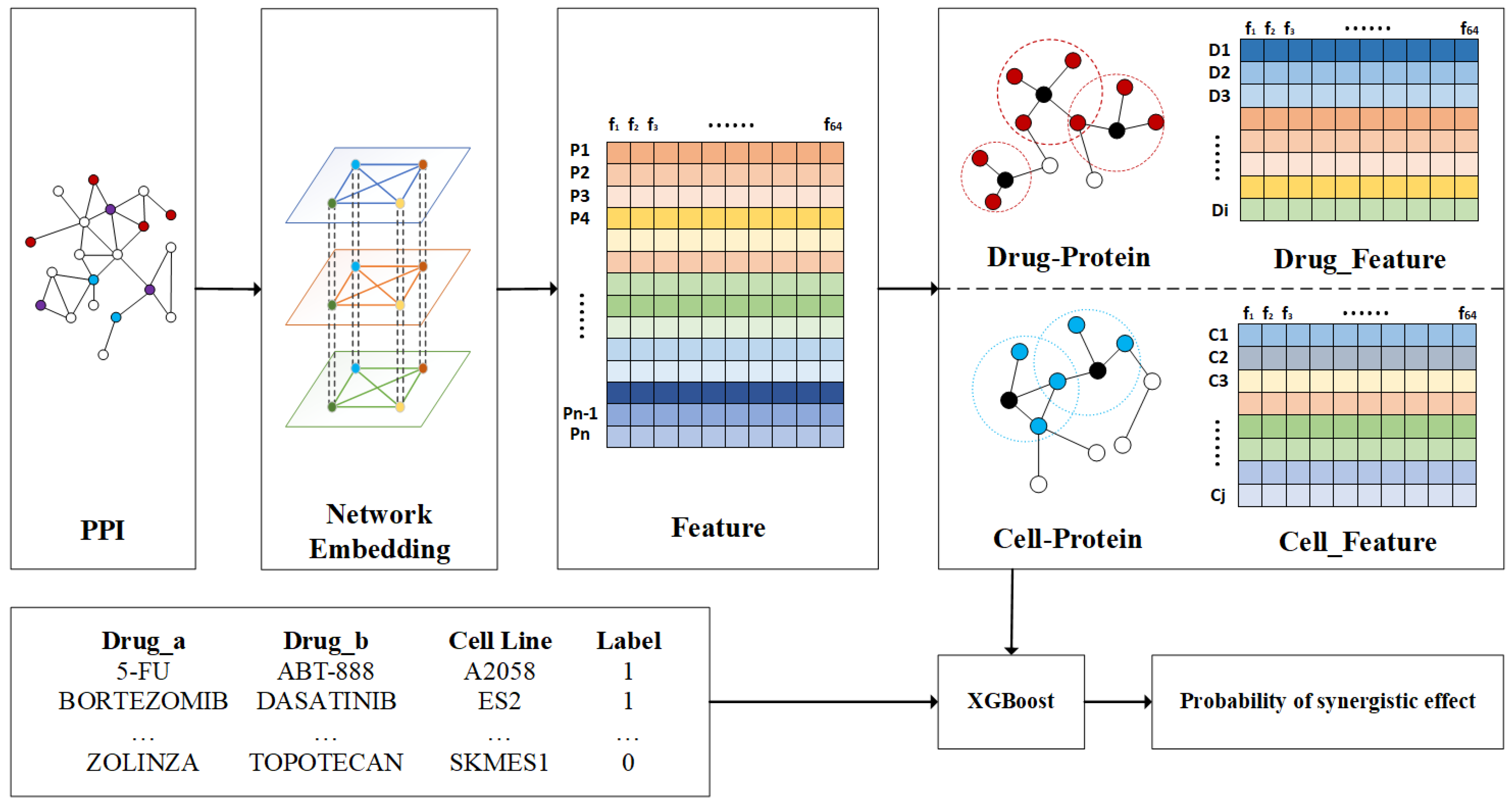
4.2. Framework of NEXGB
4.3. Network Embedding
4.3.1. Structural Similarity
4.3.2. Construction of Multilayer Weighted Graph
4.3.3. Generation of Node Sequence
4.4. Supervised Classification Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humphrey, R.W.; Brockway-Lunardi, L.M.; Bonk, D.T.; Dohoney, K.M.; Doroshow, J.H.; Meech, S.J.; Ratain, M.J.; Topalian, S.L.; Pardoll, D.M. Opportunities and challenges in the development of experimental drug combinations for cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, B.; Wennerberg, K.; Aittokallio, T.; Tang, J. Searching for drug synergy in complex dose–response landscapes using an interaction potency model. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Zhu, F.; Ma, X.; Cao, Z.W.; Li, Y.X.; Chen, Y.Z. Mechanisms of drug combinations: Interaction and network perspectives. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Csermely, P.; Korcsmáros, T.; Kiss, H.J.; London, G.; Nussinov, R. Structure and dynamics of molecular networks: A novel paradigm of drug discovery: A comprehensive review. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 138, 333–408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bajorath, J. Integration of virtual and high-throughput screening. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, D.; Siu, L.L. Approaches to modernize the combination drug development paradigm. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Kulesskiy, E.; Saarela, J.; Turunen, L.; Wennerberg, K.; Aittokallio, T.; Tang, J. Methods for high-throughput drug combination screening and synergy scoring. In Cancer Systems Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 351–398. [Google Scholar]
- Menden, M.P.; Wang, D.; Guan, Y.; Mason, M.J.; Szalai, B.; Bulusu, K.C.; Yu, T.; Kang, J.; Jeon, M.; Wolfinger, R. A cancer pharmacogenomic screen powering crowd-sourced advancement of drug combination prediction. bioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleicher, K.H.; Böhm, H.-J.; Müller, K.; Alanine, A.I. Hit and lead generation: Beyond high-throughput screening. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-M.; Iskar, M.; Zeller, G.; Kuhn, M.; Van Noort, V.; Bork, P. Prediction of drug combinations by integrating molecular and pharmacological data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, C.P.; Cheng, L.; Alexander, P.; Singal, A.; Li, L. A new drug combinatory effect prediction algorithm on the cancer cell based on gene expression and dose–response curve. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2015, 4, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulusu, K.C.; Guha, R.; Mason, D.J.; Lewis, R.P.; Muratov, E.; Motamedi, Y.K.; Cokol, M.; Bender, A. Modelling of compound combination effects and applications to efficacy and toxicity: State-of-the-art, challenges and perspectives. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Huang, C.; Fu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Ru, J.; Zheng, C.; Guo, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, W. Large-scale exploration and analysis of drug combinations. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Zhao, Z. Machine learning-based prediction of drug–drug interactions by integrating drug phenotypic, therapeutic, chemical, and genomic properties. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2014, 21, e278–e286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- An, Q.; Yu, L. A heterogeneous network embedding framework for predicting similarity-based drug-target interactions. Brief. Bioinf. 2021, 22, bbab275. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Xia, M.; An, Q. A network embedding framework based on integrating multiplex network for drug combination prediction. Brief. Bioinf. 2022, 23, bbab364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuer, K.; Lewis, R.P.; Hochreiter, S.; Bender, A.; Bulusu, K.C.; Klambauer, G. DeepSynergy: Predicting anti-cancer drug synergy with Deep Learning. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar]
- Kuru, H.I.; Tastan, O.; Cicek, E. MatchMaker: A deep learning framework for drug synergy prediction. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 2021, 19, 2334–2344. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Xie, L. TranSynergy: Mechanism-driven interpretable deep neural network for the synergistic prediction and pathway deconvolution of drug combinations. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1008653. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Ghoraie, L.S.; Men, X.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Dai, P. A comparative study of cluster detection algorithms in protein–protein interaction for drug target discovery and drug repurposing. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Guney, E.; Menche, J.; Vidal, M.; Barábasi, A.-L. Network-based in silico drug efficacy screening. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10331. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.; Kovács, I.A.; Barabási, A.-L. Network-based prediction of drug combinations. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.; Zhang, Z.-C.; Feng, J.; Zhao, X.-M. MorbidGCN: Prediction of multimorbidity with a graph convolutional network based on integration of population phenotypes and disease network. Brief. Bioinf. 2022, 23, bbac255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S. SSGraphCPI: A Novel Model for Predicting Compound-Protein Interactions Based on Deep Learning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Xu, Z.; Wu, W.K.K.; Chu, Q.; Zhang, Q. GraphSynergy: A network-inspired deep learning model for anticancer drug combination prediction. J. Am. Med. Inf. Assoc. 2021, 28, 2336–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, L.F.; Saverese, P.H.; Figueiredo, D.R. struc2vec: Learning node representations from structural identity. In Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Halifax, NS, Canada, 13–17 August 2017; pp. 385–394. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neil, J.; Benita, Y.; Feldman, I.; Chenard, M.; Roberts, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Kral, A.; Lejnine, S.; Loboda, A. An unbiased oncology compound screen to identify novel combination strategies. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Zou, B.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Deng, L. DrugCombDB: A comprehensive database of drug combinations toward the discovery of combinatorial therapy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D871–D881. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Lu, W.; Xu, Q. Grarep: Learning graph representations with global structural information. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM International on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Melbourne, Australia, 19–23 October 2015; pp. 891–900. [Google Scholar]
- Perozzi, B.; Al-Rfou, R.; Skiena, S. Deepwalk: Online learning of social representations. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, NY, USA, 24–27 August 2014; pp. 701–710. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smola, A.J.; Schölkopf, B. A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat. Comput. 2004, 14, 199–222. [Google Scholar]
- Anglesio, M.S.; Wiegand, K.C.; Melnyk, N.; Chow, C.; Salamanca, C.; Prentice, L.M.; Senz, J.; Yang, W.; Spillman, M.A.; Cochrane, D.R. Type-specific cell line models for type-specific ovarian cancer research. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72162. [Google Scholar]
- Anglesio, M.S.; Carey, M.S.; Köbel, M.; MacKay, H.; Huntsman, D.G. Clear cell carcinoma of the ovary: A report from the first Ovarian Clear Cell Symposium, June 24th, 2010. Gynecol. Oncol. 2011, 121, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, A.L.; Wong, O.G.-W.; Wong, E.S.; Tsun, O.K.-L.; Chan, K.-K.; Cheung, A.N.-Y. Caution over use of ES2 as a model of ovarian clear cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 67, 921–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barretina, J.; Caponigro, G.; Stransky, N.; Venkatesan, K.; Margolin, A.A.; Kim, S.; Wilson, C.J.; Lehár, J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Sonkin, D. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature 2012, 483, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loewe, S. The problem of synergism and antagonism of combined drugs. Arzneimittelforschung 1953, 3, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rakthanmanon, T.; Campana, B.; Mueen, A.; Batista, G.; Westover, B.; Zhu, Q.; Zakaria, J.; Keogh, E. Addressing big data time series: Mining trillions of time series subsequences under dynamic time warping. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data (TKDD) 2013, 7, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.3781. [Google Scholar]

| Network Embedding | |
|---|---|
| the number of the random walk starts for each gene | 20 |
| the length of each random walk sequence | 80 |
| the number of layers | 4 |
| the context size for optimization | 5 |
| the dimension of the node vector | 64 |
| XGBoost | |
|---|---|
| booster | gbtree |
| max_depth | 7 |
| min_child_weight | 1 |
| gamma | 0.1 |
| subsample | 0.9 |
| colasmple_bytree | 0.9 |
| learning_rate | 0.1 |
| Model | Oncology-Screen | DrugCombDB | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | Recall | AUC-ROC | AUC-PR | F1 | ACC | Recall | AUC-ROC | AUC-PR | F1 | |
| NP | 0.455 | 0.064 | 0.489 | 0.535 | 0.112 | 0.674 | 0.175 | 0.475 | 0.446 | 0.243 |
| GraRep | 0.663 | 0.767 | 0.723 | 0.702 | 0.702 | 0.667 | 0.581 | 0.728 | 0.689 | 0.613 |
| DeepWlak | 0.683 | 0.741 | 0.743 | 0.765 | 0.723 | 0.674 | 0.596 | 0.736 | 0.698 | 0.628 |
| DeepSynergy | 0.689 | 0.718 | 0.766 | 0.769 | 0.705 | 0.685 | 0.626 | 0.746 | 0.729 | 0.643 |
| GraphSynergy | 0.762 | 0.782 | 0.847 | 0.855 | 0.774 | 0.753 | 0.714 | 0.834 | 0.815 | 0.727 |
| NEXGB | 0.782 | 0.827 | 0.858 | 0.873 | 0.804 | 0.762 | 0.704 | 0.833 | 0.811 | 0.729 |
| Cell Line | Protein Quantity | NCIH460 | 305 |
| KPL1 | 369 | NCIH520 | 602 |
| MDAMB436 | 390 | SKMES1 | 208 |
| T47D | 463 | A2780 | 480 |
| ZR751 | 679 | CAOV3 | 282 |
| DLD1 | 75 | ES2 | 56 |
| HCT116 | 117 | OV90 | 505 |
| HT29 | 379 | SKOV3 | 328 |
| LOVO | 132 | VCAP | 830 |
| RKO | 147 | A2058 | 339 |
| SW620 | 381 | A375 | 156 |
| SW837 | 533 | HT144 | 147 |
| NCIH1650 | 122 | RPMI7951 | 142 |
| NCIH2122 | 346 | SKMEL30 | 107 |
| NCIH23 | 136 | UACC62 | 125 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, F.; Li, F.; Liu, J.-X.; Shang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. NEXGB: A Network Embedding Framework for Anticancer Drug Combination Prediction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179838
Meng F, Li F, Liu J-X, Shang J, Liu X, Li Y. NEXGB: A Network Embedding Framework for Anticancer Drug Combination Prediction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(17):9838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179838
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Fanjie, Feng Li, Jin-Xing Liu, Junliang Shang, Xikui Liu, and Yan Li. 2022. "NEXGB: A Network Embedding Framework for Anticancer Drug Combination Prediction" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 17: 9838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179838
APA StyleMeng, F., Li, F., Liu, J.-X., Shang, J., Liu, X., & Li, Y. (2022). NEXGB: A Network Embedding Framework for Anticancer Drug Combination Prediction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(17), 9838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179838







