The Heat Shock Protein 90 (HSP90) Is Required for the IL-33-Induced Cytokine Production in Mast Cells (MCs)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
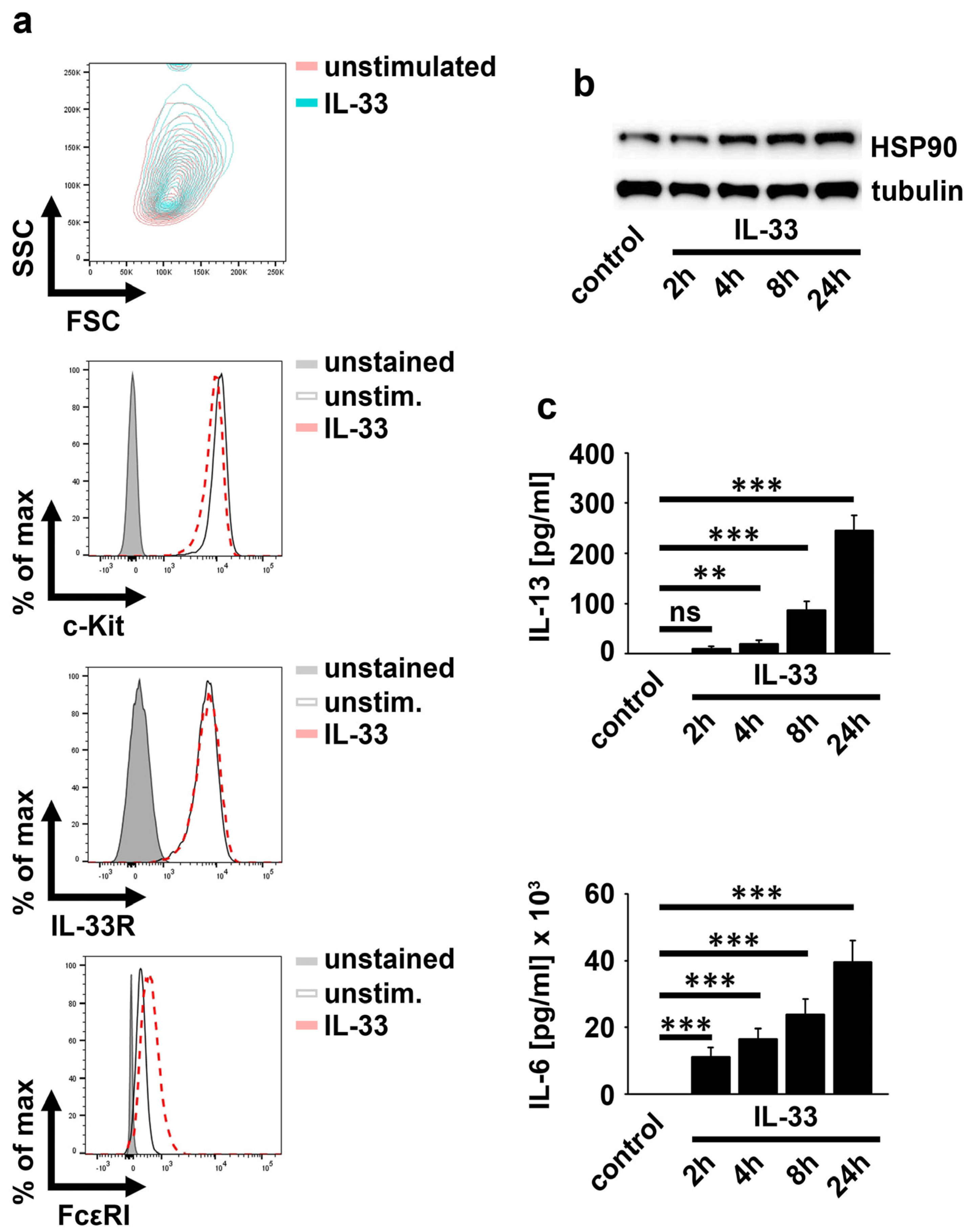
2.1. IL-33 Upregulates HSP90
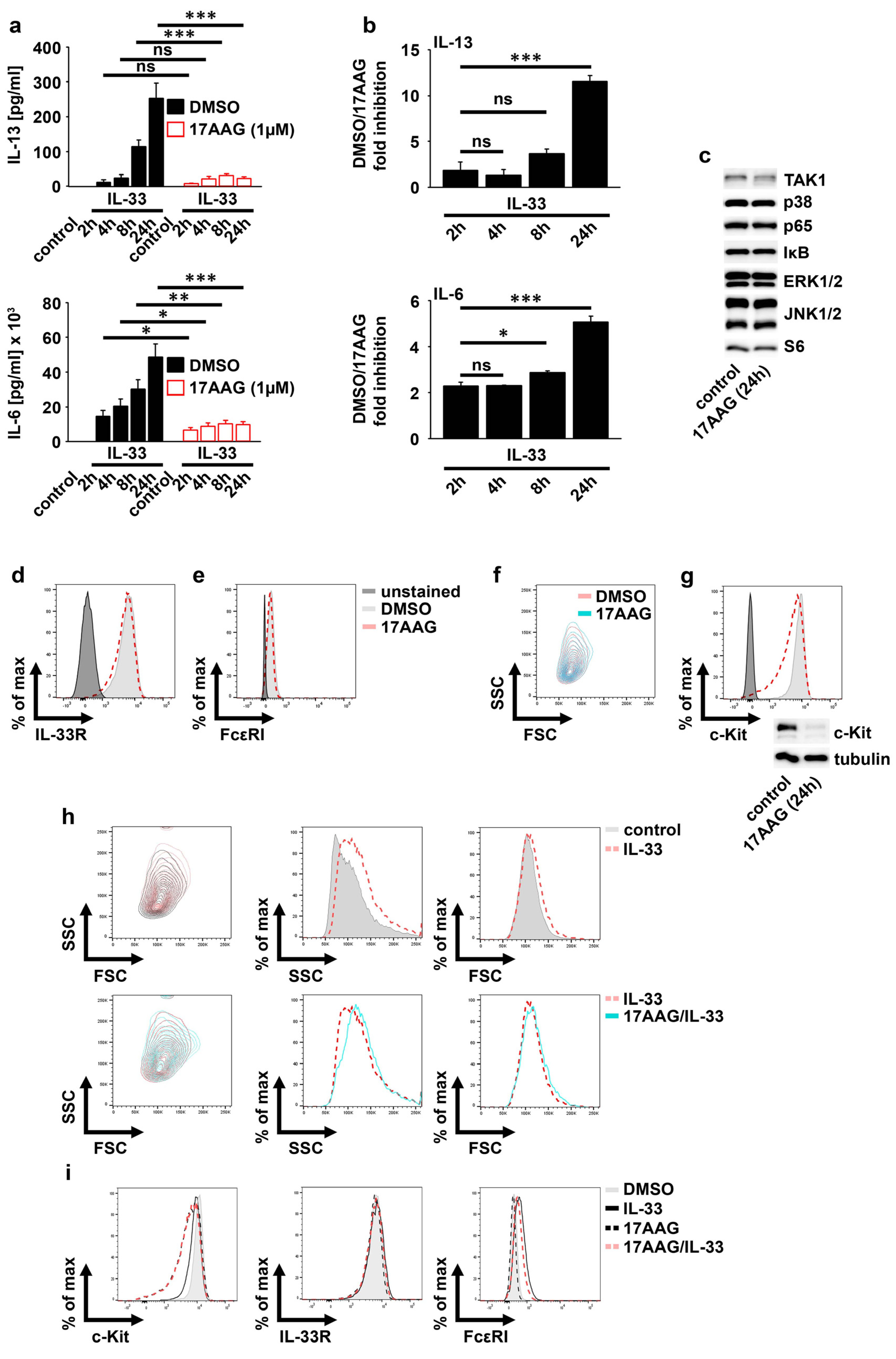
2.2. IL-33 Requires HSP90 to Mediate the Production of Cytokines in MCs
2.3. HSP90 Is Not Required for IL-33-Induced p65/RelA Activation
2.4. HSP90 Negatively Regulates the Activation of MEK1/2−ERK1/2 Signaling
2.5. HSP90 Stabilizes the IL-6 and IL-13 Transcripts
2.6. HSP90 Is Also Essential for the SCF-Supported and IL-33-Induced Cytokine Production in MCs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. BMMC Generation
4.3. Expansion of Peritoneal-Cavity-Derived MCs (PCMCs)
4.4. Culture of p65/RelA-eGFP MC/9 Reporter MC Line [28]
4.5. Stimulation of MCs (BMMCs, PCMCs, or p65/RelA−eGFP MC/9 Cells)
4.6. Flow Cytometry
4.7. Lysis and Immunoblotting
4.8. ELISA
4.9. Isolation of mRNA and qPCR
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whetstone, C.E.; Ranjbar, M.; Omer, H.; Cusack, R.P.; Gauvreau, G.M. The Role of Airway Epithelial Cell Alarmins in Asthma. Cells 2022, 11, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. Interleukin-33 (IL-33): A critical review of its biology and the mechanisms involved in its release as a potent extracellular cytokine. Cytokine 2022, 156, 155891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iznardo, H.; Puig, L. IL-1 Family Cytokines in Inflammatory Dermatoses: Pathogenetic Role and Potential Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drube, S.; Kraft, F.; Dudeck, J.; Muller, A.L.; Weber, F.; Gopfert, C.; Meininger, I.; Beyer, M.; Irmler, I.; Hafner, N.; et al. MK2/3 Are Pivotal for IL-33-Induced and Mast Cell-Dependent Leukocyte Recruitment and the Resulting Skin Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 3662–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, A.; Katsoulis-Dimitriou, K.; Edler, H.J.; Dudeck, J.; Drube, S.; Dudeck, A. Mast cells initiate the vascular response to contact allergens by sensing cell stress. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1476–1479.e1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudeck, J.; Kotrba, J.; Immler, R.; Hoffmann, A.; Voss, M.; Alexaki, V.I.; Morton, L.; Jahn, S.R.; Katsoulis-Dimitriou, K.; Winzer, S.; et al. Directional mast cell degranulation of tumor necrosis factor into blood vessels primes neutrophil extravasation. Immunity 2021, 54, 468–483.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrol, C. IL-33, an Alarmin of the IL-1 Family Involved in Allergic and Non Allergic Inflammation: Focus on the Mechanisms of Regulation of Its Activity. Cells 2022, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.V.; Iwaki, S.; Ropert, C.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; Cunha-Melo, J.R.; Beaven, M.A. Amplification of cytokine production through synergistic activation of NFAT and AP-1 following stimulation of mast cells with antigen and IL-33. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Studnitzer, B.; Esser-Kahn, A. Heat Shock Protein 90’s Mechanistic Role in Contact Hypersensitivity. J. Immunol. 2022, 208, 2622–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakeda, M.; Arock, M.; Schlapbach, C.; Yawalkar, N. Increased expression of heat shock protein 90 in keratinocytes and mast cells in patients with psoriasis. J. Am. Acad. Derm. 2014, 70, 683–690.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Yang, J.; Qi, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, B.; Zou, F.; Mei, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, Q. Heat shock proteins: Biological functions, pathological roles, and therapeutic opportunities. MedComm 2022, 3, e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Fang, F.; Luo, L.; Yin, Z. Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) regulates the stability of transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) in interleukin-1beta-induced cell signaling. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Y.; Seh, C.C.; Cheung, P.C. HSP90 is required for TAK1 stability but not for its activation in the pro-inflammatory signaling pathway. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 4023–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nardo, D.; Masendycz, P.; Ho, S.; Cross, M.; Fleetwood, A.J.; Reynolds, E.C.; Hamilton, J.A.; Scholz, G.M. A central role for the Hsp90.Cdc37 molecular chaperone module in interleukin-1 receptor-associated-kinase-dependent signaling by toll-like receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9813–9822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodromou, C.; Roe, S.M.; O’Brien, R.; Ladbury, J.E.; Piper, P.W.; Pearl, L.H. Identification and structural characterization of the ATP/ADP-binding site in the Hsp90 molecular chaperone. Cell 1997, 90, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, S.; Chi, S.; Minami, Y.; Fukushima, K.; Shibayama, H.; Hosono, N.; Yamauchi, T.; Morishita, T.; Kondo, T.; Yanada, M.; et al. Mutated KIT Tyrosine Kinase as a Novel Molecular Target in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, D.; Donze, O.; Talabot-Ayer, D.; Mezin, F.; Palmer, G.; Gabay, C. Interleukin (IL)-33 induces the release of pro-inflammatory mediators by mast cells. Cytokine 2007, 40, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, P.M.; Andreas, N.; Groth, M.; Wegner, P.; Weber, F.; Jager, U.; Kuchler, C.; Werz, O.; Serfling, E.; Kamradt, T.; et al. ATP/IL-33-triggered hyperactivation of mast cells results in an amplified production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and eicosanoids. Immunology 2021, 164, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, N.; Weber, F.; Meininger, I.; Templin, N.; Gaestel, M.; Kamradt, T.; Drube, S. IL-33-activated murine mast cells control the dichotomy between RORgammat (+) and Helios (+) Tregs via the MK2/3-mediated IL-6 production in vitro. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 2159–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, F.; Xu, W.; Karpova, T.S.; McNally, J.G.; Baron, R.; Neckers, L. Hsp90 inhibition transiently activates Src kinase and promotes Src-dependent Akt and Erk activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11318–11322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drube, S.; Weber, F.; Gopfert, C.; Loschinski, R.; Rothe, M.; Boelke, F.; Diamanti, M.A.; Lohn, T.; Ruth, J.; Schutz, D.; et al. TAK1 and IKK2, novel mediators of SCF-induced signaling and potential targets for c-Kit-driven diseases. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 28833–28850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drube, S.; Heink, S.; Walter, S.; Lohn, T.; Grusser, M.; Gerbaulet, A.; Berod, L.; Schons, J.; Dudeck, A.; Freitag, J.; et al. The receptor tyrosine kinase c-Kit controls IL-33 receptor signaling in mast cells. Blood 2010, 115, 3899–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, A.; Tsutsumi, S.; Soga, S.; Lee, M.J.; Trepel, J.; Osada, H.; Neckers, L. Inhibition of Hsp90 activates osteoclast c-Src signaling and promotes growth of prostate carcinoma cells in bone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15541–15546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.; Owyang, A.; Oldham, E.; Song, Y.; Murphy, E.; McClanahan, T.K.; Zurawski, G.; Moshrefi, M.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 2005, 23, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Louis, I.V.; Bohjanen, P.R. Post-transcriptional regulation of cytokine expression and signaling. Curr. Trends Immunol. 2018, 19, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Yombo, D.J.K.; Mentink-Kane, M.M.; Wilson, M.S.; Wynn, T.A.; Madala, S.K. Heat shock protein 70 is a positive regulator of airway inflammation and goblet cell hyperplasia in a mouse model of allergic airway inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 15082–15094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, N.; Nasti, T.H.; Huang, C.M.; Huber, B.S.; Jaleel, T.; Lin, H.Y.; Xu, H.; Elmets, C.A. Heat shock proteins HSP27 and HSP70 are present in the skin and are important mediators of allergic contact hypersensitivity. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbu, E.A.; Zhang, J.; Siraganian, R.P. The limited contribution of Fyn and Gab2 to the high affinity IgE receptor signaling in mast cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 15761–15768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peters, I.; Müller, S.; Küchler, C.; Jäger, U.; Drube, S. The Heat Shock Protein 90 (HSP90) Is Required for the IL-33-Induced Cytokine Production in Mast Cells (MCs). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810855
Peters I, Müller S, Küchler C, Jäger U, Drube S. The Heat Shock Protein 90 (HSP90) Is Required for the IL-33-Induced Cytokine Production in Mast Cells (MCs). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(18):10855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810855
Chicago/Turabian StylePeters, Isabel, Sylvia Müller, Claudia Küchler, Ute Jäger, and Sebastian Drube. 2022. "The Heat Shock Protein 90 (HSP90) Is Required for the IL-33-Induced Cytokine Production in Mast Cells (MCs)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 18: 10855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810855
APA StylePeters, I., Müller, S., Küchler, C., Jäger, U., & Drube, S. (2022). The Heat Shock Protein 90 (HSP90) Is Required for the IL-33-Induced Cytokine Production in Mast Cells (MCs). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(18), 10855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810855





