DLm6Am: A Deep-Learning-Based Tool for Identifying N6,2′-O-Dimethyladenosine Sites in RNA Sequences
Abstract
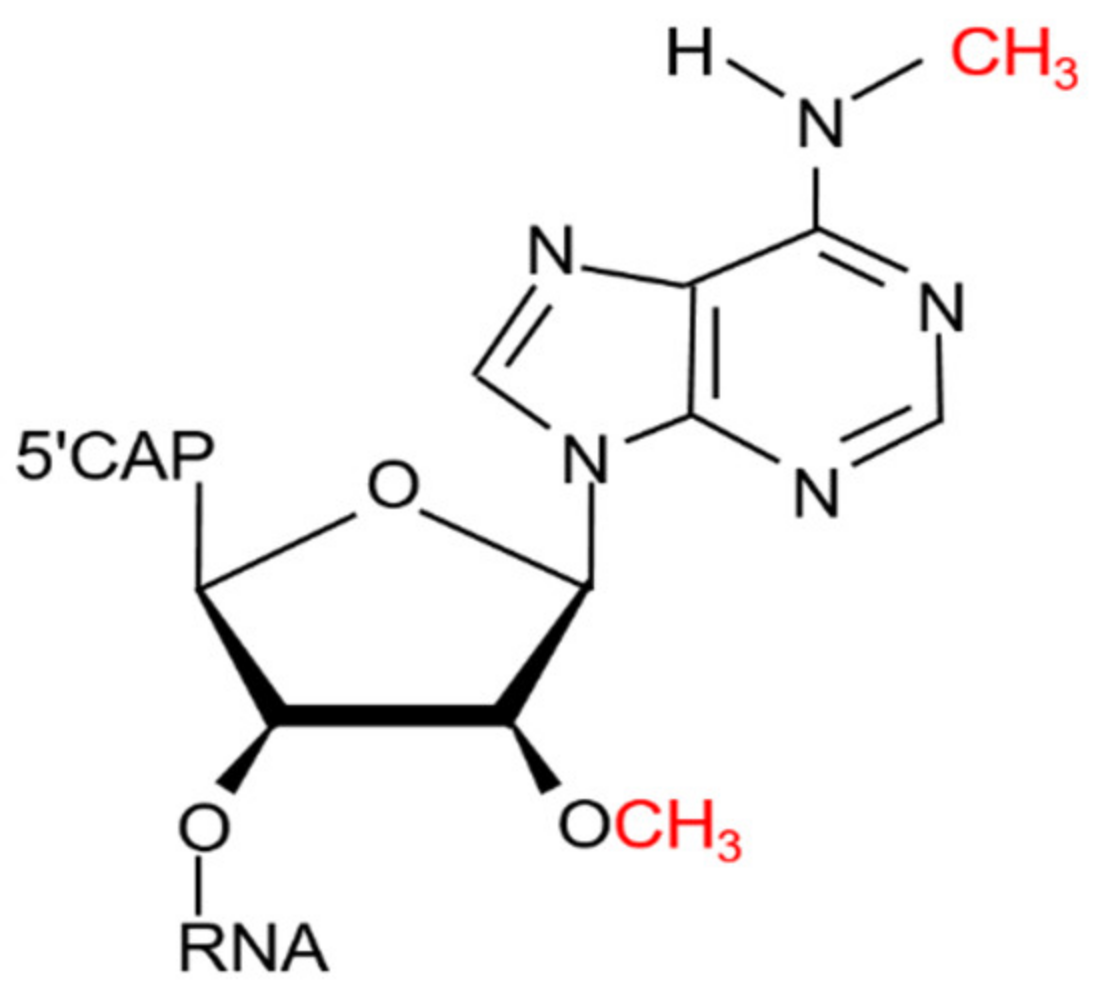
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Overview of DLm6Am
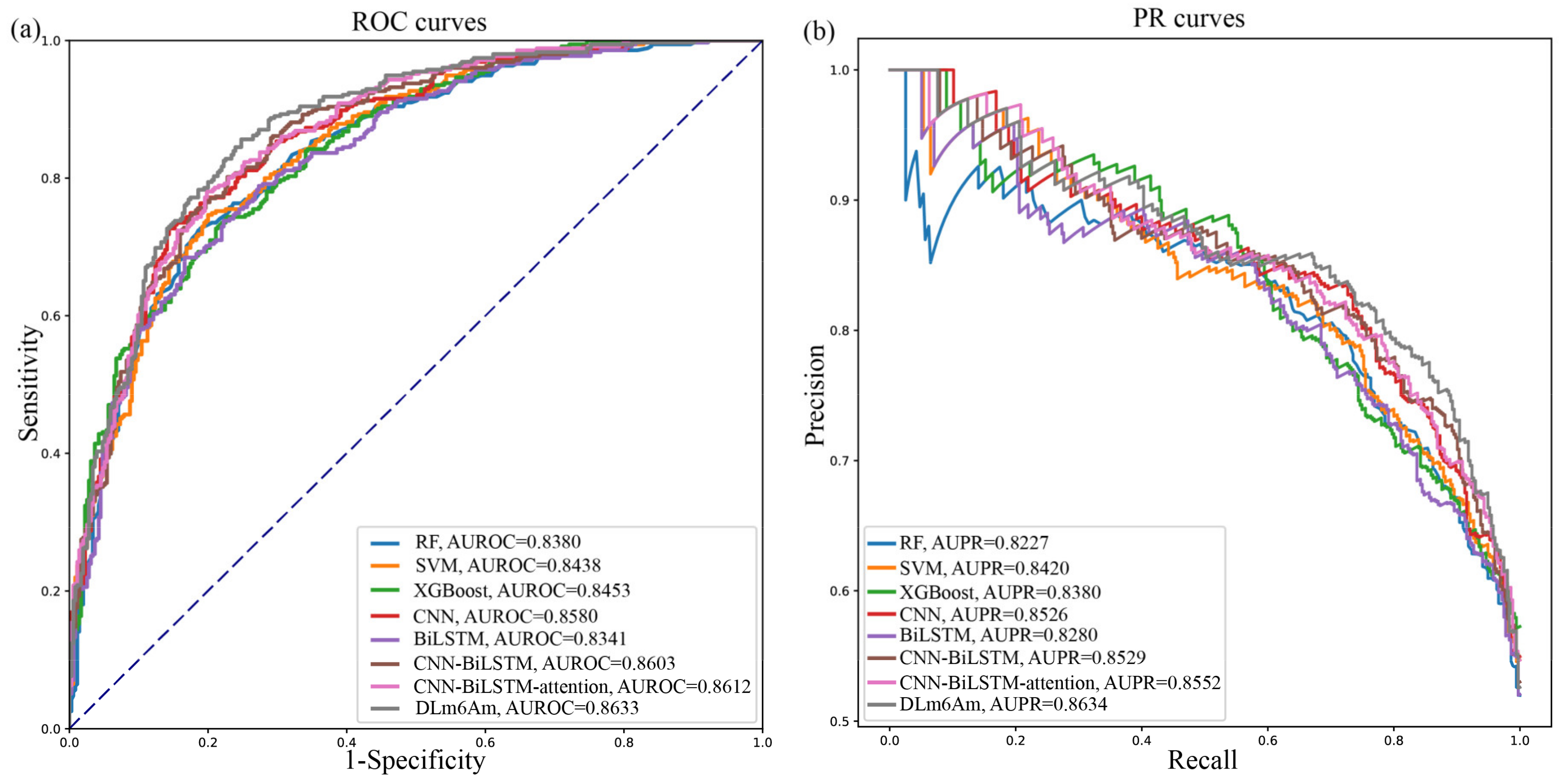
2.2. Comparison with Different Model Architectures
2.3. Hold-Out Cross-Validation on Chromosome Level
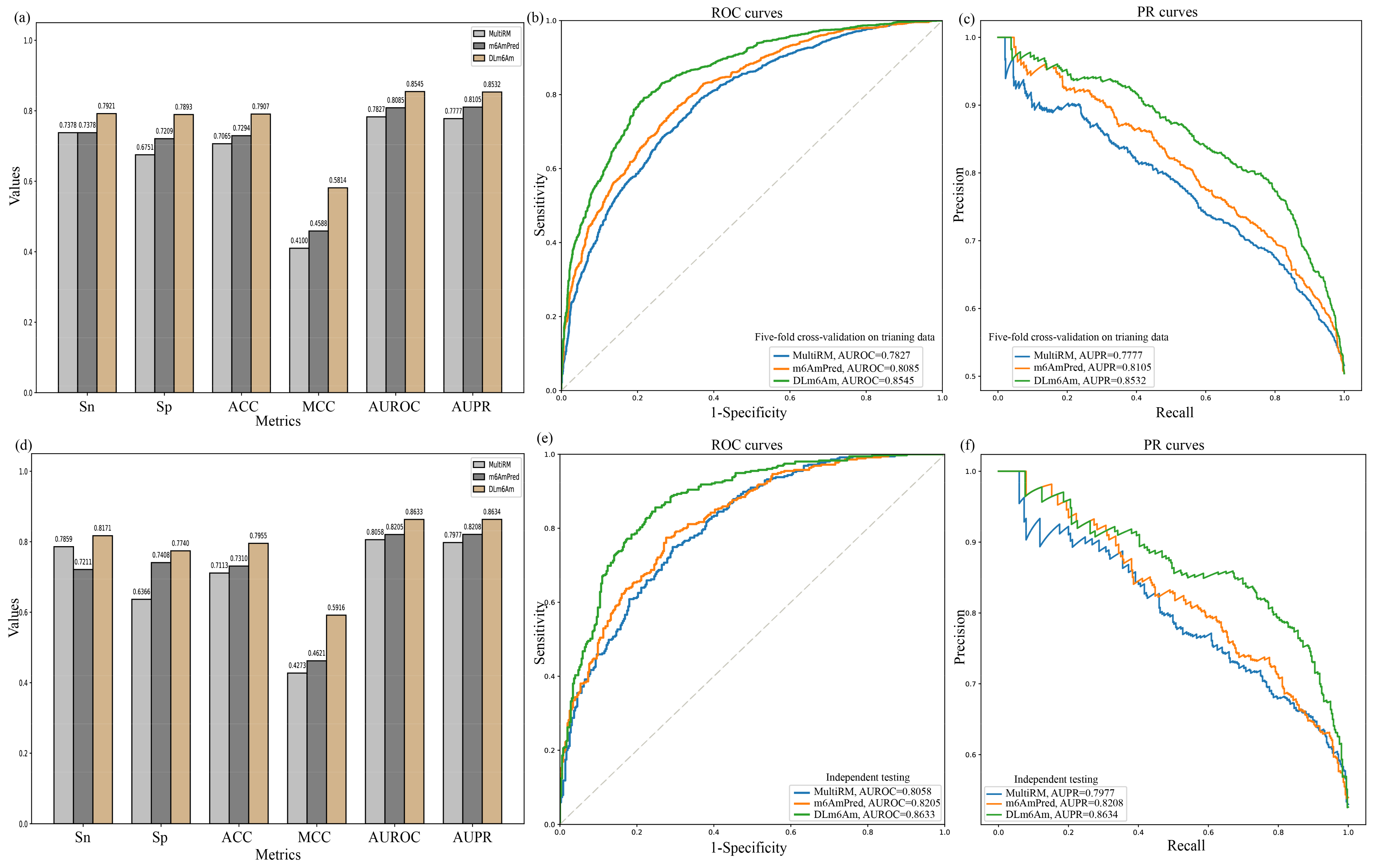
2.4. Comparison with Existing Methods
2.5. Webserver Functionality
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Benchmark Dataset
3.2. Feature Extraction from RNA Sequence
3.2.1. Binary Encoding of Nucleotide
3.2.2. Nucleotide Chemical Property (NCP)
3.2.3. Nucleotide Density (ND)
3.3. Classification Method
3.4. Performance Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boccaletto, P.; Stefaniak, F.; Ray, A.; Cappannini, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Purta, E.; Kurkowska, M.; Shirvanizadeh, N.; Destefanis, E.; Groza, P.; et al. MODOMICS: A database of RNA modification pathways. 2021 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D231–D235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.S.; Roundtree, I.A.; He, C. Post-transcriptional gene regulation by mRNA modifications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.-M.; Gershowitz, A.; Moss, B. N6, O2′-dimethyladenosine a novel methylated ribonucleoside next to the 5′ terminal of animal cell and virus mRNAs. Nature 1975, 257, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Haim, M.S.; Pinto, Y.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Hershkovitz, V.; Kol, N.; Diamant-Levi, T.; Beeri, M.S.; Amariglio, N.; Cohen, H.Y.; Rechavi, G. Dynamic regulation of N6,2′-O-dimethyladenosine (m6Am) in obesity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendinc, E.; Valle-Garcia, D.; Dhall, A.; Chen, H.; Henriques, T.; Navarrete-Perea, J.; Sheng, W.; Gygi, S.P.; Adelman, K.; Shi, Y. PCIF1 Catalyzes m6Am mRNA Methylation to Regulate Gene Expression. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 620–630.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauer, J.; Luo, X.; Blanjoie, A.; Jiao, X.; Grozhik, A.V.; Patil, D.P.; Linder, B.; Pickering, B.F.; Vasseur, J.-J.; Chen, Q.; et al. Reversible methylation of m6Am in the 5′ cap controls mRNA stability. Nature 2017, 541, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.; Mumbach, M.R.; Jovanovic, M.; Wang, T.; Maciag, K.; Bushkin, G.G.; Mertins, P.; Ter-Ovanesyan, D.; Habib, N.; Cacchiarelli, D.; et al. Perturbation of m6A Writers Reveals Two Distinct Classes of mRNA Methylation at Internal and 5′ Sites. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akichika, S.; Hirano, S.; Shichino, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Nishimasu, H.; Ishitani, R.; Sugita, A.; Hirose, Y.; Iwasaki, S.; Nureki, O.; et al. Cap-specific terminal N-6-methylation of RNA by an RNA polymerase II-associated methyltransferase. Science 2019, 363, eaav0080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.R.; Delfino, E.; Homolka, D.; Roithova, A.; Chen, K.-M.; Li, L.; Franco, G.; Vågbø, C.B.; Taillebourg, E.; Fauvarque, M.-O.; et al. The Mammalian Cap-Specific m6Am RNA Methyltransferase PCIF1 Regulates Transcript Levels in Mouse Tissues. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulias, K.; Toczydłowska-Socha, D.; Hawley, B.R.; Liberman, N.; Takashima, K.; Zaccara, S.; Guez, T.; Vasseur, J.-J.; Debart, F.; Aravind, L.; et al. Identification of the m6Am Methyltransferase PCIF1 Reveals the Location and Functions of m6Am in the Transcriptome. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 631–643.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Liu, F.; Lu, Z.; Fei, Q.; Ai, Y.; He, P.C.; Shi, H.; Cui, X.; Su, R.; Klungland, A.; et al. Differential m6A, m6Am, and m1A Demethylation Mediated by FTO in the Cell Nucleus and Cytoplasm. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 973–985.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, B.R.; Jaffrey, S.R. Transcriptome-Wide Mapping of m6A and m6Am at Single-Nucleotide Resolution Using miCLIP. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2019, 126, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.W.Q.; Goh, Y.T.; Goh, W.S.S. Atlas of quantitative single-base-resolution N6-methyl-adenine methylomes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Meng, H.; Yi, C. m6Am-seq reveals the dynamic m6Am methylation in the human transcriptome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Song, B.; Chen, K.; Lu, Z.; Rong, R.; Zhong, Y.; Meng, J. m6AmPred: Identifying RNA N6, 2’-O-dimethyladenosine (m6Am) sites based on sequence-derived infor-mation. Methods 2021, 203, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, B.; Grozhik, A.V.; Olarerin-George, A.O.; Meydan, C.; Mason, C.E.; Jaffrey, S.R. Single-nucleotide-resolution mapping of m6A and m6Am throughout the transcriptome. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Huang, D.; Song, B.; Chen, K.; Song, Y.; Liu, G.; Su, J.; de Magalhães, J.P.; Rigden, D.J.; Meng, J. Attention-based multi-label neural networks for integrated prediction and interpretation of twelve widely occurring RNA modifications. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, K.; Cai, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, X.; Meng, H.; Xu, X.; Huang, Z.; Peng, J.; et al. Landscape and Regulation of m6A and m6Am Methylome across Human and Mouse Tissues. Mol. Cell 2019, 77, 426–440.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hamada, M. DeepM6ASeq: Prediction and characterization of m6A-containing sequences using deep learning. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; He, X.; Zhao, D.; Tian, T.; Hong, L.; Jiang, T.; Zeng, J. Modeling multi-species RNA modification through multi-task curriculum learning. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 3719–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DLm6Am: A Deep-Learning-Based Tool for Identifying N6,2′-O-Dimethyladenosine Sites in RNA Sequences. Available online: http://47.94.248.117/DLm6Am/ (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Glorot, X.; Bordes, A.; Bengio, Y. Deep Sparse Rectifier Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 11–13 April 2011; pp. 315–323. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, C.; Barber, D. Bayesian classification with Gaussian processes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lei, T.-Y.; Jin, D.-C.; Lin, H.; Chou, K.-C. PseKNC: A flexible web server for generating pseudo K-tuple nucleotide composition. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 456, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, P.; Li, F.; Marquez-Lago, T.T.; Leier, A.; Revote, J.; Zhu, Y.; Powell, D.R.; Akutsu, T.; Webb, G.I.; et al. iLearn: An integrated platform and meta-learner for feature engineering, machine-learning analysis and modeling of DNA, RNA and protein sequence data. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 21, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, P.; Li, C.; Li, F.; Xiang, D.; Chen, Y.Z.; Akutsu, T.; Daly, R.J.; Webb, G.I.; Zhao, Q.; et al. iLearnPlus: A comprehensive and automated machine-learning platform for nucleic acid and protein sequence analysis, prediction and visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Tran, H.; Liang, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhang, L. Identification and analysis of the N6-methyladenosine in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcriptome. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Ding, H.; Yang, H.; Chen, W.; Lin, H.; Chou, K.C. iRNA-PseColl: Identifying the Occurrence Sites of Different RNA Modifications by Incorporating Collective Effects of Nucleotides into PseKNC. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 7, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Tang, H.; Lin, H. MethyRNA: A web server for identification of N6-methyladenosine sites. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 35, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Feng, P.; Yang, H.; Ding, H.; Lin, H.; Chou, K.-C. iRNA-3typeA: Identifying Three Types of Modification at RNA’s Adenosine Sites. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 11, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Feng, P.; Ding, H.; Lin, H. Identifying N6-methyladenosine sites in the Arabidopsis thaliana transcriptome. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 2225–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, F.-Y.; Lv, H.; Yang, Y.-H.; Zulfiqar, H.; Gao, H.; Lin, H. Computational identification of N6-methyladenosine sites in multiple tissues of mammals. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Rehman, H.U.; Habib, U.; Ijaz, U. Detecting N6-methyladenosine sites from RNA transcriptomes using random forest. J. Comput. Sci. 2020, 47, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.; Park, J. bCNN-Methylpred: Feature-Based Prediction of RNA Sequence Modification Using Branch Convolu-tional Neural Network. Genes 2021, 12, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, X.; Rong, R.; Lu, Z.; Su, J.; de Magalhães, J.P.; Rigden, D.J.; Meng, J. WHISTLE: A high-accuracy map of the human N-6-methyladenosine (m6A) epitranscriptome predicted using a machine learning approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgi, B.; Schliep, A. Context-specific independence mixture modeling for positional weight matrices. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, e166–e173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cai, L. Prediction of nucleosome occupancy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using position-correlation scoring function. Genomics 2011, 98, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rangannan, V.; Bansal, M. Relative stability of DNA as a generic criterion for promoter prediction: Whole genome annotation of microbial genomes with varying nucleotide base composition. Mol. BioSyst. 2009, 5, 1758–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forest. Mach. Learn. 1999, 45, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, C.; Stitson, M.O.; Weston, J.; Holloway, R.; Bottou, L.; Scholkopf, B.; Smola, A. Support Vector Machine. Comput. Sci. 2002, 1, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Dobson, R.J.; Munroe, P.B.; Caulfield, M.J.; Saqi, M.A. Predicting deleterious nsSNPs: An analysis of sequence and structural attributes. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruitbosch, H.T.; Mzayek, Y.; Omlor, S.; Guerra, P.; Milias-Argeitis, A. A convolutional neural network for segmentation of yeast cells without manual training annotations. Bioinformatics 2021, 38, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wu, Q.; Peng, Z.; Yang, J. Enhanced prediction of RNA solvent accessibility with long short-term memory neural networks and improved sequence profiles. Bioinformatics 2018, 35, 1686–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lena, P.; Nagata, K.; Baldi, P. Deep architectures for protein contact map prediction. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2449–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuksa, P.P.; Min, M.R.; Dugar, R.; Gerstein, M. High-order neural networks and kernel methods for peptide-MHC binding prediction. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3600–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angermueller, C.; Lee, H.; Reik, W.; Stegle, O. DeepCpG: Accurate prediction of single-cell DNA methylation states using deep learning. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Wan, F.; Tian, T.; Li, S.; Zhao, D.; Zeng, J. A deep-learning framework for multi-level peptide–protein interaction prediction. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, W.; Leier, A.; Marquez-Lago, T.T.; Akutsu, T.; Lithgow, T.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y. DeepVF: A deep learning-based hybrid framework for identifying virulence factors using the stacking strategy. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

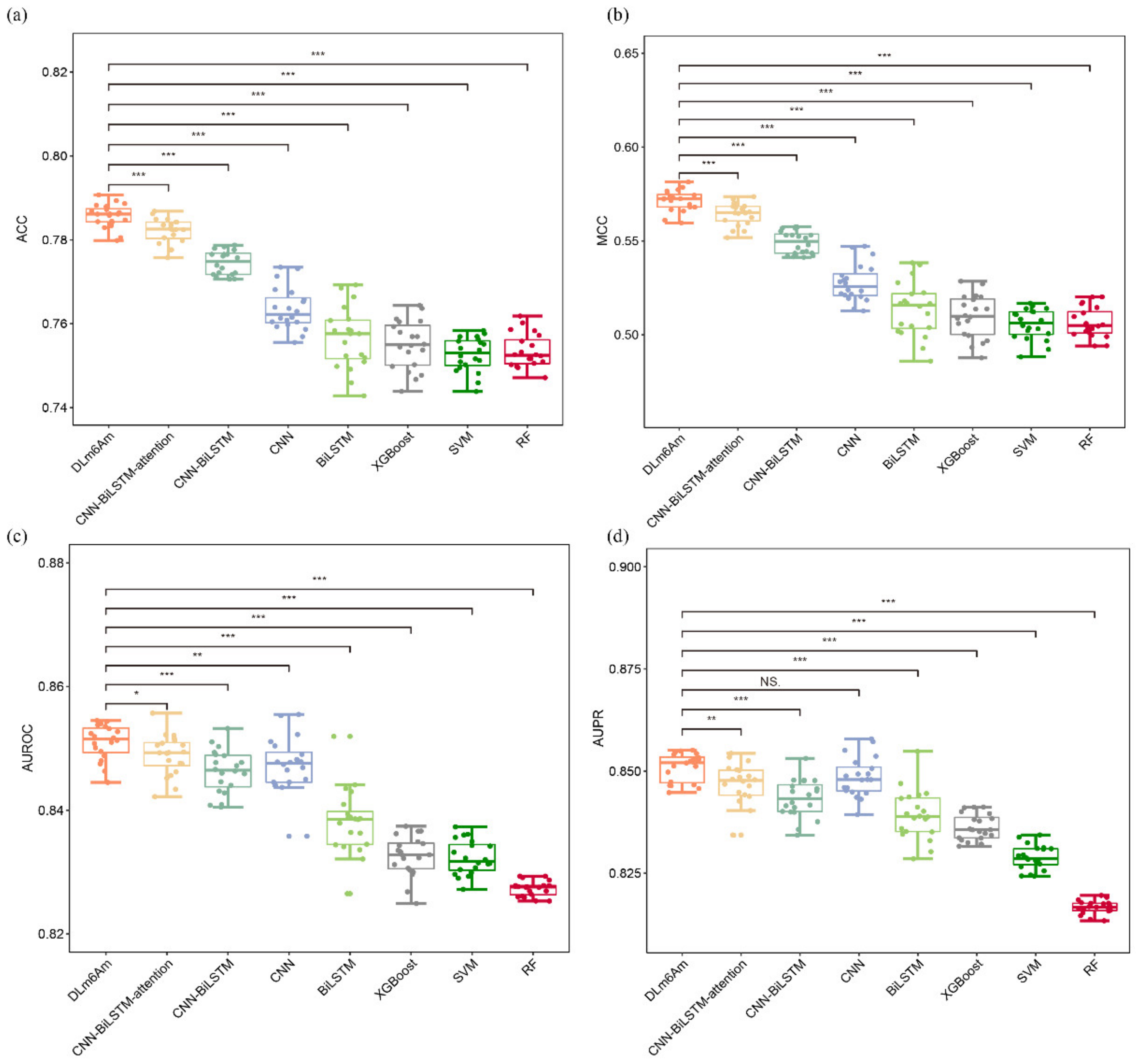
| Model | Sn ± SD (%) | Sp ± SD (%) | ACC ± SD (%) | MCC ± SD | AUROC ± SD | AUPR ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 74.74 ± 0.51 | 75.89 ± 0.54 | 75.31 ± 0.39 | 0.5063 ± 0.0078 | 0.8273 ± 0.0012 | 0.8163 ± 0.0021 |
| SVM | 77.06 ± 0.42 | 73.46 ± 0.72 | 75.26 ± 0.39 | 0.5055 ± 0.0078 | 0.8323 ± 0.0027 | 0.8288 ± 0.0029 |
| XGBoost | 75.42 ± 0.62 | 75.54 ± 0.64 | 75.48 ± 0.55 | 0.5096 ± 0.0111 | 0.8325 ± 0.0031 | 0.8362 ± 0.0031 |
| CNN | 75.95 ± 3.21 | 76.71 ± 2.73 | 76.33 ± 0.50 | 0.5275 ± 0.0097 | 0.8473 ± 0.0043 | 0.8485 ± 0.0047 |
| BiLSTM | 76.17 ± 2.32 | 75.14 ± 2.06 | 75.65 ± 0.67 | 0.5134 ± 0.0134 | 0.8381 ± 0.0047 | 0.8392 ± 0.0053 |
| CNN-BiLSTM | 78.33 ± 1.08 | 76.55 ± 1.11 | 77.45 ± 0.29 | 0.5491 ± 0.0058 | 0.8462 ± 0.0034 | 0.8432 ± 0.0045 |
| CNN-BiLSTM-attention | 78.60 ± 0.81 | 77.82 ± 0.78 | 78.21 ± 0.29 | 0.5643 ± 0.0058 | 0.8488 ± 0.0031 | 0.8464 ± 0.0053 |
| DLm6Am | 78.94 ± 0.79 | 78.18 ± 0.60 | 78.56 ± 0.27 | 0.5713 ± 0.0054 | 0.8509 ± 0.0027 | 0.8508 ± 0.0033 |
| Model | Sn (%) | Sp (%) | ACC (%) | MCC | AUROC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 75.77 | 76.90 | 76.34 | 0.5268 | 0.8380 |
| SVM | 75.49 | 77.18 | 76.34 | 0.5268 | 0.8438 |
| XGBoost | 74.37 | 76.06 | 75.21 | 0.5043 | 0.8435 |
| CNN | 69.58 | 86.20 | 77.89 | 0.5656 | 0.8580 |
| BiLSTM | 72.96 | 78.03 | 75.49 | 0.5105 | 0.8341 |
| CNN-BiLSTM | 79.89 | 77.21 | 78.55 | 0.5712 | 0.8603 |
| CNN-BiLSTM-attention | 77.21 | 80.45 | 78.84 | 0.5769 | 0.8612 |
| DLm6Am | 81.71 | 77.40 | 79.55 | 0.5916 | 0.8634 |
| Chromosome | Sn (%) | Sp (%) | ACC (%) | MCC | AUROC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr1 | 76.96 | 80.20 | 78.61 | 0.5721 | 0.8490 |
| Chr2 | 83.48 | 76.52 | 80.00 | 0.6015 | 0.8749 |
| Chr3 | 77.00 | 79.63 | 78.37 | 0.5665 | 0.8575 |
| Chr4 | 81.25 | 78.46 | 79.84 | 0.5973 | 0.8663 |
| Chr5 | 91.25 | 81.94 | 86.84 | 0.7373 | 0.9255 |
| Chr6 | 77.66 | 76.24 | 76.92 | 0.5386 | 0.8332 |
| Chr7 | 84.78 | 77.42 | 81.08 | 0.6236 | 0.8789 |
| Chr8 | 84.62 | 80.70 | 82.57 | 0.6525 | 0.8691 |
| Chr9 | 81.16 | 80.30 | 80.74 | 0.6146 | 0.8678 |
| Chr10 | 87.50 | 77.46 | 82.52 | 0.6532 | 0.8533 |
| Chr11 | 85.19 | 75.53 | 80.69 | 0.6116 | 0.8696 |
| Chr12 | 76.34 | 82.18 | 79.38 | 0.5867 | 0.8549 |
| Chr14 | 83.33 | 77.11 | 80.00 | 0.6030 | 0.8531 |
| Chr15 | 83.10 | 86.36 | 84.67 | 0.6942 | 0.9078 |
| Chr16 | 79.69 | 83.61 | 81.60 | 0.6329 | 0.8768 |
| Chr17 | 82.57 | 77.57 | 80.09 | 0.6023 | 0.8298 |
| Chr19 | 82.41 | 77.78 | 80.19 | 0.6029 | 0.8585 |
| ChrX | 75.82 | 90.28 | 82.21 | 0.6580 | 0.9087 |
| Chr13, 18, 20, 21, and 22 | 87.38 | 72.36 | 79.20 | 0.5979 | 0.8773 |
| Chromosome | Positive | Negative | Chromosome | Positive | Negative |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr1 | 191 | 197 | Chr13 | 32 | 39 |
| Chr2 | 115 | 115 | Chr14 | 72 | 83 |
| Chr3 | 100 | 108 | Chr15 | 71 | 66 |
| Chr4 | 64 | 65 | Chr16 | 64 | 61 |
| Chr5 | 80 | 72 | Chr17 | 109 | 107 |
| Chr6 | 94 | 101 | Chr18 | 16 | 18 |
| Chr7 | 92 | 93 | Chr19 | 108 | 99 |
| Chr8 | 52 | 57 | Chr20 | 37 | 44 |
| Chr9 | 69 | 66 | Chr21 | 18 | 22 |
| Chr10 | 72 | 71 | Chr22 | 26 | 23 |
| Chr11 | 108 | 94 | ChrX | 91 | 72 |
| Chr12 | 93 | 101 | Total | 1774 | 1774 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Z.; Su, W.; Lou, L.; Qiu, W.; Xiao, X.; Xu, Z. DLm6Am: A Deep-Learning-Based Tool for Identifying N6,2′-O-Dimethyladenosine Sites in RNA Sequences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11026. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911026
Luo Z, Su W, Lou L, Qiu W, Xiao X, Xu Z. DLm6Am: A Deep-Learning-Based Tool for Identifying N6,2′-O-Dimethyladenosine Sites in RNA Sequences. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11026. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911026
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Zhengtao, Wei Su, Liliang Lou, Wangren Qiu, Xuan Xiao, and Zhaochun Xu. 2022. "DLm6Am: A Deep-Learning-Based Tool for Identifying N6,2′-O-Dimethyladenosine Sites in RNA Sequences" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11026. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911026
APA StyleLuo, Z., Su, W., Lou, L., Qiu, W., Xiao, X., & Xu, Z. (2022). DLm6Am: A Deep-Learning-Based Tool for Identifying N6,2′-O-Dimethyladenosine Sites in RNA Sequences. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11026. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911026





