Heterogeneous Evolution of Sex Chromosomes in the Torrent Frog Genus Amolops
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Simplified Genomic Data Analyses
2.2. Identifying Sex-Linked Markers and Sex-Determination Systems
2.3. Identifying the Sex Chromosome
2.4. Identifying Potential Sex-Determining Genes
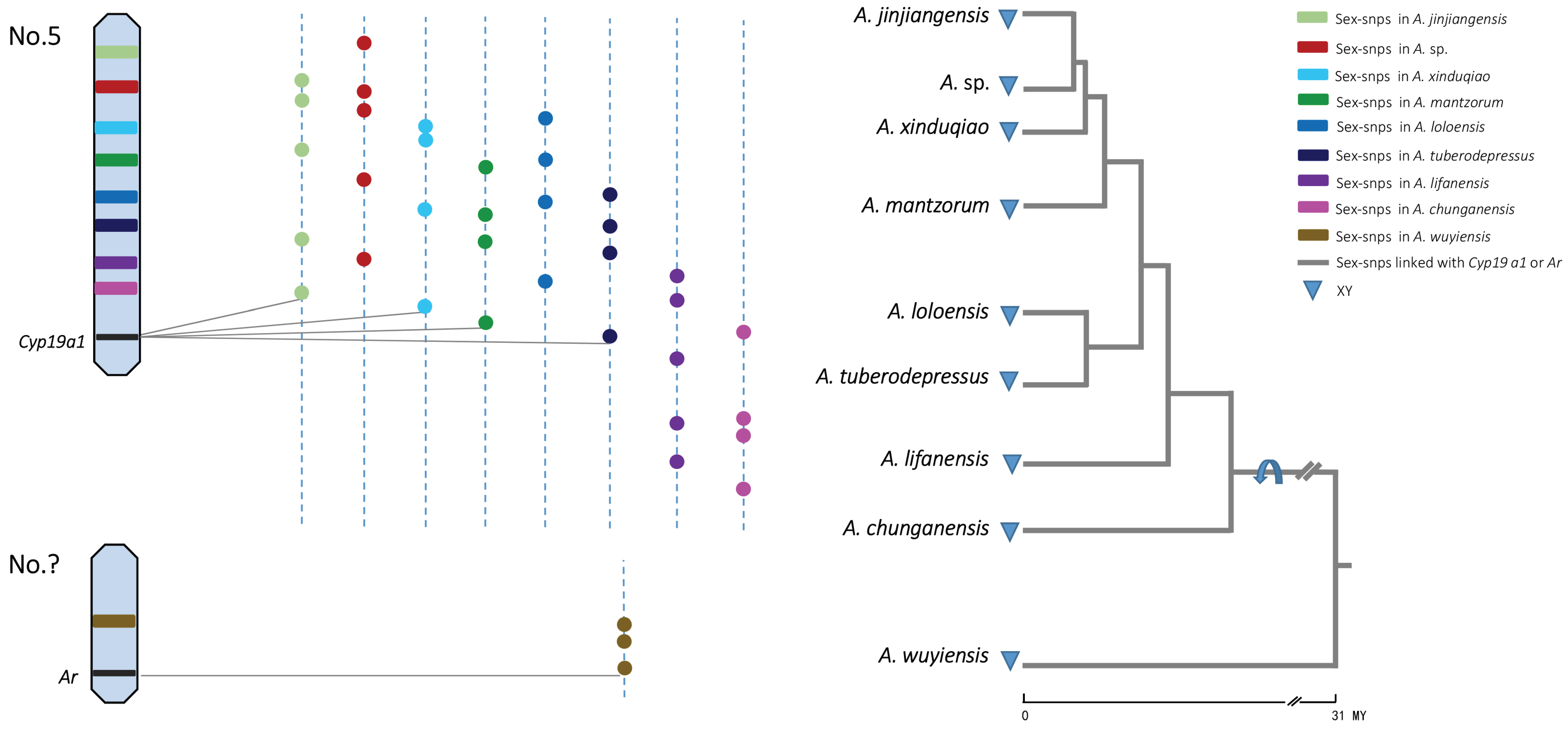
2.5. Patterns of Sex-Chromosome Turnovers
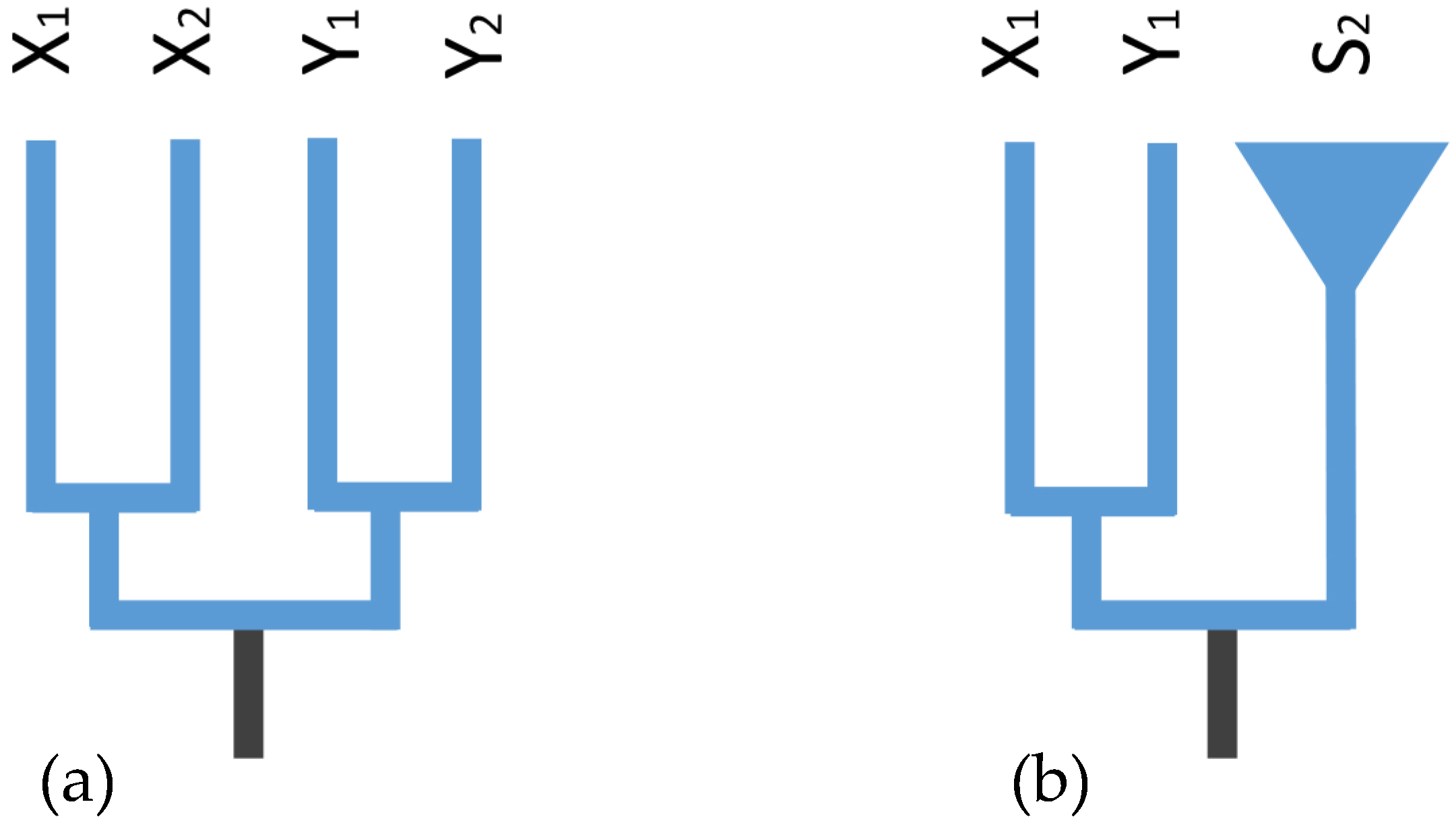
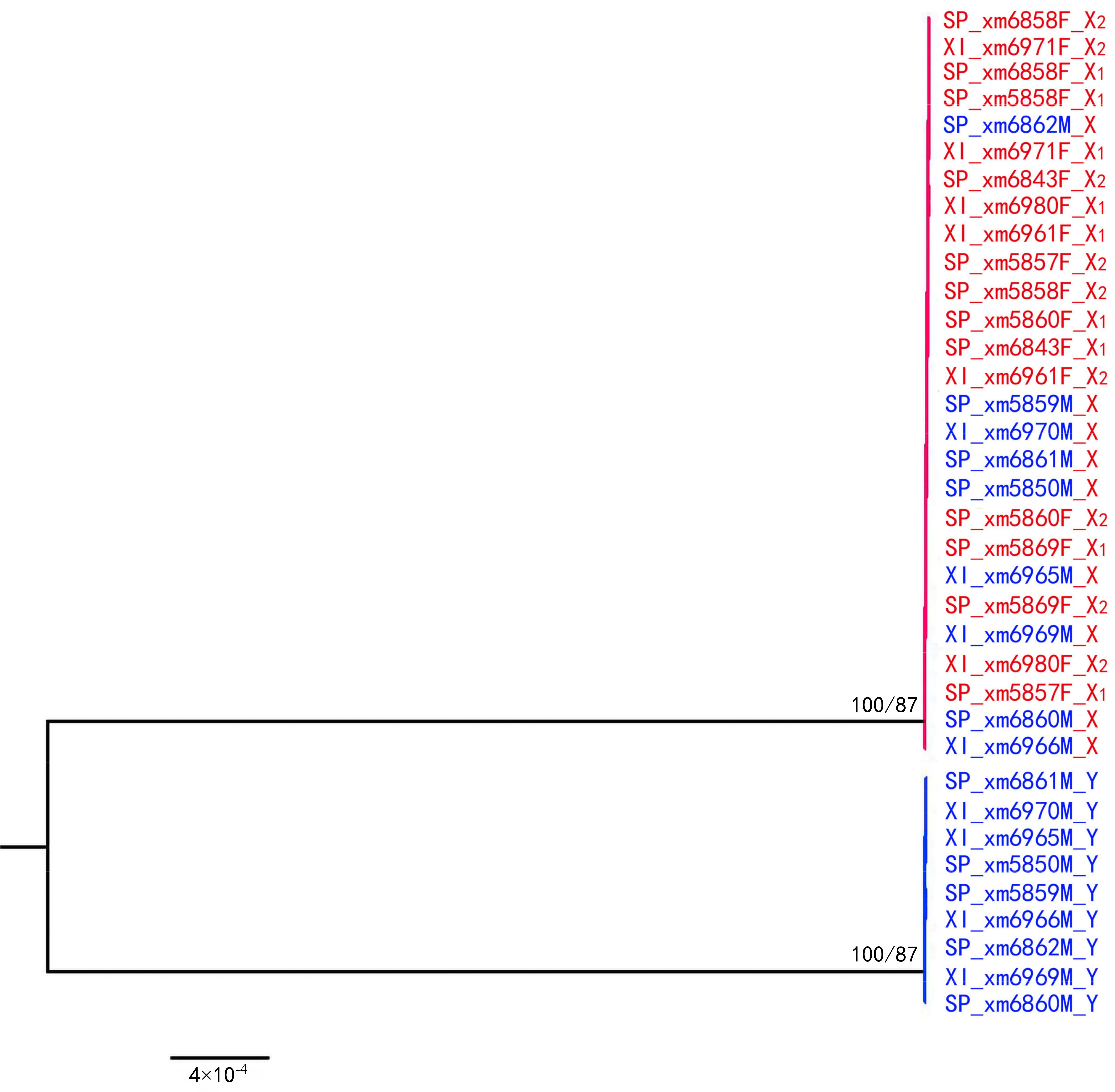
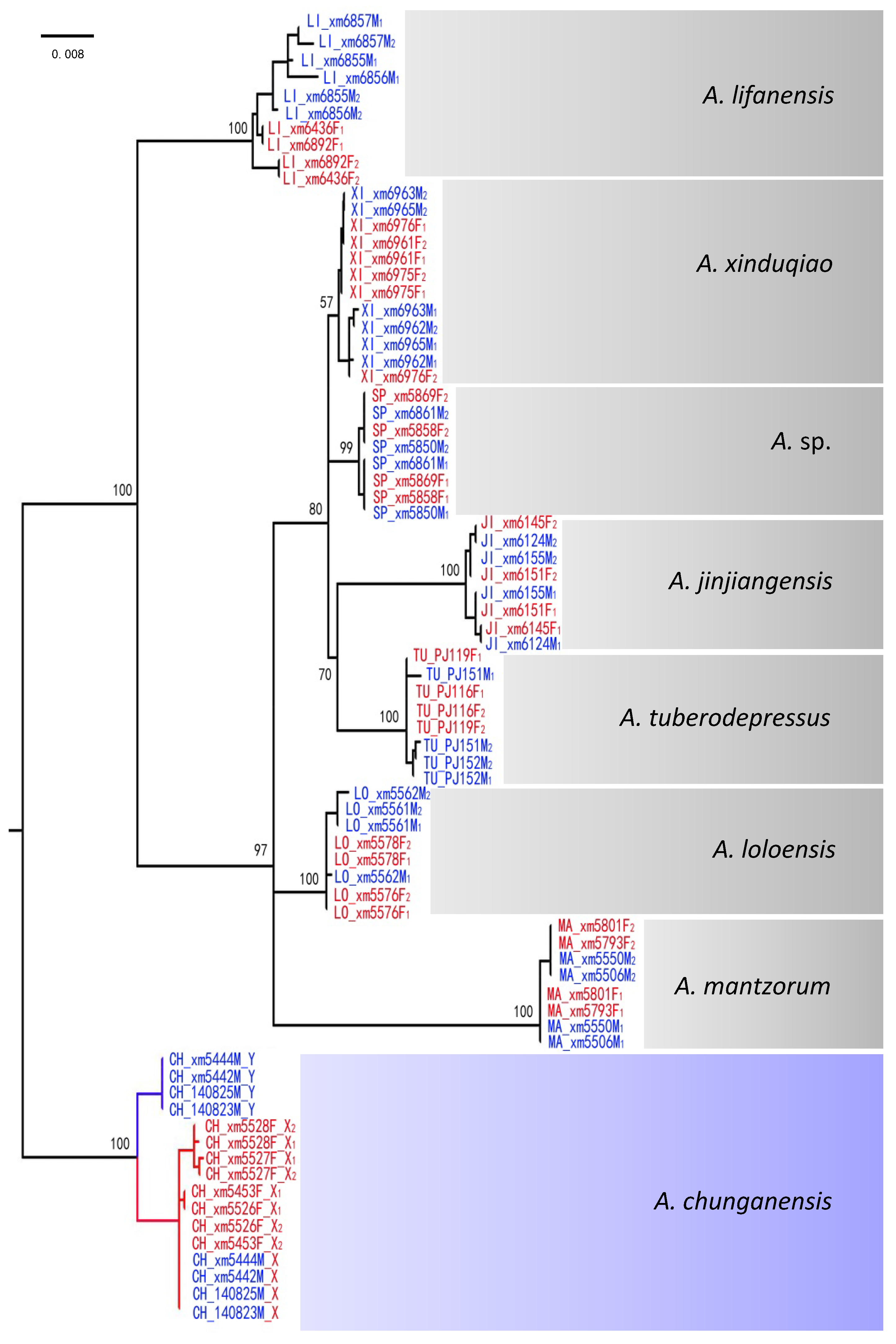
2.6. Gene Trees of X–Y Recombination
3. Discussion
3.1. Turnover between Non-Homologous Sex Chromosomes
3.2. X–Y Recombination Evolved in Homologous Sex Chromosomes
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Genomic Library Preparation
4.3. De Novo Assembly and SNP Calling
4.4. Filtering for Sex-Linked Markers
4.5. Validating Sex-Linked Markers
4.6. Assigning Sex-Linked Markers onto Sex-Chromosome
4.7. Predicting the Sex-Linked Markers Involved in Genes for Sex Determination
4.8. Assessing Patterns of Sex-Chromosome Turnover
4.9. Multispecies Gene Trees
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charlesworth, D.; Charlesworth, B.; Marais, G. Steps in the evolution of heteromorphic sex chromosomes. Heredity 2005, 95, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahn, B.T.; Page, D.C. Four evolutionary strata on the human X chromosome. Science 1999, 286, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, M. How and why chromosome inversions evolve. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, W.G.; Robertson, A. The effect of linkage on limits to artificial selection. Genet. Res. 1966, 8, 269–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergero, R.; Charlesworth, D. The evolution of restricted recombination in sex chromosomes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicoso, B.; Bachtrog, D. Numerous transitions of sex chromosomes in Diptera. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggert, C. Sex determination: The amphibian models. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2004, 44, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schartl, M. Sex chromosome evolution in non-mammalian vertebrates. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2004, 14, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachtrog, D.; Mank, J.E.; Peichel, C.L.; Kirkpatrick, M.; Otto, S.P.; Ashman, T.L.; Hahn, M.W.; Kitano, J.; Mayrose, I.; Ming, R.; et al. Sex determination: Why so many ways of doing it? PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, I. Sex determination and sex chromosomes in Amphibia. Sex. Dev. 2017, 11, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volff, J.N.; Nanda, I.; Schmid, M.; Schartl, M. Governing sex determination in fish: Regulatory putsches and ephemeral dictators. Sex. Dev. 2007, 1, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, K.; Hamaguchi, S. Novel sex-determining genes in fish and sex chromosome evolution. Dev. Dyn. 2013, 242, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.B. Evolution of the sex chromosomes in salmonid fishes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2013, 141, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, I. An evolutionary witness: The frog Rana rugosa underwent change of heterogametic sex from XY male to ZW female. Sex. Dev. 2007, 1, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresnes, C.; Borzée, A.; Horn, A.; Stöck, M.; Ostini, M.; Sermier, R.; Wassef, J.; Litvinchuck, S.N.; Kosch, T.A.; Waldman, B.; et al. Sex-chromosome homomorphy in palearctic tree frogs results from both turnovers and X-Y recombination. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, B.L.S.; Evans, B.J. Sequential turnovers of sex chromosomes in African clawed frogs (Xenopus) suggest some genomic regions are good at sex determination. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2016, 6, 3625–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufresnes, C.; Brelsford, A.; Baier, F.; Perrin, N. When sex chromosomes recombine only in the heterogametic sex: Heterochiasmy and Heterogamety in Hyla Tree Frogs. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, T.; Coryell, J.; Ezaz, T.; Lynch, J.; Scantlebury, D.P.; Zarkower, D. Restriction Site-Associated DNA Sequencing (RAD-seq) reveals an extraordinary number of transitions among Gecko sex-determining systems. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 1296–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöck, M.; Horn, A.; Grossen, C.; Lindtke, D.; Sermier, R.; Betto-Colliard, C.; Dufresnes, C.; Bonjour, E.; Dumas, Z.; Luquet, E.; et al. Ever-young sex chromosomes in European tree frogs. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, N. Sex reversal: A fountain of youth for sex chromosomes? Evolution 2009, 63, 3043–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, M.; Marais, G.; Hykelova, V.; Janousek, B.; Laporte, V.; Vyskot, B.; Mouchiroud, D.; Negrutiu, I.; Charlesworth, D.; Monéger, F. A gradual process of recombination restriction in the evolutionary history of the sex chromosomes in dioecious plants. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergero, R.; Qiu, S.; Forrest, A.; Borthwick, H.; Charlesworth, D. Expansion of the pseudo-autosomal region and ongoing recombination suppression in the Silene latifolia sex chromosomes. Genetics 2013, 194, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, P.; Proux-Wera, E.; Churcher, A.; Soler, L.; Dainat, J.; Pucholt, P.; Nordlund, J.; Martin, T.; Rönnberg-Wästljung, A.C.; Nystedt, B.; et al. Genome assembly of the basket willow, Salix viminalis, reveals earliest stages of sex chromosome expansion. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöck, M.; Savary, R.; Betto-Colliard, C.; Biollay, S.; Jourdan-Pineau, H.; Perrin, N. Low rates of X-Y recombination, not turnovers, account for homomorphic sex chromosomes in several diploid species of palearctic green toads (Bufo viridis subgroup). J. Evol. Biol. 2013, 26, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, N.; Studer, T.; Dufresnes, C.; Perrin, N. Sex-chromosome recombination in common frogs brings water to the Fountain-of-Youth. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Liang, D.; Li, J.; Lyu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P. Phylogenetic relationships of the Chinese torrent frogs (Ranidae: Amolops) revealed by phylogenomic analyses of AFLP-Capture data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 146, 106753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.F.; Zhao, E.M. Preliminary studies on karyotypes of the genes Amolops of the Hengduan mountains. Acta Herpetol. Sin. 1985, 4, 276–282. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.A.; Tan, A.M.; Zhao, E.M. Cytogenetic Studies on Four Species of Amolops in the Hengduan Rang. Acta Genet. Sin. 1987, 14, 63–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.Z.; Yang, D.T. A comparative study on karyotype and chromosome banding of three species of Amolops from southeastern China. Zool. Res. 1994, 15, 158–165. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.S. Cytotaxonomy of Amphibian in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 1–252. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Natri, H.M.; Shikano, T.; Merilä, J. Progressive recombination suppression and differentiation in recently evolved neo-sex chromosomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1131–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, G.; Kitano, J.; Kirkpatrick, M. The origin of a new sex chromosome by introgression between two stickleback fishes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darolti, I.; Wright, A.E.; Mank, J.E. Guppy Y chromosome integrity maintained by incomplete recombination suppression. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Xia, Y.; Yue, B.; Zeng, X. Assigning the sex-specific markers via Genotyping-by-Sequencing onto the Y chromosome for a Torrent Frog Amolops mantzorum. Genes 2020, 11, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, D.L.; Lavanchy, G.; Sermier, R.; Sredl, M.J.; Miura, I.; Borzée, A.; Barrow, L.N.; Canestrelli, D.; Crochet, P.A.; Dufresnes, C.; et al. A rapid rate of sex-chromosome turnover and non-random transitions in true frogs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisel, R.P. Evolution of sex determination and sex chromosomes: A Novel Alternative Paradigm. BioEssays 2020, 42, e1900212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brelsford, A.; Lavanchy, G.; Sermier, R.; Rausch, A.; Perrin, N. Identifying homomorphic sex chromosomes from wild-caught adults with limited genomic resources. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, R.D.; Kudra, R.S.; Malcom, J.W.; Preez, L.D.; Malone, J.H. The African Bullfrog (Pyxicephalus adspersus) genome unites the two ancestral ingredients for making vertebrate sex chromosomes. bioRxiv 2018, 329847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Y.; Zhang, B.L.; Raxworthy, C.J.; Weisrock, D.W.; Hime, P.M.; Jin, J.Q.; Lemmon, E.M.; Lemmon, A.R.; Holland, S.D.; Kortyna, M.L.; et al. Natatanuran frogs used the Indian Plate to step-stone disperse and radiate across the Indian Ocean. Natl Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Song, M.; Xia, Y.; Zeng, X. A tandemly arranged pattern of two 5S rDNA arrays in Amolops mantzorum (Anura, Ranidae). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2017, 151, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Song, M.; Luo, W.; Xia, Y.; Zeng, X. Chromosomal evolution in the Amolops mantzorum species group (Ranidae; Anura) aarrated by repetitive DNAs. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2019, 157, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, Y.; Nishida, C.; Yoshimoto, S.; Ito, M.; Oshima, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Nakamura, M.; Matsuda, Y. Diversity in the origins of sex chromosomes in anurans inferred from comparative mapping of sexual differentiation genes for three species of the Raninae and Xenopodinae. Chromosome Res. 2008, 16, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, Y.; Kato, T.; Wang, D.; Murakami, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Nagahama, Y.; Nakamura, M. Promoter activity and chromosomal location of the Rana rugosa P450 aromatase (CYP19) gene. Zool. Sci. 2006, 23, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Hartsfield, J.K.; Guo, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, S. Association between CYP19A1 genotype and pubertal sagittal jaw growth. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2012, 142, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, B.; Bi, K.; Fu, J. A phylogeographic evaluation of the Amolops mantzorum species group: Cryptic species and plateau uplift. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 73, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauret, C.M.S.; Gansauge, M.T.; Tupper, A.S.; Furman, B.L.S.; Knytl, M.; Song, X.Y.; Greenbaum, E.; Meyer, M.; Evans, B.J. Developmental systems drift and the drivers of sex chromosome evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, A.E.; Ronco, F.; Matschiner, M.; Salzburger, W.; Böhne, A. Dynamics of sex chromosome evolution in a rapid radiation of cichlid fishes. bioRxiv 2021, 7, eabe8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Pang, M.; Yu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Tong, J.; Fu, B. Sex-specific markers developed by next-generation sequencing confirmed an XX/XY sex determination system in bighead carp (Hypophthalmichehys nobilis) and silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). DNA Res. 2018, 25, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abinawanto; Shimada, K.; Yoshida, K.; Saito, N. Effects of aromatase inhibitor on sex differentiation and levels of P45017α and P450arom messenger ribonucleic acid of gonads in chicken embryos. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1996, 102, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, D. Sex determination: Where environment and genetics meet. Evol. Dev. 2003, 5, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, H.; Miura, I.; Ichikawa, Y. Role of aromatase and androgen receptor expression in gonadal sex differentiation of ZW/ZZ-type frogs, Rana rugosa. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 134, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Matsui, K.; Takase, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Nakamura, M. Expression of P450 aromatase protein in developing and in sex-reversed gonads of the XX/XY type of the frog Rana rugosa. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2004, 137, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruo, K.; Suda, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Oshima, Y.; Nakamura, M. Steroidogenic gene expression during sex determination in the frog Rana rugosa. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2008, 158, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawaribuchi, S.; Ikeda, N.; Fujitani, K.; Ito, Y.; Onuma, Y.; Komiya, T.; Takamatsu, N.; Ito, M. Cell-mass structures expressing the aromatase gene Cyp19a1 lead to Ovarian Cavities in Xenopus laevis. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 3996–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brelsford, A.; Dufresnes, C.; Perrin, N. High-density sex-specific linkage maps of a European tree frog (Hyla arborea) identify the sex chromosome without information on offspring sex. Heredity 2016, 116, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardell, J.M.; Josephson, M.P.; Dalziel, A.C.; Peichel, C.L.; Kirkpatrick, M. Heterogeneous histories of recombination suppression on stickleback sex chromosomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 4403–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshire, R.J.; Glaubitz, J.C.; Sun, Q.; Poland, J.A.; Kawamoto, K.; Buckler, E.S.; Mitchell, S.E. A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, N.A.; Etter, P.D.; Atwood, T.S.; Currey, M.C.; Shiver, A.L.; Lewis, Z.A.; Selker, E.U.; Cresko, W.A.; Johnson, E.A.; Fay, J.C. Rapid SNP discovery and genetic mapping using sequenced RAD markers. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catchen, J.M.; Amores, A.; Hohenlohe, P.; Cresko, W.; Postlethwait, J.H. Stacks: Building and genotyping loci de novo from short-read sequences. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2011, 1, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catchen, J.M.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; Bassham, S.; Amores, A.; Cresko, W.A. Stacks: An analysis tool set for population genomics. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 3124–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, N.C.; Catchen, J.M. Deriving genotypes from RAD-seq short-read data using Stacks. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 2640–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, J.R.; Stevens, J.R.; Catchen, J.M. Lost in parameter space: A road map for stacks. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 1360–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, B.L.S.; Buonaccorsi, V.P. Genomic characterization of sex-identification markers in Sebastes carnatus and Sebastes chrysomelas rockfishes. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 2165–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.A.; Pascoal, S.; Cezard, T.; Risse, J.E.; Ritchie, M.G.; Bailey, N.W. Opposing patterns of intraspecific and interspecific differentiation in sex chromosomes and autosomes. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 3905–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gamble, T.; McKenna, E.; Meyer, W.; Nielsen, S.V.; Pinto, B.J.; Scantlebury, D.P.; Higham, T.E. XX/XY sex chromosomes in the South American Dwarf Gecko (Gonatodes humeralis). J. Hered. 2018, 109, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotz, H.; Uzzell, T.; Berger, L. Linkage groups of protein-coding genes in western palearctic water frogs reveal extensive evolutionary conservation. Genetics 1997, 147, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brelsford, A.; Stöck, M.; Betto-Colliard, C.; Dubey, S.; Dufresnes, C.; Jourdan-Pineau, H.; Rodrigues, N.; Savary, R.; Sermier, R.; Perrin, N. Homologous sex chromosomes in three deeply divergent anuran species. Evolution 2013, 67, 2434–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brelsford, A.; Rodrigues, N.; Perrin, N. High-density linkage maps fail to detect any genetic component to sex determination in a Rana temporaria family. J. Evol. Biol. 2016, 29, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Gao, Y.D.; Jiang, D.C.; Lei, J.; Ren, J.L.; Liao, W.B.; Deng, C.; Wang, Z.; Hillis, D.M.; Zhang, Y.P.; et al. Genomic adaptations for arboreal locomotion in Asian flying treefrogs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2116342119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Roco, Á.S.; Bullejos, M. Sex differentiation in amphibians: Effect of temperature and its influence on sex reversal. Sex. Dev. 2021, 15, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Okada, E.; Umemoto, H.; Tamura, K.; Uno, Y.; Nishida-Umehara, C.; Matsuda, Y.; Takamatsu, N.; Shiba, T.; Ito, M.A. A W-linked DM-domain gene, DM-W, participates in primary ovary development in Xenopus laevis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2469–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikamo, K.; Witschi, E. The mitotic chromosomes in Xenopus laevis (Daudin): Normal, sex reversed and female WW. Cytogenetics 1966, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Ikeda, N.; Izutsu, Y.; Shiba, T.; Takamatsu, N.; Ito, M. Opposite roles of DMRT1 and its W-linked paralogue, DM-W, in sexual dimorphism of Xenopus laevis: Implications of a ZZ/ZW-type sex-determining system. Development 2010, 137, 2519–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Luo, W.; Xia, Y.; Zeng, X. Using sex-linked markers via Genotyping-by-Sequencing to identify XX/XY sex chromosomes in the Spiny frog (Quasipaa boulengeri). Genes 2022, 13, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ping, J.; Xia, Y.; Ran, J.; Zeng, X. Heterogeneous Evolution of Sex Chromosomes in the Torrent Frog Genus Amolops. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911146
Ping J, Xia Y, Ran J, Zeng X. Heterogeneous Evolution of Sex Chromosomes in the Torrent Frog Genus Amolops. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911146
Chicago/Turabian StylePing, Jun, Yun Xia, Jianghong Ran, and Xiaomao Zeng. 2022. "Heterogeneous Evolution of Sex Chromosomes in the Torrent Frog Genus Amolops" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911146
APA StylePing, J., Xia, Y., Ran, J., & Zeng, X. (2022). Heterogeneous Evolution of Sex Chromosomes in the Torrent Frog Genus Amolops. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911146








