Saffron Extract Attenuates Anxiogenic Effect and Improves Cognitive Behavior in an Adult Zebrafish Model of Traumatic Brain Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
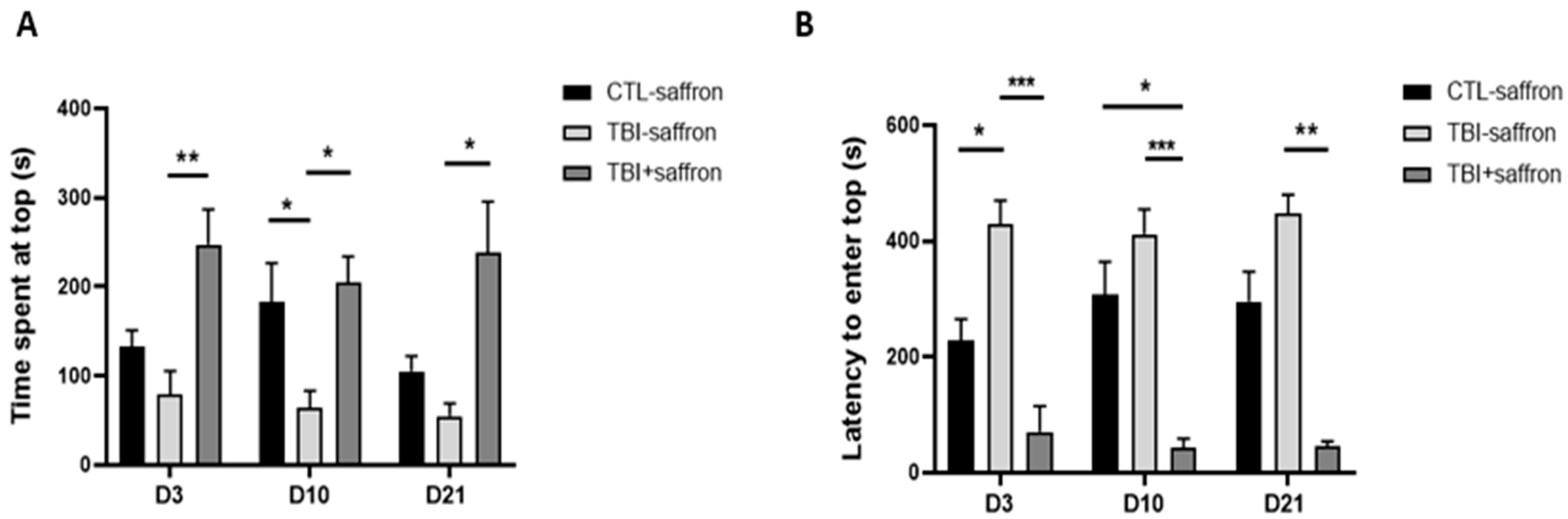
2.1. Saffron Attenuates Anxiety-like Behavior in TBI-Induced Zebrafish Model
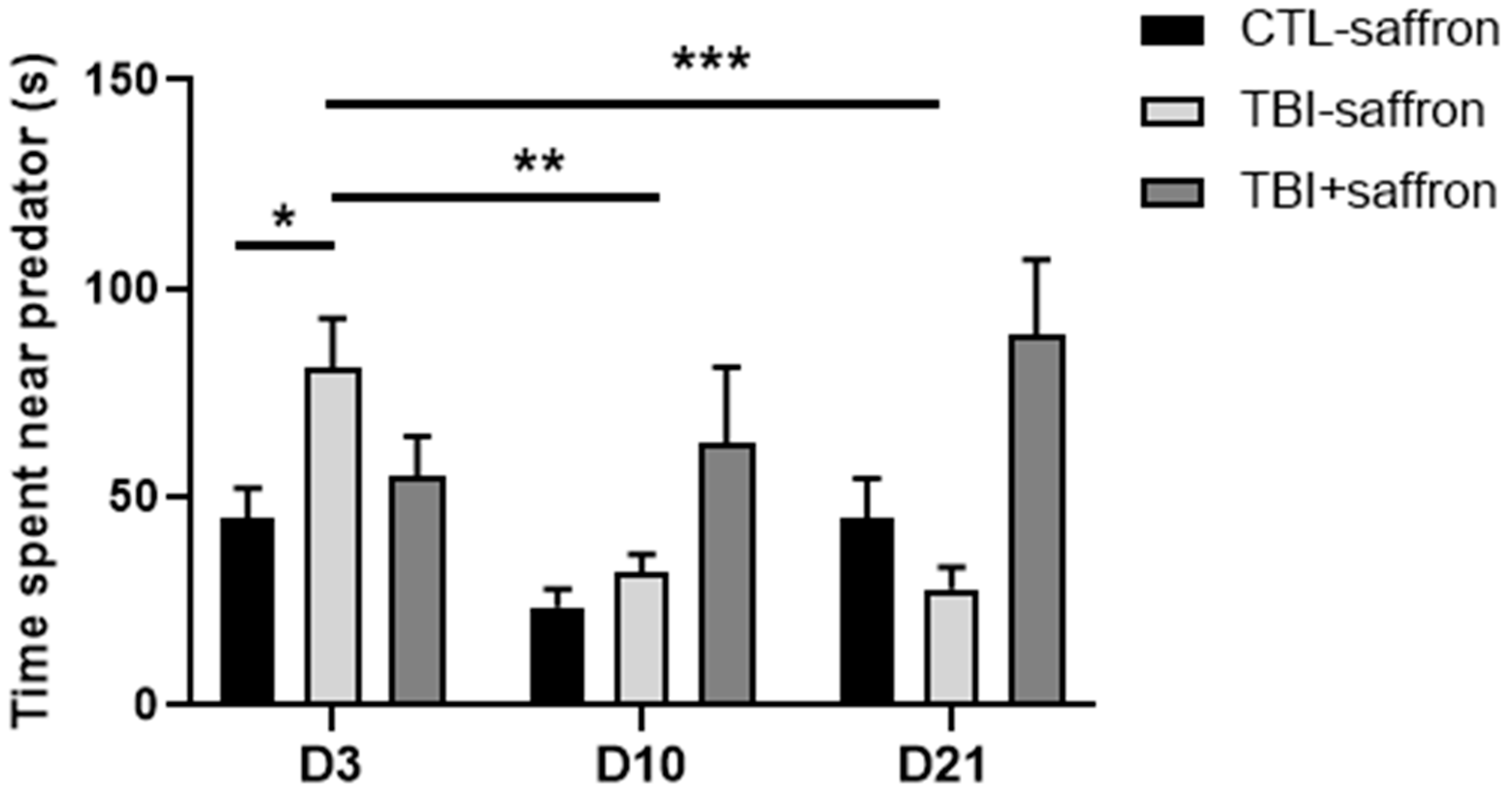
2.2. Saffron Prevents Alteration of Post-TBI Fear Processes
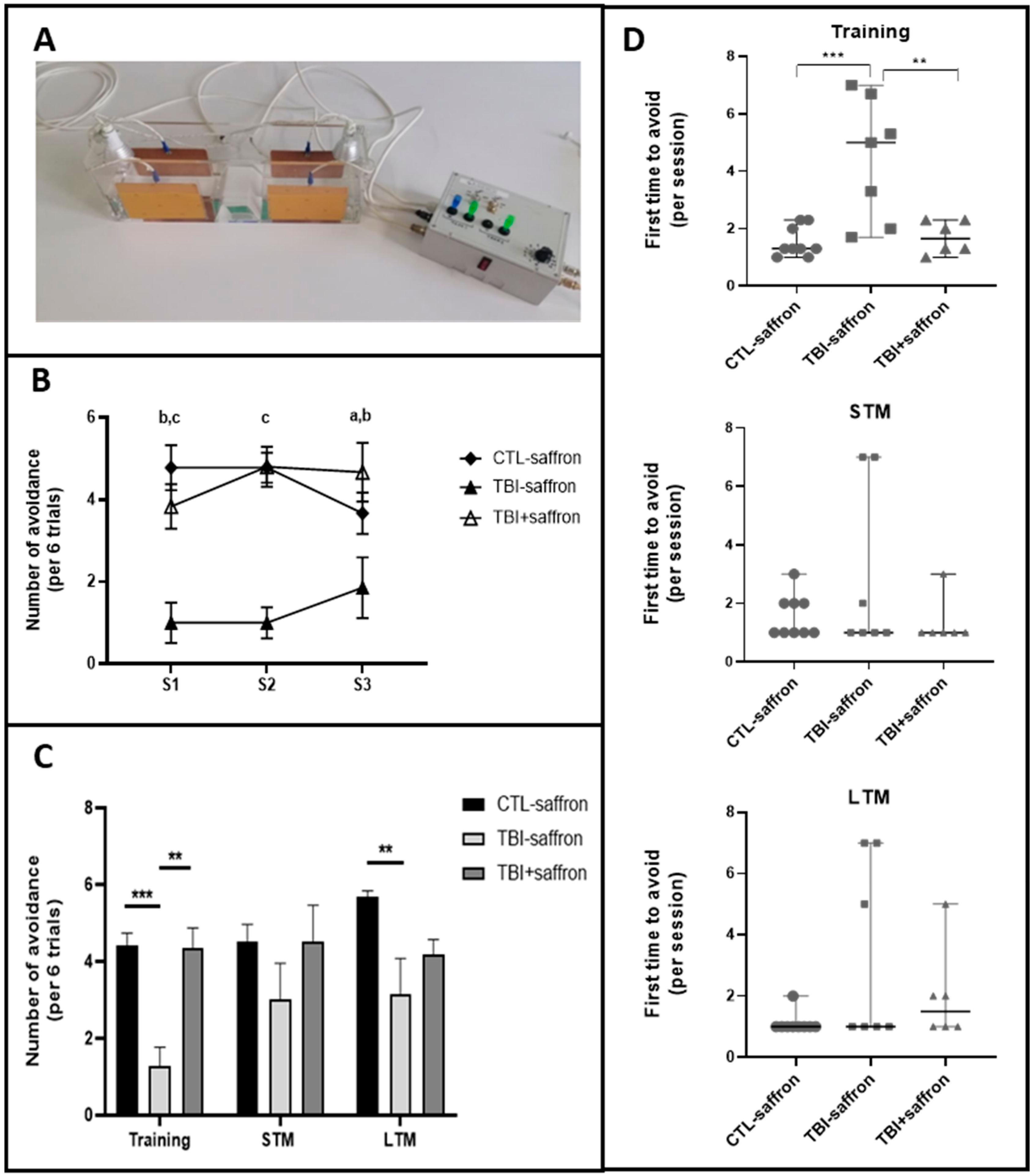
2.3. Saffron Ameliorate Learning and Memory Performance in Induced-TBI Zebrafish
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Housing
4.2. Saffron Extract Preparation
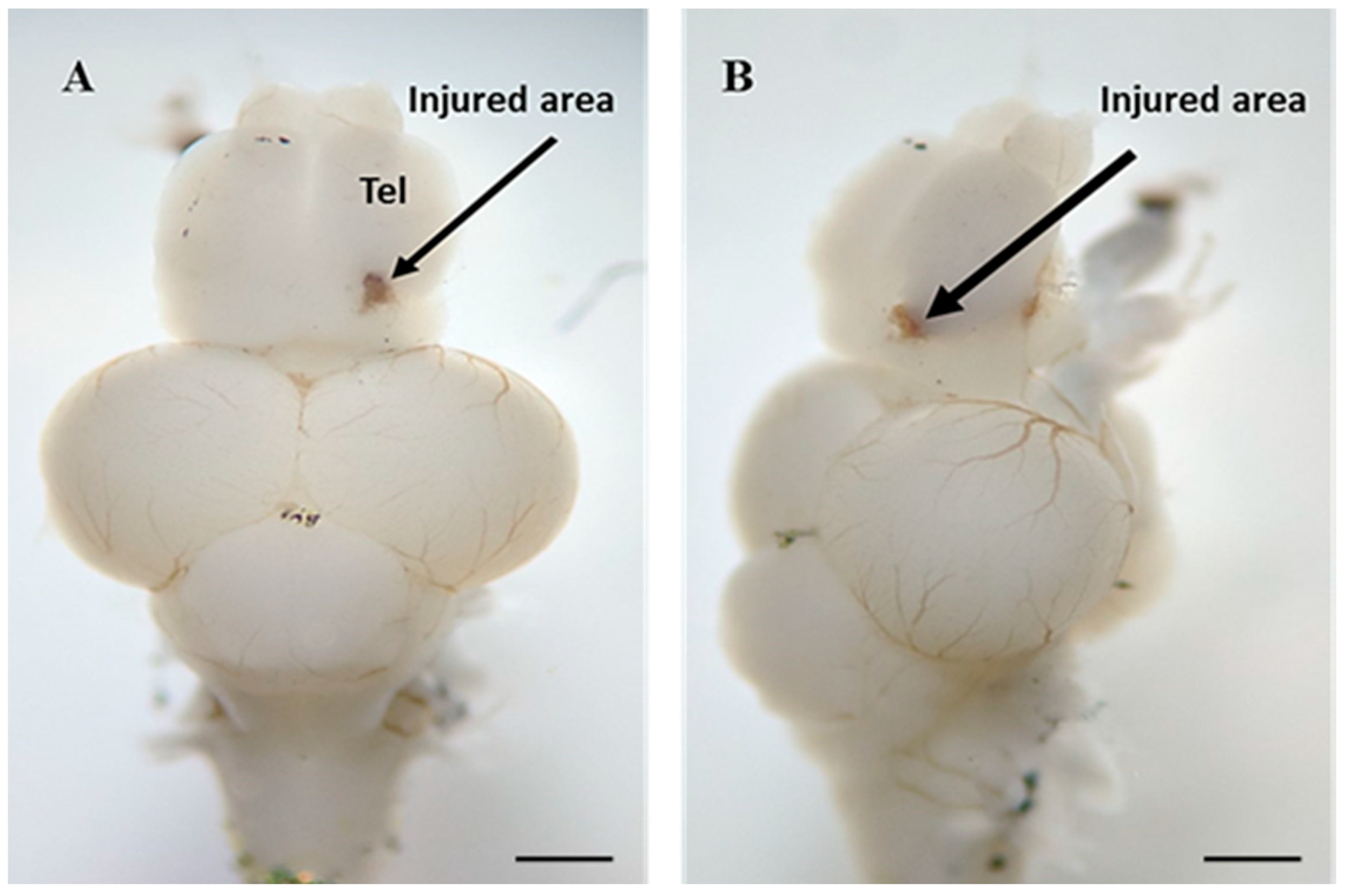
4.3. Traumatic Brain Injury Induction
4.4. Behavioral Assessment
4.5. Novel Tank Test
4.6. Light and Dark Test
4.7. Predator Test
4.8. Active Avoidance Test
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stocchetti, N.; Zanier, E.R. Chronic impact of traumatic brain injury on outcome and quality of life: A narra-tive review. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Capizzi, A.; Woo, J.; Verduzco-Gutierrez, M. Traumatic Brain Injury: An Overview of Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Medical Management. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 104, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/traumaticbraininjury/index.html (accessed on 25 September 2022).
- Dewan, M.C.; Rattani, A.; Gupta, S.; Baticulon, R.E.; Hung, Y.C.; Punchak, M.; Agrawal, A.; Adeleye, A.O.; Shrime, M.G.; Rubiano, A.M.; et al. Estimating the global incidence of traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 130, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prins, M.; Greco, T.; Alexander, D.; Giza, C.C. The pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury at a glance. Dis. Models Mech. 2013, 6, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jassam, Y.N.; Izzy, S.; Whalen, M.; McGavern, D.B.; El Khoury, J. Neuroimmunology of Traumatic Brain Injury: Time for a Paradigm Shift. Neuron 2017, 95, 1246–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hentig, J.; Cloghessy, K.; Lahne, M.; Jung, Y.J.; Petersen, R.A.; Morris, A.C.; Hyde, D.R. Zebrafish Blunt-Force TBI Induces Heterogenous Injury Pathologies That Mimic Human TBI and Responds with Sonic Hedgehog-Dependent Cell Proliferation across the Neuroaxis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsett, C.R.; McGuire, J.L.; DePasquale, E.A.; Gardner, A.E.; Floyd, C.L.; McCullumsmith, R.E. Glutamate Neurotransmission in Rodent Models of Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 34, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werner, C.; Engelhard, K. Pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury. Br. J. Anaesth. 2007, 99, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galgano, M.; Toshkezi, G.; Qiu, X.; Russell, T.; Chin, L.; Zhao, L.R. Traumatic Brain Injury: Current Treatment Strategies and Future Endeavors. Cell Transplant. 2017, 26, 1118–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonathan, M.; Silver, M.D.; Thomas, W.; McAllister, M.D.; David, B. Arciniegas, M.D. Depression and Cognitive Complaints Following Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Am. J. Psychiatry 2009, 166, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaze, J.; Choi, I.; Wang, Z.; Umali, M.; Mendelev, N.; Tschiffely, A.E.; Ahlers, S.T.; Elder, G.A.; Ge, Y.; Haghighi, F. Blast-Related Mild TBI Alters Anxiety-Like Behavior and Transcriptional Signatures in the Rat Amygdala. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, D.L.; Davies, D.R.; Barr, J.L.; Manzerra, P.; Forster, G.L. Mild traumatic brain injury in the rat alters neuronal number in the limbic system and increases conditioned fear and anxiety-like behaviors. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 235, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheras, A.L.; Dix, B.; Carmo, O.M.S.; Young, A.E.; Gill, V.N.; Sun, J.L.; Booker, A.R.; Thomason, H.A.; Ibrahim, A.E.; Stanislaw, L.; et al. Genetic Pathways of Neuroregeneration in a Novel Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Model in Adult Zebrafish. eNeuro 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasquoine, P.G. Learning in post-traumatic amnesia following extremely severe closed head injury. Brain Inj. 1991, 5, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmick, K.M.; Spells, C.A.; Malik, S.Z.; Davies, C.A.; Marion, D.W.; Hinds, S.R. Traumatic brain injury in the US military: Epidemiology and key clinical and research programs. Brain Imaging Behav. 2015, 9, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, L.; Rao, W.; Su, N.; Hui, H.; Wang, L.; Peng, C.; Tu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Fei, Z. Neuroprotective effects of crocin against traumatic brain injury in mice: Involvement of notch signaling pathway. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 591, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowitz, T.; Menon, D.K. Exploring new routes for neuroprotective drug development in traumatic brain injury. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 27rv21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklund, N.; Bakshi, A.; Castelbuono, D.J.; Conte, V.; McIntosh, T.K. Evaluation of pharmacological treatment strategies in traumatic brain injury. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 1645–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aruoma, O.I.; Bahorun, T.; Jen, L.S. Neuroprotection by bioactive components in medicinal and food plant extracts. Mutat. Res. 2003, 544, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigford, G.E.; Del Rossi, G. Supplemental substances derived from foods as adjunctive therapeutic agents for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and disorders. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spencer, J.P. Flavonoids: Modulators of brain function? Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99, ES60–ES77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheff, S.W.; Ansari, M.A. Natural Compounds as a Therapeutic Intervention following Traumatic Brain Injury: The Role of Phytochemicals. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 34, 1491–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bakshi, H.A.; Hakkim, F.L.; Sam, S. Molecular Mechanism of Crocin Induced Caspase Mediated MCF-7 Cell Death: In Vivo Toxicity Profiling and Ex Vivo Macrophage Activation. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Razavi, B.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Saffron: A promising natural medicine in the treatment of metabolic syndrome. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1679–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razak, S.I.A.; Anwar Hamzah, M.S.; Yee, F.C.; Kadir, M.R.A.; Nayan, N.H.M. A Review on Medicinal Properties of Saffron toward Major Diseases. J. Herbs Spices Med. Plants 2017, 23, 98–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finley, J.W.; Gao, S. A Perspective on Crocus sativus L. (Saffron) Constituent Crocin: A Potent Water-Soluble Antioxidant and Potential Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 1005–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milajerdi, A.; Jazayeri, S.; Hashemzadeh, N.; Shirzadi, E.; Derakhshan, Z.; Djazayeri, A.; Akhondzadeh, S. The effect of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) hydroalcoholic extract on metabolic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A triple-blinded randomized clinical trial. J. Res. Med. Sci. Off. J. Isfahan Univ. Med. Sci. 2018, 23, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaei, A.; Hassanpour Moghadam, M.; Sajadi Tabassi, S.A.; Mohajeri, S.A. Crocin, the main active saffron constituent, as an adjunctive treatment in major depressive disorder: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, pilot clinical trial. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 174, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashmoul, M.; Azlan, A.; Khaza’ai, H.; Yusof, B.N.; Noor, S.M. Saffron: A Natural Potent Antioxidant as a Promising Anti-Obesity Drug. Antioxidants 2013, 2, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salem, M.; Shaheen, M.; Tabbara, A.; Borjac, J. Saffron extract and crocin exert anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects in a repetitive mild traumatic brain injury mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, J.; Schwab, M.E.; Popovich, P.G. Central nervous system regenerative failure: Role of oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, and microglia. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 7, a020602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindsey, B.W.; Douek, A.M.; Loosli, F.; Kaslin, J. A Whole Brain Staining, Embedding, and Clearing Pipeline for Adult Zebrafish to Visualize Cell Proliferation and Morphology in 3-Dimensions. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haffter, P.; Granato, M.; Brand, M.; Mullins, M.C.; Hammerschmidt, M.; Kane, D.A.; Odenthal, J.; van Eeden, F.J.; Jiang, Y.J.; Heisenberg, C.P.; et al. The identification of genes with unique and essential functions in the development of the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Development 1996, 123, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbosa, J.S.; Ninkovic, J. Adult neural stem cell behavior underlying constitutive and restorative neurogenesis in zebrafish. Neurogenesis 2016, 3, e1148101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, N. Studies on the teleost brain morphology in search of the origin of cognition. Jpn. Psychol. Res. 2009, 51, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, N.; Shimizu, K.; Sawamoto, K. Neuronal regeneration in a zebrafish model of adult brain injury. Dis. Models Mech. 2012, 5, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cacialli, P.; Lucini, C. Adult neurogenesis and regeneration in zebrafish brain: Are the neurotrophins involved in? Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 2067–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacialli, P. Neurotrophins Time Point Intervention after Traumatic Brain Injury: From Zebrafish to Human. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.K.; Sahu, M.R.; Mondal, A.C. Induction of oxidative stress and apoptosis in the injured brain: Potential relevance to brain regeneration in zebrafish. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 5099–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.D.; Cerutti, D.T. Frontiers in Neuroscience Behavioral Neuroscience of Zebrafish. In Methods of Behavior Analysis in Neuroscience; Buccafusco, J.J., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Magno, L.D.; Fontes, A.; Gonçalves, B.M.; Gouveia, A., Jr. Pharmacological study of the light/dark preference test in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Waterborne administration. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 135, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Betti, G.; Hensel, A. Saffron in phytotherapy: Pharmacology and clinical uses. Wien Med. Wochenschr. 2007, 157, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javadi, B.; Sahebkar, A.; Emami, S.A. A survey on saffron in major islamic traditional medicine books. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 2013, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer, A.V.; Whitten, D.L.; Hawrelak, J.A. Herbal medicines, other than St. John’s Wort, in the treatment of depression: A systematic review. Altern Med. Rev. 2011, 16, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khazdair, M.R.; Boskabady, M.H.; Hosseini, M.; Rezaee, R.; A, M.T. The effects of Crocus sativus (saffron) and its constituents on nervous system: A review. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2015, 5, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El Midaoui, A.; Ghzaiel, I.; Vervandier-Fasseur, D.; Ksila, M.; Zarrouk, A.; Nury, T.; Khallouki, F.; El Hessni, A.; Ibrahimi, S.O.; Latruffe, N.; et al. Saffron (Crocus sativus L.): A Source of Nutrients for Health and for the Treatment of Neuropsychiatric and Age-Related Diseases. Nutrients 2022, 14, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.J.; Saleh, M.S.M.; Basharuddin, S.; Zamri, S.H.B.; Mohd Najib, M.H.B.; Che Ibrahim, M.Z.B.; Binti Mohd Noor, N.A.; Binti Mazha, H.N.; Mohd Hassan, N.; Khatib, A. Saffron (Crocus sativus L.): As an Antidepressant. J. Pharm. Bioallied. Sci. 2018, 10, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlouf, H.; Saksouk, M.; Habib, J.; Chahine, R. Determination of antioxidant activity of saffron taken from the flower of Crocus sativus grown in Lebanon. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 8093–8100. [Google Scholar]
- Samaha, H.; Chahine, N.; Sobolev, A.P.; Menghini, L.; Makhlouf, H. (1)H-NMR Metabolic Profiling and Antioxidant Activity of Saffron (Crocus sativus) Cultivated in Lebanon. Molecules 2021, 26, 4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallya, S.; Sutherland, J.; Pongracic, S.; Mainland, B.; Ornstein, T.J. The manifestation of anxiety disorders after traumatic brain injury: A review. J. Neurotrauma 2015, 32, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker-Collo, S.; Theadom, A.; Jones, K.; Starkey, N.; Kahan, M.; Feigin, V. Depression and anxiety across the first 4 years after mild traumatic brain injury: Findings from a community-based study. Brain Inj. 2018, 32, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Noraei, N.B. Anxiolytic and hypnotic effect of Crocus sativus aqueous extract and its constituents, crocin and safranal, in mice. Phyther. Res. 2009, 23, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monchaux De Oliveira, C.; Pourtau, L.; Vancassel, S.; Pouchieu, C.; Capuron, L.; Gaudout, D.; Castanon, N. Saffron Extract-Induced Improvement of Depressive-Like Behavior in Mice Is Associated with Modulation of Monoaminergic Neurotransmission. Nutrients 2021, 13, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitsikas, N. Constituents of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) as Potential Candidates for the Treatment of Anxiety Disorders and Schizophrenia. Molecules 2016, 21, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirsiger, S.; Simmen, H.-P.; Werner, C.M.L.; Wanner, G.A.; Rittirsch, D. Danger Signals Activating the Immune Response after Trauma. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 315941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pugin, J. How tissue injury alarms the immune system and causes a systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Ann. Intensive Care 2012, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramlackhansingh, A.F.; Brooks, D.J.; Greenwood, R.J.; Bose, S.K.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Kinnunen, K.M.; Gentleman, S.; Heckemann, R.A.; Gunanayagam, K.; Gelosa, G.; et al. Inflammation after trauma: Microglial activation and traumatic brain injury. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, K.M.; Bercum, F.M.; McCallum, D.L.; Rudy, J.W.; Frey, L.C.; Johnson, K.W.; Watkins, L.R.; Barth, D.S. Acute neuroimmune modulation attenuates the development of anxiety-like freezing behavior in an animal model of traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 1886–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Younesi, H.M. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of Crocus sativus L. stigma and petal extracts in mice. BMC Pharm. 2002, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerriero, R.M.; Giza, C.C.; Rotenberg, A. Glutamate and GABA imbalance following traumatic brain injury. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2015, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatziagapiou, K.; Lambrou, G.I. The Protective Role of Crocus Sativus L. (Saffron) Against Ischemia- Reperfusion Injury, Hyperlipidemia and Atherosclerosis: Nature Opposing Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2018, 14, 272–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaee, R.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Safranal: From an aromatic natural product to a rewarding pharmacological agent. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 2013, 16, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jackson, P.A.; Forster, J.; Khan, J.; Pouchieu, C.; Dubreuil, S.; Gaudout, D.; Moras, B.; Pourtau, L.; Joffre, F.; Vaysse, C.; et al. Effects of Saffron Extract Supplementation on Mood, Well-Being, and Response to a Psychosocial Stressor in Healthy Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Parallel Group, Clinical Trial. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 606124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, S.K.; Mondal, A.C. TrkB receptor antagonism inhibits stab injury induced proliferative response in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 672, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, T.; Abnous, K.; Vahdati, F.; Mehri, S.; Razavi, B.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Antidepressant Effect of Crocus sativus Aqueous Extract and its Effect on CREB, BDNF, and VGF Transcript and Protein Levels in Rat Hippocampus. Drug Res. 2015, 65, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari-Fakhrabadi, M.; Najafi, M.; Mortazavian, S.; Memari, A.H.; Shidfar, F.; Shahbazi, A.; Heshmati, J. Saffron (Crocus Sativus L.), Combined with Endurance Exercise, Synergistically Enhances BDNF, Serotonin, and NT-3 in Wistar Rats. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 9, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximino, C.; Benzecry, R.; Rosemberg, D.; Losch de Oliveira, D.; Blaser, R.; Oliveira, K.R.H.; Herculano, A.; Batista, E. A comparison of the light/dark and novel tank tests in zebrafish. Behaviour 2012, 149, 1099–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, F.; López, J.C.; Vargas, J.P.; Gómez, Y.; Broglio, C.; Salas, C. Conservation of spatial memory function in the pallial forebrain of reptiles and ray-finned fishes. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 2894–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Portavella, M.; Torres, B.; Salas, C. Avoidance Response in Goldfish: Emotional and Temporal Involvement of Medial and Lateral Telencephalic Pallium. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baxter, M.G.; Croxson, P.L. Facing the role of the amygdala in emotional information processing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21180–21181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmer, C.P.; Metheny, H.E.; Elkind, J.A.; Cohen, A.S. Diminished amygdala activation and behavioral threat response following traumatic brain injury. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 277, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hadj-Bouziane, F.; Liu, N.; Bell, A.H.; Gothard, K.M.; Luh, W.-M.; Tootell, R.B.H.; Murray, E.A.; Ungerleider, L.G. Amygdala lesions disrupt modulation of functional MRI activity evoked by facial expression in the monkey inferior temporal cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E3640–E3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lan, Y.L.; Li, S.; Lou, J.C.; Ma, X.C.; Zhang, B. The potential roles of dopamine in traumatic brain injury: A preclinical and clinical update. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 2616–2631. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kayser, A.S.; Allen, D.C.; Navarro-Cebrian, A.; Mitchell, J.M.; Fields, H.L. Dopamine, corticostriatal connectivity, and intertemporal choice. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 9402–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettehadi, H.; Mojabi, S.; Ranjbaran, M.; Shams, J.; Sahraei, H.; Hedayati, M.; Asefi, F. Aqueous Extract of Saffron (Crocus sativus) Increases Brain Dopamine and Glutamate Concentrations in Rats. J. Behav. Brain Sci. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayati, Z.; Yang, G.; Ayati, M.H.; Emami, S.A.; Chang, D. Saffron for mild cognitive impairment and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. BMC Complement Med. 2020, 20, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bains, M.; Hall, E.D. Antioxidant therapies in traumatic brain and spinal cord injury. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2012, 1822, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aoki, T.; Kinoshita, M.; Aoki, R.; Agetsuma, M.; Aizawa, H.; Yamazaki, M.; Takahoko, M.; Amo, R.; Arata, A.; Higashijima, S.; et al. Imaging of neural ensemble for the retrieval of a learned behavioral program. Neuron 2013, 78, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceci, M.; Mariano, V.; Romano, N. Zebrafish as a translational regeneration model to study the activation of neural stem cells and role of their environment. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 30, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupte, R.; Brooks, W.; Vukas, R.; Pierce, J.; Harris, J. Sex Differences in Traumatic Brain Injury: What We Know and What We Should Know. J. Neurotrauma 2019, 36, 3063–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodard, A.; Barbery, B.; Wilkinson, R.; Strozyk, J.; Milner, M.; Doucette, P.; Doran, J.; Appleby, K.; Atwill, H.; Bell, W.E.; et al. The role of neuronal nitric oxide and its pathways in the protection and recovery from neurotoxin-induced de novo hypokinetic motor behaviors in the embryonic zebrafish (Danio rerio). AIMS Neurosci. 2019, 6, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, R.; Eid, S.; Chahine, R.; Chabi, B.; Bonnieu, A.; Sabban, M.E.; Najjar, F.; Hamade, A. Antioxidant effects of lebanese Crocus sativus L. and its main components, crocin and safranal, on human skeletal muscle cells. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 40, 101250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaoul, V.; Awad, M.; Harb, F.; Najjar, F.; Hamade, A.; Nabout, R.; Soueid, J. Saffron Extract Attenuates Anxiogenic Effect and Improves Cognitive Behavior in an Adult Zebrafish Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911600
Chaoul V, Awad M, Harb F, Najjar F, Hamade A, Nabout R, Soueid J. Saffron Extract Attenuates Anxiogenic Effect and Improves Cognitive Behavior in an Adult Zebrafish Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911600
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaoul, Victoria, Maria Awad, Frederic Harb, Fadia Najjar, Aline Hamade, Rita Nabout, and Jihane Soueid. 2022. "Saffron Extract Attenuates Anxiogenic Effect and Improves Cognitive Behavior in an Adult Zebrafish Model of Traumatic Brain Injury" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911600
APA StyleChaoul, V., Awad, M., Harb, F., Najjar, F., Hamade, A., Nabout, R., & Soueid, J. (2022). Saffron Extract Attenuates Anxiogenic Effect and Improves Cognitive Behavior in an Adult Zebrafish Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911600





