Lasting Peripheral and Central Effects of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Experimental Muscle Hypertonia in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Early Effects of BoNT-A on Spastic Paralysis Are Concomitant with Local Muscular Neuroparalytic Effect
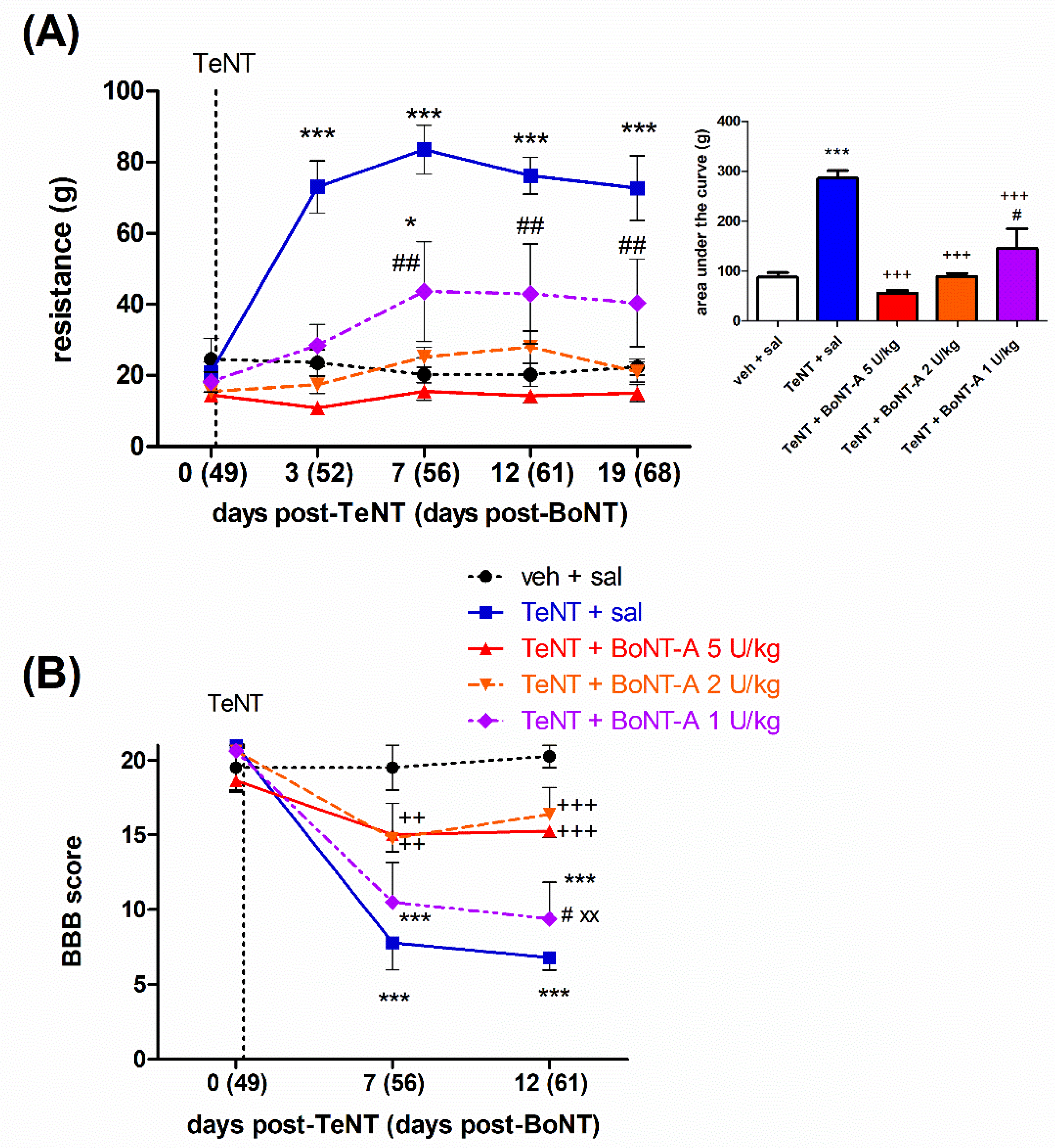
2.2. Late Effects of BoNT-A on Spastic Paralysis Are Dose-Dependent and Augmented by Central Toxin Action
2.3. Lasting Effects of BoNT-A Are Accompanied by Toxin’s Ongoing Enzymatic Activity in Both, Injected Muscle and Spinal Cord
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Pharmacological Treatment
4.3. Behavioral Motor Assessment
4.3.1. Digit Abduction Score
4.3.2. Resistance to Ankle Dorsiflexion
4.3.3. Basso Beattie Bresnahan Locomotor Scale
4.3.4. Measurement of Lower Leg Muscle Atrophy
4.4. Time-Course of Experiments
4.4.1. Experiment No 1. The Dose-Response Assessment of Early and Late BoNT-A Antispastic Action
4.4.2. Experiment No 2. Assessment of the Role of Central Action and Transcytosis in the Late BoNT-A Antispastic Activity
4.5. Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, M.; Masuyer, G.; Stenmark, P. Botulinum and Tetanus Neurotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 811–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C. Tables of Toxicity of Botulinum and Tetanus Neurotoxins. Toxins 2019, 11, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arnon, S.S.; Schechter, R.; Inglesby, T.V.; Henderson, D.A.; Bartlett, J.G.; Ascher, M.S.; Eitzen, E.; Fine, A.D.; Hauer, J.; Layton, M.; et al. Botulinum Toxin as a Biological Weapon. JAMA 2001, 285, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, G.; Benfenati, F.; Poulain, B.; Rossetto, O.; Polverino de Laureto, P.; DasGupta, B.R.; Montecucco, C. Tetanus and Botulinum-B Neurotoxins Block Neurotransmitter Release by Proteolytic Cleavage of Synaptobrevin. Nature 1992, 359, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, J.; Chapman, E.R.; Link, E.; Binz, T.; Yamasaki, S.; De Camilli, P.; Südhof, T.C.; Niemann, H.; Jahn, R. Botulinum Neurotoxin A Selectively Cleaves the Synaptic Protein SNAP-25. Nature 1993, 365, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J. Botulinum Toxin: State of the Art. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledda, C.; Artusi, C.A.; Tribolo, A.; Rinaldi, D.; Imbalzano, G.; Lopiano, L.; Zibetti, M. Time to Onset and Duration of Botulinum Toxin Efficacy in Movement Disorders. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 3706–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallett, M. Explanation of Timing of Botulinum Neurotoxin Effects, Onset and Duration, and Clinical Ways of Influencing Them. Toxicon 2015, 107, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogozhin, A.A.; Pang, K.K.; Bukharaeva, E.; Young, C.; Slater, C.R. Recovery of Mouse Neuromuscular Junctions from Single and Repeated Injections of Botulinum Neurotoxin A. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 3163–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijmeijer, S.W.R.; Koelman, J.H.T.M.; Standaar, T.S.M.; Postma, M.; Tijssen, M.A.J. Cervical Dystonia: Improved Treatment Response to Botulinum Toxin after Referral to a Tertiary Centre and the Use of Polymyography. Park. Relat. Disord. 2013, 19, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gracies, J.-M.; Lugassy, M.; Weisz, D.J.; Vecchio, M.; Flanagan, S.; Simpson, D.M. Botulinum Toxin Dilution and Endplate Targeting in Spasticity: A Double-Blind Controlled Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 90, 9–16.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallett, M. Mechanism of Action of Botulinum Neurotoxin: Unexpected Consequences. Toxicon 2018, 147, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchio, R.; Caleo, M. More than at the Neuromuscular Synapse: Actions of Botulinum Neurotoxin A in the Central Nervous System. Neuroscientist 2015, 21, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weise, D.; Weise, C.M.; Naumann, M. Central Effects of Botulinum Neurotoxin-Evidence from Human Studies. Toxins 2019, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gracies, J.-M. Physiological Effects of Botulinum Toxin in Spasticity. Mov. Disord. 2004, 19 (Suppl. S8), S120–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, R.L.; Dressler, D. On Muscle Spindles, Dystonia and Botulinum Toxin. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17 (Suppl. S1), 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinti, M.; Costantino, F.; Bayle, N.; Simpson, D.M.; Weisz, D.J.; Gracies, J.-M. Spastic Cocontraction in Hemiparesis: Effects of Botulinum Toxin. Muscle Nerve 2012, 46, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymard, C.; Giboin, L.-S.; Lackmy-Vallée, A.; Marchand-Pauvert, V. Spinal Plasticity in Stroke Patients after Botulinum Neurotoxin A Injection in Ankle Plantar Flexors. Physiol. Rep. 2013, 1, e00173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand-Pauvert, V.; Aymard, C.; Giboin, L.-S.; Dominici, F.; Rossi, A.; Mazzocchio, R. Beyond Muscular Effects: Depression of Spinal Recurrent Inhibition after Botulinum Neurotoxin A. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wohlfarth, K.; Schubert, M.; Rothe, B.; Elek, J.; Dengler, R. Remote F-Wave Changes after Local Botulinum Toxin Application. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 112, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Takashima, K.; Kamochi, H.; Kusaka, G.; Shinoda, S.; Watanabe, E. Treatment with Botulinum Toxin Improves the Hyperexcitability of the Facial Motoneuron in Patients with Hemifacial Spasm. Neurol. Res. 2010, 32, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-López, B.; de la Cruz, R.R.; Pastor, A.M.; Delgado-García, J.M. Effects of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A on Abducens Motoneurons in the Cat: Alterations of the Discharge Pattern. Neuroscience 1997, 81, 437–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, A.M.; Moreno-López, B.; De La Cruz, R.R.; Delgado-García, J.M. Effects of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A on Abducens Motoneurons in the Cat: Ultrastructural and Synaptic Alterations. Neuroscience 1997, 81, 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Forero, D.; Pastor, A.M.; Geiman, E.J.; Benítez-Temiño, B.; Alvarez, F.J. Regulation of Gephyrin Cluster Size and Inhibitory Synaptic Currents on Renshaw Cells by Motor Axon Excitatory Inputs. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antonucci, F.; Rossi, C.; Gianfranceschi, L.; Rossetto, O.; Caleo, M. Long-Distance Retrograde Effects of Botulinum Neurotoxin A. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3689–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matak, I.; Riederer, P.; Lacković, Z. Botulinum Toxin’s Axonal Transport from Periphery to the Spinal Cord. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 61, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koizumi, H.; Goto, S.; Okita, S.; Morigaki, R.; Akaike, N.; Torii, Y.; Harakawa, T.; Ginnaga, A.; Kaji, R. Spinal Central Effects of Peripherally Applied Botulinum Neurotoxin A in Comparison between Its Subtypes A1 and A2. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caleo, M.; Spinelli, M.; Colosimo, F.; Matak, I.; Rossetto, O.; Lackovic, Z.; Restani, L. Transynaptic Action of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type a at Central Cholinergic Boutons. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 10329–10337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marinelli, S.; Vacca, V.; Ricordy, R.; Uggenti, C.; Tata, A.M.; Luvisetto, S.; Pavone, F. The analgesic effect on neuropathic pain of retrogradely transported botulinum neurotoxin A involves Schwann cells and astrocytes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matak, I. Evidence for Central Antispastic Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type A. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornson, K.; Hays, R.; Graubert, C.; Price, R.; Won, F.; McLaughlin, J.F.; Cohen, M. Botulinum Toxin for Spasticity in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Comprehensive Evaluation. Pediatrics 2007, 120, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eek, M.N.; Himmelmann, K. No Decrease in Muscle Strength after Botulinum Neurotoxin-A Injection in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cosgrove, A.P.; Graham, H.K. Botulinum Toxin A Prevents the Development of Contractures in the Hereditary Spastic Mouse. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1994, 36, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.M.; Dou, Z.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Dai, M.; Yu, F.; Wang, Q.Y.; Jiang, L. Effects of Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection for Pathological Characteristic of Calf in Rats with Spinal Cord Injure. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2017, 97, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sätilä, H.; Kotamäki, A.; Koivikko, M.; Autti-Rämö, I. Low- and High-Dose Botulinum Toxin A Treatment: A Retrospective Analysis. Pediatr. Neurol. 2006, 34, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broide, R.S.; Rubino, J.; Nicholson, G.S.; Ardila, M.C.; Brown, M.S.; Aoki, K.R.; Francis, J. The Rat Digit Abduction Score (DAS) Assay: A Physiological Model for Assessing Botulinum Neurotoxin-Induced Skeletal Muscle Paralysis. Toxicon 2013, 71, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Périer, C.; Martin, V.; Cornet, S.; Favre-Guilmard, C.; Rocher, M.; Bindler, J.; Wagner, S.; Andriambeloson, E.; Rudkin, B.B.; Marty, R.; et al. Recombinant Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype A1 in Vivo Characterization. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2021, 9, e00857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichon, J.V.; McCaffrey, T.V.; Litchy, W.J.; Knops, J.L. The Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection on Compound Muscle Action Potential in an in Vivo Rat Model. Laryngoscope 1995, 105, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Deuschl, G.; Nebe, A.; Feifel, E.; Wissel, J.; Benecke, R.; Kessler, K.R.; Ceballos-Baumann, A.O.; Ohly, A.; Oertel, W.; et al. What Is the Optimal Dose of Botulinum Toxin A in the Treatment of Cervical Dystonia? Results of a Double Blind, Placebo Controlled, Dose Ranging Study Using Dysport. German Dystonia Study Group. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1998, 64, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rystedt, A.; Zetterberg, L.; Burman, J.; Nyholm, D.; Johansson, A. A Comparison of Botox 100 U/ML and Dysport 100 U/ML Using Dose Conversion Ratio 1. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 38, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priori, A.; Berardelli, A.; Mercuri, B.; Manfredi, M. Physiological Effects Produced by Botulinum Toxin Treatment of Upper Limb Dystonia. Changes in Reciprocal Inhibition between Forearm Muscles. Brain 1995, 118 Pt 3, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wree, A.; Mix, E.; Hawlitschka, A.; Antipova, V.; Witt, M.; Schmitt, O.; Benecke, R. Intrastriatal botulinum toxin abolishes pathologic rotational behaviour and induces axonal varicosities in the 6-OHDA rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 41, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawlitschka, A.; Wree, A. Experimental Intrastriatal Applications of Botulinum Neurotoxin-A: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, B.B.; Francis, J.; Brin, M.F.; Broide, R.S. Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A-Cleaved SNAP25 Is Confined to Primary Motor Neurons and Localized on the Plasma Membrane Following Intramuscular Toxin Injection. Neuroscience 2017, 352, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagoraiou, L.; Akay, T.; Martin, J.F.; Brownstone, R.M.; Jessell, T.M.; Miles, G.B. A Cluster of Cholinergic Premotor Interneurons Modulates Mouse Locomotor Activity. Neuron 2009, 64, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basso, D.M.; Beattie, M.S.; Bresnahan, J.C. A Sensitive and Reliable Locomotor Rating Scale for Open Field Testing in Rats. J. Neurotrauma 1995, 12, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homolak, J.; Babic Perhoc, A.; Knezovic, A.; Osmanovic Barilar, J.; Koc, F.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Salkovic-Petrisic, M. Disbalance of the Duodenal Epithelial Cell Turnover and Apoptosis Accompanies Insensitivity of Intestinal Redox Homeostasis to Inhibition of the Brain Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptors in a Rat Model of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuroendocrinology 2022, 112, 744–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šoštarić, P.; Vukić, B.; Tomašić, L.; Matak, I. Lasting Peripheral and Central Effects of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Experimental Muscle Hypertonia in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911626
Šoštarić P, Vukić B, Tomašić L, Matak I. Lasting Peripheral and Central Effects of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Experimental Muscle Hypertonia in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911626
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠoštarić, Petra, Barbara Vukić, Lea Tomašić, and Ivica Matak. 2022. "Lasting Peripheral and Central Effects of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Experimental Muscle Hypertonia in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911626
APA StyleŠoštarić, P., Vukić, B., Tomašić, L., & Matak, I. (2022). Lasting Peripheral and Central Effects of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Experimental Muscle Hypertonia in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911626





