Cancer Stem Cells and Their Vesicles, Together with Other Stem and Non-Stem Cells, Govern Critical Cancer Processes: Perspectives for Medical Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. CSCs and Their EVs Are Essential for Cancer Initiation and Its Processes
3. Role of MSCs and MSC-EVs
4. The Tumor Microenvironment: The Role of CSCs and Cooperative Cells
5. Development of Therapies: Methods and Tools
6. Progress in Clinical Medicine
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CSCs | cancer stem cells |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EVs | extracellular vesicles |
| GMP | good manufacturing practice |
| miRNAs, miR-number | microRNAs |
| MSCs | mesenchymal stem cells |
| MVB | multivesicular body |
| TME | tumoral microenvironment |
References
- Caplan, A.I. Mesenchymal stem cells. J. Orthop. Res. 1991, 9, 541–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, H.E.; Ceballos, E.M.; Smith, J.C.; Mancini, M.L.; Wrigh, R.P.; Regan, B.L.; Bishell, I.; Lucas, P.A. Pluripotent mesenchymal stem cells reside within avian connective tissue matrices. Vitr. Cell Dev. Biol.-Anim. 1993, 29, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballas, C.B.; Zieske, S.P.; Gerson, S.L. Adult bone marrow stem cells for cell and gene therapies: Implications for greater use. J. Cell Biochem. Suppl. 2002, 38, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devine, S.M. Mesenchymal stem cells: Will they have a role in the clinic? J. Cell Biochem. Suppl. 2002, 38, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuda, T.; Kosaka, N.; Takeshita, F.; Ochiya, T. The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal, stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Proteomics 2013, 13, 1637–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askenase, P.W. Ancient evolutionary origin and properties of universally produced natural exosomes contribute to their therapeutic superiority compared to artificial nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racchetti, G.; Meldolesi, J. Extracellular vesicles of mesenchymal stem cells: Therapeutic properties discovered with extraordinary success. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, D.; Dick, J.E. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Clarke, I.D.; Terasaki, M.; Bonn, V.E.; Hawkins, C.; Squire, J.; Dirks, P.B. Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5821–5828. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Halj, M.; Wicha, M.S.; Benito-Hernandez, A.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F. Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3983–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.K.; Hawkins, C.; Clarke, J.D.; Squire, J.A.; Bayani, J.; Hide, T.; Henkelman, R.M.; Cusimano, M.D.; Dirks, P.D. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 2004, 432, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.B.; Quin, L.X.; Liu, Y.K. Adult stem cells and cancer stem cells: Tie or tear apart? J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 131, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Thiennanga, K.N.; Leishear, K.; Finko, R.; Kulo, A.N.; Holz, S.; Van Belle, P.A.; Xu, X.; Elder, D.E.; Herlyn, M. A tumorigenic sub-population with stem cell properties in melanoma. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9328–9337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalerba, P.; Scott, J.D.; Park, I.K.; Liu, R.; Wang, X.; Cho, R.W.; Hoey, T.; Gurney, A.; Huang, E.H.; Simeone, D.M.; et al. Phenotypical characterization of human colorectal cancer stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 104, 10158–10163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attar-Schneider, O.; Dabbah, M.; Drucker, L.; Gottfried, M. Niche origin of mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles determines opposing effects on NSCLC: Primary versus metastatic. Cell Signal. 2020, 65, 109456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Han, S.; Wan, L.; Sun, X.; Chen, H. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles confer antitumor activity in preclinical treatment of breast cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 157, 104843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gener, P.; Gonzalez-Callejo, P.; Serra-Franzoso, J.; Andrade, F.; Rafael, D.; Albasolo, I.; Schwartz, S. The potential nanomedicine to alter cancer stem-cell dynamics: The impact of extracellular vesicles. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 2785–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.T.; Zheng, Y.Y. Dissecting the multi-omic atlas of the exosomes released by human lung carcinoma stem-like cells. NPJ Genom. Med. 2021, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Wu, D.; Wu, P.; Chen, Z.; Huang, J. The cancer stem cell niche: Cross talk between cancer, stem cells and their microenvironment. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 3945–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afify, S.M.; Seno, M. Conversion of stem cells to cancer stem cells: Undercurrent of cancer initiation. Cancers 2019, 11, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afify, S.M.; Hassan, G.; Yan, T.; Seno, A.; Seno, M. Cancer stem cell initiation by tumor-derived extracellular vesicles. In Methods in Molecular Biolog; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Kim, Y.N.; Kim, Y.E.; Lee, S.Y.; Shin, M.J.; Do, E.K.; Choi, K.U.; Kim, S.C.; Suh, D.S.; Kim, J.H. TRIB2 stimulates cancer stem-like properties through activation of AKT-Wnt-β-catenin signaling axis. Mol. Cells 2021, 44, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Gao, T.; Xie, J.; Hung, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Qi, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Gao, G.; et al. FUBP1 promotes colorectal cancer stemness and metastasis via DVL1-mediated activation of WNT/β-catenin signaling. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 3490–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, L.P.; Diaz, E.; Reya, T. The role of the microenvironment and immune system in regulating stem cell fate in cancer. Trends Cancer 2021, 7, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Rubenich, D.S.; Zareba, L.; Siewiera, J.; Pieper, J.; Braganhol, E.; Reichert, T.E.; Szczepanski, M.J. Potential role of tumor cell and stroma cell-derived small in promoting a pro-angiogenic tumor microenvironment. Cancers 2020, 12, 3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushi, D.; Takahashi, R.S.; Mochizuki, M.; Fujimori, S.; Kokure, T.; Sugai, T.; Iwai, W.; Wakui, T.; Abue, M.; Murakami, K.; et al. BEX2 is required for maintaining dormant cancer stem cell in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 4580–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares Lindoso, R.S.; Collini, F.; Vieyra, A. Extracellular vesicles as regulatory of tumor fate: Crosstalk among cancer stem cells, tumor cells and mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Investig. 2017, 4, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desrochers, L.M.; Antonyak, M.A.; Crione, R. Extracellular vesicles: Satellites of information transfer in cancer and stem cell biology. Dev. Cell 2016, 37, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bajetto, A.; Thellung, S.; Dellacasagrande, I.; Pagano, A.; Barbieri, F.; Florio, T. Cross talk between mesenchymal and glioblastoma stem cells: Communication beyond controversies. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 1310–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, D.; Ren, X.; Han, M.; Xu, X.; Gu, Y.; Wang, X. Cancer-associated fibroblasts-driven exosomes suppress immune cell function in breast cancer via the miR-92/PD-L1 pathway. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramini, B.; Masciale, V.; Grisendi, G.; Banchelli, F.; D’Amico, R.; Majorana, A.; Morandi, U.; Dominici, M.; Haider, K.H. Cancer stem cells and macrophages: Molecular connections and future perspectives against cancer. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 230–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnoli, L.; De Santis, F.; Volpari, T.; Vernieri, C.; Tagliabue, E.; Di Nicola, M.; Pupa, S.M. Cancer stem cells: Devil or savior-looking behind the scenes of immunotherapy failure. Cells 2020, 9, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.S.; Lin, E.Y.; Chiou, T.W.; Harn, H.J. Exosomes in clinical trial and their production in compliance with good manufacturing practice. Ci Ji Yi Xue Za Zhi 2019, 32, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshkin, S.A.; Anatskaya, O.V.; Vinogradov, A.E.; Uversky, V.N.; Dayhoff, G.W.; Bystriakova, M.A.; Pospelov, V.A.; Tolkunova, E.N. Isolation and characterization of human colon adenocarcinoma stem-like cells based on the endogenous expression of stem markers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshimori, N.; Guo, Y.; Taniguchi, S. An emerging role of cellular crosstalk in the cancer stem cell niche. J. Pathol. 2021, 254, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Song, Q.; Wu, M.; Zheng, W. Emerging roles of exosomes in the chemoresistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raudenska, M.; Balvan, J.; Masarik, M. Crosstalk between autophagy and endosome-related secretory pathways: A challenge for autophagy-based treatment of solid cancer. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kwak, M.S.; Lee, B.; Shin, J.M.; Aum, S.; Park, I.H.; Lee, M.G.; Shin, J.S. Secretory autophagy machinery and vesicular trafficking are involved in HMG1 secretion. Autophagy 2021, 17, 2345–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, S.; Pacussi, J.M.; Gifu, E.P.; Bestion, E.; Macek-Ilikova, Z.; Wong, G.; Bassissi, F.; Mehar, S.; Courcambeck, J.; Merle, P.; et al. GNS561, a new autophagy inhibitor active against cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma and metastasis from colorectal cancer. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 5432–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, T.; Xu, J.; Zhu, X. Self renewal molecular mechanisms of colorectal cancer stem cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez de Andres, J.; Grinan-Sison, C.; Jimenez, G.; Marchal, J.A. Cancer stem cell secretome in the tumor micro-environment: A key point for an effective personalized cancer treatment. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebelman, M.P.; Janssen, E.; Peftel, D.M.; Crudden, C. The forces driving cancer extracellular vesicle secretion. Neoplasia 2021, 23, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Zhang, J.; Yarden, Y.; Fu, L. The key roles of cancer stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, M.; Nakano, Y.; Nashimura, T.; Ivata, R.; Matsuda, S.; Hayashi, M.; Nakai, Y.; Nonaka, M.; Sugimoto, T. PC3-secreted microproteins expressed in glioblastoma stem-like cells and human glioma tissues. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 44, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Chen, J.J.; Song, S.H.; Su, J.; Zhao, L.H.; Liu, Q.G.; Yang, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Fu, Z.R.; et al. Inhibition of SIRTI1 limits self-renewal and oncogenesis by inducing senescence of liver cancer stem cells. Hepatol. Carcinoma 2021, 8, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiboonchalyanan, P.P.; Puthogking, P.; Chawlarean, V.; Harikarnpakdee, S.; Sukprasansap, M.; Chanvorachote, P.; Priprem, A.; Goyitraprom, P. Melatonin and its derivative disrupt cancer stem-like phenotypes of lung cancer cells via AKT down-regulation. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2021, 48, 1712–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Xu, X.; Ying, J.; Xie, T.; Cao, C. Transfer of metastatic traits via miR-200c in extracellular vesicles derived from colorectal cancer stem cells is inhibited by atractylenolide. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brossa, A.; Fonsato, V.; Grange, C.; Tritta, S.; Tappar, M.; Calvetti, R.; Cedrino, M.; Fallo, S.; Gontero, P.; Camussi, G.; et al. Extracellular vesicles from human liver stem cell-derived tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 1694–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Dong, C.; Chen, M.; Yang, T.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Wen, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; et al. Extracellular vesicle-mediated delivery of miR-101 inhibits lung metastasis in osteosarcoma. Theranostics 2020, 10, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Q.; Yuan, T.; Jiang, H.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, L.; Fu, R.M.; Luo, S.Q.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Z.Y.; Wen, K.M. MicroRNA-8063 targets heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein AB to inhibit the self renewal of colorectal cancer cells via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 46, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alraouil, N.N.; Hendrayani, S.F.; Ghebeh, H.; Al-Mohanna, F.H.; Aboussekhra, A. Osteoprotegerin (OPG) mediates the anti-carcinogenic effects of normal breast fibroblasts and target cancer stem cells via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cancer Lett. 2021, 520, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wei, W.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Liang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, W.; et al. Cancer-secreted exosomal miR-1468-5p promotes tumor immune escape via the immunosuppressive reprogramming of lymphatic vessels. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 1512–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, J.; Hu, K. Upregulation of the miR-663a inhibits the cancer stem cell-like properties of glioma via repressing the KDM2A-mediated TGF-β/SMAD signaling pathway. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 1935–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Huang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gu, J.; Yan, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, M.; Qian, H.; Xu, W. Exosomes derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2012, 315, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccaro, A.M.; Sacco, A.; Maiso, P.; Azab, A.K.; Tai, Y.T.; Reagan, M.; Azab, F.; Flores, L.M.; Campigotto, F.; Weller, E.; et al. BM mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes facilitate multiple myeloma progression. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1542–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.; Xue, J.; Yuan, X.; Yan, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhu, W.; Qian, H.; Xu, W. Exosomes derived from human mesenchymal stem cells confer drug resistance in gastric cancer. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2473–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Del Fattore, A.; Luciano, R.; Saracino, R.; Battafarano, G.; Rizzo, C.; Pascucci, L.; Alessandri, G.; Pessina, A.; Perrotta, A.; Fierabracci, A.; et al. Differential effects of extracellular vesicles secreted by mesenchymal stem cells from differential sources on glioblastoma cells. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2015, 15, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, A.J.M.; Tieu, A.; Gupta, M.; Slobodian, M.; Schorr, R.; Ramsay, T.; Rodriguez, R.A.; Fergusson, D.A.; Lalu, M.M.; Allan, D.S. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles in preclinical animal models of tumor growth: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2021, 12, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakhshiteh, F.; Atyabi, F.; Ostad, S.N. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes: A two edged sward in cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2847–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ying, H.; Lin, F.; Ding, R.; Wang, W.; Hong, W. Extracellular vesicles carrying MiR-193a derived from mesenchymal stem cells impede cell proliferation, migration and invasion in colon cancer by down-regulating FAK. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 394, 112144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Tian, R.; Zeng, H.; Wang, L.; Xia, M.; Zhu, H.; Zuo, C. Exosomal miRNA-1231 derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibits the activity of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 7728–7740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katakowski, M.; Buller, B.; Zheng, X.; Lu, Y.; Rogers, T.; Osobamiro, O.; Shu, W.; Jiang, F.; Chopp, M. Exosomes from marrow stromal cells expressing miR-146b inhibit glioma growth. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, H.; Wang, W.; Zhao, D.; Hong, J.; Yu, H.; Qi, L. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal micro-RNA-133b suppresses glioma progression via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by targeting EZH2. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vakhshiteh, F.; Rahmani, S.; Ostad, S.N.; Madjd, Z.; Dinarvand, R.; Atyabi, F. Exosomes derived from miR-34a-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells inhibit in vitro tumor growth: A new approach for drug delivery. Life Sci. 2021, 266, 118871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Chen, L.; Xia, C.; Wang, W.; Qi, J.; Li, A.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y. MiR-199a-modified exosomes from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve hepatocellular carcinoma chemosensitivity through mTOR pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quin, F.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, P.; Zhu, J. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosonal microRNA-208a promotes osteosarcoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 4734–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Hou, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Lu, C. Extracellular vesicles secreted by hypoxia pre-challenged mesenchymal stem cells promote non-small cell lung cancer cell growth and mobility as well as macrophage M2 polarization via miR-21-5p delivery. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Yan, J.; Song, T.; Zhong, C.; Kuang, J.; Mo, Y.; Tan, J.; Li, D.; Sui, Z.; Cai, K.; et al. MicroRNA-130b-3p contained in MSC-derived EVs promotes lung cancer progression by regulating the FOXO3/NFE2L2/TXNRD1 axis. Mol. Ther.-Oncolytics 2021, 20, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Smith, S.E.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Wu, D.; Meneses-Giles, P.I.; Wang, Y.; Hembree, M.; Yi, K.; Zhao, X.; et al. Tumor-intiating stem cell shapes its microenvironment into an immunosuppressive barrier and pro-tumorigenic niche. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, N.; Blandano, G.; Pelicci, P.D. Blood vessels and peripheral nerves as key player in cancer progression and therapy resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wan, D.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S.; Lin, S.; Qiao, Y. Extracellular matrix and its therapeutic potential for cancer treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Parikh, P.; Zhao, H.; Givens, N.T.; Beck, D.B.; Willson, C.M.; Bai, Q.; Wakefield, M.R.; Peng, Y. Targeting immune-metabolism of neoplasm by interleukin. A promising immunotherapeutic strategy for cancer. Cancer Lett. 2021, 518, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.A.; Nisar, S.; Maacha, S.; Carneiro-Lobo, T.C.; Akhtar, S.; Siveen, K.S.; Wani, N.A.; Rizwan, A.; Bagga, P.; Singh, M.; et al. Cytokine-chemokine network driven metastasis in esophageal cancer; promising avenue for targeted therapy. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakhshiteh, F.; Zheng, P.; Li, W. Crosstalk between mesenchymal stromal cells and tumor-associated macrophages in gastric cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 571516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, J.C.; Puntigam, L.; Hofmann, L.; Jeske, S.S.; Beccard, J.J.; Doescher, J.; Laban, S.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Brunner, C.; Theodoraki, M.-N.; et al. Circulating exosomes inhibit B cell proliferation and activity. Cancers 2020, 12, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Geng, Y. Exosomes derived from chronic lymphocyte leukemia cells transfer miR-146a to induce the transition from mesenchymal stromal cells into cancer-associated fibroblasts. J. Biochem. 2020, 168, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olejarz, W.; Kubiak-Tomaszewska, G.; Chrzanowska, A.; Lorenc, T. Exosomes in angiogenesis and anti-oncogenic therapy in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Fu, B.M. Resistance mechanisms of anti-angiogenic therapy and exosome-mediated revascularization in cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 10661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiya, H.; Frisbie, L.; Pressimone, C.; Coffman, L. Mesenchymal stem cells in the tumor microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1234, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Deng, T.; Zhu, K.; Ning, T.; Fan, Q.; Ying, G.; et al. miR-135b delivered by gastric tumor exosomes inhibits FOXO1 expression in endothelial cells and promotes angiogenesis. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1772–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Lindsey-Boltz, L.A.; Vaughn, C.M.; Selby, C.P.; Cao, X.; Liu, Z.; Hsu, D.S.; Sancar, A. Circadian clock, carcinogenesis chrono-chemotherapy connections. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, W.; Khan, F.; James, C.D.; Heimberger, A.B.; Lenniak, M.S.; Chen, P. Circadian regulation of cancer and tumor microenviranment crosstalk. Trends Cell Biol. 2021, 31, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ochiya, T. miRNA signaling network in cancer stem cells. Regen. Ther. 2021, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, P.; Liang, Y.; Long, M.; Liu, H.; Mao, J.; Liu, Q.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote the in vitro proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells through the activation of the ERK pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.A.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, B.J.; Wu, Y.T.; Juan, J.R.; Chen, L.Y.; Teng, Y.C.; Wei, Y.H. Potential therapies targeting metabolic pathways in cancer stem cells. Cells 2021, 10, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieu, A.; Lalu, M.M.; Slobodian, M.; Gnyra, C.; Fergussson, D.A.; Montroy, J.; Burger, D.; Stewart, D.J.; Allan, D.S. An analysis of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for preclinical use. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 9728–9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.; Kim, H.S.; Hong, I.S. Stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles as immunomodulatory therapeutics. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 5126156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.; Marengon, I.; Meréaux, J.; Nicolàs-Boluda, A.; Lavieu, G.; Wilhelm, C.; Sarda-Mantel, L.; Silva, A.K.A.; Pocard, M.; Gazeau, F. Immune reprogramming precision photodynamic therapy of peritoneal metastasis of scalable stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3251–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoe, I.; Omata, D.; Unga, J.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Osaki, T. Lipid bubbles combined with low-intensity ultrasound enhance the intratumoral accumulation and antitumor effect of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in vivo. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bageri, E.; Abnous, K.; Ferzad, S.A.; Taghdisi, M.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Targeted doxorubicin-loaded mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a versatile platform for fighting against cholorectal cancer. Life Sci. 2020, 261, 118369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiest, E.F.; Zubair, A.C. Challenges of manufacturing mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles in regenerative medicine. Cytotherapy 2020, 22, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.Y.; Xu, W.H.; Yin, C.; Zhang, G.Q.; Zhong, Y.Q.; Gao, J. Nanomedicine strategies for sustained, controlled and targeted treatment of cancer stem cells of digestive system. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2016, 8, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Hai, B.; Kelly, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, F. Extracellular vesicle mimics made from iPS cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, H.; Hayat, H.; Dwan, B.F.; Gudi, M.; Bishop, J.O.; Wang, P. A concise review: The role of stem cells in cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2021, 20, 2761–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervieu, C.; Christou, N.; Battu, S.; Mathonnet, M. The role of cancer stem cells in colorectal cancer: From the basic to novel clinical trials. Cancers 2021, 13, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.F.; Lin, Y.Y.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, C.Q.; Yang, M.; Li, J.Q.; Ceng, M.Y.; Wang, K. Adjuvant inhibitors combined with endocrine therapy in HR-positive HER2-negative early breast cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Breast 2021, 59, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Oller, L.; Seras-Franzoso, J.; Andrade, F.; Rafael, D.; Abasolo, I.; Gener, P.; Schwartz, S. Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery system in cancer. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riazifar, M.; Pone, E.J.; Lotvall, J.; Zhao, W. Stem cell extracellular vesicles: Extended messages and regeneration. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 570, 125–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Movahed, Z.G.; Yarami, R.; Mohammadi, P.; Mansouri, K. Sustained oxidative stress instigates differentiation of cancer stem cells into tumor endothelial cells: Pentose phosphate pathway, reactive oxygen species and autophagy crosstalk. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 139, 111643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsalias, A.; Kozovska, Z. Personalized medicine: Stem cells in colorectal cancer treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanzadek, A.; Rahman, H.S.; Markov, A.; Endiun, J.J.; Zekiv, A.O.; Chardrand, S.; Beheshtkoo, N.; Kouhbanani, A.J.; Marofi, F.; Nikoo, M.; et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived exosomes in regenerative medicine and cancer; overview of development, challenges, and opportunities. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trosko, J.E. The role of stem cells and gap junctions as targets for cancer prevention and chemotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2005, 59, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Niekerk, G.; Davids, L.M.; Hattingh, S.M.; Engebrecht, A.M. Cancer stem cells: A product of clonal evolution? Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, V.; Kukkarni, Y.; Felix, K.; Azad, N.; Iver, A.K.V.; Yakisich, J.S. Alternative models of cancer stem cells: The stemness phenotype model, 10 years later. World J. Stem Cells 2021, 13, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
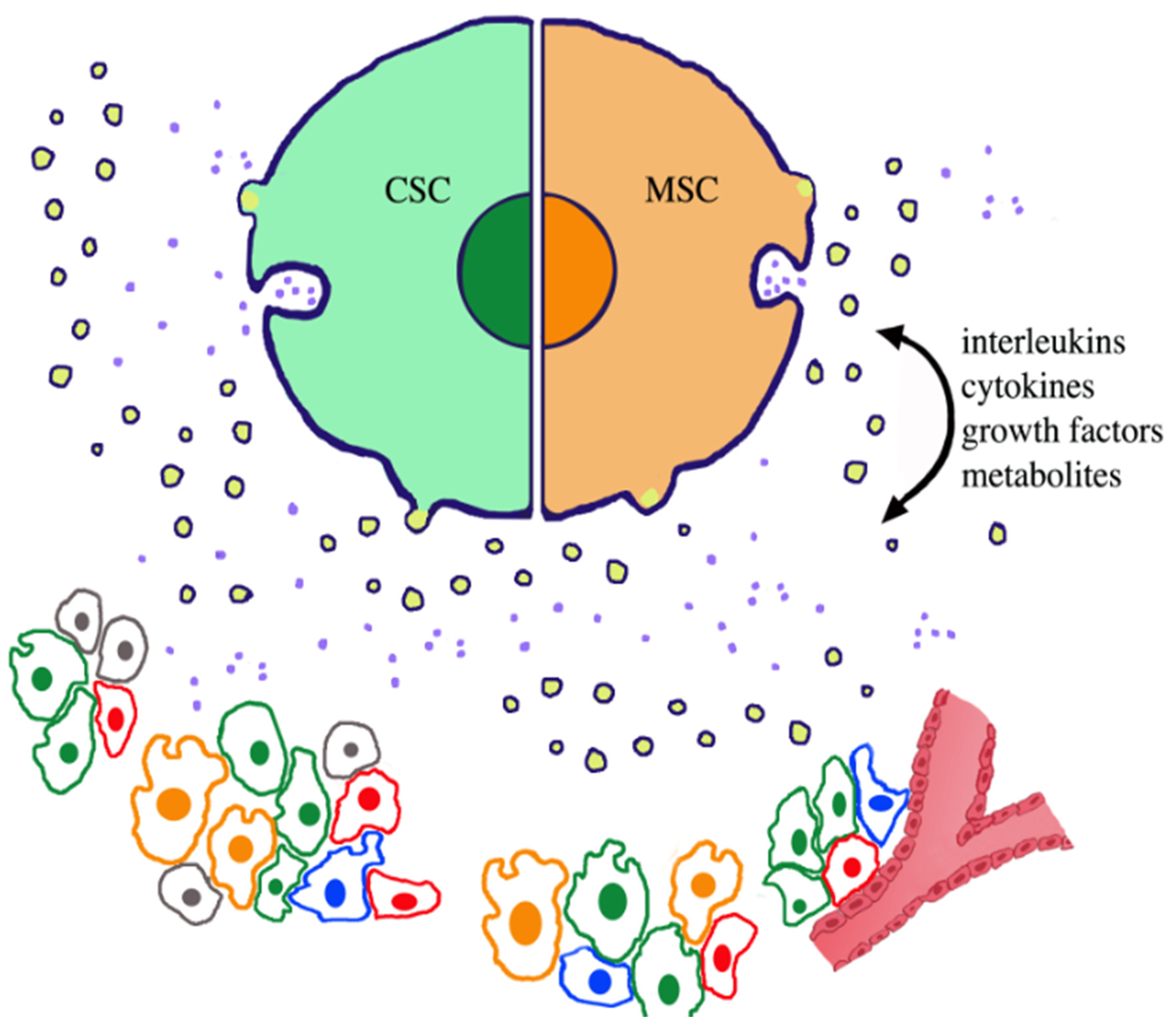
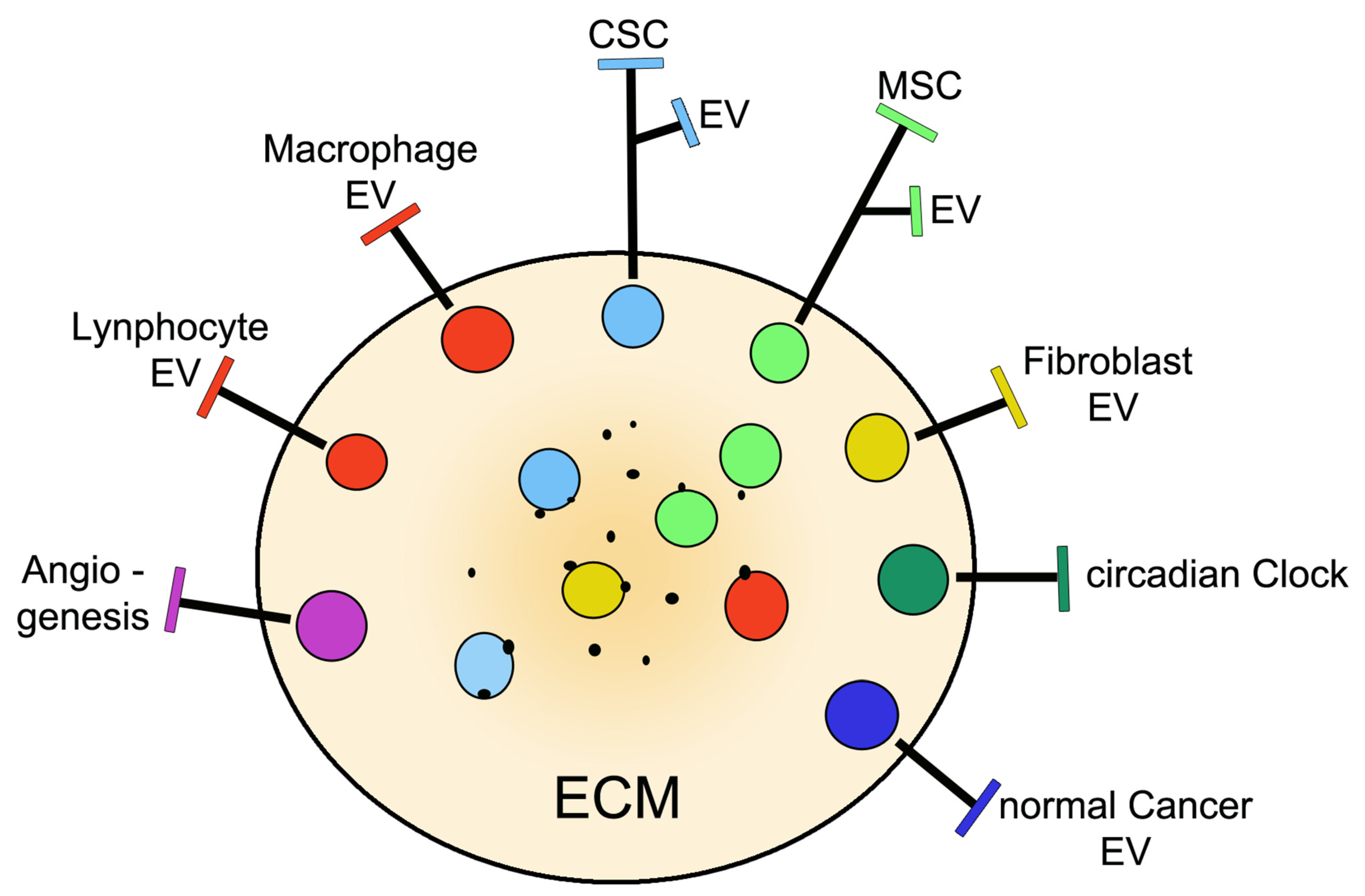
| Discovery | 1997–2004: First discovered in leukemia, then in cancers of the brain and other organs | [8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. |
| Concentrated in: | Niches and tumor microenvironments (TMEs). | |
| Co-distribution and co-operation of CSCs with: | MSCs, normal. Cancer cells, fibroblasts, macrophages, other immune cells | [15,16,17]. |
| Basic functions: | Cancer-cell initiation, immortality, self renewal, multi-lineage divergence, differentiation | [18,19,20,21]. |
| Peculiar functions: | Progression, functional plasticity, metastases, therapy resistance, cancer relapse | [17,19,21,22,23]. |
| Secretions: | Cytokines, interleukins, growth factors | [24,25]. |
| Released extracellular vesicles: | Exosomes and ectosomes | [3,4,5,6,7,19,26]. |
| Replacement (if needed): | By surrounding normal cancer cells | [20,21]. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meldolesi, J. Cancer Stem Cells and Their Vesicles, Together with Other Stem and Non-Stem Cells, Govern Critical Cancer Processes: Perspectives for Medical Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020625
Meldolesi J. Cancer Stem Cells and Their Vesicles, Together with Other Stem and Non-Stem Cells, Govern Critical Cancer Processes: Perspectives for Medical Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(2):625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020625
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeldolesi, Jacopo. 2022. "Cancer Stem Cells and Their Vesicles, Together with Other Stem and Non-Stem Cells, Govern Critical Cancer Processes: Perspectives for Medical Development" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 2: 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020625
APA StyleMeldolesi, J. (2022). Cancer Stem Cells and Their Vesicles, Together with Other Stem and Non-Stem Cells, Govern Critical Cancer Processes: Perspectives for Medical Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(2), 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020625






