Biological Role, Mechanism of Action and the Importance of Interleukins in Kidney Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Characteristics, Biological Role and Mechanism of Action of Interleukins in the Human Body
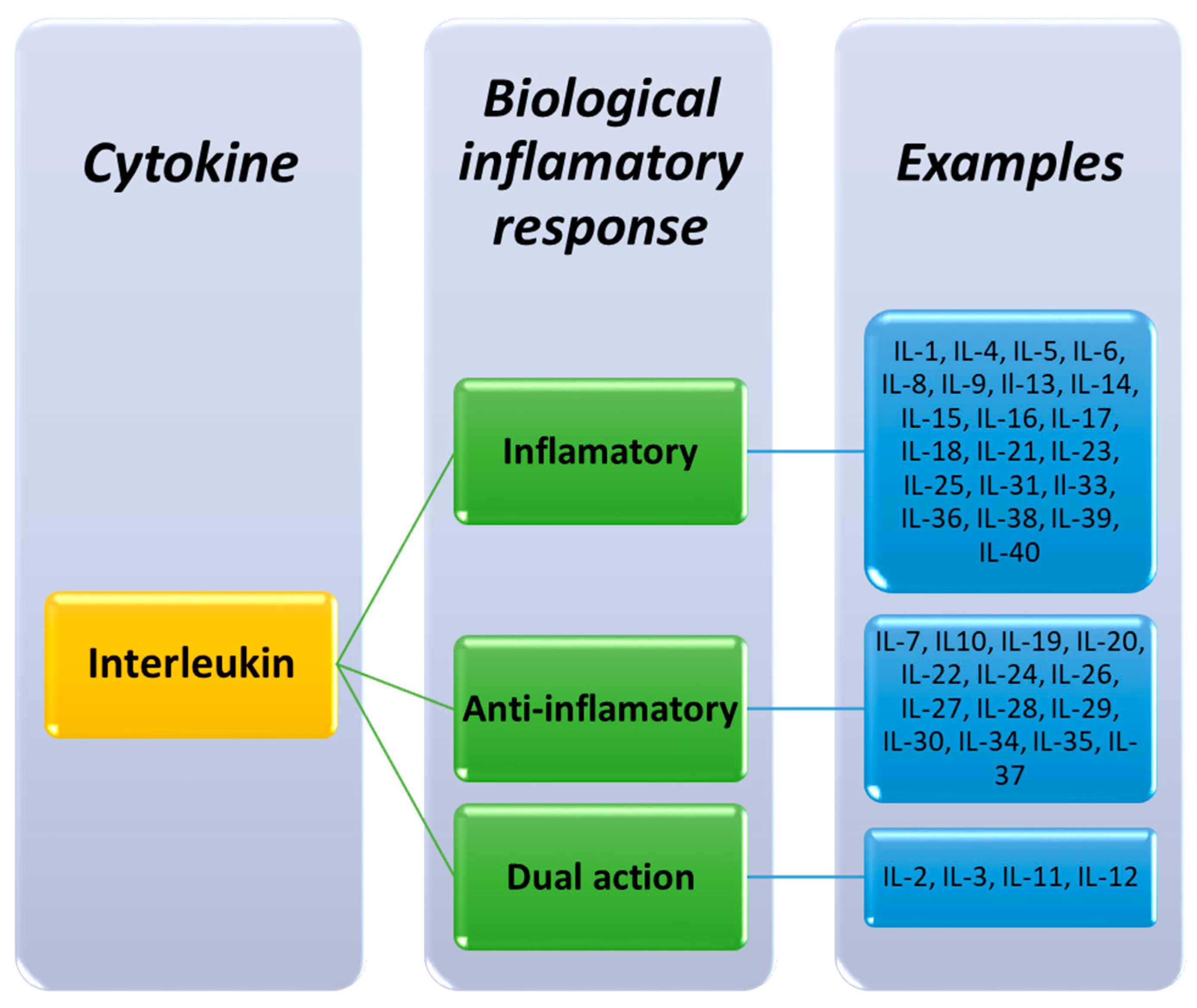
2.1. Classification of Interleukins
2.2. Molecular Characterization of Interleukins
2.3. Origin and Biological Functions of Interleukins in Health and Disease
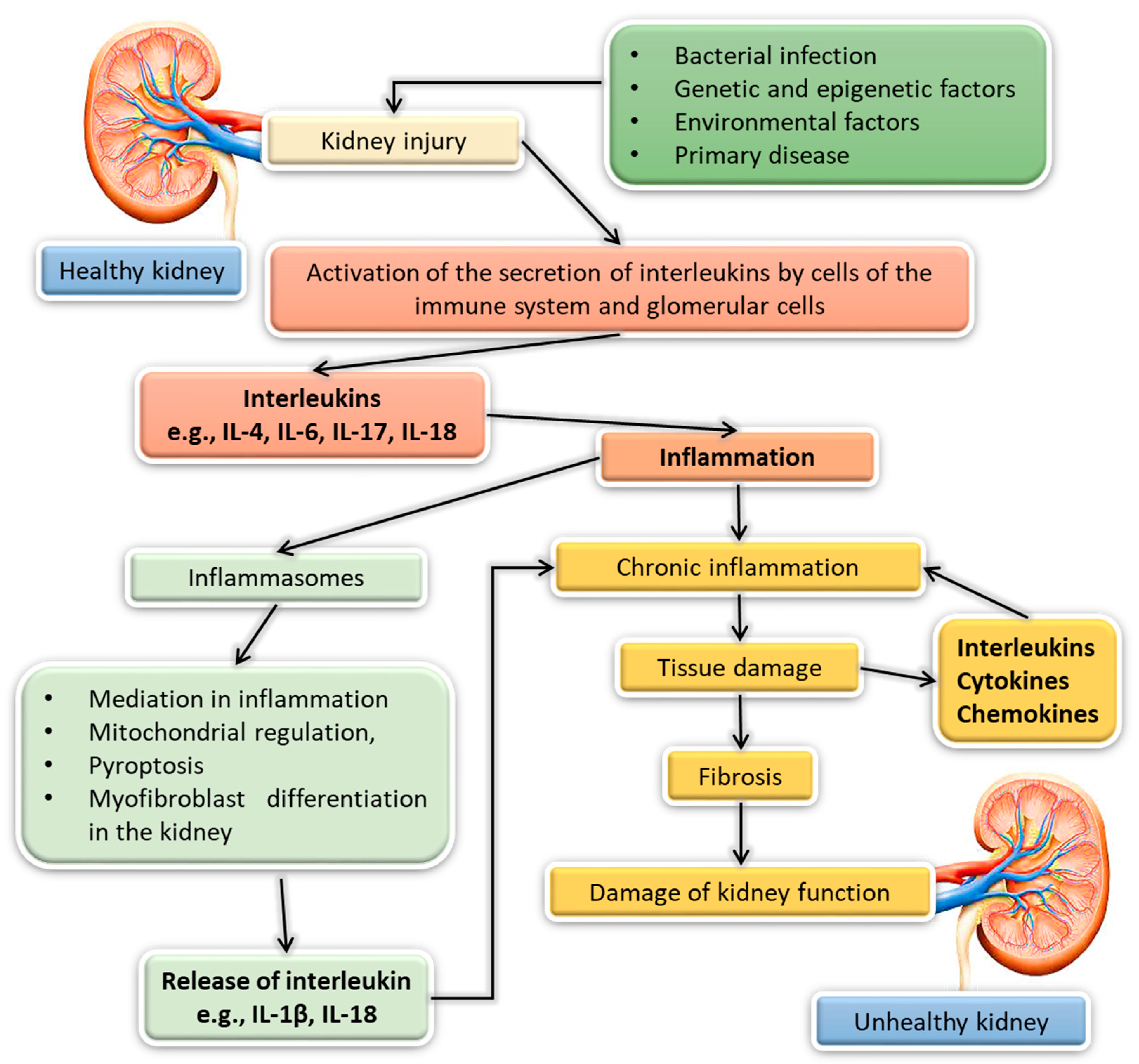
3. The Importance of Interleukins in Kidney Diseases
3.1. Acute Kidney Injury
3.2. Chronic Kidney Disease
3.2.1. Membranous Nephropathy (MN)
3.2.2. Nephropathy IgA (IgAN)
3.2.3. Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
3.2.4. Diabetic Nephropathy (DN)
3.3. Kidney Transplantation
3.4. Lupus Nephritis (LN)
3.5. Prospects of Interleukin Research in Kidney Diseases
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bioinformatic Analyses of the Amino Acid Sequences of Interleukins
4.2. Analysis of the Amino Acid Sequence Identity of Interleukins
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferreira, V.L.; Borba, H.H.L.; Bonetti, A.D.F.; Leonart, L.P.; Pontarolo, R. Cytokines and Interferons: Types and Functions; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 978-1-78984-853-3. [Google Scholar]
- Brocker, C.; Thompson, D.; Matsumoto, A.; Nebert, D.W.; Vasiliou, V. Evolutionary Divergence and Functions of the Human Interleukin (IL) Gene Family. Hum. Genom. 2010, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-M.; An, J. Cytokines, Inflammation, and Pain. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007, 45, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lissoni, P.; Messina, G.; Pelizzoni, F.; Rovelli, F.; Brivio, F.; Monzon, A.; Crivelli, N.; Lissoni, A.; Tassoni, S.; Sassola, A.; et al. The Fascination of Cytokine Immunological Science. J. Infect. 2020, 3, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, E.J. Understanding Cytokines Part I: Physiology and Mechanism of Action. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2000, 2, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, L.M.; Fornoni, A. Role of Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease, Glomerulonephritis, and End-Stage Kidney Disease. Int. J. Interferon Cytokine Mediat. Res. 2010, 2, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrero, J.J.; Yilmaz, M.I.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. Cytokine Dysregulation in Chronic Kidney Disease: How Can We Treat It? Blood Purif. 2008, 26, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, W.; Bernhagen, J.; Bucala, R. Cytokines in Sepsis: Potent Immunoregulators and Potential Therapeutic Targets—An Updated View. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, e165974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeraro, N.; Ammollo, C.T.; Semeraro, F.; Colucci, M. Sepsis-associated disseminated intravascular coagulation and thromboembolic disease. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 2, e2010024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facts about Chronic Kidney Disease. Available online: https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/about-chronic-kidney-disease (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Coca, S.G.; Singanamala, S.; Parikh, C.R. Chronic Kidney Disease after Acute Kidney Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lameire, N.H.; Levin, A.; Kellum, J.A.; Cheung, M.; Jadoul, M.; Winkelmayer, W.C.; Stevens, P.E.; Caskey, F.J.; Farmer, C.K.T.; Ferreiro Fuentes, A.; et al. Harmonizing Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition and Classification: Report of a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Consensus Conference. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronic Kidney Disease Prevalence Rates by World Region 2017. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1105452/chronic-kidney-disease-prevalence-rates-by-world-region/ (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Chronic Kidney Disease in the United States. 2021. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/kidneydisease/publications-resources/ckd-national-facts.html (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Gellert, R.; Durlik, M.; Małgorzewicz, S. Kidney Disease: A Population-Based Polish Nationwide Study. Ren. Dis. Transplant. Forum 2020, 13, 149–163. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.-H.; Wang, X.-G.; Wang, L.-Q.; Zhou, L.-N.; Tang, M.; Li, P.; Wu, X.-Y.; Chen, M.-B.; Zhang, Y. Serum Level of Interleukin-35 as a Potential Prognostic Factor for Gastric Cancer. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 17, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Chen, L. Plasma Level of Interleukin-35 as an Independent Prognostic Indicator in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 3513–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, H.; Szmitkowski, M.; Mäkinen, M.J.; Li, P.; Xia, D.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Wu, H. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Serum Interleukin-6 in Colorectal Cancer. Medicine 2016, 95, e2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ren, Y.; Dai, Z.-J.; Wu, C.-J.; Ji, Y.-H.; Xu, J. IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α Levels Correlate with Disease Stage in Breast Cancer Patients. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 26, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Povar-Echeverría, M.; Auquilla-Clavijo, P.E.; Andrès, E.; Martin-Sánchez, F.J.; Laguna-Calle, M.V.; Calvo-Elías, A.E.; Lorenzo-Villalba, N.; Méndez-Bailón, M. Interleukin-6 Could Be a Potential Prognostic Factor in Ambulatory Elderly Patients with Stable Heart Failure: Results from a Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gager, G.M.; Biesinger, B.; Hofer, F.; Winter, M.-P.; Hengstenberg, C.; Jilma, B.; Eyileten, C.; Postula, M.; Lang, I.M.; Siller-Matula, J.M. Interleukin-6 Level Is a Powerful Predictor of Long-Term Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome. Vasc. Pharm. 2020, 135, 106806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Waresi, M.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Wu, B.; Xiong, N.; Li, H.; Huang, Q.; Luo, X.; Li, J. Increased Serum Interleukin-6 Level as a Predictive Biomarker for Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Rev. Port. Cardiol (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 39, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, A.K.Y.; Hung, K.-W.; Yuen, M.Y.F.; Zhou, X.; Mak, D.S.Y.; Chan, I.C.W.; Cheung, T.H.; Zhang, B.; Fu, W.-Y.; Liew, F.Y.; et al. IL-33 Ameliorates Alzheimer’s Disease-like Pathology and Cognitive Decline. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2705–E2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ting, E.Y.-C.; Yang, A.C.; Tsai, S.-J. Role of Interleukin-6 in Depressive Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balasa, R.; Maier, S.; Voidazan, S.; Hutanu, A.; Bajko, Z.; Motataianu, A.; Tilea, B.; Tiu, C. Assessment of Interleukin-17A, Interleukin-10 and Transforming Growth Factor-Beta1 Serum Titers in Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Patients Treated with Avonex, Possible Biomarkers for Treatment Response. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Liu, M.; Liu, B. Interleukin-35 as a New Biomarker of Renal Involvement in Lupus Nephritis Patients. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2018, 244, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tawfik, M.G.; Nasef, S.I.; Omar, H.H.; Ghaly, M.S. Serum Interleukin-37: A New Player in Lupus Nephritis? Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipiec, K.; Adamczyk, P.; Świętochowska, E.; Ziora, K.; Szczepańska, M. Angiotensinogen and Interleukin-18 as Markers of Chronic Kidney Damage in Children with a History of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Physiol. Res. 2017, 66, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, T.; Sugiyama, N.; Otsuki, Y.; Kondo, Y. Interleukin-24 Is a Novel Diagnostic Biomarker for the Severity of Acute Kidney Injury. Med. Mol. Morphol. 2020, 53, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, J.H.; Whitlock, R.; Zhang, W.R.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.R.; Zappitelli, M.; Devarajan, P.; Eikelboom, J.; Kavsak, P.A.; Devereaux, P.J.; Shortt, C.; et al. Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-10 as Acute Kidney Injury Biomarkers in Pediatric Cardiac Surgery. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2015, 30, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kveler, K.; Starosvetsky, E.; Ziv-Kenet, A.; Kalugny, Y.; Gorelik, Y.; Shalev-Malul, G.; Aizenbud-Reshef, N.; Dubovik, T.; Briller, M.; Campbell, J.; et al. Immune-Centric Network of Cytokines and Cells in Disease Context Identified by Computational Mining of PubMed. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, K.; Leonard, W.J. Cytokine and Cytokine Receptor Pleiotropy and Redundancy. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 29355–29358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartee, E.; McFadden, G. Cytokine Synergy: An Underappreciated Contributor to Innate Anti-Viral Immunity. Cytokine 2013, 63, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Chu, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; George, J.; Young, H.A.; Liu, G. Cytokines: From Clinical Significance to Quantification. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briukhovetska, D.; Dörr, J.; Endres, S.; Libby, P.; Dinarello, C.A.; Kobold, S. Interleukins in Cancer: From Biology to Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 481–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priestle, J.P.; Schär, H.P.; Grütter, M.G. Crystallographic Refinement of Interleukin 1 Beta at 2.0 A Resolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 9667–9671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vigers, G.P.; Caffes, P.; Evans, R.J.; Thompson, R.C.; Eisenberg, S.P.; Brandhuber, B.J. X-ray Structure of Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist at 2.0-A Resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 12874–12879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, B.J.; Hatada, M.H.; Hendrickson, W.A.; Miller, J.K.; Madison, V.S.; Satow, Y. Structure of Interleukin 1 Alpha at 2.7-A Resolution. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 2679–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulay, J.-L.; O’Shea, J.J.; Paul, W.E. Molecular Phylogeny within Type I Cytokines and Their Cognate Receptors. Immunity 2003, 19, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinarello, C.A. Overview of the IL-1 Family in Innate Inflammation and Acquired Immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6 Family Cytokines. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novak, J.; Lehuen, A. Mechanism of Regulation of Autoimmunity by INKT Cells. Cytokine 2011, 53, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignali, D.A.A.; Kuchroo, V.K. IL-12 Family Cytokines: Immunological Playmakers. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, C.; Wu, L.; Li, X. IL-17 Family: Cytokines, Receptors and Signaling. Cytokine 2013, 64, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Z.; Xu, K.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, M. Interleukin 39: A New Member of Interleukin 12 Family. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 45, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Interleukin-1—Homo Sapiens (Human). Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q7RU00 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL2—Interleukin-2 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL2 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P60568 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL3—Interleukin-3 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL3 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P08700 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL4—Interleukin-4 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL4 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P05112 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL5—Interleukin-5 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL5 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P05113 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL6—Interleukin-6 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL6 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P05231 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL7—Interleukin-7 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL7 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P13232 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- CXCL8—Interleukin-8 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—CXCL8 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P10145 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL9—Interleukin-9 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL9 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P15248 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL10—Interleukin-10 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL10 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P22301 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL11—Interleukin-11 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL11 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P20809 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL12A—Interleukin-12 Subunit Alpha Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL12A Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P29459 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL12B—Interleukin-12 Subunit Beta Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL12B Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P29460 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL13—Interleukin-13 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL13 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P35225 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- TXLNA—Alpha-Taxilin—Homo Sapiens (Human)—TXLNA Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P40222 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL15—Interleukin-15 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL15 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P40933 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL16—Pro-Interleukin-16—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL16 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q14005 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL17A—Interleukin-17A Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL17A Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q16552 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL18—Interleukin-18 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL18 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q14116 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL19—Interleukin-19 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL19 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9UHD0 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL20—Interleukin-20 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL20 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9NYY1 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL21—Interleukin-21 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL21 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9HBE4 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL22—Interleukin-22 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL22 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9GZX6 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL23A—Interleukin-23 Subunit Alpha Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL23A Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9NPF7 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL24—Interleukin-24 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL24 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q13007 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL25—Interleukin-25 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL25 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9H293 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL26—Interleukin-26 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL26 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9NPH9 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL27—Interleukin-27 Subunit Alpha Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL27 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8NEV9 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- EBI3—Interleukin-27 Subunit Beta Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—EBI3 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q14213 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IFNLR1—Interferon Lambda Receptor 1 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IFNLR1 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8IU57 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IFNL1—Interferon Lambda-1 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IFNL1 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8IU54 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Catalan-Dibene, J.; McIntyre, L.L.; Zlotnik, A. Interleukin 30 to Interleukin 40. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2018, 38, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IL31—Interleukin-31 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL31 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q6EBC2 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL32—Interleukin-32 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL32 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P24001 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL33—Interleukin-33 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL33 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O95760 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL34—Interleukin-34 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL34 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q6ZMJ4 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL36A—Interleukin-36 Alpha Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL36A Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9UHA7 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL36B—Interleukin-36 Beta Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL36B Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9NZH7 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL36G—Interleukin-36 Gamma Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL36G Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9NZH8 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL37—Interleukin-37 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL37 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9NZH6 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- IL1F10—Interleukin-1 Family Member 10—Homo Sapiens (Human)—IL1F10 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8WWZ1 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- C17orf99—Protein IL-40 Precursor—Homo Sapiens (Human)—C17orf99 Gene & Protein. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q6UX52 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Lütticken, C.; Krüttgen, A.; Möller, C.; Heinrich, P.C.; Rose-John, S. Evidence for the Importance of a Positive Charge and an Alpha-Helical Structure of the C-Terminus for Biological Activity of Human IL-6. FEBS Lett. 1991, 282, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goepfert, A.; Lehmann, S.; Wirth, E.; Rondeau, J.-M. The Human IL-17A/F Heterodimer: A Two-Faced Cytokine with Unique Receptor Recognition Properties. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Song, X.; Chrunyk, B.A.; Shanker, S.; Hoth, L.R.; Marr, E.S.; Griffor, M.C. Crystal Structures of Interleukin 17A and Its Complex with IL-17 Receptor A. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Z.; Jee, J.; Shikano, H.; Mishima, M.; Ohki, I.; Ohnishi, H.; Li, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Matsukuma, E.; Omoya, K.; et al. The Structure and Binding Mode of Interleukin-18. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003, 10, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hammel, M.; He, Y.; Tainer, J.A.; Jeng, U.-S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Structural Insights into the Interaction of IL-33 with Its Receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14918–14923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaneko, N.; Kurata, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Morikawa, S.; Masumoto, J. The Role of Interleukin-1 in General Pathology. Inflamm. Regen. 2019, 39, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schett, G.; Dayer, J.-M.; Manger, B. Interleukin-1 Function and Role in Rheumatic Disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyman, O.; Sprent, J. The Role of Interleukin-2 during Homeostasis and Activation of the Immune System. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, S.H.; Cantrell, D.A. Signaling and Function of Interleukin-2 in T Lymphocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 411–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, T.R. The Main Function of IL-2 Is to Promote the Development of T Regulatory Cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 74, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougan, M.; Dranoff, G.; Dougan, S.K. GM-CSF, IL-3, and IL-5 Family of Cytokines: Regulators of Inflammation. Immunity 2019, 50, 796–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, H.V.; Bailey, D.; Kashyap, M.; Kepley, C.L.; Drutskaya, M.S.; Nedospasov, S.A.; Ryan, J.J. IL-3-Mediated TNF Production Is Necessary for Mast Cell Development. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 2114–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gadani, S.P.; Cronk, J.C.; Norris, G.T.; Kipnis, J. IL-4 in the Brain: A Cytokine to Remember. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 4213–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeb, L.E.M.; Egholm, C.; Boyman, O. Evolution and Function of Interleukin-4 Receptor Signaling in Adaptive Immunity and Neutrophils. Genes Immun. 2020, 21, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takatsu, K. Interleukin-5 and IL-5 Receptor in Health and Diseases. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2011, 87, 463–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelaia, C.; Paoletti, G.; Puggioni, F.; Racca, F.; Pelaia, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Heffler, E. Interleukin-5 in the Pathophysiology of Severe Asthma. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in Inflammation, Immunity, and Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez-Salinas, L.; Verdugo-Rodriguez, A.; Rodriguez, L.L.; Borca, M.V. The Role of Interleukin 6 during Viral Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ElKassar, N.; Gress, R.E. An Overview of IL-7 Biology and Its Use in Immunotherapy. J. Immunotoxicol. 2010, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, A.; Abraham, N. Interleukin-7 Receptor Alpha in Innate Lymphoid Cells: More Than a Marker. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, S.; Hug, S.; Stratmann, A.E.P.; Erber, M.; Vidoni, L.; Knapp, C.L.; Thomaß, B.D.; Fauler, M.; Nilsson, B.; Ekdahl, K.N.; et al. Interleukin 8 Elicits Rapid Physiological Changes in Neutrophils That Are Altered by Inflammatory Conditions. J. Innate Immun. 2021, 13, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benakanakere, M.R.; Finoti, L.S.; Tanaka, U.; Grant, G.R.; Scarel-Caminaga, R.M.; Kinane, D.F. Investigation of the Functional Role of Human Interleukin-8 Gene Haplotypes by CRISPR/Cas9. Mediat. Genome Editing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noelle, R.J.; Nowak, E.C. Cellular Sources and Immune Functions of Interleukin-9. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Zuleta, W.G.; Sanchez, E. IL-9: Function, Sources, and Detection. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1585, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.S.; Cheng, G. Role of Interleukin 10 Transcriptional Regulation in Inflammation and Autoimmune Disease. CRI 2012, 32, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burmeister, A.R.; Marriott, I. The Interleukin-10 Family of Cytokines and Their Role in the CNS. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, S.; Teramura, M.; Oshimi, K.; Mizoguchi, H. Interleukin-11. Leuk. Lymphoma 1994, 15, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishina, T.; Deguchi, Y.; Ohshima, D.; Takeda, W.; Ohtsuka, M.; Shichino, S.; Ueha, S.; Yamazaki, S.; Kawauchi, M.; Nakamura, E.; et al. Interleukin-11-Expressing Fibroblasts Have a Unique Gene Signature Correlated with Poor Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinchieri, G. Interleukin-12 and the Regulation of Innate Resistance and Adaptive Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zundler, S.; Neurath, M.F. Interleukin-12: Functional Activities and Implications for Disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, G.; Granata, F.; Pucino, V.; Pecoraro, A.; Heffler, E.; Loffredo, S.; Scadding, G.W.; Varricchi, G. The Intriguing Role of Interleukin 13 in the Pathophysiology of Asthma. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mannon, P.; Reinisch, W. Interleukin 13 and Its Role in Gut Defence and Inflammation. Gut 2012, 61, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, L.; Suresh, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Kumar, V.; Pankewycz, O.; Ambrus, J.L. IL-14 Alpha, the Nexus for Primary Sjögren’s Disease in Mice and Humans. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 130, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, P.-Y.; Lichy, J.H.; Waldmann, T.A.; Perera, L.P. The Role of Interleukin-15 in Inflammation and Immune Responses to Infection: Implications for Its Therapeutic Use. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liew, F.Y.; McInnes, I.B. Role of Interleukin 15 and Interleukin 18 in Inflammatory Response. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61, ii100–ii102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruikshank, W.; Kornfeld, H.; Center, D. Interleukin-16. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2000, 67, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenobia, C.; Hajishengallis, G. Basic Biology and Role of Interleukin-17 in Immunity and Inflammation. Periodontology 2000 2015, 69, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onishi, R.M.; Gaffen, S.L. Interleukin-17 and Its Target Genes: Mechanisms of Interleukin-17 Function in Disease. Immunology 2010, 129, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.; Novick, D.; Kim, S.; Kaplanski, G. Interleukin-18 and IL-18 Binding Protein. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakanishi, K. Unique Action of Interleukin-18 on T Cells and Other Immune Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabunia, K.; Autieri, M.V. Interleukin-19 Can Enhance Angiogenesis by Macrophage Polarization. Macrophage 2015, 2, e562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, G. Interleukin-19: Multiple Roles in Immune Regulation and Disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010, 21, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumberg, H.; Conklin, D.; Xu, W.; Grossmann, A.; Brender, T.; Carollo, S.; Eagan, M.; Foster, D.; Haldeman, B.A.; Hammond, A.; et al. Interleukin 20: Discovery, Receptor Identification, and Role in Epidermal Function. Cell 2001, 104, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, Y.-H.; Li, H.-H.; Hsieh, M.-Y.; Liu, M.-F.; Huang, K.-Y.; Chin, L.-S.; Chen, P.-C.; Cheng, H.-H.; Chang, M.-S. Function of Interleukin-20 as a Proinflammatory Molecule in Rheumatoid and Experimental Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2722–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, M.; Girard, D. Biological Functions of Interleukin-21 and Its Role in Inflammation. Sci. World J. 2007, 7, 1715–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.-Y.; Jen, H.-Y.; Chiang, B.-L.; Sheu, F.; Chuang, Y.-H. Interleukin-21 Suppresses the Differentiation and Functions of T Helper 2 Cells. Immunology 2015, 144, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solaymani-Mohammadi, S.; Eckmann, L.; Singer, S.M. Interleukin (IL)-21 in Inflammation and Immunity during Parasitic Diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabgah, A.G.; Navashenaq, J.G.; Shabgah, O.G.; Mohammadi, H.; Sahebkar, A. Interleukin-22 in Human Inflammatory Diseases and Viral Infections. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, O.B.; Pociask, D.A.; Hodzic, Z.; Kolls, J.K.; Good, M. Interleukin-22 Signaling in the Regulation of Intestinal Health and Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 3, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arshad, T.; Mansur, F.; Palek, R.; Manzoor, S.; Liska, V. A Double Edged Sword Role of Interleukin-22 in Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Chen, S.; Qian, H.; Huang, W. Interleukin-23: As a Drug Target for Autoimmune Inflammatory Diseases. Immunology 2012, 135, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Shou, P.; Smith, C.; Chen, Y.; Du, H.; Sun, C.; Porterfield Kren, N.; Michaud, D.; Ahn, S.; Vincent, B.; et al. Interleukin-23 Engineering Improves CAR T Cell Function in Solid Tumors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, L.; De Jesus, D.; Brannigan, O.; Richiez-Paredes, M.; Huaman, J.; Alvarado, G.; Riker, L.; Mendez, G.; Dejoie, J.; Sauane, M. Mechanism of Action and Applications of Interleukin 24 in Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitamura, Y.; Nunomura, S.; Furue, M.; Izuhara, K. IL-24: A New Player in the Pathogenesis of pro-Inflammatory and Allergic Skin Diseases. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y. Interleukin-24 Regulates T Cell Activity in Patients With Colorectal Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh, A.; Khosravi, A.; Zadeh, L.J.; Parizad, E.G. Role of IL-25 in Immunity. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, OE01–OE04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadoun, D.; Terrier, B.; Cacoub, P. Interleukin-25: Key Regulator of Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 3781–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broux, B.; Zandee, S.; Gowing, E.; Charabati, M.; Lécuyer, M.-A.; Tastet, O.; Hachehouche, L.; Bourbonnière, L.; Ouimet, J.-P.; Lemaitre, F.; et al. Interleukin-26, Preferentially Produced by TH17 Lymphocytes, Regulates CNS Barrier Function. Neurol.—Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tengvall, S.; Che, K.F.; Lindén, A. Interleukin-26: An Emerging Player in Host Defense and Inflammation. J. Innate Immun. 2016, 8, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petes, C.; Mariani, M.K.; Yang, Y.; Grandvaux, N.; Gee, K. Interleukin (IL)-6 Inhibits IL-27- and IL-30-Mediated Inflammatory Responses in Human Monocytes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, H.; Hunter, C.A. The Immunobiology of Interleukin-27. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 417–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Siegmund, S.; Garbers, C. The Biology of Interleukin-27 Reveals Unique pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Functions in Immunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolk, K.; Witte, K.; Sabat, R. Interleukin-28 and Interleukin-29: Novel Regulators of Skin Biology. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010, 30, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Chen, F.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Interleukin-28B Dampens Airway Inflammation through up-Regulation of Natural Killer Cell-Derived IFN-γ. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelm, N.E.; Zhu, Z.; Ding, V.A.; Xiao, H.; Wakefield, M.R.; Bai, Q.; Fang, Y. The Role of IL-29 in Immunity and Cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 106, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, E. Decoding the Role of Interleukin-30 in the Crosstalk between Cancer and Myeloid Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omar, N.S.; Long, X.; Xian, J.; Afewerky, H.K.; Hussain, S.G.; Peng, X. Serum Interleukin-30 Level in Patients with Psoriasis and Its Correlation with Psoriasis Severity: A Case-Control Study. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 03000605211004039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Putheti, P.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Q.; Gao, W. Structures and Biological Functions of IL-31 and IL-31 Receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008, 19, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibbs, B.F.; Patsinakidis, N.; Raap, U. Role of the Pruritic Cytokine IL-31 in Autoimmune Skin Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, T.; Chen, M.; Duan, L.; Xu, Y.; Gao, P. Interleukin-32: Its Role in Asthma and Potential as a Therapeutic Agent. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; He, D.; Huang, X.; Zhang, E.; Chen, Q.; Xu, R.; Liu, X.; Zi, F.; Cai, Z. Role of Interleukin-32 in Cancer Biology (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, B.C.L.; Lam, C.W.K.; Tam, L.-S.; Wong, C.K. IL33: Roles in Allergic Inflammation and Therapeutic Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liew, F.Y.; Girard, J.-P.; Turnquist, H.R. Interleukin-33 in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzè, E.; Dinallo, V.; Rizzo, A.; Di Giovangiulio, M.; Bevivino, G.; Stolfi, C.; Caprioli, F.; Colantoni, A.; Ortenzi, A.; Grazia, A.D.; et al. Interleukin-34 Sustains pro-Tumorigenic Signals in Colon Cancer Tissue. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 3432–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, R.-P.; Wu, X.-S.; Xie, Y.-Y.; Dai, B.-B.; Hu, W.; Ge, J.-F.; Chen, F.-H. Functions of Interleukin-34 and Its Emerging Association with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunology 2016, 149, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Y.; Huang, M.; Yao, Y. Immunomodulation of Interleukin-34 and Its Potential Significance as a Disease Biomarker and Therapeutic Target. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, A.; Cheng, L.; He, M.; Nie, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, K. Interleukin-35 on B Cell and T Cell Induction and Regulation. J. Inflamm. 2017, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, P.L.; Jie, L.F.; Cheng, Q.; Bin, D.Y.; Dan, C.W. Pathogenesis and Function of Interleukin-35 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Todorovic, V. Interleukin-36: Structure, Signaling and Function. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 21, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.-C.; Xu, W.-D.; Liu, X.-Y.; Liu, X.-Y.; Huang, A.-F.; Su, L.-C. Biology of IL-36 Signaling and Its Role in Systemic Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santarelli, D.M.; Vincent, F.B.; Rudloff, I.; Nold-Petry, C.A.; Nold, M.F.; Russo, M.A. Circulating Interleukin-37 Levels in Healthy Adult Humans—Establishing a Reference Range. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Liu, J.; Han, B. Reviews of Interleukin-37: Functions, Receptors, and Roles in Diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3058640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, W.-D.; Huang, A.-F. Role of Interleukin-38 in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.-S.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.-Q. Biology of Interleukin-38 and Its Role in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 95, 107528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navrátilová, A.; Andrés Cerezo, L.; Hulejová, H.; Bečvář, V.; Tomčík, M.; Komarc, M.; Veigl, D.; Tegzová, D.; Závada, J.; Olejárová, M.; et al. IL-40: A New B Cell-Associated Cytokine Up-Regulated in Rheumatoid Arthritis Decreases Following the Rituximab Therapy and Correlates With Disease Activity, Autoantibodies, and NETosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipping, P.G.; Holdsworth, S.R. Cytokines in Glomerulonephritis. Semin. Nephrol. 2007, 27, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory Responses and Inflammation-Associated Diseases in Organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dyke, T.E.; Kornman, K.S. Inflammation and Factors That May Regulate Inflammatory Response. J. Periodontol. 2008, 79, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Oliveira, V.; Foresto-Neto, O.; Watanabe, I.K.M.; Zatz, R.; Câmara, N.O.S. Inflammation in Renal Diseases: New and Old Players. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inflammation in Patients with Kidney Function Impairment—UpToDate. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/inflammation-in-patients-with-kidney-function-impairment (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- Petreski, T.; Piko, N.; Ekart, R.; Hojs, R.; Bevc, S. Review on Inflammation Markers in Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludes, P.-O.; de Roquetaillade, C.; Chousterman, B.G.; Pottecher, J.; Mebazaa, A. Role of Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns in Septic Acute Kidney Injury, From Injury to Recovery. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.M.; Arulkumaran, N.; Singer, M.; Unwin, R.J.; Tam, F.W. Is the Inflammasome a Potential Therapeutic Target in Renal Disease? BMC Nephrol. 2014, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komada, T.; Muruve, D.A. The Role of Inflammasomes in Kidney Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, H.-J.; Lech, M. NOD-like and Toll-like Receptors or Inflammasomes Contribute to Kidney Disease in a Canonical and a Non-Canonical Manner. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hutton, H.L.; Ooi, J.D.; Holdsworth, S.R.; Kitching, A.R. The NLRP3 Inflammasome in Kidney Disease and Autoimmunity. Nephrology 2016, 21, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Zhu, F.; Xu, Z.; Xiong, J. Role of Inflammasomes in Kidney Diseases via Both Canonical and Non-Canonical Pathways. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirooka, Y.; Nozaki, Y. Interleukin-18 in Inflammatory Kidney Disease. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, H.-J. Of Inflammasomes and Alarmins: IL-1β and IL-1α in Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2564–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Morales, R.E.; del Pino, M.D.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Ortiz, A.; Mora-Fernández, C.; Navarro-González, J.F. Inflammation in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Nephron 2019, 143, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akchurin, O.M.; Kaskel, F. Update on Inflammation in Chronic Kidney Disease. Blood Purif. 2015, 39, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, K.K.; Zappitelli, M.; Arikan, A.A.; Loftis, L.; Yalavarthy, R.; Parikh, C.R.; Edelstein, C.L.; Goldstein, S.L. Urinary Interleukin-18 Is an Acute Kidney Injury Biomarker in Critically Ill Children. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaidya, V.S.; Ferguson, M.A.; Bonventre, J.V. Biomarkers of Acute Kidney Injury. Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 2008, 48, 463–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teo, S.H.; Endre, Z.H. Biomarkers in Acute Kidney Injury (AKI). Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2017, 31, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashani, K.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Ronco, C. Biomarkers of Acute Kidney Injury: The Pathway from Discovery to Clinical Adoption. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2017, 55, 1074–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisula, S.; Yang, R.; Poukkanen, M.; Vaara, S.T.; Kaukonen, K.M.; Tallgren, M.; Haapio, M.; Tenhunen, J.; Korhonen, A.M.; Pettilä, V.; et al. Predictive Value of Urine Interleukin-18 in the Evolution and Outcome of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Adult Patients. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 114, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Hsu, Y.-H. IL-20 in Acute Kidney Injury: Role in Pathogenesis and Potential as a Therapeutic Target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.-H.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Wei, C.-C.; Lee, P.-T.; Chen, W.-C.; Chang, M.-S. Interleukin-20 Induced Cell Death in Renal Epithelial Cells and Was Associated with Acute Renal Failure. Genes Immun. 2008, 9, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moutabarrik, A.; Nakanishi, I.; Ishibashi, M. Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-6 Receptor Are Expressed by Cultured Glomerular Epithelial Cells. Scand. J. Immunol. 1994, 40, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boswell, R.N.; Yard, B.A.; Schrama, E.; van Es, L.A.; Daha, M.R.; van der Woude, F.J. Interleukin 6 Production by Human Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells in Vitro: Analysis of the Effects of Interleukin-1α (IL-1α) and Other Cytokines. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1994, 9, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Lei, C.-T.; Zhang, C. Interleukin-6 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Kidney Disease: An Update. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nechemia-Arbely, Y.; Barkan, D.; Pizov, G.; Shriki, A.; Rose-John, S.; Galun, E.; Axelrod, J.H. IL-6/IL-6R Axis Plays a Critical Role in Acute Kidney Injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Yuan, H.; Cao, W.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Yu, H.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhou, H.; Guo, H.; et al. Blocking Interleukin-6 Trans-Signaling Protects against Renal Fibrosis by Suppressing STAT3 Activation. Theranostics 2019, 9, 3980–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkar, A.M.; Smith, J.; Tam, F.W.; Pusey, C.D.; Rees, A.J. Abrogation of Glomerular Injury in Nephrotoxic Nephritis by Continuous Infusion of Interleukin-6. Kidney Int. 1997, 52, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, K.W.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Coffman, R.L.; O’Garra, A. Interleukin-10 and the Interleukin-10 Receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 683–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Zheng, Q.; Hao, L. IL-10 -1082 A/G Polymorphism Is Related with the Risk and Clinical Characteristics of Acute Kidney Injury: A Case-Control Study. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinuani, I.; Beberashvili, I.; Averbukh, Z.; Sandbank, J. Role of IL-10 in the Progression of Kidney Disease. World J. Transpl. 2013, 3, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.K.; Knicely, D.H.; Grams, M.E. Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis and Management. JAMA 2019, 322, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.; Kanso, A.; Sedor, J.R. Chronic Kidney Disease and Its Complications. Prim. Care 2008, 35, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, S.A.; Fraser, D.J.; Fielding, C.A.; Jones, G.W. Interleukin-6 in Renal Disease and Therapy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, M.-S.; Hsu, Y.-H. The Role of IL-20 in Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetic Nephropathy: Pathogenic and Therapeutic Implications. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 104, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.-C.; Li, H.-H.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Hsing, C.-H.; Sung, J.-M.; Chang, M.-S. Interleukin-20 Targets Renal Cells and Is Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 374, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandach, I.; Segev, Y.; Landau, D. Experimental Modulation of Interleukin 1 Shows Its Key Role in Chronic Kidney Disease Progression and Anemia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, S. New ‘Antigens’ in Membranous Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couser, W.G. Primary Membranous Nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masutani, K.; Taniguchi, M.; Nakashima, H.; Yotsueda, H.; Kudoh, Y.; Tsuruya, K.; Tokumoto, M.; Fukuda, K.; Kanai, H.; Hirakata, H.; et al. Up-Regulated Interleukin-4 Production by Peripheral T-Helper Cells in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2004, 19, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomelli, M.; Kumar, R.; Tampella, G.; Ceffa, S.; Bontempelli, M. IL-4, IL-10 and TNF-α Polymorphisms in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy (IMN). Open J. Immunol. 2015, 5, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeannin, P.; Lecoanet, S.; Delneste, Y.; Gauchat, J.F.; Bonnefoy, J.Y. IgE versus IgG4 Production Can Be Differentially Regulated by IL-10. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 3555–3561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Vries, J.E.; Punnonen, J.; Cocks, B.G.; Aversa, G. The Role of T/B Cell Interactions and Cytokines in the Regulation of Human IgE Synthesis. Semin. Immunol. 1993, 5, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lécart, S.; Morel, F.; Noraz, N.; Pène, J.; Garcia, M.; Boniface, K.; Lecron, J.; Yssel, H. IL-22, in contrast to IL-10, does not induce Ig production, due to absence of a functional IL-22 receptor on activated human B cells. Immunology 2002, 14, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuroki, A.K.I.; Iyoda, M.; Shibata, T.; Sugisaki, T. Th2 Cytokines Increase and Stimulate B Cells to Produce IgG4 in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rianthavorn, P.; Chokedeemeeboon, C.; Deekajorndech, T.; Suphapeetiporn, K. Interleukin-10 Promoter Polymorphisms and Expression in Thai Children with Juvenile Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Lupus 2013, 22, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifuku, M.; Miyake, K.; Watanebe, M.; Ito, K.; Abe, Y.; Sasatomi, Y.; Ogahara, S.; Hisano, S.; Sato, H.; Saito, T.; et al. Various Roles of Th Cytokine MRNA Expression in Different Forms of Glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2013, 38, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenzwajg, M.; Languille, E.; Debiec, H.; Hygino, J.; Dahan, K.; Simon, T.; Klatzmann, D.; Ronco, P. B- and T-Cell Subpopulations in Patients with Severe Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy May Predict an Early Response to Rituximab. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Wu, H.; Guo, Q.; Yu, H.; Xu, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, Z.; Yi, H. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Promote the Progression of Primary Membranous Nephropathy by Enhancing Th17 Response. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremoni, M.; Brglez, V.; Perez, S.; Decoupigny, F.; Zorzi, K.; Andreani, M.; Gérard, A.; Boyer-Suavet, S.; Ruetsch, C.; Benzaken, S.; et al. Th17-Immune Response in Patients With Membranous Nephropathy Is Associated With Thrombosis and Relapses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Li, X.-K. The Role of Immune Modulation in Pathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswas, P.S. IL-17 in Renal Immunity and Autoimmunity. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 3153–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hahn, W.H.; Cho, B.S.; Kim, S.D.; Kim, S.K.; Kang, S. Interleukin-1 Cluster Gene Polymorphisms in Childhood IgA Nephropathy. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2009, 24, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, Y.; Yorioka, N.; Kumagai, J.; Katsutani, M.; Kuratsune, M.; Amimoto, D.; Yamakido, M. Interleukin-6 Localization and the Prognosis of IgA Nephropathy. Nephron 1999, 81, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.; Akai, Y.; Kurumatani, N.; Iwano, M.; Saito, Y. Prognostic Value of Urinary Interleukin 6 in Patients with IgA Nephropathy: An 8-Year Follow-Up Study. Nephron 2002, 92, 824–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruswamy Sangameswaran, K.D.; Baradhi, K.M. Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kronbichler, A.; Leierer, J.; Oh, J.; Meijers, B.; Shin, J.I. Immunologic Changes Implicated in the Pathogenesis of Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2150451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Tao, H. The Role of Th17/IL-17 in the Pathogenesis of Primary Nephrotic Syndrome in Children. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2013, 37, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalavrizioti, D.; Gerolymos, M.; Rodi, M.; Kalliakmani, P.; Provatopoulou, S.; Eleftheriadis, T.; Mouzaki, A.; Goumenos, D.S. T Helper (Th)-Cytokines in the Urine of Patients with Primary Glomerulonephritis Treated with Immunosuppressive Drugs: Can They Predict Outcome? Cytokine 2015, 76, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, A.K. Diabetic Nephropathy—Complications and Treatment. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2014, 7, 361–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Myśliwska, J.; Zorena, K.; Semetkowska-Jurkiewicz, E.; Rachoń, D.; Suchanek, H.; Myśliwski, A. High Levels of Circulating Interleukin-10 in Diabetic Nephropathy Patients. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2005, 16, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Donate-Correa, J.; Martín-Núñez, E.; Muros-de-Fuentes, M.; Mora-Fernández, C.; Navarro-González, J.F. Inflammatory Cytokines in Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 948417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigerlová, E.; Battaglia-Hsu, S.-F. IL-6 Signaling in Diabetic Nephropathy: From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Perspectives. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017, 37, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Liu, X.; Yin, J.; Wu, H.; Cai, X.; Wang, N.; Qian, Y.; Wang, F. IL-6 Receptor Blockade Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy via Inhibiting Inflammasome in Mice. Metabolism 2018, 83, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Alamo, B.; Shabaka, A.; Cachofeiro, V.; Cases-Corona, C.; Fernandez-Juarez, G. PRONEDI study investigators Serum Interleukin-6 Levels Predict Kidney Disease Progression in Diabetic Nephropathy. Clin. Nephrol. 2021, 97, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Devalaraja, M.; Baeres, F.M.M.; Engelmann, M.D.M.; Hovingh, G.K.; Ivkovic, M.; Lo, L.; Kling, D.; Pergola, P.; Raj, D.; et al. IL-6 Inhibition with Ziltivekimab in Patients at High Atherosclerotic Risk (RESCUE): A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 2060–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, L.S.; Torquato, B.G.S.; da Silva, C.A.; dos Reis Monteiro, M.L.G.; dos Santos Martins, A.L.M.; da Silva, M.V.; dos Reis, M.A.; Machado, J.R. Renal Expression of Cytokines and Chemokines in Diabetic Nephropathy. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogacz, A.; Polaszewska, A.; Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; Tejchman, K.; Dziewanowski, K.; Ostrowski, M.; Czerny, B.; Grześkowiak, E.; Sieńko, M.; Machaliński, B.; et al. The Effect of Genetic Variations for Interleukin-10 (IL-10) on the Efficacy of Immunosuppressive Therapy in Patients after Kidney Transplantation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 89, 107059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohkamp, L.-N.; Öllinger, R.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Illigens, B.M.-W.; Siepmann, T. Intraoperative Biomarkers in Renal Transplantation. Nephrology 2016, 21, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parikh, S.V.; Almaani, S.; Brodsky, S.; Rovin, B.H. Update on Lupus Nephritis: Core Curriculum 2020. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvani, N.; Tucci, M.; Richards, H.B.; Tartaglia, P.; Silvestris, F. Th1 Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Lupus Nephritis: The Role of IL-18. Autoimmun. Rev. 2005, 4, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/ (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Kozlowski, L.P. IPC—Isoelectric Point Calculator. Biol. Direct 2016, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Services. Available online: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Align. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/align/ (accessed on 30 November 2021).

| Name | Number of Amino Acids | Molecular Mass [kDa] | Isoelectric Point | Percentage of Hydrophilic Amino Acids | Percentage of Hydrophobic Amino Acids | Secondary Structure | Receptors | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Helix | Β-Strand | ||||||||
| IL-1 | 219 | 24.243 | 6.55 | 59.82 | 40.18 | 1 | 12 | IL-1R1, IL-1R2 | [46] |
| IL-2 | 153 | 17.628 | 7.08 | 56.21 | 43.79 | 5 | 3 | IL-2RA, IL-2RB, IL-2RG | [47] |
| IL-3 | 152 | 17.233 | 7.96 | 50.66 | 49.34 | 5 | 1 | IL-3RA, IL-3RB | [48] |
| IL-4 | 153 | 17.492 | 8.15 | 62.74 | 37.26 | 7 | 2 | IL-4R | [49] |
| IL-5 | 134 | 15.238 | 7.44 | 56.72 | 43.28 | 4 | 0 | IL-5RA, IL-3RB | [50] |
| IL-6 | 212 | 23.718 | 5.98 | 56.60 | 43.40 | 6 | 0 | IL-6R | [51] |
| IL-7 | 177 | 20.187 | 7.83 | 59.32 | 40.68 | 4 | 0 | IL-7R | [52] |
| IL-8 | 99 | 11.098 | 8.11 | 53.53 | 46.47 | 2 | 4 | IL8RB | [53] |
| IL-9 | 144 | 15.909 | 7.72 | 59.03 | 40.97 | 5 | 0 | IL-9R | [54] |
| IL-10 | 178 | 20.517 | 7.23 | 59.55 | 40.45 | 4 | 0 | IL-10RA | [55] |
| IL-11 | 199 | 21.429 | 10.5 | 44.72 | 55.28 | 7 | 0 | IL-11RA | [56] |
| IL-12 subunit alpha | 219 | 24.874 | 5.93 | 55.25 | 44.75 | 5 | 0 | IL-12RB1 | [57] |
| IL-12 subunit beta | 328 | 37.169 | 5.36 | 63.11 | 36.89 | 2 | 24 | [58] | |
| IL-13 | 146 | 15.816 | 7.64 | 49.31 | 50.69 | 4 | 1 | IL-13RA1, IL-13RA2 | [59] |
| IL-14 | 546 | 61.891 | 5.93 | 69.05 | 30.95 | 2 | 0 | Unkown | [60] |
| IL-15 | 162 | 18.086 | 5.00 | 58.02 | 41.96 | 5 | 0 | IL-15RA | [61] |
| Pro-IL-16 | 1332 | 141.752 | 7.19 | 61.94 | 38.06 | 10 | 24 | CD4 | [62] |
| IL-17A | 155 | 17.504 | 7.76 | 59.35 | 40.65 | 1 | 6 | IL-17RA | [63] |
| IL-18 | 193 | 22.326 | 4.41 | 61.66 | 38.34 | 2 | 16 | IL-18R1 | [64] |
| IL-19 | 177 | 20.452 | 6.88 | 57.63 | 42.37 | 7 | 0 | IL-20R | [65] |
| IL-20 | 176 | 20.072 | 7.91 | 59.09 | 40.91 | 6 | 1 | IL-20R | [66] |
| IL-21 | 162 | 18.653 | 8.67 | 63.58 | 36.42 | 6 | 0 | IL-21R | [67] |
| IL-22 | 179 | 20.011 | 7.00 | 55.31 | 44.69 | 7 | 0 | IL2-2RA1 | [68] |
| IL-23 alfa | 189 | 20.730 | 5.73 | 53.97 | 46.03 | 7 | 0 | IL-23R | [69] |
| IL-24 | 206 | 23.825 | 8.05 | 51.94 | 48.06 | 6 | 1 | IL-20R | [70] |
| IL-25 | 177 | 20.330 | 7.55 | 62.15 | 37.85 | 0 | 6 | LY6E | [71] |
| IL-26 | 171 | 19.843 | 9.22 | 57.89 | 42.11 | 5 | 0 | IL-20R1 | [72] |
| IL-27 subunit alpha | 243 | 27.493 | 5.94 | 51.44 | 48.56 | 7 | 0 | IL-27RA | [73] |
| IL-27 subunit beta | 229 | 25.396 | 8.83 | 49.78 | 50.22 | 1 | 15 | IL-27RA | [74] |
| IL-28 Interferon lambda receptor 1 | 520 | 57.653 | 4.8 | 57.11 | 42.89 | 3 | 19 | IL-28R | [75] |
| IL-29 Interferon lambda-1 | 200 | 21.898 | 8.09 | 52.50 | 47.50 | 8 | 0 | Unknown | [76] |
| IL-30 | 243 | 27.493 | 5.94 | 51.44 | 48.56 | 7 | 0 | Unknown | [77] |
| IL-31 | 164 | 18.205 | 5.12 | 57.32 | 42.68 | 4 | 0 | IL-31RA | [77,78] |
| IL-32 | 234 | 26.676 | 5.03 | 58.97 | 41.03 | 8 | 2 | Unknown | [77,79] |
| IL-33 | 270 | 30.759 | 7.86 | 64.81 | 35.19 | 4 | 15 | Unknown | [77,80] |
| IL-34 | 242 | 27.482 | 6.47 | 54.96 | 45.04 | 7 | 1 | Unknown | [77,81] |
| IL-35 | it consists of two subunits: IL-12α and IL-27β | Unknown | [77] | ||||||
| IL-36 alpha | 158 | 17.684 | 5.65 | 56.96 | 43.04 | 2 | 12 | Unknown | [77,82] |
| IL-36 beta | 164 | 18.522 | 8.72 | 62.19 | 37.81 | 0 | 10 | Unknown | [77,83] |
| IL-36 gamma | 168 | 18.721 | 4.94 | 59.76 | 40.24 | 2 | 13 | Unknown | [77,84] |
| IL-37 | 218 | 24.126 | 5.82 | 59.17 | 40.83 | 1 | 12 | IL-18Ra, IL-18BP | [77,85] |
| IL-38 Interleukin-1 family member 10 | 152 | 16.943 | 4.88 | 57.89 | 42.11 | 2 | 12 | IL-1R1, IL-36R | [77,86] |
| IL-39 | composed of the IL-23p19 alpha subunit and Ebi3 beta subunit. | IL-23R, IL-27R, and gp130 | [45,77] | ||||||
| IL-40 | 265 | 29.091 | 7.83 | 54.72 | 45.28 | 1 | 18 | [77,87] | |
| Name | Mutation Site | Change | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | 173 | A → V | Almost no loss of activity | [51,88] |
| 185 | W → R | No loss of activity | ||
| 204 | S → P | 87% loss of activity | ||
| 210 | R → K, E, Q, T, A or P | Loss of activity | ||
| 212 | M → T, N, S or R | |||
| IL-17A | 69 | R → A | Impairs binding to IL-17RA and IL-17RC | [63,89] |
| 78 | R → V | Decreases the affinity for IL-17RA by 5-fold | [63,90] | |
| 90 | W → V | Has no effect on the affinity for IL-17RA | ||
| 108 | Y → I | Decreases the affinity for IL-17RA | ||
| 109 | H → S | |||
| IL-18 | 40 | K → A | Reduces binding to IL-18R1 and the ability to induce IFNG production | [64,91] |
| 41 | L → A | Impairs binding to IL-18R1 and the ability to induce IFNG production | ||
| 44 | K → A: | Reduces binding to IL-18R1 and the ability to induce IFNG production | ||
| 49 | R → A | |||
| 53 | D → A | |||
| 69 | M → A | Impairs binding to IL-18R1 and the ability to induce IFNG production | ||
| 71 | D → A | |||
| 94 | R → A | |||
| 96 | M → A | |||
| 115 | K → A | Reduces binding of the preformed binary complex of IL-18 and IL-18R1 to IL-18RAP resulting in impaired IFNG production | ||
| 120 | K → A | |||
| 134 | D → A | |||
| 140 | R → A | Reduces binding to IL-18R1 and the ability to induce IFNG production | ||
| 144 | G → A | Abolishes binding of the preformed binary complex of IL-18 and IL-18R1 to IL-18RAP | ||
| 145 | H → A | |||
| 146 | D → A | Reduces binding of the preformed binary complex of IL-18 and IL-18R1 to IL-18RAP | ||
| 148 | K → A | Abolishes binding of the preformed binary complex of IL-18 and IL-18R1 to IL-18RAP | ||
| 168 | D → A | Reduces binding to IL-18R1 and the ability to induce IFNG production | ||
| 183 | R → A | Reduces binding of the preformed binary complex of IL-18 and IL-18R1 to IL-18RAP | ||
| 186 | M → A | |||
| IL-33 | 144 | E → K | Decreases affinity for IL-1RL1 | [80,92] |
| 148 | E → K | 7-fold decrease in affinity for IL-1RL1 | ||
| 149 | D → K | Almost abolishes binding to IL-1RL1 | ||
| 165 | E → K | 8-fold decrease in affinity for IL-1RL1 | ||
| 244 | D → K | Decreases affinity for IL-1RL1 |
| Name | Origin/Source | Target Cells | Functions | Link to Disease | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1 | Monocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, neutrophils, fibroblasts | NK cells, Th cells, B cells | Lymphocyte activation, fever, regulates sleep, proinflamatory cytokine, maturation and proliferation | Inflamatory diseases, Autoimmune diseases | [93,94] |
| IL-2 | Th1 cells | T cells, B cells, macrophages | Stimulates growth of T cells | Autoimmune diseases (T cel-mediated) | [95,96,97] |
| IL-3 | Th cells and mast cells | Mast cells, hemapoetic stem cells | Stimulates bone marrow growth | Cancers, allergic diseases | [98,99] |
| IL-4 | Th2 cells, basophils, NKT cells | T cells, B cells | B-cell growth factor, role in tissue adhesion and inflamation | Autoimmune diseases, CLL | [100,101] |
| IL-5 | T cells | Mast cells. Eosinophils | Activated T cells, Differentiation and function of myeloid cells | Asthma, Allergy | [102,103] |
| IL-6 | Monocytes, macrophages, | hemapoetic cells | Activated T cells, contributes to host defense through the stimulation of acute phase responses, hematopoiesis | Autoimmune diseases, multiple myeloma | [104,105] |
| IL-7 | Monocytes, macrophages, epithelial cells | T cells, B cells, NK cells | T-cell development, survival and homeostasis of mature T cells, B cells and T-cell proliferation | Allergy | [106,107] |
| IL-8 | Monocytes and fibroblasts | Neutrophils, eosinofhils, basophils, endothelial cells, keratinocytes | Angiogenesis, induces chemotaxis, stimulates phagocytosis, neutrophil chemotaxis, superoxide release and granule release | Inflamatory diseases | [108,109] |
| IL-9 | Eosinophils, mast cells | T cells, B cells, mast cells | Chemokine, Mast and T-cell growth factor and enhances T-cell survival, mast cell activation and synergy with erythropoietin | Asthma, food allergy, Hodgin’s | [110,111] |
| IL-10 | Macrophages, T cells, B cells, dendritic cells | Mocnocytes, macrophages | Immune supressed | Cancer, allergic reaction | [112,113] |
| IL-11 | Bone marrow, stromal cells | Hepatocyte, myeloid | Synergistic effect on hematopoesis, growth factor for myeloid, osteoclast formation, colony stimulating factor, raised platelet count in vivo and inhibition of proinflammatory cytokine production | allergic reaction | [114,115] |
| IL-12 | stromal cells, macrophages, B cells | T cells, myeloid | Proinflammatory cytokine that regulates T-cell and natural killer cell responses, induces the production of interferon-γ, growth factor for myeloid and induction of Th1 cells | allergic reaction | [116,117] |
| IL-13 | CD4+ T cells (Th2), NKT cells and mast cells | monocytes, fibroblasts, epithelial cells and B cells | Growth factor for myeloid, B-cell growth and differentiation, stimulates isotype switching to IgE, increased collagen synthesis by fibroblasts and inhibits proinflammatory cytokine production | allergic reaction, asthma | [118,119] |
| IL-14 | T cells | B cells | Activated B-cell proliferation and inhibition of immunoglobulin secretion | allergic reaction | [120] |
| IL-15 | Monocytes, epithelium, and muscles | T cells and activated B cells | Proliferation of both B and T cells | Autoimmune diseases | [121,122] |
| Pro-IL-16 | Eosinophils and CD8+ T cells | CD4+ T cells | CD4+ T cell chemoattraction | Infectious diseases | [123] |
| IL-17A | Th-17, NK cells, neutrophils | epithelial and endothelial cells, monocytes, macrophages | Release of IL-6 and other proinflammatory cytokines; stimulates chemokine synthesis by endothelial cells | Contact hypersensitivity, atopic dermatitis | [124,125] |
| IL-18 | Macrophages, osteoblast, dendritic cells | T cells, NK cells | Causes interferon gamma production and enhances NK cell activity | Autoimmune diseases, psorasis | [126,127] |
| IL-19 | Th2 lymphocytes, monocytes, | macrophages, T cells, B cells, endothelial cells and brain resident glial cells | An anti-inflammatory molecule. It promotes immune responses mediated by regulatory lymphocytes | psorasis | [128,129] |
| IL-20 | immune cells and activated epithelial cells | Keratinocytes, monocytes | Skin biology, cellular communication between epithelial cells and the immune system under inflammatory conditions | Psorasis, RA | [130,131] |
| IL-21 | NK cells, CD4+ T cells | T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, keratinocytes | Promotes B- and T-lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation | Cancer, SLE Parasitic diseases, RA | [132,133,134] |
| IL-22 | Activated T cells | Tissue cells, keratinocytes | Inhibits IL-4 production; mucosal surface protection and tissue repair | Psorasis, cancer, IBD | [135,136,137] |
| IL-23 | Macrophages, dendritc cells | T cells, Macrophages | IL-17-producing T cells, promote memory T-cell proliferation | sensitivity to external pathogens | [138,139] |
| IL-24 | Monocytes, T and B cells | Cancer cells | Cancer-specific cell death, causes wound healing and protects against bacterial infections and cardiovascular diseases | Melanoma, psorasis | [140,141,142] |
| IL-25 | Dendritic cells | various types of cells, including Th2 cells | Stimulates the synthesis of the Th2 cytokine profile, including IL-4 and IL-13 | Asthma, autoimmune diseases | [143,144] |
| IL-26 | Activated T cells, NK cells | epithelial cells and intestinal epithelial cells | Induces IL-10 expression; stimulates the production of IL-1-beta, IL-6 and IL-8 and causes Th17 cell generation | IBD | [145,146] |
| IL-27 | T cells, activated dendritic cells | T cells, NK cells | Stimulates IL-10 production, upregulates type-2 interferon synthesis by natural killer cells | Immune pathology | [147,148,149] |
| IL-28 Interferon lambda-1 | Regulatory T-cells | keratinocytes and melanocytes | Role in immune defense against viruses, upregulates TLR-2 and TLR-3 expression. IL-28 enhances the keratinocyte capacity to recognize pathogens in the healthy skin | Allergic reaction | [150,151] |
| IL-29 Interferon lambda-1 | dendritic cells, and regulatory T cells | Tissue cells | Viral protective responses | Allergic reaction, cancer | [150,152] |
| IL-30 | Monocytes | monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, T and B lymphocytes, natural killer cells, mast cells, and endothelial cell | Regulate inflammation by inhibiting Th17 cells production using the STAT1 pathway | Cancer, psorasis | [153,154] |
| IL-31 | Th2 cells and dendritic cells | Monocytes, basophils, keratinocytes | Induces chemokines production and synthesis of IL-6, IL-16 and IL-32, helps trigger cell-mediated immunity against pathogens | Autoimmune skin diseases | [155,156] |
| IL-32 | Monocytes, NK cells | Monocytes, macrophages | Induces the synthesis of various cytokines including IL-6 and IL-1beta. It inhibits IL-15 production | Asthma, cancer | [157,158] |
| IL-33 | Mast cells and Th2 lymphocytes | dendritic cells and T and B lymphocytes | Induces helper T cells, mast cells, eosinophils and basophils to produce type 2 cytokines, protection against parasites and type-I hypersensitivity reaction | Dermatitis, allergy, infectious and inflammatory diseases | [159,160] |
| IL-34 | Heart, colon, prostate | Monocytes, macrophages | Enhances IL-6 production and participates in the differentiation and development of antigen-presenting cells, including microglia | RA, artritis | [161,162,163] |
| IL-35 | B cells | NK cells, activated T cells | Immune suppression, involvement in lymphocyte differentiation | RA, artritis | [164,165] |
| IL-36 | Tissue cells, skin cells | T lymphocytes and NK cells | Regulating the IFN-γ synthesis, stimulates the hematopoiesis and expression of both MHC class I and II molecules | Immune responsce, inflamatory diseases | [166,167] |
| IL-37 | monocytes | Dendritic cells | Regulation of the innate immunity causing immunosuppression | autoimmune disorders | [168,169] |
| IL-38 Interleukin-1 family member 10 | placenta, heart, and brain, tonsils B cells, spleen, skin, and thymus | T cells | Inhibits the synthesis of IL-17 and IL-22 | Inflamatory diseases | [170,171] |
| IL-39 | B cells | neutrophils | Neutrophils differentiation or expansion | systemic lupus erythematosus, acute coronary syndrome | [45] |
| IL-40 | bone marrow, fetal liver, and by activated B cells | B cells | Development of humoral immune responses, involved in IgA production and B cell homeostasis and development | Lymphoma | [77,172] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mertowska, P.; Mertowski, S.; Smarz-Widelska, I.; Grywalska, E. Biological Role, Mechanism of Action and the Importance of Interleukins in Kidney Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020647
Mertowska P, Mertowski S, Smarz-Widelska I, Grywalska E. Biological Role, Mechanism of Action and the Importance of Interleukins in Kidney Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(2):647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020647
Chicago/Turabian StyleMertowska, Paulina, Sebastian Mertowski, Iwona Smarz-Widelska, and Ewelina Grywalska. 2022. "Biological Role, Mechanism of Action and the Importance of Interleukins in Kidney Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 2: 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020647
APA StyleMertowska, P., Mertowski, S., Smarz-Widelska, I., & Grywalska, E. (2022). Biological Role, Mechanism of Action and the Importance of Interleukins in Kidney Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(2), 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020647






