Look Who’s Talking: Host and Pathogen Drivers of Staphylococcus epidermidis Virulence in Neonatal Sepsis
Abstract
1. Introduction
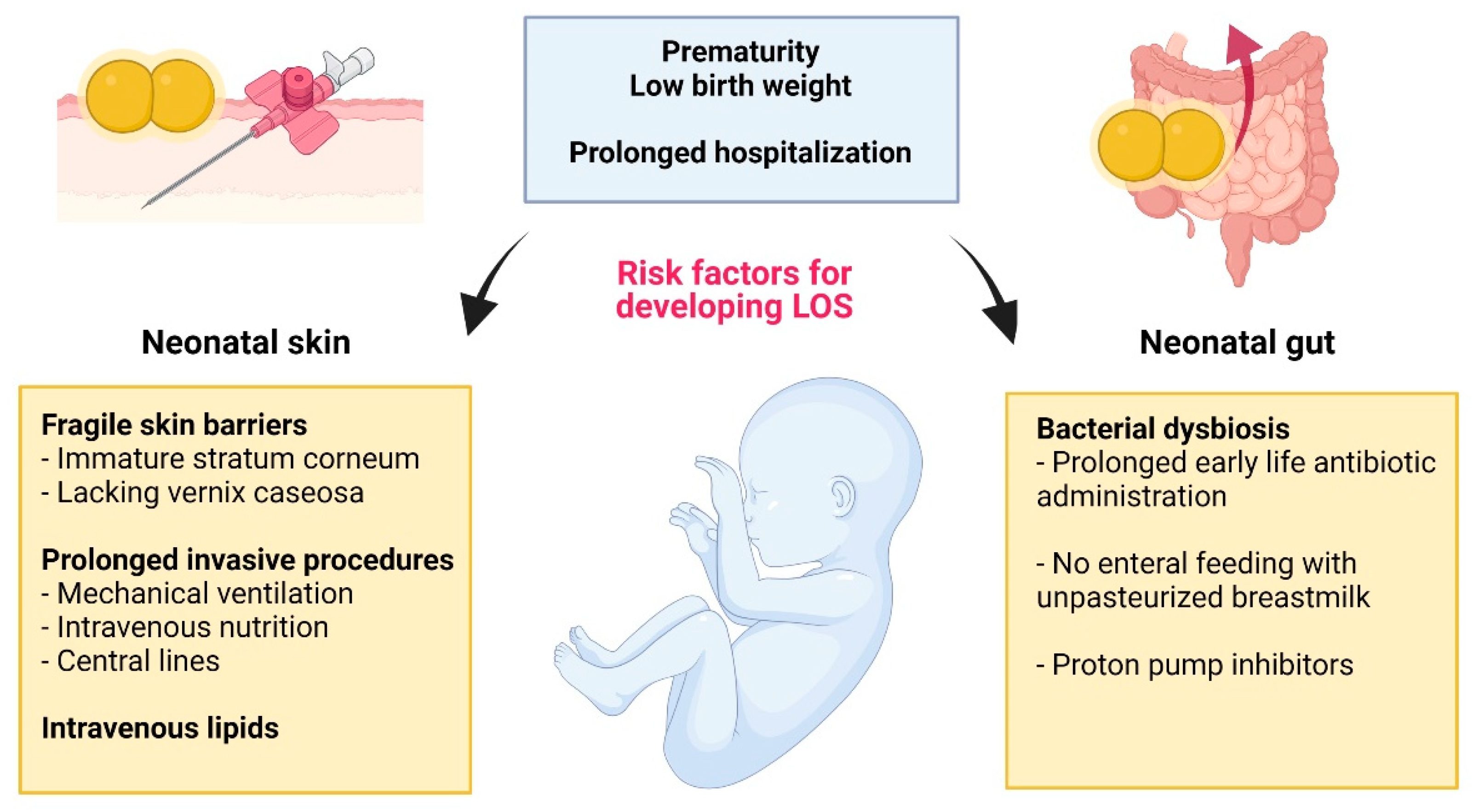
Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment of LOS
2. S. epidermidis: Friend and Foe
2.1. S. epidermidis as an Early and Ubiquitous Colonizer of the Newborn
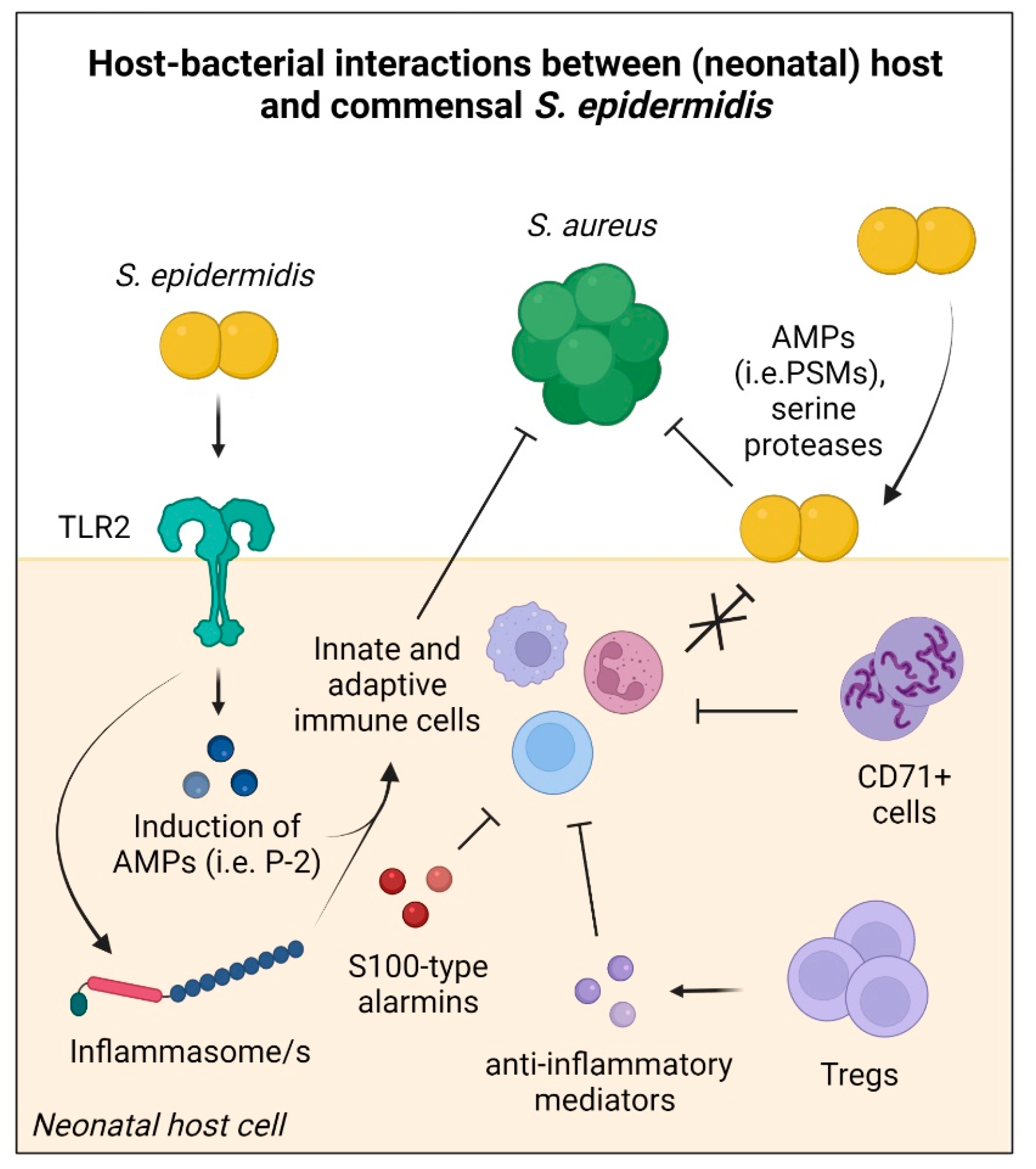
2.2. Establishing Host Tolerance to Commensal S. epidermidis
2.3. Contribution of S. epidermidis to Host Defence
2.4. S. epidermidis as a Human Pathogen
3. S. epidermidis: Inside, Outside—Everywhere?
4. Genetic Determinants of Virulence in Commensal and Invasive S. epidermidis
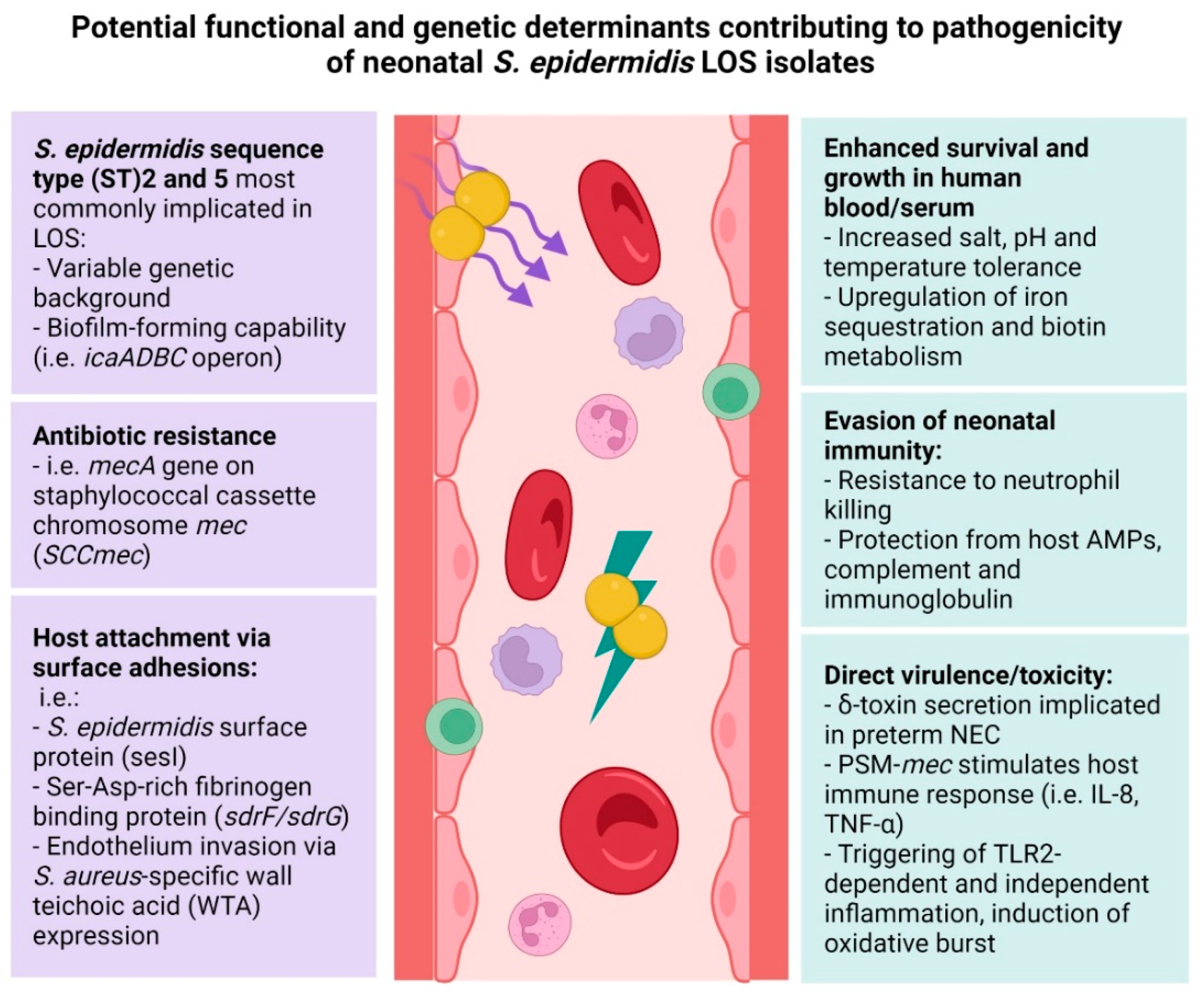
4.1. Nosocomial S. epidermidis Strains Implicated in Neonatal Infection
4.2. The Role of S. epidermidis Biofilm in Neonatal Invasive Disease
4.3. The Role of S. epidermidis Host Adhesion in Neonatal Invasive Disease
4.4. The Role of S. epidermidis Toxins in Neonatal Invasive Disease
4.5. S. epidermidis Antibiotic Resistance and Neonatal Invasive Disease
5. Phenotypic Characteristics of S. epidermidis Clinical Isolates
6. S. epidermidis Gene Expression during Neonatal Host Invasion
7. The Neonatal Host as an Important Contributor to S. epidermidis Virulence
8. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chawanpaiboon, S.; Vogel, J.P.; Moller, A.-B.; Lumbiganon, P.; Petzold, M.; Hogan, D.; Landoulsi, S.; Jampathong, N.; Kongwattanakul, K.; Laopaiboon, M.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Estimates of Levels of Preterm Birth in 2014: A Systematic Review and Modelling Analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, e37–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horbar, J.D.; Edwards, E.M.; Greenberg, L.T.; Morrow, K.A.; Soll, R.F.; Buus-Frank, M.E.; Buzas, J.S. Variation in Performance of Neonatal Intensive Care Units in the United States. JAMA Pediatrics 2017, 171, e164396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingg, W.; Hopkins, S.; Gayet-Ageron, A.; Holmes, A.; Sharland, M.; Suetens, C.; Almeida, M.; Asembergiene, J.; Borg, M.A.; Budimir, A.; et al. Health-Care-Associated Infections in Neonates, Children, and Adolescents: An Analysis of Paediatric Data from the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control Point-Prevalence Survey. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann-Struzek, C.; Goldfarb, D.M.; Schlattmann, P.; Schlapbach, L.J.; Reinhart, K.; Kissoon, N. The Global Burden of Paediatric and Neonatal Sepsis: A Systematic Review. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, B.J.; Puopolo, K.M.; Hansen, N.I.; Sánchez, P.J.; Bell, E.F.; Carlo, W.A.; Cotten, C.M.; D’Angio, C.T.; Kazzi, S.N.J.; Poindexter, B.B.; et al. Early-Onset Neonatal Sepsis 2015 to 2017, the Rise of Escherichia Coli, and the Need for Novel Prevention Strategies. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, e200593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Speer, C.P. Late-Onset Neonatal Sepsis: Recent Developments. Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2015, 100, F257–F263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boghossian, N.S.; Page, G.P.; Bell, E.F.; Stoll, B.J.; Murray, J.C.; Cotten, C.M.; Shankaran, S.; Walsh, M.C.; Laptook, A.R.; Newman, N.S.; et al. Late-Onset Sepsis in Very Low Birth Weight Infants from Singleton and Multiple-Gestation Births. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, B.J.; Hansen, N.; Fanaroff, A.A.; Wright, L.L.; Carlo, W.A.; Ehrenkranz, R.A.; Lemons, J.A.; Donovan, E.F.; Stark, A.R.; Tyson, J.E.; et al. Late-Onset Sepsis in Very Low Birth Weight Neonates: The Experience of the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics 2002, 110, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Hoogen, A.; Gerards, L.J.; Verboon-Maciolek, M.A.; Fleer, A.; Krediet, T.G. Long-Term Trends in the Epidemiology of Neonatal Sepsis and Antibiotic Susceptibility of Causative Agents. Neonatology 2010, 97, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchant, E.A.; Boyce, G.K.; Sadarangani, M.; Lavoie, P.M. Neonatal Sepsis Due to Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 586076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Speer, C.P.; Glaser, K. Beyond Sepsis: Staphylococcus Epidermidis Is an Underestimated but Significant Contributor to Neonatal Morbidity. Virulence 2018, 9, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.L.; Johnson, T.J.; Engstrom, J.L.; Fogg, L.F.; Jegier, B.J.; Bigger, H.R.; Meier, P.P. Impact of Early Human Milk on Sepsis and Health-Care Costs in Very Low Birth Weight Infants. J. Perinatol. 2013, 33, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.-Q.; Hu, H.-J.; Liu, C.-Y.; Shakya, S.; Li, Z.-Y. Probiotics for Preventing Late-Onset Sepsis in Preterm Neonates: A PRISMA-Compliant Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Medicine 2016, 95, e2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, C.; Reichert, F.; Cassini, A.; Horner, R.; Harder, T.; Markwart, R.; Tröndle, M.; Savova, Y.; Kissoon, N.; Schlattmann, P.; et al. Global Incidence and Mortality of Neonatal Sepsis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2021, 106, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Glaser, K.; Speer, C.P. Late-Onset Sepsis Caused by Gram-Negative Bacteria in Very Low Birth Weight Infants: A Systematic Review. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2019, 17, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaikh, B.; Yee, W.; Lodha, A.; Henderson, E.; Yusuf, K.; Sauve, R. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus Sepsis in Preterm Infants and Long-Term Neurodevelopmental Outcome. J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonnenberg, I.A.; van Dijk, J.; van den Dungen, F.A.M.; Vermeulen, R.J.; van Weissenbruch, M.M. The Prognostic Value of NIRS in Preterm Infants with (Suspected) Late-Onset Sepsis in Relation to Long Term Outcome: A Pilot Study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Speer, C.P. The Role of Staphylococcus Epidermidis in Neonatal Sepsis: Guarding Angel or Pathogenic Devil? Int. J. Med Microbiol. 2014, 304, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, C.M.; Palazzi, D.L.; Edwards, M.S.; Campbell, J.R.; Baker, C.J. Features of Invasive Staphylococcal Disease in Neonates. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iroh Tam, P.-Y.; Bendel, C.M. Diagnostics for Neonatal Sepsis: Current Approaches and Future Directions. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 82, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranieri, I.; Kanunfre, K.A.; Rodrigues, J.C.; Yamamoto, L.; Nadaf, M.I.V.; Palmeira, P.; Okay, T.S. Assessment and Comparison of Bacterial Load Levels Determined by Quantitative Amplifications in Blood Culture-Positive and Negative Neonatal Sepsis. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2018, 60, e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, J.A.; Manzella, J.P.; Bankert, D.A. Frequency of Low-Level Bacteremia in Children from Birth to Fifteen Years of Age. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2181–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinschmidt, S.; Huygens, F.; Faoagali, J.; Rathnayake, I.U.; Hafner, L.M. Staphylococcus Epidermidis as a Cause of Bacteremia. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 1859–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, F.; Allegaert, K.; Arribas, C.; Villamor, E.; Raffaeli, G.; Paniagua, M.; Cavallaro, G. Variations in Antibiotic Use and Sepsis Management in Neonatal Intensive Care Units: A European Survey. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Arias, C.A.; Aitken, S.L.; Galloway Peña, J.; Panesso, D.; Chang, M.; Diaz, L.; Rios, R.; Numan, Y.; Ghaoui, S.; et al. Clonal Emergence of Invasive Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus Epidermidis Deconvoluted via a Combination of Whole-Genome Sequencing and Microbiome Analyses. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, S.; Knoll, M.A.; Berktold, M.; Würzner, R.; Brindlmayer, A.; Weber, V.; Posch, A.E.; Mrazek, K.; Lepuschitz, S.; Ante, M.; et al. Genomic and Phenotypic Analysis of Linezolid-Resistant Staphylococcus Epidermidis in a Tertiary Hospital in Innsbruck, Austria. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, N.; Hernandez, A.; Amit, L.; Klinger, G.; Ashkenazi, S.; Levy, I. Persistent Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Bacteremia in Very-Low-Birth-Weight Infants. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2011, 170, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannery, D.D.; Ross, R.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Tribble, A.C.; Puopolo, K.M.; Gerber, J.S. Temporal Trends and Center Variation in Early Antibiotic Use Among Premature Infants. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e180164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantey, J.B.; Wozniak, P.S.; Sánchez, P.J. Prospective Surveillance of Antibiotic Use in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: Results from the SCOUT Study. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, J.T.; Lauren Ruoss, J.; de la Cruz, D.; Li, N.; Bazacliu, C.; Patton, L.; McKinley, K.L.; Garrett, T.J.; Polin, R.A.; Triplett, E.W.; et al. Antibiotics and the Developing Intestinal Microbiome, Metabolome and Inflammatory Environment in a Randomized Trial of Preterm Infants. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, J.Y.; Roberts, A.; Sherlock, R.; Ojah, C.; Cieslak, Z.; Dunn, M.; Barrington, K.; Yoon, E.W.; Shah, P.S. Canadian Neonatal Network Investigators Duration of Initial Empirical Antibiotic Therapy and Outcomes in Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20182286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasethu, J. Prevention and Treatment of Neonatal Nosocomial Infections. Matern. Health Neonatol. Perinatol. 2017, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunk, T.; Pupala, S.; Hibbert, J.; Doherty, D.; Patole, S. Topical Coconut Oil in Very Preterm Infants: An Open-Label Randomised Controlled Trial. Neonatology 2018, 113, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüller, S.S.; Kramer, B.W.; Villamor, E.; Spittler, A.; Berger, A.; Levy, O. Immunomodulation to Prevent or Treat Neonatal Sepsis: Past, Present, and Future. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gutierrez, E.; Walsh, C.J.; Sayavedra, L.; Diaz-Calvo, T.; Thapa, D.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Mayer, M.J.; Cotter, P.D.; Narbad, A. Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Fecal Staphylococcus Epidermidis Isolates Suggests Plasticity to Adapt to Different Human Body Sites. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, A.L.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A. The Human Skin Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Meng, H.; Lv, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; He, L.; Qin, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Staphylococcus Epidermidis Contributes to Healthy Maturation of the Nasal Microbiome by Stimulating Antimicrobial Peptide Production. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 68–78.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinson, L.F.; Boyce, M.C.; Payne, M.S.; Keelan, J.A. The Not-so-Sterile Womb: Evidence That the Human Fetus Is Exposed to Bacteria Prior to Birth. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGiulio, D.B.; Romero, R.; Amogan, H.P.; Kusanovic, J.P.; Bik, E.M.; Gotsch, F.; Kim, C.J.; Erez, O.; Edwin, S.; Relman, D.A. Microbial Prevalence, Diversity and Abundance in Amniotic Fluid during Preterm Labor: A Molecular and Culture-Based Investigation. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Moles, L.; Melgar, A.; Ureta, N.; Bustos, G.; Fernández, L.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Jiménez, E. Early Gut Colonization of Preterm Infants: Effect of Enteral Feeding Tubes. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 62, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, R.L.; Culhane, J.F.; Iams, J.D.; Romero, R. Epidemiology and Causes of Preterm Birth. Lancet 2008, 371, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, F.; Tun, H.M.; Konya, T.B.; Guttman, D.S.; Chari, R.S.; Field, C.J.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; Subbarao, P.; et al. Cesarean Section, Formula Feeding, and Infant Antibiotic Exposure: Separate and Combined Impacts on Gut Microbial Changes in Later Infancy. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damaceno, Q.S.; Souza, J.P.; Nicoli, J.R.; Paula, R.L.; Assis, G.B.; Figueiredo, H.C.; Azevedo, V.; Martins, F.S. Evaluation of Potential Probiotics Isolated from Human Milk and Colostrum. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 9, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, K.E.; Ryan, C.A.; Dempsey, E.M.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Breast Milk, a Source of Beneficial Microbes and Associated Benefits for Infant Health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soeorg, H.; Metsvaht, T.; Eelmäe, I.; Metsvaht, H.K.; Treumuth, S.; Merila, M.; Ilmoja, M.-L.; Lutsar, I. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in Human Milk from Mothers of Preterm Compared with Term Neonates. J. Hum. Lact. 2017, 33, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeorg, H.; Treumuth, S.; Metsvaht, H.K.; Eelmäe, I.; Merila, M.; Ilmoja, M.-L.; Lutsar, I.; Metsvaht, T. Higher Intake of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci from Maternal Milk Promotes Gut Colonization with MecA-Negative Staphylococcus Epidermidis in Preterm Neonates. J. Perinatol. 2018, 38, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bæk, O.; Brunse, A.; Nguyen, D.N.; Moodley, A.; Thymann, T.; Sangild, P.T. Diet Modulates the High Sensitivity to Systemic Infection in Newborn Preterm Pigs. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.; Olm, M.R.; Firek, B.A.; Baker, R.; Geller-McGrath, D.; Reimer, S.R.; Soenjoyo, K.R.; Yip, J.S.; Dahan, D.; Thomas, B.C.; et al. The Developing Premature Infant Gut Microbiome Is a Major Factor Shaping the Microbiome of Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Rooms. Microbiome 2018, 6, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, M.K.; Wang, B.; Ahmadi, S.; Burnham, C.-A.D.; Tarr, P.I.; Warner, B.B.; Dantas, G. Developmental Dynamics of the Preterm Infant Gut Microbiota and Antibiotic Resistome. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparrini, A.J.; Wang, B.; Sun, X.; Kennedy, E.A.; Hernandez-Leyva, A.; Ndao, I.M.; Tarr, P.I.; Warner, B.B.; Dantas, G. Metagenomic Signatures of Early Life Hospitalization and Antibiotic Treatment in the Infant Gut Microbiota and Resistome Persist Long after Discharge. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2285–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, I.; Morowitz, M.J.; Thomas, B.C.; Costello, E.K.; Relman, D.A.; Banfield, J.F. Time Series Community Genomics Analysis Reveals Rapid Shifts in Bacterial Species, Strains, and Phage during Infant Gut Colonization. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Spoto, M.; Hardy, R.; Guan, C.; Fleming, E.; Larson, P.J.; Brown, J.S.; Oh, J. Host-Specific Evolutionary and Transmission Dynamics Shape the Functional Diversification of Staphylococcus Epidermidis in Human Skin. Cell 2020, 180, 454–470.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R.; Schneider, D.S.; Soares, M.P. Disease Tolerance as a Defense Strategy. Science 2012, 335, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbeson, D.; Ben-Othman, R.; Amenyogbe, N.; Kollmann, T.R. Outgrowing the Immaturity Myth: The Cost of Defending from Neonatal Infectious Disease. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, E.A.; You, D.; Shrestha, B.; Siefker, D.; Patel, V.S.; Yadav, N.; Jaligama, S.; Cormier, S.A. A Neonatal Murine Model of MRSA Pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagel, J.; Twisselmann, N.; Rausch, T.K.; Waschina, S.; Hartz, A.; Steinbeis, M.; Olbertz, J.; Nagel, K.; Steinmetz, A.; Faust, K.; et al. Increased Regulatory T Cells Precede the Development of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Preterm Infants. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 565257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharschmidt, T.C.; Vasquez, K.S.; Truong, H.-A.; Gearty, S.V.; Pauli, M.L.; Nosbaum, A.; Gratz, I.K.; Otto, M.; Moon, J.J.; Liese, J.; et al. A Wave of Regulatory T Cells into Neonatal Skin Mediates Tolerance to Commensal Microbes. Immunity 2015, 43, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, J.M.; Dhariwala, M.O.; Lowe, M.M.; Chu, K.; Merana, G.R.; Cornuot, C.; Weckel, A.; Ma, J.M.; Leitner, E.G.; Gonzalez, J.R.; et al. Toxin-Triggered Interleukin-1 Receptor Signaling Enables Early-Life Discrimination of Pathogenic versus Commensal Skin Bacteria. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 795–809.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagel, J.; Hartz, A.; Figge, J.; Gille, C.; Eschweiler, S.; Petersen, K.; Schreiter, L.; Hammer, J.; Karsten, C.M.; Friedrich, D.; et al. Regulatory T Cell Frequencies Are Increased in Preterm Infants with Clinical Early-Onset Sepsis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 185, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- He, Y.-M.; Li, X.; Perego, M.; Nefedova, Y.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Jensen, E.A.; Kagan, V.; Liu, Y.-F.; Fu, S.-Y.; Ye, Q.-J.; et al. Transitory Presence of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Neonates Is Critical for Control of Inflammation. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzywa, T.M.; Nowis, D.; Golab, J. The Role of CD71+ Erythroid Cells in the Regulation of the Immune Response. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 228, 107927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elahi, S.; Vega-López, M.A.; Herman-Miguel, V.; Ramírez-Estudillo, C.; Mancilla-Ramírez, J.; Motyka, B.; West, L.; Oyegbami, O. CD71+ Erythroid Cells in Human Neonates Exhibit Immunosuppressive Properties and Compromise Immune Response Against Systemic Infection in Neonatal Mice. Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 597433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namdar, A.; Koleva, P.; Shahbaz, S.; Strom, S.; Gerdts, V.; Elahi, S. CD71+ Erythroid Suppressor Cells Impair Adaptive Immunity against Bordetella Pertussis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, J.L.; Scumpia, P.O.; Stocks, B.T.; Romano-Keeler, J.; Alrifai, M.W.; Liu, J.-H.; Kim, A.S.; Alford, C.E.; Matta, P.; Weitkamp, J.-H.; et al. Neonatal CD71+ Erythroid Cells Do Not Modify Murine Sepsis Mortality. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirr, S.; Richter, M.; Fehlhaber, B.; Pagel, J.; Härtel, C.; Roth, J.; Vogl, T.; Viemann, D. High Amounts of S100-Alarmins Confer Antimicrobial Activity on Human Breast Milk Targeting Pathogens Relevant in Neonatal Sepsis. Front Immunol. 2017, 8, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulas, T.; Pirr, S.; Fehlhaber, B.; Bickes, M.S.; Loof, T.G.; Vogl, T.; Mellinger, L.; Heinemann, A.S.; Burgmann, J.; Schöning, J.; et al. S100-Alarmin-Induced Innate Immune Programming Protects Newborn Infants from Sepsis. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willers, M.; Ulas, T.; Völlger, L.; Vogl, T.; Heinemann, A.S.; Pirr, S.; Pagel, J.; Fehlhaber, B.; Halle, O.; Schöning, J.; et al. S100A8 and S100A9 Are Important for Postnatal Development of Gut Microbiota and Immune System in Mice and Infants. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 2130–2145.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzidic, M.; Boix-Amorós, A.; Selma-Royo, M.; Mira, A.; Collado, M.C. Gut Microbiota and Mucosal Immunity in the Neonate. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastar, I.; O’Neill, K.; Padula, L.; Head, C.R.; Burgess, J.L.; Chen, V.; Garcia, D.; Stojadinovic, O.; Hower, S.; Plano, G.V.; et al. Staphylococcus Epidermidis Boosts Innate Immune Response by Activation of Gamma Delta T Cells and Induction of Perforin-2 in Human Skin. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.; Bouladoux, N.; Linehan, J.L.; Han, S.-J.; Harrison, O.J.; Wilhelm, C.; Conlan, S.; Himmelfarb, S.; Byrd, A.L.; Deming, C.; et al. Commensal-Dendritic-Cell Interaction Specifies a Unique Protective Skin Immune Signature. Nature 2015, 520, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Jo, A.; Jeon, Y.J.; An, S.; Lee, K.-M.; Yoon, S.S.; Choi, J.Y. Nasal Commensal Staphylococcus Epidermidis Enhances Interferon-λ-Dependent Immunity against Influenza Virus. Microbiome 2019, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuji, T.; Chen, T.H.; Narala, S.; Chun, K.A.; Two, A.M.; Yun, T.; Shafiq, F.; Kotol, P.F.; Bouslimani, A.; Melnik, A.V.; et al. Antimicrobials from Human Skin Commensal Bacteria Protect against Staphylococcus Aureus and Are Deficient in Atopic Dermatitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaah4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwase, T.; Uehara, Y.; Shinji, H.; Tajima, A.; Seo, H.; Takada, K.; Agata, T.; Mizunoe, Y. Staphylococcus Epidermidis Esp Inhibits Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilm Formation and Nasal Colonization. Nature 2010, 465, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, S.; Iwamoto, T.; Takada, K.; Okuda, K.-I.; Tajima, A.; Iwase, T.; Mizunoe, Y. Staphylococcus Epidermidis Esp Degrades Specific Proteins Associated with Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilm Formation and Host-Pathogen Interaction. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.C.; Kananurak, A.; Tran, M.T.; Connolly, P.A.; Polage, C.R.; Iwase, T.; Bevins, C.L.; Underwood, M.A. Bacterial Colonization of the Hospitalized Newborn: Competition Between Staphylococcus Aureus and Staphylococcus Epidermidis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2019, 38, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogen, A.L.; Yamasaki, K.; Muto, J.; Sanchez, K.M.; Crotty Alexander, L.; Tanios, J.; Lai, Y.; Kim, J.E.; Nizet, V.; Gallo, R.L. Staphylococcus Epidermidis Antimicrobial Delta-Toxin (Phenol-Soluble Modulin-Gamma) Cooperates with Host Antimicrobial Peptides to Kill Group A Streptococcus. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linehan, J.L.; Harrison, O.J.; Han, S.-J.; Byrd, A.L.; Vujkovic-Cvijin, I.; Villarino, A.V.; Sen, S.K.; Shaik, J.; Smelkinson, M.; Tamoutounour, S.; et al. Non-Classical Immunity Controls Microbiota Impact on Skin Immunity and Tissue Repair. Cell 2018, 172, 784–796.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogen, A.L.; Yamasaki, K.; Sanchez, K.M.; Dorschner, R.A.; Lai, Y.; MacLeod, D.T.; Torpey, J.W.; Otto, M.; Nizet, V.; Kim, J.E.; et al. Selective Antimicrobial Action Is Provided by Phenol-Soluble Modulins Derived from Staphylococcus Epidermidis, a Normal Resident of the Skin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborel-Préneron, E.; Bianchi, P.; Boralevi, F.; Lehours, P.; Fraysse, F.; Morice-Picard, F.; Sugai, M.; Sato’o, Y.; Badiou, C.; Lina, G.; et al. Effects of the Staphylococcus Aureus and Staphylococcus Epidermidis Secretomes Isolated from the Skin Microbiota of Atopic Children on CD4+ T Cell Activation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, H.-S.; Cheung, G.Y.C.; Otto, M. Antimicrobial Activity of Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Is Caused by Phenol-Soluble Modulin Derivatives. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 8933–8940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Joo, H.-S.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Otto, M. Phenol-Soluble Modulins--Critical Determinants of Staphylococcal Virulence. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 698–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cau, L.; Williams, M.R.; Butcher, A.M.; Nakatsuji, T.; Kavanaugh, J.S.; Cheng, J.Y.; Shafiq, F.; Higbee, K.; Hata, T.R.; Horswill, A.R.; et al. Staphylococcus epidermidis Protease EcpA Can Be a Deleterious Component of the Skin Microbiome in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 955–966.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Im, M.A.; Lee, J.-S.; Mun, J.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Gu, A.; Kim, I.S. Effect of S100A8 and S100A9 on Expressions of Cytokine and Skin Barrier Protein in Human Keratinocytes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 2476–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuji, T.; Chen, T.H.; Butcher, A.M.; Trzoss, L.L.; Nam, S.-J.; Shirakawa, K.T.; Zhou, W.; Oh, J.; Otto, M.; Fenical, W.; et al. A Commensal Strain of Staphylococcus epidermidis Protects against Skin Neoplasia. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaao4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLeo, F.R.; Otto, M.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Chambers, H.F. Community-Associated Meticillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Lancet 2010, 375, 1557–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis—the “accidental” Pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus Aureus Toxins. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 17, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Phenol-Soluble Modulins. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, K.Y.; Villaruz, A.E.; Zheng, Y.; He, L.; Fisher, E.L.; Nguyen, T.H.; Ho, T.V.; Yeh, A.J.; Joo, H.-S.; Cheung, G.Y.C.; et al. Role of Phenol-Soluble Modulins in Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm Formation and Infection of Indwelling Medical Devices. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3015–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis: A Major Player in Bacterial Sepsis? Future Microbiol. 2017, 12, 1031–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, M. Molecular Basis of Staphylococcus epidermidis Infections. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; He, L.; Asiamah, T.K.; Otto, M. Colonization of Medical Devices by Staphylococci. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 3141–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaté Brescó, M.; Harris, L.G.; Thompson, K.; Stanic, B.; Morgenstern, M.; O’Mahony, L.; Richards, R.G.; Moriarty, T.F. Pathogenic Mechanisms and Host Interactions in Staphylococcus epidermidis Device-Related Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcal Biofilms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 6.4.27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büttner, H.; Mack, D.; Rohde, H. Structural Basis of Staphylococcus Epidermidis Biofilm Formation: Mechanisms and Molecular Interactions. Front Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmann, C.; Schweitzer, O.; Gerke, C.; Vanittanakom, N.; Mack, D.; Götz, F. Molecular Basis of Intercellular Adhesion in the Biofilm-Forming Staphylococcus Epidermidis. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 20, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, D.; Fischer, W.; Krokotsch, A.; Leopold, K.; Hartmann, R.; Egge, H.; Laufs, R. The Intercellular Adhesin Involved in Biofilm Accumulation of Staphylococcus Epidermidis Is a Linear Beta-1,6-Linked Glucosaminoglycan: Purification and Structural Analysis. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christner, M.; Franke, G.C.; Schommer, N.N.; Wendt, U.; Wegert, K.; Pehle, P.; Kroll, G.; Schulze, C.; Buck, F.; Mack, D.; et al. The Giant Extracellular Matrix-Binding Protein of Staphylococcus Epidermidis Mediates Biofilm Accumulation and Attachment to Fibronectin. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 75, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, H.; Burdelski, C.; Bartscht, K.; Hussain, M.; Buck, F.; Horstkotte, M.A.; Knobloch, J.K.-M.; Heilmann, C.; Herrmann, M.; Mack, D. Induction of Staphylococcus Epidermidis Biofilm Formation via Proteolytic Processing of the Accumulation-Associated Protein by Staphylococcal and Host Proteases. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1883–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tormo, M.Á.; Knecht, E.; Götz, F.; Lasa, I.; Penadés, J.R. Bap-Dependent Biofilm Formation by Pathogenic Species of Staphylococcus: Evidence of Horizontal Gene Transfer? Microbiology 2005, 151, 2465–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, M.E.; Fey, P.D.; Heilmann, C.; Götz, F. Characterization of the Importance of Staphylococcus Epidermidis Autolysin and Polysaccharide Intercellular Adhesin in the Pathogenesis of Intravascular Catheter-Associated Infection in a Rat Model. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 1038–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmann, C.; Thumm, G.; Chhatwal, G.S.; Hartleib, J.; Uekötter, A.; Peters, G. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Autolysin (Aae) with Adhesive Properties from Staphylococcus Epidermidis. Microbiology 2003, 149, 2769–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R. Extracellular DNA (EDNA). A Major Ubiquitous Element of the Bacterial Biofilm Architecture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Ou, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Molin, S.; Qu, D. Role of Autolysin-Mediated DNA Release in Biofilm Formation of Staphylococcus Epidermidis. Microbiology 2007, 153, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.E.; Todd, D.A.; Schaeffer, C.R.; Paharik, A.E.; Van Dyke, M.J.; Büttner, H.; Dunman, P.M.; Rohde, H.; Cech, N.B.; Fey, P.D.; et al. Staphylococcus epidermidis agr Quorum-Sensing System: Signal Identification, Cross Talk, and Importance in Colonization. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 3482–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, M.; Süssmuth, R.; Jung, G.; Götz, F. Structure of the Pheromone Peptide of the Staphylococcus epidermidis agr System. FEBS Lett. 1998, 424, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, P.; Jarraud, S.; Vandenesch, F.; Greenland, T.; Novick, R.P.; Bes, M.; Etienne, J.; Lina, G. High Genetic Variability of the Agr Locus in Staphylococcus Species. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, M.; Echner, H.; Voelter, W.; Götz, F. Pheromone Cross-Inhibition between Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 1957–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuong, C.; Dürr, M.; Carmody, A.B.; Peschel, A.; Klebanoff, S.J.; Otto, M. Regulated Expression of Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern Molecules in Staphylococcus epidermidis: Quorum-Sensing Determines pro-Inflammatory Capacity and Production of Phenol-Soluble Modulins. Cell Microbiol. 2004, 6, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Khan, B.A.; Cheung, G.Y.C.; Bach, T.-H.L.; Jameson-Lee, M.; Kong, K.-F.; Queck, S.Y.; Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis Surfactant Peptides Promote Biofilm Maturation and Dissemination of Biofilm-Associated Infection in Mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periasamy, S.; Joo, H.-S.; Duong, A.C.; Bach, T.-H.L.; Tan, V.Y.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Cheung, G.Y.C.; Otto, M. How Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms Develop Their Characteristic Structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Otto, M. Genomewide Analysis of Gene Expression in Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilms: Insights into the Pathophysiology of S. epidermidis Biofilms and the Role of Phenol-Soluble Modulins in Formation of Biofilms. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, C.; Voyich, J.M.; Fischer, E.R.; Braughton, K.R.; Whitney, A.R.; DeLeo, F.R.; Otto, M. Polysaccharide Intercellular Adhesin (PIA) Protects Staphylococcus epidermidis against Major Components of the Human Innate Immune System. Cell Microbiol. 2004, 6, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Rigby, K.; Wang, R.; Queck, S.Y.; Braughton, K.R.; Whitney, A.R.; Teintze, M.; DeLeo, F.R.; Otto, M. Staphylococcus Epidermidis Strategies to Avoid Killing by Human Neutrophils. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardan, A.; Nizet, V.; Gallo, R.L. Antimicrobial Peptides and the Skin. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2004, 4, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorschner, R.A.; Lin, K.H.; Murakami, M.; Gallo, R.L. Neonatal Skin in Mice and Humans Expresses Increased Levels of Antimicrobial Peptides: Innate Immunity during Development of the Adaptive Response. Pediatr. Res. 2003, 53, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, V.P.; Akinbi, H.T.; Meinzen-Derr, J.; Narendran, V.; Visscher, M.; Hoath, S.B. Host Defense Proteins on the Surface of Neonatal Skin: Implications for Innate Immunity. J. Pediatr. 2008, 152, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, K.Y.; Park, M.D.; Otto, M. Immune Evasion Mechanisms of Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, M. Bacterial Evasion of Antimicrobial Peptides by Biofilm Formation. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2006, 306, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristian, S.A.; Birkenstock, T.A.; Sauder, U.; Mack, D.; Götz, F.; Landmann, R. Biofilm Formation Induces C3a Release and Protects Staphylococcus epidermidis from IgG and Complement Deposition and from Neutrophil-Dependent Killing. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Lai, Y.; Villaruz, A.E.; Cha, D.J.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Otto, M. Gram-Positive Three-Component Antimicrobial Peptide-Sensing System. Proc. Natl Acad Sci USA 2007, 104, 9469–9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, S.K.; Cho, J.; Cheung, A.L. GraS Sensory Activity in Staphylococcus epidermidis Is Modulated by the “Guard Loop” of VraG and the ATPase Activity of VraF. J. Bacteriol. 2021, 203, e0017821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widerström, M.; Wiström, J.; Edebro, H.; Marklund, E.; Backman, M.; Lindqvist, P.; Monsen, T. Colonization of Patients, Healthcare Workers, and the Environment with Healthcare-Associated Staphylococcus epidermidis Genotypes in an Intensive Care Unit: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lepainteur, M.; Desroches, M.; Bourrel, A.S.; Aberrane, S.; Fihman, V.; L’Hériteau, F.; Razafimahefa, H.; Derouin, V.; Doucet-Populaire, F.; Decousser, J.-W. Role of the Central Venous Catheter in Bloodstream Infections Caused by Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in Very Preterm Neonates. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 32, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golińska, E.; Strus, M.; Tomusiak-Plebanek, A.; Więcek, G.; Kozień, Ł.; Lauterbach, R.; Pawlik, D.; Rzepecka-Węglarz, B.; Kędzierska, J.; Dorycka, M.; et al. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Contained in Gut Microbiota as a Primary Source of Sepsis in Low- and Very Low Birth Weight Neonates. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensollen, T.; Iyer, S.S.; Kasper, D.L.; Blumberg, R.S. How Colonization by Microbiota in Early Life Shapes the Immune System. Science 2016, 352, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, E.I.; Hoang, D.M.; Vandenplas, Y. The Effects of Proton Pump Inhibitors on the Microbiome in Young Children. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Borbet, T.C.; Fallegger, A.; Wipperman, M.F.; Blaser, M.J.; Müller, A. An Antibiotic-Impacted Microbiota Compromises the Development of Colonic Regulatory T Cells and Predisposes to Dysregulated Immune Responses. mBio 2021, 12, e03335-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirpuri, J. The Emerging Role of Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells in the Neonate: Interaction with the Maternal and Neonatal Microbiome. Oxford Open Immunol. 2021, 2, iqab009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Daniel, S.; Kumar, D.; Ding, E.Y.; Savani, R.C.; Koh, A.Y.; Mirpuri, J. Transient Neonatal Antibiotic Exposure Increases Susceptibility to Late-Onset Sepsis Driven by Microbiota-Dependent Suppression of Type 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpela, K.; Blakstad, E.W.; Moltu, S.J.; Strømmen, K.; Nakstad, B.; Rønnestad, A.E.; Brække, K.; Iversen, P.O.; Drevon, C.A.; de Vos, W. Intestinal Microbiota Development and Gestational Age in Preterm Neonates. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Dharmaprakash, V.; Nighot, P.; Guo, S.; Nighot, M.; Do, T.; Ma, T.Y. Bifidobacterium Bifidum Enhances the Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction Barrier and Protects against Intestinal Inflammation by Targeting the Toll-like Receptor-2 Pathway in an NF-ΚB-Independent Manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Linglong, P.; Weixia, D.; Hong, W. Protective Effects of Bifidobacterium on Intestinal Barrier Function in LPS-Induced Enterocyte Barrier Injury of Caco-2 Monolayers and in a Rat NEC Model. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moles, L.; Gómez, M.; Moroder, E.; Bustos, G.; Melgar, A.; del Campo, R.; Rodríguez, J.M. Staphylococcus epidermidis in Feedings and Feces of Preterm Neonates. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.J.; Embleton, N.D.; Marrs, E.C.L.; Smith, D.P.; Fofanova, T.; Nelson, A.; Skeath, T.; Perry, J.D.; Petrosino, J.F.; Berrington, J.E.; et al. Longitudinal Development of the Gut Microbiome and Metabolome in Preterm Neonates with Late Onset Sepsis and Healthy Controls. Microbiome 2017, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlan, S.; Mijares, L.A.; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Becker, J.; Blakesley, R.W.; Bouffard, G.G.; Brooks, S.; Coleman, H.; Gupta, J.; Gurson, N.; et al. Staphylococcus epidermidis Pan-Genome Sequence Analysis Reveals Diversity of Skin Commensal and Hospital Infection-Associated Isolates. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, F.; Tian, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, G.; Li, Y.; Han, B.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, G.; et al. Comparative Genome Analysis Reveals the Molecular Basis of Niche Adaptation of Staphylococcus epidermidis Strains. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 566080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méric, G.; Mageiros, L.; Pensar, J.; Laabei, M.; Yahara, K.; Pascoe, B.; Kittiwan, N.; Tadee, P.; Post, V.; Lamble, S.; et al. Disease-Associated Genotypes of the Commensal Skin Bacterium Staphylococcus epidermidis. Nat. Commun 2018, 9, 5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Quiles-Puchalt, N.; Chiang, Y.N.; Bacigalupe, R.; Fillol-Salom, A.; Chee, M.S.J.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Penadés, J.R. Genome Hypermobility by Lateral Transduction. Science 2018, 362, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Larsen, J.; Li, M.; Walter, A.; Slavetinsky, C.; Both, A.; Sanchez Carballo, P.M.; Stegger, M.; Lehmann, E.; Liu, Y.; et al. Staphylococcus epidermidis Clones Express Staphylococcus aureus-Type Wall Teichoic Acid to Shift from a Commensal to Pathogen Lifestyle. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méric, G.; Miragaia, M.; de Been, M.; Yahara, K.; Pascoe, B.; Mageiros, L.; Mikhail, J.; Harris, L.G.; Wilkinson, T.S.; Rolo, J.; et al. Ecological Overlap and Horizontal Gene Transfer in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 1313–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafini, F.; Nguyen, L.T.T.; Higashide, M.; Román, F.; Prieto, J.; Morikawa, K. Horizontal Gene Transmission of the Cfr Gene to MRSA and Enterococcus: Role of Staphylococcus epidermidis as a Reservoir and Alternative Pathway for the Spread of Linezolid Resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci as Reservoirs of Genes Facilitating MRSA Infection: Staphylococcal Commensal Species Such as Staphylococcus epidermidis Are Being Recognized as Important Sources of Genes Promoting MRSA Colonization and Virulence. Bioessays 2013, 35, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeorg, H.; Huik, K.; Parm, Ü.; Ilmoja, M.-L.; Metsvaht, T.; Lutsar, I. Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus epidermidis in Neonatal Intensive Care Units. APMIS 2017, 125, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espadinha, D.; Sobral, R.G.; Mendes, C.I.; Méric, G.; Sheppard, S.K.; Carriço, J.A.; de Lencastre, H.; Miragaia, M. Distinct Phenotypic and Genomic Signatures Underlie Contrasting Pathogenic Potential of Staphylococcus epidermidis Clonal Lineages. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Satorius, A.E.; Raff, M.R.; Rivera, A.; Newton, D.W.; Younger, J.G. Multilocus Sequence Typing for Interpreting Blood Isolates of Staphylococcus Epidermidis. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2014, 2014, 787458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.H.; Monk, I.R.; Gonçalves da Silva, A.; Seemann, T.; Chua, K.Y.L.; Kearns, A.; Hill, R.; Woodford, N.; Bartels, M.D.; Strommenger, B.; et al. Global Spread of Three Multidrug-Resistant Lineages of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelburne, S.A.; Dib, R.W.; Endres, B.T.; Reitzel, R.; Li, X.; Kalia, A.; Sahasrabhojane, P.; Chaftari, A.-M.; Hachem, R.; Vargas-Cruz, N.S.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Staphylococcus Epidermidis Bloodstream Isolates from a Prospective Clinical Trial Reveals That Complicated Bacteraemia Is Caused by a Limited Number of Closely Related Sequence Types. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 646.e1–646.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgueiro, V.C.; Iorio, N.L.P.; Ferreira, M.C.; Chamon, R.C.; dos Santos, K.R.N. Methicillin Resistance and Virulence Genes in Invasive and Nasal Staphylococcus epidermidis Isolates from Neonates. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Both, A.; Huang, J.; Qi, M.; Lausmann, C.; Weißelberg, S.; Büttner, H.; Lezius, S.; Failla, A.V.; Christner, M.; Stegger, M.; et al. Distinct Clonal Lineages and Within-Host Diversification Shape Invasive Staphylococcus epidermidis Populations. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Vuong, C.; Kocianova, S.; Villaruz, A.E.; Lai, Y.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Otto, M. Characterization of the Staphylococcus epidermidis Accessory-Gene Regulator Response: Quorum-Sensing Regulation of Resistance to Human Innate Host Defense. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 193, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozitskaya, S.; Olson, M.E.; Fey, P.D.; Witte, W.; Ohlsen, K.; Ziebuhr, W. Clonal Analysis of Staphylococcus epidermidis Isolates Carrying or Lacking Biofilm-Mediating Genes by Multilocus Sequence Typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4751–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Vuong, C.; Otto, M.; Wen, Y.; Gao, Q. Bacterial Insertion Sequence IS256 as a Potential Molecular Marker to Discriminate Invasive Strains from Commensal Strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Hosp. Infect. 2005, 61, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdbart, J.O.; Allignet, J.; Tung, H.S.; Rydèn, C.; El Solh, N. Screening for Staphylococcus epidermidis Markers Discriminating between Skin-Flora Strains and Those Responsible for Infections of Joint Prostheses. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 182, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K.L.; Rupp, M.E.; Fey, P.D. The Presence of IcaADBC Is Detrimental to the Colonization of Human Skin by Staphylococcus epidermidis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 6155–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härtel, C.; Osthues, I.; Rupp, J.; Haase, B.; Röder, K.; Göpel, W.; Herting, E.; Schultz, C. Characterisation of the Host Inflammatory Response to Staphylococcus Epidermidis in Neonatal Whole Blood. Arch. Dis Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2008, 93, F140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, K.Y.; Otto, M. Quorum-Sensing Regulation in Staphylococci-an Overview. Front Microbiol 2015, 6, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, C.; Gerke, C.; Somerville, G.A.; Fischer, E.R.; Otto, M. Quorum-Sensing Control of Biofilm Factors in Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, C.; Kocianova, S.; Yao, Y.; Carmody, A.B.; Otto, M. Increased Colonization of Indwelling Medical Devices by Quorum-Sensing Mutants of Staphylococcus epidermidis in Vivo. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Park, M.D.; Otto, M. Host Response to Staphylococcus epidermidis Colonization and Infections. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haqan, A.; Boswihi, S.S.; Pathan, S.; Udo, E.E. Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Determinants in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated Mainly from Preterm Neonates. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skiba-Kurek, I.; Nowak, P.; Empel, J.; Tomczak, M.; Klepacka, J.; Sowa-Sierant, I.; Żak, I.; Pomierny, B.; Karczewska, E. Evaluation of Biofilm Formation and Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistant Strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis Isolated from Neonates with Sepsis in Southern Poland. Pathogens 2021, 10, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eftekhar, F.; Speert, D.P. Biofilm Formation by Persistent and Non-Persistent Isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis from a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. J. Hosp. Infect. 2009, 71, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohde, H.; Kalitzky, M.; Kröger, N.; Scherpe, S.; Horstkotte, M.A.; Knobloch, J.K.-M.; Zander, A.R.; Mack, D. Detection of Virulence-Associated Genes Not Useful for Discriminating between Invasive and Commensal Staphylococcus epidermidis Strains from a Bone Marrow Transplant Unit. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 5614–5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrecubieta, C.; Toba, F.A.; von Bayern, M.; Akashi, H.; Deng, M.C.; Naka, Y.; Lowy, F.D. SdrF, a Staphylococcus epidermidis Surface Protein, Contributes to the Initiation of Ventricular Assist Device Driveline-Related Infections. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zhao, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, Y. Pathogenic Implication of a Fibrinogen-Binding Protein of Staphylococcus epidermidis in a Rat Model of Intravascular-Catheter-Associated Infection. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 2991–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Söderquist, B.; Andersson, M.; Nilsson, M.; Nilsdotter-Augustinsson, Å.; Persson, L.; Friberg, Ö.; Jacobsson, S. Staphylococcus epidermidis Surface Protein I (SesI): A Marker of the Invasive Capacity of S. Epidermidis? J. Med Microbiol. 2009, 58, 1395–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Jin, Y.; Duan, J.; Hao, Z.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Lv, J.; Hu, L.; Wang, L.; Yu, F. SesI May Be Associated with the Invasiveness of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamet, A.; Guglielmini, J.; Brancotte, B.; Coureuil, M.; Euphrasie, D.; Meyer, J.; Roux, J.; Barnier, J.-P.; Bille, E.; Ferroni, A.; et al. High-Resolution Typing of Staphylococcus epidermidis Based on Core Genome Multilocus Sequence Typing to Investigate the Hospital Spread of Multidrug-Resistant Clones. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e02454-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, M.G.; Chen, W.; Singvall, J.; Xu, Y.; Peacock, S.J.; Valtulina, V.; Speziale, P.; Höök, M. Identification and Preliminary Characterization of Cell-Wall-Anchored Proteins of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Microbiology 2005, 151, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartford, O.; O’Brien, L.; Schofield, K.; Wells, J.; Foster, T.J. The Fbe (SdrG) Protein of Staphylococcus epidermidis HB Promotes Bacterial Adherence to Fibrinogen. Microbiology 2001, 147, 2545–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schommer, N.N.; Christner, M.; Hentschke, M.; Ruckdeschel, K.; Aepfelbacher, M.; Rohde, H. Staphylococcus epidermidis Uses Distinct Mechanisms of Biofilm Formation to Interfere with Phagocytosis and Activation of Mouse Macrophage-like Cells 774A.1. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 2267–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.J. Surface Proteins of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Da, F.; Fisher, E.L.; Tan, D.C.S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Fu, C.-L.; Tan, V.Y.; McCausland, J.W.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Joo, H.-S.; et al. Toxin Mediates Sepsis Caused by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheifele, D.W.; Bjornson, G.L.; Dyer, R.A.; Dimmick, J.E. Delta-like Toxin Produced by Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Is Associated with Neonatal Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Infect. Immun. 1987, 55, 2268–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, K.; Hellmark, B.; Söderquist, B. Characterization of SCCmec Elements in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis Isolated from Blood Cultures from Neonates during Three Decades. APMIS 2011, 119, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivarsson, M.; Schollin, J.; Björkqvist, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus Trigger Different Interleukin-8 and Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 in Lung Cells: Implications for Inflammatory Complications Following Neonatal Sepsis. Acta Paediatr. 2013, 102, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Månsson, E.; Bech Johannesen, T.; Nilsdotter-Augustinsson, Å.; Söderquist, B.; Stegger, M. Comparative Genomics of Staphylococcus epidermidis from Prosthetic-Joint Infections and Nares Highlights Genetic Traits Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance, Not Virulence. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, H.R.; Holzman, R.S.; Altman, D.R.; Smyth, D.S.; Wasserman, G.A.; Kafer, J.M.; Wible, M.; Mendes, R.E.; Torres, V.J.; Shopsin, B. Cytotoxic Virulence Predicts Mortality in Nosocomial Pneumonia Due to Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 1862–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.J.; Miragaia, M.; Weinberg, A.D.; Lee, C.J.; Rolo, J.; Giacalone, J.C.; Slaughter, M.S.; Pappas, P.; Naka, Y.; Tector, A.J.; et al. Staphylococcus epidermidis Colonization Is Highly Clonal across US Cardiac Centers. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widerström, M.; Monsen, T.; Karlsson, C.; Edebro, H.; Johansson, A.; Wiström, J. Clonality among Multidrug-Resistant Hospital-Associated Staphylococcus epidermidis in Northern Europe. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 41, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, M.; Post, V.; Erichsen, C.; Hungerer, S.; Bühren, V.; Militz, M.; Richards, R.G.; Moriarty, T.F. Biofilm Formation Increases Treatment Failure in Staphylococcus epidermidis Device-Related Osteomyelitis of the Lower Extremity in Human Patients. J. Orthop. Res. 2016, 34, 1905–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granslo, H.N.; Klingenberg, C.; Fredheim, E.G.A.; Rønnestad, A.; Mollnes, T.E.; Flægstad, T. Arginine Catabolic Mobile Element Is Associated with Low Antibiotic Resistance and Low Pathogenicity in Staphylococcus epidermidis From Neonates. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 68, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanAken, S.M.; Newton, D.; VanEpps, J.S. Improved Diagnostic Prediction of the Pathogenicity of Bloodstream Isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0241457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morioka, S.; Ichikawa, M.; Mori, K.; Kurai, H. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcal Bacteraemia in Cancer Patients. Time to Positive Culture Can Distinguish Bacteraemia from Contamination. Infect. Dis. 2018, 50, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Kretschmer, D.; Duong, A.C.; Yeh, A.J.; Ho, T.V.; Chen, Y.; Joo, H.-S.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Peschel, A.; Otto, M. Production of an Attenuated Phenol-Soluble Modulin Variant Unique to the MRSA Clonal Complex 30 Increases Severity of Bloodstream Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laabei, M.; Uhlemann, A.-C.; Lowy, F.D.; Austin, E.D.; Yokoyama, M.; Ouadi, K.; Feil, E.; Thorpe, H.A.; Williams, B.; Perkins, M.; et al. Evolutionary Trade-Offs Underlie the Multi-Faceted Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroza-Dávila, U.; Uribe-Alvarez, C.; Morales-García, L.; Espinoza-Simón, E.; Méndez-Romero, O.; Muhlia-Almazán, A.; Chiquete-Félix, N.; Uribe-Carvajal, S. Metabolism, ATP Production and Biofilm Generation by Staphylococcus epidermidis in Either Respiratory or Fermentative Conditions. AMB Express 2020, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, E.J.; Bates, K.A.; King, K.C. Host Microbiota Can Facilitate Pathogen Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Alvarez, C.; Chiquete-Félix, N.; Contreras-Zentella, M.; Guerrero-Castillo, S.; Peña, A.; Uribe-Carvajal, S. Staphylococcus epidermidis: Metabolic Adaptation and Biofilm Formation in Response to Different Oxygen Concentrations. Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74, ftv111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, A.; Pier, G.B.; Vilanova, M.; Cerca, N. Transcriptomic Analysis of Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm-Released Cells upon Interaction with Human Blood Circulating Immune Cells and Soluble Factors. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, A.; Cerca, N. Plasma Is the Main Regulator of Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilms Virulence Genes Transcription in Human Blood. Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74, ftv125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matinaho, S.; von Bonsdorff, L.; Rouhiainen, A.; Lönnroth, M.; Parkkinen, J. Dependence of Staphylococcus epidermidis on Non-Transferrin-Bound Iron for Growth. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 196, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, F.; França, Â.; Cerca, N. Staphylococcus epidermidis Is Largely Dependent on Iron Availability to Form Biofilms. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 307, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, E.D. Nutritional Immunity. Host’s Attempt to Withold Iron from Microbial Invaders. JAMA 1975, 231, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- França, A.; Carvalhais, V.; Maira-Litrán, T.; Vilanova, M.; Cerca, N.; Pier, G. Alterations in the Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm Transcriptome Following Interaction with Whole Human Blood. Pathog. Dis. 2014, 70, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, N.; Chen, H.; Huang, Y. RNA-Seq Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes of Staphylococcus epidermidis Isolated from Postoperative Endophthalmitis and the Healthy Conjunctiva. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunk, T.; Hibbert, J.; Doherty, D.; Nathan, E.; Simmer, K.; Richmond, P.; Currie, A.; Burgner, D. Impaired Cytokine Responses to Live Staphylococcus epidermidis in Preterm Infants Precede Gram-Positive, Late-Onset Sepsis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Cunningham-Rundles, S.; Dean, C.R.; Hammad, T.A.; Nesin, M. Levels of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Produced from Cord Blood in-Vitro Are Pathogen Dependent and Increased in Comparison to Adult Controls. Cytokine 2007, 39, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravina, G.; Svedin, P.; Ardalan, M.; Levy, O.; Ek, C.J.; Mallard, C.; Lai, J.C.Y. Staphylococcus epidermidis Sensitizes Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Male but Not Female Mice. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, D.; Siemssen, N.; Laufs, R. Parallel Induction by Glucose of Adherence and a Polysaccharide Antigen Specific for Plastic-Adherent Staphylococcus epidermidis: Evidence for Functional Relation to Intercellular Adhesion. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibbert, J.E.; Currie, A.; Strunk, T. Sepsis-Induced Immunosuppression in Neonates. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, A.; Hibbert, J.; Strunk, T.; Kok, C.H.; Simmer, K.; Richmond, P.; Burgner, D.; Currie, A. Phagocytosis of Neonatal Pathogens by Peripheral Blood Neutrophils and Monocytes from Newborn Preterm and Term Infants. Pediatr. Res. 2013, 74, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronforst, K.D.; Mancuso, C.J.; Pettengill, M.; Ninkovic, J.; Coombs, M.R.P.; Stevens, C.; Otto, M.; Mallard, C.; Wang, X.; Goldmann, D.; et al. A Neonatal Model of Intravenous Staphylococcus epidermidis Infection in Mice <24 h Old Enables Characterization of Early Innate Immune Responses. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, D.; Qiao, L.; Bergelson, I.; Ek, C.J.; Duan, L.; Zhang, X.; Albertsson, A.-M.; Pettengill, M.; Kronforst, K.; Ninkovic, J.; et al. Staphylococcus epidermidis Bacteremia Induces Brain Injury in Neonatal Mice via Toll-like Receptor 2-Dependent and -Independent Pathways. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1480–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lai, J.C.Y.; Svedin, P.; Ek, C.J.; Mottahedin, A.; Wang, X.; Levy, O.; Currie, A.; Strunk, T.; Mallard, C. Vancomycin Is Protective in a Neonatal Mouse Model of Staphylococcus epidermidis-Potentiated Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e02003-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strunk, T.; Inder, T.; Wang, X.; Burgner, D.; Mallard, C.; Levy, O. Infection-Induced Inflammation and Cerebral Injury in Preterm Infants. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.; Strunk, T.; Lee, A.H.; Gill, E.E.; Falsafi, R.; Woodman, T.; Hibbert, J.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Currie, A. Whole Blood Transcriptional Responses of Very Preterm Infants during Late-Onset Sepsis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernada, M.; Pinilla-González, A.; Kuligowski, J.; Morales, J.M.; Lorente-Pozo, S.; Piñeiro-Ramos, J.D.; Parra-Llorca, A.; Lara-Cantón, I.; Vento, M.; Serna, E. Transcriptome Profiles Discriminate between Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Sepsis in Preterm Neonates. Pediatr. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, E.; Hancock, D.G.; Hibbert, J.; Wells, C.; Richmond, P.; Simmer, K.; Burgner, D.; Strunk, T.; Currie, A.J. Identification of Generic and Pathogen-Specific Cord Blood Monocyte Transcriptomes Reveals a Largely Conserved Response in Preterm and Term Newborn Infants. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 96, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, E.; Strunk, T.; Burgner, D.; Lavoie, P.M.; Currie, A. The Phenotype and Function of Preterm Infant Monocytes: Implications for Susceptibility to Infection. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunk, T.; Currie, A.; Richmond, P.; Simmer, K.; Burgner, D. Innate Immunity in Human Newborn Infants: Prematurity Means More than Immaturity. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011, 24, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermann, A.J.; Förstner, K.U.; Amman, F.; Barquist, L.; Chao, Y.; Schulte, L.N.; Müller, L.; Reinhardt, R.; Stadler, P.F.; Vogel, J. Dual RNA-Seq Unveils Noncoding RNA Functions in Host-Pathogen Interactions. Nature 2016, 529, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minhas, V.; Aprianto, R.; McAllister, L.J.; Wang, H.; David, S.C.; McLean, K.T.; Comerford, I.; McColl, S.R.; Paton, J.C.; Veening, J.-W.; et al. In Vivo Dual RNA-Seq Analysis Reveals the Basis for Differential Tissue Tropism of Clinical Isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. bioRxiv 2019, 862755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, V.; Aprianto, R.; McAllister, L.J.; Wang, H.; David, S.C.; McLean, K.T.; Comerford, I.; McColl, S.R.; Paton, J.C.; Veening, J.-W.; et al. In Vivo Dual RNA-Seq Reveals That Neutrophil Recruitment Underlies Differential Tissue Tropism of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, A.T.; Brissac, T.; Gilley, R.P.; Kumar, N.; Wang, Y.; Gonzalez-Juarbe, N.; Hinkle, W.S.; Daugherty, S.C.; Shetty, A.C.; Ott, S.; et al. Streptococcus pneumoniae in the Heart Subvert the Host Response through Biofilm-Mediated Resident Macrophage Killing. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Mello, A.; Riegler, A.N.; Martínez, E.; Beno, S.M.; Ricketts, T.D.; Foxman, E.F.; Orihuela, C.J.; Tettelin, H. An in Vivo Atlas of Host–Pathogen Transcriptomes during Streptococcus pneumoniae Colonization and Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 33507–33518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thänert, R.; Goldmann, O.; Beineke, A.; Medina, E. Host-Inherent Variability Influences the Transcriptional Response of Staphylococcus aureus during in Vivo Infection. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joubert, I.A.; Otto, M.; Strunk, T.; Currie, A.J. Look Who’s Talking: Host and Pathogen Drivers of Staphylococcus epidermidis Virulence in Neonatal Sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020860
Joubert IA, Otto M, Strunk T, Currie AJ. Look Who’s Talking: Host and Pathogen Drivers of Staphylococcus epidermidis Virulence in Neonatal Sepsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(2):860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020860
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoubert, Isabella A., Michael Otto, Tobias Strunk, and Andrew J. Currie. 2022. "Look Who’s Talking: Host and Pathogen Drivers of Staphylococcus epidermidis Virulence in Neonatal Sepsis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 2: 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020860
APA StyleJoubert, I. A., Otto, M., Strunk, T., & Currie, A. J. (2022). Look Who’s Talking: Host and Pathogen Drivers of Staphylococcus epidermidis Virulence in Neonatal Sepsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(2), 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020860




