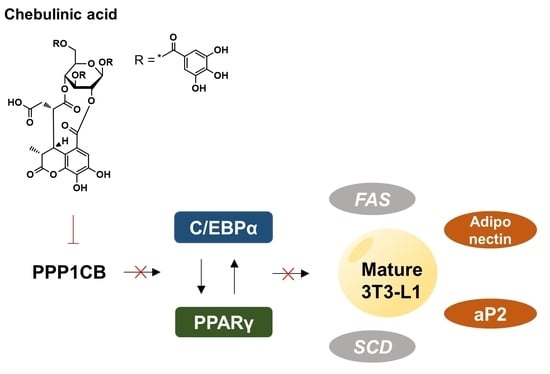
Chebulinic Acid Suppresses Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Inhibiting PPP1CB Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Purification of PPP1CB with Various Affinity Tags
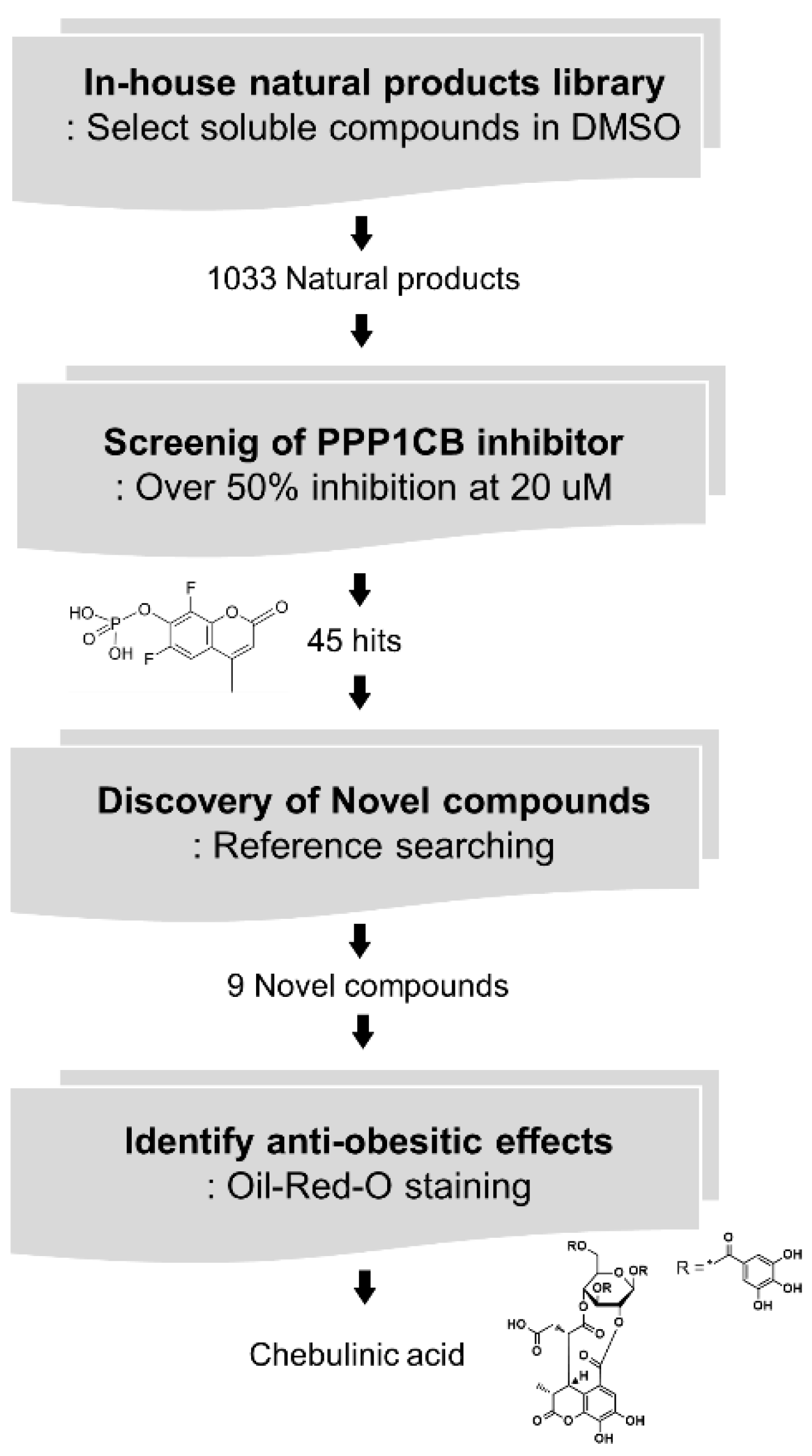
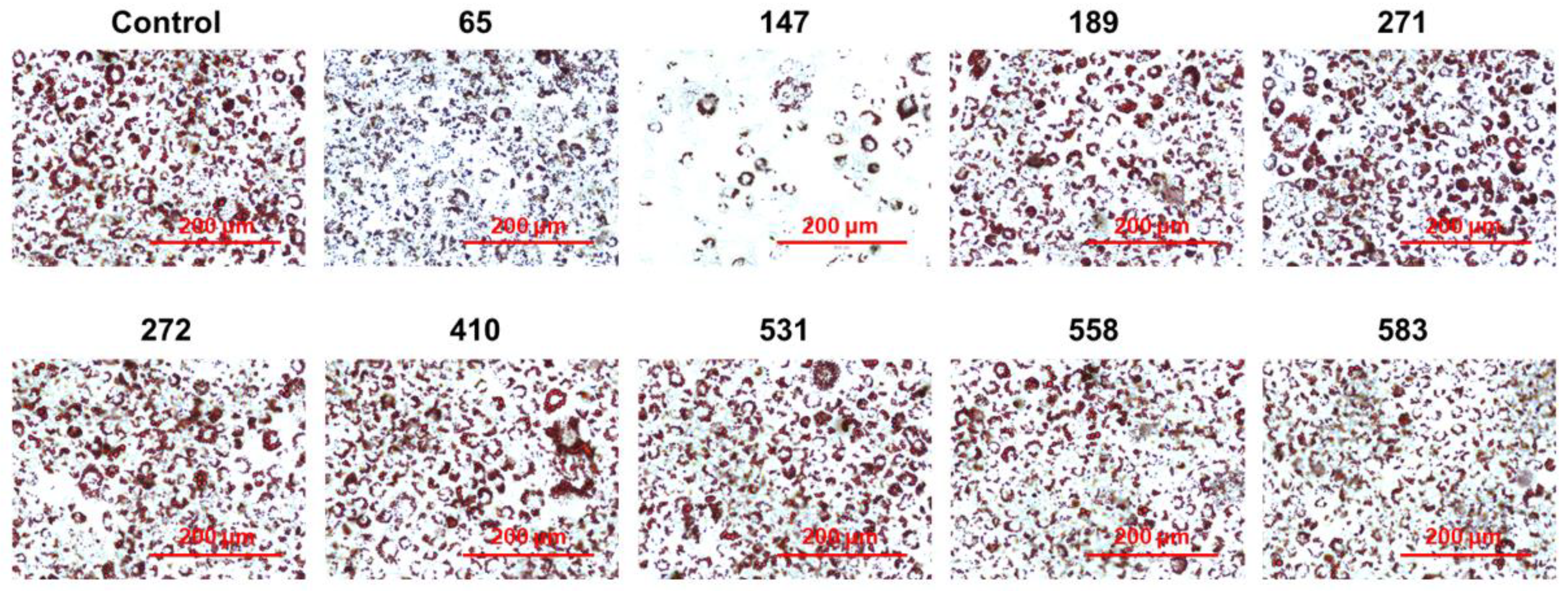
2.2. Screening of PPP1CB Inhibitors and Discovery of Novel Anti-Adipogenic Natural Products
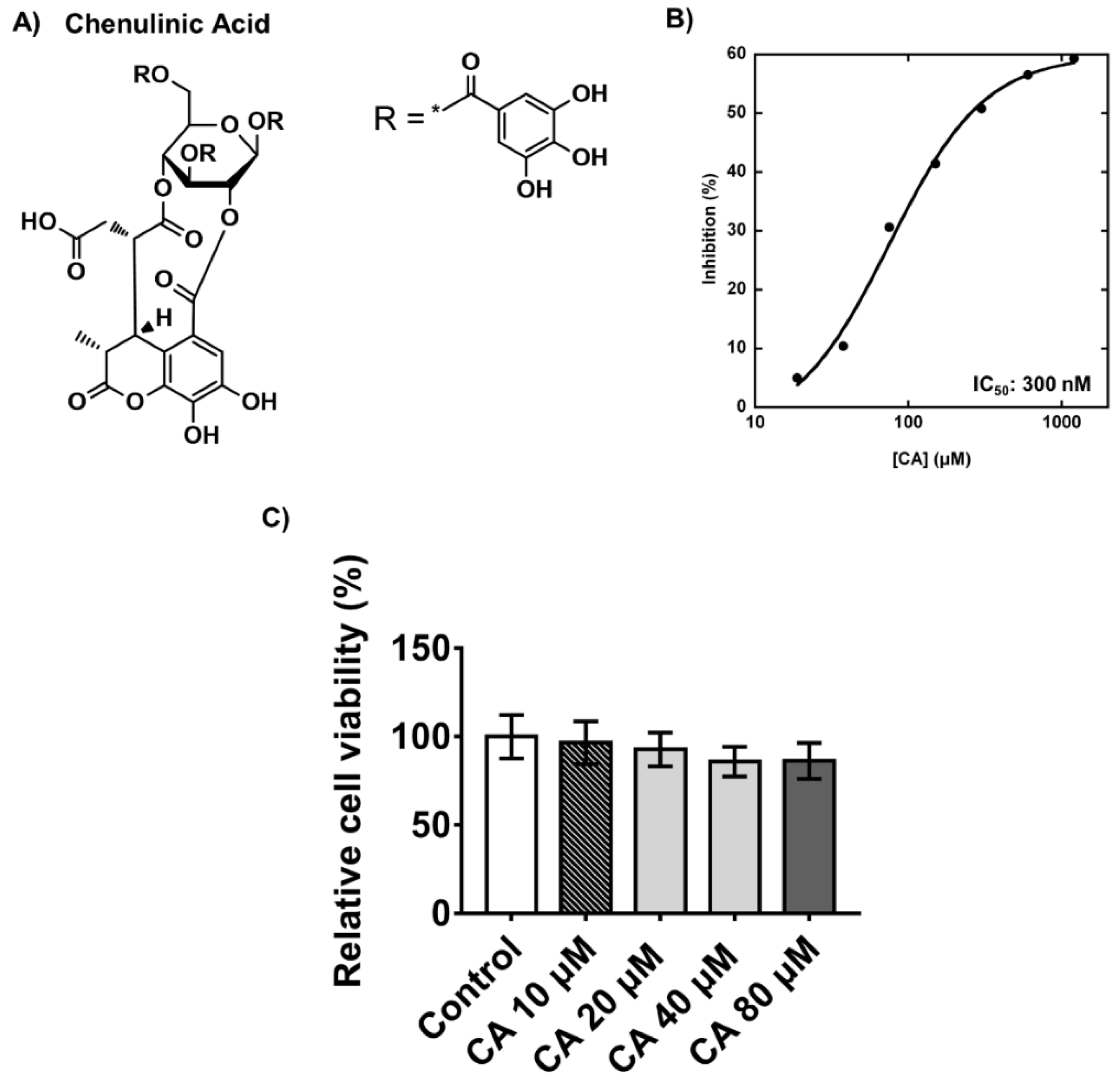
2.3. Inhibitory Effects and Cytotoxicity of Chebulinic Acid in PPP1CB and 3T3-L1 Cells
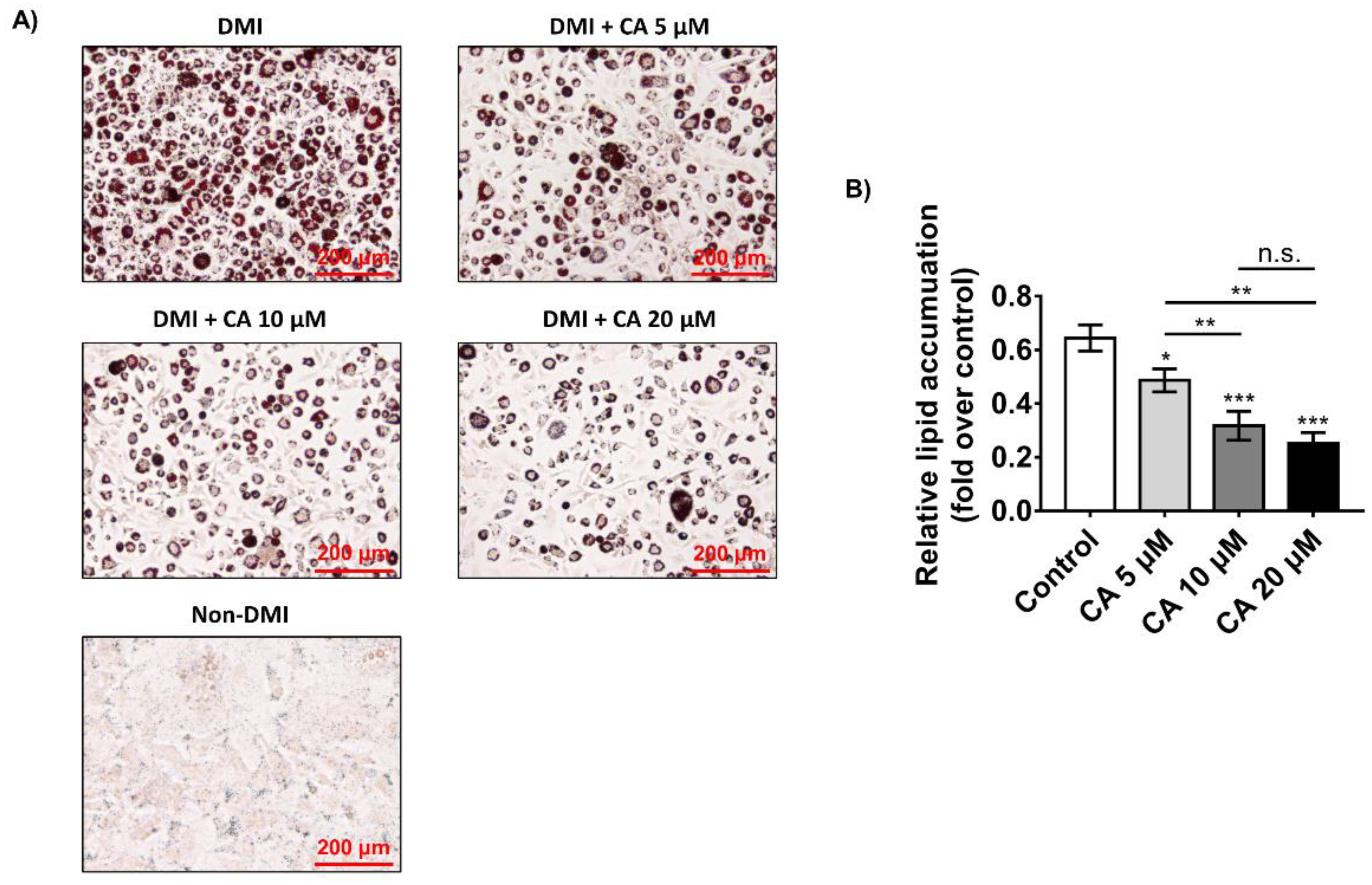
2.4. Chebulinic Acid Suppressed Adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 Cells in Concentration-Dependent Manner
2.5. Chebulinic Acid Mainly Suppressed the Adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 Cells in the Early Stage
2.6. Chebulinic Acid Downregulated the Adipogenic Transcriptional Factors and Adipokines
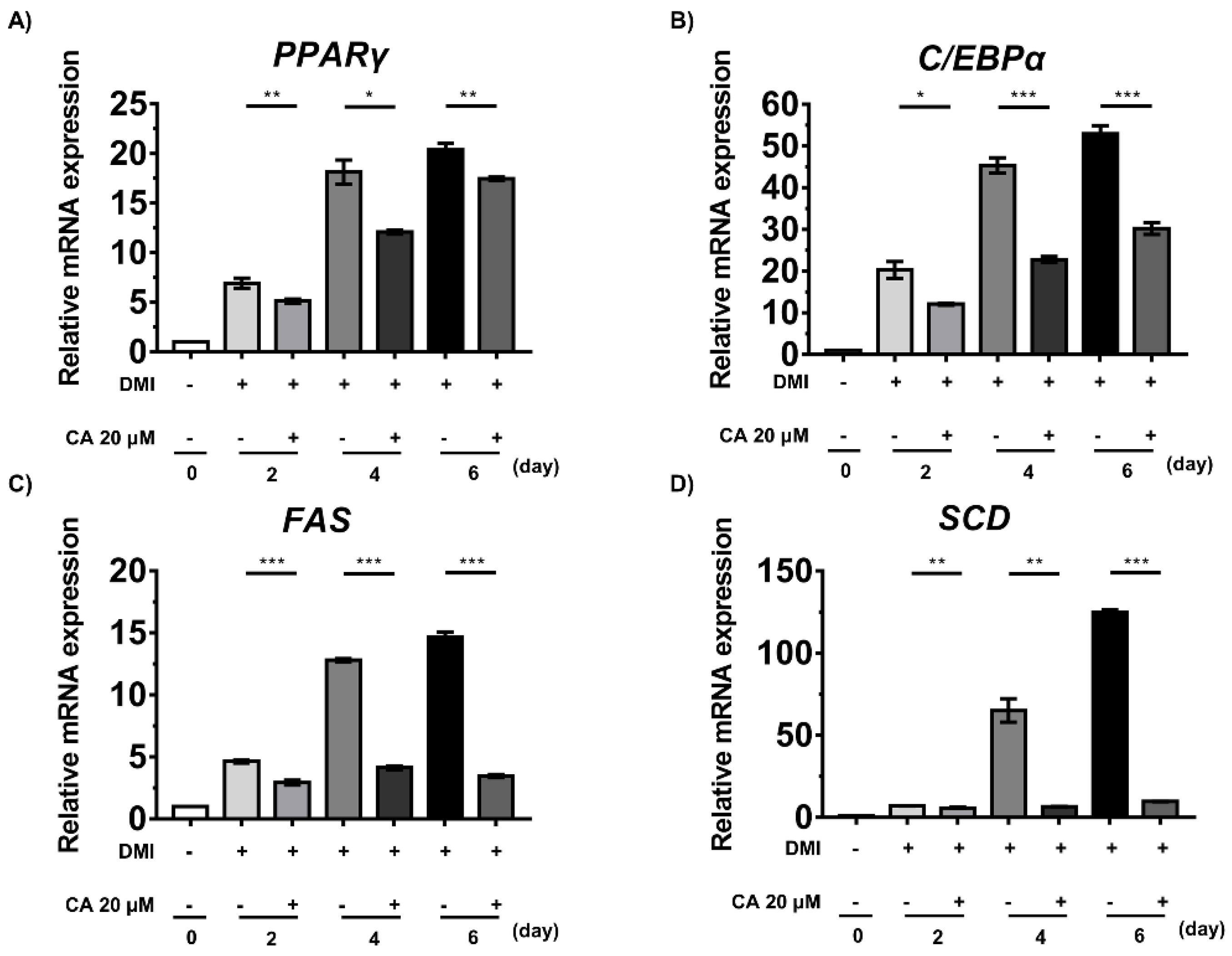
2.7. Chebulinic Acid Suppressed the mRNA Expression of Factors Associated with the Adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Purification of PPP1CB
4.2. Enzymatic Assays
4.3. Cell Culture and Differentiation
4.4. Cell Viability Assays
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Oil Red O Staining
4.7. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis and RT-PCR
4.8. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambele, M.A.; Dhanraj, P.; Giles, R.; Pepper, M.S. Adipogenesis: A Complex Interplay of Multiple Molecular Determinants and Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, I.P.; Elliott, S.A.; Siervo, M.; Padwal, R.; Bertoli, S.; Battezzati, A.; Prado, C.M. Is obesity associated with altered energy expenditure? Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iozzo, P. Myocardial, perivascular, and epicardial fat. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, S371–S379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitade, H.; Chen, G.; Ni, Y.; Ota, T. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance: New insights and potential new treatments. Nutrients 2017, 9, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. Natural products with anti-obesity effects and different mechanisms of action. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 9571–9585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Xu, S.; Huang, L.; Chen, C. Obesity and insulin resistance: Pathophysiology and treatment. Drug Discov. Today 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneschvar, H.L.; Aronson, M.D.; Smetana, G.W. FDA-approved anti-obesity drugs in the United States. Am. J. Med. 2016, 129, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanaswami, V.; Dwoskin, L.P. Obesity: Current and potential pharmacotherapeutics and targets. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 170, 116–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, B.M.Y.; Cheung, T.T.; Samaranayake, N.R. Safety of antiobesity drugs. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2013, 4, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Zolotaryov, F.N.; Hong, K.S.; Kitazawa, R.; Iida, K.; Okimura, Y.; Kaji, H.; Kitazawa, S.; et al. Chemerin enhances insulin signaling and potentiates insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, S.A.; Cerosaletti, K.; Wan, J.Y.; Ho, J.C.; Tatum, M.; Wei, S.; Shilling, H.G.; Buckner, J.H. An autoimmune-associated variant in PTPN2 reveals an impairment of IL-2R signaling in CD4(+) T cells. Genes Immun. 2011, 12, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prusty, D.; Park, B.-H.; Davis, K.E.; Farmer, S.R. Activation of MEK/ERK signaling promotes adipogenesis by enhancing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) and C/EBPα gene expression during the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 46226–46232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosen, E.D.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipocytes as regulators of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Nature 2006, 444, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.-Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Da hye Jang, S.J.L.; Cho, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-H. Inhibitory effects of Porphyra dentata extract on 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2020, 62, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korrodi-Gregório, L.; Esteves, S.L.; Fardilha, M. Protein phosphatase 1 catalytic isoforms: Specificity toward interacting proteins. Transl. Res. 2014, 164, 366–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cruz e Silva, E.; Fox, C.A.; Ouimet, C.C.; Gustafson, E.; Watson, S.J.; Greengard, P. Differential expression of protein phosphatase 1 isoforms in mammalian brain. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 3375–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.L.; Min, J.K.; Roh, K.M.; Kim, W.K.; Han, B.S.; Bae, K.H.; Lee, S.C.; Chung, S.J.; Kang, H.J. Phosphoprotein phosphatase 1CB (PPP1CB), a novel adipogenic activator, promotes 3T3-L1 adipogenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 467, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DV, S.P.; Vangalapati, M. A REVIEW ON CHEBULINIC ACID FROM MEDICINAL HERBS. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 2016, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, G.; Priyadarsini, K.; Naik, D.; Gangabhagirathi, R.; Mohan, H. Studies on the aqueous extract of Terminalia chebula as a potent antioxidant and a probable radioprotector. Phytomedicine 2004, 11, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, G.; Shanmugamprema, D.; Subramani, R.; Muthuswamy, K.; Ponnusamy, V.; Tankay, K.; Velusamy, T.; Krishnan, V.; Subramaniam, S. Anti-Obesity Effect of T. Chebula Fruit Extract on High Fat Diet Induced Obese Mice: A Possible Alternative Therapy. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 2001224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apovian, C.M. Obesity: Definition, comorbidities, causes, and burden. Am. J. Manag. Care 2016, 22, s176–s185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kopelman, P.G. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 2000, 404, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Obesity: Identification, Assessment and Management; NICE: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.; Elkhayat, E.S.; El Dine, R.S. Natural anti-obesity agents. Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. 2014, 52, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, S.M.; Aronne, L.J. Causes of obesity. Abdom. Radiol. 2012, 37, 730–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langin, D. In and out: Adipose tissue lipid turnover in obesity and dyslipidemia. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 569–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sørensen, T.I. From fat cells through an obesity theory. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haczeyni, F.; Bell-Anderson, K.S.; Farrell, G. Causes and mechanisms of adipocyte enlargement and adipose expansion. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarjeant, K.; Stephens, J.M. Adipogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a008417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Rupérez, A.I.; Gomez-Llorente, C.; Gil, A.; Aguilera, C.M. Cell models and their application for studying adipogenic differentiation in relation to obesity: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-E.; Ge, K. Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of PPARγ expression during adipogenesis. Cell Biosci. 2014, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Q.-Q.; Lane, M.D. Activation and centromeric localization of CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins during the mitotic clonal expansion of adipocyte differentiation. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 2231–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bae, K.-H.; Kim, W.K.; Lee, S.C. Involvement of protein tyrosine phosphatases in adipogenesis: New anti-obesity targets? BMB Rep. 2012, 45, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoon, S.-Y.; Kang, H.J.; Ahn, D.; Hwang, J.Y.; Kwon, S.J.; Chung, S.J. Identification of chebulinic acid as a dual targeting inhibitor of protein tyrosine phosphatases relevant to insulin resistance. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 90, 103087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanuelli, B.; Eberlé, D.; Suzuki, R.; Kahn, C.R. Overexpression of the dual-specificity phosphatase MKP-4/DUSP-9 protects against stress-induced insulin resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3545–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, S.-Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kwon, S.J.; Kang, H.J.; Chung, S.J. Ginkgolic acid as a dual-targeting inhibitor for protein tyrosine phosphatases relevant to insulin resistance. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 81, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Sun, T.; Bookout, A.L.; Downes, M.; Yu, R.T.; Evans, R.M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. A nuclear receptor atlas: 3T3-L1 adipogenesis. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 2437–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farmer, S.R. Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.-L.; Park, J.-G.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, W.; Cho, M.J.; Jang, J.-H.; Kwon, M.-G.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, J. Ginkgetin, a biflavone from Ginkgo biloba leaves, prevents adipogenesis through STAT5-mediated PPARγ and C/EBPα regulation. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 139, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| [E] (nM) | KM (μM) | Vmax (μM min−1) | kcat (min−1) | kcat/KM (μM min−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GST-1CB 1 (A) | 5.0 | 102 | 3.0 | 6.0 × 102 | 5.9 |
| MBP-1CB 2 (B) | 100 | - | 0.064 | - | - |
| 6xHis-1CB 3 (C-1) | 10 | 152.2 | 3.8 | 3.8 × 102 | 2.5 |
| 1CB 4 (C-3) | 1.5 | 186.2 | 3.4 | 2.3 × 103 | 12.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Ahn, D.; Chung, S.J. Chebulinic Acid Suppresses Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Inhibiting PPP1CB Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020865
Kim J, Ahn D, Chung SJ. Chebulinic Acid Suppresses Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Inhibiting PPP1CB Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(2):865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020865
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jinsoo, Dohee Ahn, and Sang J. Chung. 2022. "Chebulinic Acid Suppresses Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Inhibiting PPP1CB Activity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 2: 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020865
APA StyleKim, J., Ahn, D., & Chung, S. J. (2022). Chebulinic Acid Suppresses Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Inhibiting PPP1CB Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(2), 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020865