Shigella Outer Membrane Vesicles as Promising Targets for Vaccination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Shigella spp. and Shigellosis
3. Vaccination Approaches
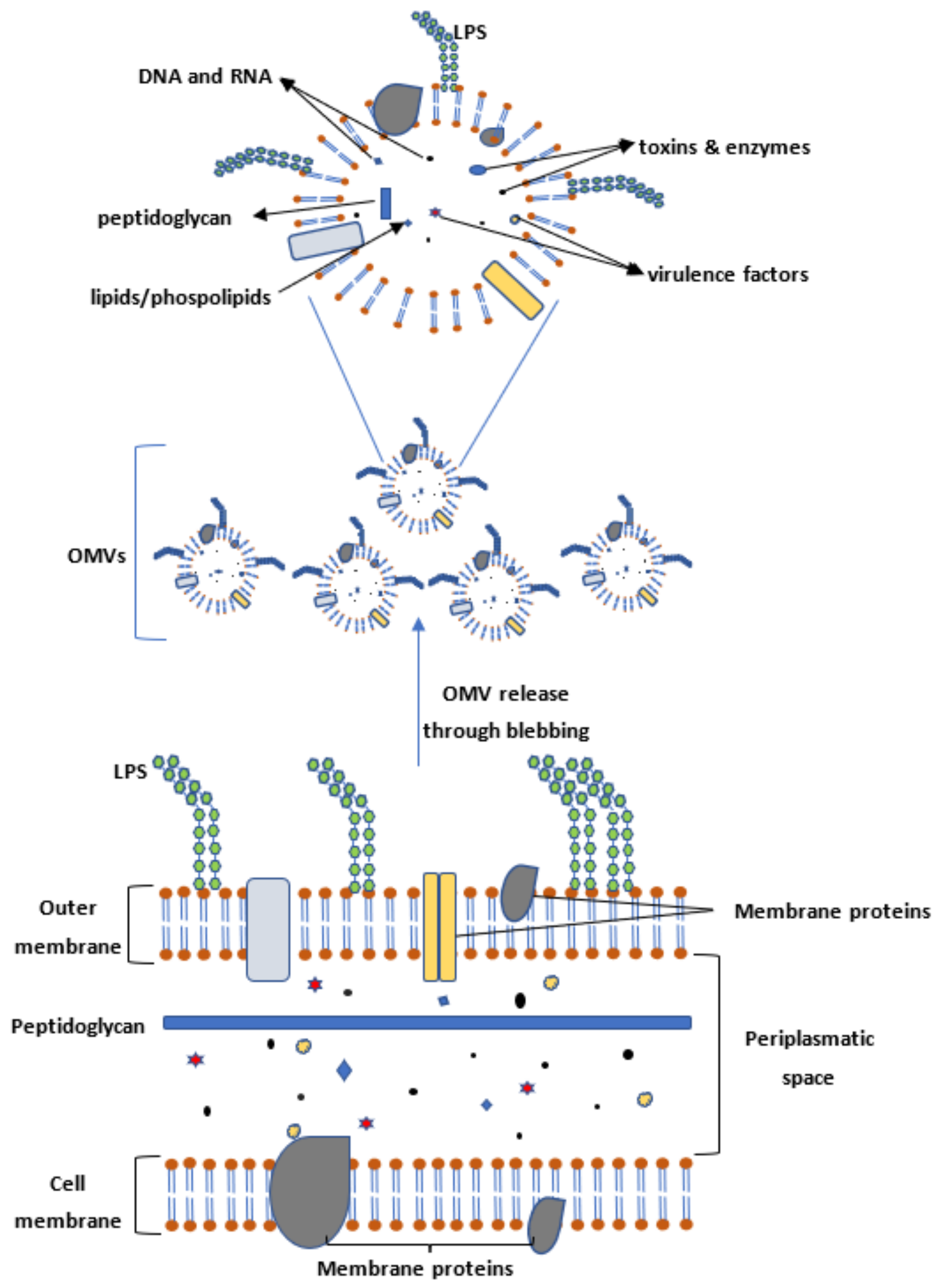
4. Outer Membrane Vesicles (OMVs) as Targets for Vaccination
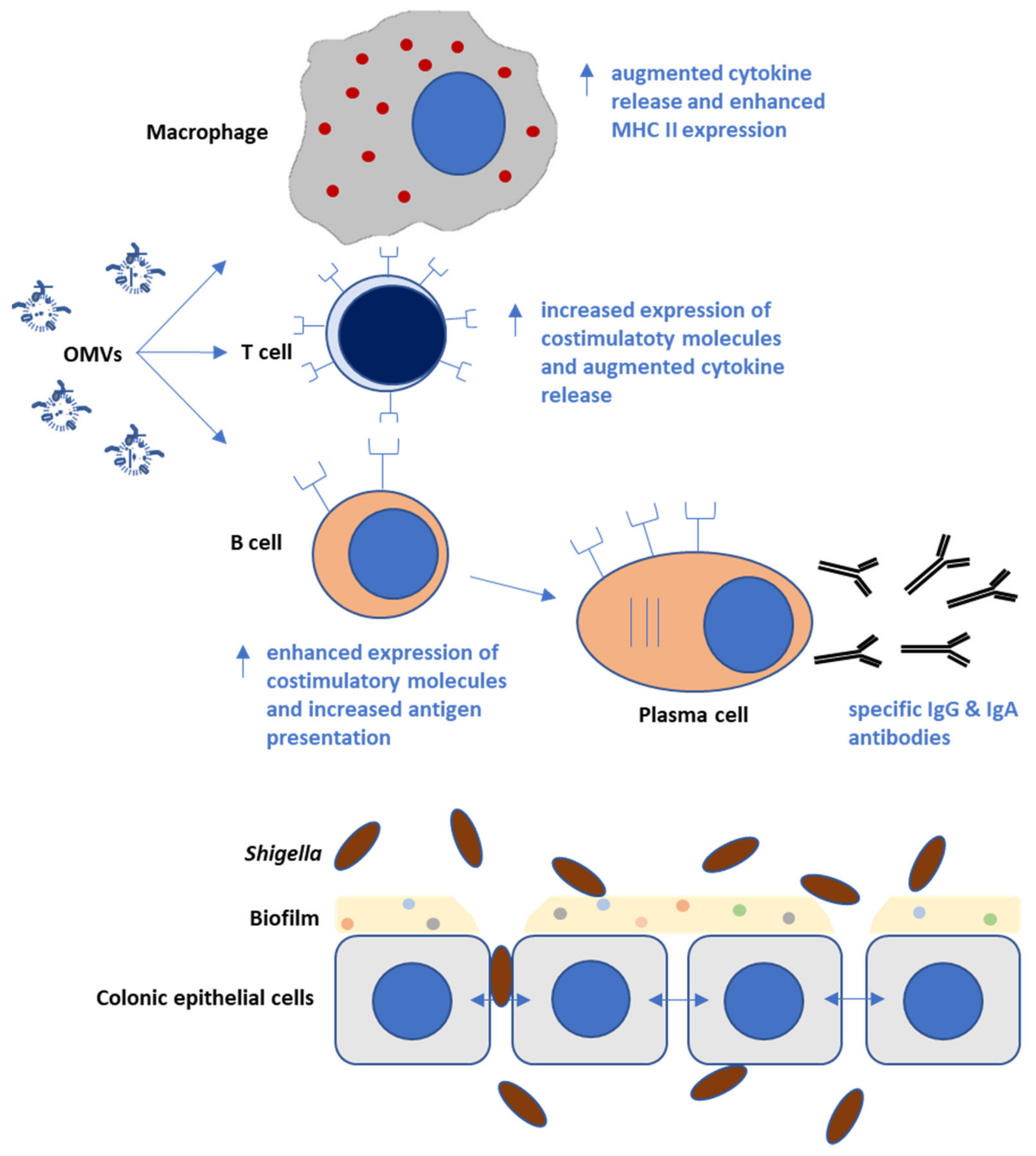
5. Immunological Responses Triggered by Shigella OMVs in Infection Models
6. Immunoreactive Proteins in OMVs
7. Virulence Factors of Shigella OMVs
8. Methods for Enhancing Shigella OMV Release and Yield
9. Augmenting OMV Immune-Reactivity
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akhondi, H.; Simonsen, K.A. Bacterial Diarrhea. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, I.A.; Troeger, C.; Blacker, B.F.; Rao, P.C.; Brown, A.; Atherly, D.E.; Brewer, T.G.; Engmann, C.M.; Houpt, E.R.; Kang, G.; et al. Morbidity and mortality due to shigella and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea: The Global Burden of Disease Study 1990–2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotloff, K.L.; Riddle, M.S.; Platts-Mills, J.A.; Pavlinac, P.; Zaidi, A.K.M. Shigellosis. Lancet 2018, 391, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, N.; Tiewsoh, J.B.A.; Gupta, S.; Mohan, B.; Verma, R.; Shankar, P.; Narayan, C.; Yadav, V.K.; Jayashree, M.; Singh, S. Antimicrobial resistance in Shigella species: Our five years (2015–2019) experience in a tertiary care center in north India. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 39, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmino, C.J.D.; Kakkanat, A.; Forde, B.M.; Rubenach, S.; Merone, L.; Stafford, R.; Graham, R.M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Jennison, A.V. Outbreak of multi-drug-resistant (MDR) Shigella flexneri in northern Australia due to an endemic regional clone acquiring an IncFII plasmid. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect Dis. 2021, 40, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.; Wierzba, T.; Walker, R.I. Status of vaccine research and development for Shigella. Vaccine 2016, 34, 2887–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, S.; Harro, C.; DeNearing, B.; Bream, J.; Bauers, N.; Dally, L.; Flores, J.; Van de Verg, L.; Sack, D.A.; Walker, R. Evaluation of the Safety, Tolerability, and Immunogenicity of an Oral, Inactivated Whole-Cell Shigella flexneri 2a Vaccine in Healthy Adult Subjects. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2016, 23, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christensen, H.; Nordentoft, S.; Olsen, J.E. Phylogenetic relationships of Salmonella based on rRNA sequences. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sims, G.E.; Kim, S.H. Whole-genome phylogeny of Escherichia coli/Shigella group by feature frequency profiles (FFPs). Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8329–8334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lecointre, G.; Rachdi, L.; Darlu, P.; Denamur, E. Escherichia coli molecular phylogeny using the incongruence length difference test. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1998, 15, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hale, T.L. Genetic basis of virulence in Shigella species. Microbiol. Rev. 1991, 55, 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khot, P.D.; Fisher, M.A. Novel approach for differentiating Shigella species and Escherichia coli by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3711–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paauw, A.; Jonker, D.; Roeselers, G.; Heng, J.M.; Mars-Groenendijk, R.H.; Trip, H.; Molhoek, E.M.; Jansen, H.J.; van der Plas, J.; de Jong, A.L.; et al. Rapid and reliable discrimination between Shigella species and Escherichia coli using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 305, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devanga Ragupathi, N.K.; Muthuirulandi Sethuvel, D.P.; Inbanathan, F.Y.; Veeraraghavan, B. Accurate differentiation of Escherichia coli and Shigella serogroups: Challenges and strategies. New Microbes New Infect. 2018, 21, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Pholwat, S.; Zhang, J.; Taniuchi, M.; Haque, R.; Alam, M.; Ochieng, J.B.; Jones, J.A.; Platts-Mills, J.A.; Tennant, S.M.; et al. Evaluation of Molecular Serotyping Assays for Shigella flexneri Directly on Stool Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e02455-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Marteyn, B.S. Shigella Diversity and Changing Landscape: Insights for the Twenty-First Century. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattock, E.; Blocker, A.J. How Do the Virulence Factors of Shigella Work Together to Cause Disease? Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, M.M.; Kotloff, K.L.; Barry, E.M.; Pasetti, M.F.; Sztein, M.B. Clinical trials of Shigella vaccines: Two steps forward and one step back on a long, hard road. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotloff, K.L. Shigella infection in children and adults: A formidable foe. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e1166–e1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connor, T.R.; Barker, C.R.; Baker, K.S.; Weill, F.X.; Talukder, K.A.; Smith, A.M.; Baker, S.; Gouali, M.; Pham Thanh, D.; Jahan Azmi, I.; et al. Species-wide whole genome sequencing reveals historical global spread and recent local persistence in Shigella flexneri. Elife 2015, 4, e07335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Lu, S.; Chen, L.; Jin, Q.; Yang, J. Causative species and serotypes of shigellosis in mainland China: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Seidlein, L.; Kim, D.R.; Ali, M.; Lee, H.; Wang, X.; Thiem, V.D.; Canh, D.G.; Chaicumpa, W.; Agtini, M.D.; Hossain, A.; et al. A multicentre study of Shigella diarrhoea in six Asian countries: Disease burden, clinical manifestations, and microbiology. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seol, S.Y.; Kim, Y.T.; Jeong, Y.S.; Oh, J.Y.; Kang, H.Y.; Moon, D.C.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.C.; Cho, D.T.; Lee, J.C. Molecular characterization of antimicrobial resistance in Shigella sonnei isolates in Korea. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, H.L.; Wang, Y.W.; Li, C.C.; Tung, S.K.; Chiou, C.S. Epidemiology and evolution of genotype and antimicrobial resistance of an imported Shigella sonnei clone circulating in central Taiwan. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 58, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, K.M.; Arifeen, S.E.; Zaman, K.; Rahman, M.; Raqib, R.; Yunus, M.; Begum, N.; Islam, M.S.; Sohel, B.M.; Rahman, M.; et al. Safety, dose, immunogenicity, and transmissibility of an oral live attenuated Shigella flexneri 2a vaccine candidate (SC602) among healthy adults and school children in Matlab, Bangladesh. Vaccine 2011, 29, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenck, R.W., Jr.; Baqar, S.; Alexander, W.; Dickey, M.; McNeal, M.; El-Khorazaty, J.; Baughman, H.; Hoeper, A.; Barnoy, S.; Suvarnapunya, A.E.; et al. A Phase I trial to evaluate the safety and immunogenicity of WRSs2 and WRSs3; two live oral candidate vaccines against Shigella sonnei. Vaccine 2018, 36, 4880–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweon, M.N. Shigellosis: The current status of vaccine development. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 21, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuyama, N.; Sircili, M.P. Outer Membrane Vesicles (OMVs) Produced by Gram-Negative Bacteria: Structure, Functions, Biogenesis, and Vaccine Application. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 1490732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwechheimer, C.; Kuehn, M.J. Outer-membrane vesicles from Gram-negative bacteria: Biogenesis and functions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bittel, M.; Reichert, P.; Sarfati, I.; Dressel, A.; Leikam, S.; Uderhardt, S.; Stolzer, I.; Phu, T.A.; Ng, M.; Vu, N.K.; et al. Visualizing transfer of microbial biomolecules by outer membrane vesicles in microbe-host-communication in vivo. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balhuizen, M.D.; Veldhuizen, E.J.A.; Haagsman, H.P. Outer Membrane Vesicle Induction and Isolation for Vaccine Development. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 629090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Kesavan, D.K.; Wan, J.; Abdelaziz, M.H.; Su, Z.; Xu, H. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles, a potential vaccine candidate in interactions with host cells based. Diagn. Pathol. 2018, 13, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Yoon, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Dinh, N.T.H.; Go, G.; Tae, S.; Park, K.S.; Park, H.T.; Lee, C.; Roh, T.Y.; et al. Outer Membrane Vesicles Derived From Escherichia coli Regulate Neutrophil Migration by Induction of Endothelial IL-8. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zanella, I.; Konig, E.; Tomasi, M.; Gagliardi, A.; Frattini, L.; Fantappie, L.; Irene, C.; Zerbini, F.; Caproni, E.; Isaac, S.J.; et al. Proteome-minimized outer membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli as a generalized vaccine platform. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriani, R.; Mousavi Gargari, S.L.; Nazarian, S.; Sarvary, S.; Noroozi, N. Immunogenicity of Vibrio cholerae outer membrane vesicles secreted at various environmental conditions. Vaccine 2018, 36, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritzen, M.J.H.; Martens, D.E.; Uittenbogaard, J.P.; Wijffels, R.H.; Stork, M. Sulfate depletion triggers overproduction of phospholipids and the release of outer membrane vesicles by Neisseria meningitidis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritzen, M.J.H.; Salverda, M.L.M.; Martens, D.E.; Wijffels, R.H.; Stork, M. Spontaneously released Neisseria meningitidis outer membrane vesicles as vaccine platform: Production and purification. Vaccine 2019, 37, 6978–6986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Sinha, R.; Mitobe, J.; Koley, H. Development of a cost-effective vaccine candidate with outer membrane vesicles of a tolA-disrupted Shigella boydii strain. Vaccine 2016, 34, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, A.I.; Irache, J.M.; de Souza, J.; Sanchez-Gomez, S.; Gamazo, C. Nanoparticle-based vaccine for mucosal protection against Shigella flexneri in mice. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3288–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, Y.; Camacho, A.; Gil, A.G.; Ramos, R.; Cerain, A.L.; Penuelas, I.; Irache, J.M.; Gamazo, C. Effective protection of mice against Shigella flexneri with a new self-adjuvant multicomponent vaccine. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Barman, S.; Nag, D.; Sinha, R.; Saha, D.R.; Koley, H. Outer membrane vesicles of Shigella boydii type 4 induce passive immunity in neonatal mice. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitra, S.; Chakrabarti, M.K.; Koley, H. Multi-serotype outer membrane vesicles of Shigellae confer passive protection to the neonatal mice against shigellosis. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3163–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nag, D.; Sinha, R.; Mitra, S.; Barman, S.; Takeda, Y.; Shinoda, S.; Chakrabarti, M.K.; Koley, H. Heat killed multi-serotype Shigella immunogens induced humoral immunity and protection against heterologous challenge in rabbit model. Immunobiology 2015, 220, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, A.I.; de Souza, J.; Sanchez-Gomez, S.; Pardo-Ros, M.; Irache, J.M.; Gamazo, C. Mucosal immunization with Shigella flexneri outer membrane vesicles induced protection in mice. Vaccine 2011, 29, 8222–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pore, D.; Mahata, N.; Pal, A.; Chakrabarti, M.K. Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) of Shigella flexneri 2a, induces protective immune response in a mouse model. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pore, D.; Chakrabarti, M.K. Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) from Shigella flexneri 2a: A promising subunit vaccine candidate. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3644–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M.; Schimpl, A.; Hunig, T. Control of T cell hyperactivation in IL-2-deficient mice by CD4(+)CD25(-) and CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells: Evidence for two distinct regulatory mechanisms. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzab, A.; Witkowska, D.; Ziomek, E.; Dabrowska, A.; Szewczuk, Z.; Gamian, A. Shigella flexneri 3a outer membrane protein C epitope is recognized by human umbilical cord sera and associated with protective activity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berlanda Scorza, F.; Colucci, A.M.; Maggiore, L.; Sanzone, S.; Rossi, O.; Ferlenghi, I.; Pesce, I.; Caboni, M.; Norais, N.; Di Cioccio, V.; et al. High yield production process for Shigella outer membrane particles. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerke, C.; Colucci, A.M.; Giannelli, C.; Sanzone, S.; Vitali, C.G.; Sollai, L.; Rossi, O.; Martin, L.B.; Auerbach, J.; Di Cioccio, V.; et al. Production of a Shigella sonnei Vaccine Based on Generalized Modules for Membrane Antigens (GMMA), 1790GAHB. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.O.; Rho, S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.; Song, H.J.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, R.Y.; Kim, E.H.; Sinha, A.; Dey, A.; et al. Shigella outer membrane protein PSSP-1 is broadly protective against Shigella infection. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2015, 22, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pore, D.; Chowdhury, P.; Mahata, N.; Pal, A.; Yamasaki, S.; Mahalanabis, D.; Chakrabarti, M.K. Purification and characterization of an immunogenic outer membrane protein of Shigella flexneri 2a. Vaccine 2009, 27, 5855–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pore, D.; Mahata, N.; Pal, A.; Chakrabarti, M.K. 34 kDa MOMP of Shigella flexneri promotes TLR2 mediated macrophage activation with the engagement of NF-kappaB and p38 MAP kinase signaling. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhaya, A.; Mahalanabis, D.; Chakrabarti, M.K. Role of Shigella flexneri 2a 34 kDa outer membrane protein in induction of protective immune response. Vaccine 2006, 24, 6028–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, A.K.; Sinha, A.K. Role of 57 kDa major antigenic component of Shigella dysenteriae outer membrane proteins in induction of major histocompatibility complex II-restricted T-cell response. Arch. Med. Res. 2004, 35, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, R.; Pore, D.; Chakrabarti, M.K. Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) of Shigella flexneri 2a induces TLR2-mediated activation of B cells: Involvement of protein tyrosine kinase, ERK and NF-kappaB. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, D.; Yagnik, B.; Baksi, R.; Desai, N.; Padh, H.; Desai, P. Shigellosis murine model established by intraperitoneal and intranasal route of administration: A comparative comprehension overview. Microbes Infect. 2017, 19, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagnik, B.; Sharma, D.; Padh, H.; Desai, P. Oral immunization with LacVax(R) OmpA induces protective immune response against Shigella flexneri 2a ATCC 12022 in a murine model. Vaccine 2019, 37, 3097–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padh, H.; Yagnik, B.; Sharma, D.; Desai, P. EpiMix Based Novel Vaccine Candidate for Shigella: Evidence of Prophylactic Immunity in Balb/c Mice. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2021, 27, 1095–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciello, I.; Silipo, A.; Lembo-Fazio, L.; Curcuru, L.; Zumsteg, A.; Noel, G.; Ciancarella, V.; Sturiale, L.; Molinaro, A.; Bernardini, M.L. Intracellular Shigella remodels its LPS to dampen the innate immune recognition and evade inflammasome activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E4345–E4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, D.; Meron-Sudai, S.; Bialik, A.; Asato, V.; Goren, S.; Ariel-Cohen, O.; Reizis, A.; Hochberg, A.; Ashkenazi, S. Serum IgG antibodies to Shigella lipopolysaccharide antigens—A correlate of protection against shigellosis. Hum. Vaccin Immunother. 2019, 15, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barel, L.A.; Mulard, L.A. Classical and novel strategies to develop a Shigella glycoconjugate vaccine: From concept to efficacy in human. Hum. Vaccin Immunother. 2019, 15, 1338–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silipo, A.; Molinaro, A. The diversity of the core oligosaccharide in lipopolysaccharides. Subcell. Biochem. 2010, 53, 69–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akesson, K.; Tompa, A.; Ryden, A.; Faresjo, M. Low expression of CD39(+) /CD45RA(+) on regulatory T cells (Treg) cells in type 1 diabetic children in contrast to high expression of CD101(+) /CD129(+) on Treg cells in children with coeliac disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 180, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pore, D.; Mahata, N.; Chakrabarti, M.K. Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) of Shigella flexneri 2a links innate and adaptive immunity in a TLR2-dependent manner and involvement of IL-12 and nitric oxide. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 12589–12601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allaoui, A.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Parsot, C. MxiD, an outer membrane protein necessary for the secretion of the Shigella flexneri lpa invasins. Mol. Microbiol. 1993, 7, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuch, R.; Maurelli, A.T. MxiM and MxiJ, base elements of the Mxi-Spa type III secretion system of Shigella, interact with and stabilize the MxiD secretin in the cell envelope. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 6991–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schroeder, G.N.; Hilbi, H. Molecular pathogenesis of Shigella spp.: Controlling host cell signaling, invasion, and death by type III secretion. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 134–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernardini, M.L.; Sanna, M.G.; Fontaine, A.; Sansonetti, P.J. OmpC is involved in invasion of epithelial cells by Shigella flexneri. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 3625–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allaoui, A.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Parsot, C. MxiJ, a lipoprotein involved in secretion of Shigella Ipa invasins, is homologous to YscJ, a secretion factor of the Yersinia Yop proteins. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 7661–7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ambrosi, C.; Pompili, M.; Scribano, D.; Zagaglia, C.; Ripa, S.; Nicoletti, M. Outer membrane protein A (OmpA): A new player in shigella flexneri protrusion formation and inter-cellular spreading. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiku, V.; Kofoed, E.M.; Yan, D.; Kang, J.; Xu, M.; Reichelt, M.; Dikic, I.; Tan, M.W. Outer membrane vesicles containing OmpA induce mitochondrial fragmentation to promote pathogenesis of Acinetobacter baumannii. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.R.; Rossmanith, J.; Sieg, J.; Fris, M.E.; Hussein, H.; Kouse, A.B.; Gross, K.; Zeng, C.; Hines, J.V.; Narberhaus, F.; et al. Regulation of OmpA Translation and Shigella dysenteriae Virulence by an RNA Thermometer. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, e00871-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confer, A.W.; Ayalew, S. The OmpA family of proteins: Roles in bacterial pathogenesis and immunity. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 163, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.G.; Mahon, V.; Lambert, M.A.; Fagan, R.P. A molecular Swiss army knife: OmpA structure, function and expression. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 273, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotcke Zumsteg, A.; Goosmann, C.; Brinkmann, V.; Morona, R.; Zychlinsky, A. IcsA is a Shigella flexneri adhesin regulated by the type III secretion system and required for pathogenesis. Cell Host Microbe. 2014, 15, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robbins, J.R.; Monack, D.; McCallum, S.J.; Vegas, A.; Pham, E.; Goldberg, M.B.; Theriot, J.A. The making of a gradient: IcsA (VirG) polarity in Shigella flexneri. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 41, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldberg, M.B.; Theriot, J.A. Shigella flexneri surface protein IcsA is sufficient to direct actin-based motility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 6572–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- d’Hauteville, H.; Sansonetti, P.J. Phosphorylation of IcsA by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and its effect on intracellular spread of Shigella flexneri. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseoglu, V.K.; Hall, C.P.; Rodriguez-Lopez, E.M.; Agaisse, H. The Autotransporter IcsA Promotes Shigella flexneri Biofilm Formation in the Presence of Bile Salts. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00861-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egile, C.; d’Hauteville, H.; Parsot, C.; Sansonetti, P.J. SopA, the outer membrane protease responsible for polar localization of IcsA in Shigella flexneri. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 23, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffatellu, M.; Wilson, R.P.; Chessa, D.; Andrews-Polymenis, H.; Tran, Q.T.; Lawhon, S.; Khare, S.; Adams, L.G.; Baumler, A.J. SipA, SopA, SopB, SopD, and SopE2 contribute to Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium invasion of epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Santos, R.L.; Tsolis, R.M.; Stender, S.; Hardt, W.D.; Baumler, A.J.; Adams, L.G. The Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium effector proteins SipA, SopA, SopB, SopD, and SopE2 act in concert to induce diarrhea in calves. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 3843–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, S.; Goldberg, M.B. Requirement for YaeT in the outer membrane assembly of autotransporter proteins. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 5393–5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doerrler, W.T.; Raetz, C.R. Loss of outer membrane proteins without inhibition of lipid export in an Escherichia coli YaeT mutant. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 27679–27687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, D.L.; James, C.E.; Sergeant, M.J.; Yaxian, Y.; Saunders, J.R.; McCarthy, A.J.; Allison, H.E. Short-tailed stx phages exploit the conserved YaeT protein to disseminate Shiga toxin genes among enterobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 7223–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werner, J.; Misra, R. YaeT (Omp85) affects the assembly of lipid-dependent and lipid-independent outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 57, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shere, K.D.; Sallustio, S.; Manessis, A.; D’Aversa, T.G.; Goldberg, M.B. Disruption of IcsP, the major Shigella protease that cleaves IcsA, accelerates actin-based motility. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 25, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauer, J.; Agha, R.; Pham, T.; Varga, A.W.; Goldberg, M.B. The unipolar Shigella surface protein IcsA is targeted directly to the bacterial old pole: IcsP cleavage of IcsA occurs over the entire bacterial surface. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 32, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wing, H.J.; Goldman, S.R.; Ally, S.; Goldberg, M.B. Modulation of an outer membrane protease contributes to the virulence defect of Shigella flexneri strains carrying a mutation in the virK locus. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hensley, C.T.; Kamneva, O.K.; Levy, K.M.; Labahn, S.K.; Africa, L.A.; Wing, H.J. Two promoters and two translation start sites control the expression of the Shigella flexneri outer membrane protease IcsP. Arch. Microbiol. 2011, 193, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Africa, L.A.; Murphy, E.R.; Egan, N.R.; Wigley, A.F.; Wing, H.J. The iron-responsive Fur/RyhB regulatory cascade modulates the Shigella outer membrane protease IcsP. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 4543–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, R.M.; Yum, L.; Agaisse, H.; Payne, S.M. Cardiolipin Synthesis and Outer Membrane Localization Are Required for Shigella flexneri Virulence. MBio 2017, 8, e01199-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douglass, M.V.; Cleon, F.; Trent, M.S. Cardiolipin aids in lipopolysaccharide transport to the gram-negative outer membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2018329118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, F.; Zheng, J.; Chen, L.; Dong, J.; Sun, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Yang, G.; et al. The outer membrane phospholipase A is essential for membrane integrity and type III secretion in Shigella flexneri. Open Biol. 2016, 6, 160073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, E.L.; Fleming, P.J.; Yeom, M.S.; Widmalm, G.; Klauda, J.B.; Fleming, K.G.; Im, W.E. coli outer membrane and interactions with OmpLA. Biophys. J. 2014, 106, 2493–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schuch, R.; Maurelli, A.T. The mxi-Spa type III secretory pathway of Shigella flexneri requires an outer membrane lipoprotein, MxiM, for invasin translocation. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 1982–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojima, Y.; Sawabe, T.; Konami, K.; Azuma, M. Construction of hypervesiculation Escherichia coli strains and application for secretory protein production. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micoli, F.; Alfini, R.; Di Benedetto, R.; Necchi, F.; Schiavo, F.; Mancini, F.; Carducci, M.; Palmieri, E.; Balocchi, C.; Gasperini, G.; et al. GMMA Is a Versatile Platform to Design Effective Multivalent Combination Vaccines. Vaccines 2020, 8, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Valentine, J.L.; Huang, C.J.; Endicott, C.E.; Moeller, T.D.; Rasmussen, J.A.; Fletcher, J.R.; Boll, J.M.; Rosenthal, J.A.; Dobruchowska, J.; et al. Outer membrane vesicles displaying engineered glycotopes elicit protective antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3609–E3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, G.; Garaguso, I.; Adu-Bobie, J.; Doro, F.; Taddei, A.R.; Biolchi, A.; Brunelli, B.; Giuliani, M.M.; Pizza, M.; Norais, N.; et al. Outer membrane vesicles from group B Neisseria meningitidis delta gna33 mutant: Proteomic and immunological comparison with detergent-derived outer membrane vesicles. Proteomics 2006, 6, 1856–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhenawy, W.; Bording-Jorgensen, M.; Valguarnera, E.; Haurat, M.F.; Wine, E.; Feldman, M.F. LPS Remodeling Triggers Formation of Outer Membrane Vesicles in Salmonella. MBio 2016, 7, e00940-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerritzen, M.J.H.; Maas, R.H.W.; van den Ijssel, J.; van Keulen, L.; Martens, D.E.; Wijffels, R.H.; Stork, M. High dissolved oxygen tension triggers outer membrane vesicle formation by Neisseria meningitidis. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgarten, T.; Sperling, S.; Seifert, J.; von Bergen, M.; Steiniger, F.; Wick, L.Y.; Heipieper, H.J. Membrane vesicle formation as a multiple-stress response mechanism enhances Pseudomonas putida DOT-T1E cell surface hydrophobicity and biofilm formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 6217–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eberlein, C.; Baumgarten, T.; Starke, S.; Heipieper, H.J. Immediate response mechanisms of Gram-negative solvent-tolerant bacteria to cope with environmental stress: Cis-trans isomerization of unsaturated fatty acids and outer membrane vesicle secretion. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 2583–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acevedo, R.; Fernandez, S.; Zayas, C.; Acosta, A.; Sarmiento, M.E.; Ferro, V.A.; Rosenqvist, E.; Campa, C.; Cardoso, D.; Garcia, L.; et al. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles and vaccine applications. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van der Pol, L.; Stork, M.; van der Ley, P. Outer membrane vesicles as platform vaccine technology. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 1689–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schertzer, J.W.; Whiteley, M. A bilayer-couple model of bacterial outer membrane vesicle biogenesis. MBio 2012, 3, e00297-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuerban, K.; Gao, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Dong, M.; Wu, L.; Ye, R.; Feng, M.; Ye, L. Doxorubicin-loaded bacterial outer-membrane vesicles exert enhanced anti-tumor efficacy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 1534–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.W.; Shone, C.; Hesp, J.R. Antibiotics and iron-limiting conditions and their effect on the production and composition of outer membrane vesicles secreted from clinical isolates of extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2017, 11, 1600091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, A.J.; Kuehn, M.J. Contribution of bacterial outer membrane vesicles to innate bacterial defense. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, R.; Moreno, G.; Bottero, D.; Gaillard, M.E.; Fingermann, M.; Graieb, A.; Rumbo, M.; Hozbor, D. Outer membrane vesicles as acellular vaccine against pertussis. Vaccine 2008, 26, 4639–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, C.J.; Gaillard, M.E.; Moreno, G.; Bottero, D.; Zurita, E.; Rumbo, M.; van der Ley, P.; van der Ark, A.; Hozbor, D. Outer membrane vesicles obtained from Bordetella pertussis Tohama expressing the lipid A deacylase PagL as a novel acellular vaccine candidate. Vaccine 2011, 29, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottero, D.; Zurita, M.E.; Gaillard, M.E.; Bartel, E.; Vercellini, C.; Hozbor, D. Membrane Vesicles Derived from Bordetella bronchiseptica: Active Constituent of a New Vaccine against Infections Caused by This Pathogen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01877-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwechheimer, C.; Kuehn, M.J. Synthetic effect between envelope stress and lack of outer membrane vesicle production in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 4161–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takaki, K.; Tahara, Y.O.; Nakamichi, N.; Hasegawa, Y.; Shintani, M.; Ohkuma, M.; Miyata, M.; Futamata, H.; Tashiro, Y. Multilamellar and Multivesicular Outer Membrane Vesicles Produced by a Buttiauxella agrestis tolB Mutant. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01131-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Cruz, C.; Canas, M.A.; Gimenez, R.; Badia, J.; Mercade, E.; Baldoma, L.; Aguilera, L. Membrane Vesicles Released by a hypervesiculating Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 tolR Mutant Are Highly Heterogeneous and Show Reduced Capacity for Epithelial Cell Interaction and Entry. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0169186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michel, L.V.; Gallardo, L.; Konovalova, A.; Bauer, M.; Jackson, N.; Zavorin, M.; McNamara, C.; Pierce, J.; Cheng, S.; Snyder, E.; et al. Ampicillin triggers the release of Pal in toxic vesicles from Escherichia coli. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.H.; Park, E.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Choi, C.W.; Yi, Y.S.; Ro, H.J.; Lee, J.C.; Jun, S.; Kim, H.Y.; et al. Antibiotic treatment modulates protein components of cytotoxic outer membrane vesicles of multidrug-resistant clinical strain, Acinetobacter baumannii DU202. Clin. Proteom. 2018, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavan, D.; Vasudevan, A.; Wu, L.; Chen, J.; Su, Z.; Wang, S.; Xu, H. Integrative analysis of outer membrane vesicles proteomics and whole-cell transcriptome analysis of eravacycline induced Acinetobacter baumannii strains. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pastor, Y.; Camacho, A.I.; Zuniga-Ripa, A.; Merchan, A.; Rosas, P.; Irache, J.M.; Gamazo, C. Towards a subunit vaccine from a Shigella flexneri DeltatolR mutant. Vaccine 2018, 36, 7509–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidik, S.; Kottwitz, H.; Benjamin, J.; Ryu, J.; Jarrar, A.; Garduno, R.; Rohde, J.R. A Shigella flexneri virulence plasmid encoded factor controls production of outer membrane vesicles. G3 2014, 4, 2493–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernandez, I.; Zeiser, R.; Karsunky, H.; Kambham, N.; Beilhack, A.; Soderstrom, K.; Negrin, R.S.; Engleman, E. CD101 surface expression discriminates potency among murine FoxP3+ regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2808–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camacho, A.I.; Irache, J.M.; Gamazo, C. Recent progress towards development of a Shigella vaccine. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2013, 12, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, A.I.; Souza-Reboucas, J.; Irache, J.M.; Gamazo, C. Towards a non-living vaccine against Shigella flexneri: From the inactivation procedure to protection studies. Methods 2013, 60, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Syeda, J.T.M.; Wasan, K.M.; Wasan, E.K. An Overview of Chitosan Nanoparticles and Its Application in Non-Parenteral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Shigella Species | Dose and Route of OMVs | Infection after Immunization | Duration of Protection | Protection | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. flexneri 2a | 20 µg OMVs i.n. | 35 days | 0–15 days | 100% | [39] |
| S. flexneri 2a | 20 μg OMVs i.n./p.o. | 28 days | 0–9 days | 50% | [40] |
| S. dysenteriae 1, S. fle-neri 2a, 3a and 6, S. sonnei. | 32 μg OMVs p.o. | 21 days | 0–120 days | Variable | [41] |
| S. dysenteriae 1 Δstx, S. flexneri 2a, 3a and 6, S. boydii type 4, S. sonnei | 50 μg MOMVs p.o. | 100% | [42] | ||
| S. flexneri | 20–100 μg OMVs i.d. or p.o. | 35 days | 20–100% | [43] | |
| S. flexneri 2a (N.Y-962/92) | 3 μg recombinant his-tag OmpA i.n. | 28 days | 14 days | 100% | [44] |
| S. flexneri 2a | 1 μg OmpA i.p. | 28 days | 0–14 days | 100% | [45] |
| S. flexneri 3a | 1.6–20 μg OmpC s.c. | 0–21 days | Variable | [46] | |
| Genetically modified S. sonnei | 0.2–2 µg GM-MA s.c. | 0–35 days | 0–49 days | [47] | |
| S. sonnei 1790GAHB | 29–238 µg GM-MA i.p. | 21 days | [48] | ||
| S. boydii | 25 μg tolA-disrupted OMVs p.o. | 54 days | 100% | [38] | |
| S. flexneri 2a and 6, S. dysenteriae 1 | 20 μg PSSP1 i.n. | 28 days | 0–10 days | Variable | [49] |
| Immune-Reactive Protein | Shigella Species | Potential Role/Function | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| 34 kDa major outer membrane protein (MOMP) | S. flexneri 2a | (i) Promotes binding to macrophages (ii) Increases the production of nitric oxide (iii) Enhances cytokine production | [52] |
| 34 kDa MOMP | S. flexneri 2a | (i) Enhances TLR2 expression on macrophages. (ii) Increases the translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus (iii) Triggers the expression of p38 MAP kinases (iv) Augments the production of MyD88 and TRAF6 (v) Pormotes cytokine and chemokine production | [53] |
| OmpA | S. flexneri 2a | (i) Enhances the secretion of IgG and IgA (ii) Activates Th1 cells & macrophages (iii) Induces the expression of MHCII, CD80, CD40 (iv) Promotes the production of cytokines | [45] |
| 34 kDa outer membrane protein | S. flexneri 2a | (i) Enhances production of nitric oxide, (ii) Increases TNF-α and interleukin-12 production | [54] |
| Outer membrane protein A [55] | S. flexneri 2a | (i) Enhances protective immunity (mucosal and systemic) by protein specific IgG and IgA responses. (ii) Increases the production of IgA secreting cells | [44] |
| Pan-Shigella surface protein 1 (PSSP-1) | S. flexneri 2a and 6; S. dysenteriae 1 | (i) Enhances local and systemic antibody responses (ii) Increases the production of interleukin 17A and gamma interferon. | [49] |
| 38-kDa OmpC | S. flexneri 3a | Increases B-cell specific antigenic epitopes (based on modelling) | [46] |
| Outer membrane protein A [55] | S. flexneri 2a | (i) Enhances the production of IgG and IgA (ii) Induces IL-6 and IL-10 production (iii) Increases MHC II and CD86 expression on B cells (iv) Promotes the differentiation of B cells into antibody secreting plasma cells | [56] |
| Outer membrane protein A [55] | S. flexneri 2a | (i) Activates NF-κB (ii) Enhances the production of cytokines and of NO (iii) Stimulates the T cells to release IFN-γ and IL-2 | [57] |
| EpiMix® | S. flexneri | (i) Increases the secretion of specific serum IgG (ii) Enhances IgA, IL-4, IL-2and IFN-γ levels in feces | [58] |
| Shigella Species | Virulence Factors | Putative Function(s) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. flexneri | MxiD, an outer membrane protein (omp) | Secretion of the Ipa invasins (IpaA, IpaB, and IpaC,) of S. flexneri. MxiD is an essential component of the Ipa secretion apparatus. | [66] |
| Outer membrane proteinA [55] | IcsA exposition, cell-to-cell-spread and protrusion formation | [67] | |
| SopA, outer mem-brane protease | Required for the polar localization of IcsA and the actin-based motility inside infected cells | [68] | |
| Outer membrane protein IcsA (VirG) | Promotes bacterial transmission from host cell to host cell, mediates actin filament nucleation and unidirectional actin-based motility of Shigellae | [69] | |
| Outer membrane protein IcsA (VirG) | Involved in the actin-based motility required for intra- and intercellular Shigella spread | [70] | |
| Outer membrane protein IcsA (VirG) | Intracellular and cell-to-cell spread through polymerization of actin. Phosphoryation of IcsA and subsequent modulation of LcsA function | [71] | |
| Outer membrane protein IcsA (VirG) | Responsible for biofilm formation and bacterial cell to cell contact | [72] | |
| Outer Membrane Lipoprotein, MxiM | Plays a role in Shigella invasion and in the type III secretion system | [73] | |
| Outer Membrane Lipoprotein, MxiM | Supports the stability and localization of MxiD, it is required for the assembly in cells | [74] | |
| MxiJ, a lipoprotein | Mediates the secretion of Shigella Ipa invasins (IpaA, IpaB, and IpaC) | [75] | |
| Outer membrane protein C (ompC) | Involved in the spread of Shigella in epithelial cells | [76] | |
| YaeT (Omp85) | Required for the secretion and expression of Shigella auto-transporters IcsA and SepA. | [77] | |
| Cardiolipin (Gene encoded on synthase ClsA) | Involved in the surface localization of IcsA and spread of Shigella | [78] | |
| Outer membrane phospholipase A (OMPLA)-PldA | Essential for membrane stability and integrity, and type III secretion | [79] | |
| S. dys-enteriae, S. flexneri | Outer membrane protease IcsP | Modulates the quantity and distribution of IcsA; role in actin-based motility-based Shigella spread | [68,80,81,82,83,84] |
| Method | Mechanism | Increase in OMV Release | Immunological Efficiency | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enhancing OMV release | Disruption of tolA, one of the genes of the Tol–Pal system of membrane | 60% | Mucosal IgG and IgA, pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IFN-γ) | [38] |
| Distruption in Tol-Pal system in outer membrane | More than 8-times | Enhanced production of anti-bodies and expression of MHC II and costimulatory molecules | [121] | |
| Development of GMMA by deletion of tolR | Economic and high yield | Highly immunogenic | [48] | |
| Null mutants of tolR and galU | High yield, increased production of GMMA | Highly immunogenic | [47] | |
| virK mutant enhance the | High yield, OMV over- production | ND | [122] | |
| Enhancing efficiency | Mixing of OMVs from multiple Shigella species to obtain MOMVs | ND | Consistent broad spectrum antibody response and protection against all tested serotypes | [42] |
| Mixing of OMVs from multiple Shigella species → MOMVs | ND | Significantly enhanced cytokine production compared to SOMVs | [38] | |
| Binary ethylenimine [123] treatment | ND | Good immunogenic properties of OMVs | [124,125] | |
| Nanoencap-sulation of the OMVs | ND | Long-term protection | [39] | |
| Heat-induced (HT) outer-membrane vesicles development | ND | Higher contents of some antigenic structures than classical OMVs | [40] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qasim, M.; Wrage, M.; Nüse, B.; Mattner, J. Shigella Outer Membrane Vesicles as Promising Targets for Vaccination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020994
Qasim M, Wrage M, Nüse B, Mattner J. Shigella Outer Membrane Vesicles as Promising Targets for Vaccination. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(2):994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020994
Chicago/Turabian StyleQasim, Muhammad, Marius Wrage, Björn Nüse, and Jochen Mattner. 2022. "Shigella Outer Membrane Vesicles as Promising Targets for Vaccination" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 2: 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020994
APA StyleQasim, M., Wrage, M., Nüse, B., & Mattner, J. (2022). Shigella Outer Membrane Vesicles as Promising Targets for Vaccination. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(2), 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020994





