Clot Morphology in Acute Ischemic Stroke Decision Making
Abstract
1. Introduction
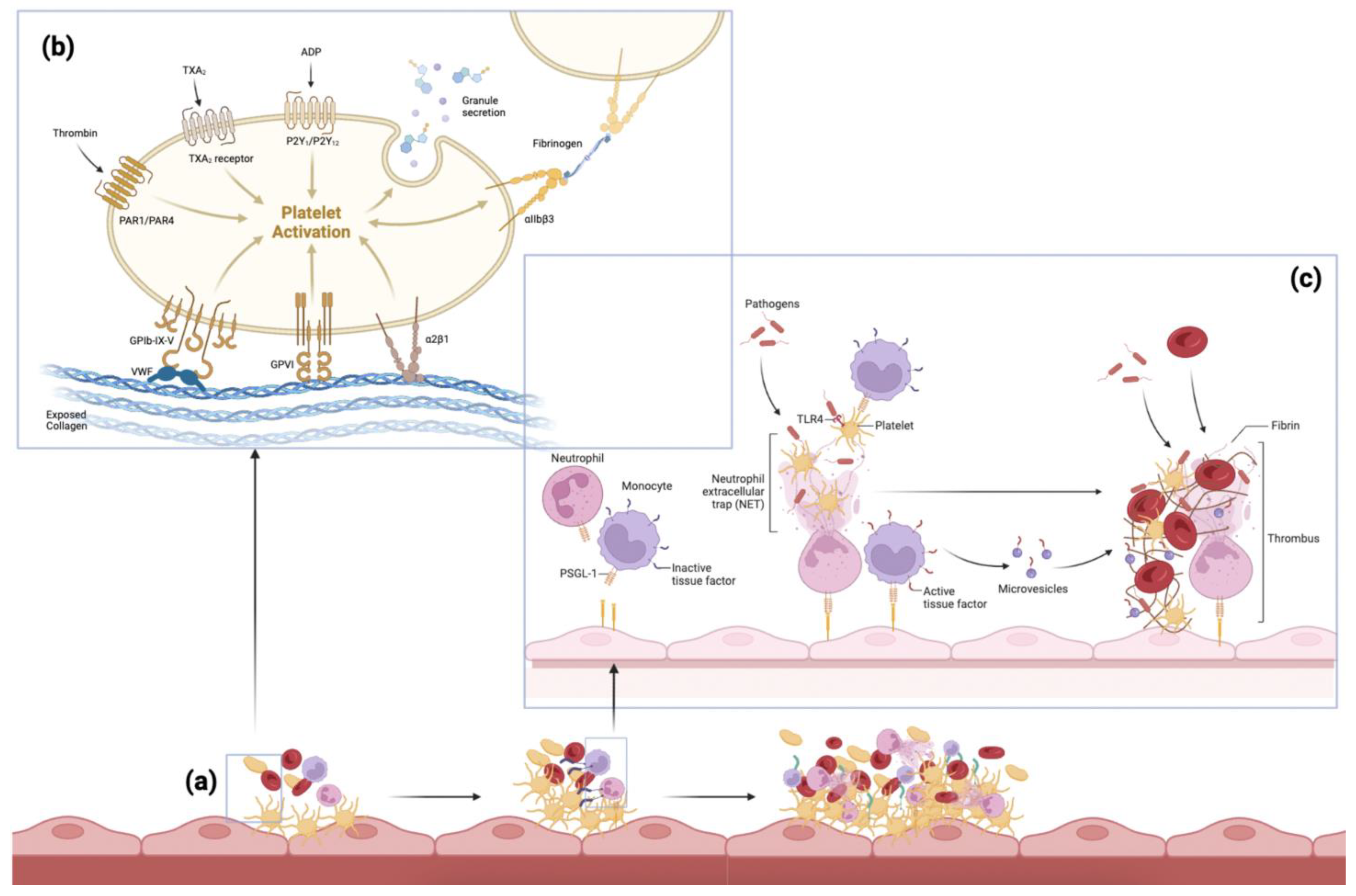
2. Pathogenesis of Thromboembolism
3. Clot Components
3.1. Red Blood Cells
3.2. Polyhedrocytes
3.3. Platelets/Fibrin
3.4. White Blood Cells
3.5. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps
3.6. Von Willebrand Factor
3.7. Extracellular DNA
3.8. Endothelial Cells
3.9. Bacteria
3.10. Calcifications
3.11. Other
4. Clot Composition and Etiology
5. Clot Composition and Imaging
6. Clot Composition and Treatment
7. Clot Composition and Clinical Outcomes
8. Gaps and Limitations
9. Future Directions
9.1. Imaging and Thrombectomy Technique
9.2. Novel Therapeutic Targets
9.3. Machine Learning
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIS | Acute Ischemic Stroke |
| LAA | Large Artery Atherosclerosis |
| EVT | Endovascular Thrombectomy |
| NCCT | Non-Contrast Computed Tomography |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| IVT | Intravenous Thrombolysis |
| rt-PA | Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator |
| VWF | von Willebrand Factor |
| NET | Neutrophil Extracellular Trap |
| RBC | Red Blood Cell |
| WBC | White Blood Cell |
| HMCAS | Hyperdense Middle Cerebral Artery Sign |
| SVS | Susceptibility Vessel Sign |
| NIHSS | National Institutes of Health Stroke Scales |
| PAI-1 | Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 |
| PN-1 | Protease Nexin-1 |
| ADAPT | A Direct Aspiration First Pass Technique |
| BGC | Balloon Guide Catheter |
References
- Truelsen, T.; Begg, S.; Mathers, C. The Global Burden of Cerebrovascular; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organisation. The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 3 March 2022).
- Vos, T.; Lim, S.S.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi, M.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.C.; De Silva, D.A.; Macleod, M.R.; Coutts, S.B.; Schwamm, L.H.; Davis, S.M.; Donnan, G.A. Ischaemic stroke. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyam Prabhakaran, M.S.E. Cryptogenic Stroke; UpToDate: Waltham, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bhaskar, S.; Cordato, D.; Cappelen-Smith, C.; Cheung, A.; Ledingham, D.; Celermajer, D.; Levi, C. Clarion call for histopathological clot analysis in “cryptogenic” ischemic stroke: Implications for diagnosis and treatment. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2017, 4, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskar, S.; Saab, J.; Cappelen-Smith, C.; Killingsworth, M.; Wu, X.J.; Cheung, A.; Manning, N.; Aouad, P.; McDougall, A.; Hodgkinson, S.; et al. Clot Histopathology in Ischemic Stroke with Infective Endocarditis. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 46, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhemer, O.A.; Fransen, P.S.; Beumer, D.; van den Berg, L.A.; Lingsma, H.F.; Yoo, A.J.; Schonewille, W.J.; Vos, J.A.; Nederkoorn, P.J.; Wermer, M.J.; et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saver, J.L.; Goyal, M.; Bonafe, A.; Diener, H.C.; Levy, E.I.; Pereira, V.M.; Albers, G.W.; Cognard, C.; Cohen, D.J.; Hacke, W.; et al. Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2285–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Demchuk, A.M.; Menon, B.K.; Eesa, M.; Rempel, J.L.; Thornton, J.; Roy, D.; Jovin, T.G.; Willinsky, R.A.; Sapkota, B.L.; et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.C.; Mitchell, P.J.; Kleinig, T.J.; Dewey, H.M.; Churilov, L.; Yassi, N.; Yan, B.; Dowling, R.J.; Parsons, M.W.; Oxley, T.J.; et al. Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovin, T.G.; Chamorro, A.; Cobo, E.; de Miquel, M.A.; Molina, C.A.; Rovira, A.; San Roman, L.; Serena, J.; Abilleira, S.; Ribo, M.; et al. Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2296–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, P.B.; Jeibmann, A.; Minnerup, J.; Broocks, G.; Nawabi, J.; Schon, G.; Fiehler, J.; Wildgruber, M.; Heindel, W.; Kemmling, A.; et al. Histological Clot Composition Is Associated With Preinterventional Clot Migration in Acute Stroke Patients. Stroke 2019, 50, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliena-Valero, A.; Baixauli-Martín, J.; Torregrosa, G.; Tembl, J.I.; Salom, J.B. Clot Composition Analysis as a Diagnostic Tool to Gain Insight into Ischemic Stroke Etiology: A Systematic Review. J. Stroke 2021, 23, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ząbczyk, M.; Natorska, J.; Undas, A. Fibrin Clot Properties in Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, T.; Connell, S.D.A.; Ariëns, R.A.S. Why fibrin biomechanical properties matter for hemostasis and thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 20, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Killingsworth, M.C.; Bhaskar, S.M.M. Is Composition of Brain Clot Retrieved by Mechanical Thrombectomy Associated with Stroke Aetiology and Clinical Outcomes in Acute Ischemic Stroke?—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurol. Int. 2022, 14, 748–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Filho, J.; Lansberg, M.G. Neuroimaging of Acute Ischemic Stroke; UpToDate: Waltham, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jilani, T.N.; Siddiqui, A.H. Tissue Plasminogen Activator; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira-Filho, J.; Mullen, M.T. Initial Assessment and Management of Acute Stroke; UpToDate: Waltham, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, S.; Darcourt, J.; Messina, P.; Bozsak, F.; Cognard, C.; Doyle, K. Characterising acute ischaemic stroke thrombi: Insights from histology, imaging and emerging impedance-based technologies. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2022, 7, svn-2021-001038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staessens, S.; De Meyer, S.F. Thrombus heterogeneity in ischemic stroke. Platelets 2021, 32, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yan, S.; Song, X.; Gong, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, M.; Yin, X.; Hu, B.; Lu, Z. Intravenous thrombolytic therapy for acute ischemic stroke in Hubei, China: A survey of thrombolysis rate and barriers. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Filho, J.; Samuels, O.B. Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke; UpToDate: Waltham, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- McMeekin, P.; White, P.; James, M.A.; Price, C.I.; Flynn, D.; Ford, G.A. Estimating the number of UK stroke patients eligible for endovascular thrombectomy. Eur. Stroke J. 2017, 2, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munich, S.A.; Vakharia, K.; Levy, E.I. Overview of Mechanical Thrombectomy Techniques. Neurosurgery 2019, 85, S60–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanagiotou, P.; Ntaios, G. Endovascular Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 11, e005362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.H.; Sim, E.H.; Goh, R.Y.; Park, J.I.; Han, J.Y. Platelet Activation: The Mechanisms and Potential Biomarkers. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9060143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelmann, B.; Massberg, S. Thrombosis as an intravascular effector of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkarithi, G.; Duval, C.; Shi, Y.; Macrae, F.L.; Ariens, R.A.S. Thrombus Structural Composition in Cardiovascular Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 2370–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, R.; Chen, S.; Chen, S.; Peng, Q.; Jin, H.; Hu, B. The role of leukocytes in acute ischemic stroke-related thrombosis: A notable but neglected topic. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 6251–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.H.; Hong, R.; Choo, I.S.; Heo, J.H.; Nam, H.S.; Kang, H.G.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, J.H. Histologic features of acute thrombi retrieved from stroke patients during mechanical reperfusion therapy. Int. J. Stroke 2016, 11, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, S.; Mereuta, O.M.; Doyle, K.M.; Dai, D.; Kadirvel, R.; Kallmes, D.F.; Brinjikji, W. Correlation of imaging and histopathology of thrombi in acute ischemic stroke with etiology and outcome. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2019, 63, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeckh-Behrens, T.; Kleine, J.F.; Zimmer, C.; Neff, F.; Scheipl, F.; Pelisek, J.; Schirmer, L.; Nguyen, K.; Karatas, D.; Poppert, H. Thrombus Histology Suggests Cardioembolic Cause in Cryptogenic Stroke. Stroke 2016, 47, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, P.B.; Hanning, U.; Schwindt, W.; Velasco, A.; Minnerup, J.; Zoubi, T.; Heindel, W.; Jeibmann, A.; Niederstadt, T.U. Ischemic Stroke: What Does the Histological Composition Tell Us about the Origin of the Thrombus? Stroke 2017, 48, 2206–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, J.; Gaida, B.J.; Wanke, I.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Koehrmann, M.; Forsting, M.; Moenninghoff, C.; Radbruch, A.; Junker, A. Is Histologic Thrombus Composition in Acute Stroke Linked to Stroke Etiology or to Interventional Parameters? AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Yoon, W.; Kim, T.S.; Kim, H.S.; Heo, T.W.; Park, M.S. Histologic Analysis of Retrieved Clots in Acute Ischemic Stroke: Correlation with Stroke Etiology and Gradient-Echo MRI. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, N.; Mitchell, P.; Dowling, R.; Gonzales, M.; Yan, B. Thrombus composition in acute ischemic stroke: A histopathological study of thrombus extracted by endovascular retrieval. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 42, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ye, G.; Cao, R.; Lu, J.; Qi, P.; Hu, S.; Chen, K.; Tan, T.; Chen, J.; Wang, D. Histological composition behind CT-based thrombus density and perviousness in acute ischemic stroke. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 207, 106804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niesten, J.M.; van der Schaaf, I.C.; van Dam, L.; Vink, A.; Vos, J.A.; Schonewille, W.J.; de Bruin, P.C.; Mali, W.P.; Velthuis, B.K. Histopathologic composition of cerebral thrombi of acute stroke patients is correlated with stroke subtype and thrombus attenuation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, T.; Hayakawa, M.; Funatsu, N.; Yamagami, H.; Satow, T.; Takahashi, J.C.; Nagatsuka, K.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Kira, J.I.; Toyoda, K. Histopathologic Analysis of Retrieved Thrombi Associated With Successful Reperfusion after Acute Stroke Thrombectomy. Stroke 2016, 47, 3035–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeckh-Behrens, T.; Schubert, M.; Forschler, A.; Prothmann, S.; Kreiser, K.; Zimmer, C.; Riegger, J.; Bauer, J.; Neff, F.; Kehl, V.; et al. The Impact of Histological Clot Composition in Embolic Stroke. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2016, 26, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Fernandez, F.; Rojas-Bartolome, L.; Garcia-Garcia, J.; Ayo-Martin, O.; Molina-Nuevo, J.D.; Barbella-Aponte, R.A.; Serrano-Heras, G.; Julia-Molla, E.; Pedrosa-Jimenez, M.J.; Segura, T. Histopathological and Bacteriological Analysis of Thrombus Material Extracted During Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Stroke Patients. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 40, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, K.; Shibata, M.; Nakajima, H.; Mizutani, A.; Kitano, Y.; Seguchi, M.; Yamasaki, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Sano, T.; Mori, G.; et al. Erythrocyte-Rich Thrombus Is Associated with Reduced Number of Maneuvers and Procedure Time in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Undergoing Mechanical Thrombectomy. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Extra 2018, 8, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, S.; McCarthy, R.; Farrell, M.; Thomas, S.; Brennan, P.; Power, S.; O’Hare, A.; Morris, L.; Rainsford, E.; MacCarthy, E.; et al. Per-Pass Analysis of Thrombus Composition in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Undergoing Mechanical Thrombectomy. Stroke 2019, 50, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Meglio, L.; Desilles, J.P.; Ollivier, V.; Nomenjanahary, M.S.; Di Meglio, S.; Deschildre, C.; Loyau, S.; Olivot, J.M.; Blanc, R.; Piotin, M.; et al. Acute ischemic stroke thrombi have an outer shell that impairs fibrinolysis. Neurology 2019, 93, e1686–e1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staessens, S.; Denorme, F.; Francois, O.; Desender, L.; Dewaele, T.; Vanacker, P.; Deckmyn, H.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Andersson, T.; De Meyer, S.F. Structural analysis of ischemic stroke thrombi: Histological indications for therapy resistance. Haematologica 2020, 105, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almekhlafi, M.A.; Hu, W.Y.; Hill, M.D.; Auer, R.N. Calcification and endothelialization of thrombi in acute stroke. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berndt, M.; Friedrich, B.; Maegerlein, C.; Moench, S.; Hedderich, D.; Lehm, M.; Zimmer, C.; Straeter, A.; Poppert, H.; Wunderlich, S.; et al. Thrombus Permeability in Admission Computed Tomographic Imaging Indicates Stroke Pathogenesis Based on Thrombus Histology. Stroke 2018, 49, 2674–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.W.; Jeong, H.S.; Kwon, H.-J.; Song, K.S.; Kim, J. High red blood cell composition in clots is associated with successful recanalization during intra-arterial thrombectomy. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, S.T.; Wang, S.; Dai, D.; Douglas, A.; Kadirvel, R.; Gounis, M.J.; Chueh, J.; Puri, A.S.; Layton, K.F.; Thacker, I.C.; et al. Platelet-rich clots as identified by Martius Scarlet Blue staining are isodense on NCCT. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2019, 11, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funatsu, N.; Hayakawa, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Yamagami, H.; Satow, T.; Takahashi, J.C.; Koga, M.; Nagatsuka, K.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Iwama, T.; et al. Vascular wall components in thrombi obtained by acute stroke thrombectomy: Clinical significance and related factors. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2019, 11, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.H.; Park, G.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.E.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, J.M. Erythrocyte Fraction within Retrieved Thrombi Contributes to Thrombolytic Response in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2018, 49, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, S.; Wang, S.; Dai, D.; Murphree, D.H., Jr.; Pandit, A.; Douglas, A.; Rizvi, A.; Kadirvel, R.; Gilvarry, M.; McCarthy, R. Orbit image analysis machine learning software can be used for the histological quantification of acute ischemic stroke blood clots. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, J.C.; Fitzgerald, S.T.; Kadirvel, R.; Johnson, C.; Dai, D.; Karen, D.; Kallmes, D.F.; Brinjikji, W. Clot permeability and histopathology: Is a clot’s perviousness on CT imaging correlated with its histologic composition? J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2020, 12, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, S.; Dai, D.; Wang, S.; Douglas, A.; Kadirvel, R.; Layton, K.F.; Thacker, I.C.; Gounis, M.J.; Chueh, J.Y.; Puri, A.S.; et al. Platelet-Rich Emboli in Cerebral Large Vessel Occlusion Are Associated with a Large Artery Atherosclerosis Source. Stroke 2019, 50, 1907–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochazka, V.; Jonszta, T.; Czerny, D.; Krajca, J.; Roubec, M.; Macak, J.; Kovar, P.; Kovarova, P.; Pulcer, M.; Zoubkova, R.; et al. The Role of von Willebrand Factor, ADAMTS13, and Cerebral Artery Thrombus Composition in Patient Outcome Following Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 3929–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaesmacher, J.; Boeckh-Behrens, T.; Simon, S.; Maegerlein, C.; Kleine, J.F.; Zimmer, C.; Schirmer, L.; Poppert, H.; Huber, T. Risk of Thrombus Fragmentation during Endovascular Stroke Treatment. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporns, P.B.; Hanning, U.; Schwindt, W.; Velasco, A.; Buerke, B.; Cnyrim, C.; Minnerup, J.; Heindel, W.; Jeibmann, A.; Niederstadt, T. Ischemic Stroke: Histological Thrombus Composition and Pre-Interventional CT Attenuation Are Associated with Intervention Time and Rate of Secondary Embolism. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 44, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, A.; Fitzgerald, S.; Mereuta, O.M.; Rossi, R.; O’Leary, S.; Pandit, A.; McCarthy, R.; Gilvarry, M.; Holmegaard, L.; Abrahamsson, M.; et al. Platelet-rich emboli are associated with von Willebrand factor levels and have poorer revascularization outcomes. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2020, 12, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazlouskaya, V.; Malhotra, S.; Lambe, J.; Idriss, M.H.; Elston, D.; Andres, C. The utility of elastic Verhoeff-Van Gieson staining in dermatopathology. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2013, 40, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalayer Naderi, N. Reporting an Experience: Improving the Feulgen Staining Technique for Better Visualizing of Nucleus. Iran. J. Pathol. 2018, 13, 106–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laridan, E.; Denorme, F.; Desender, L.; Francois, O.; Andersson, T.; Deckmyn, H.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; De Meyer, S.F. Neutrophil extracellular traps in ischemic stroke thrombi. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, J.; Oberdieck, P.; Titova, A.; Pelisek, J.; Chandraratne, S.; Nicol, P.; Hapfelmeier, A.; Joner, M.; Maegdefessel, L.; Poppert, H.; et al. Thrombus NET content is associated with clinical outcome in stroke and myocardial infarction. Neurology 2020, 94, e2346–e2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, N.; Shobayashi, K.; Morofuji, Y.; Sadakata, E.; Iki, Y.; Matsunaga, Y.; Kanamoto, T.; Tateishi, Y.; Izumo, T.; Anda, T.; et al. Impact of Mechanical Thrombectomy Device on Thrombus Histology in Acute Embolic Stroke. World Neurosurg. 2019, 132, e418–e422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khismatullin, R.R.; Nagaswami, C.; Shakirova, A.Z.; Vrtkova, A.; Prochazka, V.; Gumulec, J.; Macak, J.; Litvinov, R.I.; Weisel, J.W. Quantitative Morphology of Cerebral Thrombi Related to Intravital Contraction and Clinical Features of Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 3640–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.R.; Fricano, S.; Waqas, M.; Tso, M.; Dmytriw, A.A.; Mokin, M.; Kolega, J.; Tomaszewski, J.; Levy, E.I.; Davies, J.M.; et al. Increased Perviousness on CT for Acute Ischemic Stroke is Associated with Fibrin/Platelet-Rich Clots. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducroux, C.; Di Meglio, L.; Loyau, S.; Delbosc, S.; Boisseau, W.; Deschildre, C.; Ben Maacha, M.; Blanc, R.; Redjem, H.; Ciccio, G.; et al. Thrombus Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Content Impair tPA-Induced Thrombolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2018, 49, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Meglio, L.; Desilles, J.P.; Solonomenjanahary, M.; Labreuche, J.; Ollivier, V.; Dupont, S.; Deschildre, C.; Maacha, M.B.; Consoli, A.; Lapergue, B.; et al. DNA Content in Ischemic Stroke Thrombi Can Help Identify Cardioembolic Strokes Among Strokes of Undetermined Cause. Stroke 2020, 51, 2810–2816. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dobrocky, T.; Piechowiak, E.; Cianfoni, A.; Zibold, F.; Roccatagliata, L.; Mosimann, P.; Jung, S.; Fischer, U.; Mordasini, P.; Gralla, J. Thrombectomy of calcified emboli in stroke. Does histology of thrombi influence the effectiveness of thrombectomy? J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2018, 10, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walker, B.S.; Shah, L.M.; Osborn, A.G. Calcified cerebral emboli, a “do not miss” imaging diagnosis: 22 New cases and review of the literature. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, C.J.; Dobrocky, T.; Joachimski, F.; Neuberger, U.; Demerath, T.; Brehm, A.; Cianfoni, A.; Gory, B.; Berlis, A.; Gralla, J.; et al. Endovascular Thrombectomy of Calcified Emboli in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Multicenter Study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, R.I.; Weisel, J.W. Role of red blood cells in haemostasis and thrombosis. ISBT Sci. Ser. 2017, 12, 176–183. [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes, J.R.; Wolberg, A.S. Red blood cells in thrombosis. Blood 2017, 130, 1795–1799. [Google Scholar]
- Chernysh, I.N.; Nagaswami, C.; Kosolapova, S.; Peshkova, A.D.; Cuker, A.; Cines, D.B.; Cambor, C.L.; Litvinov, R.I.; Weisel, J.W. The distinctive structure and composition of arterial and venous thrombi and pulmonary emboli. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5112. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.G.; Ariens, R.A.S. Insights into the composition of stroke thrombi: Heterogeneity and distinct clot areas impact treatment. Haematologica 2020, 105, 257–259. [Google Scholar]
- Staessens, S.; Francois, O.; Brinjikji, W.; Doyle, K.M.; Vanacker, P.; Andersson, T.; De Meyer, S.F. Studying Stroke Thrombus Composition After Thrombectomy: What Can We Learn? Stroke 2021, 52, 3718–3727. [Google Scholar]
- Gunning, G.M.; McArdle, K.; Mirza, M.; Duffy, S.; Gilvarry, M.; Brouwer, P.A. Clot friction variation with fibrin content; implications for resistance to thrombectomy. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2018, 10, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gersh, K.C.; Nagaswami, C.; Weisel, J.W. Fibrin network structure and clot mechanical properties are altered by incorporation of erythrocytes. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 102, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinjikji, W.; Duffy, S.; Burrows, A.; Hacke, W.; Liebeskind, D.; Majoie, C.; Dippel, D.W.J.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Khatri, P.; Baxter, B.; et al. Correlation of imaging and histopathology of thrombi in acute ischemic stroke with etiology and outcome: A systematic review. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2017, 9, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swystun, L.L.; Liaw, P.C. The role of leukocytes in thrombosis. Blood 2016, 128, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacigaluppi, M.; Semerano, A.; Gullotta, G.S.; Strambo, D. Insights from thrombi retrieved in stroke due to large vessel occlusion. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 39, 1433–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valles, J.; Lago, A.; Santos, M.T.; Latorre, A.M.; Tembl, J.I.; Salom, J.B.; Nieves, C.; Moscardo, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps are increased in patients with acute ischemic stroke: Prognostic significance. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolugbo, P.; Ariens, R.A.S. Thrombus Composition and Efficacy of Thrombolysis and Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2021, 52, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wu, Z.; Long, Q.; Huang, J.; Hong, T.; Liu, W.; Lin, J. Insights Into Immunothrombosis: The Interplay among Neutrophil Extracellular Trap, von Willebrand Factor, and ADAMTS13. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 610696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denorme, F.; Portier, I.; Rustad, J.L.; Cody, M.J.; de Araujo, C.V.; Hoki, C.; Alexander, M.D.; Grandhi, R.; Dyer, M.R.; Neal, M.D.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps regulate ischemic stroke brain injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e154225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanesha, N.; Patel, R.B.; Doddapattar, P.; Ghatge, M.; Flora, G.D.; Jain, M.; Thedens, D.; Olalde, H.; Kumskova, M.; Leira, E.C.; et al. PKM2 promotes neutrophil activation and cerebral thromboinflammation: Therapeutic implications for ischemic stroke. Blood 2022, 139, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staessens, S.; Francois, O.; Desender, L.; Vanacker, P.; Dewaele, T.; Sciot, R.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Andersson, T.; De Meyer, S.F. Detailed histological analysis of a thrombectomy-resistant ischemic stroke thrombus: A case report. Thromb. J. 2021, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, M.; Saab, J.; Cordato, D.; Manning, N.; Cappelen-Smith, C. The diagnostic utility of routine clot analysis after endovascular thrombectomy in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 70, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, N.; Takahashi, M.; Katano, T.; Kutsuna, A.; Kanamaru, T.; Sakamoto, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Aoki, J.; Nishiyama, Y.; Kunugi, S. Cholesterol crystal in thrombus removed by mechanical thrombectomy should be a strong marker for aortogenic embolic stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 105178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windecker, S.; Stortecky, S.; Meier, B. Paradoxical embolism. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maron, B.A.; Shekar, P.S.; Goldhaber, S.Z. Paradoxical embolism. Circulation 2010, 122, 1968–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenz, K.T.; Just, J.; Blauenfeldt, R.A.; Drasbek, K.R. Extracellular Vesicles in Acute Stroke Diagnostics. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świtońska, M.; Słomka, A.; Sinkiewicz, W.; Żekanowska, E. Tissue-factor-bearing microparticles (MPs-TF) in patients with acute ischaemic stroke: The influence of stroke treatment on MPs-TF generation. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 395–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarà, M.; Guidetti, G.F.; Camera, M.; Canobbio, I.; Amadio, P.; Torti, M.; Tremoli, E.; Barbieri, S.S. Biology and Role of Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) in the Pathogenesis of Thrombosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darcourt, J.; Withayasuk, P.; Vukasinovic, I.; Michelozzi, C.; Bellanger, G.; Guenego, A.; Adam, G.; Roques, M.; Januel, A.C.; Tall, P.; et al. Predictive Value of Susceptibility Vessel Sign for Arterial Recanalization and Clinical Improvement in Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2019, 50, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutra, B.G.; Tolhuisen, M.L.; Alves, H.; Treurniet, K.M.; Kappelhof, M.; Yoo, A.J.; Jansen, I.G.H.; Dippel, D.W.J.; van Zwam, W.H.; van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; et al. Thrombus Imaging Characteristics and Outcomes in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients Undergoing Endovascular Treatment. Stroke 2019, 50, 2057–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.M.; Dankbaar, J.W.; Treurniet, K.M.; Horsch, A.D.; Roos, Y.B.; Kappelle, L.J.; Niessen, W.J.; Majoie, C.B.; Velthuis, B.; Marquering, H.A.; et al. Permeable Thrombi Are Associated with Higher Intravenous Recombinant Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator Treatment Success in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2016, 47, 2058–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Kimura, K.; Sakai, K. M1 susceptibility vessel sign and hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign in hyperacute stroke patients. Eur. Neurol. 2012, 68, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, M.; Longstaff, C. Extracellular Histones Inhibit Fibrinolysis through Noncovalent and Covalent Interactions with Fibrin. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 121, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, E.; De Michele, M.; Falcou, A.; Petraglia, L.; Berto, I.; Toni, D. Histological analysis of thrombi retrieved after acute ischemic stroke from large vessel occlusion: From research to clinical practice. Vessel Plus 2022, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, A.C.; Avins, A.L.; Eaton, A.; Uong, S.; Cullen, S.P.; Hsu, D.P.; Edwards, N.J.; Reddy, P.A.; Klingman, J.G.; Rao, V.A.; et al. Risk of Distal Embolization From tPA (Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator) Administration Prior to Endovascular Stroke Treatment. Stroke 2020, 51, 2697–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chueh, J.Y.; Kang, D.H.; Kim, B.M.; Gounis, M.J. Role of Balloon Guide Catheter in Modern Endovascular Thrombectomy. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2020, 63, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chueh, J.Y.; Puri, A.S.; Wakhloo, A.K.; Gounis, M.J. Risk of distal embolization with stent retriever thrombectomy and ADAPT. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2016, 8, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.; Langan, S.; Cooke, J. Increasing Efficacy of Thrombectomy by Using Digital Subtraction Angiography to Confirm Stent Retriever Clot Integration. Cureus 2016, 8, e559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chueh, J.Y.; Marosfoi, M.G.; Brooks, O.W.; King, R.M.; Puri, A.S.; Gounis, M.J. Novel Distal Emboli Protection Technology: The EmboTrap. Interv. Neurol. 2017, 6, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.Y.; Ng, G.; Liao, P. Therapeutic antibodies in stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2013, 4, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Histological Stain | Uses | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hematoxylin and Eosin |
|
|
| [7,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59] |
| Martius Scarlet Blue |
|
|
| [33,39,45,47,48,51,53,55,56,60] |
| Gram Stain |
|
|
| [7,43] |
| Elastica van Gieson |
|
|
| [7,35,36,42,52,59] |
| Prussian Blue |
|
|
| [7,35,36,59] |
| Masson’s Trichrome |
|
|
| [7,33,41,48,52] |
| Ladewig’s Trichrome |
|
|
| [36] |
| Feulgen’s Stain |
|
|
| [47] |
| Von Kossa |
|
|
| [7,33,36,48] |
| Naphthol AS-D chloroacetate stain |
|
|
| [36] |
| Mallory’s phosphotungstic acid hematoxylin |
|
|
| [36,40] |
| Carstair’s Method |
|
|
| [57] |
| Immunohistochemical analysis |
|
| As per the second column |
| Clot Component | Treatment Success | Etiology | Imaging Markers | Clinical Outcome/Severity/Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBC | Associated with favorable reperfusion outcomes [41,44,50,53] No significant association [32,37,38,56] | Associated with LAA or non-cardioembolic origin [32,34,40,44] Associated with the cardioembolic origin [37,50] No significant association [38,51] | Associated with higher attenuation on NCCT or HMCAS [39,40,42,44,50,54] Associated with positive SVS [37,53] No significant association [32,65] Associated with increased perviousness [55] | No significant association [60] |
| Polyhedrocytes | Associated with worse reperfusion outcome [66] | None found | None found | Associated with higher NIHSS score [66] |
| Platelets/Fibrin | Associated with worse reperfusion outcomes [35,60] No significant association [32,37,38,56] | Associated with cardioembolic origin [32,34,35,49] Associated with LAA or non-cardioembolic origin [50] No significant association [38,40] Platelets (without fibrin) higher in LAA origin [56] | Associated with negative SVS [37] Associated with isodense clots on NCCT [51] Associated with decreased perviousness [39,55] Associated with increased perviousness [49,67] | Higher chance of distal embolism [35] No significant association [60] |
| WBCs | Associated with worse reperfusion outcomes [42] | Associated with cardioembolic origin [34,35,42] | Associated with decreased perviousness [55] | Associated with higher NIHSS score at discharge [42] Associated with higher mRS score at 90 days [42] |
| NETs | Associated with worse reperfusion outcomes [63,68] | Associated with the cardioembolic origin [63] | None found | Associated with higher NIHSS score at discharge [64] Associated with higher mRS score at 90 days [64] |
| VWF | Associated with worse reperfusion outcomes [57] | None found | None found | Associated with higher pre-intervention NIHSS score [57] |
| Extracellular DNA | None found | Associated with the cardioembolic origin [69] | None found | None found |
| Endothelial Cells | None found | None found | None found | None found |
| Bacteria | Associated with worse reperfusion outcomes [43] | Associated with infectious pathologies [7,43] | None found | None found |
| Calcifications | Associated with worse reperfusion outcomes [48,70] | None found | Associated with rounder and more hyperdense clots on imaging [71] | Associated with higher mortality and recurrent stroke [72] |
| Other | Vascular wall components are associated with increased thrombectomy passes [52] | None found | None found | None found |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.C.; Bhaskar, S.M.M. Clot Morphology in Acute Ischemic Stroke Decision Making. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012373
Huang JC, Bhaskar SMM. Clot Morphology in Acute Ischemic Stroke Decision Making. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(20):12373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012373
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Joanna C., and Sonu M. M. Bhaskar. 2022. "Clot Morphology in Acute Ischemic Stroke Decision Making" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 20: 12373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012373
APA StyleHuang, J. C., & Bhaskar, S. M. M. (2022). Clot Morphology in Acute Ischemic Stroke Decision Making. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(20), 12373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012373