YM750, an ACAT Inhibitor, Acts on Adrenocortical Cells to Inhibit Aldosterone Secretion Due to Depolarization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of YM750 on CYP11B2 Expression Induced by Various Stimuli
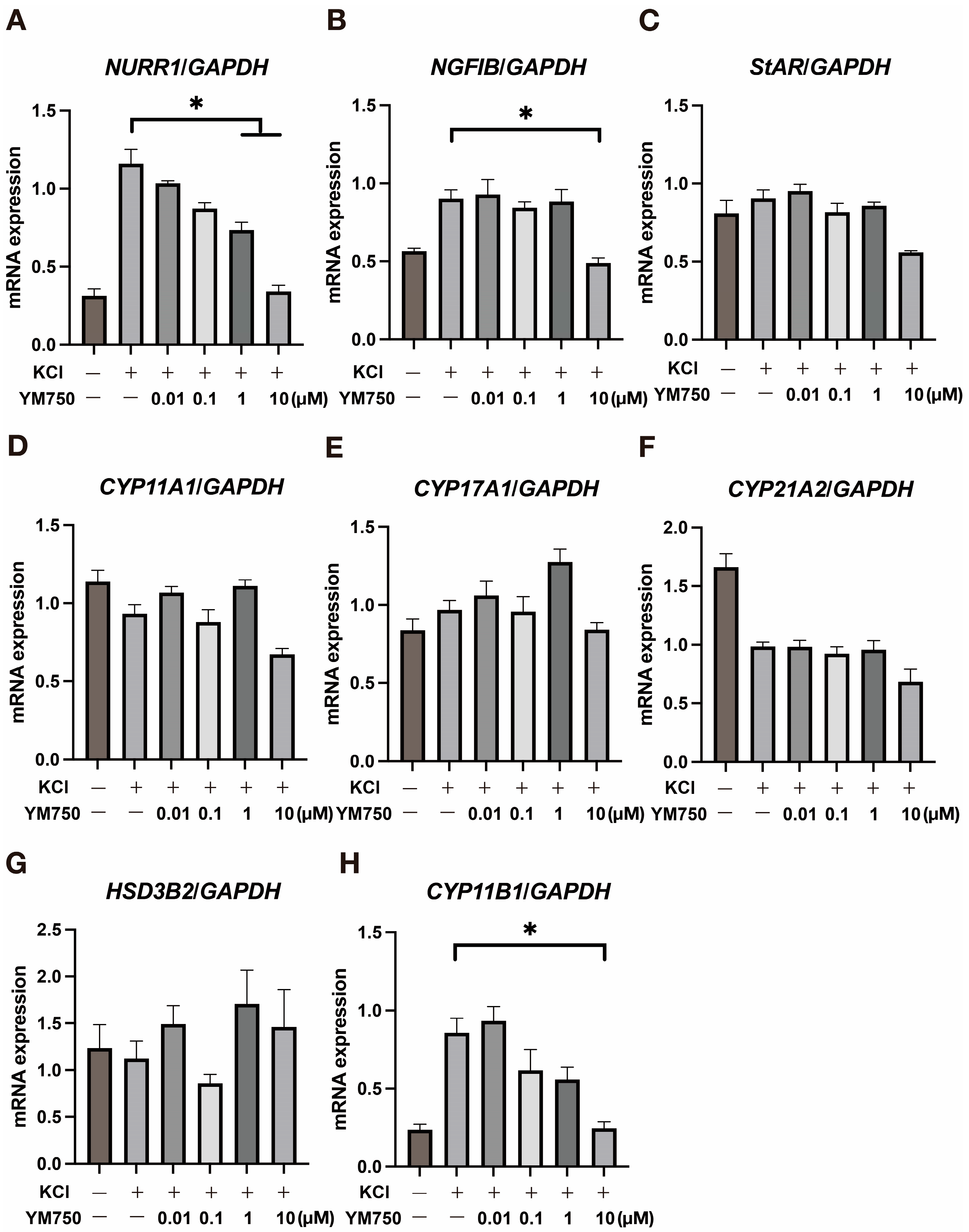
2.2. Effect of YM750 on the Expression of Various Steroidogenic Enzymes and CYP11B2 Related Genes
2.3. Effect of YM750 on Aldosterone Secretion
2.4. Effect of YM750 on Intracellular Calcium Concentration
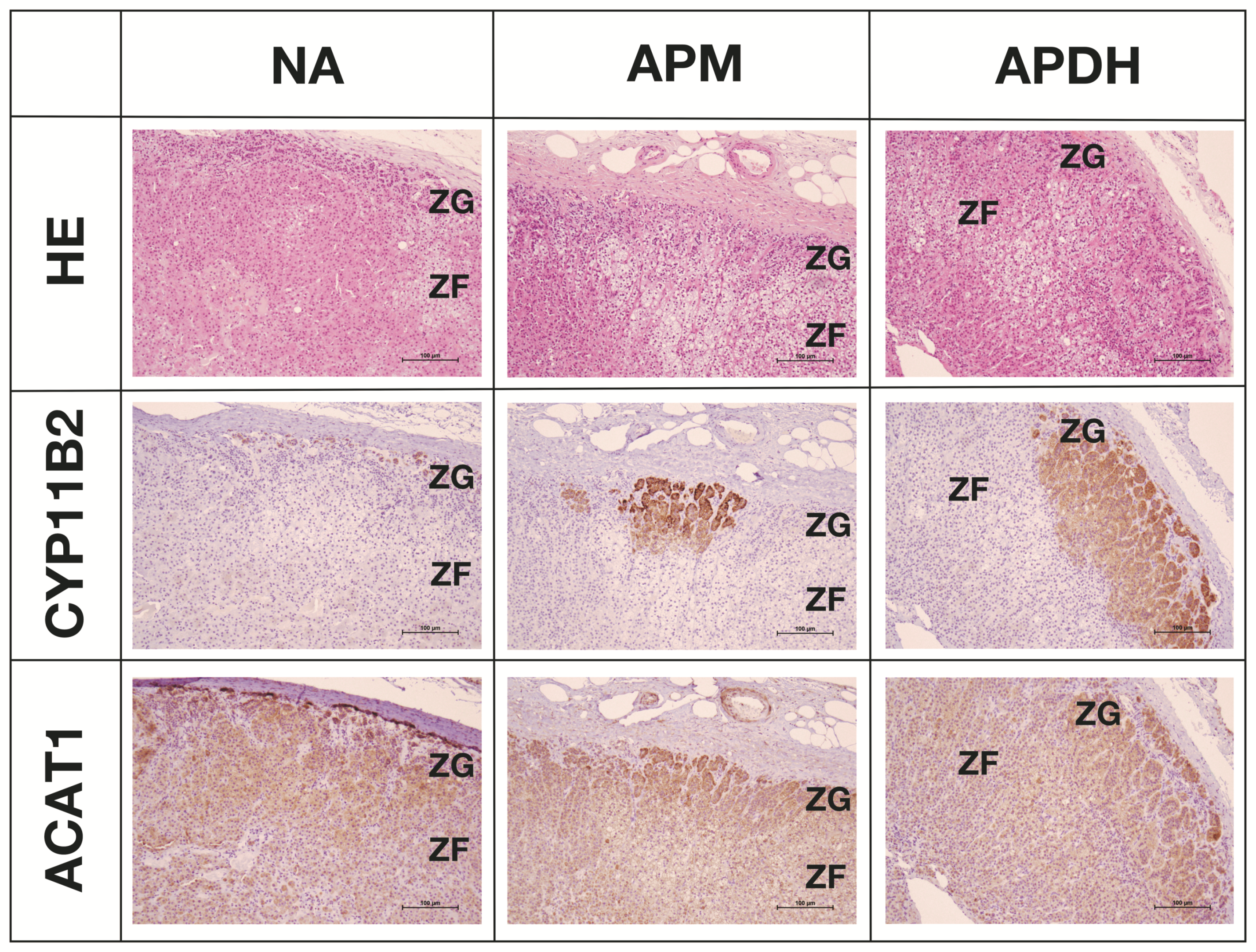
2.5. Expression and Localization of ACAT1 in the Adrenal Cortex
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Quantitative Reverse Trascription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.4. Cell Viability Assay
4.5. Aldosterone EIA
4.6. Intracellular Calcium Ion Concentration Assay
4.7. Human Adrenal Tissue Samples for Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.8. Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Funder, J.W. The Genetics of Primary Aldosteronism. Science 2011, 331, 685–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, G.P.; Bernini, G.; Caliumi, C.; Desideri, G.; Fabris, B.; Ferri, C.; Ganzaroli, C.; Giacchetti, G.; Letizia, C.; Maccario, M.; et al. A Prospective Study of the Prevalence of Primary Aldosteronism in 1,125 Hypertensive Patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 2293–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.S.; Williams, G.H.; Raji, A.; Jeunemaitre, X.; Brown, N.J.; Hopkins, P.N.; Conlin, P.R. Prevalence of Primary Hyperaldosteronism in Mild to Moderate Hypertension without Hypokalaemia. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2005, 20, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mete, O.; Erickson, L.A.; Juhlin, C.C.; de Krijger, R.R.; Sasano, H.; Volante, M.; Papotti, M.G. Overview of the 2022 WHO Classification of Adrenal Cortical Tumors. Endocr. Pathol. 2022, 33, 155–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, K.; Satoh, F.; Morimoto, R.; Ito, S.; Yamazaki, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Anand, S.K.; Guo, Z.; Stowasser, M.; Sasano, H.; et al. Cellular and Genetic Causes of Idiopathic Hyperaldosteronism. Hypertension 2018, 72, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Li, D.; Kosaka, T.; Oya, M.; Mikami, S.; Shibata, H.; Itoh, H.; Mitani, F.; Yamazaki, T.; et al. Adrenocortical Zonation in Humans under Normal and Pathological Conditions. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 2296–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hattangady, N.G.; Olala, L.O.; Bollag, W.B.; Rainey, W.E. Acute and Chronic Regulation of Aldosterone Production. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 350, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Omata, K.; Ise, K.; Tezuka, Y.; Ono, Y.; Morimoto, R.; Nozawa, Y.; Gomez-Sanchez, C.E.; Tomlins, S.A.; et al. Histopathological Classification of Cross-Sectional Image–Negative Hyperaldosteronism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholl, U.I.; Goh, G.; Stölting, G.; de Oliveira, R.C.; Choi, M.; Overton, J.D.; Fonseca, A.L.; Korah, R.; Starker, L.F.; Kunstman, J.W.; et al. Somatic and Germline CACNA1D Calcium Channel Mutations in Aldosterone-Producing Adenomas and Primary Aldosteronism. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuschlein, F.; Boulkroun, S.; Osswald, A.; Wieland, T.; Nielsen, H.N.; Lichtenauer, U.D.; Penton, D.; Schack, V.R.; Amar, L.; Fischer, E.; et al. Somatic Mutations in ATP1A1 and ATP2B3 Lead to Aldosterone-Producing Adenomas and Secondary Hypertension. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizan, E.A.B.; Poulsen, H.; Tuluc, P.; Zhou, J.; Clausen, M.V.; Lieb, A.; Maniero, C.; Garg, S.; Bochukova, E.G.; Zhao, W.; et al. Somatic Mutations in ATP1A1 and CACNA1D Underlie a Common Subtype of Adrenal Hypertension. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.; Scholl, U.I.; Yue, P.; Björklund, P.; Zhao, B.; Nelson-Williams, C.; Ji, W.; Cho, Y.; Patel, A.; Men, C.J.; et al. K+ Channel Mutations in Adrenal Aldosterone-Producing Adenomas and Hereditary Hypertension. Science 2011, 331, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, Y.; Yamazaki, Y.; Tezuka, Y.; Satoh, F.; Sasano, H. Expression of CYP11B2 in Aldosterone-Producing Adrenocortical Adenoma: Regulatory Mechanisms and Clinical Significance. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2016, 240, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scholl, U.I.; Abriola, L.; Zhang, C.; Reimer, E.N.; Plummer, M.; Kazmierczak, B.I.; Zhang, J.; Hoyer, D.; Merkel, J.S.; Wang, W.; et al. Macrolides Selectively Inhibit Mutant KCNJ5 Potassium Channels That Cause Aldosterone-Producing Adenoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 2739–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sparks, S.M.; Danger, D.P.; Hoekstra, W.J.; Leesnitzer, T.; Schotzinger, R.J.; Yates, C.M.; Becherer, J.D. Development of Highly Selective Pyrimidine-Based Aldosterone Synthase (CYP11B2) Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harashima, S.; Yamazaki, Y.; Motomura, N.; Ono, Y.; Omata, K.; Tezuka, Y.; Morimoto, R.; Nakamura, Y.; Satoh, F.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Phenotype-Genotype Correlation in Aldosterone-Producing Adenomas Characterized by Intracellular Cholesterol Metabolism. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 221, 106116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.G.; Willingham, M.C.; Davis, M.A.; Skinner, K.A.; Rudel, L.L. Differential Expression of ACAT1 and ACAT2 among Cells within Liver, Intestine, Kidney, and Adrenal of Nonhuman Primates. J. Lipid Res. 2000, 41, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.L. Steroid Hormone Synthesis in Mitochondria. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 379, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekeres, M.; Turu, G.; Orient, A.; Szalai, B.; Süpeki, K.; Cserzo, M.; Várnai, P.; Hunyady, L. Mechanisms of Angiotensin II-Mediated Regulation of Aldosterone Synthase Expression in H295R Human Adrenocortical and Rat Adrenal Glomerulosa Cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 302, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miike, T.; Shirahase, H.; Jino, H.; Kunishiro, K.; Kanda, M.; Kurahashi, K. Effects of an Anti-Oxidative ACAT Inhibitor on Apoptosis/Necrosis and Cholesterol Accumulation under Oxidative Stress in THP-1 Cell-Derived Foam Cells. Life Sci. 2008, 82, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, M.H.; Suzuki, T.; Sasano, H.; White, P.C.; Rainey, W.E. The Orphan Nuclear Receptors NURR1 and NGFIB Regulate Adrenal Aldosterone Production. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ota, T.; Doi, M.; Yamazaki, F.; Yarimizu, D.; Okada, K.; Murai, I.; Hayashi, H.; Kunisue, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Okamura, H. Angiotensin II Triggers Expression of the Adrenal Gland Zona Glomerulosa-Specific 3β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Isoenzyme through De Novo Protein Synthesis of the Orphan Nuclear Receptors NGFIB and NURR1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 3880–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bassett, M.H.; Suzuki, T.; Sasano, H.; de Vries, C.J.M.; Jimenez, P.T.; Carr, B.R.; Rainey, W.E. The Orphan Nuclear Receptor NGFIB Regulates Transcription of 3β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase: Implications for the control of adrenal functional zonation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 37622–37630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yarimizu, D.; Doi, M.; Ota, T.; Okamura, H. Stimulus-Selective Induction of the Orphan Nuclear Receptor NGFIB Underlies Different Influences of Angiotensin II and Potassium on the Human Adrenal Gland Zona Glomerulosa-Specific 3β-HSD Isoform Gene Expression in Adrenocortical H295R Cells. Endocr. J. 2015, 62, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denner, K.; Rainey, W.E.; Pezzi, V.; Bird, I.M.; Bernhardt, R.; Mathis, J.M. Differential Regulation of 11β-Hydroxylase and Aldosterone Synthase in Human Adrenocortical H295R Cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1996, 121, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.Y.; Weng, J.; Anderson, R.G.W. OSBP Is a Cholesterol-Regulated Scaffolding Protein in Control of ERK1/2 Activation. Science 2005, 307, 1472–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-Based Map of the Human Proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, D.K.; Fritz, M.C.; Schall, W.D.; Bari Olivier, N.; Smedley, R.C.; Pearson, P.G.; Bailie, M.B.; Hunt, S.W. ATR-101, a Selective ACAT1 Inhibitor, Decreases ACTH-Stimulated Cortisol Concentrations in Dogs with Naturally Occurring Cushing’s Syndrome. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2018, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motomura, N.; Yamazaki, Y.; Koga, D.; Harashima, S.; Gao, X.; Tezuka, Y.; Omata, K.; Ono, Y.; Morimoto, R.; Satoh, F.; et al. The Association of Cholesterol Uptake and Synthesis with Histology and Genotype in Cortisol-Producing Adenoma (CPA). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Suzuki, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Murakami, O.; Miki, Y.; Moriya, T.; Bassett, M.H.; Rainey, W.E.; Hayashi, Y.; Sasano, H. Nur-Related Factor 1 and Nerve Growth Factor-Induced Clone B in Human Adrenal Cortex and Its Disorders. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 4113–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, D.; Saito-Hakoda, A.; Ito, R.; Shimizu, K.; Parvin, R.; Shimada, H.; Noro, E.; Suzuki, S.; Fujiwara, I.; Kagechika, H.; et al. Suppressive Effects of RXR Agonist PA024 on Adrenal CYP11B2 Expression, Aldosterone Secretion and Blood Pressure. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimada, H.; Kogure, N.; Noro, E.; Kudo, M.; Sugawara, K.; Sato, I.; Shimizu, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, D.; Parvin, R.; et al. High Glucose Stimulates Expression of Aldosterone Synthase (CYP11B2) and Secretion of Aldosterone in Human Adrenal Cells. FEBS Open Bio 2017, 7, 1410–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenauer, U.D.; Shapiro, I.; Osswald, A.; Meurer, S.; Kulle, A.; Reincke, M.; Riepe, F.; Beuschlein, F. Characterization of NCI-H295R Cells as an in Vitro Model of Hyperaldosteronism. Horm. Metab. Res. 2013, 45, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomez-Sanchez, C.E.; Qi, X.; Velarde-Miranda, C.; Plonczynski, M.W.; Parker, C.R.; Rainey, W.; Satoh, F.; Maekawa, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Sasano, H.; et al. Development of Monoclonal Antibodies against Human CYP11B1 and CYP11B2. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 383, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Gene | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (3′→5′) |
|---|---|---|
| CYP11B2 | GGCAGAGGCAGAGATGCTG | CTTGAGTTAGTGTCTCCACCAGGA |
| NURR1 | AGAGAAGATCCCTGGCTTCG | CAAGACCACCCCATTGCAAAA |
| NGFIB | CCTGGAGCTCTTCATCCTCC | TGTCAATCCAGTCCCCGAAG |
| StAR | GCATCCTTAGCAACCAAGAG | TCACTTTGTCCCCATTGTCC |
| CYP11A1 | TTCCGCTTTGCCTTTGAGTC | TGGCATCAATGAATCGCTGG |
| CYP17A1 | CAGAATGTGGGTTTCAGCCG | CTCACCGATGCTGGAGTCAA |
| CYP21A2 | AGACTACTCCCTGCTCTGGA | CTCATGCGCTCACAGAACTC |
| HSD3B2 | GCGGCTAATGGGTGGAATCTA | CATTGTTGTTCAGGGCCTCAT |
| CYP11B1 | GGCAGAGGCAGAGATGCTG | TCTTGGGTTAGTGTCTCCACCTG |
| GAPDH | ATCCCATCACCATCTTCCAG | ATGAGTCCTTCCACGATACC |
| Gene | Probe | |
| CYP11B2 | [6-FAM]CTGCACCACGTGCTGAAGCACT[TAMPA6-FAM] | |
| HSD3B2 | [6-FAM]TGATACCTTGTACACTTGTGC[TAMPA6-FAM] | |
| CYP11B1 | [6-FAM]TGCTGCACCATGTGCTGAAACACCT[TAMRA-6-FAM] | |
| Primary Antibody | Dilution | Species | Clone | Company | Antigen Retrieval Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACAT1 | 1:100 | Rabbit | Monoclonal (EPR10359) | Abcam | AC 121 °C 5 min, pH = 9 Buffer |
| CYP11B2 | 1:500 | Mouse | Monoclonal | Gomez-Sanchez et al., 2014 [34] | AC 121 °C 5 min, pH high Buffer |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shimada, H.; Hata, S.; Yamazaki, Y.; Otsubo, Y.; Sato, I.; Ise, K.; Yokoyama, A.; Suzuki, T.; Sasano, H.; Sugawara, A.; et al. YM750, an ACAT Inhibitor, Acts on Adrenocortical Cells to Inhibit Aldosterone Secretion Due to Depolarization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112803
Shimada H, Hata S, Yamazaki Y, Otsubo Y, Sato I, Ise K, Yokoyama A, Suzuki T, Sasano H, Sugawara A, et al. YM750, an ACAT Inhibitor, Acts on Adrenocortical Cells to Inhibit Aldosterone Secretion Due to Depolarization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(21):12803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112803
Chicago/Turabian StyleShimada, Hiroki, Shuko Hata, Yuto Yamazaki, Yuri Otsubo, Ikuko Sato, Kazue Ise, Atsushi Yokoyama, Takashi Suzuki, Hironobu Sasano, Akira Sugawara, and et al. 2022. "YM750, an ACAT Inhibitor, Acts on Adrenocortical Cells to Inhibit Aldosterone Secretion Due to Depolarization" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 21: 12803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112803
APA StyleShimada, H., Hata, S., Yamazaki, Y., Otsubo, Y., Sato, I., Ise, K., Yokoyama, A., Suzuki, T., Sasano, H., Sugawara, A., & Nakamura, Y. (2022). YM750, an ACAT Inhibitor, Acts on Adrenocortical Cells to Inhibit Aldosterone Secretion Due to Depolarization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 12803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112803






