Blockade of Kv1.3 Potassium Channel Inhibits Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Epilepsy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
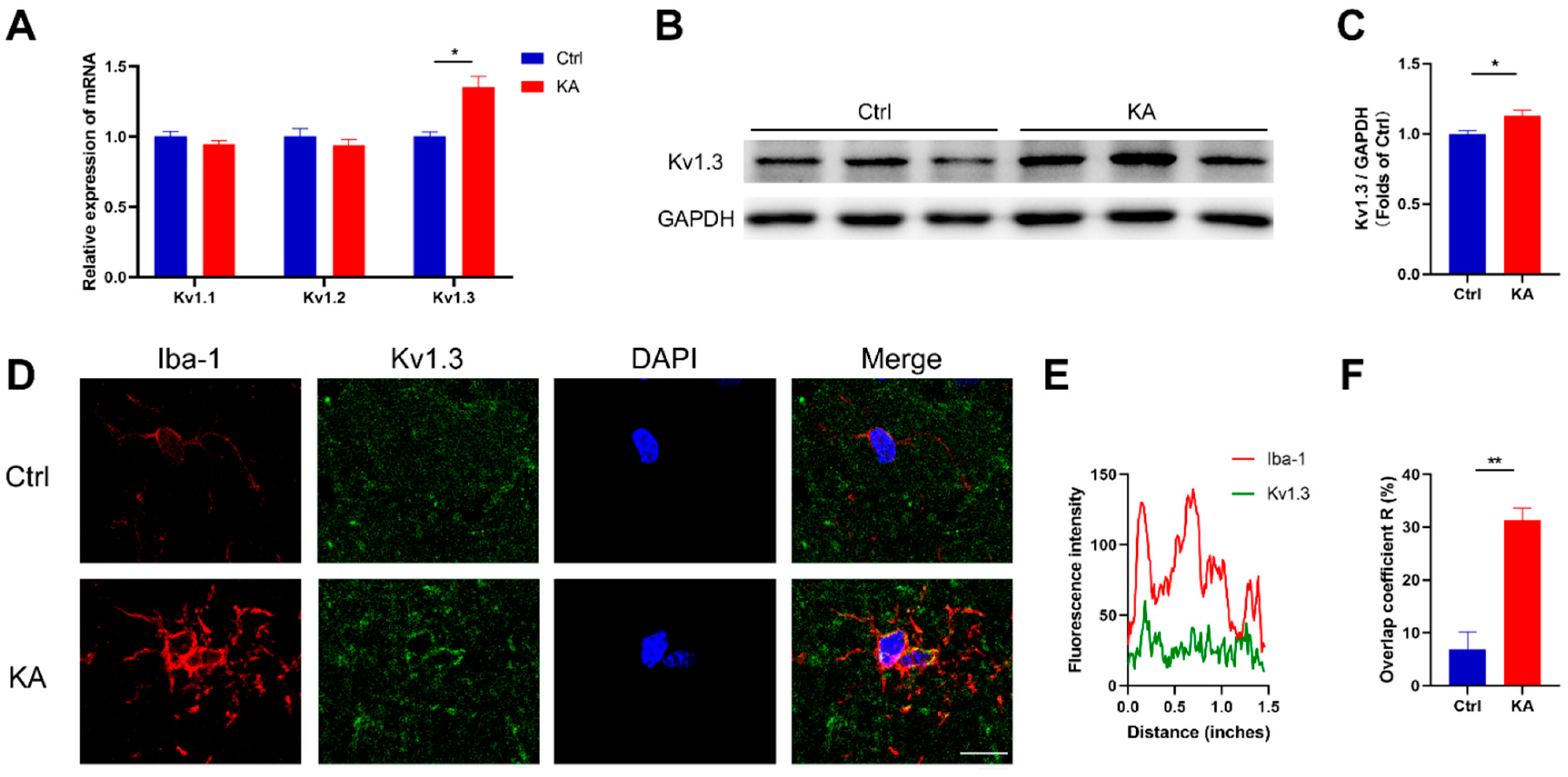
2.1. Kv1.3 Potassium Channel in Microglia Is Upregulated in KA-Induced Epileptic Mice
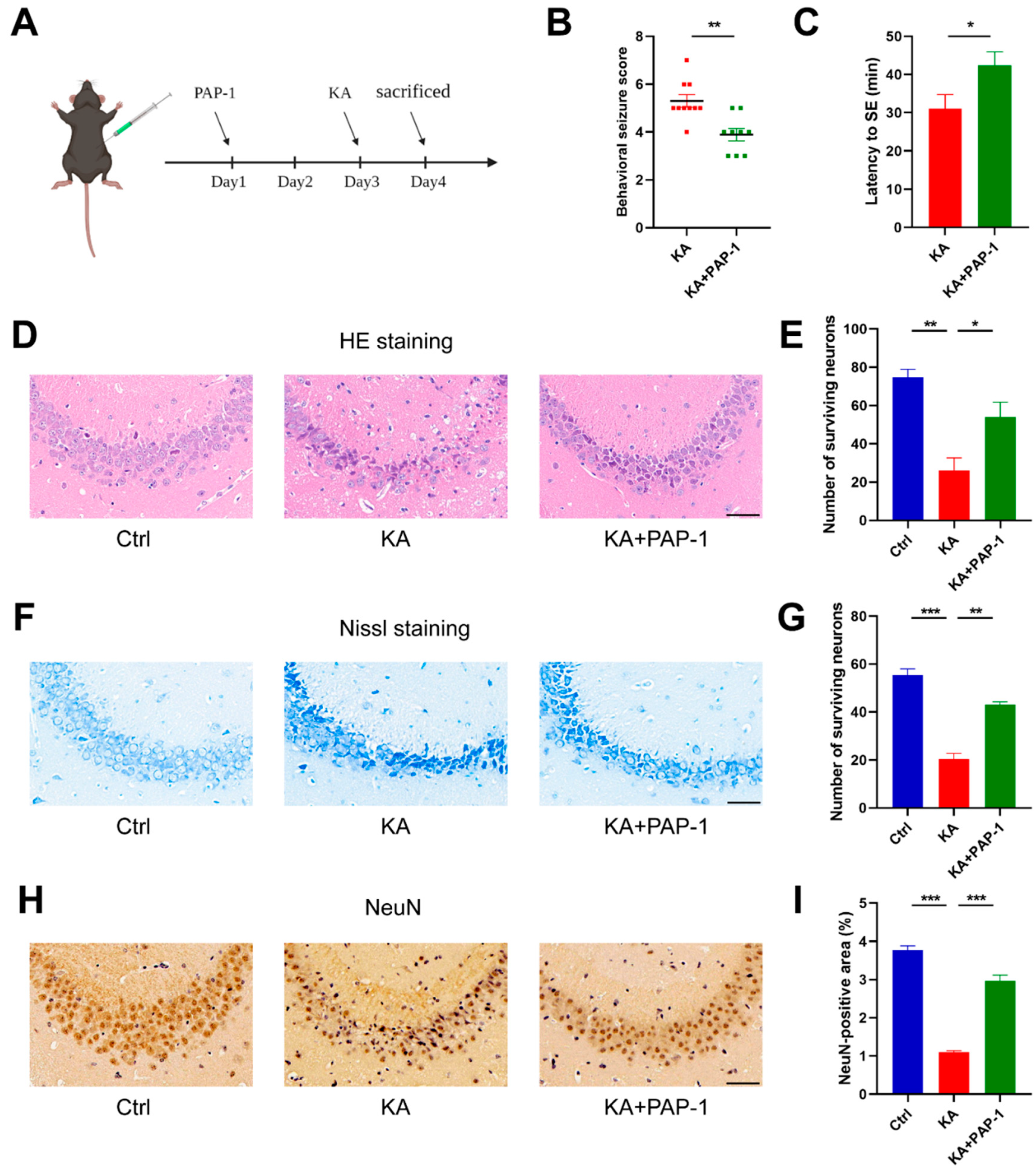
2.2. Blockade of Kv1.3 Attenuates KA-Induced Epilepsy
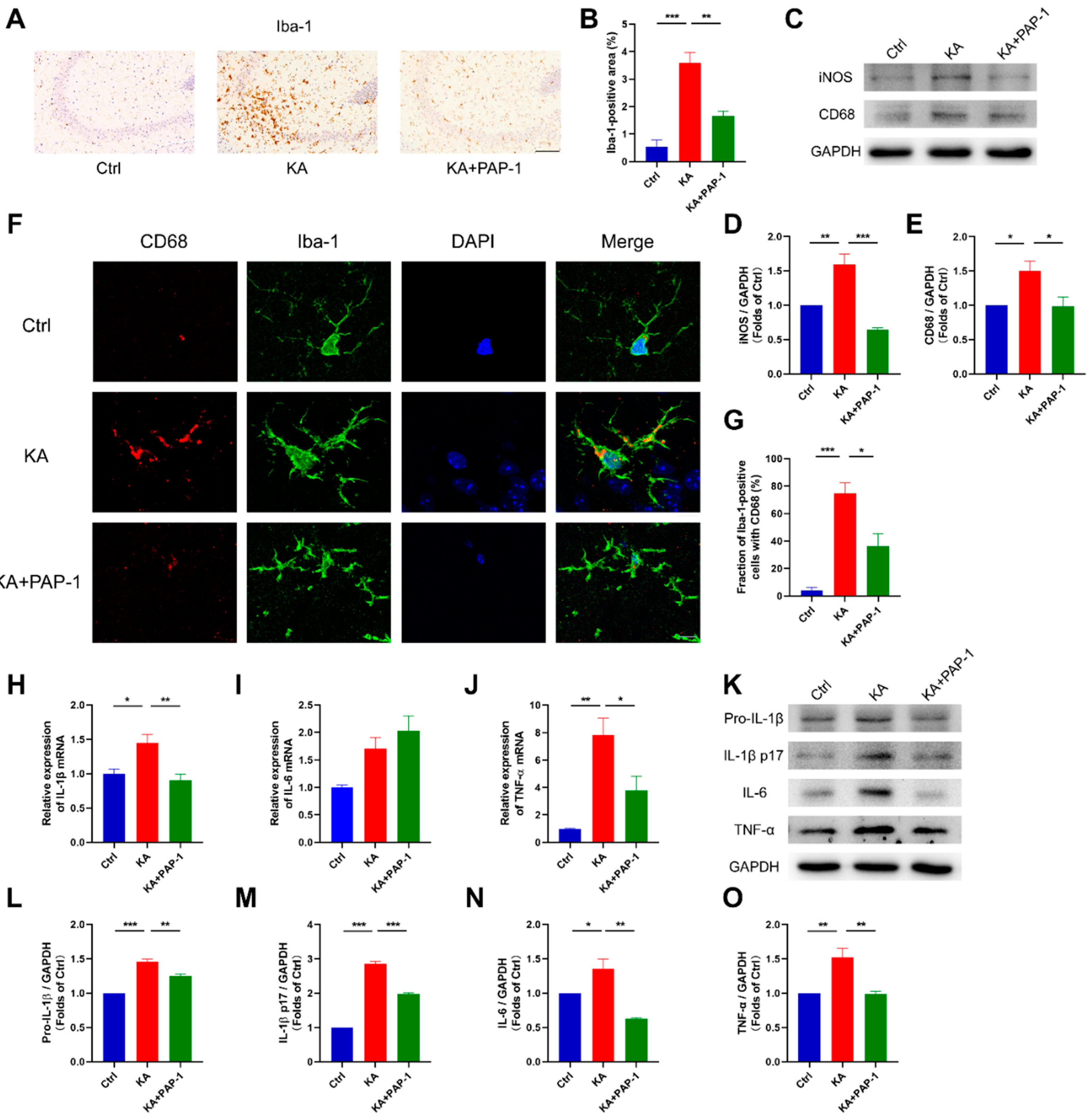
2.3. Blockade of Kv1.3 Inhibits the Activation of Microglia in KA-Induced Epileptic Mice
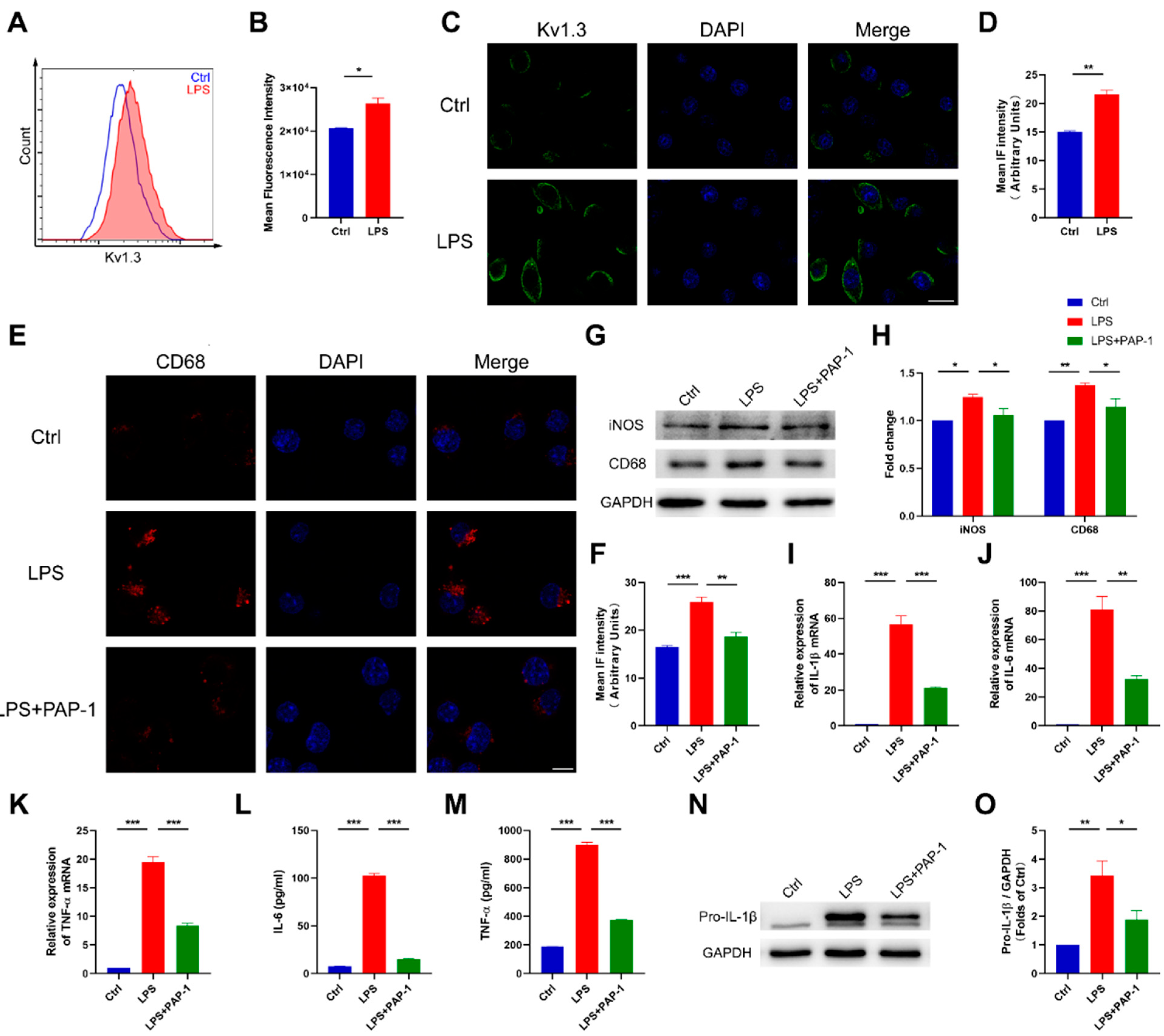
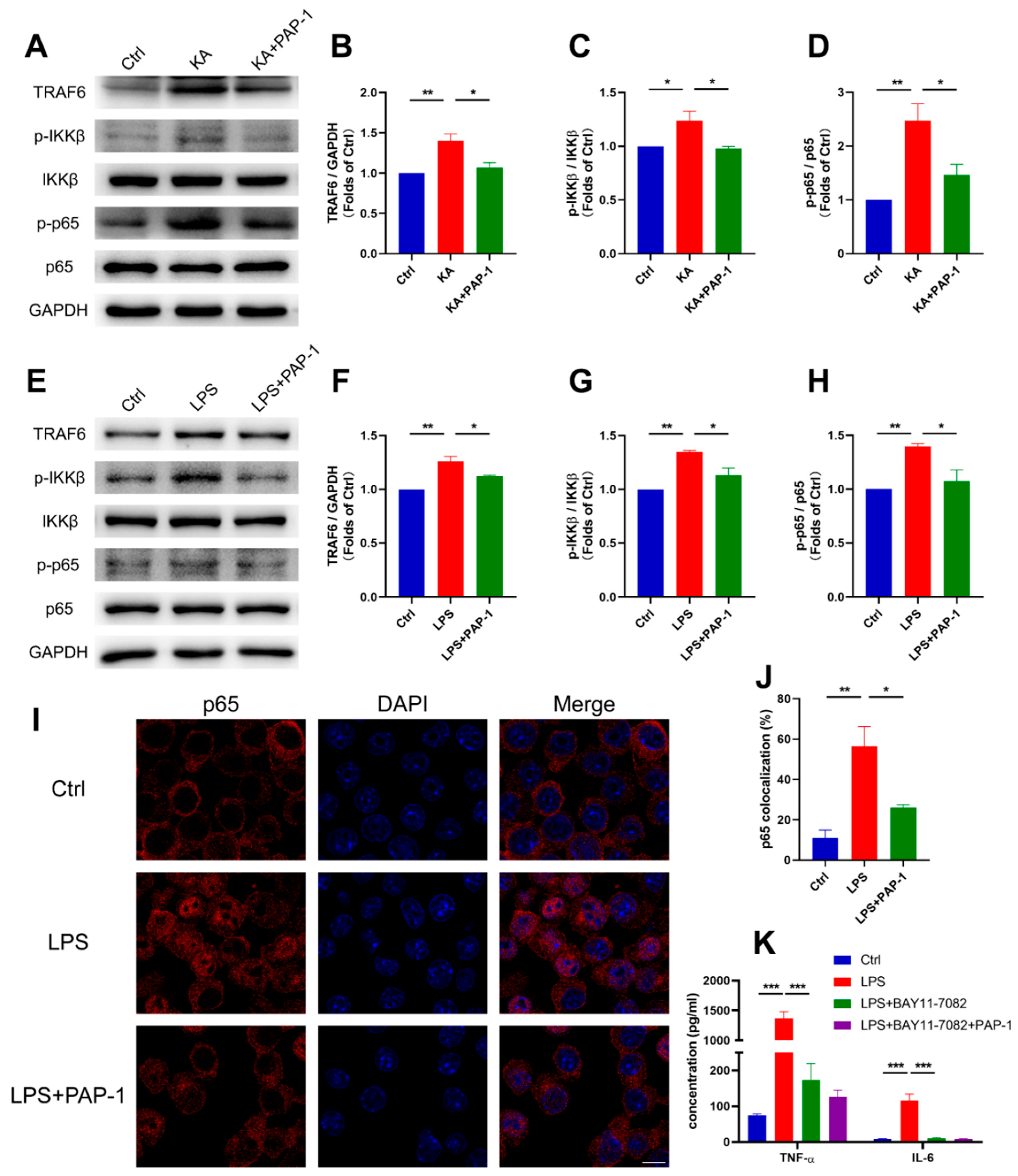
2.4. Blockade of Kv1.3 Suppresses Proinflammatory Activation of Microglia In Vitro
2.5. Blockade of Kv1.3 Attenuates Microglial Activation through the Ca2+/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Mouse Model and Drug Administration
4.3. Tissue Collection
4.4. Microglia Culture and Drug Treatment
4.5. Nissl and HE Staining
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Immunofluorescence
4.8. Quantitative PCR
4.9. Western Blot
4.10. Flow Cytometry
4.11. ELISA
4.12. The Intracellular Concentration of Ca2+ Determination Assay
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hauser, W.; Rich, S.; Lee, J.; Annegers, J.; Anderson, V.E. Risk of recurrent seizures after two unprovoked seizures. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, A.; French, J.; Bartfai, T.; Baram, T.Z. The role of inflammation in epilepsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Golarai, G.; Greenwood, A.; Feeney, D.; Connor, J. Physiological and structural evidence for hippocampal involvement in persistent seizure susceptibility after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 8523–8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simons, C.; Rash, L.D.; Crawford, J.; Ma, L.; Cristofori-Armstrong, B.; Miller, D.; Ru, K.; Baillie, G.J.; Alanay, Y.; Jacquinet, A.; et al. Mutations in the voltage-gated potassium channel gene KCNH1 cause Temple-Baraitser syndrome and epilepsy. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngugi, A.K.; Bottomley, C.; Kleinschmidt, I.; Wagner, R.G.; Kakooza-Mwesige, A.; Ae-Ngibise, K.; Owusu-Agyei, S.; Masanja, H.; Kamuyu, G.; Odhiambo, R.; et al. Prevalence of active convulsive epilepsy in sub-Saharan Africa and associated risk factors: Cross-sectional and case-control studies. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiebe, S.; Jette, N. Pharmacoresistance and the role of surgery in difficult to treat epilepsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, A.; Lang, B.; Aronica, E. Immunity and Inflammation in Epilepsy. Cold. Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 6, a022699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaneko, K.I.; Irie, S.; Mawatari, A.; Igesaka, A.; Hu, D.; Nakaoka, T.; Hayashinaka, E.; Wada, Y.; Doi, H.; Watanabe, Y.; et al. [(18)F]DPA-714 PET imaging for the quantitative evaluation of early spatiotemporal changes of neuroinflammation in rat brain following status epilepticus. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 2265–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; Viviani, B. Neuromodulatory properties of inflammatory cytokines and their impact on neuronal excitability. Neuropharmacology 2015, 96, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtimaki, K.A.; Keranen, T.; Palmio, J.; Makinen, R.; Hurme, M.; Honkaniemi, J.; Peltola, J. Increased plasma levels of cytokines after seizures in localization-related epilepsy. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2007, 116, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; Conti, M.; De Luigi, A.; Ravizza, T.; Moneta, D.; Marchesi, F.; De Simoni, M.G. Interleukin-1beta immunoreactivity and microglia are enhanced in the rat hippocampus by focal kainate application: Functional evidence for enhancement of electrographic seizures. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 5054–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frigerio, F.; Pasqualini, G.; Craparotta, I.; Marchini, S.; van Vliet, E.A.; Foerch, P.; Vandenplas, C.; Leclercq, K.; Aronica, E.; Porcu, L.; et al. n-3 Docosapentaenoic acid-derived protectin D1 promotes resolution of neuroinflammation and arrests epileptogenesis. Brain 2018, 141, 3130–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeSena, A.D.; Do, T.; Schulert, G.S. Systemic autoinflammation with intractable epilepsy managed with interleukin-1 blockade. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jun, J.S.; Lee, S.T.; Kim, R.; Chu, K.; Lee, S.K. Tocilizumab treatment for new onset refractory status epilepticus. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 84, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarde, S.; Villeneuve, N.; Trebuchon, A.; Kaphan, E.; Lepine, A.; McGonigal, A.; Roubertie, A.; Barthez, M.A.; Trommsdorff, V.; Lefranc, J.; et al. Anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy (adalimumab) in Rasmussen’s encephalitis: An open pilot study. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vitaliti, G.; Pavone, P.; Mahmood, F.; Nunnari, G.; Falsaperla, R. Targeting inflammation as a therapeutic strategy for drug-resistant epilepsies: An update of new immune-modulating approaches. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2014, 10, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sano, F.; Shigetomi, E.; Shinozaki, Y.; Tsuzukiyama, H.; Saito, K.; Mikoshiba, K.; Horiuchi, H.; Cheung, D.L.; Nabekura, J.; Sugita, K.; et al. Reactive astrocyte-driven epileptogenesis is induced by microglia initially activated following status epilepticus. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e135391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R.; Xia, L.; Cai, Y.; Tong, F.; Gao, Y.; Ding, J.; Wang, X. Conditional knockout of ASK1 in microglia/macrophages attenuates epileptic seizures and long-term neurobehavioural comorbidities by modulating the inflammatory responses of microglia/macrophages. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, E.S.; Vinogradova, L.V. Potassium channels as prominent targets and tools for the treatment of epilepsy. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets. 2021, 25, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niday, Z.; Tzingounis, A.V. Potassium Channel Gain of Function in Epilepsy: An Unresolved Paradox. Neuroscientist 2018, 24, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, K.; Pennington, M.W.; Lanigan, M.D.; Nguyen, A.; Rauer, H.; Mahnir, V.; Paschetto, K.; Kem, W.R.; Grissmer, S.; Gutman, G.A.; et al. ShK-Dap22, a potent Kv1.3-specific immunosuppressive polypeptide. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 32697–32707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wulff, H.; Knaus, H.G.; Pennington, M.; Chandy, K.G. K+ channel expression during B cell differentiation: Implications for immunomodulation and autoimmunity. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vicente, R.; Escalada, A.; Coma, M.; Fuster, G.; Sanchez-Tillo, E.; Lopez-Iglesias, C.; Soler, C.; Solsona, C.; Celada, A.; Felipe, A. Differential voltage-dependent K+ channel responses during proliferation and activation in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 46307–46320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reeves, T.; Trimmer, P.; Colley, B.; Phillips, L.J.E.n. Targeting Kv1.3 channels to reduce white matter pathology after traumatic brain injury. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 283, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarkar, S.; Nguyen, H.M.; Malovic, E.; Luo, J.; Langley, M.; Palanisamy, B.N.; Singh, N.; Manne, S.; Neal, M.; Gabrielle, M.; et al. Kv1.3 modulates neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 4195–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesha, S.; Rayaprolu, S.; Bowen, C.A.; Giver, C.R.; Bitarafan, S.; Nguyen, H.M.; Gao, T.; Chen, M.J.; Nwabueze, N.; Dammer, E.B.; et al. Unique molecular characteristics and microglial origin of Kv1.3 channel-positive brain myeloid cells in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2013545118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maezawa, I.; Nguyen, H.M.; Di Lucente, J.; Jenkins, D.P.; Singh, V.; Hilt, S.; Kim, K.; Rangaraju, S.; Levey, A.I.; Wulff, H.; et al. Kv1.3 inhibition as a potential microglia-targeted therapy for Alzheimer’s disease: Preclinical proof of concept. Brain 2018, 141, 596–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, D.C.; Zhang, N.N.; Zhang, Y.N.; Chen, H.S. Kv1.3 channel blockade alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by reshaping M1/M2 phenotypes and compromising the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 332, 113399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcon-Moya, R.; Sihra, T.S.; Rodriguez-Moreno, A. Kainate Receptors: Role in Epilepsy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsicano, G.; Goodenough, S.; Monory, K.; Hermann, H.; Eder, M.; Cannich, A.; Azad, S.C.; Cascio, M.G.; Gutierrez, S.O.; van der Stelt, M.; et al. CB1 cannabinoid receptors and on-demand defense against excitotoxicity. Science 2003, 302, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Dai, H.; Tan, S.; Mao, X.; Chen, Z. Dynorphin activation of kappa opioid receptor promotes microglial polarization toward M2 phenotype via TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, S.; Wan, D.; Fan, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, K.; Huo, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.; Xie, X.; Wang, F.; et al. Amentoflavone Affects Epileptogenesis and Exerts Neuroprotective Effects by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Lin, J.; Hua, Y.; Gong, J.; Ding, S.; Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, R.; Xu, H. Agmatine Alleviates Epileptic Seizures and Hippocampal Neuronal Damage by Inhibiting Gasdermin D-Mediated Pyroptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 627557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.M.; di Lucente, J.; Chen, Y.J.; Cui, Y.; Ibrahim, R.H.; Pennington, M.W.; Jin, L.W.; Maezawa, I.; Wulff, H. Biophysical basis for Kv1.3 regulation of membrane potential changes induced by P2X4-mediated calcium entry in microglia. Glia 2020, 68, 2377–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksoud, M.J.E.; Tellios, V.; Xiang, Y.Y.; Lu, W.Y. Nitric oxide displays a biphasic effect on calcium dynamics in microglia. Nitric. Oxide 2021, 108, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Ota, A.; Tohyama, J.; Kirino, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Ikeda, C.; Tanaka, S.; Takahashi, J.; Shinoki, T.; Shiraga, H.; et al. Different pharmacoresistance of focal epileptic spasms, generalized epileptic spasms, and generalized epileptic spasms combined with focal seizures. Epilepsia Open 2022, 7, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy, S.; Beck, H. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pharmacoresistance in epilepsy. Brain 2006, 129, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kingwell, K. Genetics: Mutations in potassium channel KCNT1-a novel driver of epilepsy pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiffault, I.; Speca, D.J.; Austin, D.C.; Cobb, M.M.; Eum, K.S.; Safina, N.P.; Grote, L.; Farrow, E.G.; Miller, N.; Soden, S.; et al. A novel epileptic encephalopathy mutation in KCNB1 disrupts Kv2.1 ion selectivity, expression, and localization. J. Gen. Physiol. 2015, 146, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vetri, L.; Cali, F.; Vinci, M.; Amato, C.; Roccella, M.; Granata, T.; Freri, E.; Solazzi, R.; Romano, V.; Elia, M. A de novo heterozygous mutation in KCNC2 gene implicated in severe developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 63, 103848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, A.; Moutton, S.; Longobardi, E.; Tran Mau-Them, F.; Laudati, G.; Nappi, P.; Soldovieri, M.V.; Ambrosino, P.; Cataldi, M.; Jouan, T.; et al. A novel homozygous KCNQ3 loss-of-function variant causes non-syndromic intellectual disability and neonatal-onset pharmacodependent epilepsy. Epilepsia Open 2019, 4, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zuberi, S.; Eunson, L.; Spauschus, A.; De Silva, R.; Tolmie, J.; Wood, N.; McWilliam, R.; Stephenson, J.; Stephenson, J.; Kullmann, D.; et al. A novel mutation in the human voltage-gated potassium channel gene (Kv1.1) associates with episodic ataxia type 1 and sometimes with partial epilepsy. Brain 1999, 122, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corbett, M.; Bellows, S.; Li, M.; Carroll, R.; Micallef, S.; Carvill, G.; Myers, C.; Howell, K.; Maljevic, S.; Lerche, H.; et al. Dominant KCNA2 mutation causes episodic ataxia and pharmacoresponsive epilepsy. Neurology 2016, 87, 1975–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Hou, G.Q.; He, S.W.; Xiao, Z.; Xu, H.J.; Qiu, Y.T.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, H.; Li, Z.Y. Psora-4, a Kv1.3 Blocker, Enhances Differentiation and Maturation in Neural Progenitor Cells. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2015, 21, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, J.E.; Kwak, S.E.; Won, M.H.; Kang, T.C. Seizure activity affects neuroglial Kv1 channel immunoreactivities in the gerbil hippocampus. Brain Res. 2007, 1151, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton, R.; Ghenghea, M.; Ristoiu, V.; Gattlen, C.; Suter, M.R.; Cojocaru, P.A.; Popa-Wagner, A.; Catalin, B.; Deftu, A.F. Potassium Channels Kv1.3 and Kir2.1 But Not Kv1.5 Contribute to BV2 Cell Line and Primary Microglial Migration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fordyce, C.B.; Jagasia, R.; Zhu, X.; Schlichter, L.C. Microglia Kv1.3 channels contribute to their ability to kill neurons. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 7139–7149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.M.; Grossinger, E.M.; Horiuchi, M.; Davis, K.W.; Jin, L.W.; Maezawa, I.; Wulff, H. Differential Kv1.3, KCa3.1, and Kir2.1 expression in “classically” and “alternatively” activated microglia. Glia 2017, 65, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charolidi, N.; Schilling, T.; Eder, C. Microglial Kv1.3 Channels and P2Y12 Receptors Differentially Regulate Cytokine and Chemokine Release from Brain Slices of Young Adult and Aged Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Munch, A.E.; Chung, W.S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.L.; Cheng, J.J.; Kong, S.; Yang, X.L.; Jia, X.L.; Cheng, X.L.; Chen, L.; He, F.G.; Liu, Y.M.; Fan, Y.T.; et al. Inhibition of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) Mitigates Seizures. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, 660–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunakaran, D.; Nguyen, M.A.; Geoffrion, M.; Vreeken, D.; Lister, Z.; Cheng, H.S.; Otte, N.; Essebier, P.; Wyatt, H.; Kandiah, J.W.; et al. RIPK1 Expression Associates With Inflammation in Early Atherosclerosis in Humans and Can Be Therapeutically Silenced to Reduce NF-kappaB Activation and Atherogenesis in Mice. Circulation 2021, 143, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Somma, D.; Kerrigan, D.; McIntyre, Z.; Cole, J.J.; Liang, K.L.; Kiely, P.A.; Keeshan, K.; Carmody, R.J. The regulation of sequence specific NF-kappaB DNA binding and transcription by IKKbeta phosphorylation of NF-kappaB p50 at serine 80. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2019, 47, 11151–11163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. NF-kappaB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. Targeting NF-kappaB pathway for the therapy of diseases: Mechanism and clinical study. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Liang, P.; Hou, B.; Lu, X.; Ma, Q.; Yu, X.; Han, S.; Peng, B.; Chen, T.; Liu, W.; et al. The effect of dipeptidyl peptidase IV on disease-associated microglia phenotypic transformation in epilepsy. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, A.C.; Rajan, N.; Gastaldo, D.; Telley, L.; Hilal, M.L.; Buzzi, A.; Simonato, M.; Achsel, T.; Bagni, C. Absence of RNA-binding protein FXR2P prevents prolonged phase of kainate-induced seizures. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e51404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, B.; Liang, P.; Lu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Liu, W.; et al. TRPV1 channel mediates NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent neuroinflammation in microglia. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Kv1.1 | GCATCGACAACACCACAGTC | CGGCGGCTGAGGTCACTGTCAGAGGCTAAGT |
| Kv1.2 | GGTTGAGGCGACCTGTGAAC | TCCTCCCGAAACATCTCCATT |
| Kv1.3 | GGAGACCTTGTGCATCATCTG | CCCATTACCTTGTCGTTCAGC |
| IL-1β | GAAATGCCACCTTTTGACAGTG | TGGATGCTCTCATCAGGACAG |
| IL-6 | CATGTTCTCTGGGAAATCGTGG | GTACTCCAGGTAGCTATGGTAC |
| TNF-α | GGCATGGATCTCAAAGACAACC | CAGGTATATGGGCTCATACCAG |
| GAPDH | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Liang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Peng, B.; Liu, W.; Yin, J.; et al. Blockade of Kv1.3 Potassium Channel Inhibits Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Epilepsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314693
Zhang X, Liang P, Zhang Y, Wu Y, Song Y, Wang X, Chen T, Peng B, Liu W, Yin J, et al. Blockade of Kv1.3 Potassium Channel Inhibits Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Epilepsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314693
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinyi, Peiyu Liang, Yahui Zhang, Yifan Wu, Yinghao Song, Xueyang Wang, Taoxiang Chen, Biwen Peng, Wanhong Liu, Jun Yin, and et al. 2022. "Blockade of Kv1.3 Potassium Channel Inhibits Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Epilepsy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314693
APA StyleZhang, X., Liang, P., Zhang, Y., Wu, Y., Song, Y., Wang, X., Chen, T., Peng, B., Liu, W., Yin, J., Han, S., & He, X. (2022). Blockade of Kv1.3 Potassium Channel Inhibits Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Epilepsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314693





