RyhB in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Regulates the Expression of Virulence-Related Genes and Contributes to Meningitis Development in a Mouse Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
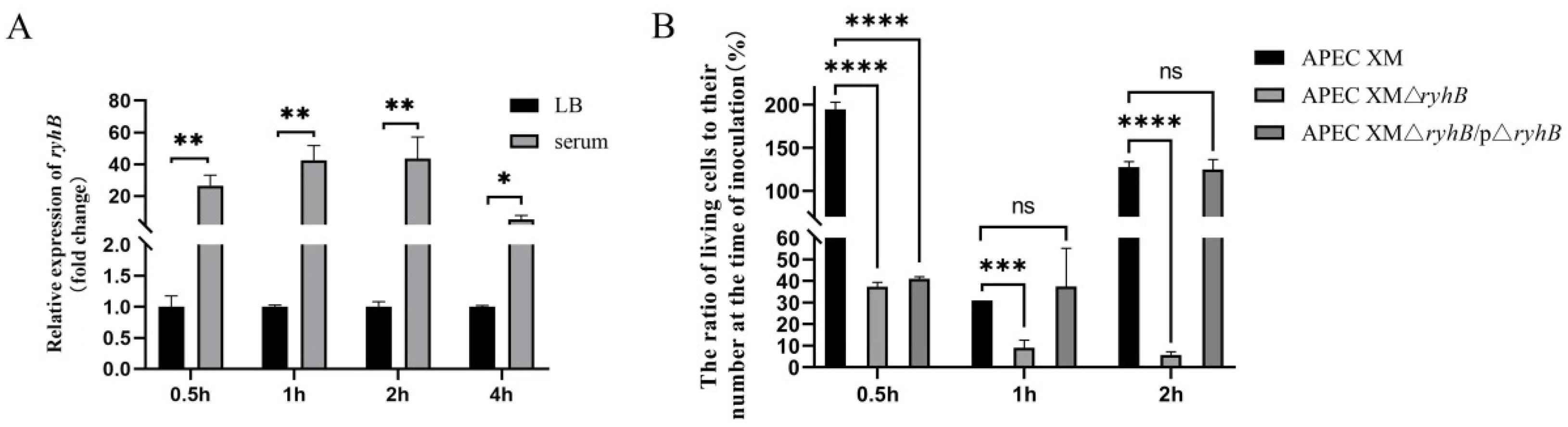
2.1. RyhB Is Induced by Duck Serum and Contributes to the Survival of APEC in Duck Serum
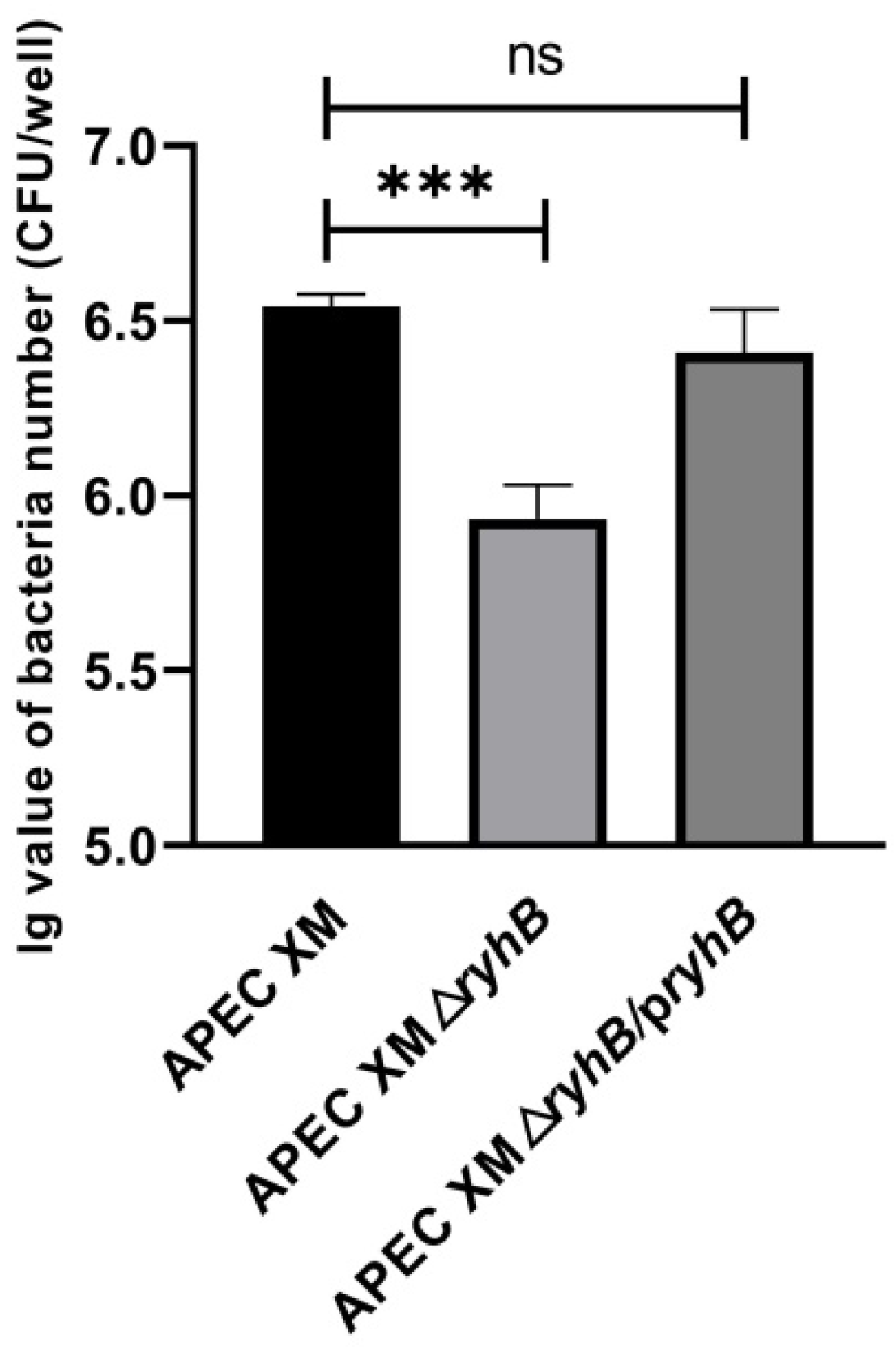
2.2. RyhB Contributes to Adhesion to bEnd.3 Cells
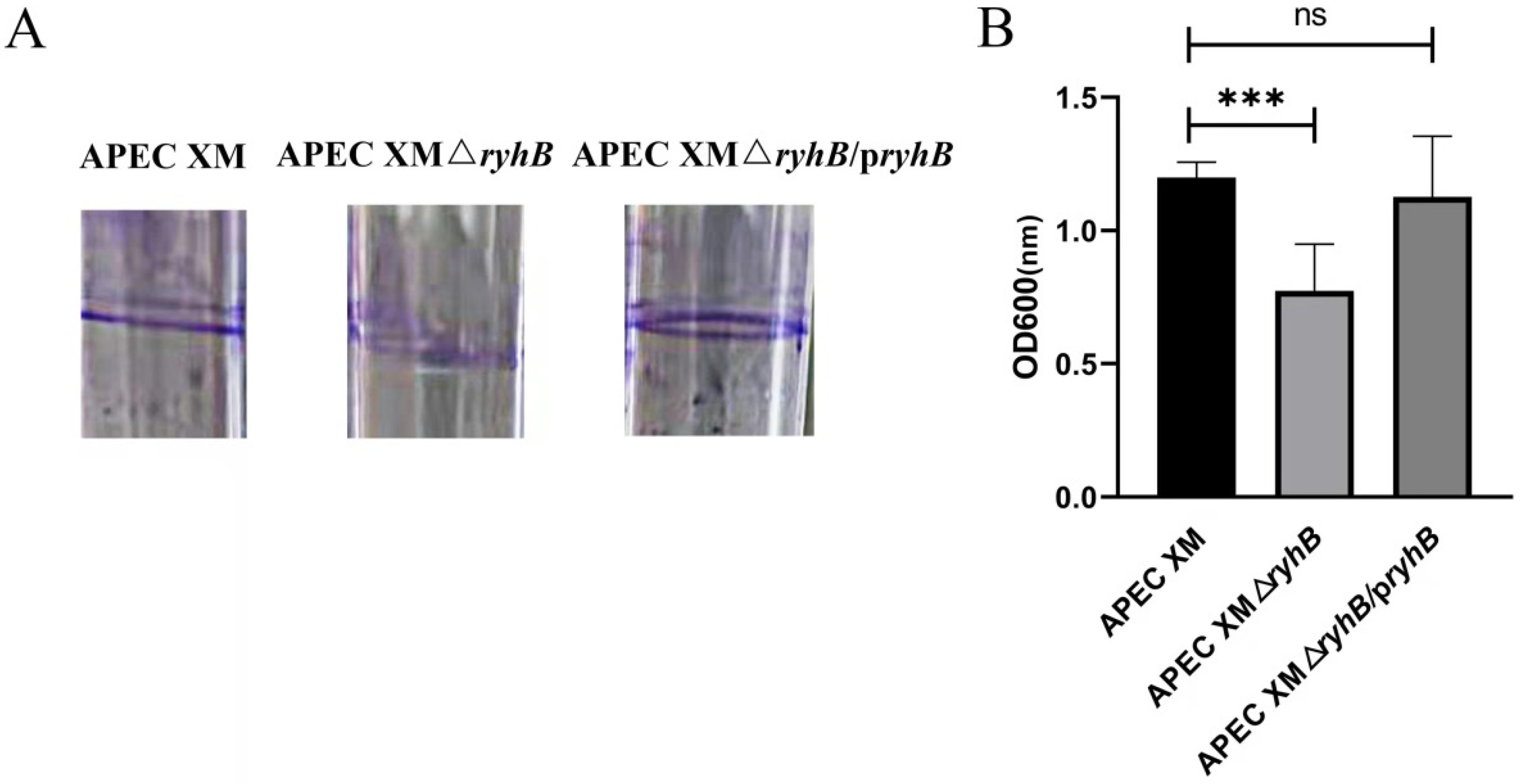
2.3. RyhB Contributes to the Biofilm Formation of APEC XM
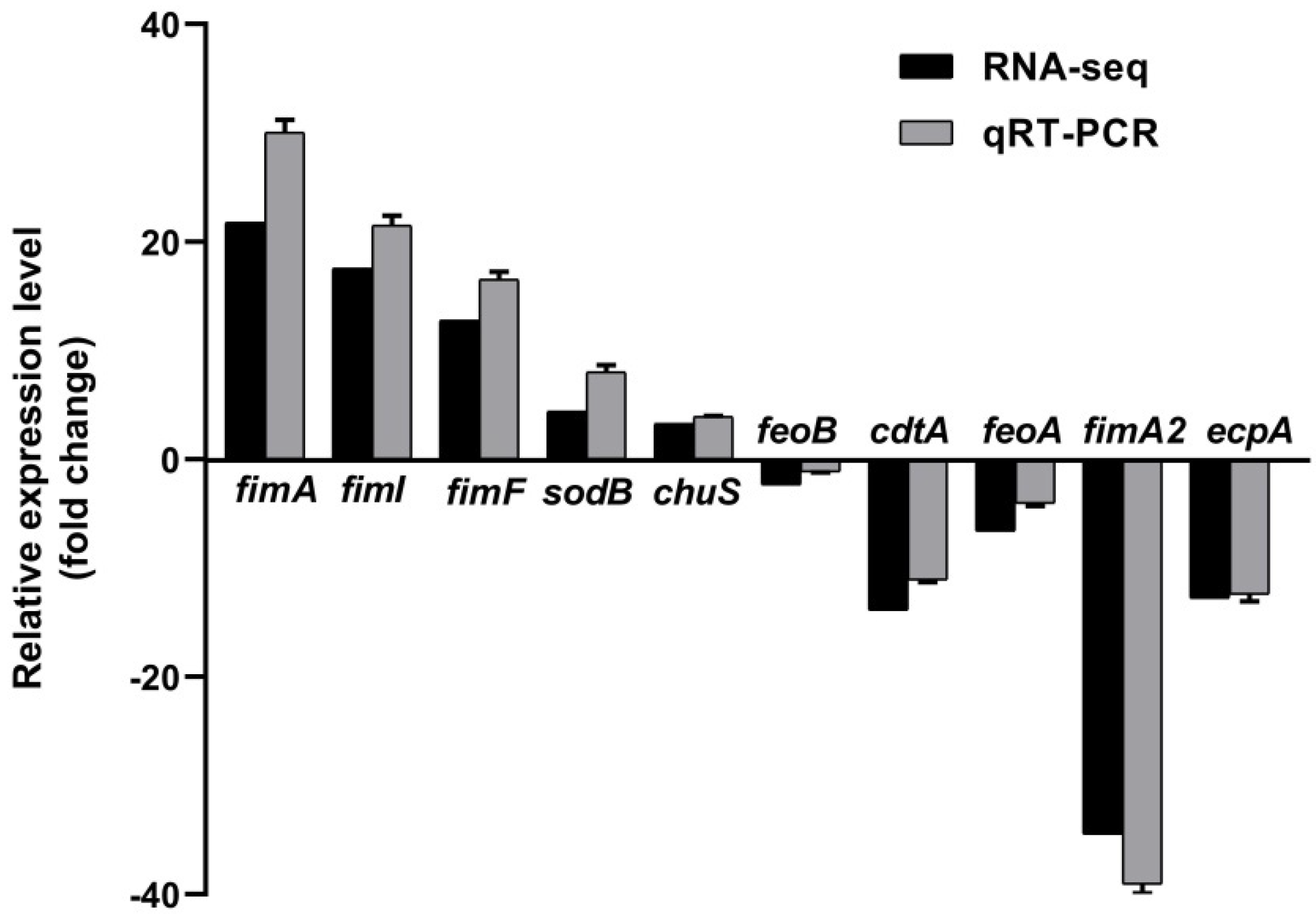
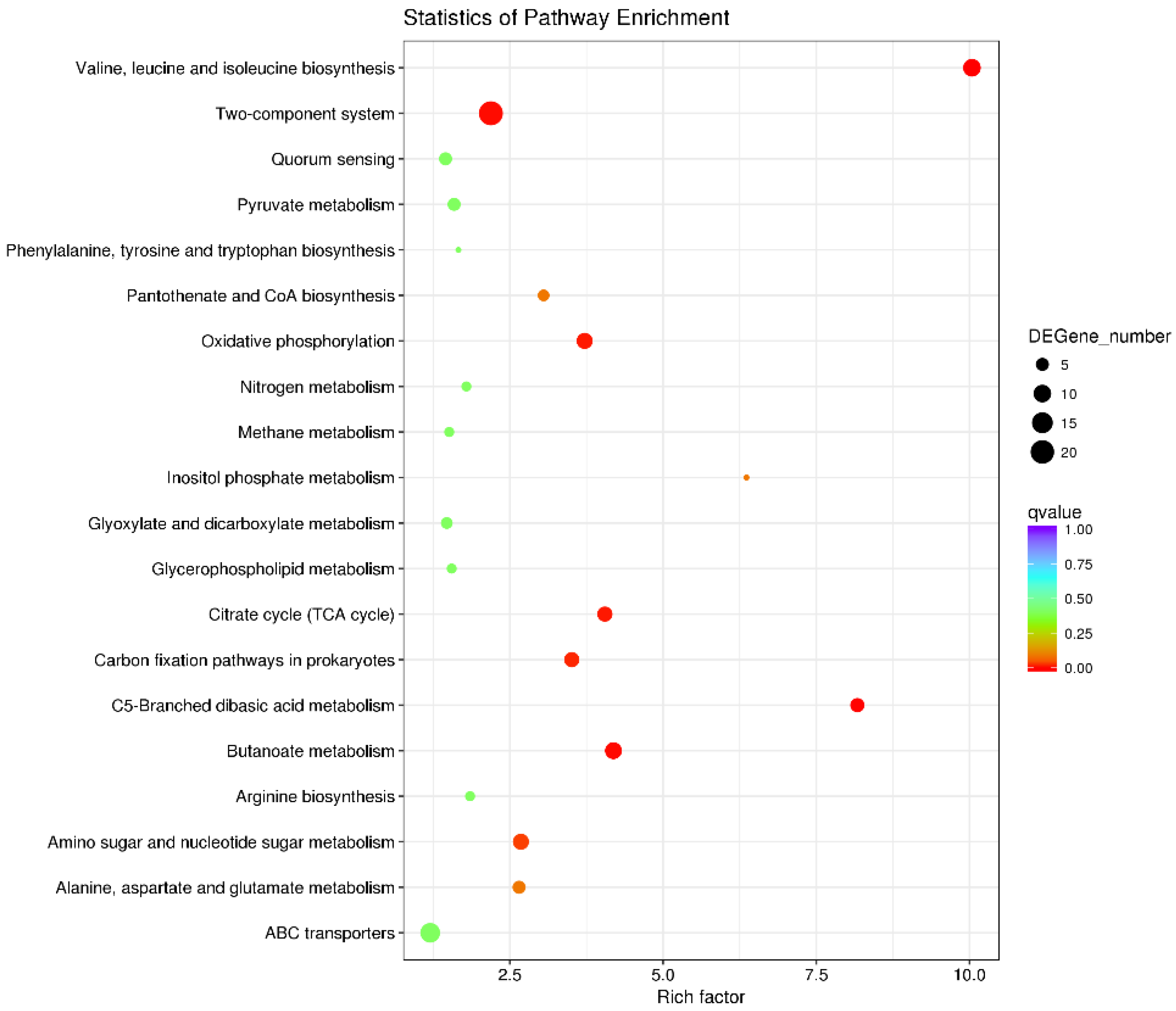
2.4. RyhB Affects the Expression of Multiple Virulence-Related Genes When Growing in Duck Serum
2.5. RyhB Is Required for the Pathogenicity of APEC XM to ICR Mice
2.6. RyhB Contributes to Brain Lesions of Mice
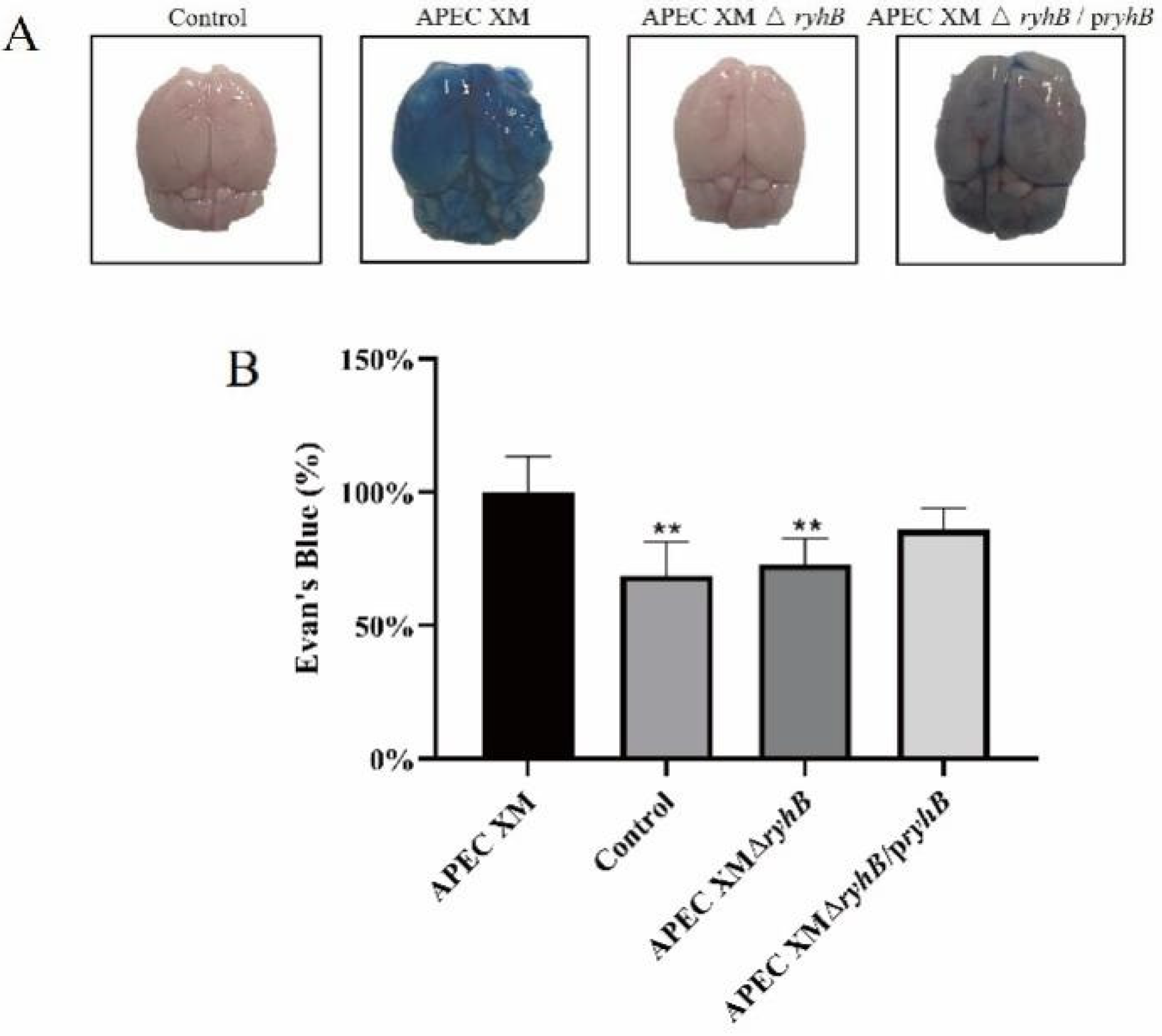
2.7. RyhB Helped APEC XM to Damage the Integrity of the Blood–Brain Barrier
2.8. RyhB Affects the Expressions of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α
2.9. RyhB Affects the Expression of Tight Junction Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids and Growth Conditions
4.2. Construction of the ryhB Deletion Mutant and the Complemented Strain
4.3. Survival of APEC in Duck Serum
4.4. Adhesion Assay
4.5. Determination of Biofilm Formation
4.6. qRT- PCR
4.7. RNA-Seq and Data Analysis
4.8. Establishment of Mouse Meningitis Model Infected with APEC
4.9. Determination of Bacterial Loadings in the Tissues of Mice
4.10. Detection of Lesions of the Brain by MRI Scanning and Histological Analysis
4.11. Brain Permeability of Evans Blue
4.12. Detection of Tight Junction Protein Expression by Western Blot and Immunohistochemistry
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kasuya, K.; Shimokubo, N.; Kosuge, C.; Takayama, K.; Yoshida, E.; Osaka, H. Three cases of Escherichia coli meningitis in chicks imported to Japan. Avian Dis. 2016, 61, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tivendale, K.A.; Logue, C.M.; Kariyawasam, S.; Jordan, D.; Hussein, A.; Li, G.W.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Nolan, L.K. Avian-pathogenic Escherichia coli strains are similar to neonatal meningitis E. coli strains and are able to cause meningitis in the rat model of human disease. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 3412–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulin-Schouleur, M.; Schouler, C.; Tailliez, P.; Kao, M.R.; Brée, A.; Germon, P.; Oswald, E.; Mainil, J.; Blanco, M.; Blanco, J. Common virulence factors and genetic relationships between O18:K1:H7 Escherichia coli isolates of human and avian origin. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3484–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewers, C.; Li, G.; Wilking, H.; Kiessling, S.; Alt, K.; Antáo, E.M.; Laturnus, C.; Diehl, I.; Glodde, S.; Homeier, T.; et al. Avian pathogenic, uropathogenic, and newborn meningitis-causing Escherichia coli: How closely related are they? Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 297, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Kariyawasam, S.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Mangiamele, P.; Johnson, S.J.; Doetkott, C.; Skyberg, J.A.; Lynne, A.M.; Johnson, J.R.; Nolan, L.K. The genome sequence of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strain O1:K1:H7 shares strong similarities with human extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli genomes. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 3228–3236. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, S.; Chang, A.C.; Hodges, J.; Couraud, P.O.; Romero, I.A.; Weksler, B.; Nicholson, B.A.; Nolan, L.K.; Prasadarao, N.V. Serotype O18 avian pathogenic and neonatal meningitis Escherichia coli strains employ similar pathogenic strategies for the onset of meningitis. Virulence 2015, 6, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S. Investigating Bacterial Penetration of the Blood Brain Barrier for the Pathogenesis, Prevention, and Therapy of Bacterial Meningitis. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S. Pathogenesis of bacterial meningitis: From bacteraemia to neuronal injury. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Bao, Y.; Sun, M.; Dong, W.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C.; Yao, H. Two Functional Type VI Secretion Systems in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Are Involved in Different Pathogenic Pathways. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 3867–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; An, C.; Jiang, F.; Yao, H.; Logue, C.; Nolan, L.K.; Li, G. Extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli increase extracytoplasmic polysaccharide biosynthesis for serum resistance in response to bloodstream signals. Mol. Microbiol. 2018, 110, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejair, H.M.A.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yao, H. Functional role of ompF and ompC porins in pathogenesis of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 107, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Song, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhou, C.; Liu, P.; Fan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wan, X.; Feng, L. An ArcA-Modulated Small RNA in Pathogenic Escherichia coli K1. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 574833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahendran, G.; Jayasinghe, O.T.; Thavakumaran, D.; Arachchilage, G.M.; Silva, G.N. Key players in regulatory RNA realm of bacteria. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2022, 30, 101276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, M.G.; Pettersen, J.S.; Kallipolitis, B.H. sRNA-mediated control in bacteria: An increasing diversity of regulatory mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2020, 1863, 194504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felden, B.; Augagneur, Y. Diversity and Versatility in Small RNA-Mediated Regulation in Bacterial Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 719977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, T.; Srivastava, S. Small RNA-mediated regulation in bacteria: A growing palette of diverse mechanisms. Gene 2018, 656, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassarman, K.M.; Repoila, F.; Rosenow, C.; Storz, G.; Gottesman, S. Identification of novel small RNAs using comparative genomics and microarrays. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 1637–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.N.; Kwon, Y.M. Genetic and phenotypic characterization of the RyhB regulon in Salmonella Typhimurium. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclerc, J.M.; Dozois, C.M.; Daigle, F. Role of the Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi Fur regulator and small RNAs RfrA and RfrB in iron homeostasis and interaction with host cells. Microbiology 2013, 159 Pt 3, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mey, A.R.; Craig, S.A.; Payne, S.M. Characterization of Vibrio cholerae RyhB: The RyhB regulon and role of ryhB in biofilm formation. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 5706–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Meng, X.; Su, S.; Liu, Z.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, R.; Han, Y. Two sRNA RyhB homologs from Yersinia pestis biovar microtus expressed in vivo have differential Hfq-dependent stability. Res. Microbiol. 2012, 163, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.H.; Wang, C.K.; Peng, H.L.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Hong, Y.M.; Lin, C.T. Role of the small RNA RyhB in the Fur regulon in mediating the capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis and iron acquisition systems in Klebsiella pneumoniae. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.R.; Payne, S.M. RyhB, an iron-responsive small RNA molecule, regulates Shigella dysenteriae virulence. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 3470–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massé, E.; Gottesman, S. A small RNA regulates the expression of genes involved in iron metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4620–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.N. Roles of two RyhB paralogs in the physiology of Salmonella enterica. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 186–187, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chareyre, S.; Mandin, P. Bacterial Iron Homeostasis Regulation by sRNAs. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, P.F.; Morales, E.H.; Acuña, L.G.; Fuentes, D.N.; Gil, F.; Porwollik, S.; McClelland, M.; Saavedra, C.P.; Calderón, I.L. The small RNA RyhB homologs from Salmonella typhimurium participate in the response to S-nitrosoglutathione-induced stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oglesby, A.G.; Murphy, E.R.; Iyer, V.R.; Payne, S.M. Fur regulates acid resistance in Shigella flexneri via RyhB and ydeP. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 58, 1354–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, I.L.; Morales, E.H.; Collao, B.; Calderón, P.F.; Chahuán, C.A.; Acuña, L.G.; Gil, F.; Saavedra, C.P. Role of Salmonella Typhimurium small RNAs RyhB-1 and RyhB-2 in the oxidative stress response. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 165, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.N.; Kwon, Y.M. Identification of target transcripts regulated by small RNA RyhB homologs in Salmonella: RyhB-2 regulates motility phenotype. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñaloza, D.; Acuña, L.G.; Barros, M.J.; Núñez, P.; Montt, F.; Gil, F.; Fuentes, J.A.; Calderón, I.L. The Small RNA RyhB Homologs from Salmonella Typhimurium Restrain the Intracellular Growth and Modulate the SPI-1 Gene Expression within RAW264.7 Macrophages. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcheron, G.; Habib, R.; Houle, S.; Caza, M.; Lépine, F.; Daigle, F.; Massé, E.; Dozois, C.M. The small RNA RyhB contributes to siderophore production and virulence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 5056–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilla-Vaca, F.; Mondragón-Jaimes, V.; Franco, B. General Aspects of Two-Component Regulatory Circuits in Bacteria: Domains, Signals and Roles. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2017, 18, 990–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abisado, R.G.; Benomar, S.; Klaus, J.R.; Dandekar, A.A.; Chandler, J.R. Bacterial Quorum Sensing and Microbial Community Interactions. mBio 2018, 9, e02331-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S. Human Meningitis-Associated Escherichia coli. EcoSal Plus 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papenfort, K.; Vogel, J. Regulatory RNA in bacterial pathogens. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 8, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellata, M.; Dho-Moulin, M.; Dozois, C.M.; Curtiss, R., 3rd; Brown, P.K.; Arné, P.; Brée, A.; Desautels, C.; Fairbrother, J.M. Role of virulence factors in resistance of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli to serum and in pathogenicity. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oglesby-Sherrouse, A.G.; Murphy, E.R. Iron-responsive bacterial small RNAs: Variations on a theme. Metallomics 2013, 5, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Meng, X.; Ni, J.; He, M.; Chen, Y.; Xia, P.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Zhu, G.; Meng, X. Positive regulation of Type III secretion effectors and virulence by RyhB paralogs in Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchene, N.A.; Myers, K.S.; Chung, D.; Park, D.M.; Weisnicht, A.M.; Keleş, S.; Kiley, P.J. Impact of Anaerobiosis on Expression of the Iron-Responsive Fur and RyhB Regulons. mBio 2015, 6, e01947-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padalon-Brauch, G.; Hershberg, R.; Elgrably-Weiss, M.; Baruch, K.; Rosenshine, I.; Margalit, H.; Altuvia, S. Small RNAs encoded within genetic islands of Salmonella typhimurium show host-induced expression and role in virulence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 1913–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suerbaum, S.; Friedrich, S.; Leying, H.; Opferkuch, W. Expression of capsular polysaccharide determines serum resistance in Escherichia coli K92. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. 1994, 281, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, A.S.; Kim, K.S.; Wright, D.C.; Sadoff, J.C.; Gemski, P. Role of lipopolysaccharide and capsule in the serum resistance of bacteremic strains of Escherichia coli. J. Infect. Dis. 1986, 154, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasadarao, N.V.; Blom, A.M.; Villoutreix, B.O.; Linsangan, L.C. A novel interaction of outer membrane protein A with C4b binding protein mediates serum resistance of Escherichia coli K1. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 6352–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yair, Y.; Michaux, C.; Biran, D.; Bernhard, J.; Vogel, J.; Barquist, L.; Ron, E.Z. Cellular RNA Targets of Cold Shock Proteins CspC and CspE and Their Importance for Serum Resistance in Septicemic Escherichia coli. mSystems 2022, 7, e0008622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huja, S.; Oren, Y.; Biran, D.; Meyer, S.; Dobrindt, U.; Bernhard, J.; Becher, D.; Hecker, M.; Sorek, R.; Ron, E.Z. Fur is the master regulator of the extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli response to serum. mBio 2014, 5, e01460-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Niu, C.; Shi, Z.; Xia, Y.; Yaqoob, M.; Dai, J.; Lu, C. Effects of ibeA deletion on virulence and biofilm formation of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuge, X.; Wang, S.; Fan, H.; Pan, Z.; Ren, J.; Yi, L.; Meng, Q.; Yang, X.; Lu, C.; Dai, J. Characterization and functional analysis of AatB, a novel autotransporter adhesin and virulence factor of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 2437–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmela, C.; Chevarin, C.; Xu, Z.; Torres, J.; Sevrin, G.; Hirten, R.; Barnich, N.; Ng, S.C.; Colombel, J.F. Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2018, 67, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, P. Classical chaperone-usher (CU) adhesive fimbriome: Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) and urinary tract infections (UTIs). Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 2020, 65, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Bao, W.; Wu, S.; Ruan, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, G. Flagella from F18+Escherichia coli play a role in adhesion to pig epithelial cell lines. Microb. Pathog. 2013, 55, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pozo, J.L. Biofilm-related disease. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2018, 16, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Tang, H.; Zhang, S.; Ren, H.; Dai, J.; Lai, L.; Lu, C.; Yao, H.; Fan, H.; Wu, Z. Streptococcus suis small RNA rss04 contributes to the induction of meningitis by regulating capsule synthesis and by inducing biofilm formation in a mouse infection model. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, H.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, G.; Xia, P.; Cui, L.; Li, J.; et al. Colibactin in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli contributes to the development of meningitis in a mouse model. Virulence 2021, 12, 2382–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S. Mechanisms of microbial traversal of the blood-brain barrier. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuse, M. Molecular basis of the core structure of tight junctions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a002907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coureuil, M.; Lécuyer, H.; Bourdoulous, S.; Nassif, X. A journey into the brain: Insight into how bacterial pathogens cross blood-brain barriers. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Wang, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, G.; Cui, L.; Meng, X. ClpV1 in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli is a crucial virulence factor contributing to meningitis in a mouse model in vivo. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 263, 109273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Meng, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, C.; Ni, J.; Zhu, G. Small non-coding RNA STnc640 regulates expression of fimA fimbrial gene and virulence of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Tsuyumu, S. Flagella-mediated motility is required for biofilm formation by Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora. J. Gen. Plant. Pathol. 2006, 72, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, H.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, G.; Xia, P.; Cui, L.; Li, J.; et al. ClbG in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli contributes to meningitis development in a mouse model. Toxins 2021, 13, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, J.; Raivich, G.; Wellmer, A.; Noeske, C.; Kunst, T.; Werner, A.; Brück, W.; Nau, R. A mouse model of Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis mimicking several features of human disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2001, 101, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyu, L.Y.; Tsai, H.H.; Lin, D.P.; Chang, H.H.; Tyan, Y.S.; Weng, J.C. An 8-week brain MRI follow-up analysis of rat eosinophilic meningitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection. Zoonoses Public Health 2014, 61, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, P.; Xia, P.; Wang, J.; He, M.; Zhu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhu, G. Phosphopantetheinyl transferase ClbA contributes to the virulence of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli in meningitis infection of mice. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaenko, A.; Chen, H.; Kammer, J.; Zhang, J.H.; Tang, J. Comparison Evans Blue injection routes: Intravenous versus intraperitoneal, for measurement of blood-brain barrier in a mice hemorrhage model. J. Neurosci. Methods 2011, 195, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Strain or Plasmid | Characteristic or Function | Source and Reference |
|---|---|---|
| APEC XM | Virulent strain of APEC, isolated from the brain of duck | Donated by Dr. Chengping Lu |
| APEC XMΔryhB | Deletion mutant of ryhB with APEC XM background | This study |
| APEC XMΔryhB/pryhB | APEC XM ΔryhB carrying the vector pBR-ryhB, Amp r | This study |
| pKD46 | Amp r, λ red recombinase expression | [59] |
| pKD3 | Cm r; Cm cassette template | [59] |
| pCP20 | Ampr, Cm r, Flp recombinase expression | [59] |
| pBR-ryhB | Amp r, pBR322 carrying the full ryhB gene sequence | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, P.; He, M.; Shi, Y.; Lai, Y.; Zhu, G.; Wang, H. RyhB in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Regulates the Expression of Virulence-Related Genes and Contributes to Meningitis Development in a Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415532
Meng X, Chen Y, Wang P, He M, Shi Y, Lai Y, Zhu G, Wang H. RyhB in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Regulates the Expression of Virulence-Related Genes and Contributes to Meningitis Development in a Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(24):15532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415532
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Xia, Yanfei Chen, Peili Wang, Mengping He, Yuxing Shi, Yuxin Lai, Guoqiang Zhu, and Heng Wang. 2022. "RyhB in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Regulates the Expression of Virulence-Related Genes and Contributes to Meningitis Development in a Mouse Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 24: 15532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415532
APA StyleMeng, X., Chen, Y., Wang, P., He, M., Shi, Y., Lai, Y., Zhu, G., & Wang, H. (2022). RyhB in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Regulates the Expression of Virulence-Related Genes and Contributes to Meningitis Development in a Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(24), 15532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415532







