Molecular Characterisation of Epstein–Barr Virus in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma
Abstract
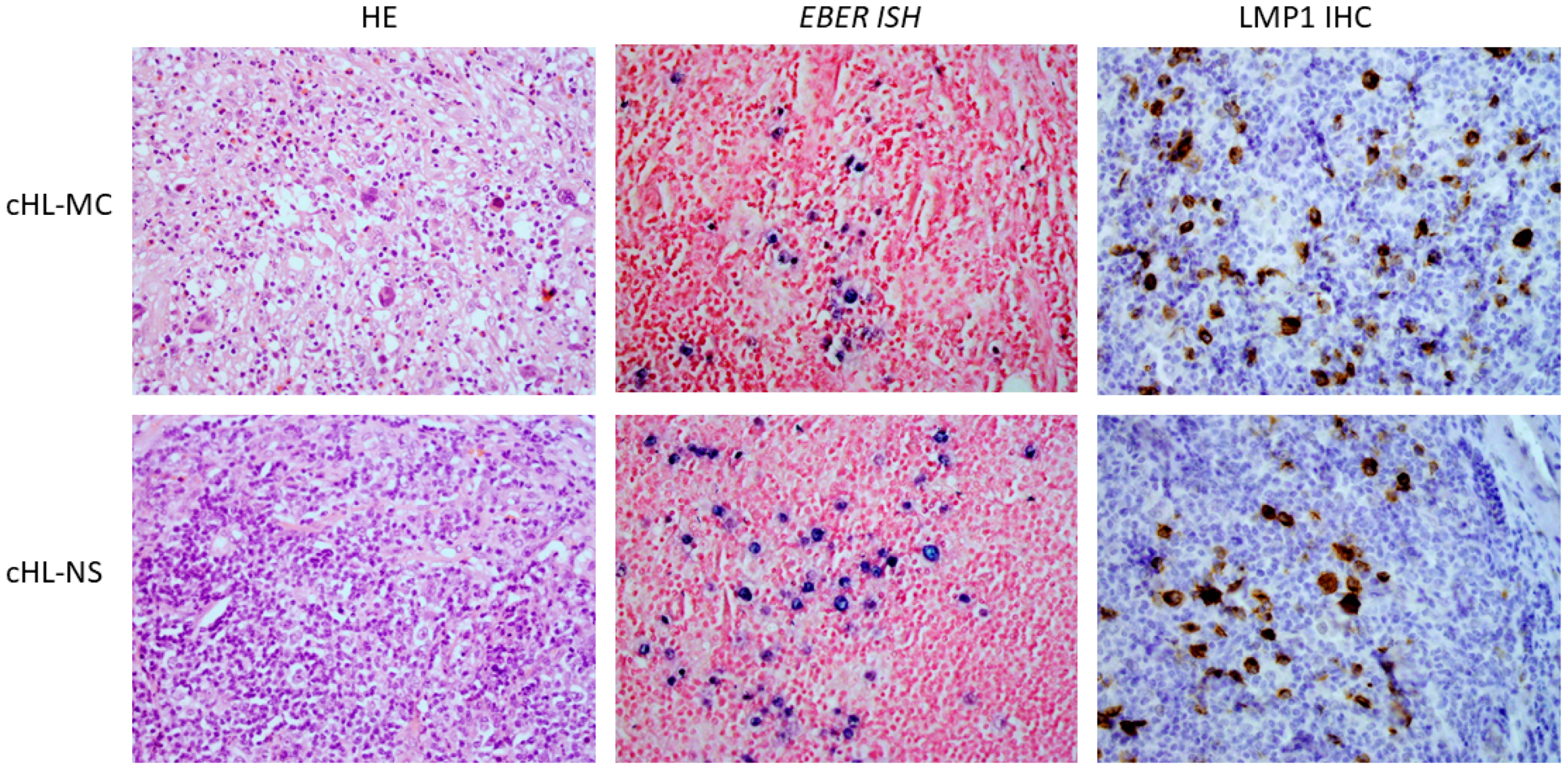
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients and Methods
2.2. EBV Variants and Clinical Data
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Methods
- Detection of EBV LMP1 protein or EBER (Epstein–Barr encoding RNA) in tumor tissue samples
- EBV detection in tumor tissue samples was performed by immunohistochemical staining of LMP1 protein and/or in situ hybridization of EBER. In brief, immunohistochemical staining was performed on 2 µm thick tumor tissue sections. After the heat-induced epitope retrieval, incubation with primary anti-LMP1 antibody (Agilent Dako, Santa Clara, CA, USA) followed, and polymer-based detection system EnVision (Dako/Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was used according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Chromogenic detection was performed by secondary antibody conjugated with horseradish peroxidase after the addition of 3,30-diaminobenzidine.
- In situ hybridization was performed on 3 µm thick tumor tissue sections. Slides were deparaffinized in xylene substitution, rehydrated in decreasing concentrations of ethanol and incubated in proteinase K solution. After washing and dehydration in absolute ethanol, slides were dried, and EBER PNA probe (Dako/Agilent (Santa Clara, CA, USA) was added. Slides were incubated at 55 °C for 90 min, washed and anti-FITC/AP was added to samples that were then incubated for 30 min in humid conditions at room temperature. After washings, the substrate 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolylphosphate and nitroblue tetrazolium were added and slides were incubated for another 30 min. Samples were then stained with Nuclear Fast red dye (Dako/Agilent (Santa Clara, CA, USA).
- Determination of EBV types 1/2 and LMP1 variant determination
- DNA was isolated from two 10 µm thick FFPE sections of each case using commercially available kit Quick-DNA/RNA FFPE Miniprep Kit (ZymoResearch, CA, USA) according to manufacturer’s instructions. Fragments of EBNA3C and LMP1 genes were amplified using previously described primers (Table S2) [28,36]. Amplicons were purified using ChargeSwitch PCR Clean-Up Kit (Life technologies, CA, USA) and then sent to Macrogen (Republic of Korea) for Sanger sequencing. The Benchling program was used to overlap the forward and reverse sequences that were further aligned and analyzed using ClustalX2 and MEGA11 software. EBV genotype was determined using EBNA3C gene amplicon. Amplicons that were 153 bp long were classified as EBV-1 and amplicons that were 246 bp long were classified as EBV-2 according to Sample J et al. [62]. According to Edwards et al., LMP1 variants were identified using algorithm based on DNA sequence coding for a specific amino acid of the LMP1 C-terminus region [13] (Table 3).
4.3. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Bian, H.; Liu, Z. CD20 expression is closely associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection and an inferior survival in nodular sclerosis classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 993768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the world health organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stein, H.; Pileri, S.A.; Weiss, L.M.; Popppema, S.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Jaffe, E.S. Hodgkin lymphomas. In WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; Swerdlow, S.H., Campo, E., Harris, N.L., Jaffe, E.S., Pileri, S.A., Stein, H., Thiele, J., Eds.; International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC): Lyon, France, 2017; pp. 424–442. [Google Scholar]
- Satou, A.; Takahara, T.; Nakamura, S. An Update on the Pathology and Molecular Features of Hodgkin Lymphoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Židovec Lepej, S.; Matulić, M.; Gršković, P.; Pavlica, M.; Radmanić, L.; Korać, P. miRNAs: EBV Mechanism for Escaping Host’s Immune Response and Supporting Tumorigenesis. Pathogens 2020, 9, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon-Lowe, C.; Rickinson, A. The Global Landscape of EBV-Associated Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozman, M.; Korać, P.; Jambrosic, K.; Židovec Lepej, S. Progress in Prophylactic and Therapeutic EBV Vaccine Development Based on Molecular Characteristics of EBV Target Antigens. Pathogens 2022, 11, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, G.; Fitzmaurice, C.; Naghavi, M.; Ahmed, L.A. Global and regional incidence, mortality and disability-adjusted life-years for Epstein-Barr virus-attributable malignancies, 1990–2017. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e037505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.W.; Jiang, S.; Gewurz, B.E. Epstein-Barr Virus LMP1-Mediated Oncogenicity. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01718-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hulse, M.; Johnson, S.M.; Boyle, S.; Caruso, L.B.; Tempera, I. Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded Latent Membrane Protein 1 and B-Cell Growth Transformation Induce Lipogenesis through Fatty Acid Synthase. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e01857-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palser, A.L.; Grayson, N.E.; White, R.E.; Corton, C.; Correia, S.; Ba Abdullah, M.M.; Watson, S.J.; Cotton, M.; Arrand, J.R.; Murray, P.G.; et al. Genome diversity of Epstein-Barr virus from multiple tumor types and normal infection. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5222–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, M.; Marinho-Dias, J.; Ribeiro, J.; Sousa, H. Epstein-Barr virus strains and variations: Geographic or disease-specific variants? J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, R.H.; Seillier-Moiseiwitsch, F.; Raab-Traub, N. Signature amino acid changes in latent membrane protein 1 distinguish Epstein-Barr virus strains. Virology 1999, 261, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gantuz, M.; Lorenzetti, M.A.; Chabay, P.A.; Preciado, M.V. A novel recombinant variant of latent membrane protein 1 from Epstein Barr virus in Argentina denotes phylogeographical association. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanella, L.; Riquelme, I.; Buchegger, K.; Abanto, M.; Ili, C.; Brebi, P. A reliable Epstein-Barr Virus classification based on phylogenomic and population analyses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knecht, H.; Bachmann, E.; Brousset, P.; Sandvej, K.; Nadal, D.; Bachmann, F.; Odermatt, B.F.; Delsol, G.; Pallesen, G. Deletions within the LMP1 oncogene of Epstein-Barr virus are clustered in Hodgkin’s disease and identical to those observed in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Blood 1993, 82, 2937–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sandvej, K.; Peh, S.; Andresen, B.; Pallesen, G. Identification of potential hot spots in the carboxy-terminal part of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BNLF-1 gene in both malignant and benign EBV-associated diseases: High frequency of a 30-bp deletion in Malaysian and Danish peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Blood 1994, 84, 4053–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.S.; Su, I.J.; Chung, P.J.; Shu, C.H.; Ng, C.K.; Wu, S.J.; Liu, S.T. Detection of an Epstein-Barr-virus variant in T-cell-lymphoma tissues identical to the distinct strain observed in nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the Taiwanese population. Int. J. Cancer 1995, 62, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanim, F.; Yao, Q.Y.; Niedobitek, G.; Sihota, S.; Rickinson, A.B.; Young, L.S. Analysis of Epstein-Barr virus gene polymorphisms in normal donors and in virus-associated tumors from different geographic locations. Blood 1996, 88, 3491–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elenitoba-Johnson, K.S.; Zarate-Osorno, A.; Meneses, A.; Krenacs, L.; Kingma, D.W.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S. Cytotoxic granular protein expression, Epstein-Barr virus strain type, and latent membrane protein-1 oncogene deletions in nasal T-lymphocyte/natural killer cell lymphomas from Mexico. Mod. Pathol. 1998, 11, 754–761. [Google Scholar]
- Dirnhofer, S.; Angeles-Angeles, A.; Ortiz-Hidalgo, C.; Reyes, E.; Gredler, E.; Krugmann, J.; Fend, F.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L. High prevalence of a 30-base pair deletion in the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 1 gene and of strain type B EBV in Mexican classical Hodgkin’s disease and reactive lymphoid tissue. Hum. Pathol. 1999, 30, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, A.K.; Wong, K.Y.; Liang, A.C.; Srivastava, G. Comparative analysis of Epstein-Barr virus gene polymorphisms in nasal T/NK-cell lymphomas and normal nasal tissues: Implications on virus strain selection in malignancy. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 80, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Baarle, D.; Hovenkamp, E.; Dukers, N.H.; Renwick, N.; Kersten, M.J.; Goudsmit, J.; Coutinho, R.A.; Miedema, F.; van Oers, M.H. High prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus type 2 among homosexual men is caused by sexual transmission. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 2045–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicholls, J.; Hahn, P.; Kremmer, E.; Fröhlich, T.; Arnold, G.J.; Sham, J.; Kwong, D.; Grässer, F.A. Detection of wild type and deleted latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) of Epstein-Barr virus in clinical biopsy material. J. Virol. Methods 2004, 116, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, D.H.; Macsween, K.F.; Higgins, C.D.; Thomas, R.; McAulay, K.; Williams, H.; Harrison, N.; Reid, S.; Conacher, M.; Douglas, J.; et al. A cohort study among university students: Identification of risk factors for Epstein-Barr virus seroconversion and infectious mononucleosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, C.D.; Swerdlow, A.J.; Macsween, K.F.; Harrison, N.; Williams, H.; McAulay, K.; Thomas, R.; Reid, S.; Conacher, M.; Britton, K.; et al. A study of risk factors for acquisition of Epstein-Barr virus and its subtypes. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Wu, Q.-L.; Zong, Y.-S.; Feng, Y.-F.; Hou, J.-H. Nasopharyngeal Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type: Retrospective Study of 18 Consecutive Cases in Guangzhou, China. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2011, 19, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Xie, Z.; Liu, C.; Huang, Z.; Xu, J. Analysis of EBNA-1 and LMP-1 variants in diseases associated with EBV infection in Chinese children. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banko, A.; Lazarevic, I.; Cupic, M.; Stevanovic, G.; Boricic, I.; Jovanovic, T. Carboxy-terminal sequence variation of LMP1 gene in Epstein-Barr-virus-associated mononucleosis and tumors from Serbian patients. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, I.; Sánchez, A.E.; Jiménez-Hernández, E.; Alvarez-Rodríguez, F.; Nava-Frias, M.; Valencia-Mayoral, P.; Salinas-Lara, C.; Velazquez-Guadarrama, N.; Portilla-Aguilar, J.; Pena, R.Y.; et al. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus and genotyping based on EBNA2 protein in Mexican patients with hodgkin lymphoma: A comparative study in children and adults. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013, 13, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorley-Lawson, D.A. EBV Persistence–Introducing the Virus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 390, 151–209. [Google Scholar]
- Banko, A.; Lazarevic, I.; Stevanovic, G.; Cirkovic, A.; Karalic, D.; Cupic, M.; Banko, B.; Milovanovic, J.; Jovanovic, T. Analysis of the Variability of Epstein-Barr Virus Genes in Infectious Mononucleosis: Investigation of the Potential Correlation with Biochemical Parameters of Hepatic Involvement. J. Med. Biochem. 2016, 35, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Correia, S.; Palser, A.; Elgueta Karstegl, C.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Ramayanti, O.; Cohen, J.I.; Hildesheim, A.; Fellner, M.D.; Wiels, J.; White, R.E.; et al. Natural Variation of Epstein-Barr Virus Genes, Proteins, and Primary MicroRNA. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00375-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salahuddin, S.; Khan, J.; Azhar, J.B.; Whitehurst, C.; Qadri, I.; Shackelford, J.; Pagano, J.S.; Muhammad, D.; Richards, K.L. Prevalence of Epstein–Barr Virus Genotypes in Pakistani Lymphoma Patients. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 3153–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafita, D.; Kaile, T.; Malyangu, E.; Tembo, R.; Zulu, E.; Chisanga, C.; Kalonda, A.; Samutela, M.; Polepole, P.; Kwenda, G. Evidence of EBV infection in lymphomas diagnosed in Lusaka, Zambia. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2018, 29, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbalaie Niya, M.H.; Safarnezhad Tameshkel, F.; Keyvani, H.; Esghaei, M.; Panahi, M.; Zamani, F.; Tabibzadeh, A. Epstein-Barr virus molecular epidemiology and variants identification in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 29, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibzadeh, A.; Karbalaie Niya, M.H.; Esghaei, M.; Bokharaei-Salim, F.; Ataei-Pirkooh, A.; Kiani, S.J.; Monavari, S.H.R. Molecular Epidemiology of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in Patients with Hematologic Malignancies. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymaz, Y.; Oduor, C.I.; Aydemir, O.; Luftig, M.A.; Otieno, J.A.; Ong’echa, J.M.; Bailey, J.A.; Moormann, A.M. Epstein-Barr Virus Genomes Reveal Population Structure and Type 1 Association with Endemic Burkitt Lymphoma. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e02007-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banko, A.; Miljanovic, D.; Lazarevic, I.; Cirkovic, A. A Systematic Review of Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1) Gene Variants in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Ba, Y.; Chen, Q.Y.; Han, Y.Q. Clinical Significance of Peripheral Blood EBV-DNA Determination and Genotyping in Lymphoma Patients. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2021, 29, 1802–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Montes-Mojarro, I.A.; Fend, F.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L. EBV and the Pathogenesis of NK/T Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, P.; Larrate, M.; Garcia-Costa, A.; Rohan, P.; Gama, B.E.; Abdelhay, E.; Delatorre, E.; Hassan, R. Spatial Dispersal of Epstein-Barr Virus in South America Reveals an African American Variant in Brazilian Lymphomas. Viruses 2022, 12, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Mojarro, I.A.; Chen, B.J.; Ramirez-Ibarguen, A.F.; Quezada-Fiallos, C.M.; Perez-Baez, W.B.; Duenas, D.; CasavilcaZambrano, S.; Ortiz-Mayor, M.; Rojas-Bilbao, E.; Garcia-Rivello, H.; et al. Mutational profile and EBV strains of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type in Latin America. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickinson, A.B.; Young, L.S.; Rowe, M. Influence of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA 2 on the growth phenotype of virus-transformed B cells. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, C.B.; Lang, J.; Sweet, L.A.; Smith, N.A.; Freed, B.M.; Pan, Z.; Haverkos, B.; Pelanda, R.; Rochford, R. Epstein-Barr Virus Type 2 Infects T Cells and Induces B Cell Lymphomagenesis in Humanized Mice. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00813-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simbiri, K.O.; Smith, N.A.; Otieno, R.; Wohlford, E.E.; Daud, I.I.; Odada, S.P.; Middleton, F.; Rochford, R. Epstein-Barr virus genetic variation in lymphoblastoid cell lines derived from Kenyan pediatric population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coleman, C.B.; Wohlford, E.M.; Smith, N.A.; King, C.A.; Ritchie, J.A.; Baresel, P.C.; Kimura, H.; Rochford, R. Epstein-Barr virus type 2 latently infects T cells, inducing an atypical activation characterized by expression of lymphotactic cytokines. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2301–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coleman, C.B.; Daud, I.I.; Ogolla, S.O.; Ritchie, J.A.; Smith, N.A.; Sumba, P.O.; Dent, A.E.; Rochford, R. Epstein-Barr Virus Type 2 Infects T Cells in Healthy Kenyan Children. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.F.; Chen, F.; Zheng, X.; Ernberg, I.; Cao, S.L.; Christensson, B.; Klein, G.; Winberg, G. Clonability and tumorigenicity of human epithelial cells expressing the EBV encoded membrane protein LMP1. Oncogene 1993, 6, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar]
- Odermatt, B.F.; Heitz, P.U.; Bachmann, E.; Brousset, P.; Sandvej, K.; Knecht, H. Deletionen innerhalb des latenten Membran-Protein-Onkogens des Epstein-Barr Virus bei Morbus Hodgkin sind weitgehend identisch mit denjenigen beim asiatischen nasopharyngealen Karzinom [Internal deletions of the latent membrane protein oncogenes of Epstein-Barr virus in Hodgkin’s disease are almost identical with those of Asiatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma]. Verh. Dtsch. Ges Pathol. 1994, 78, 324–328. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.L.; Tsai, C.N.; Liang, C.L.; Shu, C.H.; Huang, C.R.; Sulitzeanu, D.; Liu, S.T.; Chang, Y.S. Cloning and characterization of the latent membrane protein (LMP) of a specific Epstein-Barr virus variant derived from the nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the Taiwanese population. Oncogene 1992, 7, 2131–2140. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Troyanovsky, B.; Zhang, X.; Trivedi, P.; Ernberg, I.; Klein, G. Differences in the immunogenicity of latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) encoded by Epstein-Barr virus genomes derived from LMP1-positive and -negative nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 5589–5593. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santisteban-Espejo, A.; Perez-Requena, J.; Atienza-Cuevas, L.; Moran-Sanchez, J.; Fernandez-Valle, M.D.C.; Bernal-Florindo, I.; Romero-Garcia, R.; Garcia-Rojo, M. Prognostic Role of the Expression of Latent-Membrane Protein 1 of Epstein-Barr Virus in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Viruses 2021, 13, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Tao, H.; Jia, Y. The prognostic value of Epstein-Barr virus infection in Hodgkin lymphoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1034398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nohtani, M.; Vrzalikova, K.; Ibrahim, M.; Powell, J.E.; Fennell, É.; Morgan, S.; Grundy, R.; McCarthy, K.; Dewberry, S.; Bouchal, J.; et al. Impact of Tumour Epstein-Barr Virus Status on Clinical Outcome in Patients with Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (cHL): A Review of the Literature and Analysis of a Clinical Trial Cohort of Children with cHL. Cancers 2022, 14, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammous-Boukhris, N.; Mosbah, A.; Ayadi, W.; Sahli, E.; Chevance, S.; Bondon, A.; Gargouri, A.; Baudy-Floc’h, M.; Mokdad-Gargouri, R. B1.12: A novel peptide interacting with the extracellular loop of the EBV oncoprotein LMP1. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zha, S.; Chau, H.F.; Chau, W.Y.; Chan, L.S.; Lin, J.; Lo, K.W.; Cho, W.C.; Yip, Y.L.; Tsao, S.W.; Farrell, P.J.; et al. Dual-Targeting Peptide-Guided Approach for Precision Delivery and Cancer Monitoring by Using a Safe Upconversion Nanoplatform. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2002919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, A.K.; Dawson, C.W.; Lung, H.L.; Wong, K.L.; Young, L.S. The Role of EBV-Encoded LMP1 in the NPC Tumor Microenvironment: From Function to Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 640207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Pierre, V.; Lupo, J.; Buisson, M.; Morand, P.; Germi, R. Main Targets of Interest for the Development of a Prophylactic or Therapeutic Epstein-Barr Virus Vaccine. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 701611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croatian Bureau of Statistics. First Digital Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of Croatia. Available online: https://dzs.gov.hr/en (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- The World Bank. GDP per Capita—Croatia. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.PCAP.CD?locations=HR (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Sample, J.; Young, L.; Martin, B.; Chatman, T.; Kieff, E.; Rickinson, A.; Kieff, E. Epstein-Barr virus types 1 and 2 differ in their EBNA-3A, EBNA-3B, and EBNA-3C genes. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 4084–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patients | Number of Samples | Age (Years) | Histological Subtype | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC | NS | LR | LD | SLL Transformations to cHL | Subtype Not Determined | |||
| Female | 12 | 39–84 (median 67) | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| Male | 34 | 10–87 (median 55) | 13 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| Sample | Histological Subtype | LMP1 | EBV Genotype (EBNA3C) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 331 Gly-Gln/Ala | 334 Gln-Arg | 338 Leu-Ser/Pro | 343–352 del | 344 Gly-Asp | 345 Gly-Ser | 352 His-Arg/del/Asn | 354 Gly-Asp | 355 Gly-Ala/Thr/Val | 358 His-Pro | 366 Ser-Thr/Asn/Ala | del 30 bp | Subtype | |||
| cHL1 | NS | Gly | Pro | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL2 | MC | Gly | Pro | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL3 | MC | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL5 | MC | Gly | Arg | Ser | WD | Gly | Gly | Arg | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | Med− | EBV-1 |
| cHL6 | MC | Gly | Arg | Leu | / | Gly | Gly | del | / | / | His | Thr | del | Med+ | EBV-1 |
| cHL7 | NS | Gly | Arg | Ser | / | / | / | del | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | del | Med+ | EBV-1 |
| cHL9 | ND | Gly | Arg | Ser | / | / | / | del | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | del | Med+ | EBV-1 |
| cHL10 | ND | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL11 | NS | Gly | Pro | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL12 | NS | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL13 | TR | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL14 | MC | Arg | Arg | Ser | / | / | / | del | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | del | Med+ | EBV-1 |
| cHL15 | NS | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL16 | NS | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL17 | NS | Gly | Arg | Leu | / | Gly | Gly | del | / | / | His | Thr | del | Med+ | EBV-1 |
| cHL18 | NS | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL19 | MC | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL21 | MC | Gly | Arg | Ser | / | / | / | del | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | del | Med+ | EBV-1 |
| cHL22 | MC | Gln | Gln | Pro | WD | Gly | Gly | Asn | Gly | Gly | Pro | Thr | WD | NC | EBV-1 |
| cHL24 | MC | Gly | Arg | Ser | / | / | / | del | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | del | Med+ | EBV-1 |
| cHL25 | MC | Gly | Pro | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL26 | NS | Gly | Arg | Ser | WD | Gly | Gly | Arg | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | Med− | EBV-1 |
| cHL27 | TR | Gly | Arg | Ser | / | / | / | del | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | del | Med+ | EBV-1 |
| cHL28 | ND | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL29 | NS | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL30 | ND | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL31 | NS | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL32 | MC | Gly | Arg | Ser | / | / | / | del | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | del | Med+ | EBV-1 |
| cHL33 | LD | Gly | Arg | Ser | WD | Gly | Gly | Arg | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | Med− | EBV-1 |
| cHL34 | LR | Gly | Arg | Ser | / | / | / | del | Gly | Gly | His | Ala | del | Med+ | EBV-1 |
| cHL35 | MC | Gly | Pro | Ser | / | / | / | del | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | del | Med+ | EBV-1 |
| cHL36 | MC | Gly | Arg | Ser | / | / | / | del | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | del | Med+ | EBV-1 |
| cHL38 | MC | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Ala | WD | B95-8/Med | EBV-1 |
| cHL39 | MC | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL40 | ND | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL41 | MC | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL42 | MC | Gly | Arg | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | Unknown | EBV-1 |
| cHL43 | MC | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL44 | LR | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL45 | TR | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL46 | ND | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL47 | ND | Gly | Gln | Leu | WD | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8 | EBV-1 |
| cHL48 | ND | Gln | Gln | Pro | WD | Gly | Gly | Asn | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8/NC | EBV-1 |
| cHL49 | MC | Gln | Gln | Pro | WD | Gly | Gly | Asn | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | WD | B95-8/NC | EBV-1 |
| cHL50 | ND | Gly | Arg | Ser | / | / | / | del | Gly | Gly | His | Thr | del | Med+ | EBV-1 |
| cHL52 | LR | Gln | Gln | Pro | WD | Gly | Gly | Asn | Gly | Gly | Pro | Thr | WD | NC | EBV-1 |
| EBV Variants | Positions in the C-Terminus Region of LMP1 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 331 | 334 | 338 | 343–352 | 344 | 345 | 352 | 354 | 355 | 358 | 366 | Deletion 30 bp | |
| B95-8 | Gly | Gln | Leu | without deletion | Gly | Gly | His | Gly | Gly | His | Ser | |
| China 1 | Arg | Ser | deletion | Thr | ||||||||
| China 2 | Gln | Pro | Asp | Ala/Thr | Thr | |||||||
| Mediterranean | Arg | Ser | Arg/deletion | Asn/Thr/Ala | deletion/without deletion | |||||||
| Alaskan | Ala | Pro | Ser | Asp | Val | |||||||
| North Carolina | Gln | Pro | Asn | Pro | ||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Begić, V.; Korać, P.; Gašparov, S.; Rozman, M.; Simicic, P.; Zidovec-Lepej, S. Molecular Characterisation of Epstein–Barr Virus in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415635
Begić V, Korać P, Gašparov S, Rozman M, Simicic P, Zidovec-Lepej S. Molecular Characterisation of Epstein–Barr Virus in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(24):15635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415635
Chicago/Turabian StyleBegić, Valerija, Petra Korać, Slavko Gašparov, Marija Rozman, Petra Simicic, and Snjezana Zidovec-Lepej. 2022. "Molecular Characterisation of Epstein–Barr Virus in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 24: 15635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415635
APA StyleBegić, V., Korać, P., Gašparov, S., Rozman, M., Simicic, P., & Zidovec-Lepej, S. (2022). Molecular Characterisation of Epstein–Barr Virus in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(24), 15635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415635





