Genome-Wide Identification of AMT2-Type Ammonium Transporters Reveal That CsAMT2.2 and CsAMT2.3 Potentially Regulate NH4+ Absorption among Three Different Cultivars of Camellia sinensis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Characterization of CsAMT2s
2.2. Cis-Elements in the CsAMT2 Promoters
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of CsAMT2 Proteins in Different Plants
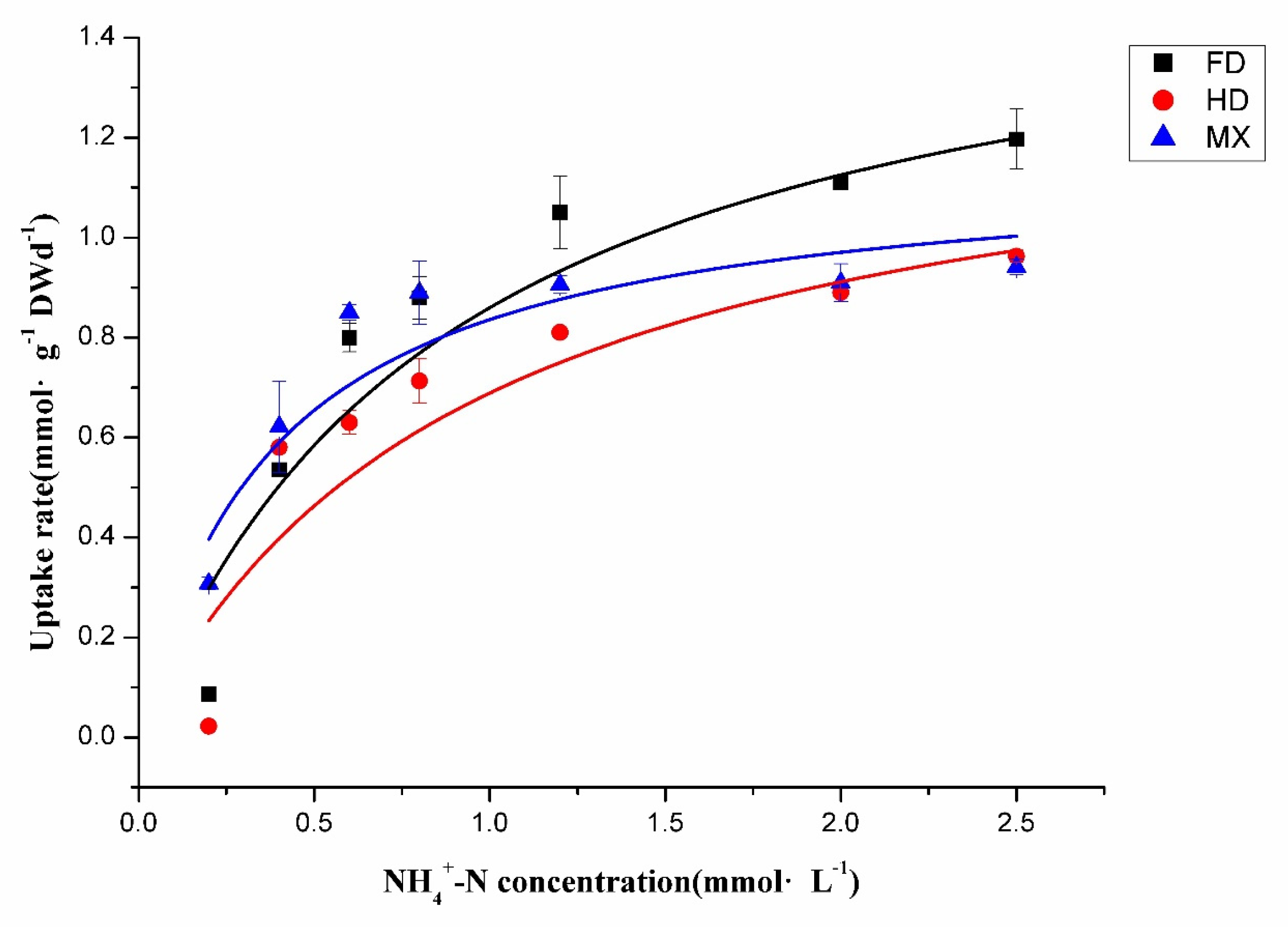
2.4. Determination of N Nutrient Adaptation Types in Different Cultivars
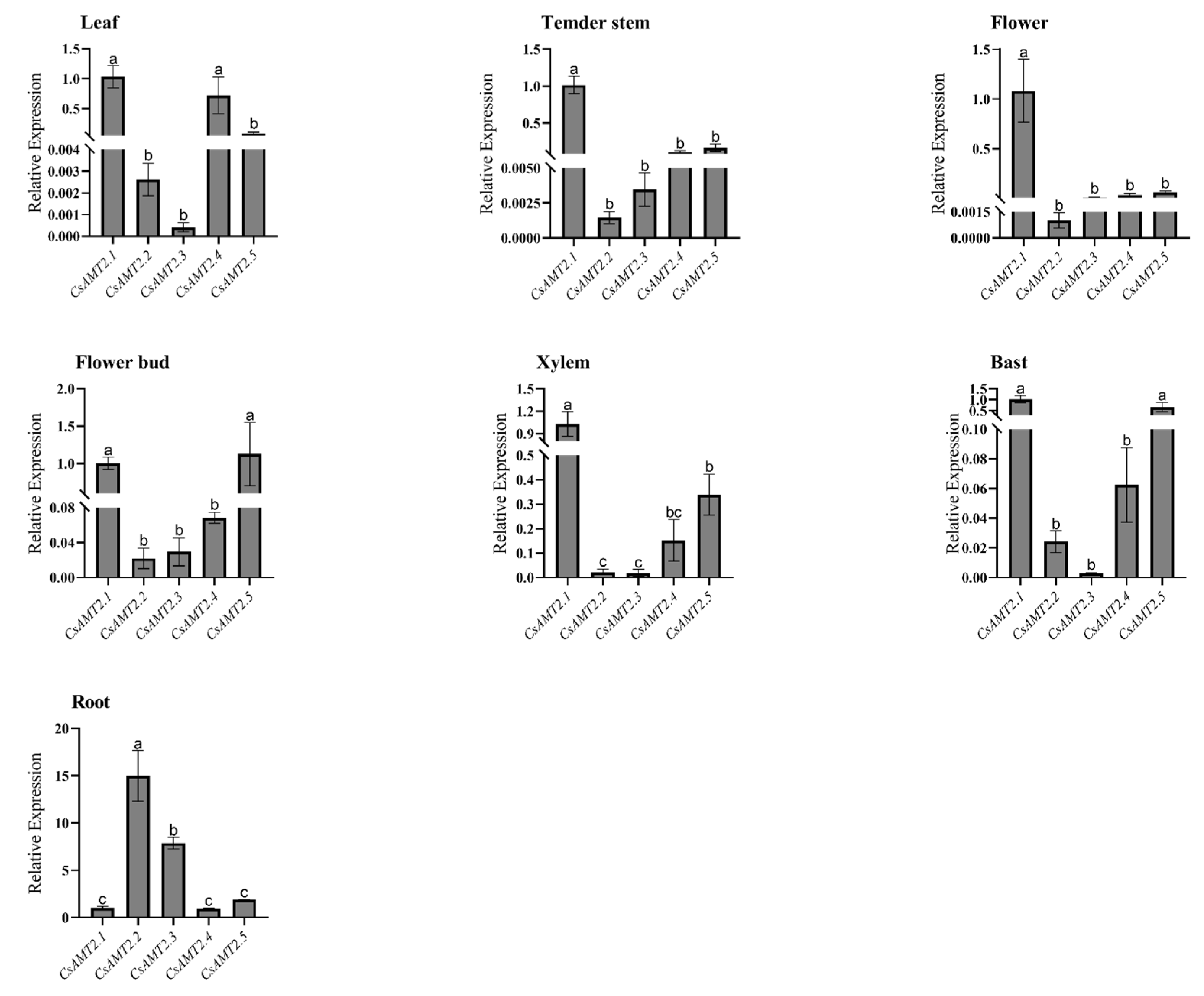
2.5. Tissue-Specific Expression Patterns of CsAMT2s
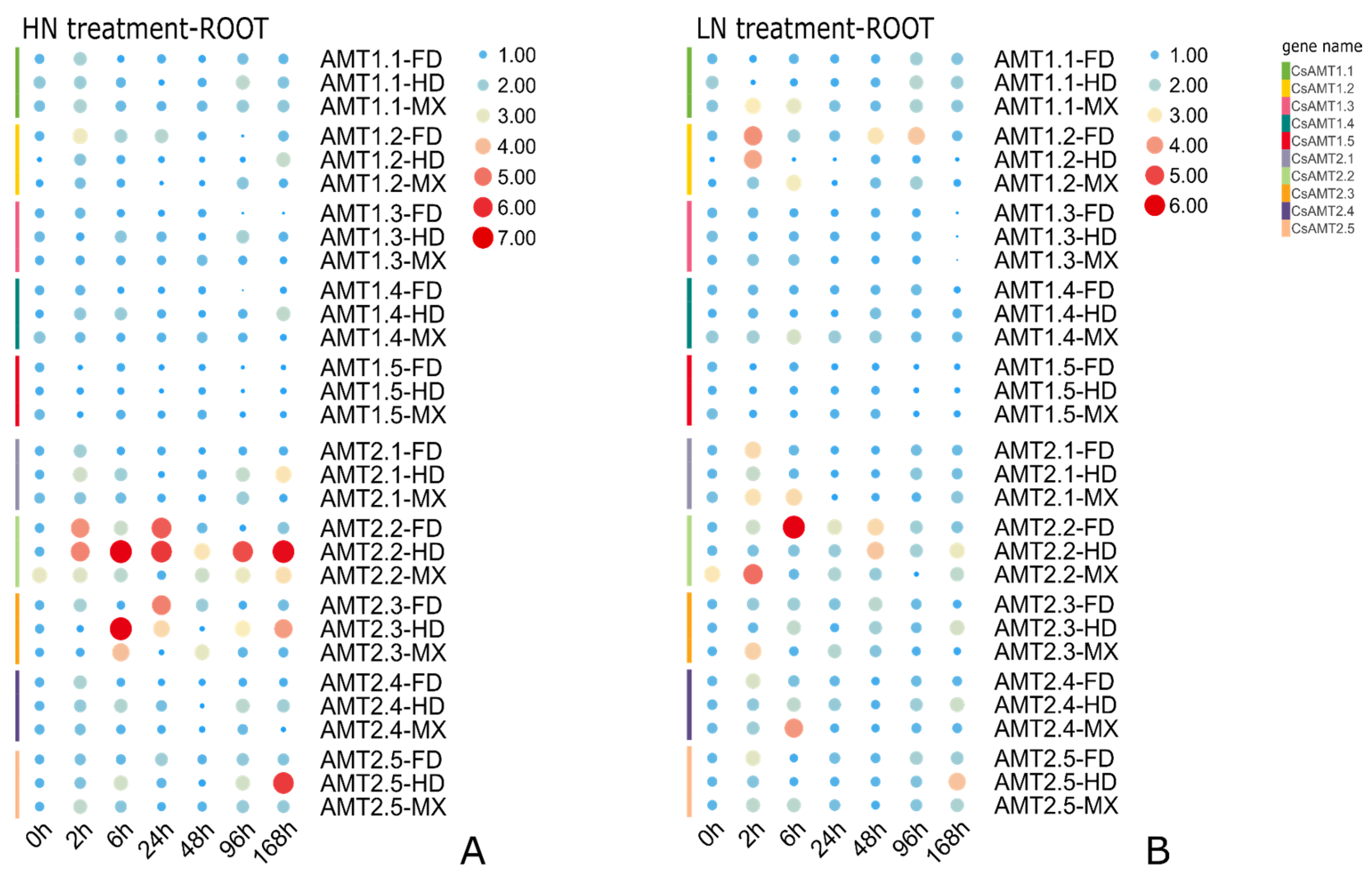
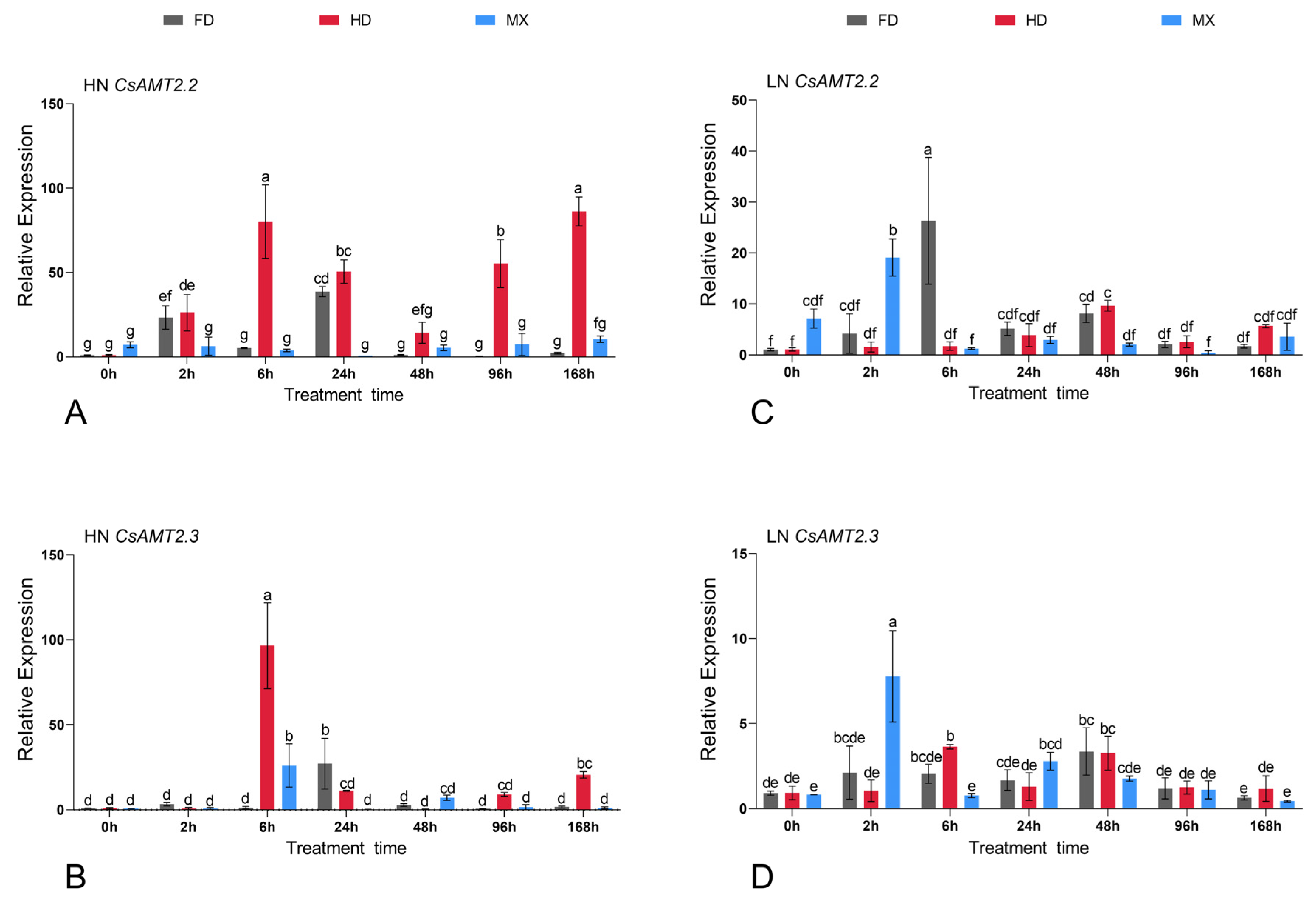
2.6. Expression Profiles of CsAMTs in Response to Different NH4+ Resupply Concentrations
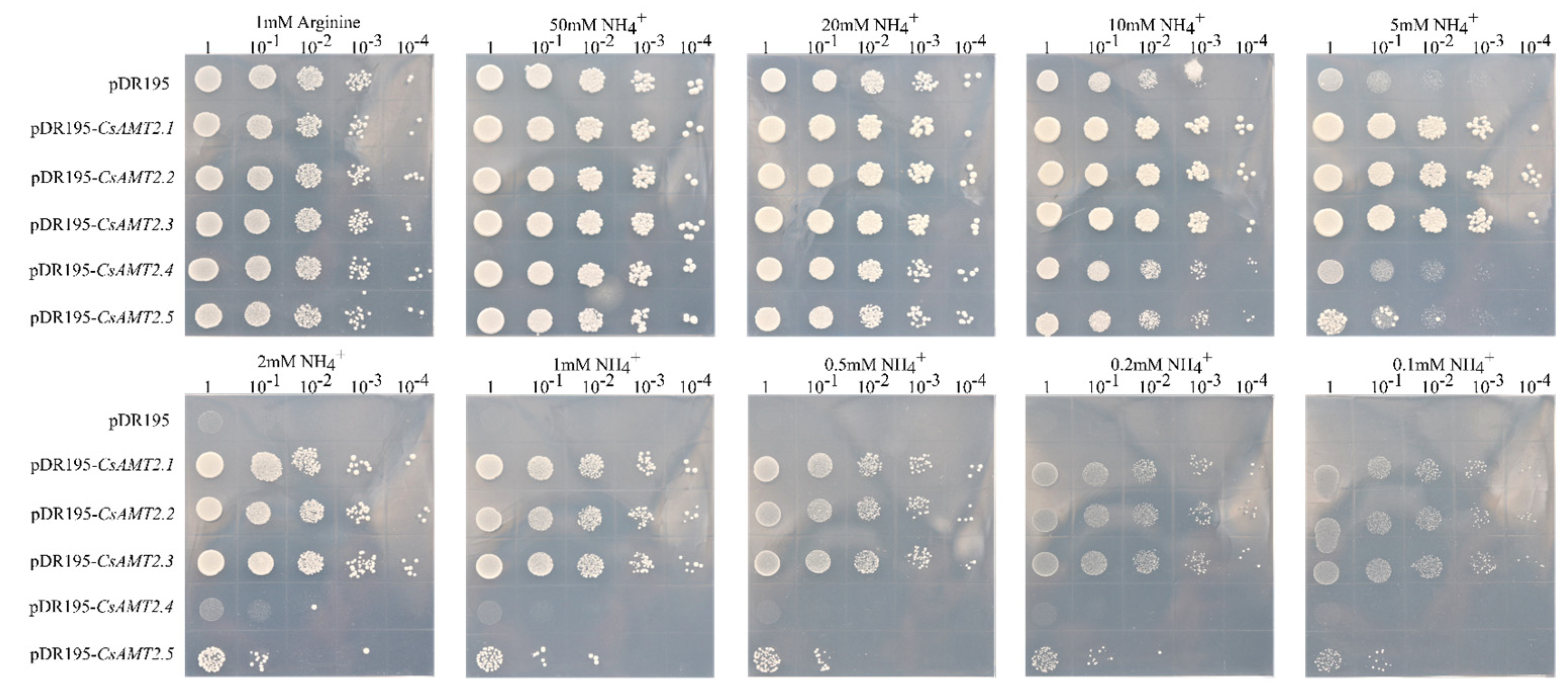
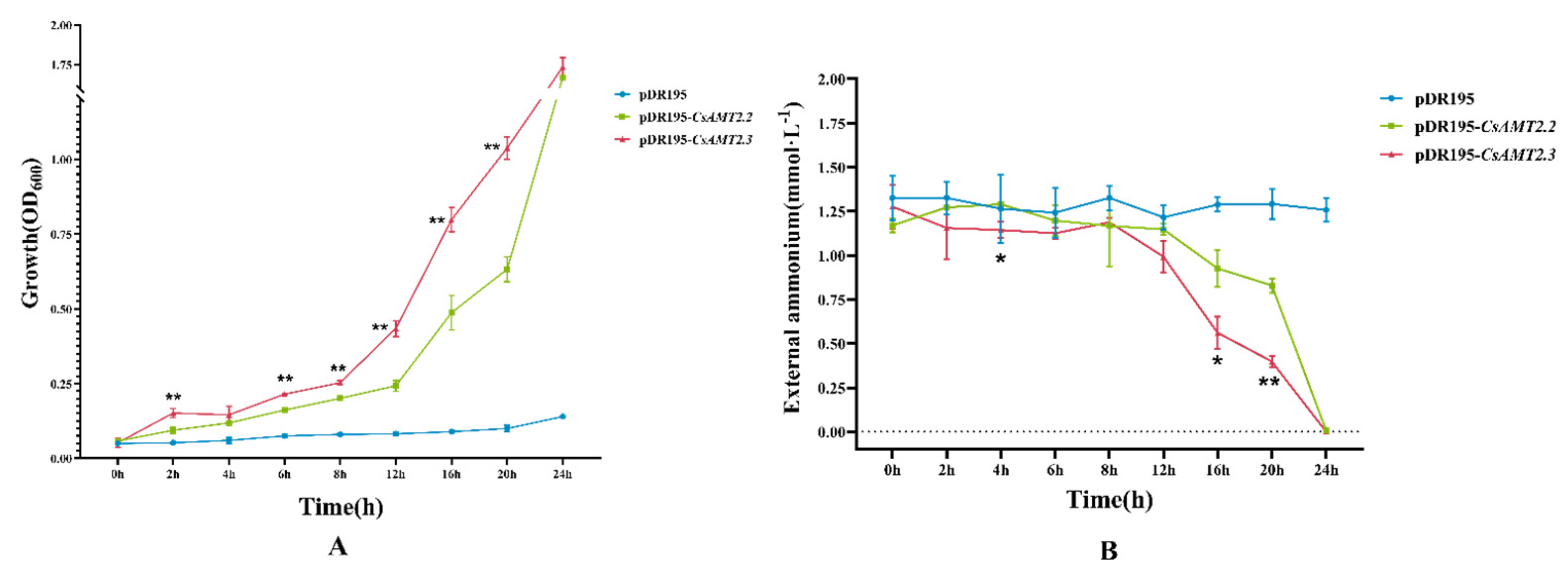
2.7. Functional Analysis of CsAMT2.2 and CsAMT2.3 in Yeast
3. Discussion
3.1. N Adaptation Types Varied in Different Cultivars of Tea Plants
3.2. Tissue-Specific Expression Patterns of CsAMT2 Subfamily Genes
3.3. CsAMT2.2 and CsAMT2.3 Play Roles of NH4+ Absorption in Different Cultivars
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
4.3. Database Sequence Analysis and Molecular Cloning
4.4. Determination of NH4+ Dynamic Kinetic Characteristics
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time (qRT)-PCR Analysis
4.6. Functional Validation of CsAMT2.2 and CsAMT2.3 in Yeast
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruan, L.; Wei, K.; Wang, L.; Cheng, H.; Wu, L.; Li, H. Characteristics of free amino acids (the quality chemical components of tea) under spatial heterogeneity of different nitrogen forms in tea (Camellia sinensis) plants. Molecules 2019, 24, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, X.H.; Peng, F.R.; Jiang, J.; Tan, P.P.; Wu, Z.Z.; Liang, Y.W.; Zhong, Z.K. Inorganic nitrogen fertilizers induce changes in ammonium assimilation and gas exchange in Camellia sinensis L. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2015, 39, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Burgos, A.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, D.; Ruan, J. Lipidomics analysis unravels the effect of nitrogen fertilization on lipid metabolism in tea plant (Camellia sinensis L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, F.; Hu, J.; Shi, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Ruan, J. Effects of nitrogen supply on flavonol glycoside biosynthesis and accumulation in tea leaves (Camellia sinensis). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 138, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodirsky, B.L.; Popp, A.; Lotze-Campen, H.; Dietrich, J.P.; Rolinski, S.; Weindl, I.; Schmitz, C.; Müller, C.; Bonsch, M.; Humpenöder, F.; et al. Reactive nitrogen requirements to feed the world in 2050 and potential to mitigate nitrogen pollution. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, K.; Liao, W.Y.; Yi, X.Y.; Niu, S.Y.; Ma, L.F.; Shi, Y.Z.; Zhang, Q.F.; Liu, M.Y.; Ruan, J.Y. Fertilization status and reduction potential in tea gardens of China. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 25, 421–432. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; You, L.; Amini, M.; Obersteiner, M.; Herrero, M.; Zehnder, A.J.B.; Yang, H. A high-resolution assessment on global nitrogen flows in cropland. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8035–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konieczna, A.; Roman, K.; Borek, K.; Grzegorzewska, E. GHG and NH3 emissions vs. energy efficiency of maize production technology: Evidence from polish farms; a further study. Energies 2021, 14, 5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krapp, A.; David, L.C.; Chardin, C.; Girin, T.; Marmagne, A.; Leprince, A.S.; Chaillou, S.; Ferrario-Méry, S.; Meyer, C.; Daniel-Vedele, F. Nitrate transport and signalling in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, L.; Wei, K.; Wang, L.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, F.; Wu, L.; Bai, P.; Zhang, C. Characteristics of NH4+ and NO3− fluxes in tea (Camellia sinensis) roots measured by scanning ion-selective electrode technique. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruan, J.; Haerdter, R.; Gerendás, J. Impact of nitrogen supply on carbon/nitrogen allocation: A case study on amino acids and catechins in green tea [Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze] plants. Plant Biol. 2010, 12, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninnemann, O.; Jauniaux, J.C.; Frommer, W.B. Identification of a high affinity NH4+ transporter from plants. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 3464–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, T.R.; Dietrich, F.S.; Lutzoni, F. Multiple horizontal gene transfers of ammonium transporters/ ammonia permeases from prokaryotes to eukaryotes: Toward a new functional and evolutionary classification. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 29, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howitt, S.M.; Udvardi, M.K. Structure, function and regulation of ammonium transporters in plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1465, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, L.; Graff, L.; Loqué, D.; Kojima, S.; Tsuchiya, Y.N.; Takahashi, H.; von Wirén, N. AtAMT1;4, a pollen-specific high-affinity ammonium transporter of the plasma membrane in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Loque, D.; Kojima, S.; Rauch, S.; Ishiyama, K.; Inoue, E.; Takahashi, H.; von Wiren, N. The organization of high-affinity ammonium uptake in Arabidopsis roots depends on the spatial arrangement and biochemical properties of AMT1-type transporters. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2636–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neuhauser, B.; Dynowski, M.; Ludewig, U. Channel-like NH3 flux by ammonium transporter AtAMT2. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 2833–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sohlenkamp, C.; Shelden, M.; Howitt, S.; Udvardi, M. Characterization of Arabidopsis AtAMT2, a novel ammonium transporter in plants. FEBS Lett. 2000, 467, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.Z.; Merrick, M.; Li, S.M.; Li, H.Y.; Zhu, S.W.; Shi, W.M.; Su, Y.H. Molecular basis and regulation of ammonium transporter in rice. Rice Sci. 2009, 16, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenaga, A.; Moriya, K.; Sonoda, Y.; Ikeda, A.; von Wirén, N.; Hayakawa, T.; Yamaguchi, J.; Yamaya, T. Constitutive expression of a novel-type ammonium transporter OsAMT2 in rice plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.M.; Li, B.Z.; Shi, W.M. Expression patterns of nine ammonium transporters in rice in response to N status. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couturier, J.; Montanini, B.; Martin, F.; Brun, A.; Blaudez, D.; Chalot, M. The expanded family of ammonium transporters in the perennial poplar plant. New Phytol. 2007, 174, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Cong, Y.; Chang, Y.H.; Lin, J. Two AMT2-Type ammonium transporters from pyrus betulaefolia demonstrate distinct expression characteristics. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2016, 34, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Rosin, U.; Wood, C.; Udvardi, M.K. Molecular and cellular characterisation of LjAMT2;1, an ammonium transporter from the model legume Lotus japonicus. Plant Mol. Biol. 2003, 51, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guether, M.; Neuhäuser, B.; Balestrini, R.; Dynowski, M.; Ludewig, U.; Bonfante, P. A mycorrhizal-specific ammonium transporter from Lotus japonicus acquires nitrogen released by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goel, P.; Singh, A.K. Abiotic stresses downregulate key genes involved in nitrogen uptake and assimilation in Brassica juncea L. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Li, M.; Shao, Y.; Sun, T.; Li, C.; Ma, F. Ammonium uptake increases in response to PEG-induced drought stress in Malus hupehensis Rehd. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 151, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohlenkamp, C.; Wood, C.C.; Roeb, G.W.; Udvardi, M.K. Characterization of Arabidopsis AtAMT2, a high-affinity ammonium transporter of the plasma membrane. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.M.; Shi, W.M. Quantitative characterization of nitrogen regulation of OsAMT1;1, OsAMT1;2, and OsAMT2;2 expression in rice seedlings. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 53, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, V.S.; Singh, U.S.; Gupta, A.K.; Kumar, A. Influence of different nitrogen inputs on the members of ammonium transporter and glutamine synthetase genes in two rice genotypes having differential responsiveness to nitrogen. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 8035–8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, V.S.; Singh, U.S.; Gupta, A.K.; Kumar, A. Understanding the differential nitrogen sensing mechanism in rice genotypes through expression analysis of high and low affinity ammonium transporter genes. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giehl, R.F.H.; Laginha, A.M.; Duan, F.; Rentsch, D.; Yuan, L.; von Wiren, N. A critical role of AMT2;1 in root-to-shoot translocation of ammonium in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1449–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuillin-Sessoms, F.; Floss, D.S.; Gomez, S.K.; Pumplin, N.; Ding, Y.; Levesque-Tremblay, V.; Noar, R.D.; Daniels, D.A.; Bravo, A.; Eaglesham, J.B.; et al. Suppression of arbuscule degeneration in Medicago truncatula phosphate transporter4 mutants is dependent on the ammonium transporter 2 family protein AMT2;3. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koegel, S.; Ait Lahmidi, N.; Arnould, C.; Chatagnier, O.; Walder, F.; Ineichen, K.; Boller, T.; Wipf, D.; Wiemken, A.; Courty, P.E. The family of ammonium transporters (AMT) in Sorghum bicolor: Two AMT members are induced locally, but not systemically in roots colonized by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liao, K.; Xu, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Jia, B.; Xuan, Y. Wheat ammonium transporter (AMT) gene family: Diversity and possible role in host-pathogen interaction with stem rust. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Bai, P.X.; Ruan, L.; Zhang, C.C.; Wei, K.; Cheng, H. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of ammonium transporters in tea plants (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) under different nitrogen treatments. Gene 2018, 658, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.J.; Li, W.; Li, K.; Nan, H.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Z.Y.; Lin, Y.L.; Yang, X.L.; Tong, Y.; et al. The chromosome-level reference genome of tea tree unveils recent bursts of non-autonomous LTR retrotransposons to drive genome size evolution. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.H.; Li, F.D.; Tong, W.; Li, P.H.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, H.J.; Ge, R.H.; Li, R.P.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.Z.; et al. Tea plant information archive: A comprehensive genomics and bioinformatics platform for tea plant. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1938–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.H.; Zhang, H.B.; Sheng, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, Q.J.; Kim, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, T.; Li, W.; et al. The tea tree genome provides insights into tea flavor and independent evolution of caffeine biosynthesis. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Gao, L.; Xia, E.; Lu, Y.; Tai, Y.; She, G.; et al. Draft genome sequence of Camellia sinensis var. sinensis provides insights into the evolution of the tea genome and tea quality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E4151–E4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J.; Lin, L.; Chen, M.J.; Sun, W.J. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of CsAMT1s gene subfamily in Camellia sinensis. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2022, 28, 57–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, A.M.; Soussi-Boudekou, S.; Vissers, S.; Andre, B. A Family of Ammonium Transporters in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell Biol. 1997, 17, 4282–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.C.; Yang, Y.J.; Chen, L.; Wu, W. Study on the efficiency difference of nitrogen fertilizer utilization in different cultivars of tea plants (Camellia sinensis) with 15N marker. Tea Fujian 2005, 1, 4–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.C.; Yang, Y.J.; Chen, L.; Ruan, J.Y. Genotypic Difference of Nitrogen Efficiency in Tea Plant [Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze]. J. Tea Sci. 2004, 24, 93–98. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.C. Study on the Genotypic Difference of Nitrogen Nutrient and Its Mechanism in Tea Plant [Camellia sinensis (L.)O.Kuntze]. Master’s Thesis, Tea Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agriculture Sciences, Hangzhou, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, J.Y.; Wang, X.P.; Cui, S.Z.; Yao, G.K. Study on the mechanism of Difference Nitrogen Nutrition among Different Cultivars of Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis). China Tea 1993, 15, 35–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. The Altered Expression of Genes Related to Nitrogen Absorption and Utilization of Tea Cultivars with Different Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Master’s Thesis, Tea Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agriculture Sciences, Hangzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.X.; Gazzarrini, S.; Lejay, L.; Gojon, A.; Ninnemann, O.; Frommer, W.B.; von Wirén, N. Three functional transporters for constitutive, diurnally regulated, and starvation-induced uptake of ammonium into Arabidopsis roots. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoque, M.S.; Masle, J.; Udvardi, M.K.; Ryan, P.R.; Upadhyaya, N.M. Over-expression of the rice OsAMT1-1 gene increases ammonium uptake and content, but impairs growth and development of plants under high ammonium nutrition. Funct. Plant Biol. 2006, 33, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Bai, P.; Wei, K.; Zhang, Y.; Ruan, L.; Wu, L.; Cheng, H. Identification of regulatory networks and hub genes controlling nitrogen uptake in tea plants (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2445–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Li, X.H.; Ratcliffe, R.G.; Ruan, J.Y. Characterization of ammonium and nitrate uptake and assimilation in roots of tea plants. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 60, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Shen, J.; Xing, H.; Zou, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, W. Genome-wide identification, characterization and expression analysis of the amino acid permease gene family in tea plants (Camellia sinensis). Genomics 2020, 112, 2866–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Xiang, F.; Zhong, M.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Transcriptome and metabolite analysis identifies nitrogen utilization genes in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bao, A.; Liang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, H. Overexpressing of OsAMT1-3, a high affinity ammonium transporter gene, modifies rice growth and carbon-nitrogen metabolic status. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 9037–9063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruan, J.; Gerendás, J.; Härdter, R.; Sattelmacher, B. Effect of nitrogen form and root-zone pH on growth and nitrogen uptake of tea (Camellia sinensis) plants. Ann. Bot. 2007, 99, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.; Li, F.; Tong, W.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Gao, L.; Tai, Y.; She, G.; et al. The tea plant reference genome and improved gene annotation using long-read and paired-end sequencing data. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, E.H.; Tong, W.; Hou, Y.; An, Y.L.; Chen, L.B.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.L.; Yu, J.; Li, F.D.; Li, R.P.; et al. The reference genome of tea plant and resequencing of 81 diverse accessions provide insights into its genome evolution and adaptation. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, B.G. Building phylogenetic trees from molecular data with MEGA. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Rengel, Z.; Meney, K. Kinetics of ammonium, nitrate and phosphorus uptake by Canna indica and Schoenoplectus validus. Aquat. Bot. 2009, 91, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngdahl, L.J.; Pacheco, R.; Street, J.J.; Vlek, P.L.G. The kinetics of ammonium and nitrate uptake by young rice plants. Plant Soil 1982, 69, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Horvath, D.P.; Chao, W.S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiao, B. Identification and evaluation of reliable reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis in tea plant (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22155–22172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
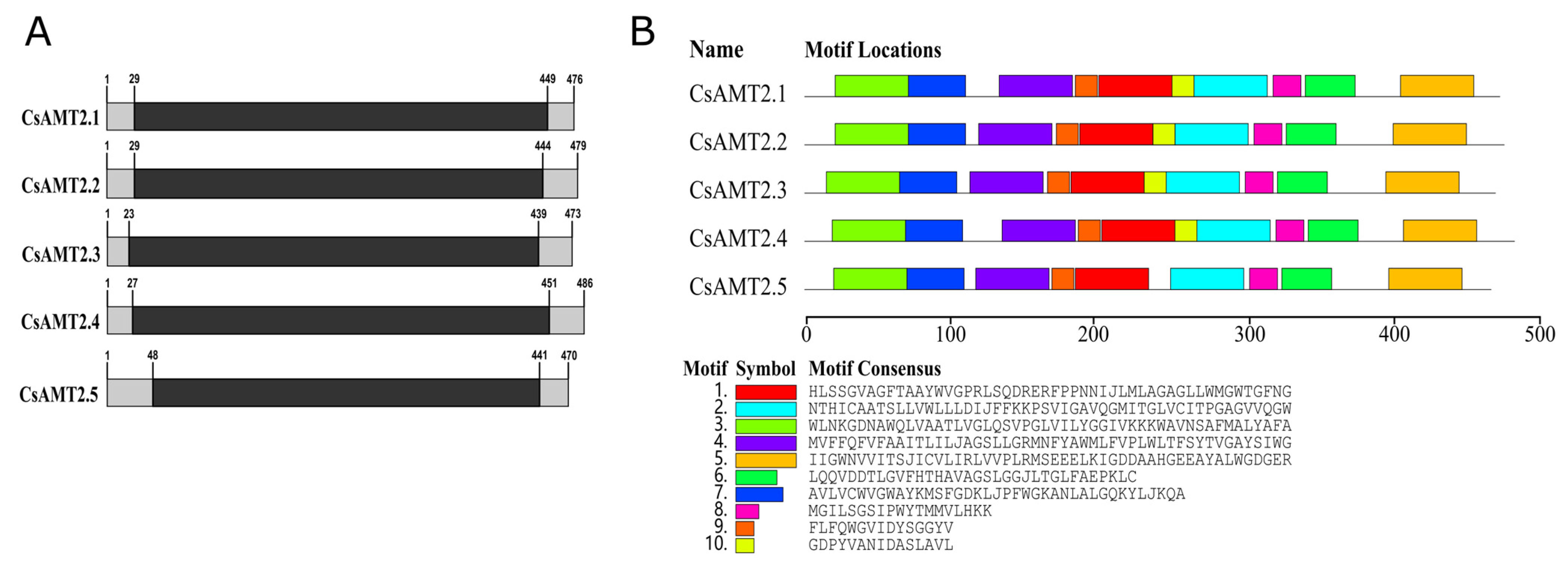
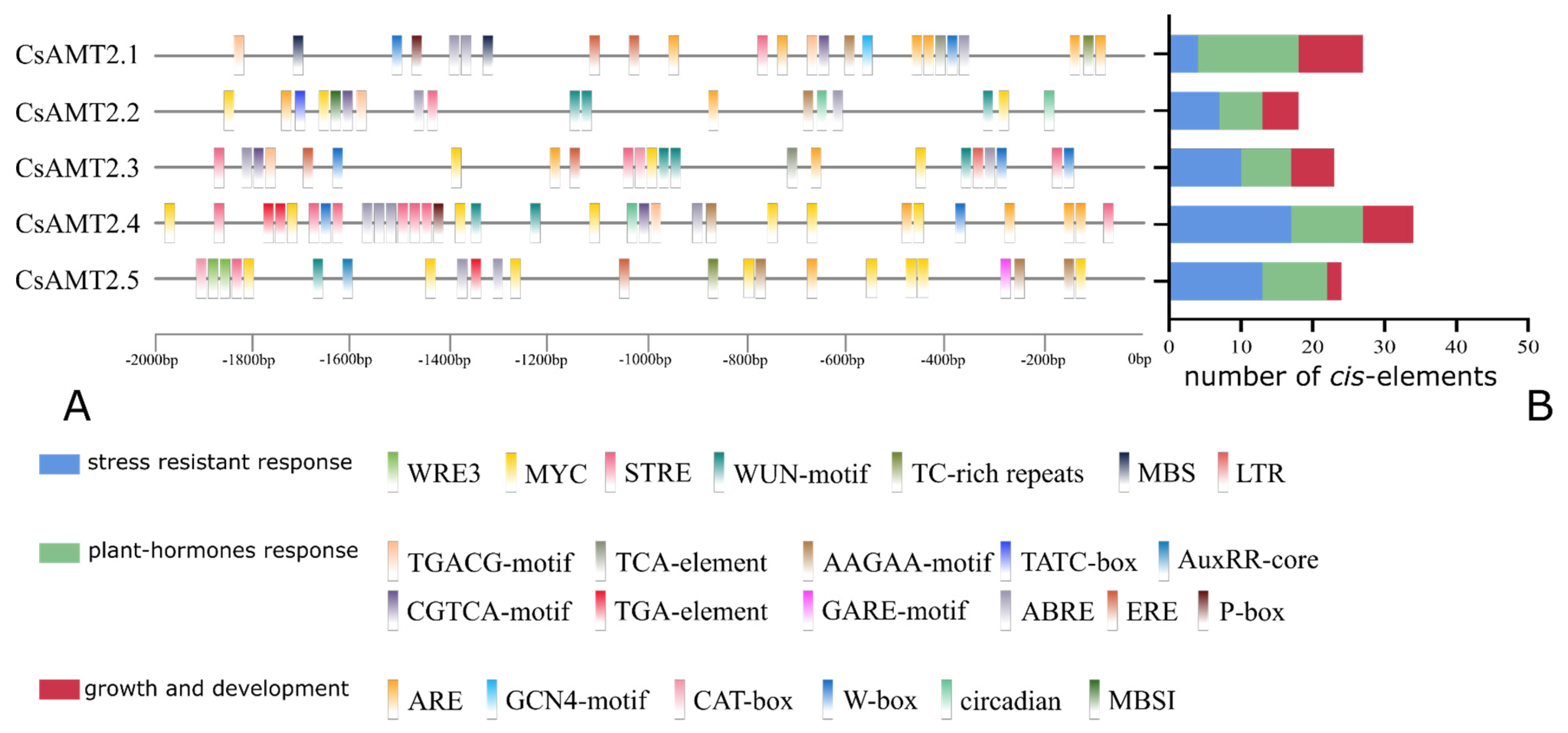
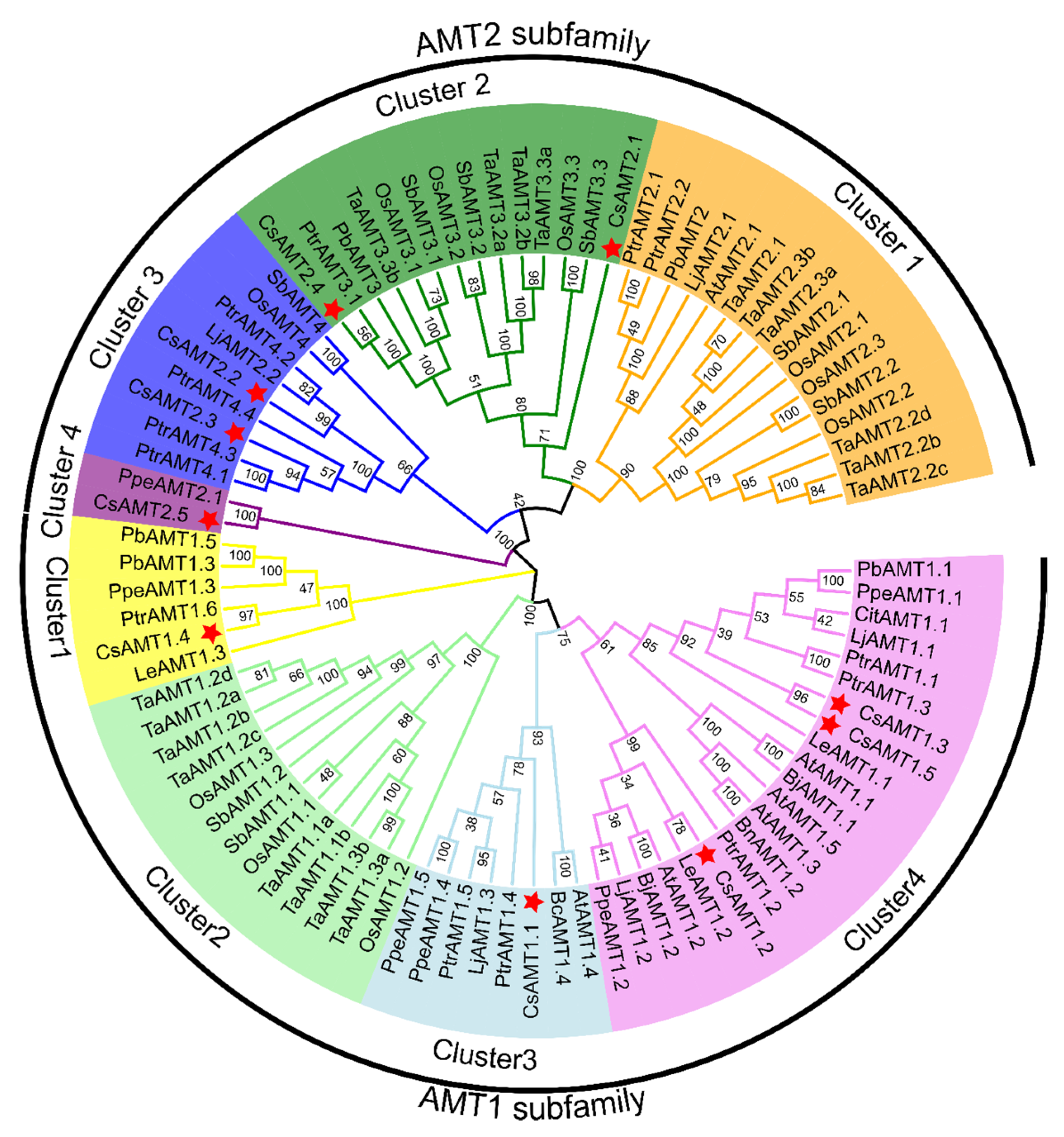
| Gene Name | CDS Length | Amino Acids | MW (Da) | pI | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | GRAVY | Subcellular Localization | Number of Transmembrane Domain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CsAMT2.1 | 1428 | 475 | 51,052.80 | 7.07 | 31.26 | 103.96 | 0.537 | Plasma membrane | 11 |
| CsAMT2.2 | 1437 | 478 | 51,958.98 | 6.06 | 28.83 | 108.33 | 0.572 | Plasma membrane | 11 |
| CsAMT2.3 | 1419 | 472 | 51,984.00 | 6.35 | 34.28 | 102.08 | 0.529 | Plasma membrane | 11 |
| CsAMT2.4 | 1458 | 485 | 52,467.24 | 7.07 | 30.20 | 99.15 | 0.470 | Plasma membrane | 11 |
| CsAMT2.5 | 1410 | 469 | 51,564.57 | 9.12 | 35.29 | 102.94 | 0.455 | Plasma membrane | 11 |
| Cultivars | Vmax (mmol·N·g−1·root·DW d−1) | Km (mmol·N·L−1) | α (Vmax/Km) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FD | 1.628 ± 0.24 | 0.893 ± 0.27 | 1.823 | 0.911 |
| HD | 1.346 ± 0.35 | 0.953 ± 0.64 | 1.412 | 0.840 |
| MX | 1.157 ± 0.39 | 0.384 ± 0.13 | 3.013 | 0.873 |
| Mean | 1.377 | 0.743 | 2.083 | / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Lin, L.; Wang, T.; Chen, M.; Song, B.; Sun, W. Genome-Wide Identification of AMT2-Type Ammonium Transporters Reveal That CsAMT2.2 and CsAMT2.3 Potentially Regulate NH4+ Absorption among Three Different Cultivars of Camellia sinensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415661
Zhang W, Lin L, Wang T, Chen M, Song B, Sun W. Genome-Wide Identification of AMT2-Type Ammonium Transporters Reveal That CsAMT2.2 and CsAMT2.3 Potentially Regulate NH4+ Absorption among Three Different Cultivars of Camellia sinensis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(24):15661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415661
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenjing, Lin Lin, Tao Wang, Mingjie Chen, Bo Song, and Weijiang Sun. 2022. "Genome-Wide Identification of AMT2-Type Ammonium Transporters Reveal That CsAMT2.2 and CsAMT2.3 Potentially Regulate NH4+ Absorption among Three Different Cultivars of Camellia sinensis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 24: 15661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415661
APA StyleZhang, W., Lin, L., Wang, T., Chen, M., Song, B., & Sun, W. (2022). Genome-Wide Identification of AMT2-Type Ammonium Transporters Reveal That CsAMT2.2 and CsAMT2.3 Potentially Regulate NH4+ Absorption among Three Different Cultivars of Camellia sinensis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(24), 15661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415661






