Olfactory Gene Families in Scopula subpunctaria and Candidates for Type-II Sex Pheromone Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Overview of Antennae Transcriptomes and Identification of Olfactory Gene Families in S. subpunctaria
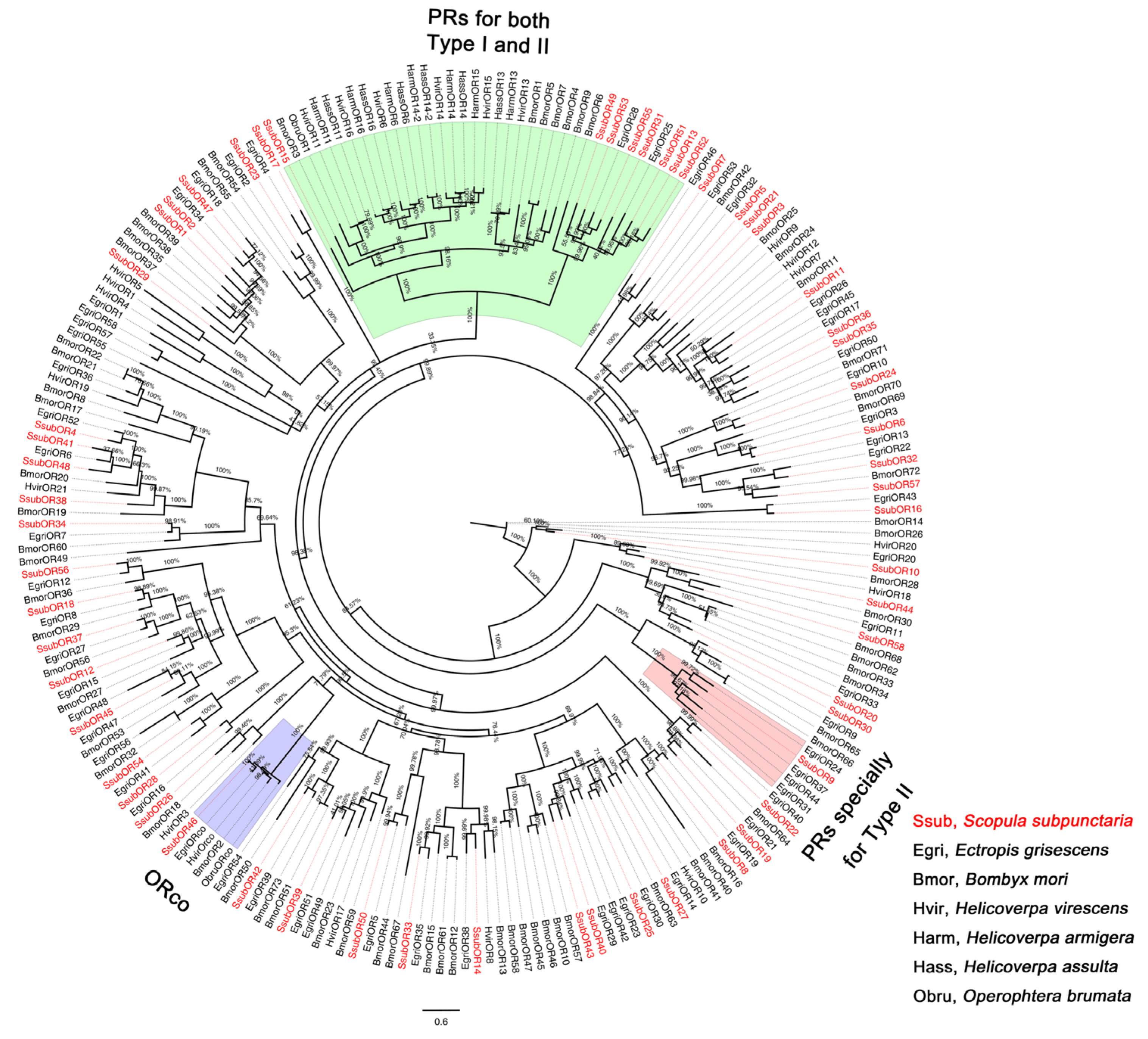
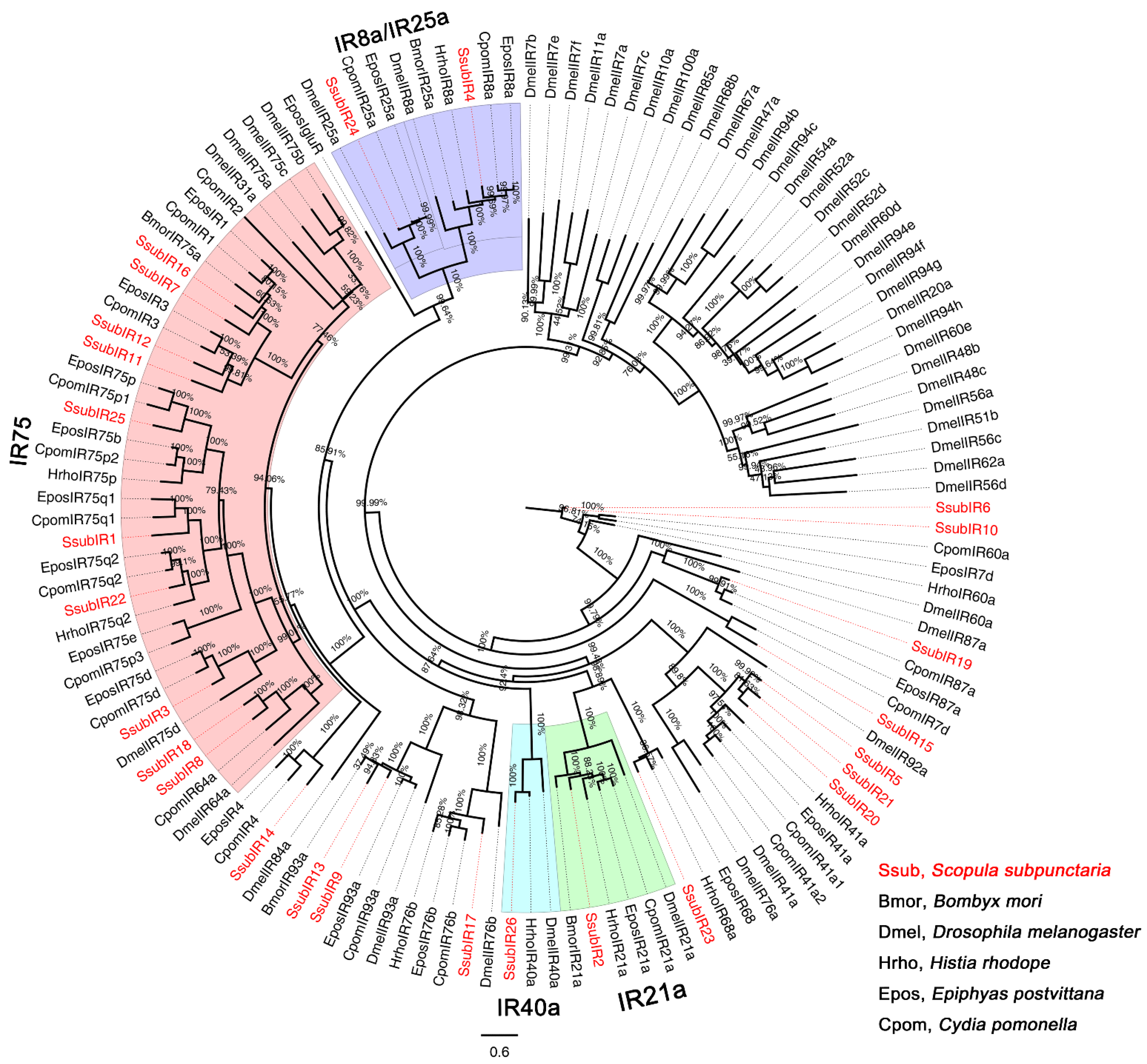
2.2. Phylogenetic Analyses of S. subpunctaria OR, IR, and OBP Genes
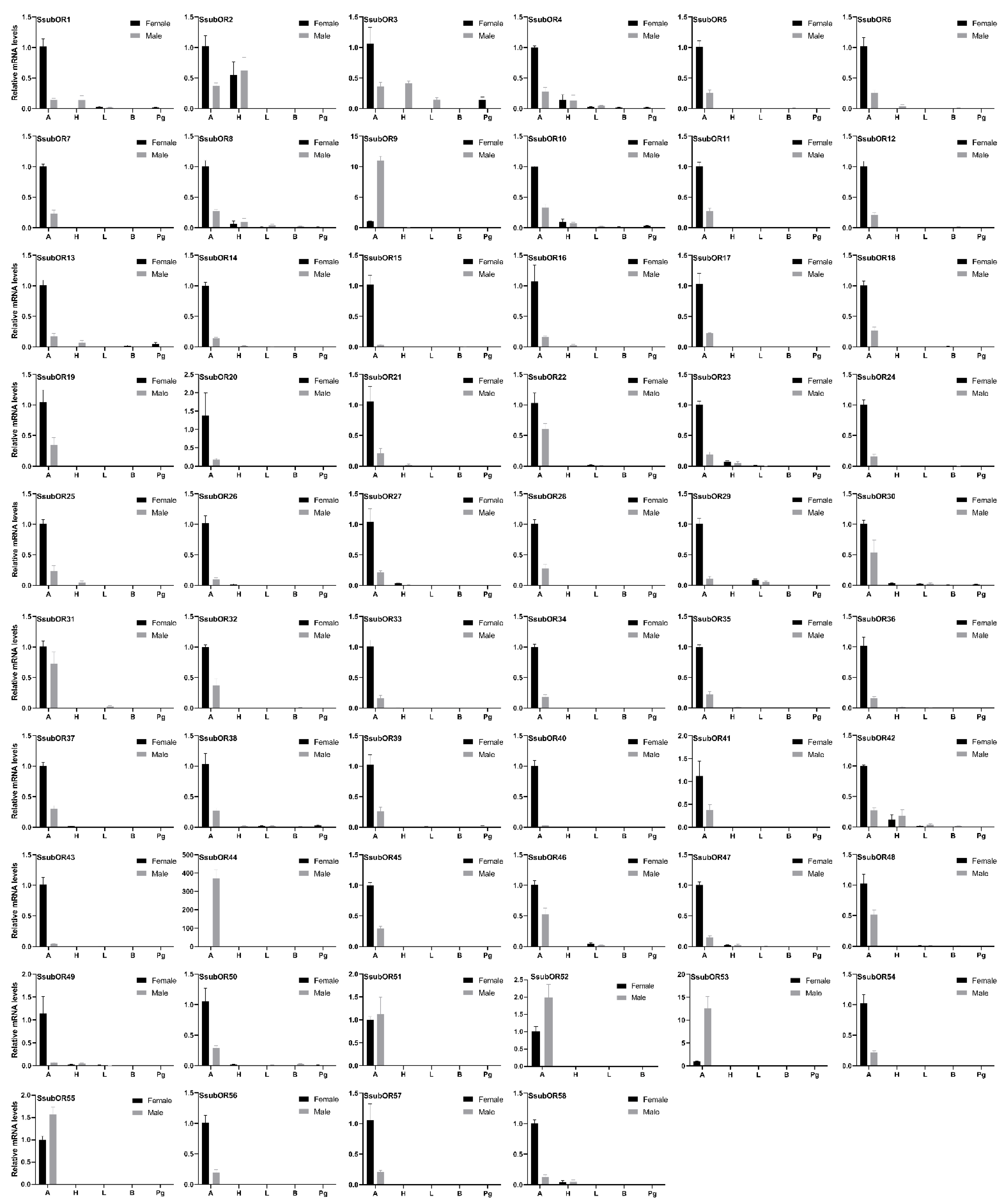
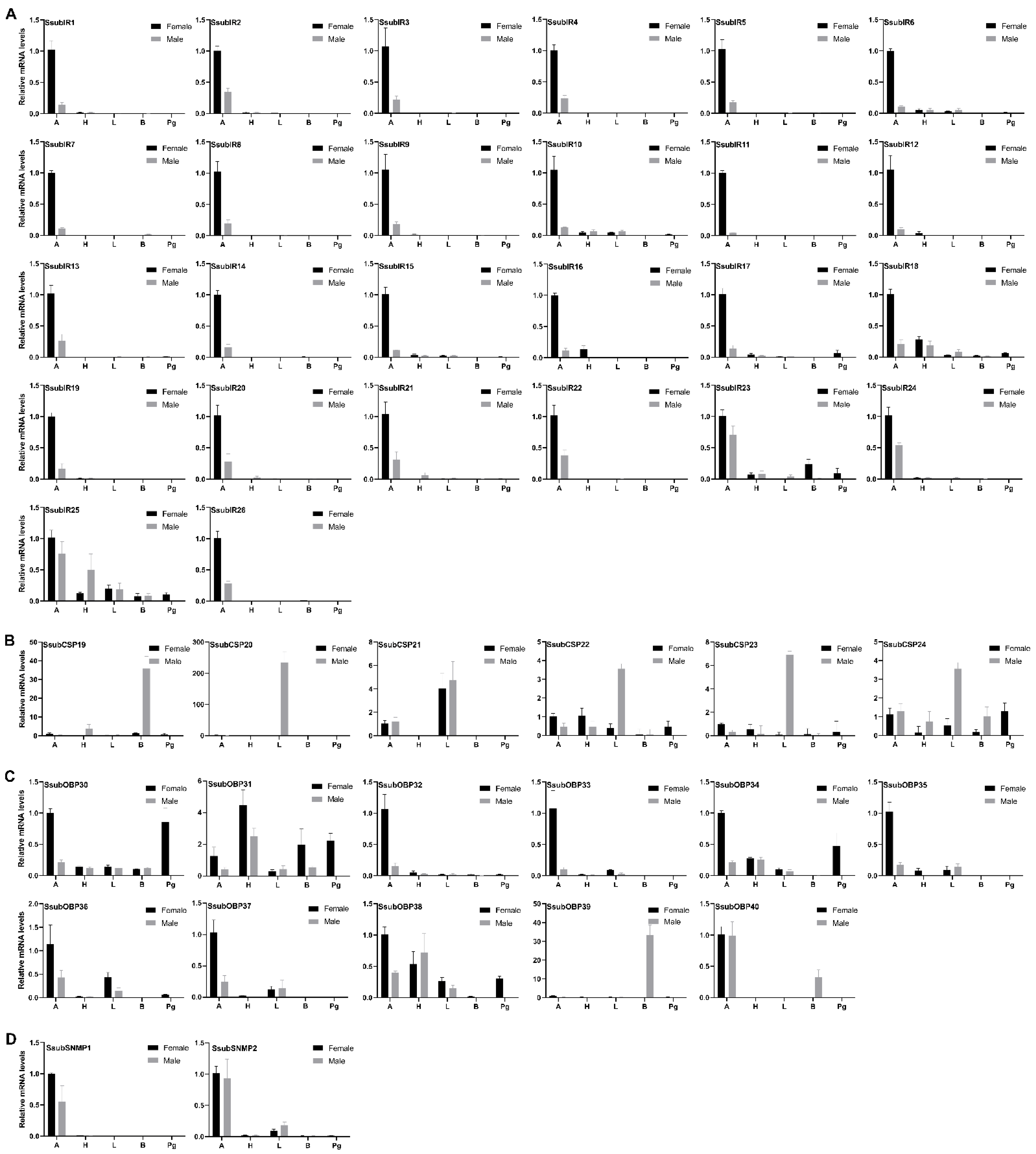
2.3. Tissue Expression Profile of S. subpunctaria Olfactory Genes
2.4. Abundance of S. subpunctaria Olfactory Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insect Samples and Tissue Collection
4.2. cDNA Library Construction, Illumina Sequencing, Assembly, and Annotation
4.3. Identification and Phylogenetic Tree Analysis of Olfactory Gene Families in S. subpunctaria
4.4. Analysis of Differential Gene Expression
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Validation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Segura-Leon, O.L.; Torres-Huerta, B.; Estrada-Perez, A.R.; Cibrian-Tovar, J.; Hernandez-Hernandez, F.C.; Cruz-Jaramillo, J.L.; Meza-Hernandez, J.S.; Sanchez-Galicia, F. Identification of candidate chemosensory gene families by head transcriptomes analysis in the mexican fruit fly, Anastrepha ludens Loew (Diptera: Tephritidae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, W.S. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, B.S.; Stensmyr, M.C. Evolution of insect olfaction. Neuron 2011, 72, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Li, Z.Q.; Luo, Z.X.; Cai, X.M.; Bian, L.; Xin, Z.J.; Chen, Z.M. Comparison of male antennal morphology and sensilla physiology for sex pheromone olfactory sensing between sibling moth species: Ectropis grisescens and Ectropis obliqua (Geometridae). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 101, e21545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofstedt, C.; Wahlberg, N.; Millar, J.G. Evolutionary Patterns of Pheromone Diversity in Lepidoptera; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 43–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ando, T.; Inomata, S.; Yamamoto, M. Lepidopteran sex pheromones. In Chemistry of Pheromones and Other Semiochemicals I; Schulz, S., Ed.; Springer-Verlag Press: Berlin, Germany, 2004; Volume 239, pp. 51–96. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Guo, P.P.; Sun, Y.L.; Huang, L.Q.; Wang, C.Z. Contribution of odorant binding proteins to olfactory detection of (Z)-11-hexadecenal in Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 131, 103554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damberger, F.F.; Michel, E.; Ishida, Y.; Leal, W.S.; Wuthrich, K. Pheromone discrimination by a pH-tuned polymorphism of the Bombyx mori pheromone-binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18680–18685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, H.T.; Liu, Y.; Ai, D.; Jiang, X.C.; Dong, S.L.; Wang, G.R. A pheromone antagonist regulates optimal mating time in the moth Helicoverpa armigera. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1610–1615.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.J.; Xu, W.; Chen, Q.M.; Sun, L.N.; Anderson, A.; Xia, Q.Y.; Papanicolaou, A. A phylogenomics approach to characterizing sensory neuron membrane proteins (SNMPs) in Lepidoptera. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 118, 103313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ban, L.P.; Song, L.M.; Liu, Y.; Pelosi, P.L.; Wang, G.R. General odorant-binding proteins and sex pheromone guide larvae of Plutella xylostella to better food. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 72, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.Y.; Yang, K.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Anderson, A.; Dong, S.L. Two general-odorant binding proteins in Spodoptera litura are differentially tuned to sex pheromones and plant odorants. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 180, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.Y.; Yang, F.; Yang, K.; He, P.; Niu, X.H.; Xu, W.; Anderson, A.; Dong, S.L. Two subclasses of odorant-binding proteins in Spodoptera exigua display structural conservation and functional divergence. Insect Mol. Biol. 2014, 24, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, S.; Luo, J.Y.; Zhu, J.; Cui, J.J.; Dong, S.L. Expression analysis and binding assays in the chemosensory protein gene family indicate multiple roles in Helicoverpa armigera. J. Chem. Ecol. 2015, 41, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Ye, Z.F.; Yang, K.; Dong, S.L. Antenna-predominant and male-biased CSP19 of Sesamia inferens is able to bind the female sex pheromones and host plant volatiles. Gene 2014, 536, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, T.W.; He, Z.; Gorur-Shandilya, S.; Menuz, K.; Larter, N.K.; Stewart, S.; Carlson, J.R. The Drosophila IR20a clade of ionotropic receptors are candidate taste and pheromone receptors. Neuron 2014, 83, 850–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, J.L.; Luo, Z.X.; Li, J.L.; Cai, X.M.; Bian, L.; Xiu, C.L.; Li, Z.Q.; Chen, Z.M.; Zhang, L.W. Identification of cytochrome P450, odorant-binding protein, and chemosensory protein genes involved in Type II sex pheromone biosynthesis and transportation in the tea pest, Scopula subpunctaria. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 169, 104650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.P.; Li, G.C.; Dong, J.F.; Gong, X.L.; Wang, L.; Yang, K.; Yang, J.; Huang, L.Q.; Wang, C.Z. The genetic basis of gene expression divergence in antennae of two closely related moth species, Helicoverpa armigera and Helicoverpa assulta. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Vasquez, G.M.; Schal, C.; Zwiebel, L.J.; Gould, F. Functional characterization of pheromone receptors in the tobacco budworm Heliothis virescens. Insect Mol. Biol. 2011, 20, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-Q.; Luo, Z.-X.; Cai, X.-M.; Bian, L.; Xin, Z.-J.; Liu, Y.; Chu, B.; Chen, Z.-M. Chemosensory gene families in Ectropis grisescens and candidates for detection of Type-II sex pheromones. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Huang, L.Q.; Gong, X.L.; Wang, C.Z. Comparison of functions of pheromone receptor repertoires in Helicoverpa armigera and Helicoverpa assulta using a Drosophila expression system. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 141, 103702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-Q.; Cai, X.-M.; Luo, Z.-X.; Bian, L.; Xin, Z.-J.; Chu, B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.-M. Comparison of olfactory genes in two Ectropis species: Emphasis on candidates involved in the detection of Type-II sex pheromones. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Liao, X.; Walker, W.B.; Li, J.; Wang, G. Identification of candidate olfactory genes in Chilo suppressalis by antennal transcriptome analysis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 846–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bastin-Heline, L.; de Fouchier, A.; Cao, S.; Koutroumpa, F.; Caballero-Vidal, G.; Robakiewicz, S.; Monsempes, C.; Francois, M.C.; Ribeyre, T.; Maria, A.; et al. A novel lineage of candidate pheromone receptors for sex communication in moths. eLife 2019, 8, e49826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, D.D.; Yuvaraj, J.K.; Corcoran, J.A.; Andersson, M.N.; Lofstedt, C. Functional characterization of odorant receptors from the moth Eriocrania semipurpurella: A comparison of results in the Xenopus oocyte and HEK cell systems. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 117, 103289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuvaraj, J.K.; Corcoran, J.A.; Andersson, M.N.; Newcomb, R.D.; Anderbrant, O.; Lofstedt, C. Characterization of odorant receptors from a non-ditrysian moth, Eriocrania semipurpurella sheds light on the origin of sex pheromone receptors in lepidoptera. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2733–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Raza, S.A.K.; Wei, Z.; Keesey, I.W.; Parker, A.L.; Feistel, F.; Chen, J.; Cassau, S.; Fandino, R.A.; Grosse-Wilde, E.; et al. Competing beetles attract egg laying in a hawkmoth. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Zhang, J.; Yan, Q.; Miao, C.L.; Han, W.K.; Hou, W.; Yang, K.; Hansson, B.S.; Peng, Y.C.; Guo, J.M.; et al. The molecular basis of host selection in a crucifer-specialized moth. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 4476–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, R.; Vannice, K.S.; Gomez-Diaz, C.; Vosshall, L.B. Variant ionotropic glutamate receptors as chemosensory receptors in Drosophila. Cell 2009, 136, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, A.; Zhang, M.; Ucpunar, H.K.; Svensson, T.; Quillery, E.; Gompel, N.; Ignell, R.; Grunwald Kadow, I.C. Ionotropic chemosensory receptors mediate the taste and smell of polyamines. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganguly, A.; Pang, L.; Duong, V.K.; Lee, A.; Schoniger, H.; Varady, E.; Dahanukar, A. A molecular and cellular context-dependent role for Ir76b in detection of amino acid taste. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Godino, L.L.; Rytz, R.; Cruchet, S.; Bargeton, B.; Abuin, L.; Silbering, A.F.; Ruta, V.; Dal Peraro, M.; Benton, R. Evolution of acid-sensing olfactory circuits in Drosophilids. Neuron 2017, 93, 661–676.e666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bisch-Knaden, S.; Fandino, R.A.; Yan, S.; Obiero, G.F.; Grosse-Wilde, E.; Hansson, B.S.; Knaden, M. The olfactory coreceptor IR8a governs larval feces-mediated competition avoidance in a hawkmoth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 21828–21833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, T.-T.; Luo, Z.-J.; Luo, Z.-X.; Cai, X.-M.; Bian, L.; Xiu, C.-L.; Fu, N.-X.; Chen, Z.-M.; Zhang, L.-W.; Li, Z.-Q. Olfactory Gene Families in Scopula subpunctaria and Candidates for Type-II Sex Pheromone Detection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15775. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415775
Yuan T-T, Luo Z-J, Luo Z-X, Cai X-M, Bian L, Xiu C-L, Fu N-X, Chen Z-M, Zhang L-W, Li Z-Q. Olfactory Gene Families in Scopula subpunctaria and Candidates for Type-II Sex Pheromone Detection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(24):15775. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415775
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Ting-Ting, Zi-Jun Luo, Zong-Xiu Luo, Xiao-Ming Cai, Lei Bian, Chun-Li Xiu, Nan-Xia Fu, Zong-Mao Chen, Long-Wa Zhang, and Zhao-Qun Li. 2022. "Olfactory Gene Families in Scopula subpunctaria and Candidates for Type-II Sex Pheromone Detection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 24: 15775. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415775
APA StyleYuan, T.-T., Luo, Z.-J., Luo, Z.-X., Cai, X.-M., Bian, L., Xiu, C.-L., Fu, N.-X., Chen, Z.-M., Zhang, L.-W., & Li, Z.-Q. (2022). Olfactory Gene Families in Scopula subpunctaria and Candidates for Type-II Sex Pheromone Detection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(24), 15775. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415775






