The Role of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 6 Regulation in Inflammation and Pain
Abstract
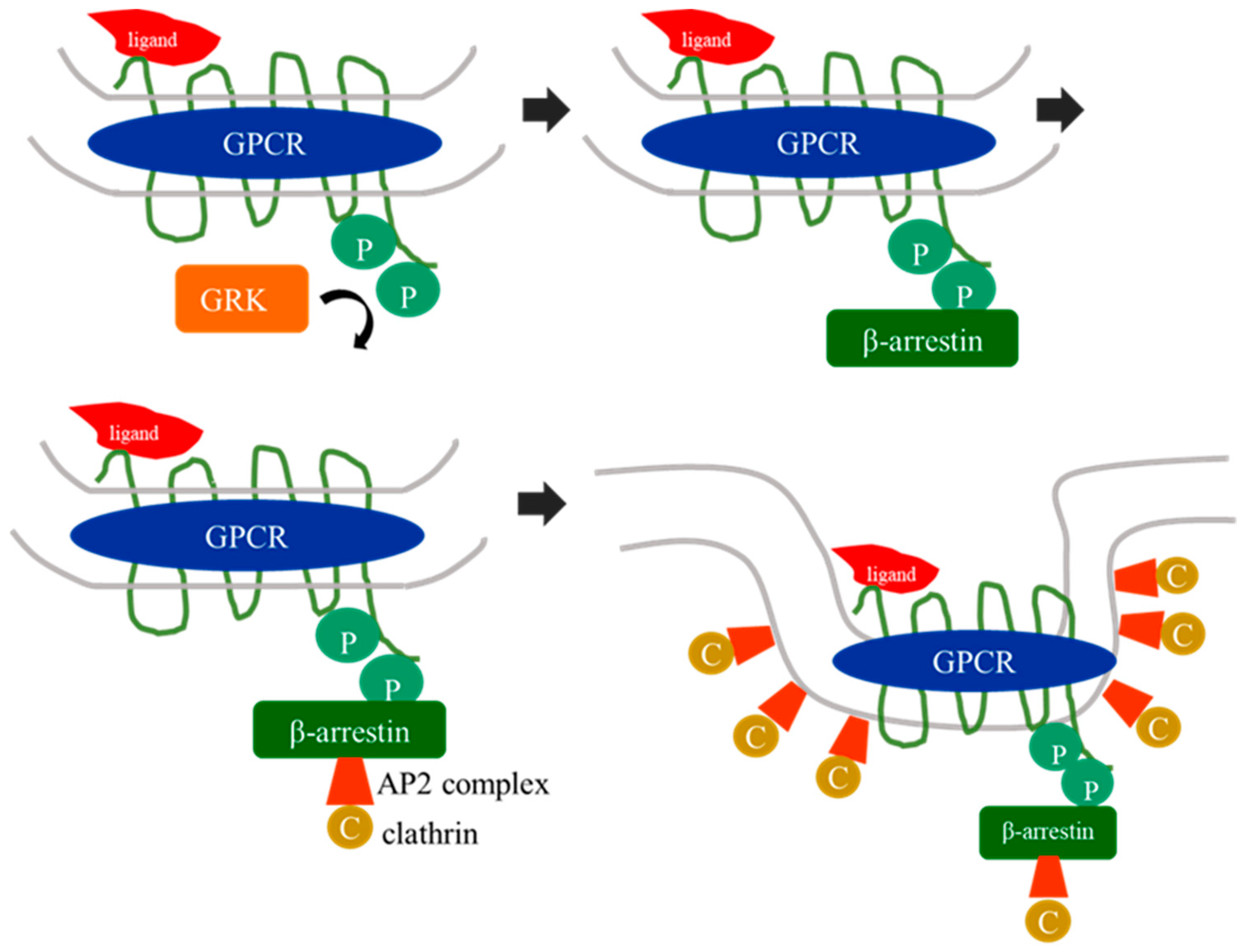
1. G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinases
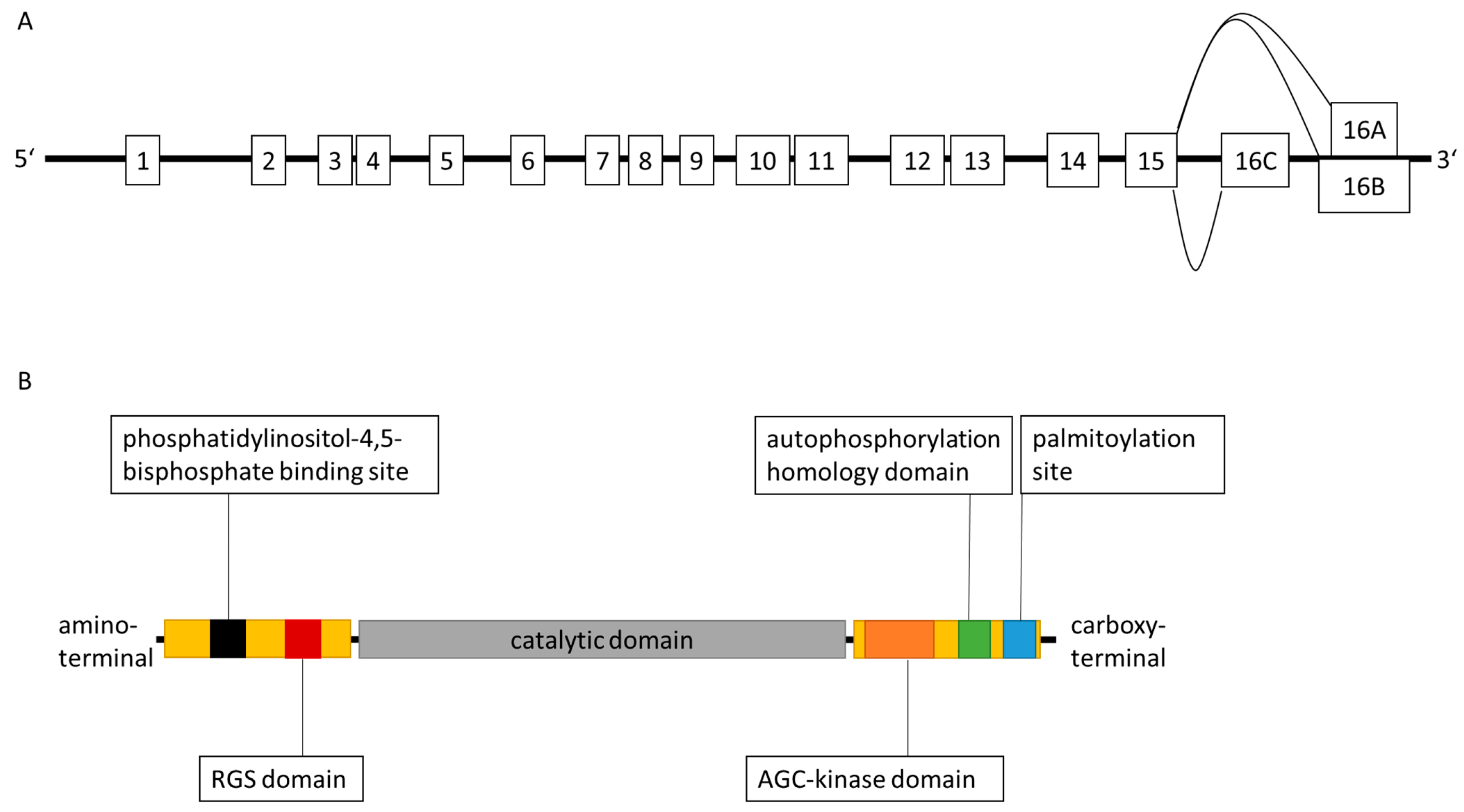
2. Characteristics of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 6
3. GRK6 in the Clinical Setting of Inflammation and Inflammatory Hyperalgesia
4. GRK6-Knockout Studies Addressing Inflammation and Hyperalgesia
5. GRK6 in Autoimmunity
6. The Potential Role of GRK6 in Chemotaxis
| Receptor | Main G Protein Coupled | Main Ligand | Main Signaling Pathways Induced | Impact of GRK6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor (CGRP-R) | Gs Gi/o Gaq/11 | calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) | - activation of cAMP production via adenylate cyclase - calcium mobilisation via phospholipase C β [80] | GRK6 is involved in receptor downregulation [79] |
| C-C receptor 7 (CCR7) | Gi | CCL19 > CCL21 | - inhibition of cAMP production - β arrestin- mediated MAP kinase signaling [81] | GRK6 deficiency impairs β arrestin recruitment to CCR7 [73] |
| chemokine-like receptor 1 (CMKLR1) | Gi Go | chemerin resolvin E1 | - calcium mobilisation via phospholipase C β - inhibition of cAMP production - MAP kinase signaling - phosphatidylinositol 3- kinase (PI3K) signaling [82] | GRK6- and β arrestin 2-deficiency leads to increased migration upon chemerin binding [74] GRK6 deficiency leads to increased Akt phosphorylation upon chemerin binding [74] |
| C-X-C receptor type 4 (CXCR4) | Gi | CXCL12 (also titled SDF1α) | - extracellular signal-related kinases (ERK) 1/2 | mutation of CXCR4 leads to impaired receptor silencing inter alia by GRK6 and results in WHIM syndrome (papilloma-virus induced warts, hypogammaglobulinemia, bacterial infection, myelokathexis) [66] GRK6-deficiency leads to impaired chemotaxis and transepithelial migration in B and T lymphocytes [67] GRK6-deficient neutrophils showed enhanced chemotaxis but reduced mobilisation from the bone marrow to the peripheral blood circulation [68] |
| leukotriene B4 receptor 1 (BLT1) | Gi [83] | leukotriene B4 | - activation of phospholipase C β via the Gβγ subunit, Ras, PI3K [84] | GRK6 deficiency promotes increased chemotactic activity in neutrophils and leads to an increased inflammatory reaction in response to arachidonic acid [72] |
| platelet- derived growth factor β receptor (PDGF-R) | tyrosine kinase receptor | platelet-derived growth factor | - MAP kinase signaling [85] - phospholipase C γ [85] - phosphatidyl- inositol 3-kinase [85] | activation of PDGF-R is associated with decreased GRK6 expression [86] |
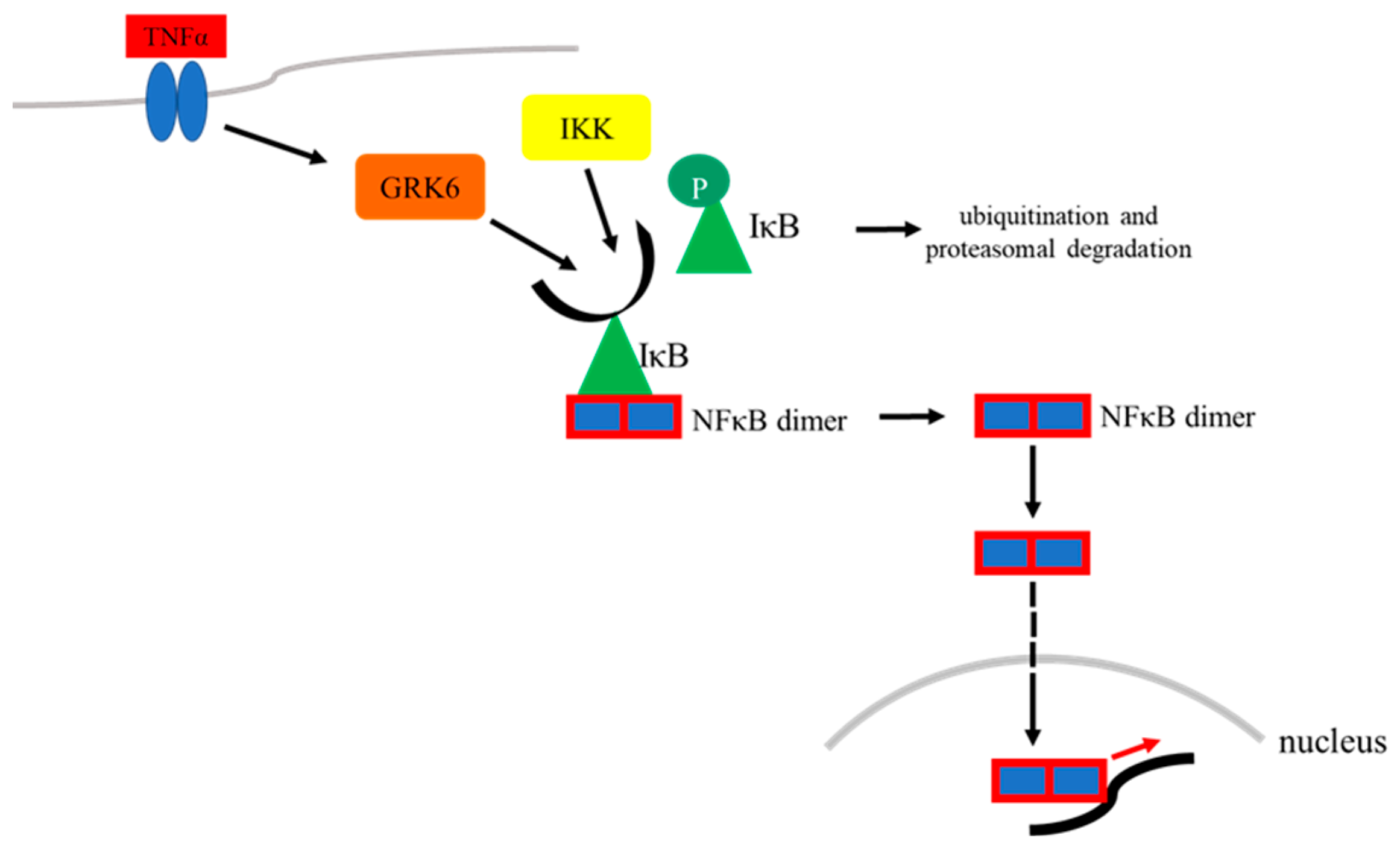
7. GRK6 in the Context of Transcriptional Regulation Mediated by NFκB
8. GRK6 Contributes to Reduced Hypoxia-Induced Factor 1-α Activity
9. GRK6 as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Treating Chronic Inflammatory Diseases
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ribas, C.; Penela, P.; Murga, C.; Salcedo, A.; Garcia-Hoz, C.; Jurado-Pueyo, M.; Aymerich, I.; Mayor, F., Jr. The G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) interactome: Role of GRKs in GPCR regulation and signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1768, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisatomi, O.; Matsuda, S.; Satoh, T.; Kotaka, S.; Imanishi, Y.; Tokunaga, F. A novel subtype of G-protein-coupled receptor kinase, GRK7, in teleost cone photoreceptors. FEBS Lett. 1998, 424, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.; Virmaux, N.; Mandel, P. Light-stimulated phosphorylation of rhodopsin in the retina: The presence of a protein kinase that is specific for photobleached rhodopsin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premont, R.T.; Macrae, A.D.; Aparicio, S.A.J.R.; Kendall, H.E.; Welch, J.E.; Lefkowitz, R.J. The GRK4 subfamily of G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 29381–29389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallese, M.; Marrigio, S.; Collodel, G.; Moretti, E.; Piomboni, P.; Baccetti, B.; De Blasi, A. G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinase 4: GRK4. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 10188–10195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virlon, B.; Firsov, D.; Cheval, L.; Reiter, E.; Troispoux, C.; Guillou, F.; Elalouf, J.M. Rat G protein-coupled receptor kinase GRK4: Identification, functional expression, and differential tissue distribution of two splice variants. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 2784–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedemann, R.E.; Zhu, Y.X.; Schmidt, J.; Yin, H.; Shi, C.X.; Que, Q.; Basu, G.; Azorsa, D.; Perkins, L.M.; Braggio, E.; et al. Kinome-wide RNAi studies in human multiple myeloma identify vulnerable kinase targets, including a lymphoid-restricted kinase, GRK6. Blood 2010, 115, 1594–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallese, M.; Salvatore, L.; d’Urbano, E.; Sala, G.; Storto, M.; Launey, T.; Nicoletti, F.; Knöpfel, T.; De Blasi, A. The G-protein-coupled receptor kinase GRK4 mediates homologous desensitization of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 2569–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, E.; Lefkowitz, R.J. GRKs and beta-arrestins: Roles in receptor silencing, trafficking and signaling. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 17, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S.K.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Multifaceted roles of beta-arrestins in the regulation of seven-membrane-spanning receptor trafficking and signalling. Biochem. J. 2003, 375, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefkowitz, R.J. Seven transmembrane receptors: Something old, something new. Acta Physiol. 2007, 190, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, L.S.; Molliver, D.C. In search of analgesia—Emerging roles of GPCRs in pain. Mol. Interv. 2009, 9, 234–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lymperopoulos, A.; Cora, N.; Maning, J.; Brill, A.R.; Sizova, A. Signaling and function of cardiac autonomic nervous system receptors: Insights from the GPCR signalling universe. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 2645–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palczewski, K. Chemistry and biology of vision. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spehr, M.; Munger, S.D. Olfactory receptors: G protein-coupled receptors and beyond. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, T. Advances in the Treatment of Chronic Pain by Targeting GPCRs. Biochemistry 2021, 60, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Ye, R.D. Role of G protein-coupled receptors in inflammation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leurs, R.; Smit, M.J.; Alewijnse, A.E.; Timmerman, H. Agonist-independent regulation of constitutively active G protein-coupled receptors. TIBS 1998, 23, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smrcka, A.V. G protein betagamma subunits: Central mediators of G protein-coupled receptor signaling. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 2191–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisyunov, A.I. Molecular mechanisms of G protein-independent signaling mediated by 7-transmembrane receptors. Neurophysiology 2012, 44, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, J.A.; Freedman, N.J.; Lefkowitz, R.J. G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 652–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, K.L.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Classical and new roles of b-arrestins in the regulation of G-protein-coupled receptors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maib, H.; Smythe, E.; Ayscough, K. Forty years on: Clathrin-coated pits continue to fascinate. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobles, K.N.; Xiao, K.; Ahn, S.; Shukla, A.K.; Lam, C.M.; Rajagopal, S.; Strachan, R.T.; Huang, T.Y.; Bressler, E.A.; Hara, M.R.; et al. Distinct phosphorylation sites on the beta(2)-adrenergic receptor establish a barcode that encodes differential functions of beta-arrestin. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, ra51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, A.; Fujimoto, J.; Miyata, H.; Stumm, R.; Narazaki, M.; Schulz, S.; Baba, Y.; Kumanogoh, A.; Suzuki, K. The COMMD3/8 complex determines GRK6 specificity for chemoattractant receptors. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 1630–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, A.; Benovic, J.L. Identification and chromosomal localization of a processed pseudogene of human GRK6. Gene 1997, 184, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullrich, F.; Druck, T.; Kunapuli, P.; Gomez, J.; Gripp, K.W.; Schlegelberger, B.; Lasota, J.; Aronson, M.; Cannizzarro, L.A.; Huebner, K.; et al. Chromosomal mapping of the genes GPRK5 und GPRK6 encoding G protein-coupled receptor kinases GRK5 und GRK6. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1995, 70, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benovic, J.L.; Gomez, J. Molecular cloning and expression of GRK6. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 19521–19527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palczewski, K. GTP-binding-protein-coupled receptor kinases: Two mechanistic models. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 248, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffel, R.H.; Randall, R.R.; Premont, R.T.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Inglese, J. Palmitoylation of G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinase, GRK6. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 27791–27794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Benovic, J.L.; Wedegaertner, P.B. Plasma membrane and nuclear localization of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6A. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 2960–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moepps, B.; Vatter, P.; Frodl, R.; Waechter, F.; Dixkens, C.; Hameister, H.; Gierschick, P. Alternative splicing produces transcripts encoding four variants of mouse G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 6. Genomics 1999, 60, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.R.; Scott, M.G.; Pitcher, J.A. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 contains a DNA-binding nuclear localization sequence. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 10169–10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.R.; Robinson, J.D.; Lester, K.N.; Pitcher, J.A. Distinct structural features of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 (GRK5) regulate its nuclear localization and DNA-binding ability. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Gomez, A.; Mellstrom, B.; Tornero, D.; Morato, E.; Savignac, M.; Holguin, H.; Aurrekoetxea, K.; Gonzalez, P.; Gonzalez-Garcia, C.; Cena, V.; et al. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2-mediated phosphorylation of downstream regulatory element antagonist modulator regulates membrane trafficking of Kv4.2 potassium channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Wu, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, P.; Lv, X.; Huang, J. Hypermethylation of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 (GRK6) promoter inhibits binding of C/EBPα, and GRK6 knockdown promotes cell migration and invasion in lung adenocarcinoma cells. FEBS Open Bio. 2019, 9, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, M.; Engler, A.; Ochsenfarth, C.; Manthey, I.; Peters, J.; Siffert, W.; Frey, U.H. Characterization of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 promoter reveals a functional CREB binding site. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Zhong, L.; Liu, J.; Feng, J.; Bian, T.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Lv, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y. Prognostic value of decreased GRK6 expression in lung adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 2541–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; You, Y.; Wang, Z. Aberrant GRK6 promoter methylation is associated with poor prognosis in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hepler, J.R. Emerging roles for RGS proteins in signaling. TiPS 1999, 20, 376–382. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, L.R.; Komander, D.; Alessi, D.R. The nuts and bolts of AGC kinases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loudon, R.P.; Benovic, J.L. Expression, purification, and characterization of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase GRK6. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 36, 22691–22697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, M.S.; Kavelaars, A.; Schedlowski, M.; Bijlsma, J.; Okihara, K.; van de Pol, M.; Ochsmann, S.; Pawlak, C.; Schmidt, R.E.; Heijnen, C.J. Decreased expression and activity of G-protein coupled receptor kinases in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. FASEB J. 1999, 13, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, M.S.; Kavelaars, A.; Cobelens, P.M.; Schmidt, R.E.; Schedlowski, M.; Heijnen, C.J. Adjuvant arthritis induces down-regulation of G protein-coupled receptor kinases in the immune system. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 1635–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroon, A.; Lombardi, M.S.; Kavelaars, A.; Heijnen, C.J. Changes in the G protein-coupled receptor desensitization machinery during relapsing-progressive experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2003, 137, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, S.A.; Kondyra, A.L.; Grocott, H.P.; El-Moalem, H.; Bainbridge, D.; Mathew, J.P.; Newman, M.F.; Reves, J.G.; Schwinn, D.A.; Kwatra, M.M. Cardiopulmonary bypass decreases G protein–coupled receptor kinase activity and expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Anesthesiology 2003, 98, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijkelkamp, N.; Heijnen, C.J.; Elsenbruch, S.; Holtmann, G.; Schedlowski, M.; Kavelaars, A. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 controls post-inflammatory visceral hyperalgesia. Brain Behav. Immun. 2009, 23, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijkelkamp, N.; Heijnen, C.J.; Lucas, A.; Premont, R.T.; Elsenbruch, S.; Schedlowski, M.; Kavelaars, A. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 controls chronicity and severity of dextran sodium sulphate-induced colitis in mice. Gut 2007, 56, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijkelkamp, N.; Heijnen, C.J.; Carbajal, A.G.; Willemen, H.L.; Wang, H.; Minett, M.S.; Wood, J.N.; Schedlowski, M.; Dantzer, R.; Kelley, K.W.; et al. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 acts as a critical regulator of cytokine-induced hyperalgesia by promoting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and inhibiting p38 signaling. Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Packiriswamy, N.; Lee, E.; Lucas, P.C.; McCabe, L.R.; Parameswaran, N. Role of G protein-coupled receptor kinase-6 in Escherichia coli lung infection model in mice. Physiol. Genom. 2017, 49, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrant, T.K.; Rampersad, R.R.; Esserman, D.; Rothlein, L.R.; Liu, P.; Premont, R.T.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Lee, D.M.; Patel, D.D. Granulocyte chemotaxis and disease expression are differentially regulated by GRK subtype in an acute inflammatory arthritis model (K/BxN). Clin. Immunol. 2008, 129, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, R.J.; Li, M.; Liu, X.; Zhu, H.Y.; Ju, Z.; Miao, X.; Xu, G.Y. Overexpression of GRK6 attenuates neuropathic pain via suppression of CXCR2 in rat dorsal root ganglion. Mol. Pain 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Gao, Y.; Lou, D.; Wu, X.; Wei, H.; Wen, H.; Deng, X.; Zhang, F. Expression of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 (GRK6) after acute spinal cord injury in adult rat. J. Mol. Histol. 2013, 44, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaya, M.; Tajima, M.; Kosako, H.; Nakaya, T.; Hashimoto, A.; Watari, K.; Nishihara, H.; Ohba, M.; Komiya, S.; Tani, N.; et al. GRK6 deficiency in mice causes autoimmune disease due to impaired apoptotic cell clearance. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, I.K.; Lucas, C.D.; Rossi, A.G.; Ravichandran, K.S. Apoptotic cell clearance: Basic biology and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proots, P.; Wuyts, A.; Van Damme, J. The role of chemokines in inflammation. Int. J. Clin. Lab. Res. 1996, 26, 211–223. [Google Scholar]
- Cardona, A.E.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Savarin, C.; Ransohoff, R.M. Chemokines in and out of the central nervous system: Much more than chemotaxis and inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 84, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, R.; Struyf, S.; Proost, P. The unique structural and functional features of CXCL12. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, B.; Willimann, K. Chemokines: Role in inflammation and immune surveillance. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, ii84–ii89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagana, M.; Schlecht-Louf, G.; Bachelerie, F. The G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) in chemokine receptor-mediated immune cell migration: From molecular cues to physiopathology. Cell 2021, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircher, M.; Herhaus, P.; Schottelius, M.; Buck, A.K.; Werner, R.A.; Wester, H.J.; Keller, U.; Lapa, C. CXCR4-directed theranostics in oncology and inflammation. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2018, 32, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, I.B.; Ellingsen, T.; Hornung, N.; Poulsen, J.H.; Lottenburger, T.; Stengaard-Petersen, K. Plasma level of CXC-chemokine CXCL12 is increased in rheumtoid arthritis and is independent of disease activity and methotrexate treatment. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 9, 1754–1759. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, L.; Guzner-Gur, H.; Dotan, I. Involvement of CXCR4/CXCR7/CXCL12 Interactions in Inflammatory bowel disease. Theranostics 2013, 3, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero, A.; Mahn, S.A.; Ali, M.S.; Rogers, M.R.; Marchese, A. Heterologous regulation of CXCR4 lysosomal trafficking. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 8023–8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busillo, J.M.; Armando, S.; Sengupta, R.; Meucci, O.; Bouvier, M.; Benovic, J.L. Site-specific phosphorylation of CXCR4 is dynamically regulated by multiple kinases and results in differential modulation of CXCR4 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 7805–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, P.J.; Segarra, M.; Gasperini, P.; Gulino, A.V.; Tosato, G. Impaired recruitment of Grk6 and beta-Arrestin 2 causes delayed internalization and desensitization of a WHIM syndrome-associated CXCR4 mutant receptor. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, A.M.; Premont, R.T.; Richardson, R.M.; Yu, Y.-R.A.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Patel, D.D. Defective lymphocyte chemotaxis in b-arrestin2- and GRK6-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7478–7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroon, A.; Heijnen, C.J.; Raatgever, R.; Touw, I.P.; Ploemacher, R.E.; Premont, R.T.; Kavelaars, A. GRK6 deficiency is associated with enhanced CXCR4-mediated neutrophil chemotaxis in vitro and impaired responsiveness to G-CSF in vivo. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gennaro, A.; Haeggstrom, J.Z. Targeting leukotriene B4 in inflammation. Expert Opin. Targets 2014, 18, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lam, B.K.; Luster, A.D.; Zarini, S.; Murphy, R.C.; Bair, A.M.; Soberman, R.J.; Lee, D.M. Joint tissues amplify inflammation and alter their invasive behavior via leukotriene B4 in experimental inflammatory arthritis. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 5503–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudreau, R.; Le Gouill, C.; Venne, M.H.; Stankova, J.; Rola-Pleszczynski, M. Threonine 308 within a putative casein kinase 2 site of the cytoplasmic tail of leukotriene B(4) receptor (BLT1) is crucial for ligand-induced, G-protein-coupled receptor-specific kinase 6-mediated desensitization. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 31567–31576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavelaars, A.; Vroon, A.; Raatgever, R.P.; Fong, A.M.; Premont, R.T.; Patel, D.D.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Heijnen, C.J. Increased Acute Inflammation, Leukotriene B4-Induced Chemotaxis, and Signaling in Mice Deficient for G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 6. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 6128–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zidar, D.A.; Violin, J.D.; Whalen, E.J.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Selective engagement of G protein coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) encodes distanct functions of biased ligands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9649–9654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafin, D.S.; Allyn, B.; Sassano, M.F.; Timoshchenko, R.G.; Mattox, D.; Brozowski, J.M.; Siderovski, D.P.; Truong, Y.K.; Esserman, D.; Tarrant, T.K.; et al. Chemerin-activated functions of CMKLR1 are regulated by G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 (GRK6) and beta-arrestin 2 in inflammatory macrophages. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 106, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, K.; Miyabe, Y.; Takayasu, A.; Fukuda, S.; Miyabe, C.; Ebisawa, M.; Yokoyama, W.; Watanabe, K.; Imai, T.; Muramoto, K.; et al. Chemerin activates fibroblast-like synoviocytes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Palma, G.; Castellano, G.; Del Prete, A.; Sozzani, S.; Fiore, N.; Loverre, A.; Parmentier, M.; Gesualdo, L.; Grandaliano, G.; Schena, F.P. The possible role of ChemR23/Chemerin axis in the recruitment of dendritic cells in lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiyar, N.; Disa, J.; Dang, K.; Pronin, A.; Benovic, J.L.; Nambi, P. Involvement of G Protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 in Desensitization of CGRP receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 403, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schou, W.S.; Ashina, S.; Amin, F.M.; Goadsby, P.J.; Ashina, M. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and pain: A systematic review. J. Headache. Pain 2017, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuoha, G.N.; Alpar, E.K. Levels of vasodilatators (SP, CGRP) and vasoconstrictor (NPY) in early human burns. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 31, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, F.A.; King, R.; Smillie, S.J.; Kodji, X.; Brain, S.D. Calcitonin gene-related peptide: Physiology and pathophysiology. Brain Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 1099–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.D.; Lane, R.; Canals, M.; Stone, M.J. Systematic assessment of chemokine signalling at chemokine receptors CCR4, CCR7 and CCR10. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Henau, O.; Degroot, G.N.; Imbault, V.; Robert, V.; de Poorter, C.; Mcheik, S.; Gale, C.; Parmentier, M.; Springael, J.-Y. Signaling properties of chemerin receptors CMKLR1, GPR1 and CCRL2. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; He, X.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, X.; Xia, Y.; Xu, E.; He, Y. Structural basis of leukotriene B4 receptor 1 activation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, B.C.; Majumdar, R.; Parent, C.A. The role of LTB4-BLT1 axis in chemotactic gradient sensing and directed leukocyte migration. Semin. Immunol. 2021, 33, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montmayeur, J.P.; Valius, M.; Vandenheede, J.; Kazlaukas, A. The platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor triggers multiple cytoplasmic signaling cascades that arrive at the nucleus as distinguishable inputs. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 51, 32670–32678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Rubin, J.B.; Cho, Y.-J.; Shu, H.K.; Schniederjan, M.; MacDonald, T.J. Growth factor receptor-Src-mediated suppression of GRK6 dysregulates CXCR4 signaling and promotes medulloblastoma migration. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serasanambati, M.; Chilakapati, S.R. Function of Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-kB) in human diseases-A Review. South Indian J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 4, 368–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, Y.; Nakaya, M.; Watari, K.; Nagasaka, A.; Kurose, H. GRK6 phosphorylates IkappaBalpha at Ser(32)/Ser(36) and enhances TNF-alpha-induced inflammation. Biochem. Biophys Res. Commun. 2015, 461, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, Y.C.; Tian, Y.Q.; Zhang, P.A.; Hu, S.F.; Wang, L.H.; Jiang, X.H.; Xu, G.Y. Downregulation of GRK6 in arcuate nucleus promotes chronic visceral hypersensitivity via NF-kappaB upregulation in adult rats with neonatal maternal deprivation. Mol. Pain 2020, 16, 1744806920930858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Duan, D.; Wei, W.; Sun, Z.; Xu, H.; Guo, L.; Wu, X. MiR-19b-3p attenuates IL-1beta induced extracellular matrix degradation and inflammatory injury in chondrocytes by targeting GRK6. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2019, 459, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Ertay, A.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, L.; Hill, C.; Chen, J.; Guan, Y.; Sun, H.; Ewing, R.M.; Liu, Y.; et al. GRK6 Depletion Induces HIF Activity in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. 2021, 11, 654812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorres, K.L.; Raines, R.T. Prolyl 4-hydroxylase. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 45, 106–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, V.H. The VHL tumor suppressor: Master regulator of HIF. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balamurugan, K. HIF-1 at the crossroads of hypoxia, inflammation, and cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Sen, C.K. miRNA in wound inflammation and angiogenesis. Microcirculation 2012, 19, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thal, D.M.; Homan, K.T.; Chen, J.; Wu, E.K.; Hinkle, P.M.; Huang, Z.M.; Chuprun, J.K.; Song, J.; Gao, E.; Cheung, J.Y.; et al. Paroxetine is a direct inhibitor of g protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 and increases myocardial contractility. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1830–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehling, D.E.; Joseph, B.; Chung, K.C.; Zhang, A.X.; Ler, S.; Prakesch, M.A.; Poda, G.; Grouleff, J.; Aman, A.; Kiyota, T.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Characterization of 4-Aminoquinazolines as Potent Inhibitors of the G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 6 (GRK6) for the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 11129–11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stegen, M.; Frey, U.H. The Role of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 6 Regulation in Inflammation and Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415880
Stegen M, Frey UH. The Role of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 6 Regulation in Inflammation and Pain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(24):15880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415880
Chicago/Turabian StyleStegen, Maike, and Ulrich H. Frey. 2022. "The Role of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 6 Regulation in Inflammation and Pain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 24: 15880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415880
APA StyleStegen, M., & Frey, U. H. (2022). The Role of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 6 Regulation in Inflammation and Pain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(24), 15880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415880








