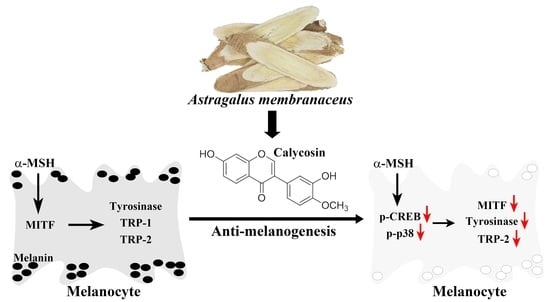
Calycosin, a Common Dietary Isoflavonoid, Suppresses Melanogenesis through the Downregulation of PKA/CREB and p38 MAPK Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
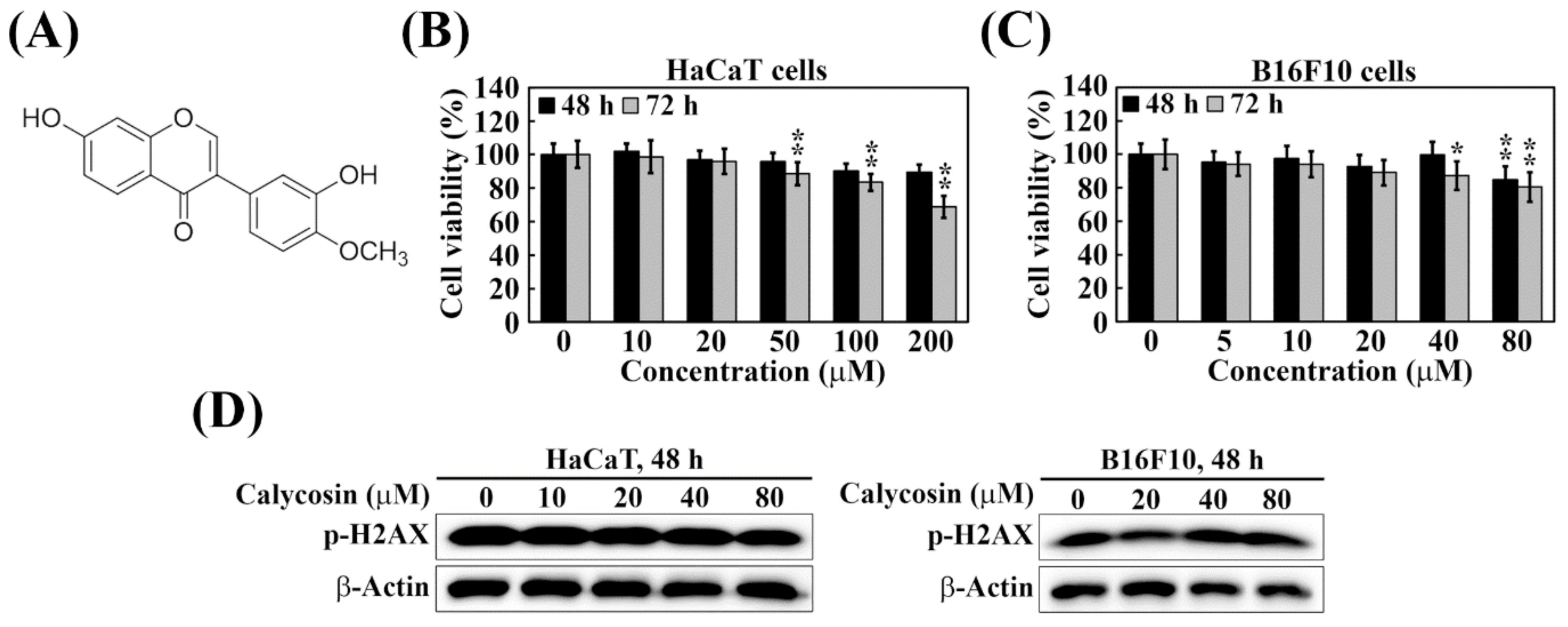
2.1. Calycosin Shows No Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity in B16F10 and HaCaT Cells
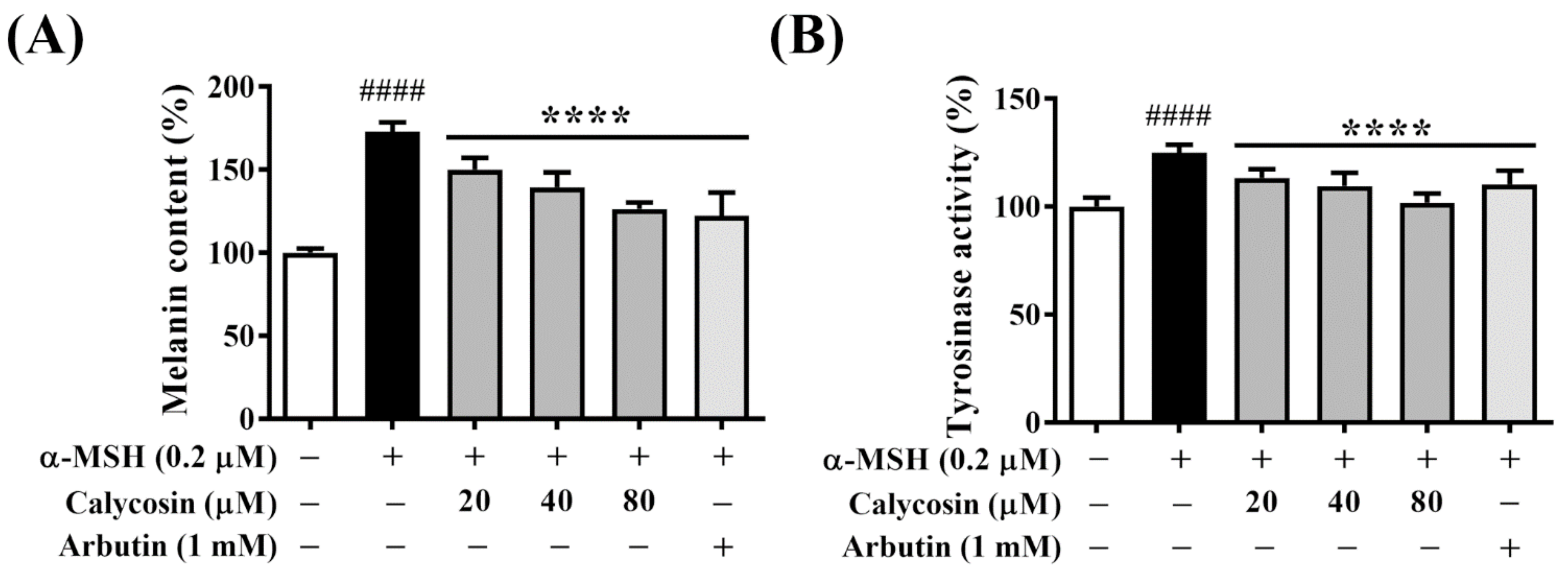
2.2. Calycosin Suppresses Melanin Synthesis and Tyrosinase Activity in B16F10 Cells
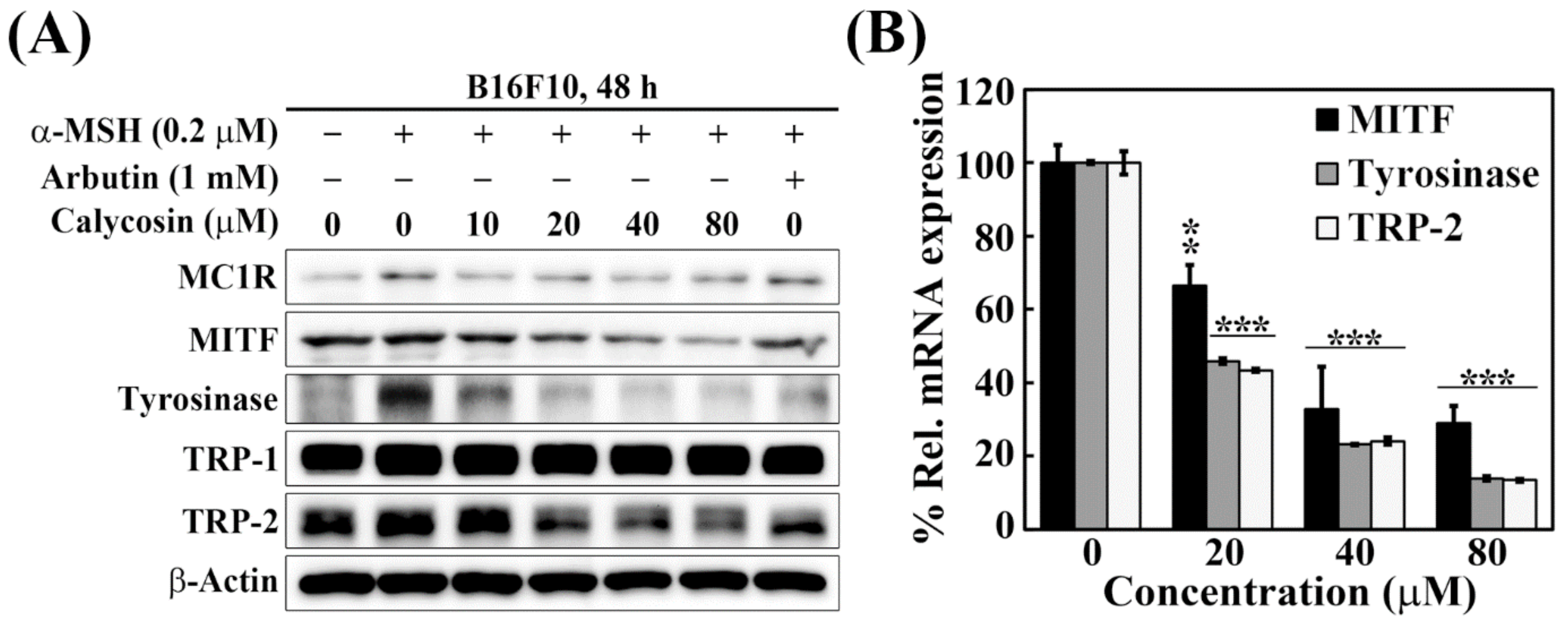
2.3. Effects of Calycosin on the Expression of Key Mediators of Melanogenesis
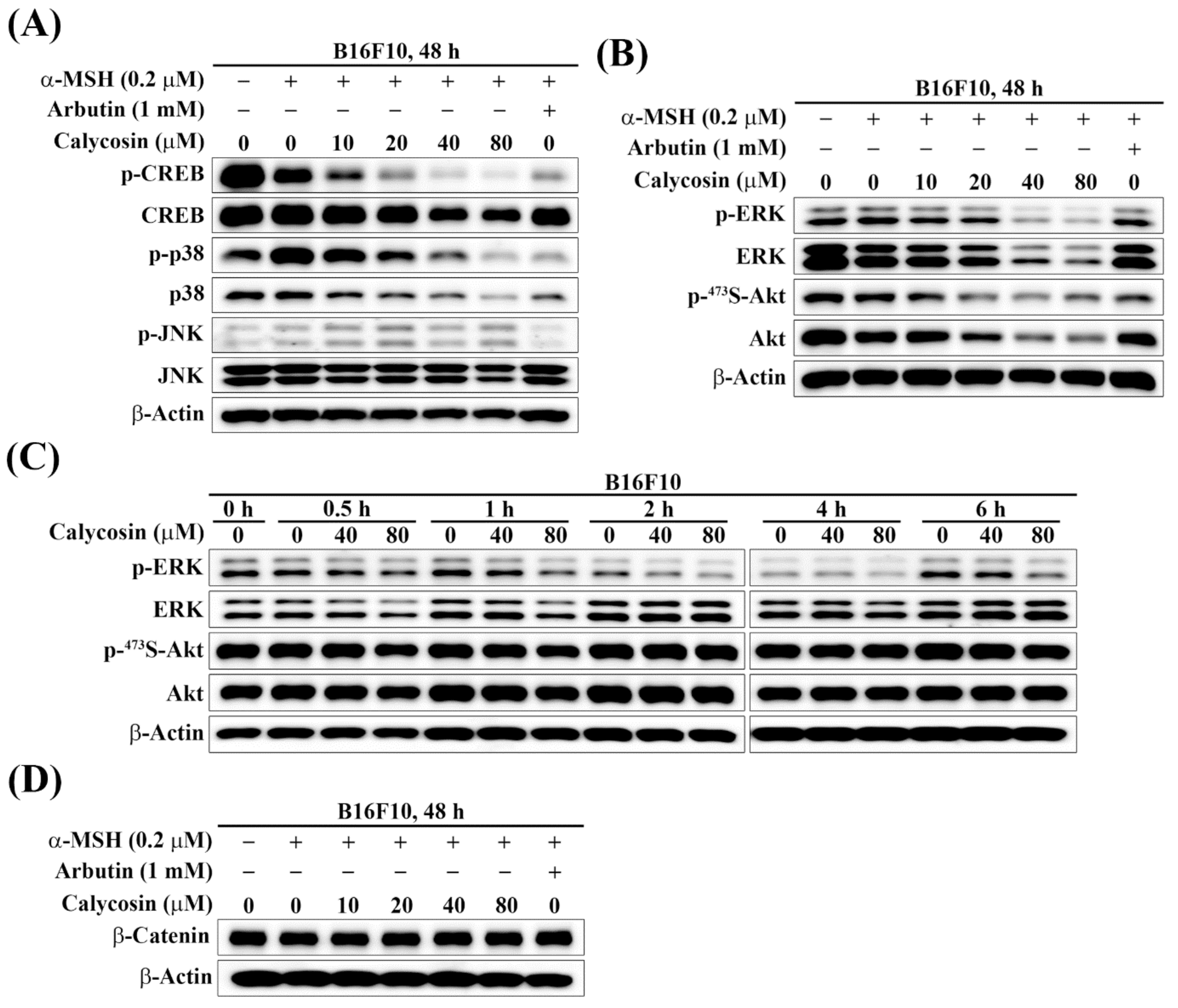
2.4. Effect of Calycosin on the Phosphorylation of CREB, p38, JNK, ERK, and Akt
2.5. Effect of Calycosin on the Expression of β-Catenin
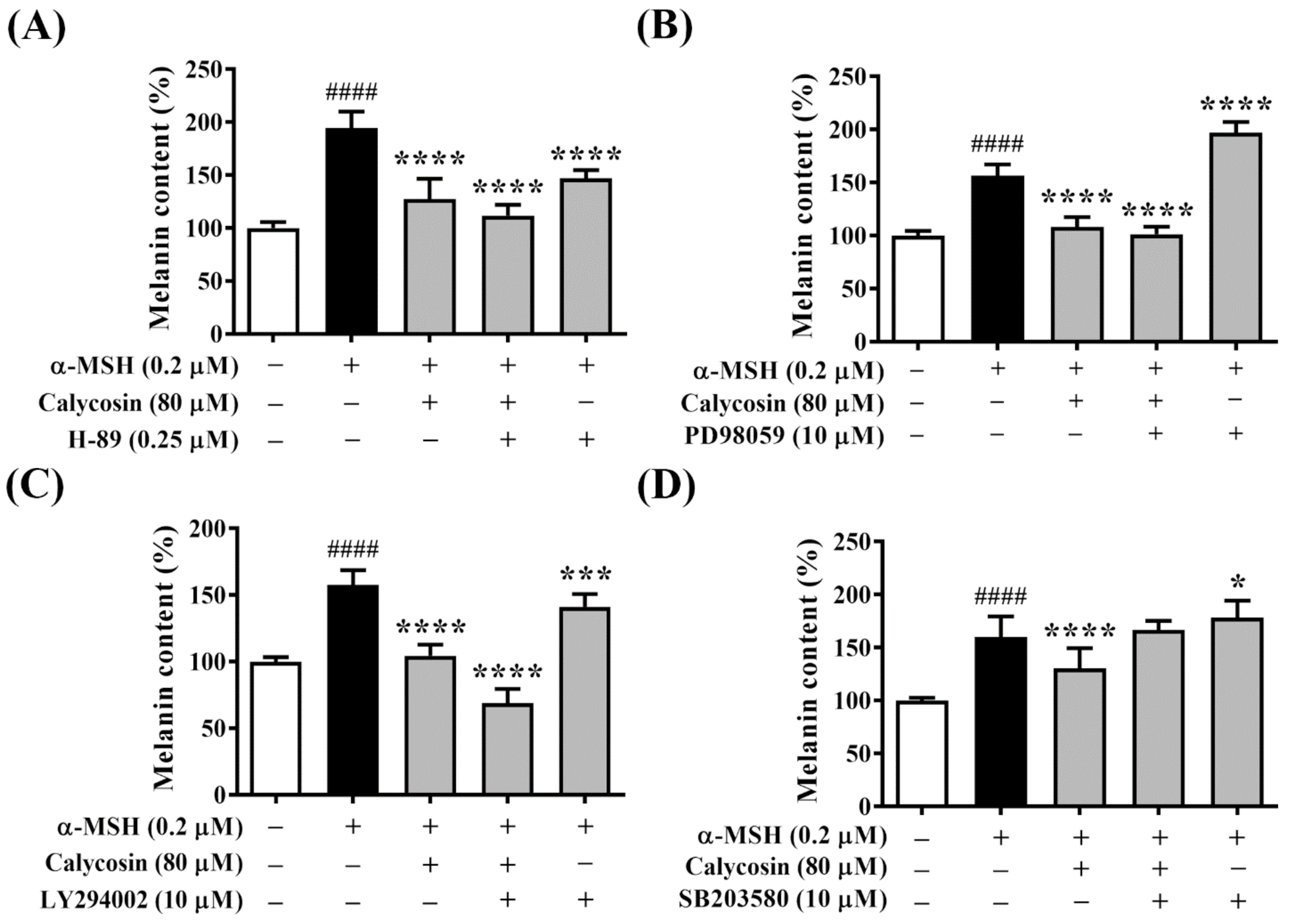
2.6. Effect of Calycosin on Melanogenesis-Related Signaling Pathways
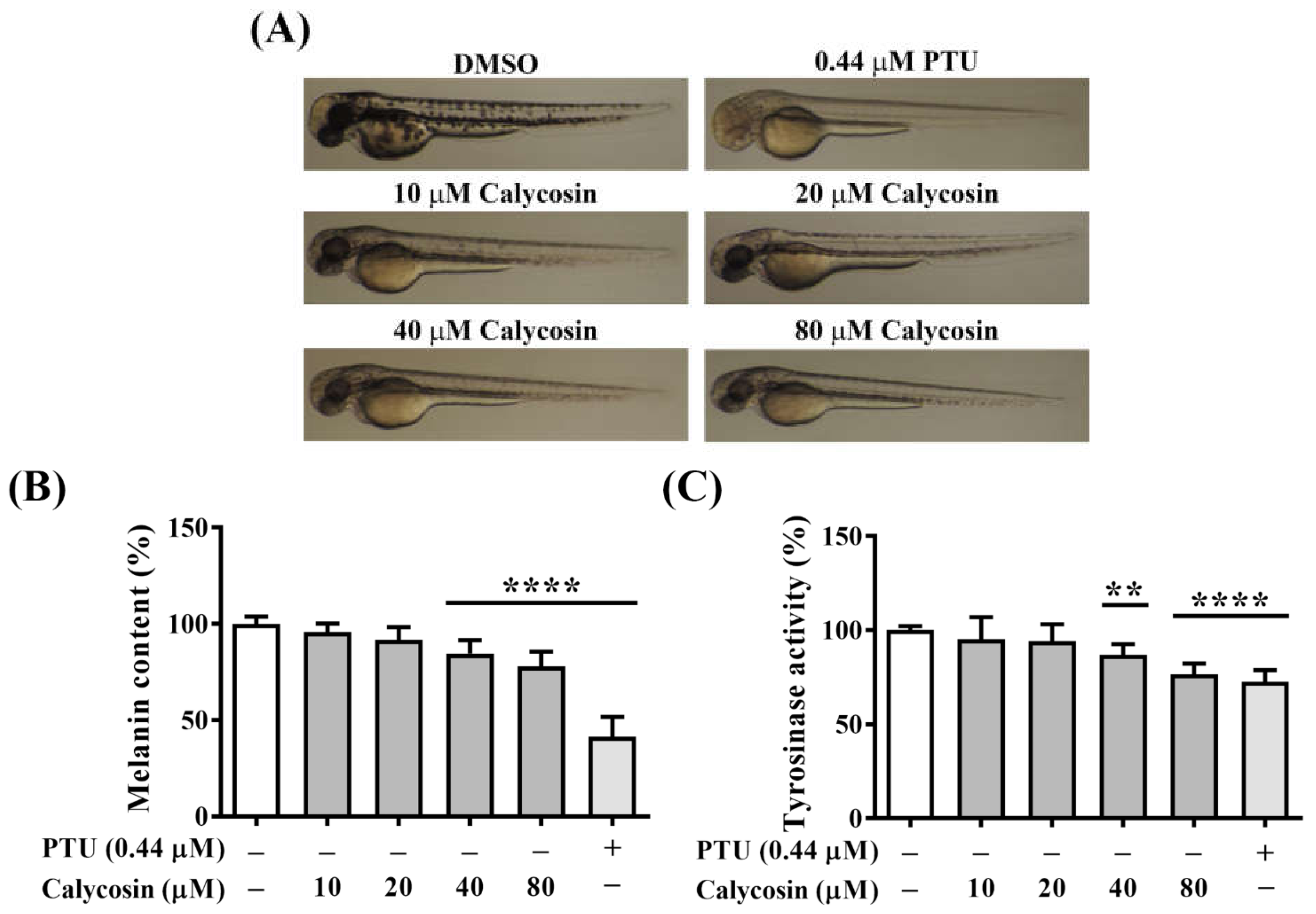
2.7. In Vivo Antimelanogenesis Effect of Calycosin
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture, Chemicals, and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.3. Melanin Content Assay
4.4. Cellular Tyrosinase Activity Assay
4.5. Immunoblotting
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.7. Melanin Contents of Zebrafish
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| α-MSH | α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone |
| MC1R | melanocortin 1 receptor |
| MITF | microphthalmia-associated transcription factor |
| TRP-1 | tyrosinase-related protein-1 |
| TRP-2 | tyrosinase-related protein-2 |
| cAMP | cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| PKA | protein kinase A |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| JNK | Jun N-terminal kinas |
| CREB | cAMP response element-binding protein |
| GSK3β | glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta |
References
- Chaita, E.; Lambrinidis, G.; Cheimonidi, C.; Agalou, A.; Beis, D.; Trougakos, I.; Mikros, E.; Skaltsounis, A.-L.; Aligiannis, N. Anti-Melanogenic Properties of Greek Plants. A Novel Depigmenting Agent from Morus alba Wood. Molecules 2017, 22, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qian, W.; Liu, W.; Zhu, D.; Cao, Y.; Tang, A.; Gong, G.; Su, H. Natural skin-whitening compounds for the treatment of melanogenesis (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Huang, J.; Jiang, L.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Q. Traditional Asian Herbs in Skin Whitening: The Current Development and Limitations. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanlayavattanakul, M.; Lourith, N. Plants and Natural Products for the Treatment of Skin Hyperpigmentation—A Review. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 988–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, T.-I.; Yun, J.-M.; Park, E.-J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, Y.-M.; Lim, J.-H. Plumbagin Suppresses alpha-MSH-Induced Melanogenesis in B16F10 Mouse Melanoma Cells by Inhibiting Tyrosinase Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bentley, N.J.; Eisen, T.; Goding, C.R. Melanocyte-specific expression of the human tyrosinase promoter: Activation by the microphthalmia gene product and role of the initiator. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 7996–8006. [Google Scholar]
- Vachtenheim, J.; Borovanský, J. "Transcription physiology" of pigment formation in melanocytes: Central role of MITF. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Xie, H.-F.; Tang, Y.; Lin, S.-Q.; Li, J.-M.; Sun, S.-N.; Hu, X.-L.; Huang, Y.-X.; Shi, W.; Jian, D. G protein-coupled estrogen receptor enhances melanogenesis via cAMP-protein kinase (PKA) by upregulating microphthalmia-related transcription factor-tyrosinase in melanoma. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 165, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearing, V.J.; Jiménez, M. Mammalian tyrosinase—The critical regulatory control point in melanocyte pigmentation. Int. J. Biochem. 1987, 19, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Namasivayam, V.; Manickam, M.; Jung, S.-H. Inhibitors of Melanogenesis: An Updated Review. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 7395–7418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Mello, S.A.N.; Finlay, G.J.; Baguley, B.C.; Askarian-Amiri, M.E. Signaling Pathways in Melanogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horrell, E.M.W.; Boulanger, M.C.; D’Orazio, J.A. Melanocortin 1 Receptor: Structure, Function, and Regulation. Front. Genet. 2016, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slominski, A.; Tobin, D.J.; Shibahara, S.; Wortsman, J. Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1155–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.Y.; Kosmadaki, M.; Yaar, M.; Gilchrest, B.A. Cellular mechanisms regulating human melanogenesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, C.I.; Setaluri, V. Cyclic AMP (cAMP) signaling in melanocytes and melanoma. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 563, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Jin, C.L.; Oh, J.-H.; Oh, I.G.; Park, C.-H.; Chung, J.H. Ardisia crenata extract stimulates melanogenesis in B16F10 melanoma cells through inhibiting ERK1/2 and Akt activation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, M.L.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, G.; Son, H.-J.; Lee, S.-J. Suppression of alpha-MSH and IBMX-induced melanogenesis by cordycepin via inhibition of CREB and MITF, and activation of PI3K/Akt and ERK-dependent mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 29, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Bellei, B.; Pitisci, A.; Catricalà, C.; Larue, L.; Picardo, M. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is stimulated by alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone in melanoma and melanocyte cells: Implication in cell differentiation. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2011, 24, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-Z.; He, X.-G.; Lindenmaier, M.; Nolan, G.; Yang, J.; Cleary, M.; Qiu, S.-X.; Cordell, G.A. Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry study of the flavonoids of the roots of Astragalus mongholicus and A. membranaceus. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 876, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-Q.; Wang, H.-B.; Wang, S.-F.; Wang, D.-Q. [Research achievements on biological activities of calycosin]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2015, 40, 4339–4345. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Li, R.; Shi, W.; Huang, Z. Discovery of the Anti-Tumor Mechanism of Calycosin Against Colorectal Cancer by Using System Pharmacology Approach. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 5589–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.R.; Lee, E.S.; Lee, C.H. Inhibitory effects of calycosin isolated from the root of Astragalus membranaceus on melanin biosynthesis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikolova, T.; Dvorak, M.; Jung, F.; Adam, I.; Kramer, E.; Gerhold-Ay, A.; Kaina, B. The gammaH2AX assay for genotoxic and nongenotoxic agents: Comparison of H2AX phosphorylation with cell death response. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 140, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Manickam, M.; Namasivayam, V. Skin whitening agents: Medicinal chemistry perspective of tyrosinase inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 403–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Cho, K.M.; Kim, K.H.; Kang, N.J. Effect of 3,6-anhydro-l-galactose on alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone-induced melanogenesis in human melanocytes and a skin-equivalent model. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 7643–7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, W.-J.; Ma, H.-J.; Zhao, G.; Yuan, X.-Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, W.; Ma, L.-J.; Lei, X.-B. Additive effect of heat on the UVB-induced tyrosinase activation and melanogenesis via ERK/p38/MITF pathway in human epidermal melanocytes. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2014, 306, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; Jin, S.H.; Kang, H.Y. LPS induces melanogenesis through p38 MAPK activation in human melanocytes. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2008, 300, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corre, S.; Primot, A.; Sviderskaya, E.; Bennett, D.C.; Vaulont, S.; Goding, C.R.; Galibert, M.-D. UV-induced expression of key component of the tanning process, the POMC and MC1R genes, is dependent on the p-38-activated upstream stimulating factor-1 (USF-1). J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 51226–51233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Englaro, W.; Bertolotto, C.; Buscà, R.; Brunet, A.; Pagès, G.; Ortonne, J.-P.; Ballotti, R. Inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway triggers B16 melanoma cell differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 9966–9970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.-S.; Hwang, E.-S.; Lee, J.-E.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kwon, S.-B.; Park, K.-C. Sphingosine-1-phosphate decreases melanin synthesis via sustained ERK activation and subsequent MITF degradation. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Jung, K.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, D. Diosgenin inhibits melanogenesis through the activation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathway (PI3K) signaling. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, M.; Nagai, H.; Ando, H.; Fukunaga, M.; Matsumura, M.; Araki, K.; Ogawa, W.; Miki, T.; Sakaue, M.; Tsukamoto, K.; et al. Regulation of melanogenesis through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway in human G361 melanoma cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 115, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsang, T.-F.; Chan, B.; Tai, W.C.-S.; Huang, G.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, Z.H.; Hsiao, W.L.W. Gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins induce melanogenesis and activate cAMP/PKA and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2019, 60, 153008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Yu, S.-M.; Kim, S.J. Inhibitory effects on melanogenesis by thymoquinone are mediated through the betacatenin pathway in B16F10 mouse melanoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, C.; Pan, N.; Hong, J.; Xiao, H.; Xie, Z. The 308-nm excimer laser stimulates melanogenesis via the wnt/beta-Catenin signaling pathway in B16 cells. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2019, 30, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Sakamoto, K. Pyruvic acid/ethyl pyruvate inhibits melanogenesis in B16F10 melanoma cells through PI3K/AKT, GSK3beta, and ROS-ERK signaling pathways. Genes Cells 2019, 24, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alaluf, S.; Atkins, D.; Barrett, K.; Blount, M.; Carter, N.; Heath, A. The impact of epidermal melanin on objective measurements of human skin colour. Pigment Cell Res. 2002, 15, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serre, C.; Busuttil, V.; Botto, J.-M. Intrinsic and extrinsic regulation of human skin melanogenesis and pigmentation. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2018, 40, 328–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Malek, Z.A.; Kadekaro, A.L.; Swope, V.B. Stepping up melanocytes to the challenge of UV exposure. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2010, 23, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auyeung, K.K.; Han, Q.B.; Ko, J.K. Astragalus membranaceus: A Review of its Protection Against Inflammation and Gastrointestinal Cancers. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Q.; Shi, Q.; Duan, J.A.; Dong, T.T.; Tsim, K.W. Chemical analysis of Radix Astragali (Huangqi) in China: A comparison with its adulterants and seasonal variations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4861–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-S.; Park, S.-H.; Kwon, S.-B.; Li, K.; Youn, S.-W.; Park, K.-C. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate and hinokitiol reduce melanin synthesis via decreased MITF production. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004, 27, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, W.J.; Chang, S.E.; Lee, G.-Y. Hesperidin, A Popular Antioxidant Inhibits Melanogenesis via Erk1/2 Mediated MITF Degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18384–18395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Guo, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, J.; Gu, Y.; Li, Y. Baicalein inhibits melanogenesis through activation of the ERK signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 25, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujii, T.; Saito, M. Inhibitory effect of quercetin isolated from rose hip (Rosa canina L.) against melanogenesis by mouse melanoma cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 1989–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsao, Y.-T.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Kuan, Y.-D.; Lin, H.-C.; Wu, L.-H.; Lee, C.-H. The Extracts of Astragalus membranaceus Inhibit Melanogenesis through the ERK Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, Y.C.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, G.S.; Lee, J.N.; Lee, N.H.; Hyun, C.-G. Pratol, an O-Methylated Flavone, Induces Melanogenesis in B16F10 Melanoma Cells via p-p38 and p-JNK Upregulation. Molecules 2017, 22, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-Y.; You, Y.-J.; Liu, Y.-J.; Hou, C.-W.; Wu, C.-S.; Wen, K.-C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chiang, H.-M. Sesamol Inhibited Melanogenesis by Regulating Melanin-Related Signal Transduction in B16F10 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cha, S.-H.; Ko, S.-C.; Kim, D.; Jeon, Y.-J. Screening of marine algae for potential tyrosinase inhibitor: Those inhibitors reduced tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis in zebrafish. J. Dermatol. 2011, 38, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, K.-C.; Hseu, Y.-C.; Shih, Y.-C.; Sivakumar, G.; Syu, J.-T.; Chen, G.-L.; Lu, M.-T.; Chu, P.-C. Calycosin, a Common Dietary Isoflavonoid, Suppresses Melanogenesis through the Downregulation of PKA/CREB and p38 MAPK Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031358
Wu K-C, Hseu Y-C, Shih Y-C, Sivakumar G, Syu J-T, Chen G-L, Lu M-T, Chu P-C. Calycosin, a Common Dietary Isoflavonoid, Suppresses Melanogenesis through the Downregulation of PKA/CREB and p38 MAPK Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(3):1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031358
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Kun-Chang, You-Cheng Hseu, Yu-Ching Shih, Govindan Sivakumar, Jyun-Ting Syu, Guan-Lin Chen, Meng-Tien Lu, and Po-Chen Chu. 2022. "Calycosin, a Common Dietary Isoflavonoid, Suppresses Melanogenesis through the Downregulation of PKA/CREB and p38 MAPK Signaling Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 3: 1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031358
APA StyleWu, K.-C., Hseu, Y.-C., Shih, Y.-C., Sivakumar, G., Syu, J.-T., Chen, G.-L., Lu, M.-T., & Chu, P.-C. (2022). Calycosin, a Common Dietary Isoflavonoid, Suppresses Melanogenesis through the Downregulation of PKA/CREB and p38 MAPK Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(3), 1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031358