Pharmacological Effects of Cisplatin Combination with Natural Products in Cancer Chemotherapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Approach
3. Cisplatin in Cancer Therapy
3.1. Structure and Synthesis
3.2. Cisplatin Aquation
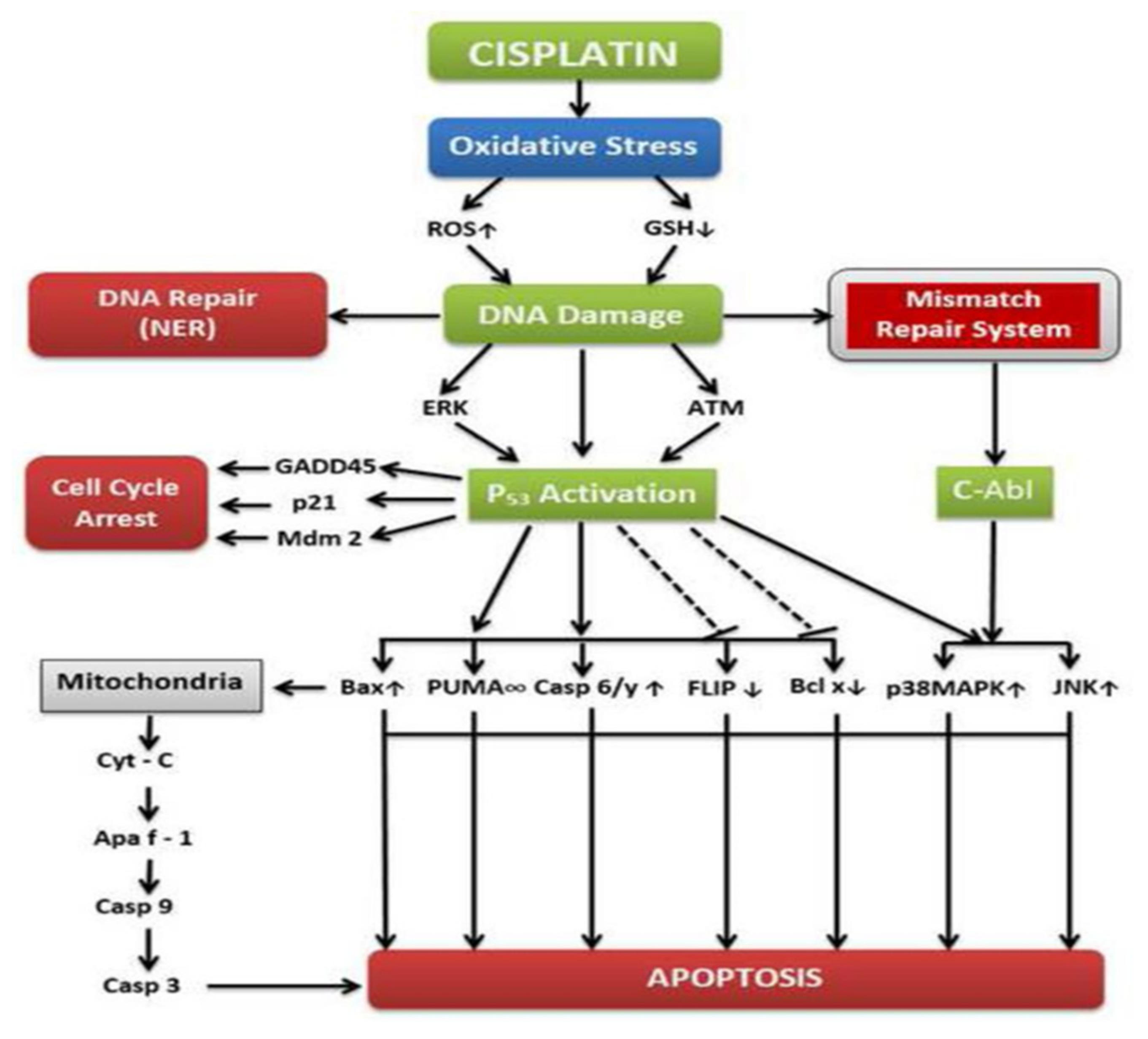
3.3. Mechanisms of Action
3.4. Clinical Studies on Cisplatin Use for Cancer Treatment
3.5. Cisplatin Resistance
3.5.1. Pharmacokinetics of Drug
3.5.2. Increased Affinity
3.5.3. DNA Repair and DNA Damage
3.5.4. Other Control Mechanisms
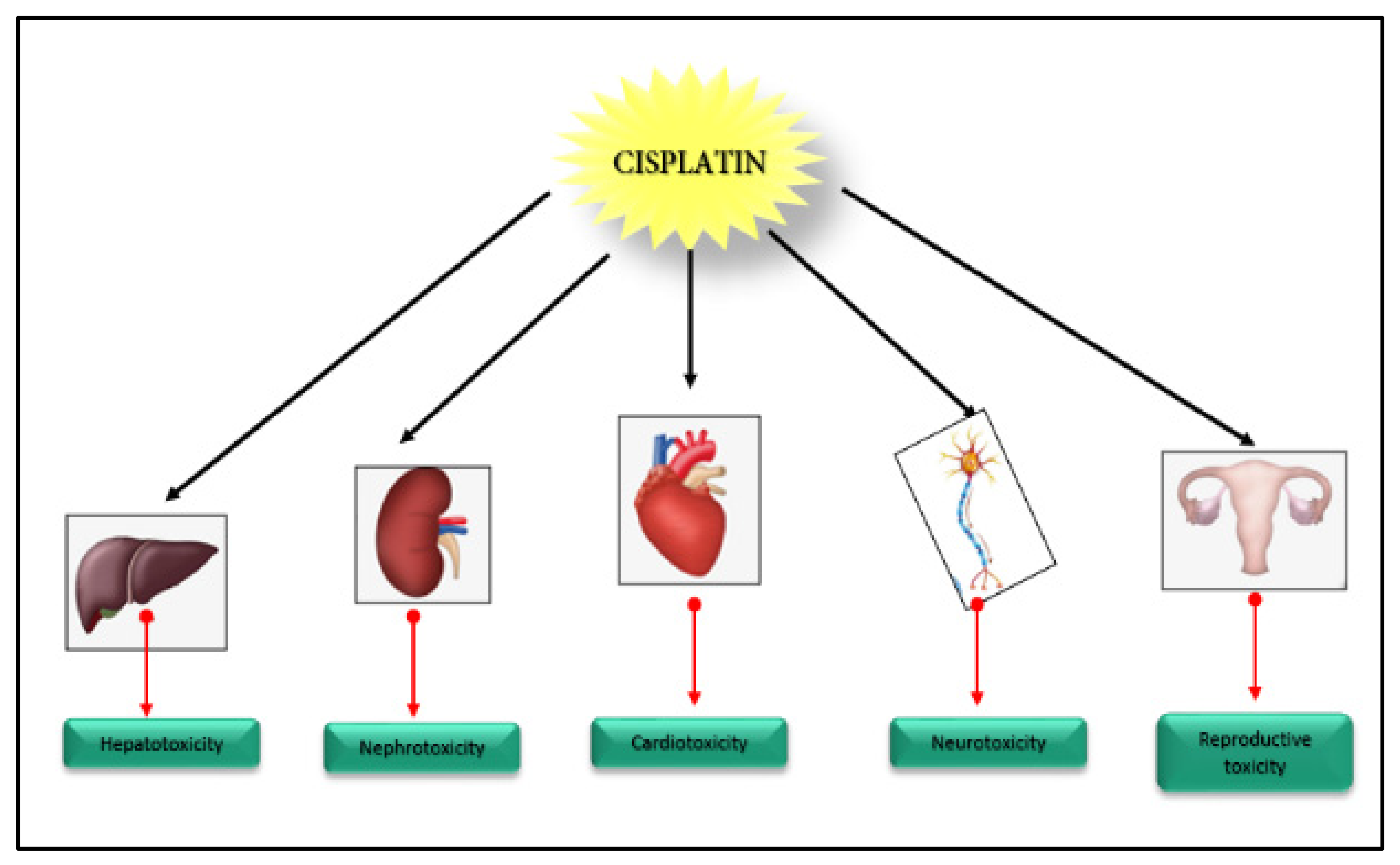
3.6. Organ Toxicity
3.6.1. Nephrotoxicity
3.6.2. Hepatotoxicity
3.6.3. Neurotoxicity
3.6.4. Cardiotoxicity
3.6.5. Other Organ Toxicity
4. Natural Products in Cancer Management
4.1. Garlic and Cancer Treatment
4.2. Curcumin and Cancer Treatment
4.3. Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Cancer Treatment
4.4. Ginger and Cancer Treatment
4.5. Vernonia amagdalina (VA) and Cancer Treatment
5. Cisplatin Combination with Natural Products
5.1. Combination with Flavonoids
5.2. Combination with Saponins
5.3. Combination with Alkaloids
5.4. Combination with Polysaccharides
5.5. Combination with Phenylpropanoids
5.6. Combination with Napthoquinones
5.7. Combination with HSP90 Inhibitors
5.8. Combination with Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
5.9. Combination with Other Natural Products
6. Natural Product–Cisplatin Nanoparticle Formulations
6.1. Clinical Trials
6.2. Mechanism of Action
6.3. Other Natural Nanoparticle Formulations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Cancer Institute Cancer Statistics—National Cancer Institute. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/understanding/statistics (accessed on 27 April 2018).
- Islami, F.; Goding Sauer, A.; Miller, K.D.; Siegel, R.L.; Fedewa, S.A.; Jacobs, E.J.; McCullough, M.L.; Patel, A.V.; Ma, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; et al. Proportion and number of cancer cases and deaths attributable to potentially modifiable risk factors in the United States. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New Treatments Spur Sharp Reduction in Lung Cancer Mortality Rate. Oncol. Times 2020, 42, 28. [CrossRef]
- Henley, S.J.; Ward, E.M.; Scott, S.; Ma, J.; Anderson, R.N.; Firth, A.U.; Thomas, C.C.; Islami, F.; Weir, H.K.; Lewis, D.R.; et al. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, Part I: National Cancer Statistics. Cancer 2020, 126, 2225–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilman, A. The initial clinical trial of nitrogen mustard. Am. J. Surg. 1963, 105, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, S.; Diamond, L.K.; Mercer, R.D.; Sylvester, R.F., Jr.; Wolff, J.A. Temporary Remissions in Acute Leukemia in Children Produced by Folic Acid Antagonist, 4-Aminopteroyl-Glutamic Acid (Aminopterin). N. Engl. J. Med. 1948, 238, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonadonna, G.; Brusamolino, E.; Valagussa, P.; Rossi, A.; Brugnatelli, L.; Brambilla, C.; De Lena, M.; Tancini, G.; Bajetta, E.; Musumeci, R.; et al. Combination Chemotherapy as an Adjuvant Treatment in Operable Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1976, 294, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, N.; Frei, E.; Traggis, D.; Bishop, Y. Adjuvant Methotrexate and Citrovorum-Factor Treatment of Osteogenic Sarcoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1974, 291, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skipper, H.E.; Thomson, J.R.; Elion, G.B.; Hitchings, G.H. Observations on the anticancer activity of 6-mercaptopurine. Cancer Res. 1954, 14, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chabner, B.A.; Roberts, T.G., Jr. Chemotherapy and the war on cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grever, M.R.; Schepartz, S.A.; Chabner, B.A. The National Cancer Institute: Cancer drug discovery and development program. Semin. Oncol. 1992, 19, 622–638. [Google Scholar]
- Moertel, C.G.; Fleming, T.R.; Macdonald, J.S.; Haller, D.G.; Laurie, J.A.; Goodman, P.J.; Ungerleider, J.S.; Emerson, W.A.; Tormey, D.C.; Glick, J.H.; et al. Levamisole and Fluorouracil for Adjuvant Therapy of Resected Colon Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippert, B. Cisplatin: Chemistry and Biochemistry of a Leading Anticancer Drug; Wiley-VCH: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 9783906390420. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, B.H.; Vancamp, L.; Trosko, J.E.; Mansour, V.H. Platinum Compounds: A New Class of Potent Antitumour Agents. Nature 1969, 222, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, D.P. The Sterochemistry of Square Complexes. Chem. Rev. 1943, 33, 137–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramberg, P.J. Alfred Werner and Coordination Chemistry, 1893–1914. In Chemical Structure, Spatial Arrangement; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dhara, S.C. A Rapid Method for the Synthesis of Cis-[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]. Indian J. Chem. 1970, 8, 193–194. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, R.B.; Christian, M.C. New Cisplatin Analogues in Development: A Review. Drugs 1993, 46, 360–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corinti, D.; Coletti, C.; Re, N.; Piccirillo, S.; Giampà, M.; Crestoni, M.E.; Fornarini, S. Hydrolysis of cis- and transplatin: Structure and reactivity of the aqua complexes in a solvent free environment. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15877–15884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reedijk, J. Increased understanding of platinum anticancer chemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddell, I.A.; Lippard, S.J. 1. Cisplatin and oxaliplatin: Our current understanding of their actions. In Metallo-Drugs: Development and Action of Anticancer Agents; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Okuda, T.; Holzer, A.; Howell, S.B. The Copper Transporter CTR1 Regulates Cisplatin Uptake in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 62, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvesen, G.S.; Abrams, J.M. Caspase activation—Stepping on the gas or releasing the brakes? Lessons from humans and flies. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2774–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvesen, G.S.; Dixit, V.M. Caspases: Intracellular Signaling by Proteolysis. Cell 1997, 91, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.T.; Chen, H.H.W.; Song, I.-S.; Savaraj, N.; Ishikawa, T. The roles of copper transporters in cisplatin resistance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007, 26, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, S.; Lee, J.; Thiele, D.J.; Herskowitz, I. Uptake of the anticancer drug cisplatin mediated by the copper transporter Ctr1 in yeast and mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 14298–14302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, N.; Wang, H.; Jia, X.; Wang, X.; Luo, J. Altered microRNA expression in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells and upregulation of miR-130a associated with MDR1/P-glycoprotein-mediated drug resistance. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Chae, J.-W.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, H.J.; Chung, J.Y.; Kim, Y.-H. Inhibition of cisplatin-resistance by RNA interference targeting metallothionein using reducible oligo-peptoplex. J. Control. Release 2015, 215, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A.; Parker, L.J.; Ang, W.H.; Rodolfo, C.; Gabbarini, V.; Hancock, N.C.; Palone, F.; Mazzetti, A.P.; Menin, L.; Morton, C.J.; et al. A structure-based mechanism of cisplatin resistance mediated by glutathione transferase P1-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 13943–13951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köberle, B.; Grimaldi, K.A.; Sunters, A.; Hartley, J.A.; Kelland, L.R.; Masters, J.R. DNA Repair capacity and cisplatin sensitivity of human testis tumour cells. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 70, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathdee, G.; MacKean, M.J.; Illand, M.; Brown, R. A role for methylation of the hMLH1 promoter in loss of hMLH1 expression and drug resistance in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 1999, 18, 2335–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sheng, W.; Yu, C.; Cao, J.; Zhou, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. REV3L modulates cisplatin sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer H1299 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottenberg, S.; Jaspers, J.E.; Kersbergen, A.; Van Der Burg, E.; Nygren, A.O.H.; Zander, S.A.L.; Derksen, P.W.B.; De Bruin, M.; Zevenhoven, J.; Lau, A.; et al. High sensitivity of BRCA1-deficient mammary tumors to the PARP inhibitor AZD2281 alone and in combination with platinum drugs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17079–17084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-M.; Manandhar, S.; Lee, H.-R.; Park, H.-M.; Kwak, M.-K. Role of the Nrf2-antioxidant system in cytotoxicity mediated by anticancer cisplatin: Implication to cancer cell resistance. Cancer Lett. 2008, 260, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryczek, I.; Lin, Y.; Nagarsheth, N.; Peng, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, E.; Vatan, L.; Szeliga, W.; Dou, Y.; Owens, S.; et al. IL-22+CD4+ T Cells Promote Colorectal Cancer Stemness via STAT3 Transcription Factor Activation and Induction of the Methyltransferase DOT1L. Immunity 2014, 40, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranasinghe, R.; Eri, R. Modulation of the CCR6-CCL20 Axis: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Inflammation and Cancer. Medicina 2018, 54, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, Z.; Yin, H.; Yang, G. Interaction between p53 and Ras signaling controls cisplatin resistance via HDAC4- and HIF-1α-mediated regulation of apoptosis and autophagy. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1096–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldossary, S.A. Review on Pharmacology of Cisplatin: Clinical Use, Toxicity and Mechanism of Resistance of Cisplatin. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2019, 12, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, N.; Engel, F.; Rothweiler, F.; Cinatl, J.; Michaelis, M.; Frötschl, R.; Fröhlich, H.; Kalayda, G.V. Key Players of Cisplatin Resistance: Towards a Systems Pharmacology Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulz, S.; Asselborn, N.H.; Dieckmann, K.-P.; Matthies, C.; Wagner, W.; Weidmann, J.; Seidel, C.; Oing, C.; Berger, L.A.; Alsdorf, W.; et al. Retinal toxicity after cisplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with germ cell cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, F.M.; Pitton, M.; Brambilla, G.; Colombi, A. A study of the glutathione metaboloma peptides by energy-resolved mass spectrometry as a tool to investigate into the interference of toxic heavy metals with their metabolic processes. Biol. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 41, 1578–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, O.Y. Mechanism of Tumor Resistance to Cisplatin Mediated by the Copper Transporter ATP7B. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 89, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematbakhsh, M.; Ashrafi, F.; Pezeshki, Z.; Fatahi, Z.; Kianpoor, F.; Sanei, M.H.; Talebi, A. A histopathological study of nephrotoxicity, hepatoxicity or testicular toxicity: Which one is the first observation as side effect of Cisplatin-induced toxicity in animal model? J. Nephropathol. 2012, 1, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Park, D.J.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, E.Y.; Jung, M.H.; Kim, T.-H.; Yang, J.I.; Lee, G.-W.; Chung, H.J.; Chang, S.-H. Glutamine protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by decreasing cisplatin accumulation. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 127, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Cederbaum, A.I. Cisplatin-Induced Hepatotoxicity Is Enhanced by Elevated Expression of Cytochrome P450 2E1. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 89, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Lu, X.; Lu, C.; Li, G.; Jin, Y.; Tang, H. Selection of agents for prevention of cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity. Pharmacol. Res. 2008, 57, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausheer, F.H.; Schilsky, R.L.; Bain, S.; Berghorn, E.J.; Lieberman, F. Diagnosis, Management, and Evaluation of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Semin. Oncol. 2006, 33, 15–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tlili, N.; Feriani, A.; Allagui, M.S.; Saadoui, E.; Khaldi, A.; Nasri, N. Effects of Rhus tripartitum fruit extract on CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity and cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 94, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.; Naseem, I.; Hassan, I.; Khan, A.A.; Alhazza, I.M. Riboflavin Arrests Cisplatin-Induced Neurotoxicity by Ameliorating Cellular Damage in Dorsal Root Ganglion Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 603543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Awady, E.-S.E.; Moustafa, Y.M.; Abo-Elmatty, D.M.; Radwan, A. Cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity: Mechanisms and cardioprotective strategies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 650, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharz, J.; Michalowska-Kaczmarczyk, A.; Zygulska, A.L.; Wojtak, J.; Pawlik, W.; Herman, R.M.; Krzemieniecki, K. Bradycardia as a rare symptom of cisplatin cardiotoxicity: A case report. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 2297–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- El-Sawalhi, M.M.; Ahmed, L.A. Exploring the protective role of apocynin, a specific NADPH oxidase inhibitor, in cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Chem. Interact. 2014, 207, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, L.P. Mechanisms of cisplatin ototoxicity and progress in otoprotection. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 15, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osanto, S.; Bukman, A.; Van Hoek, F.; Sterk, P.J.; De Laat, J.A.; Hermans, J. Long-term effects of chemotherapy in patients with testicular cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1992, 10, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M.; Snader, K.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Period 1981−2002. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokina, M.; Steinbeck, C. Review on natural products databases: Where to find data in 2020. J. Cheminform. 2020, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastings, J.; De Matos, P.; Dekker, A.; Ennis, M.; Harsha, B.; Kale, N.; Muthukrishnan, V.; Owen, G.; Turner, S.; Williams, M.; et al. The ChEBI reference database and ontology for biologically relevant chemistry: Enhancements for 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D456–D463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.S.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Cooper, M.A. Natural product and natural product derived drugs in clinical trials. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 1612–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, D.A.; Locatelli, D.A.; González, R.E.; Cavagnaro, P.; Camargo, A.B. Analytical methods for bioactive sulfur compounds in Allium: An integrated review and future directions. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 61, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemaker, H.H.; Weisberger, A.S.; Pensky, J. Tumor-Inhibiting Effects Derived from an Active Principle of Garlic (Allium Sativum). Science 1957, 126, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahanukar, S.; Thatte, U. Current status of ayurveda in phytomedicine. Phytomedicine 1997, 4, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surh, Y.-J. Cancer chemoprevention with dietary phytochemicals. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.-Y.; Wu, M.; Han, R.-Q.; Zhang, X.-F.; Wang, X.-S.; Liu, A.-M.; Zhou, J.-Y.; Lu, Q.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Zhao, J. Raw Garlic Consumption as a Protective Factor for Lung Cancer, a Population-Based Case–Control Study in a Chinese Population. Cancer Prev. Res. 2013, 6, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreher, F.; Gabard, B.; Schwindt, D.A.; Maibach, H.I. Topical melatonin in combination with vitamins E and C protects skin from ultraviolet-induced erythema: A human study in vivo. Br. J. Dermatol. 1998, 139, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, K.C. Therapeutic Actions of Garlic Constituents. Med. Res. Rev. 1996, 16, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikaili, P.; Maadirad, S.; Moloudizargari, M.; Aghajanshakeri, S.; Sarahroodi, S. Therapeutic Uses and Pharmacological Properties of Garlic, Shallot, and Their Biologically Active Compounds. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2013, 16, 1031–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, J.A. Mechanisms by Which Garlic and Allyl Sulfur Compounds Suppress Carcinogen Bioactivation: Garlic and Carcinogenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2001, 492, 69–81. [Google Scholar]
- Amagase, H. Clarifying the Real Bioactive Constituents of Garlic. J. Nutr. 2006, 136 (Suppl. 3), 716S–725S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerella, C.; Dicato, M.; Jacob, C.; Diederich, M. Chemical properties and mechanisms determining the anti-cancer action of garlic-derived organic sulfur compounds. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szychowski, K.A.; Binduga, U.E.; Rybczyńska-Tkaczyk, K.; Leja, M.L.; Gmiński, J. Cytotoxic effects of two extracts from garlic (Allium sativum L.) cultivars on the human squamous carcinoma cell line SCC-15. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 25, 1703–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, L.M.; Milner, J.A. Possible mechanism by which allyl sulfides suppress neoplastic cell proliferation. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 1061S–1066S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Herman-Antosiewicz, A.; Antosiewicz, J.; Xiao, H.; Brisson, M.; Lazo, J.S.; Singh, S.V. Diallyl trisulfide-induced G2–M phase cell cycle arrest in human prostate cancer cells is caused by reactive oxygen species-dependent destruction and hyperphosphorylation of Cdc25C. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6256–6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.B.; Huang, S.; Yin, X.R.; Zhang, Y.; Di, Z.L. Apoptotic pathway induced by diallyl trisulfide in pancreatic cancer cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Sang, X. Diallyl disulfide suppresses FOXM1-mediated proliferation and invasion in osteosarcoma by upregulating miR-134. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 120, 7286–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.-S.; Ham, Y.-A.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, J. Effects of allyl sulfur compounds and garlic extract on the expression of Bcl-2, Bax, and p53 in non small cell lung cancer cell lines. Exp. Mol. Med. 2000, 32, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahab, N.A.A.; Lajis, N.H.; Abas, F.; Othman, I.; Naidu, R. Mechanism of Anti-Cancer Activity of Curcumin on Androgen-Dependent and Androgen-Independent Prostate Cancer. Nutrients 2020, 12, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilken, R.; Veena, M.S.; Wang, M.B.; Srivatsan, E.S. Curcumin: A review of anti-cancer properties and therapeutic activity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyadarsini, K.I. The Chemistry of Curcumin: From Extraction to Therapeutic Agent. Molecules 2014, 19, 20091–20112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulucci, V.P.; Couto, R.O.; Teixeira, C.C.; Freitas, L. Optimization of the extraction of curcumin from Curcuma longa rhizomes. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2013, 23, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oyanguren, F.J.S.; Rainey, N.E.; Moustapha, A.; Saric, A.; Sureau, F.; O’Connor, J.-E.; Petit, P.X. Highlighting Curcumin-Induced Crosstalk between Autophagy and Apoptosis as Supported by Its Specific Subcellular Localization. Cells 2020, 9, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Panda, A.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Sa, G. Curcumin and tumor immune-editing: Resurrecting the immune system. Cell Div. 2015, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, L.; Yu, F.; Ding, H.; Li, P.; Zhou, M.; Wang, K. Potential Mechanisms of Action of Curcumin for Cancer Prevention: Focus on Cellular Signaling Pathways and miRNAs. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 1200–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.I.; Othman, I.; Abas, F.; Lajis, N.H.; Naidu, R. Mechanism of Apoptosis Induced by Curcumin in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomeh, M.A.; Hadianamrei, R.; Zhao, X. A Review of Curcumin and Its Derivatives as Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.Q.; Ahmed, E.I.; Elareer, N.; Fathima, H.; Prabhu, K.S.; Siveen, K.S.; Kulinski, M.; Azizi, F.; Dermime, S.; Ahmad, A.; et al. Curcumin-Mediated Apoptotic Cell Death in Papillary Thyroid Cancer and Cancer Stem-Like Cells through Targeting of the JAK/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.H.; Lim, J.E.; Jeon, H.G.; Seo, S.I.; Lee, H.M.; Choi, H.Y.; Jeon, S.S.; Jeong, B.C. Curcumin potentiates antitumor activity of cisplatin in bladder cancer cell lines via ROS-mediated activation of ERK1/2. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 63870–63886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baharuddin, P.; Satar, N.; Fakiruddin, K.S.; Zakaria, N.; Lim, M.N.; Yusoff, N.M.; Zakaria, Z.; Yahaya, B.H. Curcumin improves the efficacy of cisplatin by targeting cancer stem-like cells through p21 and cyclin D1-mediated tumour cell inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 35, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutz, J.; Janicova, A.; Woidacki, K.; Chun, F.K.-H.; Blaheta, R.A.; Relja, B. Curcumin—A Viable Agent for Better Bladder Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Yadav, A.; Hideg, K.; Kuppusamy, P.; Teknos, T.N.; Kumar, P. A Novel Curcumin Analog (H-4073) Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of Cisplatin Treatment in Head and Neck Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghatelyan, T.; Tananyan, A.; Janoyan, N.; Tadevosyan, A.; Petrosyan, H.; Hovhannisyan, A.; Hayrapetyan, L.; Arustamyan, M.; Arnhold, J.; Rotmann, A.-R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of curcumin in combination with paclitaxel in patients with advanced, metastatic breast cancer: A comparative, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytomedicine 2020, 70, 153218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazi, J.; Rastmanesh, R.; Taleban, F.A.; Molana, S.H.; Ehtejab, G. A Pilot Clinical Trial of Radioprotective Effects of Curcumin Supplementation in Patients with Prostate Cancer. J. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2013, 5, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Patchva, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Therapeutic Roles of Curcumin: Lessons Learned from Clinical Trials. AAPS J. 2013, 15, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.J.; Miranda-Massari, J.R. New Insights on Vitamin C and Cancer; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Longchar, A.; Prasad, S. Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C)-Mediated Protection on Mutagenic Potentials of Cisplatin in Mice Bearing Ascites Dalton ’s Lymphoma. Res. J. Mutagen. 2016, 6, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alabi, Q.K.; Akomolafe, R.O.; Olukiran, O.S.; Nafiu, A.O.; Adefisayo, M.A.; Owotomo, O.I.; Omole, J.G.; Olamilosoye, K.P. Combined Administration ofl-Carnitine and Ascorbic Acid Ameliorates Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2018, 37, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghavami, G.; Sardari, S. Synergistic Effect of Vitamin C with Cisplatin for Inhibiting Proliferation of Gastric Cancer Cells. Iran. Biomed. J. 2020, 24, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortekin, S.; Kocyigit, M.; Yagiz, R.; Tas, A.; Bulut, E.; Koten, M.; Kanter, M.; Karasaliihoglu, A. Assessment of protective effect of ascorbic acid in cisplatin ototoxicity on guinea pigs with electrophysiological tests and ultrastructural study: A Preliminary Study. Int. J. Surg. Med. 2019, 5, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbacher, C.M.; Wagner, U.; Kolster, B.; Andreotti, P.E.; Krebs, D.; Bruckner, H.W. Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) improves the antineoplastic activity of doxorubicin, cisplatin, and paclitaxel in human breast carcinoma cells in vitro. Cancer Lett. 1996, 103, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, B.S.; Bianchi, M.D.L.P. Effect of vitamin C supplementation against cisplatin-induced toxicity and oxidative DNA damage in rats. Pharmacol. Res. 2001, 44, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajith, T.; Usha, S.; Nivitha, V. Ascorbic acid and α-tocopherol protect anticancer drug cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in mice: A comparative study. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 375, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarladacalisir, Y.T.; Kanter, M.; Uygun, M. Protective Effects of Vitamin C on Cisplatin-Induced Renal Damage: A Light and Electron Microscopic Study. Ren. Fail. 2008, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longchar, A.; Prasad, S.B. Biochemical changes associated with ascorbic acid–cisplatin combination therapeutic efficacy and protective effect on cisplatin-induced toxicity in tumor-bearing mice. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, L.M.G.; Darin, J.D.C.; Bianchi, M.D.L.P. Protective Effects of Vitamin C Against Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity and Lipid Peroxidation in Adult Rats: A Dose-Dependent Study. Pharmacol. Res. 2000, 41, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleisa, A.M.; Al-Majed, A.A.; Al-Yahya, A.A.; Al-Rejaie, S.S.; Bakheet, S.A.; Al-Shabanah, O.A.; Sayed-Ahmed, M.M. Reversal of Cisplatin-Induced Carnitine Deficiency and Energy Starvation by Propionyl-L-Carnitine In Rat Kidney Tissues. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 34, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.L.; Heckler, C.E.; Roscoe, J.A.; Dakhil, S.R.; Kirshner, J.; Flynn, P.J.; Hickok, J.T.; Morrow, G.R. Ginger (Zingiber officinale) reduces acute chemotherapy-induced nausea: A URCC CCOP study of 576 patients. Support. Care Cancer 2011, 20, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-M.; Wang, D.; Lu, F.; Zhao, R.; Ye, X.; He, L.; Ai, L.; Wu, C.-J. Identification of the active substances and mechanisms of ginger for the treatment of colon cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. BioData Min. 2021, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadorozhna, M.; Mangieri, D. Mechanisms of Chemopreventive and Therapeutic Proprieties of Ginger Extracts in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, J.F.; Stoner, G.D. Gingers and Their Purified Components as Cancer Chemopreventative Agents. Molecules 2019, 24, 2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semwal, R.B.; Semwal, D.; Combrinck, S.; Viljoen, A.M. Gingerols and shogaols: Important nutraceutical principles from ginger. Phytochemistry 2015, 117, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, Y.A.; Chalamaiah, M.; Ramesh, B.; Balaji, G.; Indira, P. Ameliorating activity of ginger (Zingiber officinale) extract against lead induced renal toxicity in male rats. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 51, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Famurewa, A.C.; Ekeleme--Egedigwe, C.A.; Onwe, C.S.; Egedigwe, U.O.; Okoro, C.O.; Egedigwe, U.J.; Asogwa, N.T. Ginger juice prevents cisplatin--induced oxidative stress, endocrine imbalance and NO/iNOS/NF--κB signalling via modulating testicular redox--inflammatory mechanism in rats. Andrologia 2020, 52, e13786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghlissi, Z.; Atheymen, R.; Boujbiha, M.A.; Sahnoun, Z.; Ayedi, F.M.; Zeghal, K.; El Feki, A.; Hakim, A. Antioxidant and androgenic effects of dietary ginger on reproductive function of male diabetic rats. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 64, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yao, M.; Wang, Y.; Ho, C.-T.; Li, S.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, H. 6-Shogaol ameliorates injury to the intestinal mucosa and increases survival after high-dose abdominal irradiation. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 36, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirino, Y.I.; Hernández-Pando, R.; Pedraza-Chaverrí, J. Peroxynitrite decomposition catalyst ameliorates renal damage and protein nitration in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. BMC Pharmacol. 2004, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colpi, G.; Contalbi, G.; Nerva, F.; Sagone, P.; Piediferro, G. Testicular function following chemo–radiotherapy. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2004, 113, S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.G.; Nie, Z.; Ramkumar, V. Cisplatin up-regulates adenosine A1 receptors in rat testes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 382, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türk, G.; Ateşşahin, A.; Sönmez, M.; Ceribasi, A.O.; Yüce, A. Improvement of cisplatin-induced injuries to sperm quality, the oxidant-antioxidant system, and the histologic structure of the rat testis by ellagic acid. Fertil. Steril. 2008, 89, 1474–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, M.U.; Ahmad, S.B.; Arif, A.; Rasool, S.; Farooq, A.; Razzaq, R.; Bhat, S.A.; Bashir, S.; Shabir, O.; Amin, I.; et al. Zingerone protects against cisplatin-induced oxidative damage in the jejunum of Wistar rats. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2015, 15, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheikh S., E.; El-Khayat, Z.; Hassan, A.A.; Mohamed, N.; El-Naggar, M.; Omara, E. Possible Protective Role of Sodium Salicylate Nanoemulsion and Ginger on Cisplatin-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats (Biochemical and Histopathological Study). Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 2020, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejoh, R.A.; Nkonga, D.V.; Inocent, G.; Moses, M.C. Nutritional Components of Some Non-Conventional Leafy Vegetables Consumed in Cameroon. Pak. J. Nutr. 2007, 6, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedjou, C.G.; Izevbigie, E.B.; Tchounwou, P.B. Vernonia amygdalina—Induced Growth Arrest and Apoptosis of Breast Cancer (MCF-7) Cells. Pharmacol. Pharm. 2013, 4, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedjou, C.G.; Mbemi, A.T.; Noubissi, F.; Tchounwou, S.S.; Tsabang, N.; Payton, M.; Miele, L.; Tchounwou, P.B. Prostate Cancer Disparity, Chemoprevention, and Treatment by Specific Medicinal Plants. Nutrients 2019, 11, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farombi, E.O.; Owoeye, O. Antioxidative and Chemopreventive Properties of Vernonia Amygdalina and Garcinia Biflavo-noid. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 2533–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udochukwu, U.; Omeje, F.I.; Uloma, I.S.; Oseiwe, F.D.; Udochukwu, U. Phytochemical Analysis of Vernonia Amyg-Dalina and Ocimum Gratissimum Extracts and Their Antibacterial Activity on Some Drug Resistant Bacteria. Am. J. Res. Commun. 2015, 3, 225–235. [Google Scholar]
- Erasto, P.; Grierson, D.S.; Afolayan, A.J. Evaluation of antioxidant activity and the fatty acid profile of the leaves of Vernonia amygdalina growing in South Africa. Food Chem. 2006, 104, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbemi, A.T.; Sims, J.N.; Yedjou, C.G.; Noubissi, F.K.; Gomez, C.R.; Tchounwou, P.B. Vernonia calvoana Shows Promise towards the Treatment of Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, W.; Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G. Therapeutic Mechanisms of Vernonia amygdalina Delile in the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Molecules 2017, 22, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, H.; Daley-Beckford, D.; Toyang, N.; Watson, C.; Hartley, S.; Bryant, J. The Anti-cancer Activity of Vernonia divaricata Sw against Leukaemia, Breast and Prostate Cancers In Vitro. West Indian Med. J. 2014, 63, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyang, N.J.; Ateh, E.N.; Davis, H.; Tane, P.; Sondengam, L.B.; Bryant, J.; Verpoorte, R. In vivo antiprostate tumor potential of Vernonia guineensis Benth. (Asteraceae) tuber extract (VGDE) and the cytotoxicity of its major compound pentaisovaleryl sucrose. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekor, M. The growing use of herbal medicines: Issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tona, L.; Cimanga, R.; Mesia, K.; Musuamba, C.; De Bruyne, T.; Apers, S.; Hernans, N.; Van Miert, S.; Pieters, L.; Totté, J.; et al. In vitro antiplasmodial activity of extracts and fractions from seven medicinal plants used in the Democratic Republic of Congo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 93, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izevbigie, E.B. Discovery of Water-Soluble Anticancer Agents (Edotides) from a Vegetable Found in Benin City, Nigeria. Exp. Biol. Med. 2003, 228, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraina, I.A.; Adaudi, A.O.; Mamman, M.; Kazeem, H.M.; Picard, J.; McGaw, L.J.; Eloff, J.N. Antimycoplasmal activity of some plant species from northern Nigeria compared to the currently used therapeutic agent. Pharm. Biol. 2010, 48, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erasto, P.; Grierson, D.S.; Afolayan, A.J. Antioxidant Constituents inVernonia amygdalina. Leaves. Pharm. Biol. 2007, 45, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwanauta, R.W.; Mtei, K.A.; Ndakidemi, P.A. Prospective Bioactive Compounds from Vernonia amygdalina, Lippia javanica, Dysphania ambrosioides and Tithonia diversifolia in Controlling Legume Insect Pests. Agric. Sci. 2014, 5, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alara, O.R.; Abdurahman, N.H.; Ukaegbu, C.I.; Kabbashi, N.A. Extraction and characterization of bioactive compounds in Vernonia amygdalina leaf ethanolic extract comparing Soxhlet and microwave-assisted extraction techniques. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2019, 13, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessie, Y.; Tadesse, S.; Eswaramoorthy, R. Physicochemical parameter influences and their optimization on the biosynthesis of MnO2 nanoparticles using Vernonia amygdalina leaf extract. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 6472–6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedjou, C.; Izevbigie, E.; Tchounwou, P.B. Preclinical Assessment of Vernonia amygdalina Leaf Extracts as DNA Damaging Anti-cancer Agent in the Management of Breast Cancer. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2008, 5, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, F.C.; Woo, C.C.; Hsu, A.; Tan, B.K.H. The Anti-Cancer Activities of Vernonia amygdalina Extract in Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines Are Mediated through Caspase-Dependent and p53-Independent Pathways. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Li, M.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, L.; et al. Oroxylin A reverses hypoxia-induced cisplatin resistance through inhibiting HIF-1α mediated XPC transcription. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6893–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Lei, J.-C.; Hao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, C.-X.; Yu, J.-Q. Sensitisation of ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin by flavonoids fromScutellaria barbata. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 28, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, S.; Turkekul, K.; Serttas, R.; Erdogan, Z. The natural flavonoid apigenin sensitizes human CD44 + prostate cancer stem cells to cisplatin therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachadourian, R.; Leitner, H.; Day, B. Selected flavonoids potentiate the toxicity of cisplatin in human lung adenocarcinoma cells: A role for glutathione depletion. Int. J. Oncol. 2007, 31, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, N.N.N.N.M.; Septama, A.W.; Simbak, N.; Abu Bakar, N.H.; Rahmi, E.P. Synergistic Effect of Flavonoids from Artocarpus heterophyllus Heartwoods on Anticancer Activity of Cisplatin Against H460 and MCF-7 Cell Lines. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2019, 25, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, A.G.; Prieto, M.; Colino, C.I.; Gutiérrez-Millán, C.; Ruszkowska-Ciastek, B.; De Paz, E.; Martín, A.; Morales, A.I.; López-Hernández, F.J. A Micellar Formulation of Quercetin Prevents Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghavami, G.; Muhammadnejad, S.; Amanpour, S.; Sardari, S. Fraction Bioactivity Screening of Mulberry Leaf and Two Flavonoids in Combination with Cisplatin on Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 19, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Subhan, F.; Ahmad, N.; Sewell, R.D. The flavonoid 6-methoxyflavone allays cisplatin-induced neuropathic allodynia and hypoalgesia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athira, K.V.; Madhana, R.M.; Lahkar, M. Flavonoids, the Emerging Dietary Supplement against Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 248, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tomar, A.; Vasisth, S.; Khan, S.I.; Malik, S.; Nag, T.; Arya, D.S.; Bhatia, J. Galangin ameliorates cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in vivo by modulation of oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation through interplay of MAPK signaling cascade. Phytomedicine 2017, 34, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, K.M.; El-Raouf, O.M.A.; Metwally, S.A.; El-Latif, H.A.A.; El-Sayed, M.E. Hesperidin and Rutin, Antioxidant Citrus Flavonoids, Attenuate Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2014, 28, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.M.; Kang, J.G.; Bae, J.S.; Pae, H.O.; Lyu, Y.S.; Jeon, B.H. The Flavonoid Apigenin Ameliorates Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity through Reduction of p53 Activation and Promotion of PI3K/Akt Pathway in Human Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 186436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-W.; Xu, Y.; Weng, Y.-Y.; Fan, X.-Y.; Bai, Y.-F.; Zheng, X.-Y.; Lou, L.-J.; Zhang, F. Astilbin ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 114, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, S.; Zou, X.; Wei, C.; Liang, T.; Zhong, X. Panax notoginseng saponins reduces the cisplatin-induced acute renal injury by increasing HIF-1α/BNIP3 to inhibit mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 111965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, B.; Liu, Z.; Xie, L.; Lv, L.; Zhu, W.; Liu, J.; Dai, Y.; She, W. Panax notoginseng Saponins protect auditory cells against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity by inducing the AKT/Nrf2 signaling-mediated redox pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 3533–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.-N.; Li, Y.-Z.; Li, W.; Yan, X.-T.; Yang, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.-C.; Yang, L.-M. Nephroprotective Effects of Saponins from Leaves of Panax quinquefolius against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, S.; Lv, P.; Cui, J.; Liu, F.; Peng, L.; Ma, L.; Liu, C.; Gao, W. Paris saponin II-induced paraptosis-associated cell death increased the sensitivity of cisplatin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 406, 115206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Zhong, X. Panax notoginseng saponins mitigate cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity by inducing mitophagy via HIF-1α. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 102989–103003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koczurkiewicz, P.; Klaś, K.; Grabowska, K.; Piska, K.; Rogowska, K.; Wojcik-Pszczoła, K.; Podolak, I.; Galanty, A.; Michalik, M.; Pękala, E. Saponins as chemosensitizing substances that improve effectiveness and selectivity of anticancer drug—Minireview of in vitro studies. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N.; Chen, L.; Li, B.; Rankin, G.O.; Chen, Y.C.; Tu, Y. Purified Tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze) Flower Saponins Induce the p53-Dependent Intrinsic Apoptosis of Cisplatin-Resistant Ovarian Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avato, P.; Migoni, D.; Argentieri, M.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Tava, A. Activity of Saponins from Medicago species Against HeLa and MCF-7 Cell Lines and their Capacity to Potentiate Cisplatin Effect. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1508–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yu, Y. Synergistic Cytotoxicity of β-Elemene and Cisplatin in Gingival Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Inhibition of STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.-H.; Guo, J.-M.; Xie, Y.-T.; Hua, J.; Dai, Y.-Y.; Zhang, W.; Lin, T.-C.; Liu, Y.-P. Structural characterization, antiproliferative and anti-inflammatory activities of alkaloids from the roots of Zanthoxylum austrosinense. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 102, 104101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mon, M.T.; Yodkeeree, S.; Punfa, W.; Pompimon, W.; Limtrakul, P. Alkaloids from Stephania venosa as Chemo-Sensitizers in SKOV3 Ovarian Cancer Cells via Akt/NF-κB Signaling. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 66, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Xue, C.; Zhang, L. Piperine Alkaloid Induces Anticancer and Apoptotic Effects in Cisplatin Resistant Ovarian Car-cinoma by Inducing G2/M Phase Cell Cycle Arrest, Caspase Activation and Inhibition of Cell Migration and PI3K/Akt/GSK3β Signalling Pathway. JBUON 2019, 24, 2316–2321. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkhosh-Inanlou, R.; Molaparast, M.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Shafiei-Irannejad, V. Sanguinarine enhances cisplatin sensitivity via glutathione depletion in cisplatin--resistant ovarian cancer (A2780) cells. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 95, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.-H.; Chen, X.-X.; Lee, C.K.-F.; Sze, S.C.-W.; Feng, Y.-B.; Yang, Z.-J.; Chen, H.-Y.; Li, S.-T.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Wei, G.; et al. Dendrobine targeting JNK stress signaling to sensitize chemotoxicity of cisplatin against non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Phytomedicine 2018, 53, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuai, C.-P.; Ju, L.-J.; Hu, P.-P.; Huang, F. Corydalis saxicola Alkaloids Attenuate Cisplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain by Reducing Loss of IENF and Blocking TRPV1 Activation. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 407–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sioud, F.; Ben Toumia, I.; Lahmer, A.; Khlifi, R.; Dhaouefi, Z.; Maatouk, M.; Ghedira, K.; Chekir-Ghedira, L. Methanolic extract of Ephedra alata ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity through reducing oxidative stress and genotoxicity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12792–12801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xu, J.; Jiang, L.; Huang, J.; Yan, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Q. Improved antitumor activity of cisplatin combined with Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides in U14 cervical carcinoma--bearing mice. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2019, 35, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Xu, Y.; Tang, L.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Wei, Y.; Shao, X.; Shao, X.; Xin, Z.; Cai, B.; et al. Astragalus Polysaccharide Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Suppressing Oxidative Damage and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2851349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Caihong, L.; Liu, C.; Min, J.; Hu, M.; Guo, W. Astragalus polysaccharides increase the sensitivity of SKOV3 cells to cisplatin. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2017, 297, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.-L.; Hu, X.-D.; Xiao, J.; Yu, D.-Q. Astragalus polysaccharide may increase sensitivity of cervical cancer HeLa cells to cisplatin by regulating cell autophagy. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2018, 43, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelam; Khatkar, A.; Sharma, K.K. Phenylpropanoids and Its Derivatives: Biological Activities and Its Role in Food, Phar-maceutical and Cosmetic Industries. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2655–2675. [Google Scholar]
- Taofiq, O.; González-Paramás, A.M.; Barreiro, M.F.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; McPhee, D.J. Hydroxycinnamic Acids and Their De-rivatives: Cosmeceutical Significance, Challenges and Future Perspectives, a review. Molecules 2017, 22, 281. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Dahiya, V.; Kasala, E.R.; Bodduluru, L.N.; Lahkar, M. The renoprotective activity of hesperetin in cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in rats: Molecular and biochemical evidence. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdemir, F.N.E.; Albayrak, M.; Çalik, M.; Bayir, Y.; Gülçin, I. The Protective Effects of p-Coumaric Acid on Acute Liver and Kidney Damages Induced by Cisplatin. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abass, S.A.; Abdel-Hamid, N.M.; Abouzed, T.K.; El-Shishtawy, M.M. Chemosensitizing effect of Alpinia officinarum rhizome extract in cisplatin-treated rats with hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.-B.; Hou, M.; Ma, W.-B.; Zhang, J.-X.; Li, Z.-Y.; Luo, H.-B.; Tang, K.-H.; Cao, S.-H. First total synthesis of a new phenylpropanoid glycoside: Natural cytotoxic compound from Cirsium japonicum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 20, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, V.K.; Kumar, S. Recent Development on Naphthoquinone Derivatives and Their Therapeutic Applications as Anti-cancer Agents. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 1087–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, S.; Rohbogner, C.J.; Cieslak, M.; Kazmierczak-Baranska, J.; Donevski, S.; Nawrot, B.; Lorenz, I.-P. Rhodium(III) and iridium(III) complexes with 1,2-naphthoquinone-1-oximate as a bidentate ligand: Synthesis, structure, and biological activity. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 15, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daltoe, R.; Madeira, K.; Herleinger, A.; Filho, J.; Rezende, L.; Cerri, M.; Guimares, I.; Valadao, I.; Teixeira, S.; Greco, S.; et al. 21 In Vitro Study of the Potential Antineoplastic Effect of Synthetic Naphthoquinones in Cisplatin-Resistant Ovarian Cancer Lineage. Maturitas 2012, 71, S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunassee, S.N.; Veale, C.G.; Shunmoogam-Gounden, N.; Osoniyi, O.; Hendricks, D.T.; Caira, M.R.; de la Mare, J.-A.; Edkins, A.L.; Pinto, A.V.; Júnior, E.N.D.S.; et al. Cytotoxicity of lapachol, β-lapachone and related synthetic 1,4-naphthoquinones against oesophageal cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 62, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukić, M.; Vukovic, N.L.; Obradović, A.; Popovic, S.; Zaric, M.; Djurdjevic, P.; Marković, S.; Baskic, D.D. Naphthoquinone rich Onosma visianii Clem (Boraginaceae) root extracts induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in HCT-116 and MDA-MB-231 cancer cell lines. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 32, 2712–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilnikova, K.; Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Ryu, Y.S.; Park, J.E.; Hyun, Y.J.; Zhen, A.X.; Jeong, Y.J.; Jung, U.; Kim, I.G.; et al. Shikonin induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis and attenuates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cisplatin-resistant human ovarian cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 5417–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.N.S.; Rashtchizadeh, N.; Argani, H.; Roshangar, L.; Haghjo, A.G.; Sanajou, D.; Panah, F.; Jigheh, Z.A.; Dastmalchi, S.; Mesgari-Abbasi, M. Dunnione protects against experimental cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by modulating NQO1 and NAD+ levels. Free Radic. Res. 2018, 52, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagatell, R.; Beliakoff, J.; David, C.L.; Marron, M.T.; Whitesell, L. Hsp90 inhibitors deplete key anti-apoptotic proteins in pediatric solid tumor cells and demonstrate synergistic anticancer activity with cisplatin. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 113, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatokoro, M.; Koga, F.; Yoshida, S.; Kawakami, S.; Fujii, Y.; Neckers, L.; Kihara, K. Potential role of Hsp90 inhibitors in overcoming cisplatin resistance of bladder cancer-initiating cells. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 131, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, T.E.; Raghavendra, N.M.; Penido, C. Natural heat shock protein 90 inhibitors in cancer and inflammation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 189, 112063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerji, U.; O’Donnell, A.; Scurr, M.; Pacey, S.C.; Stapleton, S.; Asad, Y.; Simmons, L.; Maloney, A.; Raynaud, F.; Campbell, M.; et al. Phase I Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Study of 17-Allylamino, 17-Demethoxygeldanamycin in Patients with Advanced Malignancies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 4152–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.A.; Omar, H.M.; Elghaffar, S.K.A.; Ragb, S.M.; Nasser, A.Y. The antioxidant activity of Vitamin C, DPPD and l-cysteine against Cisplatin-induced testicular oxidative damage in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaied, F.A.; Elballat, S.E. Reduction in the Formation of Micronucleated Polychromatic Erythrocytes Induced by Cisplatin in Bone Marrow Cells of Rats by using Antioxidants. Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. C Physiol. Mol. Biol. 2019, 11, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leekha, A.; Gurjar, B.S.; Tyagi, A.; Rizvi, M.A.; Verma, A.K. Vitamin C in synergism with cisplatin induces cell death in cervical cancer cells through altered redox cycling and p53 upregulation. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 2503–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, N.; Nawaz, A.; Ullah, H.; Ullah, R.; Nabi, G.; Ullah, A.; Wahab, F.; Jahan, S.; Fu, J. Therapeutic effects of chitosan-embedded vitamin C, E nanoparticles against cisplatin-induced gametogenic and androgenic toxicity in adult male rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 56319–56332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, K.; Li, X.; Xu, R.; Ye, L.; Kong, H.; Zeng, X.; Wang, H.; Xie, W. The synergistic effect of resveratrol in combination with cisplatin on apoptosis via modulating autophagy in A549 cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2016, 48, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsenduny, F.; Badria, F.A.; El-Waseef, A.M.; Chauhan, S.C.; Halaweish, F. Approach for chemosensitization of cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer by cucurbitacin B. Tumor Biol. 2015, 37, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Hong, K.O.; Hwang, J.K.; Park, K.-K. Xanthorrhizol has a potential to attenuate the high dose cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.; Eldaim, M.A.; Abdel-Daim, M. Nephroprotective effect of bee honey and royal jelly against subchronic cisplatin toxicity in rats. Cytotechnology 2015, 68, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, M.-J.; Wang, C.-W.; Lin, J.-T.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Hsi, Y.-T.; Lo, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-C.; Chen, M.-K. Celastrol, a plant-derived triterpene, induces cisplatin-resistance nasopharyngeal carcinoma cancer cell apoptosis though ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2018, 58, 152805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Wei, C.; Rankin, G.O.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Ren, N.; Ye, X.; Chen, Y.C. Dietary compound proanthocyanidins from Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra Sieb. et Zucc.) leaves inhibit angiogenesis and regulate cell cycle of cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells via targeting Akt pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 40, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulos, G.P.; Boulikas, T. Lipoplatin Formulation Review Article. J. Drug Deliv. 2011, 2012, 581363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Lu, C.; Khuri, F.R.; Tonda, M.; Glisson, B.S.; Liu, D.; Jung, M.; Hong, W.K.; Herbst, R.S. A phase II study of STEALTH cisplatin (SPI-77) in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2001, 34, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kashio, A.; Cabral, H.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K.; Yamasoba, T. Micellization of cisplatin (NC-6004) reduces its ototoxicity in guinea pigs. J. Control. Release 2012, 157, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragovich, T.; Mendelson, D.; Hoos, A.; Lewis, J.; Kurtin, S.; Richardson, K.; Von Hoff, D. 268 A phase II trial of aroplatin (L-NDDP), a liposomal DACH platinum, in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC)—A preliminary report. Eur. J. Cancer Suppl. 2003, 1, S82–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhiutami, N.M.D.; Arozal, W.; Louisa, M.; Rahmat, D.; Wuyung, P.E. Curcumin Nanoparticle Enhances the Anticancer Effect of Cisplatin by Inhibiting PI3K/AKT and JAK/STAT3 Pathway in Rat Ovarian Carcinoma Induced by DMBA. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, A.; Villares, G.J.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Lewis, A.; Landua, J.; Dobrolecki, L.E.; Wilson, L.J.; Lewis, M.T. Carbon nanotube capsules enhance the in vivo efficacy of cisplatin. Acta Biomater. 2017, 58, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarra, J.; Encinas, D.; Blanco, M.; Barbosa, S.; Taboada, P.; Juarez, J.E.; Valdez, M.A. Co-encapsulation of magnetic nanoparticles and cisplatin within biocompatible polymers as multifunctional nanoplatforms: Synthesis, characterization, andin vitroassays. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 5, 015023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, M.M.; Al-Mahallawi, A.M.; Nassar, N.; Stork, B.; Shouman, S.A. Targeting colorectal cancer cell metabolism through development of cisplatin and metformin nano-cubosomes. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, J.; Kumar Panigrahi, A.; Rahman Khuda-Bukhsh, A.; Rahman Khuda, A. Physico-Chemical and Ultra-Structural Characterizations of PLGA-Loaded Nanoparticles of Boldine and Their Efficacy in Ameliorating Cisplatin Induced Hepato-toxicity in Normal Liver Cells in Vitro. J. Innov. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2015, 2, 506–521. [Google Scholar]
- Yavuz, B.; Zeki, J.; Taylor, J.; Harrington, K.; Coburn, J.M.; Ikegaki, N.; Kaplan, D.L.; Chiu, B. Silk Reservoirs for Local Delivery of Cisplatin for Neuroblastoma Treatment: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 2748–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Pérez, A.A.; Gil, A.L.; Pérez, S.A.; Cutillas, N.; Meyer, H.; Pedreño, M.; Aznar-Cervantes, S.D.; Janiak, C.; Cenis, J.L.; Ruiz, J. Antitumor properties of platinum(iv) prodrug-loaded silk fibroin nanoparticles. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 13513–13521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, C.; Wu, W.; Jiang, X. Cellular uptake, antitumor response and tumor penetration of cisplatin-loaded milk protein nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etman, S.M.; Elnaggar, Y.S.R.; Abdallah, O.Y. Fucoidan, a natural biopolymer in cancer combating: From edible algae to nanocarrier tailoring. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-Y.; Lin, T.-Y.; Hu, C.-H.; Shu, D.T.F.; Lu, M.-K. Fucoidan upregulates TLR4/CHOP-mediated caspase-3 and PARP activation to enhance cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in human lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 432, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Yoon, Y.M.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Protective Role of Fucoidan on Cisplatin-mediated ER Stress in Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 5515–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.Y.; Ku, S.K.; Kim, H.J.; Han, J.S. Low molecular weight fucoidan ameliorating the chronic cisplatin-induced delayed gastrointestinal motility in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 4468–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Binders | HSP90 Inhibitor | Source | Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-terminal domain binders | Ansamycins | Streptomyces hygroscopicus | Benzoquinone ansamycin |
| Radicicol and pochonins | Monosporium bonorden | Macrocyclic lactone | |
| Geraniin | Geranium thunbergii | Tannin | |
| Gambogic acid | Garcinia hanburyi | Xanthonoid | |
| Panaxynol | Panax ginseng | Polyacetylene | |
| Deguelin | Fabaceae (Leguminosae) plants | Rotenoid | |
| Heteronemin | Marine sponges | Sesterpene | |
| C9-type iridoids | Bignoniaceae plants | C9-type iridoids | |
| Middle-domain binders | Lentiginosine | Astragalus lentiginosus | Dihydroxyindolizidine alkaloid |
| Kongensin A | Croton kongensis | Diterpene | |
| Sansalvamide | Fusarium species | Cyclic pentadepsipeptide | |
| C-terminal domain binders | Derrubone | Derris robusta | Isoflavone |
| Coumarin antibiotics | Streptomyces niveus | Aminocoumarin | |
| Epigallocathechin | Camellia sinensis | Catechins | |
| Fusicoccane diterpenes | Alternaria brassicicola, Hypoestes forsskaolii | Fusicoccane diterpene | |
| Co-chaperone binders | Withaferin A | Solanacea plants | Steroidal lactones |
| Cucurtabicin D | Cucurbitacea plants | Tetracyclic triterpenes | |
| Celastrol | Tripterygium wilfordii; Celastrus regelii | Triterpene | |
| Gedunin | Meliaceae plants | Triterpene |
| Type of Nanodrug Delivery | Examples |
|---|---|
| Polymeric CDDP-based nanodrug delivery systems | Polylactic-co-glycolic acid nanoparticles |
| Polyethylene glycol (PEG) nanoparticles | |
| Chitosan nanoparticles | |
| Micelles | |
| Dendrimers | |
| Polymer–drug conjugates | |
| Poly butyl cyanoacrylate (PBCA) based nanoparticles | |
| Poly aspartic acid (PAA) nanoparticles | |
| Polydopamine nanoparticles | |
| Glutathione-scavenging poly (disulfide amide) nanoparticles | |
| Albumin-based nano-formulations | |
| Gelatin NPs | |
| Lipid-based nanocarriers for cisplatin | Liposomes |
| Cubosomes | |
| Transfersomes | |
| Inorganic nanoparticle-based nanodelivery systems | Gold nanoparticles |
| Mesoporous silica nanoparticles | |
| Magnetic iron oxide NPs | |
| Calcium-based nanoparticles | |
| NaGdF4:Yb3þ/Er3þ nanoparticles | |
| Europium (III) doped yttrium vanadate nanoparticles | |
| Aluminum-doped MCM-41 nanoparticles | |
| Photothermal conversion nanoparticles | |
| Melanin nanoparticles | |
| Coordination polymer nanoparticles | |
| Carbon-based nano-formulations for cisplatin | Carbon nanotubes |
| Graphene | |
| Fullerene |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dasari, S.; Njiki, S.; Mbemi, A.; Yedjou, C.G.; Tchounwou, P.B. Pharmacological Effects of Cisplatin Combination with Natural Products in Cancer Chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031532
Dasari S, Njiki S, Mbemi A, Yedjou CG, Tchounwou PB. Pharmacological Effects of Cisplatin Combination with Natural Products in Cancer Chemotherapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(3):1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031532
Chicago/Turabian StyleDasari, Shaloam, Sylvianne Njiki, Ariane Mbemi, Clement G. Yedjou, and Paul B. Tchounwou. 2022. "Pharmacological Effects of Cisplatin Combination with Natural Products in Cancer Chemotherapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 3: 1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031532
APA StyleDasari, S., Njiki, S., Mbemi, A., Yedjou, C. G., & Tchounwou, P. B. (2022). Pharmacological Effects of Cisplatin Combination with Natural Products in Cancer Chemotherapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(3), 1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031532







