The SDF1-CXCR4 Axis Is Involved in the Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy-Mediated Neuronal Cells Migration in Transient Brain Ischemic Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
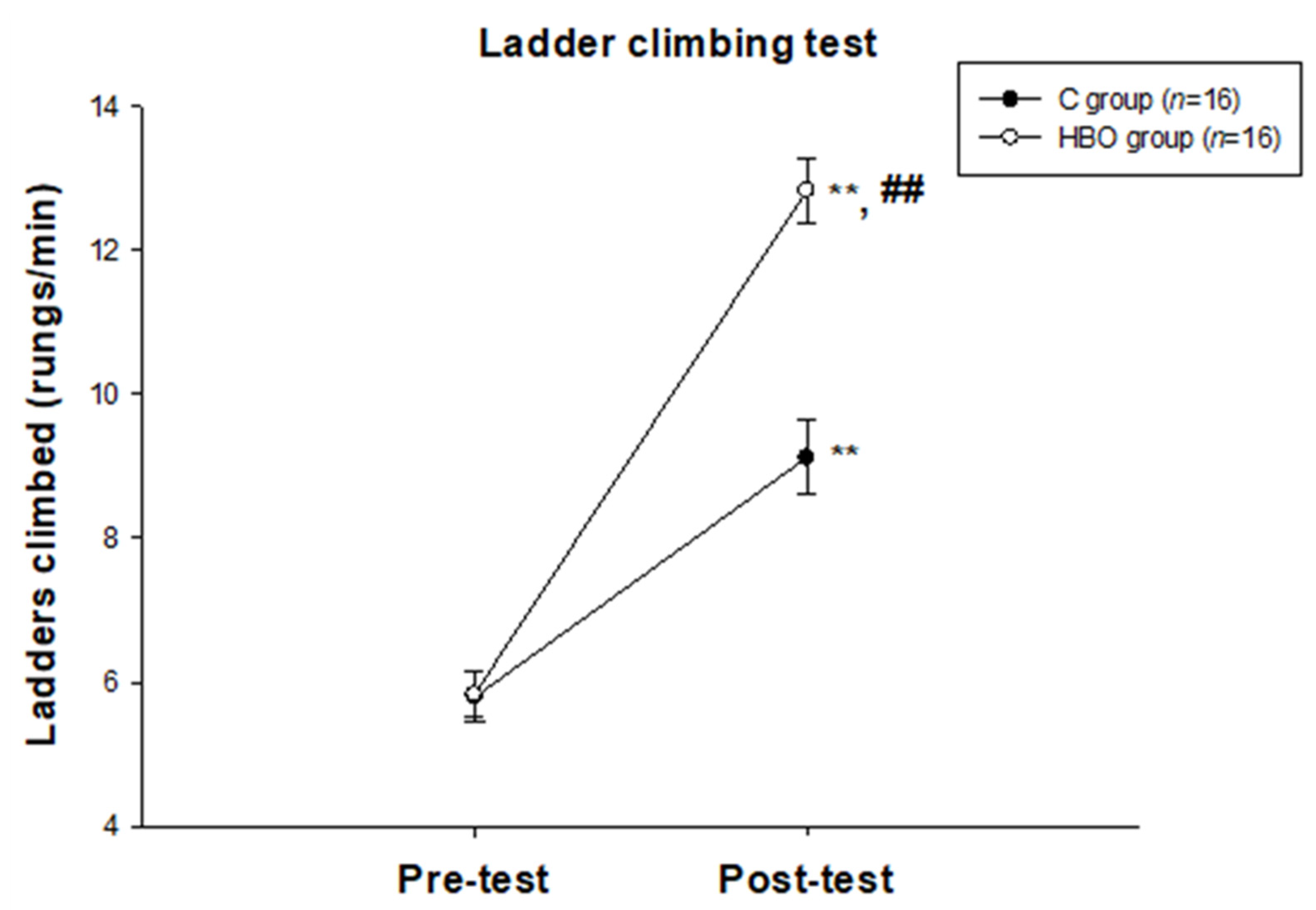
2.1. HBO Improves the Motor Function
2.2. HBOT Enhances SDF1 and CXCR4 Expressions in the Affected Motor Cortex
2.3. HBOT Enhances Neurogenesis and Cell Migration
2.4. HBOT Promotes Differentiation of Neurons
2.5. HBOT Up-Regulates BDNF Expression in the Affected Motor Cortex and Serum
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Grouping
4.2. Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
4.3. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
4.4. Motor Behavior Test
4.5. Tracking the Neurogenesis Cells
4.6. Sample Preparation
4.7. Immunofluorescent Examination
4.8. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Examination
4.9. SDF1 and CXCR4 Protein Examination
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heiss, W.D. The ischemic penumbra: Correlates in imaging and implications for treatment of ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2011, 32, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Peron, S.; Murray, K.; Jaber, M.; Gaillard, A. Cortical lesion stimulates adult subventricular zone neural progenitor cell proliferation and migration to the site of injury. Stem Cell Res. 2013, 11, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkowski, M.P.; Bettio, L.; Woo, E.K.; Patten, A.; Yau, S.Y.; Gil-Mohapel, J. Beyond the Hippocampus and the SVZ: Adult Neurogenesis Throughout the Brain. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2020, 14, 576444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillen, Y.; Kemps, H.; Gervois, P.; Wolfs, E.; Bronckaers, A. Adult Neurogenesis in the Subventricular Zone and Its Regulation After Ischemic Stroke: Implications for Therapeutic Approaches. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequerra, E.B. Subventricular zone progenitors in time and space: Generating neuronal diversity. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2014, 8, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imitola, J.; Raddassi, K.; Park, K.I.; Mueller, F.J.; Nieto, M.; Teng, Y.D.; Frenkel, D.; Li, J.; Sidman, R.L.; Walsh, C.A.; et al. Directed migration of neural stem cells to sites of CNS injury by the stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha/CXC chemokine receptor 4 pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 18117–18122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönemeier, B.; Schulz, S.; Hoellt, V.; Stumm, R. Enhanced expression of the CXCl12/SDF-1 chemokine receptor CXCR7 after cerebral ischemia in the rat brain. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 198, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.Y. Roles of chemokine CXCL12 and its receptors in ischemic stroke. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, G.Q. SDF-1alpha/CXCR4-mediated migration of systemically transplanted bone marrow stromal cells towards ischemic brain lesion in a rat model. Brain Res. 2008, 1195, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shichinohe, H.; Kuroda, S.; Yano, S.; Hida, K.; Iwasaki, Y. Role of SDF-1/CXCR4 system in survival and migration of bone marrow stromal cells after transplantation into mice cerebral infarct. Brain Res. 2007, 1183, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, Z.; Hu, Z.; Hu, M.; Ding, P. The effect of stromal cell-derived factor 1 in the migration of neural stem cells. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 70, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Qu, H.; Xiao, T.; Zhao, M.; Jolkkonen, J.; Zhao, C. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 and its receptor CXCR4 in adult neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2013, 31, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.; Zhou, C.; Kusaka, I.; Calvert, J.W.; Parent, A.D.; Nanda, A.; Zhang, J.H. Inhibition of apoptosis by hyperbaric oxygen in a rat focal cerebral ischemic model. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2003, 23, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veltkamp, R.; Siebing, D.A.; Sun, L.; Heiland, S.; Bieber, K.; Marti, H.H.; Nagel, S.; Schwab, S.; Schwaninger, M. Hyperbaric oxygen reduces blood-brain barrier damage and edema after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2005, 36, 1679–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matchett, G.A.; Martin, R.D.; Zhang, J.H. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and cerebral ischemia: Neuroprotective mechanisms. Neurol. Res. 2009, 31, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milovanova, T.N.; Bhopale, V.M.; Sorokina, E.M.; Moore, J.S.; Hunt, T.K.; Hauer-Jensen, M.; Velazquez, O.C.; Thom, S.R. Hyperbaric oxygen stimulates vasculogenic stem cell growth and differentiation in vivo. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.J.; Xie, Y.; Bosco, G.M.; Chen, C.; Camporesi, E.M. Hyperbaric oxygenation alleviates MCAO-induced brain injury and reduces hydroxyl radical formation and glutamate release. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Strelow, H.; Mies, G.; Veltkamp, R. Oxygen therapy improves energy metabolism in focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2011, 1415, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hei, M.Y.; Dai, J.J.; Hu, N.; Xiang, X.Y. Effect of hyperbaric oxygenation on mitochondrial function of neuronal cells in the cortex of neonatal rats after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2016, 49, e5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Chen, J.F.; Liu, M.; Shen, J. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on the permeability of the blood-brain barrier in rats with global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.C.; Yang, Y.R.; Wang, R.Y. Effects of repetitive hyperbaric oxygen therapy on neuroprotection in middle cerebral artery occlusion rats. Brain Res. 2020, 1748, 147097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Y.H.; Lv, H.Y.; Chen, L.T. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on lipid peroxidation and visual development in neonatal rats with hypoxia-ischemia brain damage. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 5, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Feng, Z.; Liu, J.; Ju, R. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment promotes neural stem cell proliferation in the subventricular zone of neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 8, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Chio, C.C.; Chang, C.P.; Wang, L.C.; Chiang, P.M.; Niu, K.C.; Tsai, K.J. Long course hyperbaric oxygen stimulates neurogenesis and attenuates inflammation after ischemic stroke. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 512978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Ostrowski, R.P.; Soejima, Y.; Rolland, W.B.; Krafft, P.R.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. Delayed hyperbaric oxygen therapy induces cell proliferation through stabilization of cAMP responsive element binding protein in the rat model of MCAo-induced ischemic brain injury. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 51, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Liang, X.; Chen, D.; Chen, Y.; Doycheva, D.; Tang, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. Delayed hyperbaric oxygen therapy promotes neurogenesis through reactive oxygen species/hypoxia-inducible factor-1α/β-catenin pathway in middle cerebral artery occlusion rats. Stroke 2014, 45, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wei, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, C. Hyperbaric oxygen promotes neural stem cell proliferation by activating vascular endothelial growth factor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling after traumatic brain injury. NeuroReport 2017, 28, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.W.; Wang, Y.Q.; Xu, M.; Shen, D.H.; Wang, J.J.; Huang, F.; Yu, Z.; Sun, F.Y. Functional integration of newly generated neurons into striatum after cerebral ischemia in the adult rat brain. Stroke 2008, 39, 2837–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, K.; Furuta, T.; Hioki, H.; Nakamura, K.C.; Kuramoto, E.; Tanaka, Y.; Funatsu, N.; Shimizu, K.; Oishi, T.; Hayashi, M.; et al. Ischemia-induced neurogenesis of neocortical layer 1 progenitor cells. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuzberg, M.; Kanov, E.; Timofeev, O.; Schwaninger, M.; Monyer, H.; Khodosevich, K. Increased subventricular zone-derived cortical neurogenesis after ischemic lesion. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 226, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.F.; Xapelli, S. Intervention of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Other Neurotrophins in Adult Neurogenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1331, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Cai, J.; Kenyon, L.; Iozzo, R.; Rosenwasser, R.; Iacovitti, L. Systemic Factors Trigger Vasculature Cells to Drive Notch Signaling and Neurogenesis in Neural Stem Cells in the Adult Brain. Stem Cells 2019, 37, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Mao, X.; Xie, L.; Sun, F.; Greenberg, D.A.; Jin, K. Conditional depletion of neurogenesis inhibits long-term recovery after experimental stroke in mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Sun, H.; Wu, S.; Lee, C.C.; Akamatsu, Y.; Wang, R.K.; Kernie, S.G.; Liu, J. Conditional ablation of neuroprogenitor cells in adult mice impedes recovery of poststroke cognitive function and reduces synaptic connectivity in the perforant pathway. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 17314–17325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponti, G.; Obernier, K.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Lineage progression from stem cells to new neurons in the adult brain ventricular-subventricular zone. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 1649–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardelt, A.A.; Bhattacharyya, B.J.; Belmadani, A.; Ren, D.; Miller, R.J. Stromal derived growth factor-1 (CXCL12) modulates synaptic transmission to immature neurons during post-ischemic cerebral repair. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 248, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, Z.; Mu, X.; Zhao, C.; Teng, W. The Role of SDF-1/CXCR4/CXCR7 in Neuronal Regeneration after Cerebral Ischemia. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. Chemotactic responses of neural stem cells to SDF-1α correlate closely with their differentiation status. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 54, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.A.; Ghafghazi, S.; Pouriran, R.; Mortazavi, S.E.; Parvardeh, S. Attenuating effect of paroxetine on memory impairment following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat: The involvement of BDNF and antioxidant capacity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 893, 173821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Depression, and Physical Activity: Making the Neuroplastic Connection. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 7260130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.L.; Hai, Y.; Zhang, X.N.; Wang, Y.S.; Liu, X.H.; Ma, L.L.; Yue, R.; Xu, G.; Li, Z. Hyperbaric oxygen improves functional recovery of rats after spinal cord injury via activating stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXC chemokine receptor 4 axis and promoting brain-derived neurothrophic factor expression. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wan, M.; Yang, Q.; Ding, X.; Zhou, Z. The stromal cell-derived factor-1 α (SDF-1α)/cysteine-X-cysteine chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) axis: A possible prognostic indicator of acute ischemic stroke. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadanny, A.; Golan, H.; Fishlev, G.; Bechor, Y.; Volkov, O.; Suzin, G.; Ben-Jacob, E.; Efrati, S. Hyperbaric oxygen can induce neuroplasticity and improve cognitive functions of patients suffering from anoxic brain damage. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2015, 33, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.W.; Zhang, F.; Liu, H.J.; Li, Z. Hyperbaric oxygen ameliorated the lesion scope and nerve function in acute spinal cord injury patients: A retrospective study. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 53, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadanny, A.; Rittblat, M.; Bitterman, M.; May-Raz, I.; Suzin, G.; Boussi-Gross, R.; Zemel, Y.; Bechor, Y.; Catalogna, M.; Efrati, S. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves neurocognitive functions of post-stroke patients—A retrospective analysis. Restor Neurol. Neurosci. 2020, 38, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, E.J. Hypoxia and aging. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadanny, A.; Efrati, S. The Hyperoxic-Hypoxic Paradox. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Yao, X.; Wu, W.; Yu, Z.; Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Liu, D. HIF-1α/SDF-1/CXCR4 axis reduces neuronal apoptosis via enhancing the bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cell migration in rats with traumatic brain injury. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2020, 114, 104416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.C.; Yang, Y.R.; Wang, P.S.; Wang, R.Y. Quercetin enhances exercise-mediated neuroprotective effects in brain ischemic rats. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 1908–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.T.; Hsu, C.Y.; Hogan, E.L.; Maricq, H.; Balentine, J.D. A model of focal ischemic stroke in the rat: Reproducible extensive cortical infarction. Stroke 1986, 17, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, S.A.; Hoff, J.T.; Betz, A.L. Middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats: A neurological and pathological evaluation of a reproducible model. Neurosurgery 1992, 31, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Y.; Chang, H.C.; Chen, C.H.; Tsai, Y.W.; Yang, Y.R. Effects of hyperbaric oxygenation on oxidative stress in acute transient focal cerebral ischemic rats. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.S.; Zhang, W.; Kang, Z.M.; Ding, S.J.; Liu, W.W.; Zhang, J.H.; Guan, Y.T.; Sun, X.J. Hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning reduces ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibition of apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway in rat brain. Neuroscience 2009, 159, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Li, J.; Lai, Q.; Rafols, J.A.; Luan, X.; Clark, J.; Diaz, F.G. Motor balance and coordination training enhances functional outcome in rat with transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neuroscience 2004, 123, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. In Plates and Figures, 6th ed.; Harcourt Brace Jovanovich: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 72–106. [Google Scholar]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.-Y.; Yang, Y.-R.; Chang, H.-C. The SDF1-CXCR4 Axis Is Involved in the Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy-Mediated Neuronal Cells Migration in Transient Brain Ischemic Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031780
Wang R-Y, Yang Y-R, Chang H-C. The SDF1-CXCR4 Axis Is Involved in the Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy-Mediated Neuronal Cells Migration in Transient Brain Ischemic Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(3):1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031780
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ray-Yau, Yea-Ru Yang, and Heng-Chih Chang. 2022. "The SDF1-CXCR4 Axis Is Involved in the Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy-Mediated Neuronal Cells Migration in Transient Brain Ischemic Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 3: 1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031780
APA StyleWang, R.-Y., Yang, Y.-R., & Chang, H.-C. (2022). The SDF1-CXCR4 Axis Is Involved in the Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy-Mediated Neuronal Cells Migration in Transient Brain Ischemic Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(3), 1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031780




