New Insights in the Control of Fat Homeostasis: The Role of Neurotensin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Central NT in the Regulation of Metabolism
| Brain Area Involved | NT Effects | References |
|---|---|---|
| Ventral tegmental area | Reduced feeding Increased activity | Hawkins et al. [34] Kelley et al. [35] Kalivas et al. [42] |
| Substantia nigra | Reduced feeding | Vaughn et al. [36] |
| Nucleus accumbens | Reduced activity Increased resting behavior No effects on feeding | Kalivas et al. [43] Ervin et al. [44] Robledo et al. [45] |
| Hippocampus | Increased activity | Cador et al. [46] |
3. NT as a Gut Hormone—Lipids and Fat Homeostasis
3.1. NT and Lipid Metabolism
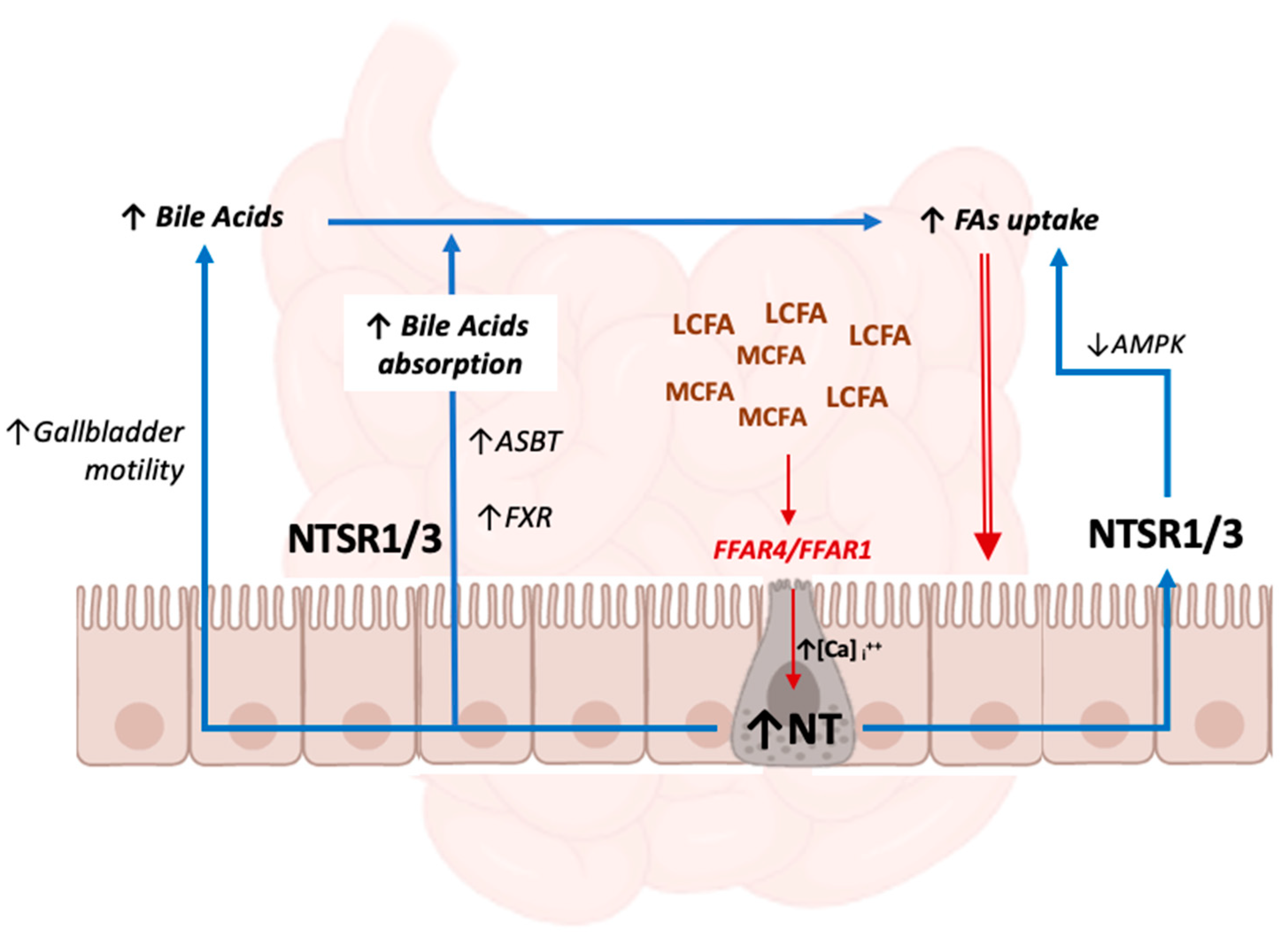
3.2. NT and Bile Acid Metabolism
3.3. NT, Microbiota Composition, and Gut Mucosal Homeostasis
3.4. NT and Adipose Tissue
4. NT and Glucose Metabolism
5. NT in the Pathophysiology of Insulin Resistance-Related Disorders
5.1. Obesity
5.2. Diabetes Mellitus
5.3. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Liver Cancer
6. NT and Cardiovascular Disease
7. NT as a Therapeutic Target and Screening Tool for Dysmetabolic Conditions: Evidence and Future Perspectives
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friry, C.; Feliciangeli, S.; Richard, F.; Kitabgi, P.; Rovere, C. Production of recombinant large proneurotensin/neuromedin n-derived peptides and characterization of their binding and biological activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, D.F.; Smeekens, S.P.; Ohagi, S.; Chan, S.J. The new enzymology of precursor processing endoproteases. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 23435–23438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, V.E.; Towle, A.C.; Pickel, V.M. Vesicular and cytoplasmic localization of neurotensin-like immunoreactivity (NTLI) in neurons postsynaptic to terminals containing NTLI and/or tyrosine hydroxylase in the rat central nucleus of the amygdala. J. Neurosci. Res. 1991, 30, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iversen, L.L.; Iversen, S.D.; Bloom, F.; Douglas, C.; Brown, M.; Vale, W. Calcium-dependent release of somatostatin and neurotensin from rat brain in vitro. Nature 1978, 273, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, S.; Bérod, A.; Zahm, D.S.; Rostène, W. Brain neurotensin, psychostimulants, and stress–emphasis on neuroanatomical substrates. Peptides 2006, 27, 2364–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazella, J.; Zsürger, N.; Navarro, V.; Chabry, J.; Kaghad, M.; Caput, D.; Ferrara, P.; Vita, N.; Gully, D.; Maffrand, J.P.; et al. The 100-kDa neurotensin receptor is gp95/sortilin, a non-G-protein-coupled receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 26273–26276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woodworth, H.L.; Beekly, B.G.; Batchelor, H.M.; Bugescu, R.; Perez-Bonilla, P.; Schroeder, L.E.; Leinninger, G.M. Lateral Hypothalamic Neurotensin Neurons Orchestrate Dual Weight Loss Behaviors via Distinct Mechanisms. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 3116–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalafatakis, K.; Triantafyllou, K. Contribution of neurotensin in the immune and neuroendocrine modulation of normal and abnormal enteric function. Regul. Pept. 2011, 170, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraway, R.; Leeman, S.E. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J. Biol. Chem. 1973, 248, 6854–6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boules, M.; Li, Z.; Smith, K.; Fredrickson, P.; Richelson, E. Diverse roles of neurotensin agonists in the central nervous system. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torruella-Suárez, M.L.; McElligott, Z.A. Neurotensin in reward processes. Neuropharmacology 2020, 167, 108005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, R.A.; Leeman, S.E.; Carraway, R.; Williams, R.H. Isolation of human intestinal neurotensin. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 2476–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, J.M.; Sullivan, S.N.; Bloom, S.R.; Buchan, A.M.; Facer, P.; Brown, M.R.; Pearse, A.G. Specific localisation of neurotensin to the N cell in human intestine by radioimmunoassay and immunocytochemistry. Nature 1977, 270, 183–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, N.W.; McFarlane, A.; Kinsman, R.I.; Bates, T.E.; Blackhall, N.W.; Farrar, G.B.; Hall, J.C.; Moss, G.; Morris, A.P.; O’Neill, B.; et al. Effect of infusion of nutrient solutions into the ileum on gastrointestinal transit and plasma levels of neurotensin and enteroglucagon. Gastroenterology 1984, 86, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiller, R.C.; Trotman, I.F.; Adrian, T.E.; Bloom, S.R.; Misiewicz, J.J.; Silk, D.B. Further characterisation of the ‘ileal brake’ reflex in man--effect of ileal infusion of partial digests of fat, protein, and starch on jejunal motility and release of neurotensin, enteroglucagon, and peptide YY. Gut 1988, 29, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, A.M.; Bloom, S.R.; Long, R.G.; Fletcher, D.R.; Christofides, N.D.; Fitzpatrick, M.L.; Baron, J.H. Effect of neurotensin on gastric function in man. Lancet 1980, 315, 987–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinecke, M.; Weihe, E.; Carraway, R.E.; Leeman, S.E. Localization of neurotensin immunoreactive nerve fibres in the guinea-pig heart: Evidence derived by immunohistochemistry, radioimmunoassay and chromatography. Neuroscience 1982, 7, 1785–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Reynolds, G.P.; Emson, P.C. Neurotensin in the adrenal medulla. Neurosci. Lett. 1983, 35, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, B.M. Endocrine gene neurotensin: Molecular mechanisms and a model of intestinal differentiation. World J. Surg. 2002, 26, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, S.; Qiu, S.; Fiorentino, F.; Simillis, C.; Rasheed, S.; Tekkis, P.; Kontovounisios, C. The role of Neurotensin and its receptors in non-gastrointestinal cancers: A review. Cell Commun. Signal 2020, 18, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saiyasit, N.; Chunchai, T.; Apaijai, N.; Pratchayasakul, W.; Sripetchwandee, J.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. Chronic high-fat diet consumption induces an alteration in plasma/brain neurotensin signaling, metabolic disturbance, systemic inflammation/oxidative stress, brain apoptosis, and dendritic spine loss. Neuropeptides 2020, 82, 102047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koon, H.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Xu, H.; Kumar, A.; Zhao, D.; Karagiannides, I.; Dobner, P.R.; Pothoulakis, C. Neurotensin induces IL-6 secretion in mouse preadipocytes and adipose tissues during 2,4,6,-trinitrobenzensulphonic acid-induced colitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 8766–8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Wei, F.; Cheng, Y.; Han, L.; Yu, J. Neurotensin, a Novel Messenger to Cross-Link Inflammation and Tumor Invasion via Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Pathway. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 35, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Yang, W.; Cui, H.; Xu, M.; Yi, L. Oncogenic role of neurotensin and neurotensin receptors in various cancers. Clin. Exp. Pharm. Physiol. 2017, 44, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghaemimanesh, F.; Mehravar, M.; Milani, S.; Poursani, E.M.; Saliminejad, K. The multifaceted role of sortilin/neurotensin receptor 3 in human cancer development. J. Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 6271–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorsa, D.M.; de Kloet, E.R.; Mezey, E.; de Wied, D. Pituitary-brain transport of neurotensin: Functional significance of retrograde transport. Endocrinology 1979, 104, 1663–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevaert, B.; Wynendaele, E.; Stalmans, S.; Bracke, N.; D’Hondt, M.; Smolders, I.; van Eeckhaut, A.; De Spiegeleer, B. Blood-brain barrier transport kinetics of the neuromedin peptides NMU, NMN, NMB and NT. Neuropharmacology 2016, 107, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Euler, G.; Meister, B.; Hökfelt, T.; Eneroth, P.; Fuxe, K. Intraventricular injection of neurotensin reduces dopamine D2 agonist binding in rat forebrain and intermediate lobe of the pituitary gland. Relationship to serum hormone levels and nerve terminal coexistence. Brain. Res. 1990, 531, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolakis, V.; Kalafatakis, K.; Botis, J.; Zarros, A.; Liapi, C. The regulatory role of neurotensin on the hypothalamic-anterior pituitary axons: Emphasis on the control of thyroid-related functions. Neuropeptides 2010, 44, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, A.; Rowe, W.B.; De Kloet, E.R.; Betancur, C.; Jessop, D.S.; Lightman, S.; Quirion, R.; Rostene, W.; Bérod, A. Endogenous neurotensin regulates hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity and peptidergic neurons in the rat hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. J. Neuroendocr. 1997, 9, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.A.; Bugescu, R.; Mayer, T.A.; Gata-Garcia, A.; Kurt, G.; Woodworth, H.L.; Leinninger, G.M. Loss of Action via Neurotensin-Leptin Receptor Neurons Disrupts Leptin and Ghrelin-Mediated Control of Energy Balance. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 1271–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.J.; Bello, N.T.; Pang, Z.P. Presynaptic Regulation of Leptin in a Defined Lateral Hypothalamus-Ventral Tegmental Area Neurocircuitry Depends on Energy State. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 11854–11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Virella, J.; Leinninger, G. The Role of Central Neurotensin in Regulating Feeding and Body Weight. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, M.F. Aphagia in the rat following microinjection of neurotensin into the ventral tegmental area. Life Sci. 1986, 38, 2383–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, A.E.; Cador, M. Behavioral evidence for differential neuropeptide modulation of the mesolimbic dopamine system. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1988, 537, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughn, A.W.; Baumeister, A.A.; Hawkins, M.F.; Anticich, T.G. Intranigral microinjection of neurotensin suppresses feeding in food deprived rats. Neuropharmacology 1990, 29, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.; Cardoso, H.; Lee, Y.C.; Ghatei, M.A.; Flatt, P.R.; Bailey, C.J.; Bloom, S.R. Reduced hypothalamic neurotensin concentrations in the genetically obese diabetic (ob/ob) mouse: Possible relationship to obesity. Metabolism 1991, 40, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovere, C.; Viale, A.; Nahon, J.; Kitabgi, P. Impaired processing of brain proneurotensin and promelanin-concentrating hormone in obese fat/fat mice. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 2954–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, B.; Burlet, A.; Nicolas, J.P.; Burlet, C. Hyperphagia in obesity is associated with a central peptidergic dysregulation in rats. J. Nutr. 1990, 120, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilding, J.P.; Gilbey, S.G.; Bailey, C.J.; Batt, R.A.; Williams, G.; A Ghatei, M.; Bloom, S.R. Increased neuropeptide-Y messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) and decreased neurotensin mRNA in the hypothalamus of the obese (ob/ob) mouse. Endocrinology 1993, 132, 1939–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, J.; Zaytseva, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.; Rychahou, P.; Jiang, K.; Starr, M.E.; Kim, J.T.; Harris, J.W.; Yiannikouris, F.B.; et al. An obligatory role for neurotensin in high-fat-diet-induced obesity. Nature 2016, 533, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalivas, P.W.; Taylor, S. Behavioral and neurochemical effect of daily injection with neurotensin into the ventral tegmental area. Brain Res. 1985, 358, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalivas, P.W.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Prange, A.J., Jr. Neurotensin microinjection into the nucleus accumbens antagonizes dopamine induced increase in locomotion and rearing. Neuroscience 1984, 11, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ervin, G.N.; Birkemo, L.S.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Prange, A.J., Jr. Neurotensin blocks certain amphetamine-induced behaviours. Nature 1981, 291, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robledo, P.; Maldonado, R.; Koob, G.F. Neurotensin injected into the nucleus accumbens blocks the psychostimulant effects of cocaine but does not attenuate cocaine self-administration in the rat. Brain Res. 1993, 622, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cador, M.; Kelley, A.E.; Le Moal, M.; Stinus, L. Behavioral analysis of the effect of neurotensin injected into the ventral mesencephalon on investigatory and spontaneous motor behavior in the rat. Psychopharmacology 1985, 85, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draviam, E.J.; Upp, J.R., Jr.; Greeley, G.H., Jr.; Townsend, C.M., Jr.; Thompson, J.C. Effect of oral fat on plasma levels of neurotensin and neurotensin fragments in humans. Characterization by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1990, 35, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewe, J.; Mihailovic, S.; D’Amato, M.; Beglinger, C. Regulation of fat-stimulated neurotensin secretion in healthy subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 1964–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawad, A.; Fernandez, C.; Bergmann, A.; Struck, J.; Nilsson, P.M.; Bennet, L.; Orho-Melander, M.; Melander, O. Magnitude of rise in proneurotensin is related to amount of triglyceride appearance in blood after standardized oral intake of both saturated and unsaturated fat. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, S.; Li, X.; Song, J.; Townsend, C.M., Jr.; Weiss, H.L.; Rychahou, P.; Gao, T.; Li, J.; Evers, B.M. Kinase suppressor of Ras 1 and Exo70 promote fatty acid-stimulated neurotensin secretion through ERK1/2 signaling. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, J.; Song, J.; Wang, X.; Weiss, H.L.; Townsend, C.M., Jr.; Gao, T.; Evers, B.M. mTORC1 inhibition increases neurotensin secretion and gene expression through activation of the MEK/ERK/c-Jun pathway in the human endocrine cell line BON. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 301, C213–C226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Song, J.; Weiss, H.L.; Weiss, T.; Townsend, C.M., Jr.; Evers, B.M. Activation of AMPK Stimulates Neurotensin Secretion in Neuroendocrine Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 30, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Rock, S.B.; Sinner, H.F.; Weiss, H.L.; Weiss, T.; Townsend, C.M., Jr.; Gao, T.; Evers, B.M. FFAR4 Is Involved in Regulation of Neurotensin Release from Neuroendocrine Cells and Male C57BL/6 Mice. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 2939–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mancini, A.D.; Poitout, V. The fatty acid receptor FFA1/GPR40 a decade later: How much do we know? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, G.; Alvarez-Curto, E.; Watterson, K.R.; Ulven, T.; Hudson, B.D. Characterizing pharmacological ligands to study the long-chain fatty acid receptors GPR40/FFA1 and GPR120/FFA4. Br. J. Pharm. 2015, 172, 3254–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Itoh, Y.; Kawamata, Y.; Harada, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Fujii, R.; Fukusumi, S.; Ogi, K.; Hosoya, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Uejima, H.; et al. Free fatty acids regulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells through GPR40. Nature 2003, 422, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirasawa, A.; Tsumaya, K.; Awaji, T.; Katsuma, S.; Adachi, T.; Yamada, M.; Sugimoto, Y.; Miyazaki, S.; Tsujimoto, G. Free fatty acids regulate gut incretin glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion through GPR120. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuttgen, G.M.; Sahoo, D. FFAR4: A New Player in Cardiometabolic Disease? Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carling, D.; Hardie, D.G. The substrate and sequence specificity of the AMP-activated protein kinase. Phosphorylation of glycogen synthase and phosphorylase kinase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1989, 1012, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, X.; Dobner, P.R.; Carraway, R.E. Endogenous neurotensin facilitates enterohepatic bile acid circulation by enhancing intestinal uptake in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2001, 281, G1413–G1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellstrom, P.M.; Nylander, G.; Rosell, S. Effects of neurotensin on the transit of gastrointestinal contents in the rat. Acta Physiol. Scand 1982, 115, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, R.A.; Matsumoto, B.K.; Blei, A.T.; Pearl, G.; Ingram, H. Local effect of neurotensin on canine ileal blood flow, and its release by luminal lipid. Scand J. Gastroenterol. 1988, 23, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baca, I.; Feurle, G.E.; Haas, M.; Mernitz, T. Interaction of neurotensin, CCK and secretin in the stimulation of the exocrine pancreas in the dog. Gastroenterology 1983, 84, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.G.; Hoang, H.D.; Bussjaeger, L.J.; Solomon, T.E. Effect of neurotensin on pancreatic and gastric secretion and growth in rats. Pancreas 1988, 3, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, X.; Carraway, R.E. Enhancement of jejunal absorption of conjugated bile acid by neurotensin in rats. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasato, T.; Nakayama, S. Effects of neurotensin on the motility of the isolated gallbladder, bile duct and ampulla in guinea-pigs. Eur. J. Pharm. 1988, 148, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellissier, S.; Eribon, O.; Chabert, J.; Gully, D.; Roche, M. Peripheral neurotensin participates in the modulation of pre- and postprandial intestinal motility in rats. Neuropeptides 1996, 30, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippagunta, S.M.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Adams, A.C.; Hillgartner, F.B. cholic acid supplementation of a high-fat obesogenic diet suppresses hepatic triacylglycerol accumulation in mice via a fibroblast growth factor 21-dependent mechanism. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakade, Y.; Kitano, R.; Sakamoto, K.; Kimoto, S.; Yamauchi, T.; Inoue, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ohashi, T.; Sumida, Y.; Ito, K.; et al. Characteristics of bile acid composition in high fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese diabetic rats. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Andreu-Sánchez, S.; Kuipers, F.; Fu, J. Gut microbiome and bile acids in obesity-related diseases. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 35, 101493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, J.; Yan, B.; Weiss, H.L.; Weiss, L.T.; Gao, T.; Evers, B.M. Neurotensin differentially regulates bile acid metabolism and intestinal FXR-bile acid transporter axis in response to nutrient abundance. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, F.J.; Jiang, C.; Xie, C.; Patterson, A.D. Intestinal farnesoid X receptor signaling modulates metabolic disease. Dig. Dis. 2017, 35, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, T.; Li, F.; Gonzalez, F.J. FXR signaling in the enterohepatic system. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2013, 368, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Um, S.H.; Frigerio, F.; Watanabe, M.; Picard, F.; Joaquin, M.; Sticker, M.; Fumagalli, S.; Allegrini, P.R.; Kozma, S.C.; Auwerx, J.; et al. Absence of S6K1 protects against age- and diet-induced obesity while enhancing insulin sensitivity. Nature 2004, 431, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, F.Y.; Lee, H.; Hubbert, M.L.; Edwards, P.A.; Zhang, Y. FXR, a multipurpose nuclear receptor. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006, 31, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Song, J.; Yan, B.; Rock, S.A.; Jia, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Weiss, T.; Weiss, H.L.; et al. Absence of neurotensin attenuates intestinal dysbiosis and inflammation by maintaining Mmp7/α-defensin axis in diet-induced obese mice. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 8596–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J. Microbes and Diet-Induced Obesity: Fast, Cheap, and Out of Control. Cell Host. Microbe 2017, 21, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cimini, F.A.; Barchetta, I.; Ciccarelli, G.; Leonetti, F.; Silecchia, G.; Chiappetta, C.; Di Cristofano, C.; Capoccia, D.; Bertoccini, L.; Ceccarelli, V.; et al. Adipose tissue remodelling in obese subjects is a determinant of presence and severity of fatty liver disease. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2021, 37, e3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchetta, I.; Cimini, F.A.; Ciccarelli, G.; Baroni, M.G.; Cavallo, M.G. Sick fat: The good and the bad of old and new circulating markers of adipose tissue inflammation. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchetta, I.; Angelico, F.; Del Ben, M.; Di Martino, M.; Cimini, F.A.; Bertoccini, L.; Polimeni, L.; Catalano, C.; Fraioli, A.; Del Vescovo, R.; et al. Phenotypical heterogeneity linked to adipose tissue dysfunction in patients with Type 2 diabetes. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchetta, I.; Cimini, F.A.; Capoccia, D.; Bertoccini, L.; Ceccarelli, V.; Chiappetta, C.; Leonetti, F.; Di Cristofano, C.; Silecchia, G.; Orho-Melander, M.; et al. Neurotensin Is a Lipid-Induced Gastrointestinal Peptide Associated with Visceral Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity. Nutrients 2018, 10, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linde, B.; Rosell, S.; Rökaeus, A. Blood flow in human adipose tissue after infusion of (Gln4)-neurotensin. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1982, 115, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakka, T.; Cuber, J.C.; Chayvialle, J.A. Functional coupling between the active transport of glucose and the secretion of intestinal neurotensin in rats. J. Physiol. 1993, 469, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carraway, R.E.; Demers, L.M.; Leeman, S.E. Hyperglycemic effect of neurotensin, a hypothalamic peptide. Endocrinology 1976, 99, 1452–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.; Vale, W. Effects of neurotensin and substance p on plasma insulin, glucagon and glucose levels. Endocrinology 1976, 98, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, D.B.; Holst, J.J. Peptides in the regulation of glucagon secretion. Peptides 2021, 148, 170683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolais-Kitabgi, J.; Kitabgi, P.; Brazeau, P.; Freychet, P. Effect of neurotensin on insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin release from isolated pancreatic islets. Endocrinology 1979, 105, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, A.M.; Bloom, S.R.; Edwards, A.V. Pancreatic endocrine responses to exogenous neurotensin in the conscious calf. J. Physiol. 1981, 314, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, N.J.; Ross, S.A.; Lane, W.S.; Moestrup, S.K.; Petersen, C.M.; Keller, S.R.; Lienhard, G.E. Sortilin is the major 110-kDa protein in GLUT4 vesicles from adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 3582–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Kandror, K.V. Sortilin is essential and sufficient for the formation of Glut4 storage vesicles in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Dev. Cell 2005, 9, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barchetta, I.; Ciccarelli, G.; Cimini, F.A.; Ceccarelli, V.; Orho-Melander, M.; Melander, O.; Cavallo, M.G. Association between systemic leptin and neurotensin concentration in adult individuals with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2018, 41, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchetta, I.; Cimini, F.A.; Leonetti, F.; Capoccia, D.; Di Cristofano, C.; Silecchia, G.; Orho-Melander, M.; Melander, O.; Cavallo, M.G. Increased Plasma Proneurotensin Levels Identify NAFLD in Adults with and without Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melander, O.; Maisel, A.S.; Almgren, P.; Manjer, J.; Belting, M.; Hedblad, B.; Engström, G.; Kilger, U.; Nilsson, P.; Bergmann, A.; et al. Plasma proneurotensin and incidence of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, breast cancer, and mortality. JAMA 2012, 308, 1469–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barchetta, I.; Bertoccini, L.; Sentinelli, F.; Bailetti, D.; Marini, G.; Cimini, F.A.; Ceccarelli, V.; Struck, J.; Schulte, J.; Loche, S.; et al. Circulating pro-neurotensin levels predict bodyweight gain and metabolic alterations in children. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawad, A.; Nilsson, P.M.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Melander, O.; Bennet, L. The association between plasma proneurotensin and glucose regulation is modified by country of birth. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Stadler, N.; Abbaci, A.; Liu, J.; Boullier, A.; Marie, N.; Biondi, O.; Moldes, M.; Morichon, R.; Feve, B.; et al. Effect of Monoclonal Antibody Blockade of Long Fragment Neurotensin on Weight Loss, Behavior, and Metabolic Traits After High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 739287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, E.; Czepielewski, R.S.; Chi, J.; Guo, X.; Han, Y.H.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Hu, B.; Dawes, B.; et al. Neurotensin is an anti-thermogenic peptide produced by lymphatic endothelial cells. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1449–1465.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souazé, F.; Forgez, P. Molecular and cellular regulation of neurotensin receptor under acute and chronic agonist stimulation. Peptides 2006, 27, 2493–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A. Effects of chronic central leptin infusion on proopiomelanocortin and neurotensin gene expression in the rat hypothalamus. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 440, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicoli, C.D.; Carson, A.P.; Plante, T.B.; Long, D.L.; McClure, L.A.; Schulte, J.; Cushman, M. Pro-Neurotensin/Neuromedin N and Risk of Incident Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes Mellitus in the REGARDS Cohort. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e3483–e3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawad, A.; Bergmann, A.; Struck, J.; Nilsson, P.M.; Orho-Melander, M.; Melander, O. Proneurotensin Predicts Cardiovascular Disease in an Elderly Population. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 1940–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimini, F.A.; Barchetta, I.; Bertoccini, L.; Ceccarelli, V.; Baroni, M.G.; Melander, O.; Cavallo, M.G. High pro-neurotensin levels in individuals with type 1 diabetes associate with the development of cardiovascular risk factors at follow-up. Acta Diabetol. 2022, 59, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Day, C.P.; Bonora, E. Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of NAFLD-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Henry, L. Contribution of Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease to the Burden of Liver-Related Morbidity and Mortality. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1778–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar, B.; Bertran, L.; Aguilar, C.; Binetti, J.; Martínez, S.; Sabench, F.; Real, M.; Riesco, D.; París, M.; Del Castillo, D.; et al. Circulating Levels of Pro-Neurotensin and Its Relationship with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Hepatic Lipid Metabolism. Metabolites 2021, 11, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Meroni, M.; Petta, S.; Longo, M.; Alisi, A.; Soardo, G.; Valenti, L.; Miele, L.; Grimaudo, S.; Pennisi, G.; et al. Neurotensin up-regulation is associated with advanced fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with MAFLD. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, B.; Huang, C.; Cheng, C.L.; Udduttula, A.; Yu, X.F.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Yao, Z.Y.; Long, J.; Miao, L.F.; et al. Newly identified peptide hormone inhibits intestinal fat absorption and improves NAFLD through its receptor GPRC6A. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehle, K.J.; Kenerson, H.L.; Riggle, K.M.; Turnham, R.; Sullivan, K.; Bauer, R.; Scott, J.D.; Yeung, R.S. Neurotensin as a source of cyclic AMP and co-mitogen in fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 5092–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Long, X.; Zhang, L.; Ye, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, P.; Zhang, R.; Ning, J.; Yu, W.; Wei, F.; et al. Neurotensin/IL-8 pathway orchestrates local inflammatory response and tumor invasion by inducing M2 polarization of Tumor-Associated macrophages and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1440166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ren, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Wei, X.; Li, H.; Ying, G.; Chen, K.; Winkler, H.; Hao, X. Dysfunctional activation of neurotensin/IL-8 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with increased inflammatory response in microenvironment, more epithelial mesenchymal transition in cancer and worse prognosis in patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Galmiche, A.; Liu, J.; Stadler, N.; Wendum, D.; Segal-Bendirdjian, E.; Paradis, V.; Forgez, P. Neurotensin regulation induces overexpression and activation of EGFR in HCC and restores response to erlotinib and sorafenib. Cancer Lett. 2017, 388, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettersten, N.; Cushman, M.; Howard, V.J.; Hartmann, O.; Filippatos, G.; Beri, N.; Clopton, P.; Howard, G.; Safford, M.M.; Judd, S.E.; et al. Usefulness of Proneurotensin to Predict Cardiovascular and All-Cause Mortality in a United States Population (from the Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2018, 122, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Lyass, A.; Liu, Y.; Gaggin, H.; Trebnick, A.; Maisel, A.S.; D’Agostino RBSr Wang, T.J.; Massaro, J.; Vasan, R.S. Circulating Proneurotensin Concentrations and Cardiovascular Disease Events in the Community: The Framingham Heart Study. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 1692–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicoli, C.D.; Wettersten, N.; Judd, S.E.; Howard, G.; Howard, V.J.; Struck, J.; Cushman, M. Pro-neurotensin/neuromedin N and risk of ischemic stroke: The REasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) study. Vasc. Med. 2020, 25, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Liu, M.J.; Zhai, T.S.; Zhu, H.J.; Gong, F.Y.; Yang, H.B.; Yan, K.M.; Pan, H.; Zeng, Y. Identification of U-shaped curve relation between proneurotensin and risk of coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients with premature CAD. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicoli, C.D.; Long, D.L.; Plante, T.B.; Howard, G.; Judd, S.E.; Schulte, J.; Cushman, M. Pro-Neurotensin/Neuromedin N and Hypertension Risk: A Prospective Study. Am. J. Hypertens. 2021, hpab166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kérouac, R.; St-Pierre, S.; Manning, M.; Rioux, F. Partial blockade of neurotensin-induced hypotension in rats by nephrectomy captopril and saralasin. Possible mechanisms. Neuropeptides 1983, 3, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchi, G.; Malendowicz, L.K.; Rocco, S.; Musajo, F.; Nussdorfer, G.G. Arginine-vasopressin release mediates the aldosterone secretagogue effect of neurotensin in rats. Neuropeptides 1993, 24, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowich, L.; Fishman, S.; Hubel, E.; Thurm, T.; Park, W.J.; Pewzner-Jung, Y.; Saroha, A.; Erez, N.; Halpern, Z.; Futerman, A.H.; et al. Sortilin deficiency improves the metabolic phenotype and reduces hepatic steatosis of mice subjected to diet-induced obesity. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musunuru, K.; Strong, A.; Frank-Kamenetsky, M.; Lee, N.E.; Ahfeldt, T.; Sachs, K.V.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Kuperwasser, N.; Ruda, V.M.; et al. From noncoding variant to phenotype via SORT1 at the 1p13 cholesterol locus. Nature 2010, 466, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, C.; Skov, L.J.; Raida, Z.; Bächler, T.; Bellmann-Sickert, K.; Le Foll, C.; Sivertsen, B.; Dalbøge, L.S.; Hartmann, B.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G.; et al. Effects of Peripheral Neurotensin on Appetite Regulation and Its Role in Gastric Bypass Surgery. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 3482–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratner, C.; He, Z.; Grunddal, K.V.; Skov, L.J.; Hartmann, B.; Zhang, F.; Feuchtinger, A.; Bjerregaard, A.; Christoffersen, C.; Tschöp, M.H.; et al. Long-Acting Neurotensin Synergizes with Liraglutide to Reverse Obesity Through a Melanocortin-Dependent Pathway. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.R.; Leckstrom, A.; Mizuno, T.M. Impaired anorectic effect of leptin in neurotensin receptor 1-deficient mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 194, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barchetta, I.; Baroni, M.G.; Melander, O.; Cavallo, M.G. New Insights in the Control of Fat Homeostasis: The Role of Neurotensin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042209
Barchetta I, Baroni MG, Melander O, Cavallo MG. New Insights in the Control of Fat Homeostasis: The Role of Neurotensin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(4):2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042209
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarchetta, Ilaria, Marco Giorgio Baroni, Olle Melander, and Maria Gisella Cavallo. 2022. "New Insights in the Control of Fat Homeostasis: The Role of Neurotensin" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 4: 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042209
APA StyleBarchetta, I., Baroni, M. G., Melander, O., & Cavallo, M. G. (2022). New Insights in the Control of Fat Homeostasis: The Role of Neurotensin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(4), 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042209








