Abstract
General anesthetics mainly act by modulating synaptic inhibition on the one hand (the potentiation of GABA transmission) or synaptic excitation on the other (the inhibition of NMDA receptors), but they can also have effects on numerous other proteins, receptors, and channels. The effects of general anesthetics on ion channels have been the subject of research since the publication of reports of direct actions of these drugs on ion channel proteins. In particular, there is considerable interest in T-type voltage-gated calcium channels that are abundantly expressed in the thalamus, where they control patterns of cellular excitability and thalamocortical oscillations during awake and sleep states. Here, we summarized and discussed our recent studies focused on the CaV3.1 isoform of T-channels in the nonspecific thalamus (intralaminar and midline nuclei), which acts as a key hub through which natural sleep and general anesthesia are initiated. We used mouse genetics and in vivo and ex vivo electrophysiology to study the role of thalamic T-channels in hypnosis induced by a standard general anesthetic, isoflurane, as well as novel neuroactive steroids. From the results of this study, we conclude that CaV3.1 channels contribute to thalamocortical oscillations during anesthetic-induced hypnosis, particularly the slow-frequency range of δ oscillations (0.5–4 Hz), by generating “window current” that contributes to the resting membrane potential. We posit that the role of the thalamic CaV3.1 isoform of T-channels in the effects of various classes of general anesthetics warrants consideration.
1. Introduction
Since their discoveries, T-type calcium channels (T-channels) have been studied in the context of thalamocortical oscillatory behavior, synaptic plasticity, cell excitability, and involvement in rebound burst-firing [1,2,3]. T-channels were first described in the immature egg cell membrane of a starfish (Mediaster aequalis), where two distinct calcium currents were reported: one with activation at a membrane potential of −55/−50 mV (low-voltage-activated channels, LVA channels or T-channels) and the other at −7/−6 mV (high-voltage-activated or HVA channels) [4]. One very important property of T-channels is that they need only small depolarization to open, and they have the ability to form “window” currents around resting neuronal membrane potential (see Figure 1) [5]. In the thalamus, the occurrence of neuronal membrane potential bistability or destabilization is manifested as the transition of two resting membrane potentials (from “Down to Up states”). It is generally accepted this is most likely due to the “window” current generated by T-channels [5]. Neuronal membrane destabilization is crucial for generating rhythmic (slow/δ) oscillatory behavior during hyperpolarization states typically associated with sleep, sedation, hypnosis, or anesthesia. During neuronal hyperpolarization, T-channels are de-inactivated (recovered from the inactivation), allowing them to open after depolarization and trigger a low-threshold calcium spike (LTS) crowned with a barrage of action potentials (APs, rebound burst-firing pattern, Figure 1,for details see [6]). It is well-documented that during natural sleep or general anesthesia, inhibitory synaptic inputs hyperpolarize thalamic cells enough to recover T-channels from inactivation and consequently allow them to generate characteristic burst-firing and network oscillations. Importantly, it has been shown that in the burst-firing state, the thalamus does not conduct sensory information, a property crucial for natural sleep and general anesthesia effects [7].
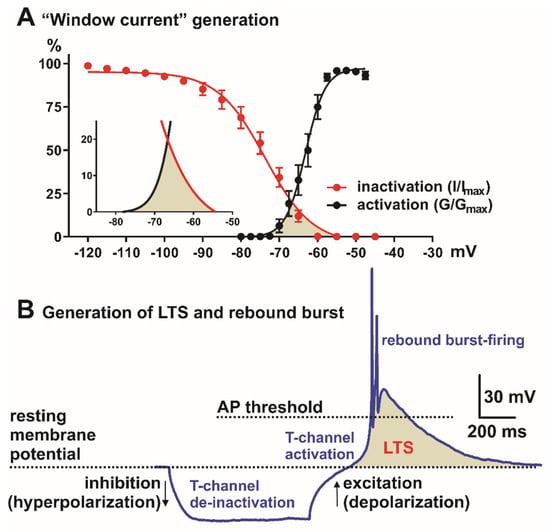
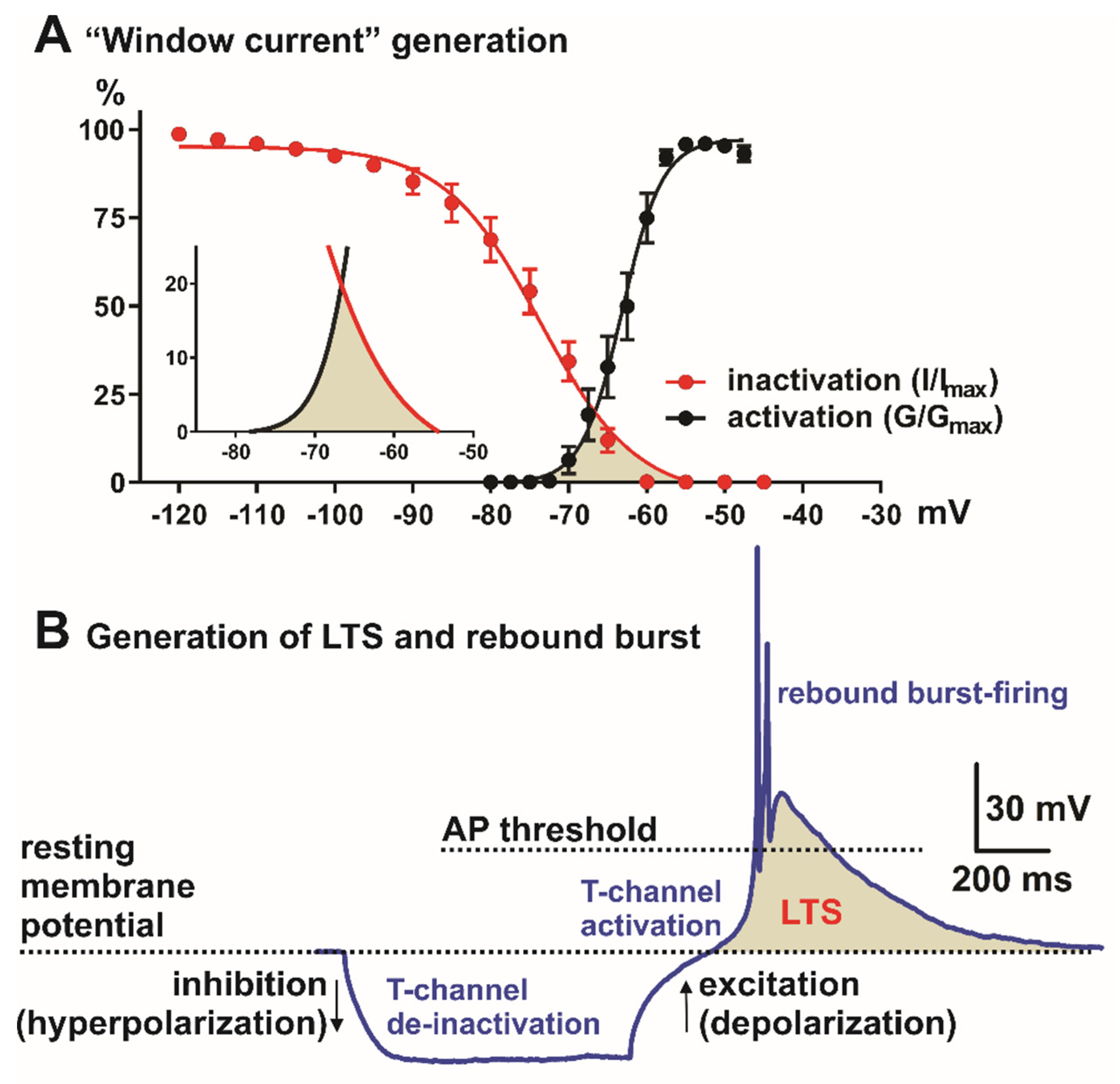
Figure 1.
Neuronal Tchannel properties in the nonspecific thalamic nucleus (CeM). (A) “Window” current generation, red trace—steady-state inactivation and black—steady-state activation T-channel kinetics (from voltage-clamp experiments). Inset in A is enlarged “window” current (shaded area) generated by overlap between steady-state activation (black) and inactivation (red) curves. (B) Role of the T-channels in LTS (low-threshold spike, shaded area) and rebound burst generation. Note that in most systems, LTS and burst-firing cannot be generated from the resting membrane potential, but neurons need hyperpolarization of the cell membrane in order to allow T-channel de-inactivation (recovery from inactivation). AP—action potential.
There are three known isoforms of pore-forming α subunit of T-channels, known as α1G (CACNA1G, CaV3.1), α1H (CACNA1H, CaV3.2), and α1I (CACNA1I, CaV3.3), which are expressed and localized in different brain regions, including the thalamus [8]. In most of the glutamatergic thalamic nuclei, the dominant subtype is the CaV3.1 channel expressed on soma and dendrites. In the thalamic reticular nucleus (TRN), which is composed of GABAergic neurons, the most abundantly expressed are CaV3.2 (mostly on cell somas) and CaV3.3 (mostly on dendrites) T-channel isoforms [8]. Consistent with their essential roles in neuronal excitability, T-channel dysfunction has been implicated in epilepsy, sleep disorders, pain, neurological disorders, neuropsychiatric disorders, cognitive disorders, as well as in chronic thalamocortical hyperexcitability following exposure to general anesthesia during brain development [9,10,11,12,13].
One of the fundamental challenges in pharmacology remains to decipher mechanisms of action of general anesthetics. General anesthesia is a drug-induced, reversible condition composed of the behavioral states of hypnosis, amnesia, analgesia, and loss of motor reflexes (immobilization) during a surgical procedure. The mechanisms of loss of consciousness (hypnosis) have been studied for decades using neuroimaging [14,15]. An early theory proposed that the nonspecific alteration of the lipid membrane in nerve cells accounts for the anesthetic state [16,17]. However, advancements in research in the last three decades have disputed the nonspecific lipid membrane theory [18] and confirmed that general anesthetics act through multiple specific proteins on the neuronal membrane, and that different ion channels that control neuronal excitability may mediate their clinical effects. It is generally accepted that general anesthetics act on synaptic inhibition on the one hand (the potentiation of GABA-mediated transmission, e.g., propofol), or glutamate-mediated synaptic excitation on the other (the inhibition of NMDA receptors, e.g., ketamine, nitrous oxide), but they can also have effects on numerous other proteins, receptors, and channels [19,20,21,22]. It is known that general anesthetics markedly reduce the global cerebral metabolic rate and blood flow, and the thalamus appears to be a common site of modulation by several anesthetics [14,23,24]. The loss of consciousness induced by anesthetics represents the disruption of higher-order cortical information integration, and it has been shown that the posterior parietal–cingulate–precuneus region and the nonspecific thalamus have a critical role in maintaining the state of consciousness (for details, see [14]).
The brain arousal system involves the nonspecific thalamus (intralaminar and midline complex) [25]. It has been shown that the repetitive low-frequency stimulation of intralaminar thalamic nuclei is associated with sleep and drowsiness, while the high-frequency stimulation of the same area can desynchronize the cortex and elicit arousal [26]. The central nucleus of the thalamus (CeM) is a part of the rostral intralaminar complex with the projections to the cortex (anterior and posterior parts), the amygdala, the nucleus accumbens, the claustrum, the caudate–putamen, and the olfactory tubercle [27]. Some studies revealed that the nonspecific thalamus acts as a crucial center for brain network connectivity and is important for alterations induced by general anesthesia and natural sleep in rodents and humans [28,29,30,31]. The stimulation of the central thalamus (including the mediodorsal and intralaminar nucleus) in monkeys during the unconscious state caused the reversal of neurophysiological signs of the hypnotic state [32]. Consistent with this idea, microinjections of general anesthetics into the CeM region in rodents was shown to facilitate hypnosis, while injections of an antibody against voltage-gated potassium channels promoted arousal and the reversal of anesthetic-induced hypnosis [33,34]. Importantly, clinical studies have shown that deep brain stimulation of adjacent nuclei in the nonspecific central thalamus improved the state of consciousness in patients with severe brain injury [35]. Hence, this motivated us to investigate the role of the CaV3.1 isoform of T-channels in regulating excitability states of the CeM and its role in neurosteroid-induced hypnosis and general anesthesia [36,37].
Interestingly, studies showed the evolutionary existence of a voltage-gated calcium current with the kinetic features of a T-channel current in C. elegans, Drosophila, and Trichoplax adhaerens [38,39]. Although there are reports that show the behavioral effects of volatile anesthetics in C. elegans, the potential involvement of T-channels in these effects was not investigated [40]. For these reasons, our studies focused on rodents with reference to humans and nonhuman primates.
2. Electroencephalographic Patterns during Unconsciousness and Anesthesia
Since the first description of electroencephalography (EEG), physiologically relevant rhythms have been investigated during different behavioral states and are classified as: δ (0.5–4 Hz), θ (4–8 Hz), α (8–13 Hz), β (13–30 Hz), low γ (30–50 Hz), and high γ (50–100 Hz) [3]. Sleep- and drug-induced unconsciousness share some similar mechanisms and involve the same brain regions [41,42]. For example, during natural sleep and under general anesthesia, the thalamocortical system can generate slow oscillations with high amplitudes, and conversely, during conscious states, distinct, faster oscillations are dominant [3,40,43]. The administration of a small dose of hypnotics, such as positive GABAA receptor modulators (propofol, barbiturate, and etomidate), induces a state of sedation with paradoxical excitation and an increase in β activity [44]. During the maintenance period of general anesthesia in phase 1 (light state), a decrease in β and increase in α EEG activity is dominant, while in phase 2 (intermediate state), both δ and α oscillations increase similarly to slow-wave non-rapid-eye movement (NREM) sleep [44]. In phase 3 (deeper state), burst-suppression activity is observed, and in phase 4, a largely flat-isoelectric EEG pattern is seen [44].
2.1. Human Data
Many different classes of anesthetics exist within common clinical use, and those of note include volatile anesthetics (such as sevoflurane), GABAA receptor modulators (propofol), and NMDA antagonists (ketamine and nitrous oxide). During sevoflurane-induced hypnosis, EEG and positron emission tomography (PET) analysis was used to identify changes in cerebral blood flow and metabolic activity in frontal, parietal, and thalamic regions [45]. While an increase in frontal β power occurs during sevoflurane-induced sedation and persists despite the loss of responsiveness, conversely δ, θ, and α band power remain unchanged (for a review, see [45]). It has been shown that frontal α power does not consistently emerge in deep hypnosis with sevoflurane but can change over the transition from wakefulness to sevoflurane-induced hypnosis [46,47,48,49]. With higher sevoflurane concentrations, α power increases and can consist of sleep-spindle-like activity during the maintenance phase of anesthesia [45]. On the other hand, specific EEG readout during sevoflurane-induced hypnosis has been shown to include the domination of δ waves and the existence of a burst-suppression pattern [45,49,50].
During propofol-induced hypnosis, coupling between low frequencies and amplitudes of α rhythms were observed with the dominant slow oscillations similar to sleep during unconsciousness in humans [51,52]. Additionally, it has been shown that in propofol-induced general anesthesia before the generation of a burst-suppression pattern, the main rhythm consists of α and δ band activity [53]. In humans with an implanted deep electrode, an increase in α and decrease in γ power were observed in both deep cortical (ACC, anterior cingulate cortex) and subcortical (sensory thalamus, periaqueductal gray) areas during propofol-induced hypnosis [54]. Moreover, hypnotic state under propofol was marked simultaneously by an increase in low-frequency EEG power (<1 Hz), the loss of spatially coherent occipital α oscillations, and the appearance of spatially coherent frontal α rhythms in humans [55].
Following ketamine-induced hypnosis in humans, a γ-burst EEG pattern was observed with alternating slow-δ and γ oscillations [56]. Additionally, ketamine hypnosis showed increased θ and decreased α/β oscillations [56].
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is usually used along with other anesthetics as an adjuvant agent as general anesthesia cannot be achieved with N2O alone under normobaric conditions. In healthy male volunteers, some studies reported a reduction in total EEG power with N2O and a paradoxical reduction in δ oscillations [57]. Others reported an increase in θ, β, and low and high γ band powers under sedative N2O concentration [58]. Interestingly, the administration of a high dose of N2O in combination with inhalation anesthetics (sevoflurane, desflurane, or isoflurane) was associated with dominant slow-δ oscillations [59]. The generation of these slow-δ rhythms could be due to the blockade of excitatory inputs (NMDA glutamate projections) from the brainstem to the thalamocortical neurons [59].
2.2. Animal Data
Similarly to human data, a low dose of sevoflurane in rats produced an increase in β/low γ power in the cortex and central thalamus [60]. During sevoflurane-induced loss of movement, β/low γ activity decreased with the generation of coherent slow-δ oscillations [60]. At higher doses, sevoflurane induced the loss of the righting reflex with the characteristic coherent slow-δ oscillations [60]. Additionally, the dominant slow waves and the burst-suppression pattern was observed with the higher isoflurane concentration in rats [61].
In rats, propofol-induced α oscillations synchronized between the thalamus and the medial prefrontal cortex, with the development of coherent thalamocortical δ oscillations at deep levels of hypnosis [62]. On the contrary, a sub-anesthetic dose of ketamine, an NMDA antagonist, induced robust, spontaneous γ oscillations that were initially modulated by slow oscillations (0.3 Hz) in monkeys [63]. In rodents, it has been shown that ketamine increased power in the 30–50 Hz frequency band (low γ) with or without a rise in high γ oscillations [64,65].
2.3. Summary
Slow-δ and α oscillations are dominant EEG signatures for propofol-induced anesthesia, which is a finding consistent with EEG patterns observed with other intravenous anesthetics targeting GABAA receptors (for details, see [66]). Similarly, during sevoflurane-induced anesthesia, slow-δ, θ, and α oscillations are predominant EEG signatures, consistent with other volatile general anesthetics (desflurane and isoflurane) [66]. The similarities between the EEG patterns of GABAA-receptor-targeting anesthetics, propofol, and volatile general anesthetics seem to include the enhancement of GABAA-receptor-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic currents [66]. On the contrary, low γ oscillations that are interspersed with slow-δ oscillations are the predominant EEG signatures of general anesthesia maintained with ketamine, a prototypical injectable general anesthetic and an NMDA receptor antagonist [66]. It is worth mentioning that these changes are dose- and state-dependent for each anesthetic/hypnotic agent.
3. T-Channels in Sleep, Hypnosis, and Anesthesia
It is well-known that T-type channels play a number of different and essential roles in neuronal oscillation generated by thalamic neurons during NREM sleep [67,68]. Additionally, the thalamus is required for slow-wave frequency tuning, which is highly dependent on T-channels, during both NREM sleep and anesthesia [68,69]. It has been shown that sleep behavior was not changed in animals that lacked a Cav3.1 channel in cortical pyramidal neurons [70]. In contrast, the focal deletion of the CaV3.1 channel in the rostral–midline thalamus caused frequent and prolonged arousal, with fragmented and reduced sleep [70]. These results support the hypothesis that thalamic T-channels play essential roles in sleep stabilization. Other studies demonstrated that mice lacking the CaV3.1 isoform of T-channels exhibited a reduction in thalamic δ oscillations and sleep spindles during urethane- and barbiturate-induced hypnosis [71,72]. Additionally, CaV3.1 KO mice under ketamine and ethanol administration displayed attenuated cortical and mediodorsal thalamic low-frequency oscillations (1–4 Hz) when compared to WT mice [73]. Towards this end, it has been previously shown that CaV3.1 KO mice did not have different ED50 for the loss of the righting reflex caused by volatile anesthetics (isoflurane and halothane), but these mutant mice had significantly delayed onset of anesthetic induction, as measured by the time to the loss of the righting reflex [74]. Surprisingly, in the same study, authors reported that the duration of the loss of the righting reflex and onset of anesthetic induction induced by injections of propofol was not different between WT and CaV3.1 KO mice. This suggests that different classes of anesthetics may have different mechanisms of interactions with CaV3.1 channels and other molecular targets in the thalamocortical circuitry. In agreement with these findings, our group reported that global CaV3.2 KO mice did not have different ED50 for the loss of the righting reflex caused by volatile anesthetics (isoflurane) but had significantly delayed onsets of anesthetic induction with isoflurane and not with propofol [75]. In contrast to these studies, the global deletion of the CaV3.3 isoform of T-channels in mice per se did not affect the ED50 for the loss of the righting reflex, but facilitated anesthetic induction caused by isoflurane [76]. These findings point to the different roles of T-channel isoforms in anesthetic-induced hypnosis.
In vivo animal electrophysiological data showed that anesthetics have the ability to modify thalamocortical signaling by altering the neuronal firing patterns of the thalamic network at the cellular level by hyperpolarizing resting membrane potentials of thalamic neurons [77,78]. It is known that most thalamic cells have prominent bursting and not tonic activity during the administration of anesthetics, similar to different sleep states [77,79]. It has been hypothesized that anesthetics may cause hypnosis because of the hyperpolarization-induced blockade of the thalamocortical cells and networks essential for consciousness [77,80]. It has been shown that the thalamus can generate spindle oscillations (7–14 Hz) at resting membrane potentials (RMPs) of −60 mV and produce a slower δ rhythm consisting of low-threshold spikes (LTS) followed by afterhyperpolarizing potentials during natural sleep and hypnosis/anesthesia at a more negative RMP (<−65 mV) [81,82]. Previously, it was thought that for the generation of thalamic δ oscillations during the hyperpolarization of the neuronal membrane, both a hyperpolarization-activated (Ih) current and T-current are required [81]. However, a recent paper showed the dominant role of T-currents in δ rhythm generation and the supporting role of Ih currents in the amplification and stabilization of δ oscillations [83].
3.1. Role of the CaV3.1 Isoform of T-Channels in Anesthesia Induced by Isoflurane
As mentioned earlier, studies with mice lacking CaV3.1 channels showed that the mutant animals exhibited delayed induction with volatile anesthetics, including isoflurane [74]. In addition, we and others revealed that CaV3.1 T-channels are inhibited by prototypical volatile anesthetic isoflurane in both the sensory thalamus (TRN, VB) and the nonspecific thalamus (CeM) at clinically relevant concentrations [37,84,85,86]. Previous studies demonstrated the role of the CeM as the neuroanatomic site in mediating arousal response during anesthetic administration in rats [28,33,34,87]. Our data confirmed that under isoflurane anesthesia, neuronal hyperpolarization is capable of removing T-channels from inactivation (de-inactivation), and the generation of bursting and oscillatory behavior within the thalamocortical loop is facilitated [37]. Not only did isoflurane hyperpolarize CeM neurons, but it inhibited both tonic and rebound burst-firing in the CeM neurons in WT, but not CaV3.1 null animals. Similarly to previous studies regarding VB thalamic neurons [88], while tonic firing was spared, CeM neurons from CaV3.1 KO animals did not show rebound burst activity. Our recordings of local field potentials (LFPs) from the CeM confirmed that under isoflurane-induced hypnosis, δ-frequency oscillations increased in WT mice but not in CaV3.1 KO animals. The lack an increase in δ activity could be partially because of the inability of isoflurane to hyperpolarize CeM neurons in mutant animals and generate slow/δ oscillations ([37], Figure 2).
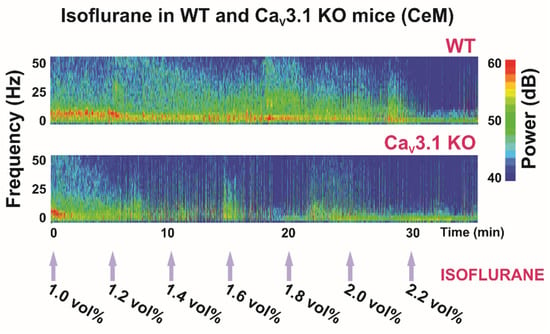
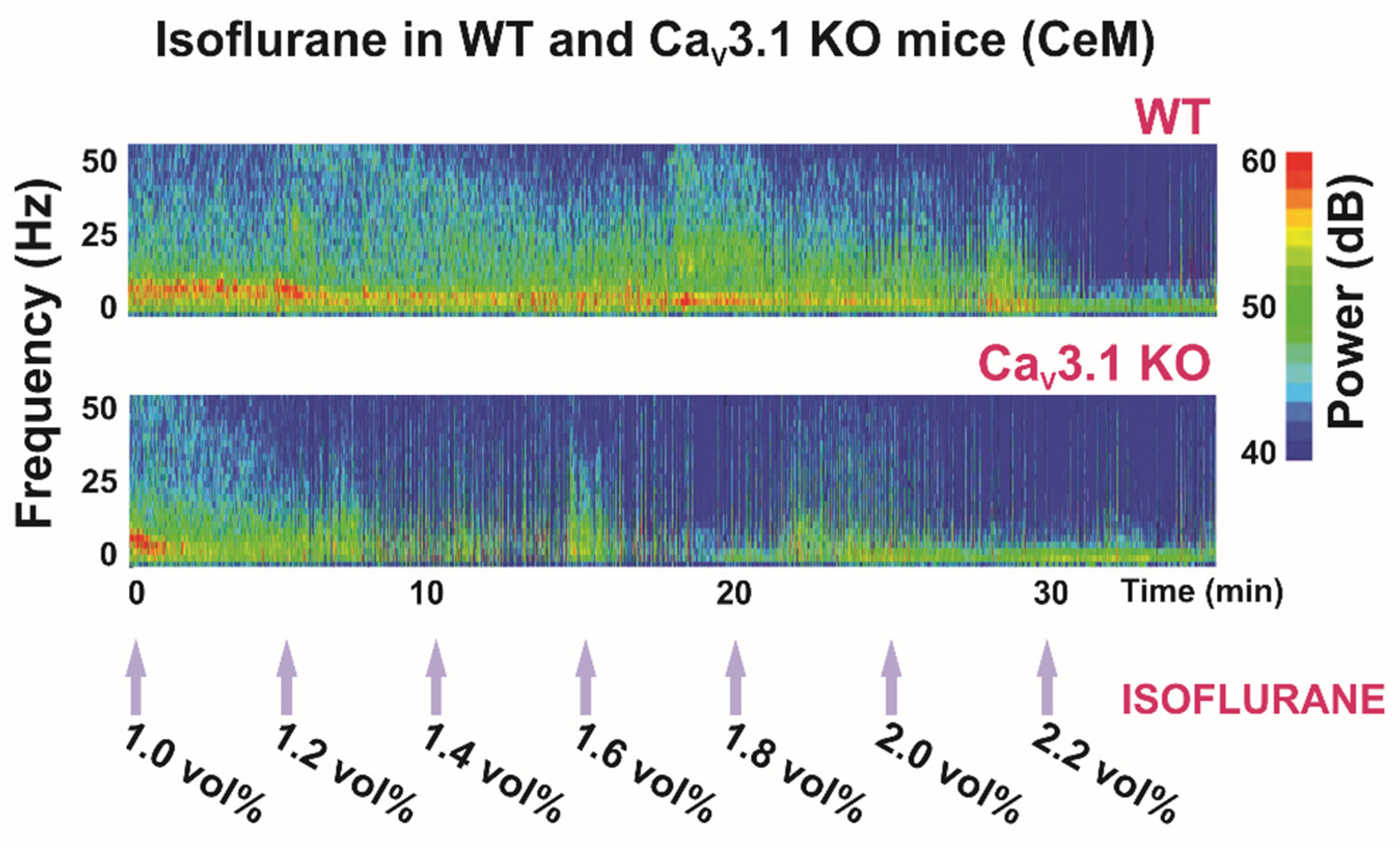
Figure 2.
Thalamic (central medial nucleus of thalamus—CeM) heat maps of local field potentials (LFPs) under isoflurane in WT and CaV3.1 KO animals.
Previous studies reported that during NREM sleep, cortical power densities in low frequencies, including the δ band, were decreased in CaV3.1 KO mice [71], but that the cortical spindles were not altered [72]. While in our study, we did not investigate the spindle component, we found increased power density in the spindle-like frequency range (8–13 Hz) in the CeM in mice lacking a CaV3.1 channel during the quiet awake state and under 1 vol%, but not under 2 vol% of isoflurane anesthesia [37]. However, note that α oscillations induced by general anesthetics occur in a frequency range and spatial distribution similar to sleep spindles (12–16 Hz), although there are important differences between these two rhythms; for details, see [66].
Most clinically used general anesthetics and some metabolic abnormalities (profound acidosis and hypercapnia) can induce a characteristic EEG pattern with a burst (high-amplitude oscillations) and suppression (silenced cortical activity) phase. In our study, the suppression to burst ratio (BSR) was higher during 1.4 vol% of isoflurane administration in CaV3.1 KO animals than in control mice, indicating greater thalamocortical suppression in the mutants (Figure 2, Table 1). Moreover, during 2 vol% isoflurane administration, the main observed thalamic rhythm was in the δ frequency range during suppression mode in the control, but not in the CaV3.1 KO mice [37]. Notably, this was not seen in cortical EEG recordings. It is important to note that the difference between mutant and WT animals in terms of the BSR disappeared with the higher isoflurane concentration (Table 1), which suggests that different targets experience different effects at higher anesthetic concentrations. As all anesthetics are promiscuous drugs, the direction and magnitude of response in CaV3.1 KO mice may depend on the effects of that anesthetic on other targets, including possible compensatory changes that exist in mutant animals.

Table 1.
Suppression to burst ratio (BSR) in WT and CaV3.1 KO animals under isoflurane (mean ± SEM).
3.2. Role of the CaV3.1 Isoform of T-Channels in Nonspecific Thalamus in Hypnosis Induced by Neuroactive Steroids
The idea that neuroactive steroids can have sedative/hypnotic properties has been around since the introduction of alphaxalone [(3α,5α)3-hydroxypregnane−11,20-dione]. The neurosteroid analogs are potent GABA modulators that potentiate postsynaptic GABAA currents, as well as inhibitors of voltage-gated calcium channels (reviewed in [89]). Neuroactive steroids mostly belonging to pregnane and androstane groups, such as the mixture of alphaxalone and alphadolone (Althesin®), were prepared for clinical use as anesthetics in the 1970s, but due to the high incidence of anaphylactic reactions, they were withdrawn from clinical use [90,91]. Today, alphaxalone is still used as an effective anesthetic in veterinary medicine (Alfaxan®) and is currently undergoing clinical trials in humans (Phaxan®) [92]. The ongoing use of alphaxalone continues to encourage the future development of synthetic neurosteroids with hypnotic/anesthetic properties.
The ability of general anesthetics to induce the safe and reversible loss of consciousness is of paramount importance; however, recent data from in vivo animal models have suggested that most commonly used general anesthetics are neurotoxic (i.e., causing neuronal apoptosis) to the developing mammalian brain and are implicated in causing cognitive deficits later in life. Thus, further research into cellular mechanisms of action of currently available anesthetics and the development of novel classes of general anesthetics for clinical practice with reduced neurotoxicity is warranted. We recently reported that the application of a neurosteroid analog (3β,5β,17β)-3-hydroxyandrostane-17-carbonitrile (3β-OH) in rats and rat pups produces a hypnotic effect without activating neuronal apoptosis, unlike other general anesthetics [93,94]. In addition, we investigated the role of 3β-OH on neuronal T-channels in the thalamus (TRN, CeM) and in sensory neurons of the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) [36,95,96]. We found that 3β-OH, although it does not act on GABAA receptors, it can still effectively induce hypnosis in rat pups [94] and adult mice [36]. This suggests that 3β-reduced neurosteroids produce their hypnotic effects through alternate mechanisms, partially as potent inhibitors of T-channels [36,96,97]. We showed that the CaV3.1 isoform is important for the inhibitory effect of 3β-OH on the CeM neuronal excitability [36]. Additionally, we confirmed that CaV3.1 T-channels are important for the 3β-OH-induced hypnotic development in vivo by measuring the loss of the righting reflex in WT and mutant CaV3.1 KO animals. Animals that lacked the CaV3.1 T-channel isoform had several-fold shorter durations and lower calculated median effective doses for the loss of the righting reflex in comparison to control (WT) animals [36].
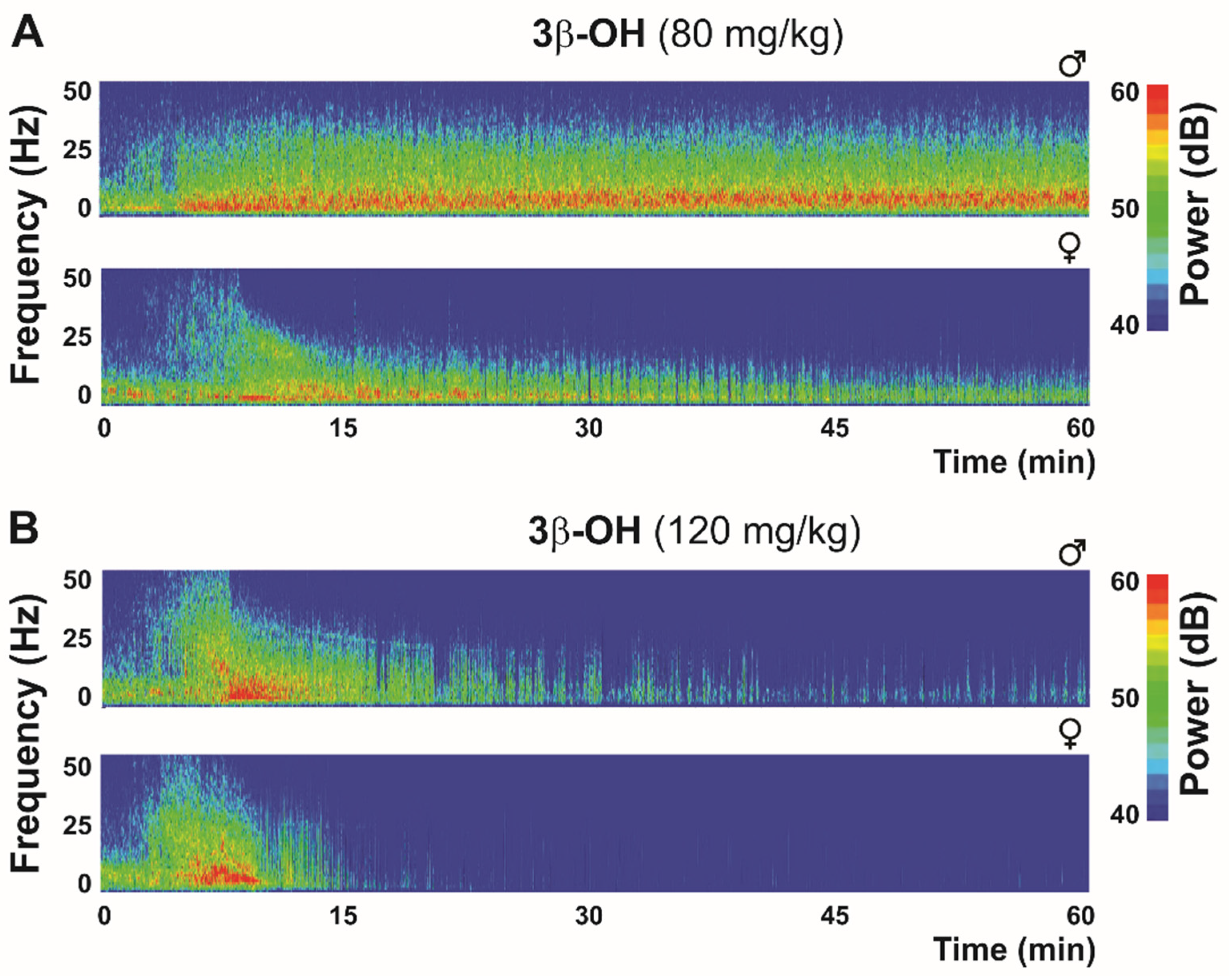
Bearing in mind the role of the CaV3.1 isoform in the generation of thalamic δ oscillations and sleep spindles during hypnosis and anesthesia, a reduction in total δ, θ and α power in CaV3.1 KO mice under a hypnotic dose (80 mg/kg) of 3β-OH was expected [36]. Similarly to the isoflurane effect in CeM neurons, 3β-OH did not hyperpolarize CeM neurons in the mutant mice, and a lack of 3β-OH-induced hyperpolarization can explain both the differences in low-frequency oscillations between WT and CaV3.1 KO mice, and also the lack of effect on LORR in the CaV3.1 null mice [36]. Furthermore, our findings revealed for the first time that injection of 3β-OH at 80 mg/kg induced a hypnotic state in WT mice (Figure 3), but was insufficient to do so in CaV3.1 KO mice [36]. The injection of a higher 3β-OH dose (120 mg/kg) induced an anesthesia state with the characteristic transient rise in β-frequency oscillations during induction and a burst-suppression pattern at later time points, suggesting deeper thalamocortical inhibition (Figure 3). A sex-dependent effect was reported regarding neuroactive steroids, which had a more pronounced effect in female animals, and in Figure 3, representative heat maps show greater suppression in female mice with both the hypnotic and anesthetic dose of 3β-OH. Similar sex differences with 3β-OH were previously reported in rats (for details, see [93]).
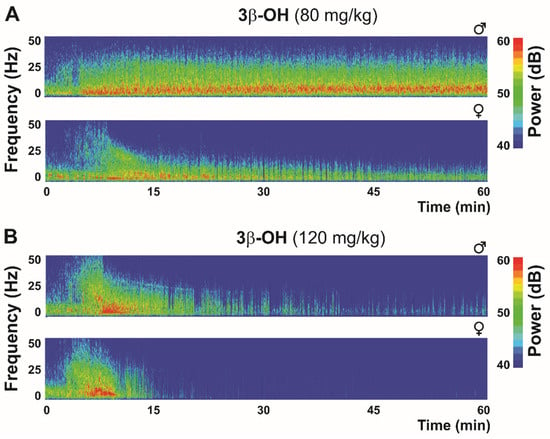
Figure 3.
Thalamic (central medial nucleus of thalamus—CeM) heat maps after hypnotic (80 mg/kg (A)) and anesthetic (120 mg/kg (B)) dose of neuroactive steroid 3β-OH in WT mice.
In our previous studies, we established the role of voltage-gated calcium channels in antinociceptive effects of an endogenous 5β-reduced neuroactive steroid molecule epipregnanolone (EpiP, [(3β,5β)-3-hydroxypregnan-20-one]) in rats and mice [97,98]. Similarly to 3β-OH, we demonstrated that EpiP blocks T-type calcium channels in sensory neurons without having an effect on GABAA currents [97,99,100]. Interestingly, we demonstrated that T-channel isoforms contribute differently to EpiP-induced hypnosis in mice [101]. We found that EpiP is an effective dose-dependent hypnotic when given alone and that it significantly lowers the isoflurane and sevoflurane concentration required to induce immobility and hypnosis [101]. Additionally, after systemic EpiP injection in WT mice, we observed a rise in total power in all EEG frequencies [101]. Similarly to changes observed using the other known sedative/hypnotic drugs, with the administration of EpiP, we detected a rise in relative δ and β power and a drop in relative γ power 30 min after EpiP administration. It has been shown that many different classes of general anesthetics first induce sedation/hypnosis with a characteristic rise in β oscillation followed by a rise in δ oscillations, which are dominant during deeper levels of anesthesia [66]. Consistent with this idea, we found that CaV3.1 KO mice, but not CaV3.2 and CaV3.3 KO mice, exhibited resistance to EpiP-induced hypnosis, as demonstrated by a shorter loss of righting reflex duration and a significant reduction in δ oscillations when compared to the control WT animals [101]. These data confirm results with 3β-OH, the synthetic neurosteroid analog of EpiP, which showed a similar EEG signature to EpiP during hypnosis induced in WT animals [36]. Interestingly, in the same study, we showed that when compared to WT mice, the onset of EpiP-induced hypnosis was delayed in CaV3.2 KO mice, but not in CaV3.1 and CaV3.3 KO mice. However, we observed that among all three T-channel isoforms, CaV3.1 had the greatest relevance with regard to EpiP-induced hypnotic effects. We speculate that the distinct hypnotic effects of EpiP and isoflurane across all three T-channel isoforms are due to their differential expression in thalamocortical circuitry.
4. Conclusions
It is well established that the loss of consciousness under anesthesia is associated with an increase in δ oscillations and that T-channels play an important role in δ oscillation generation [60,61,62]. It was demonstrated that a lack of rebound bursting and the inability of anesthetics/hypnotics to hyperpolarize neurons and to increase slow oscillations in CaV3.1 KO mice can likely explain their inability to induce hypnosis in mutant mice. Our data are consistent with idea that the inability of anesthetics to hyperpolarize CeM neurons in mutant mice is due to lack of a T-channel-dependent “window current”. At rest, a T-type “window current” provides a steady influx of calcium ions near resting membrane potentials and, in turn, depolarizes the neuronal membrane. In contrast, blocking a T-channel-dependent “window current” causes neuronal hyperpolarization. The central nucleus of the thalamus, as a part of the nonspecific thalamus, acts as a key hub in brain network connectivity alterations induced by general anesthesia and natural sleep in rodents and humans. It has been shown that central thalamic stimulation during the hypnotic state can reverse the neurophysiological signs of the unconsciousness. Due to the abundant expression of Cav3.1 T-channels in the nonspecific thalamus and their regulation of its excitability, we propose that the effects of various general anesthetics on thalamic CaV3.1 channels warrant consideration.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, T.T.S.; writing—review and editing, S.M.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported in part by funds from the Department of Anesthesiology at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus and NIH grant R35 GM141802-01 (to SMT).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Simms, B.A.; Zamponi, G.W. Neuronal voltage-gated calcium channels: Structure, function, and dysfunction. Neuron 2014, 82, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leresche, N.; Lambert, R.C. T-type calcium channels in synaptic plasticity T-type calcium channels in synaptic plasticity. Channels 2017, 11, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crunelli, V.; Lőrincz, M.L.; Connelly, W.M.; David, F.; Hughes, S.W.; Lambert, R.C.; Leresche, N.; Errington, A.C. Dual function of thalamic low-vigilance state oscillations: Rhythm-regulation and plasticity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, S.; Ozawa, S.; Sand, O. Voltage clamp analysis of two inward current mechanisms in the egg cell membrane of a starfish. J. Gen. Physiol. 1975, 65, 617–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crunelli, V.; Tóth, T.I.; Cope, D.W.; Blethyn, K.; Hughes, S.W. The ‘window’ T-type calcium current in brain dynamics of different behavioural states. J. Physiol. 2005, 562, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Reyes, E. Molecular physiology of low-voltage-activated t-type calcium channels. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 117–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, S.M.; Snutch, T.P. T-type calcium channels in burst-firing, network synchrony, and epilepsy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 1572–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, E.M.; Cribbs, L.L.; Lee, J.H.; Daud, A.; Perez-Reyes, E.; Bayliss, D.D.A. Differential distribution of three members of a gene family encoding low voltage-activated (T-type) calcium channels. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 1895–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huc, S.; Monteil, A.; Bidaud, I.; Barbara, G.; Chemin, J.; Lory, P. Regulation of T-type calcium channels: Signalling pathways and functional implications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, H.; Kondo, T. T-type calcium channel as a new therapeutic target for tremor. Cerebellum 2011, 10, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, E.; Shin, H.S. T-type Ca2+ channels in normal and abnormal brain functions. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 961–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Parker, W.D.; Wang, K. The role of T-type calcium channel genes in absence seizures. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiGruccio, M.R.; Joksimovic, S.; Joksovic, P.M.; Lunardi, N.; Salajegheh, R.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V.; Beenhakker, M.P.; Goodkin, H.P.; Todorovic, S.M. Hyperexcitability of Rat Thalamocortical Networks after Exposure to General Anesthesia during Brain Development. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudetz, A.G. General Anesthesia and Human Brain Connectivity. Brain Connect. 2012, 2, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, E.N.; Purdon, P.L.; Van Dort, C.J. General Anesthesia and Altered States of Arousal: A Systems Neuroscience Analysis. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 601–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, H. Welche Eigenschaft der Anaesthetica bedingt ihre narkotische Wirkung? Arch. Exp. Pathol. Pharmakol. 1899, 42, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overton, C.E. Studien über die Narkose: Zugleich ein Beitrag zur allgemeinen Pharmakologie; Gustav Fischer: Jena, Germany, 1901. [Google Scholar]
- Herold, K.F.; Sanford, R.L.; Lee, W.; Andersen, O.S.; Hemmings, H.C. Clinical concentrations of chemically diverse general anesthetics minimally affect lipid bilayer properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, N.P. General anaesthesia: From molecular targets to neuronal pathways of sleep and arousal. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 370–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, U.; Antkowiak, B. Molecular and neuronal substrates for general anaesthetics. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkire, M.T. Loss of effective connectivity during general anesthesia. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2008, 46, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, S.A.; Chin, V.A. General anesthetics and molecular mechanisms of unconsciousness. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2008, 46, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashour, G.A.; Alkire, M.T. Consciousness, anesthesia, and the thalamocortical system. Anesthesiology 2013, 118, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkire, M.T.; Haier, R.J.; Barker, S.J.; Shah, N.K.; Wu, J.C.; Kao, Y.J. Cerebral Metabolism during Propofol Anesthesia in Humans Studied with Positron Emission Tomography. Anesthesiology 1995, 82, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Werf, Y.D.; Witter, M.P.; Groenewegen, H.J. The intralaminar and midline nuclei of the thalamus. Anatomical and functional evidence for participation in processes of arousal and awareness. Brain Res. Rev. 2002, 39, 107–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira de Vasconcelos, A.; Cassel, J.C. The nonspecific thalamus: A place in a wedding bed for making memories last? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 54, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertes, R.P.; Hoover, W.B.; Rodriguez, J.J. Projections of the central medial nucleus of the thalamus in the rat: Node in cortical, striatal and limbic forebrain circuitry. Neuroscience 2012, 219, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.; Gent, T.C.; Yang, Q.; Parker, S.; Vyssotski, A.; Wisden, W.; Brickley, S.G.; Franks, N.P. Altered Activity in the Central Medial Thalamus Precedes Changes in the Neocortex during Transitions into Both Sleep and Propofol Anesthesia. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 13326–13335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saalmann, Y.B. Intralaminar and medial thalamic influence on cortical synchrony, information transmission and cognition. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, T.C.; Bandarabadi, M.; Herrera, C.G.; Adamantidis, A.R. Thalamic dual control of sleep and wakefulness. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gili, T.; Saxena, N.; Diukova, A.; Murphy, K.; Hall, J.E.; Wise, R.G. The Thalamus and Brainstem Act As Key Hubs in Alterations of Human Brain Network Connectivity Induced by Mild Propofol Sedation. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 4024–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, A.M.; Donoghue, J.A.; Brincat, S.L.; Mahnke, M.; Yanar, J.; Correa, J.; Waite, A.S.; Lundqvist, M.; Roy, J.; Brown, E.N.; et al. Neural effects of propofol-induced unconsciousness and its reversal using thalamic stimulation. Elife 2021, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkire, M.T.; Asher, C.D.; Franciscus, A.M.; Hahn, E.L. Thalamic microinfusion of antibody to a voltage-gated potassium channel restores consciousness during anesthesia. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lioudyno, M.I.; Birch, A.M.; Tanaka, B.S.; Sokolov, Y.; Goldin, A.L.; Chandy, K.G.; Hall, J.E.; Alkire, M.T. Shaker-Related Potassium Channels in the Central Medial Nucleus of the Thalamus Are Important Molecular Targets for Arousal Suppression by Volatile General Anesthetics. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 16310–16322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiff, N.D.; Giacino, J.T.; Kalmar, K.; Victor, J.D.; Baker, K.; Gerber, M.; Fritz, B.; Eisenberg, B.; O’connor, J.; Kobylarz, E.J.; et al. Behavioural improvements with thalamic stimulation after severe traumatic brain injury. Nature 2007, 448, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timic Stamenic, T.; Feseha, S.; Manzella, F.M.; Wallace, D.; Wilkey, D.; Corrigan, T.; Fiedler, H.; Doerr, P.; Krishnan, K.; Raol, Y.H.; et al. The T-type calcium channel isoform Cav3.1 is a target for the hypnotic effect of the anaesthetic neurosteroid (3β,5β,17β)-3-hydroxyandrostane-17-carbonitrile. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 22, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timic Stamenic, T.; Feseha, S.; Valdez, R.; Zhao, W.; Klawitter, J.; Todorovic, S.M. Alterations in Oscillatory Behavior of Central Medial Thalamic Neurons Demonstrate a Key Role of CaV3.1 Isoform of T-Channels during Isoflurane-Induced Anesthesia. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 4679–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steger, K.A.; Shtonda, B.B.; Thacker, C.; Snutch, T.P.; Avery, L. The C. elegans T-type calcium channel CCA-1 boosts neuromuscular transmission. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 2191–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.L.; Abdallah, S.; Wong, Y.Y.; Le, P.; Harracksingh, A.N.; Artinian, L.; Tamvacakis, A.N.; Rehder, V.; Reese, T.S.; Senatore, A. Evolutionary insights into T-type Ca2+ channel structure, function, and ion selectivity from the Trichoplax adhaerens homologue. J. Gen. Physiol. 2017, 149, 483–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowder, C.M.; Shebester, L.D.; Schedl, T. Behavioral Effects of Volatile Anesthetics in Caenorhabditis elegans. Anesthesiology 1996, 85, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, M.T.; Kelz, M.B. Sleep and Anesthesia Interactions: A Pharmacological Appraisal. Curr. Anesthesiol. Rep. 2013, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesbah-Oskui, L.; Horner, R.L. Enhanced Thalamic Spillover Inhibition during Non–rapid-eye-movement Sleep Triggers an Electrocortical Signature of Anesthetic Hypnosis. Anesthesiology 2016, 125, 964–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.G. The thalamic matrix and thalamocortical synchrony. Trends Neurosci. 2001, 24, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.N.; Lydic, R.; Schiff, N.D. General Anesthesia, Sleep, and Coma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanca, B.J.A.; Avidan, M.S.; Mashour, G.A. Human neural correlates of sevoflurane-induced unconsciousness. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 4, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavone, K.J.; Su, L.; Gao, L.; Eromo, E.; Vazquez, R.; Rhee, J.; Hobbs, L.E.; Ibala, R.; Demircioglu, G.; Purdon, P.L.; et al. Lack of responsiveness during the onset and offset of sevoflurane anesthesia is associated with decreased awake-alpha oscillation power. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blain-Moraes, S.; Tarnal, V.; Vanini, G.; Alexander, A.; Rosen, D.; Shortal, B.; Janke, E.; Mashour, G.A. Neurophysiological Correlates of Sevoflurane-induced Unconsciousness. Anesthesiology 2015, 122, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akeju, O.; Westover, M.B.; Pavone, K.J.; Sampson, A.L.; Hartnack, K.E.; Brown, E.N.; Purdon, P.L. Effects of Sevoflurane and Propofol on Frontal Electroencephalogram Power and Coherence. Anesthesiology 2014, 121, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamadia, S.; Pedemonte, J.C.; Hahm, E.Y.; Mekonnen, J.; Ibala, R.; Gitlin, J.; Ethridge, B.R.; Qu, J.; Vazquez, R.; Rhee, J.; et al. Delta oscillations phase limit neural activity during sevoflurane anesthesia. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskinoro, K.; Maksimow, A.; Georgiadis, S.; Längsjö, J.; Scheinin, H.; Karjalainen, P.; Jääskeläinen, S.K. Electroencephalogram reactivity to verbal command after dexmedetomidine, propofol and sevoflurane-induced unresponsiveness. Anaesthesia 2015, 70, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukamel, E.A.; Pirondini, E.; Babadi, B.; Wong, K.F.K.; Pierce, E.T.; Harrell, P.G.; Walsh, J.L.; Salazar-Gomez, A.F.; Cash, S.S.; Eskandar, E.N.; et al. A Transition in Brain State during Propofol-Induced Unconsciousness. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukamel, E.A.; Wong, K.F.; Prerau, M.J.; Brown, E.N.; Purdon, P.L. Phase-Based Measures of Cross-Frequency Coupling in Brain Electrical Dynamics under General Anesthesia. Conf. Proc. 2011, 2011, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartailler, J.; Parutto, P.; Touchard, C.; Vallée, F.; Holcman, D. Alpha rhythm collapse predicts iso-electric suppressions during anesthesia. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, D.; Bahuri, N.F.A.; Wang, S.; Hyam, J.A.; Yarrow, S.; FitzGerald, J.J.; Aziz, T.Z.; Green, A.L. Spectral and phase-amplitude coupling signatures in human deep brain oscillations during propofol-induced anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 121, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purdon, P.L.; Pierce, E.T.; Mukamel, E.A.; Prerau, M.J.; Walsh, J.L.; Wong, K.F.K.; Salazar-Gomez, A.F.; Harrell, P.G.; Sampson, A.L.; Cimenser, A.; et al. Electroencephalogram signatures of loss and recovery of consciousness from propofol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E1142–E1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akeju, O.; Song, A.H.; Hamilos, A.E.; Pavone, K.J.; Flores, F.J.; Brown, E.N.; Purdon, P.L. Electroencephalogram signatures of ketamine anesthesia-induced unconsciousness. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 2414–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, B.L.; Liley, D.T.J. Nitrous oxide paradoxically modulates slow electroencephalogram oscillations: Implications for anesthesia monitoring. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 113, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampil, I.J.; Kim, J.S.; Lenhardt, R.; Negishi, C.; Sessler, D.I. Bispectral EEG index during nitrous oxide administration. Anesthesiology 1998, 89, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavone, K.J.; Akeju, O.; Sampson, A.L.; Ling, K.; Purdon, P.L.; Brown, E.N. Nitrous oxide-induced slow and delta oscillations. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidera, J.A.; Taylor, N.E.; Lee, J.T.; Vlasov, K.Y.; Pei, J.; Stephen, E.P.; Mayo, J.P.; Brown, E.N.; Solt, K. Sevoflurane Induces Coherent Slow-Delta Oscillations in Rats. Front. Neural Circuits 2017, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Cardoso-Cruz, H.; Silva, F.; Galhardo, V.; Antunes, L. Comparison of Anesthetic Depth Indexes Based on Thalamocortical Local Field Potentials in Rats. Anesthesiology 2018, 112, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, F.J.; Hartnack, K.E.; Fath, A.B.; Kim, S.-E.; Wilson, M.A.; Brown, E.N.; Purdon, P.L. Thalamocortical synchronization during induction and emergence from propofol-induced unconsciousness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6660–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slovik, M.; Rosin, B.; Moshel, S.; Mitelman, R.; Schechtman, E.; Eitan, R.; Raz, A.; Bergman, H. Ketamine induced converged synchronous gamma oscillations in the cortico-basal ganglia network of nonhuman primates. J. Neurophysiol. 2017, 118, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulikova, S.P.; Tolmacheva, E.A.; Anderson, P.; Gaudias, J.; Adams, B.E.; Zheng, T.; Pinault, D. Opposite effects of ketamine and deep brain stimulation on rat thalamocortical information processing. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2012, 36, 3407–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, M.J.; Raynaud, B.; Garcia, R. Ketamine Dose-Dependently Induces High-Frequency Oscillations in the Nucleus Accumbens in Freely Moving Rats. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 60, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akeju, O.; Brown, E.N. Neural oscillations demonstrate that general anesthesia and sedative states are neurophysiologically distinct from sleep. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2017, 44, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crunelli, V.; Cope, D.W.; Hughes, S.W. Thalamic T-type Ca2+ channels and NREM sleep. Cell Calcium 2006, 40, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crunelli, V.; Hughes, S.W. The slow (<1 Hz) rhythm of non-REM sleep: A dialogue between three cardinal oscillators. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 13, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, F.; Schmiedt, J.T.; Taylor, H.L.; Orban, G.; Di Giovanni, G.; Uebele, V.N.; Renger, J.J.; Lambert, R.C.; Leresche, N.; Crunelli, V. Essential Thalamic Contribution to Slow Waves of Natural Sleep. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 19599–19610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.P.; Mochizuki, T.; Xie, J.; Fischler, W.; Manger, J.P.; Talley, E.M.; Scammell, T.E.; Tonegawa, S. Thalamic CaV3.1 T-type Ca2+ channel plays a crucial role in stabilizing sleep. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1743–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Shin, H.S. Lack of delta waves and sleep disturbances during non-rapid eye movement sleep in mice lacking alpha1G-subunit of T-type calcium channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 18195–18199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Song, K.; Lee, K.; Hong, J.; Lee, H.; Chae, S.; Cheong, E.; Shin, H.S. Sleep spindles are generated in the absence of T-type calcium channel-mediated low-threshold burst firing of thalamocortical neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20266–20271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Yu, E.; Lee, S.; Llinás, R.R. Altered thalamocortical rhythmicity and connectivity in mice lacking CaV3.1 T-type Ca2+ channels in unconsciousness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7839–7844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrenko, A.B.; Tsujita, M.; Kohno, T.; Sakimura, K.; Baba, H. Mutation of alpha1G T-type Calcium Channels in Mice Does Not Change Anesthetic Requirements for Loss of the Righting Reflex and Minimum Alveolar Concentration but Delays the Onset of Anesthetic Induction. Anesthesiology 2007, 106, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orestes, P.; Bojadzic, D.; Chow, R.M.; Todorovic, S.M. Mechanisms and functional significance of inhibition of neuronal T-type calcium channels by isoflurane. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feseha, S.; Timic Stamenic, T.; Wallace, D.; Tamag, C.; Yang, L.; Pan, J.Q.; Todorovic, S.M. Global genetic deletion of CaV3.3 channels facilitates anaesthetic induction and enhances isoflurane-sparing effects of T-type calcium channel blockers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkire, M.T.; Miller, J. General anesthesia and the neural correlates of consciousness. Prog. Brain Res. 2005, 150, 229–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzer, S.; Mattusch, C.; Garcia, P.S.; Schmid, S.; Kochs, E.; Rammes, G.; Schneider, G.; Kreuzer, M.; Haseneder, R. Propofol and sevoflurane differentially modulate cortical depolarization following electric stimulation of the ventrobasal thalamus. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steriade, M. Sleep oscillations and their blockage by activating systems. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 1994, 19, 354–368. [Google Scholar]
- Alkire, M.T.T.; Haier, R.J.J.; Fallon, J.H.H. Toward a unified theory of narcosis: Brain imaging evidence for a thalamocortical switch as the neurophysiologic basis of anesthetic-induced unconsciousness. Conscious. Cogn. 2000, 9, 370–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, A.; CurróDossi, R.; Contreras, D.; Steriade, M. Intracellular evidence for incompatibility between spindle and delta oscillations in thalamocortical neurons of cat. Neuroscience 1992, 48, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steriade, M.; Dossi, R.C.; Nuñez, A. Network modulation of a slow intrinsic oscillation of cat thalamocortical neurons implicated in sleep delta waves: Cortically induced synchronization and brainstem cholinergic suppression. J. Neurosci. 1991, 11, 3200–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarillo, Y.; Mato, G.; Nadal, M.S. Analysis of the role of the low threshold currents IT and Ih in intrinsic delta oscillations of thalamocortical neurons. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckle, V.-S.; DiGruccio, M.R.; Uebele, V.N.; Renger, J.J.; Todorovic, S.M. Inhibition of T-type calcium current in rat thalamocortical neurons by isoflurane. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, C.R.; Puil, E. Mechanism of anesthesia revealed by shunting actions of isoflurane on thalamocortical neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 1999, 81, 1795–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joksovic, P.M.; Todorovic, S.M. Isoflurane modulates neuronal excitability of the nucleus reticularis thalami in vitro. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1199, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkire, M.T.; McReynolds, J.R.; Hahn, E.L.; Trivedi, A.N. Thalamic microinjection of nicotine reverses sevoflurane-induced loss of righting reflex in the rat. Anesthesiology 2007, 107, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Song, I.; Keum, S.; Lee, T.; Jeong, M.J.; Kim, S.S.; McEnery, M.W.; Shin, H.S. Lack of the burst firing of thalamocortical relay neurons and resistance to absence seizures in mice lacking α1G T-type Ca2+ channels. Neuron 2001, 31, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joksimovic, S.L.; Covey, D.F.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V.; Todorovic, S.M. Neurosteroids in Pain Management: A New Perspective on an Old Player. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszlo, G.; Lester, S.; Gyermek, L.; Soyka, L.F. Steroid Anesthetics. Anesthesiology 1975, 42, 331–343. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, D.S.; Estes, W. Clinical Potential of Neurosteroids for CNS Disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodchild, C.S.; Serrao, J.M.; Sear, J.W.; Anderson, B.J. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Analysis of Alfaxalone Administered as a Bolus Intravenous Injection of Phaxan in a Phase 1 Randomized Trial. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 130, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joksimovic, S.M.; Sampath, D.; Krishnan, K.; Covey, D.F.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V.; Raol, Y.H.; Todorovic, S.M. Differential effects of the novel neurosteroid hypnotic (3β,5β,17β)-3-hydroxyandrostane-17-carbonitrile on electroencephalogram activity in male and female rats. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 127, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atluri, N.; Joksimovic, S.M.; Oklopcic, A.; Milanovic, D.; Klawitter, J.; Eggan, P.; Krishnan, K.; Covey, D.F.; Todorovic, S.M.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. A neurosteroid analogue with T-type calcium channel blocking properties is an effective hypnotic, but is not harmful to neonatal rat brain. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 120, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joksovic, P.M.; Covey, D.F.; Todorovic, S.M. Inhibition of T-type calcium current in the reticular thalamic nucleus by a novel neuroactive steroid. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1122, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorovic, S.M.; Pathirathna, S.; Brimelow, B.C.; Jagodic, M.M.; Ko, S.-H.; Jiang, X.; Nilsson, K.R.; Zorumski, C.F.; Covey, D.F.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V.; et al. 5beta-Reduced Neuroactive Steroids are Novel Voltage-Dependent Blockers of T-Type Ca2+ Channels in Rat Sensory Neurons In Vitro and Potent Peripheral Analgesics In Vivo. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoola, C.; Hwang, S.M.; Hong, S.J.; Rose, K.E.; Boyd, C.; Bozic, N.; Park, J.Y.; Osuru, H.P.; DiGruccio, M.R.; Covey, D.F.; et al. Inhibition of CaV3.2 T-type calcium channels in peripheral sensory neurons contributes to analgesic properties of epipregnanolone. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 3503–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joksimovic, S.L.; Donald, R.R.; Park, J.-Y.; Todorovic, S.M. Inhibition of multiple voltage-gated calcium channels may contribute to spinally mediated analgesia by epipregnanolone in a rat model of surgical paw incision. Channels 2019, 13, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisbeau, P.; Feltz, P.; Schlichter, R. Modulation of GABA(A) receptor-mediated IPSCs by neuroactive steroids in a rat hypothalamo-hypophyseal coculture model. J. Physiol. 1997, 500, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weir, C.J.; Ling, A.T.Y.; Belelli, D.; Wildsmith, J.A.W.; Peters, J.A.; Lambert, J.J. The interaction of anaesthetic steroids with recombinant glycine and GABAAreceptors. Br. J. Anaesth. 2004, 92, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulter, I.; Timic Stamenic, T.; Eggan, P.; Fine, B.R.; Corrigan, T.; Covey, D.F.; Yang, L.; Pan, J.Q.; Todorovic, S.M. Different roles of T-type calcium channel isoforms in hypnosis induced by an endogenous neurosteroid epipregnanolone. Neuropharmacology 2021, 197, 108739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).