Genetic Biomarkers and Their Clinical Implications in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Genetic Biomarkers
2.1. Chromosomal Alterations
2.2. Chromosome Rearrangements
2.2.1. BCR-ABL1 (Ph+) ALL and Ph-like ALL
| Genetic Alteration Class | Frequency of Occurring | Genes Involved | Targeted Therapy | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JAK-STAT signaling rearrangements | 40% | CRLF2 | JAK2 inhibitor | [58,77,102] |
| JAK2 | ||||
| EPOR | ||||
| TSLP | ||||
| IL2RB | JAK1/JAK3 inhibitor | |||
| TYK2 | TYK2 inhibitor | |||
| ABL-class fusions | 10–15% | ABL1, ABL2, PDGFRA, PDGFRB, CSFIR, LYN | Imatinib/dasatinib | [58,99] |
| RAS pathway mutations | 4% | KRAS, NRAS, PTNP11, CBL1, NF1, BRAF | MEK inhibitors | [58,102] |
| Rare subtypes | 1% | NTRK3 | Crizotinib | [58,77,95,99,102] |
| BLNK | SYK/MEK inhibitors | |||
| FGFR1 | Dasatinib/sorafenib | |||
| PT2KB | FAK inhibitors | |||
| FLT3 | FLT3 inhibitors | |||
| DGKH | - |
2.2.2. KMT2A Rearrangements
2.2.3. TCF Rearrangements
2.2.4. ETV6::RUNX1-Rearrangements and ETV6::RUNX1-like ALL
2.3. Other Rearrangements
2.3.1. IKZF1
2.3.2. PAX5
2.3.3. DUX4
2.3.4. ZNF384
2.3.5. CRLF2 Deregulation
2.3.6. MEF2D Rearrangements
2.3.7. NUTM1
2.3.8. CDKN2A
2.3.9. DIC(9;20) Rearrangements
3. Prognostic and Therapeutic Significance
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khazaei, Z.; Goodarzi, E.; Adineh, H.A.; Moradi, Y.; Sohrabivafa, M.; Darvishi, I.; Dehghani, S.L. Epidemiology, Incidence, and Mortality of Leukemia in Children Early Infancy to 14 Years Old of Age in South-Central Asia: A Global Ecological Study. J. Compr. Pediatr. 2019, 10, e82258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baade, P.D.; Youlden, D.R.; Valery, P.C.; Hassall, T.; Ward, L.; Green, A.C.; Aitken, J.F. Trends in Incidence of Childhood Cancer in Australia, 1983–2006. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linabery, A.M.; Ross, J.A. Trends in Childhood Cancer Incidence in the U.S. (1992–2004). Cancer 2008, 112, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Available online: http://gco.iarc.fr/today/home (accessed on 6 January 2022).
- Namayandeh, S.M.; Khazaei, Z.; Lari Najafi, M.; Goodarzi, E.; Moslem, A. GLOBAL Leukemia in Children 0–14 Statistics 2018, Incidence and Mortality and Human Development Index (HDI): GLOBOCAN Sources and Methods. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2020, 21, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: Sources, Methods and Major Patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Cancer Society Cancer Facts & Figures 2020. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/cancer-facts-figures-2020.html (accessed on 6 January 2022).
- Malard, F.; Mohty, M. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Lancet 2020, 395, 1146–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.M.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Bishop, K.; Kosary, C.L.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2014. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2014/#citation (accessed on 6 January 2022).
- Hunger, S.P.; Lu, X.; Devidas, M.; Camitta, B.M.; Gaynon, P.S.; Winick, N.J.; Reaman, G.H.; Carroll, W.L. Improved Survival for Children and Adolescents with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia between 1990 and 2005: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulte, D.; Gondos, A.; Brenner, H. Improvement in Survival in Younger Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia from the 1980s to the Early 21st Century. Blood 2009, 113, 1408–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Maele-Fabry, G.; Gamet-Payrastre, L.; Lison, D. Household Exposure to Pesticides and Risk of Leukemia in Children and Adolescents: Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-L.; Preston, D.L.; Soda, M.; Sugiyama, H.; Funamoto, S.; Kodama, K.; Kimura, A.; Kamada, N.; Dohy, H.; Tomonaga, M.; et al. The Incidence of Leukemia, Lymphoma and Multiple Myeloma among Atomic Bomb Survivors: 1950–2001. Radiat. Res. 2013, 179, 361–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wakeford, R. Childhood Leukaemia Following Medical Diagnostic Exposure to Ionizing Radiation in Utero or after Birth. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2008, 132, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krestinina, L.Y.; Davis, F.G.; Schonfeld, S.; Preston, D.L.; Degteva, M.; Epifanova, S.; Akleyev, A.V. Leukaemia Incidence in the Techa River Cohort: 1953–2007. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2886–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kendall, G.; Little, M.; Wakeford, R. Numbers and Proportions of Leukemias in Young People and Adults Induced by Radiation of Natural Origin. Leuk. Res. 2011, 35, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greaves, M. Infection, Immune Responses and the Aetiology of Childhood Leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinlen, L. Evidence for an Infective Cause of Childhood Leukaemia: Comparison of a Scottish New Town with Nuclear Reprocessing Sites in Britain. Lancet 1988, 2, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.; Mullighan, C.G. Molecular Markers in ALL: Clinical Implications. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2020, 33, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, H.; Pui, C.-H. Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, D.d.C.A.; Santos, S.d.S.; Monteiro, G.T.R. Leukemia Mortality Trends in Children and Adolescents in Brazilian State Capitals: 1980–2015. Epidemiol. Serv. Saude Rev. Sist. Unico Saude Bras. 2018, 27, e2017310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inaba, H.; Mullighan, C.G. Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematology 2020, 105, 2524–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsson, K.; Lilljebjörn, H.; Biloglav, A.; Olsson, L.; Rissler, M.; Castor, A.; Barbany, G.; Fogelstrand, L.; Nordgren, A.; Sjögren, H.; et al. The Genomic Landscape of High Hyperdiploid Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secker-Walker, L.M.; Lawler, S.D.; Hardisty, R.M. Prognostic Implications of Chromosomal Findings in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia at Diagnosis. BMJ 1978, 2, 1529–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Secker-Walker, L.M.; Chessells, J.M.; Stewart, E.L.; Swansbury, G.J.; Richards, S.; Lawler, S.D. Chromosomes and Other Prognostic Factors in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: A Long-Term Follow-Up. Br. J. Haematol. 1989, 72, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, M.J.; Shuster, J.J.; Sather, H.N.; Camitta, B.M.; Pullen, J.; Schultz, K.R.; Borowitz, M.J.; Gaynon, P.S.; Carroll, A.J.; Heerema, N.A. High Concordance from Independent Studies by the Children’s Cancer Group (CCG) and Pediatric Oncology Group (POG) Associating Favorable Prognosis with Combined Trisomies 4, 10, and 17 in Children with NCI Standard-Risk B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Children’s Oncology Group (COG) Initiative. Leukemia 2005, 19, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, A.V.; Ensor, H.M.; Richards, S.M.; Chilton, L.; Schwab, C.; Kinsey, S.E.; Vora, A.; Mitchell, C.D.; Harrison, C.J. Prognostic Effect of Chromosomal Abnormalities in Childhood B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: Results from the UK Medical Research Council ALL97/99 Randomised Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerema, N.A.; Sather, H.N.; Sensel, M.G.; Zhang, T.; Hutchinson, R.J.; Nachman, J.B.; Lange, B.J.; Steinherz, P.G.; Bostrom, B.C.; Reaman, G.H.; et al. Prognostic Impact of Trisomies of Chromosomes 10, 17, and 5 Among Children With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and High Hyperdiploidy (>50 Chromosomes). J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 1876–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.L.; Harrison, C.J.; Martineau, M.; Taylor, K.E.; Moorman, A.V. Is Trisomy 5 a Distinct Cytogenetic Subgroup in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia? Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2004, 148, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enshaei, A.; Vora, A.; Harrison, C.J.; Moppett, J.; Moorman, A.V. Defining Low-Risk High Hyperdiploidy in Patients with Paediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: A Retrospective Analysis of Data from the UKALL97/99 and UKALL2003 Clinical Trials. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e828–e839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilmer, E.; Suciu, S.; Ferster, A.; Bertrand, Y.; Cavé, H.; Thyss, A.; Benoit, Y.; Dastugue, N.; Fournier, M.; Souillet, G.; et al. Long-Term Results of Three Randomized Trials (58831, 58832, 58881) in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A CLCG-EORTC Report. Leukemia 2000, 14, 2257–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maloney, K.; Shuster, J.; Murphy, S.; Pullen, J.; Camitta, B. Long-Term Results of Treatment Studies for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Pediatric Oncology Group Studies from 1986–1994. Leukemia 2000, 14, 2276–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pui, C.-H.; Boyett, J.; Rivera, G.; Hancock, M.; Sandlund, J.; Ribeiro, R.; Rubnitz, J.; Behm, F.; Raimondi, S.; Gajjar, A.; et al. Long-Term Results of Total Therapy Studies 11, 12 and 13A for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia at St Jude Children’s Research Hospital. Leukemia 2000, 14, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whitehead, V.M.; Vuchich, M.J.; Lauer, S.J.; Mahoney, D.; Carroll, A.J.; Shuster, J.J.; Esseltine, D.W.; Payment, C.; Look, A.T.; Akabutu, J. Accumulation of High Levels of Methotrexate Polyglutamates in Lymphoblasts from Children with Hyperdiploid (Greater than 50 Chromosomes) B-Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Pediatric Oncology Group Study. Blood 1992, 80, 1316–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mrózek, K.; Heerema, N.A.; Bloomfield, C.D. Cytogenetics in Acute Leukemia. Blood Rev. 2004, 18, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braoudaki, M.; Tzortzatou-Stathopoulou, F. Clinical Cytogenetics in Pediatric Acute Leukemia: An Update. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2012, 12, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creasey, T.; Enshaei, A.; Nebral, K.; Schwab, C.; Watts, K.; Cuthbert, G.; Vora, A.; Moppett, J.; Harrison, C.J.; Fielding, A.K.; et al. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Array-based Signature of Low Hypodiploidy in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2021, 60, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safavi, S.; Paulsson, K. Near-Haploid and Low-Hypodiploid Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Two Distinct Subtypes with Consistently Poor Prognosis. Blood 2017, 129, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, C.J.; Moorman, A.V.; Broadfield, Z.J.; Cheung, K.L.; Harris, R.L.; Reza Jalali, G.; Robinson, H.M.; Barber, K.E.; Richards, S.M.; Mitchell, C.D.; et al. Three Distinct Subgroups of Hypodiploidy in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: Hypodiploidy in ALL. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 125, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, A.V.; Harrison, C.J.; Buck, G.A.N.; Richards, S.M.; Secker-Walker, L.M.; Martineau, M.; Vance, G.H.; Cherry, A.M.; Higgins, R.R.; Fielding, A.K.; et al. Karyotype Is an Independent Prognostic Factor in Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): Analysis of Cytogenetic Data from Patients Treated on the Medical Research Council (MRC) UKALLXII/Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) 2993 Trial. Blood 2007, 109, 3189–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmfeldt, L.; Wei, L.; Diaz-Flores, E.; Walsh, M.; Zhang, J.; Ding, L.; Payne-Turner, D.; Churchman, M.; Andersson, A.; Chen, S.-C.; et al. The Genomic Landscape of Hypodiploid Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Jeha, S.; Pei, D.; Payne-Turner, D.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Roberts, K.G.; Waanders, E.; Choi, J.K.; Ma, X.; Raimondi, S.C.; et al. Outcome of Children with Hypodiploid ALL Treated with Risk-Directed Therapy Based on MRD Levels. Blood 2015, 126, 2896–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safavi, S.; Olsson, L.; Biloglav, A.; Veerla, S.; Blendberg, M.; Tayebwa, J.; Behrendtz, M.; Castor, A.; Hansson, M.; Johansson, B.; et al. Genetic and Epigenetic Characterization of Hypodiploid Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 42793–42802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moorman, A.V.; Chilton, L.; Wilkinson, J.; Ensor, H.M.; Bown, N.; Proctor, S.J. A Population-Based Cytogenetic Study of Adults with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2010, 115, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeer, J.L.; Devidas, M.; Dai, Y.; Carroll, A.J.; Heerema, N.A.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Kahwash, S.B.; Borowitz, M.J.; Wood, B.L.; Larsen, E.; et al. Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation Does Not Improve the Poor Outcome of Children with Hypodiploid Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Report from Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talleur, A.C.; Maude, S.L. What Is the Role for HSCT or Immunotherapy in Pediatric Hypodiploid B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia? Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2020, 2020, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, T.; Arun, S.R.; Babu, G.A.; Chakrabarty, B.K.; Bhave, S.J.; Kumar, J.; Radhakrishnan, V.; Krishnan, S.; Ghara, N.; Arora, N.; et al. A Systematic Cytogenetic Strategy to Identify Masked Hypodiploidy in Precursor B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Low Resource Settings. Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2021, 37, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.J.; Shago, M.; Mikhail, F.M.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hirsch, B.A.; Loh, M.L.; Raetz, E.A.; Borowitz, M.J.; Wood, B.L.; Maloney, K.W.; et al. Masked Hypodiploidy: Hypodiploid Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) Mimicking Hyperdiploid ALL in Children: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer Genet. 2019, 238, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, R. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Chromosome 21. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1997, 94, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On Behalf of the Medical Research Council Childhood and Adult Leukaemia Working Parties; Harewood, L.; Robinson, H.; Harris, R.; Al-Obaidi, M.J.; Jalali, G.R.; Martineau, M.; Moorman, A.V.; Sumption, N.; Richards, S.; et al. Amplification of AML1 on a Duplicated Chromosome 21 in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Study of 20 Cases. Leukemia 2003, 17, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, C.J.; Moorman, A.V.; Schwab, C.; Carroll, A.J.; Raetz, E.A.; Devidas, M.; Strehl, S.; Nebral, K.; Harbott, J.; Teigler-Schlegel, A.; et al. An International Study of Intrachromosomal Amplification of Chromosome 21 (IAMP21): Cytogenetic Characterization and Outcome. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephens, P.J.; Greenman, C.D.; Fu, B.; Yang, F.; Bignell, G.R.; Mudie, L.J.; Pleasance, E.D.; Lau, K.W.; Beare, D.; Stebbings, L.A.; et al. Massive Genomic Rearrangement Acquired in a Single Catastrophic Event during Cancer Development. Cell 2011, 144, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerema, N.A.; Carroll, A.J.; Devidas, M.; Loh, M.L.; Borowitz, M.J.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Larsen, E.C.; Mattano, L.A.; Maloney, K.W.; Willman, C.L.; et al. Intrachromosomal Amplification of Chromosome 21 Is Associated with Inferior Outcomes in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated in Contemporary Standard-Risk Children’s Oncology Group Studies: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3397–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.L.; Matheson, E.; Grossmann, V.; Sinclair, P.; Bashton, M.; Schwab, C.; Towers, W.; Partington, M.; Elliott, A.; Minto, L.; et al. The Role of the RAS Pathway in IAMP21-ALL. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mateos, M.K.; Barbaric, D.; Byatt, S.-A.; Sutton, R.; Marshall, G.M. Down Syndrome and Leukemia: Insights into Leukemogenesis and Translational Targets. Transl. Pediatr. 2015, 4, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, C.J.; Schwab, C. Constitutional Abnormalities of Chromosome 21 Predispose to IAMP21-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 59, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.G.; Li, Y.; Payne-Turner, D.; Harvey, R.C.; Yang, Y.-L.; Pei, D.; McCastlain, K.; Ding, L.; Lu, C.; Song, G.; et al. Targetable Kinase-Activating Lesions in Ph-like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forghieri, F.; Luppi, M.; Potenza, L. Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Hematology 2015, 20, 618–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.-J.; Liu, Y.-F.; Xu, L.-Z.; Long, Z.-J.; Huang, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Feng, J.-X.; Pan, Y.-J.; Yan, J.-S.; et al. The Philadelphia Chromosome in Leukemogenesis. Chin. J. Cancer 2016, 35, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernt, K.M.; Hunger, S.P. Current Concepts in Pediatric Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Miller, C.B.; Radtke, I.; Phillips, L.A.; Dalton, J.; Ma, J.; White, D.; Hughes, T.P.; Le Beau, M.M.; Pui, C.-H.; et al. BCR-ABL1 Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Is Characterized by the Deletion of Ikaros. Nature 2008, 453, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobucci, I.; Lonetti, A.; Paoloni, F.; Papayannidis, C.; Ferrari, A.; Storlazzi, C.T.; Vignetti, M.; Cilloni, D.; Messa, F.; Guadagnuolo, V.; et al. The PAX5 Gene Is Frequently Rearranged in BCR-ABL1-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia but Is Not Associated with Outcome. A Report on Behalf of the GIMEMA Acute Leukemia Working Party. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notta, F.; Mullighan, C.G.; Wang, J.C.Y.; Poeppl, A.; Doulatov, S.; Phillips, L.A.; Ma, J.; Minden, M.D.; Downing, J.R.; Dick, J.E. Evolution of Human BCR–ABL1 Lymphoblastic Leukaemia-Initiating Cells. Nature 2011, 469, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soverini, S.; Bassan, R.; Lion, T. Treatment and Monitoring of Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Leukemia Patients: Recent Advances and Remaining Challenges. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aricò, M.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Camitta, B.; Schrappe, M.; Chessells, J.; Baruchel, A.; Gaynon, P.; Silverman, L.; Janka-Schaub, G.; Kamps, W.; et al. Outcome of Treatment in Children with Philadelphia Chromosome–Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricò, M.; Schrappe, M.; Hunger, S.P.; Carroll, W.L.; Conter, V.; Galimberti, S.; Manabe, A.; Saha, V.; Baruchel, A.; Vettenranta, K.; et al. Clinical Outcome of Children with Newly Diagnosed Philadelphia Chromosome–Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated Between 1995 and 2005. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4755–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paper: Multicenter Total Therapy Gimema LAL 1509 Protocol for De Novo Adult Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) Patients. Updated Results and Refined Genetic-Based Prognostic Stratification. Available online: https://ash.confex.com/ash/2015/webprogramscheduler/Paper84424.html (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- From the Children’s Oncology Group; Schultz, K.R.; Carroll, A.; Heerema, N.A.; Bowman, W.P.; Aledo, A.; Slayton, W.B.; Sather, H.; Devidas, M.; Zheng, H.W.; et al. Long-Term Follow-up of Imatinib in Pediatric Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Children’s Oncology Group Study AALL0031. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinelli, G.; Iacobucci, I.; Storlazzi, C.T.; Vignetti, M.; Paoloni, F.; Cilloni, D.; Soverini, S.; Vitale, A.; Chiaretti, S.; Cimino, G.; et al. IKZF1 (Ikaros) Deletions in BCR-ABL1 –Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Are Associated with Short Disease-Free Survival and High Rate of Cumulative Incidence of Relapse: A GIMEMA AL WP Report. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5202–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Williams, R.T.; Downing, J.R.; Sherr, C.J. Failure of CDKN2A/B (INK4A/B–ARF)-Mediated Tumor Suppression and Resistance to Targeted Therapy in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Induced by BCR-ABL. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1411–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- The Children’s Oncology Group; Schultz, K.R.; Devidas, M.; Bowman, W.P.; Aledo, A.; Slayton, W.B.; Sather, H.; Zheng, H.W.; Davies, S.M.; Gaynon, P.S.; et al. Philadelphia Chromosome-Negative Very High-Risk Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children and Adolescents: Results from Children’s Oncology Group Study AALL0031. Leukemia 2014, 28, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biondi, A.; Schrappe, M.; De Lorenzo, P.; Castor, A.; Lucchini, G.; Gandemer, V.; Pieters, R.; Stary, J.; Escherich, G.; Campbell, M.; et al. Imatinib after Induction for Treatment of Children and Adolescents with Philadelphia-Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (EsPhALL): A Randomised, Open-Label, Intergroup Study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.H.; Willis, S.G.; Stork, L.; Hunger, S.P.; Carroll, W.L.; Camitta, B.M.; Winick, N.J.; Druker, B.J.; Schultz, K.R. Imatinib Resistant BCR-ABL1 Mutations at Relapse in Children with Ph+ ALL: A Children’s Oncology Group (COG) Study. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 157, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerchione, C.; Locatelli, F.; Martinelli, G. Dasatinib in the Management of Pediatric Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 632231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Dalle, I.; Jabbour, E.; Short, N.J.; Ravandi, F. Treatment of Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2019, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Abraham, A. BCR-ABL1–like B-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma: A Comprehensive Review. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 144, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medeiros, B.C. Deletion of IKZF1 and Prognosis in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1787–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boer, J.M.; Marchante, J.R.M.; Evans, W.E.; Horstmann, M.A.; Escherich, G.; Pieters, R.; Den Boer, M.L. BCR-ABL1-like Cases in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Comparison between DCOG/Erasmus MC and COG/St. Jude Signatures. Haematologica 2015, 100, e354–e357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Den Boer, M.L.; van Slegtenhorst, M.; De Menezes, R.X.; Cheok, M.H.; Buijs-Gladdines, J.G.; Peters, S.T.; Van Zutven, L.J.; Beverloo, H.B.; Van der Spek, P.J.; Escherich, G.; et al. A Subtype of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia with Poor Treatment Outcome: A Genome-Wide Classification Study. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Su, X.; Zhang, J.; Radtke, I.; Phillips, L.A.A.; Miller, C.B.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Cheng, C.; Schulman, B.A.; et al. Deletion of IKZF1 and Prognosis in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Z.; Sherer, M.; Casey, J.; Bakos, H.A.; Vitullo, K.; Hu, J.; Friehling, E.; Gollin, S.M.; Surti, U.; Yatsenko, S.A. The Genomic Landscape of PAX5, IKZF1, and CDKN2A/B Alterations in B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2016, 150, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaretti, S.; Messina, M.; Foà, R. BCR/ABL1-like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: How to Diagnose and Treat? Open Questions in BCR/ABL1-Like ALL. Cancer 2019, 125, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, K.G.; Reshmi, S.C.; Harvey, R.C.; Chen, I.-M.; Patel, K.; Stonerock, E.; Jenkins, H.; Dai, Y.; Valentine, M.; Gu, Z.; et al. Genomic and Outcome Analyses of Ph-like ALL in NCI Standard-Risk Patients: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Blood 2018, 132, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Yu, H.; Jin, R.; Wu, X.; Chen, H. Genetic and Epigenetic Targeting Therapy for Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cells 2021, 10, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.G.; Gu, Z.; Payne-Turner, D.; McCastlain, K.; Harvey, R.C.; Chen, I.-M.; Pei, D.; Iacobucci, I.; Valentine, M.; Pounds, S.B.; et al. High Frequency and Poor Outcome of Philadelphia Chromosome-Like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Adults. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.G.; Mullighan, C.G. Genomics in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: Insights and Treatment Implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.G.; Pei, D.; Campana, D.; Payne-Turner, D.; Li, Y.; Cheng, C.; Sandlund, J.T.; Jeha, S.; Easton, J.; Becksfort, J.; et al. Outcomes of Children with BCR-ABL1-Like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated with Risk-Directed Therapy Based on the Levels of Minimal Residual Disease. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3012–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heatley, S.L.; Sadras, T.; Kok, C.H.; Nievergall, E.; Quek, K.; Dang, P.; McClure, B.; Venn, N.; Moore, S.; Suttle, J.; et al. High Prevalence of Relapse in Children with Philadelphia-like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia despite Risk-Adapted Treatment. Haematologica 2017, 102, e490–e493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, W.; Luger, S.M.; Advani, A.S.; Yin, J.; Harvey, R.C.; Mullighan, C.G.; Willman, C.L.; Fulton, N.; Laumann, K.M.; Malnassy, G.; et al. A Pediatric Regimen for Older Adolescents and Young Adults with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Results of CALGB 10403. Blood 2019, 133, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elnahass, Y.H.; Fahmy, O.A.; Samra, M.A.M.; Elrefaey, F.A.; Bokhary, M.T.; Elsherif, H.; Afifi, H.H.; Elkomy, A.S.; Hola, M.; Mahmoud, H.K. Poor Outcome of CRLF2 Rearranged Philadelphia Negative Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Adults Patients. Blood 2018, 132, 5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attarbaschi, A.; Morak, M.; Cario, G.; Cazzaniga, G.; Ensor, H.M.; te Kronnie, T.; Bradtke, J.; Mann, G.; Vendramini, E.; Palmi, C.; et al. Treatment Outcome of CRLF2-Rearranged Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: A Comparative Analysis of the AIEOP-BFM and UK NCRI-CCLG Study Groups. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 158, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, G.; Li, J.; Chen, B.; Han, Q.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Yu, M.D.; et al. High CRLF2 Expression Associates with IKZF1 Dysfunction in Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia without CRLF2 Rearrangement. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 49722–49732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iacobucci, I.; Li, Y.; Roberts, K.G.; Dobson, S.M.; Kim, J.C.; Payne-Turner, D.; Harvey, R.C.; Valentine, M.; McCastlain, K.; Easton, J.; et al. Truncating Erythropoietin Receptor Rearrangements in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, K.G.; Yang, Y.-L.; Payne-Turner, D.; Lin, W.; Files, J.K.; Dickerson, K.; Gu, Z.; Taunton, J.; Janke, L.J.; Chen, T.; et al. Oncogenic Role and Therapeutic Targeting of ABL-Class and JAK-STAT Activating Kinase Alterations in Ph-like ALL. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 1657–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Miyagawa, N.; Mitsui, K.; Matsuoka, M.; Kojima, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Ootsubo, K.; Nagai, J.; Ueno, H.; Ishibashi, T.; et al. TKI Dasatinib Monotherapy for a Patient with Ph-like ALL Bearing ATF7IP/PDGFRB Translocation: TKI Dasatinib Monotherapy for Ph-like ALL Bearing PDGFRB Translocation. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 1058–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Z. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patient with Variant ATF7IP/PDGFRB Fusion and Favorable Response to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment: A Case Report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2017, 18, 1204–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Zhang, J.; Harvey, R.C.; Collins-Underwood, J.R.; Schulman, B.A.; Phillips, L.A.; Tasian, S.K.; Loh, M.L.; Su, X.; Liu, W.; et al. JAK Mutations in High-Risk Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9414–9418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reshmi, S.C.; Harvey, R.C.; Roberts, K.G.; Stonerock, E.; Smith, A.; Jenkins, H.; Chen, I.-M.; Valentine, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Targetable Kinase Gene Fusions in High-Risk B-ALL: A Study from the Children’s Oncology Group. Blood 2017, 129, 3352–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AdisInsight. A Phase 2 Study of the JAK1/JAK2 Inhibitor Ruxolitinib with Chemotherapy in Children with De Novo High-Risk CRLF2-Rearranged and/or JAK Pathway-Mutant Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Available online: https://adisinsight.springer.com/trials/700267573 (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- Roberts, K.G.; Janke, L.J.; Zhao, Y.; Seth, A.; Ma, J.; Finkelstein, D.; Smith, S.; Ebata, K.; Tuch, B.B.; Hunger, S.P.; et al. ETV6-NTRK3 Induces Aggressive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Highly Sensitive to Selective TRK Inhibition. Blood 2018, 132, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadav, V.; Ganesan, P.; Veeramani, R.; Kumar, V.D. Philadelphia-Like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Systematic Review. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, e57–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, G.; Boissel, N.; Chevallier, P.; Ottmann, O.; Gökbuget, N.; Topp, M.S.; Fielding, A.K.; Rambaldi, A.; Ritchie, E.K.; Papayannidis, C.; et al. Complete Hematologic and Molecular Response in Adult Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Philadelphia Chromosome–Positive B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Following Treatment with Blinatumomab: Results from a Phase II, Single-Arm, Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1795–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarjian, H.; Stein, A.; Gökbuget, N.; Fielding, A.K.; Schuh, A.C.; Ribera, J.-M.; Wei, A.; Dombret, H.; Foà, R.; Bassan, R.; et al. Blinatumomab versus Chemotherapy for Advanced Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasi, I.; Ba, I.; Sirvent, N.; Braun, T.; Cuccuini, W.; Ballerini, P.; Duployez, N.; Tanguy-Schmidt, A.; Tamburini, J.; Maury, S.; et al. Efficacy of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Ph-like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Harboring ABL-Class Rearrangements. Blood 2019, 134, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moujalled, D.M.; Hanna, D.T.; Hediyeh-Zadeh, S.; Pomilio, G.; Brown, L.; Litalien, V.; Bartolo, R.; Fleming, S.; Chanrion, M.; Banquet, S.; et al. Cotargeting BCL-2 and MCL-1 in High-Risk B-ALL. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 2762–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilson, I.; Löchner, K.; Siegler, G.; Greil, J.; Beck, J.D.; Fey, G.H.; Marschalek, R. Exon/Intron Structure of the Human ALL-1 (MLL) Gene Involved in Translocations to Chromosomal Region 11q23 and Acute Leukaemias. Br. J. Haematol. 1996, 93, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Chaer, F.; Keng, M.; Ballen, K.K. MLL-Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2020, 15, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, G.; Attarbaschi, A.; Schrappe, M.; De Lorenzo, P.; Peters, C.; Hann, I.; De Rossi, G.; Felice, M.; Lausen, B.; LeBlanc, T.; et al. Improved Outcome with Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in a Poor Prognostic Subgroup of Infants with Mixed-Lineage-Leukemia (MLL)–Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Results from the Interfant-99 Study. Blood 2010, 116, 2644–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.M.; Ridge, S.A.; Cabrera, M.E.; Mahmoud, H.; Steel, C.M.; Chan, L.C.; Greaves, M. In Utero Rearrangements in the Trithorax-Related Oncogene in Infant Leukaemias. Nature 1993, 363, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalidi, H.S.; Chang, K.L.; Medeiros, L.J.; Brynes, R.K.; Slovak, M.L.; Murata-Collins, J.L.; Arber, D.A. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Survey of Immunophenotype, French-American-British Classification, Frequency of Myeloid Antigen Expression, and Karyotypic Abnormalities in 210 Pediatric and Adult Cases. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1999, 111, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, C.H.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Hancock, M.L.; Downing, J.R.; Raimondi, S.C.; Rivera, G.K.; Sandlund, J.T.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Head, D.R.; Relling, M.V.; et al. Reappraisal of the Clinical and Biologic Significance of Myeloid-Associated Antigen Expression in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 3768–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.; Burmeister, T.; Gröger, D.; Tsaur, G.; Fechina, L.; Renneville, A.; Sutton, R.; Venn, N.C.; Emerenciano, M.; Pombo-de-Oliveira, M.S.; et al. The MLL Recombinome of Acute Leukemias in 2017. Leukemia 2018, 32, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, A.C.; Bernt, K.M. MLL-Rearranged Leukemias—An Update on Science and Clinical Approaches. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pui, C.-H.; Gaynon, P.S.; Boyett, J.M.; Chessells, J.M.; Baruchel, A.; Kamps, W.; Silverman, L.B.; Biondi, A.; Harms, D.O.; Vilmer, E.; et al. Outcome of Treatment in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia with Rearrangements of the 11q23 Chromosomal Region. Lancet 2002, 359, 1909–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.; Hofmann, J.; Burmeister, T.; Gröger, D.; Park, T.S.; Emerenciano, M.; Pombo de Oliveira, M.; Renneville, A.; Villarese, P.; Macintyre, E.; et al. The MLL Recombinome of Acute Leukemias in 2013. Leukemia 2013, 27, 2165–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerenciano, M.; Meyer, C.; Mansur, M.B.; Marschalek, R.; Pombo-de-Oliveira, M.S.; Brazilian Collaborative Study Group of Infant Acute Leukaemia. The distribution of MLL breakpoints correlates with outcome in infant acute leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 161, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerkalenkova, E.; Lebedeva, S.; Borkovskaia, A.; Soldatkina, O.; Plekhanova, O.; Tsaur, G.; Maschan, M.; Maschan, A.; Novichkova, G.; Olshanskaya, Y. BTK, NUTM2A, and PRPF19 Are Novel KMT2A Partner Genes in Childhood Acute Leukemia. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, S.A.; Look, A.T. Molecular Genetics of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 6306–6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunger, S.P.; Mullighan, C.G. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tauchi, H.; Tomizawa, D.; Eguchi, M.; Eguchi-Ishimae, M.; Koh, K.; Hirayama, M.; Miyamura, N.; Kinukawa, N.; Hayashi, Y.; Horibe, K.; et al. Clinical Features and Outcome of MLL Gene Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Infants with Additional Chromosomal Abnormalities Other than 11q23 Translocation. Leuk. Res. 2008, 32, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, T.; Brady, H.J.M. Insights from Clinical Studies into the Role of the MLL Gene in Infant and Childhood Leukemia. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2008, 40, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- For the St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital–Washington University Pediatric Cancer Genome Project; Andersson, A.K.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Gedman, A.L.; Dang, J.; Nakitandwe, J.; Holmfeldt, L.; Parker, M.; et al. The Landscape of Somatic Mutations in Infant MLL-Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemias. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agraz-Doblas, A.; Bueno, C.; Bashford-Rogers, R.; Roy, A.; Schneider, P.; Bardini, M.; Ballerini, P.; Cazzaniga, G.; Moreno, T.; Revilla, C.; et al. Unraveling the Cellular Origin and Clinical Prognostic Markers of Infant B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Using Genome-Wide Analysis. Haematologica 2019, 104, 1176–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyrenius-Wittsten, A.; Pilheden, M.; Sturesson, H.; Hansson, J.; Walsh, M.P.; Song, G.; Kazi, J.U.; Liu, J.; Ramakrishan, R.; Garcia-Ruiz, C.; et al. De Novo Activating Mutations Drive Clonal Evolution and Enhance Clonal Fitness in KMT2A-Rearranged Leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-W.; Koche, R.P.; Sinha, A.U.; Deshpande, A.J.; Zhu, N.; Eng, R.; Doench, J.G.; Xu, H.; Chu, S.H.; Qi, J.; et al. DOT1L Inhibits SIRT1-Mediated Epigenetic Silencing to Maintain Leukemic Gene Expression in MLL-Rearranged Leukemia. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pui, C.H. Precision medicine in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberuyi, N.; Rahgozar, S.; Ghodousi, E.S.; Ghaedi, K. Drug Resistance Biomarkers and Their Clinical Applications in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2020, 9, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quong, M.W.; Romanow, W.J.; Murre, C. E Protein Function in Lymphocyte Development. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Churchman, M.L.; Roberts, K.G.; Moore, I.; Zhou, X.; Nakitandwe, J.; Hagiwara, K.; Pelletier, S.; Gingras, S.; Berns, H.; et al. PAX5-Driven Subtypes of B-Progenitor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeha, S.; Pei, D.; Raimondi, S.C.; Onciu, M.; Campana, D.; Cheng, C.; Sandlund, J.T.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Howard, S.C.; et al. Increased Risk for CNS Relapse in Pre-B Cell Leukemia with the t(1;19)/TCF3-PBX1. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1406–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, M.S.; Gallego, M.S.; Alonso, C.N.; Alfaro, E.M.; Guitter, M.R.; Bernasconi, A.R.; Rubio, P.L.; Zubizarreta, P.A.; Rossi, J.G. Prognostic Impact of t(1;19)/TCF3–PBX1 in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in the Context of Berlin–Frankfurt–Münster-Based Protocols. Leuk. Lymphoma 2011, 52, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.J.; Moorman, A.V.; Schwab, C.; Iacobucci, I.; Mullighan, C. Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics. In Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia; Vora, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 61–98. ISBN 9783319397078. [Google Scholar]
- Mazieres, J.; You, L.; He, B.; Xu, Z.; Lee, A.Y.; Mikami, I.; McCormick, F.; Jablons, D.M. Inhibition of Wnt16 in Human Acute Lymphoblastoid Leukemia Cells Containing the t(1;19) Translocation Induces Apoptosis. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5396–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bicocca, V.T.; Chang, B.H.; Masouleh, B.K.; Muschen, M.; Loriaux, M.M.; Druker, B.J.; Tyner, J.W. Crosstalk between ROR1 and the Pre-B Cell Receptor Promotes Survival of t(1;19) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Chen, L.; Cui, B.; Widhopf, G.F.; Shen, Z.; Wu, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Briggs, S.P.; Kipps, T.J. Wnt5a Induces ROR1/ROR2 Heterooligomerization to Enhance Leukemia Chemotaxis and Proliferation. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 126, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janovska, P.; Poppova, L.; Plevova, K.; Plesingerova, H.; Behal, M.; Kaucka, M.; Ovesna, P.; Hlozkova, M.; Borsky, M.; Stehlikova, O.; et al. Autocrine Signaling by Wnt-5a Deregulates Chemotaxis of Leukemic Cells and Predicts Clinical Outcome in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karvonen, H.; Perttilä, R.; Niininen, W.; Hautanen, V.; Barker, H.; Murumägi, A.; Heckman, C.A.; Ungureanu, D. Wnt5a and ROR1 Activate Non-Canonical Wnt Signaling via RhoA in TCF3-PBX1 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Highlight New Treatment Strategies via Bcl-2 Co-Targeting. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3288–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duque-Afonso, J.; Feng, J.; Scherer, F.; Lin, C.-H.; Wong, S.H.K.; Wang, Z.; Iwasaki, M.; Cleary, M.L. Comparative Genomics Reveals Multistep Pathogenesis of E2A-PBX1 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3667–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inukai, T.; Inaba, T.; Ikushima, S.; Look, A.T. The AD1 and AD2 Transactivation Domains of E2A Are Essential for the Antiapoptotic Activity of the Chimeric Oncoprotein E2A-HLF. Mol. Cell Biol. 1998, 18, 6035–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inukai, T.; Hirose, K.; Inaba, T.; Kurosawa, H.; Hama, A.; Inada, H.; Chin, M.; Nagatoshi, Y.; Ohtsuka, Y.; Oda, M.; et al. Hypercalcemia in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Frequent Implication of Parathyroid Hormone-Related Peptide and E2A-HLF from Translocation 17;19. Leukemia 2007, 21, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunger, S.P.; Devaraj, P.E.; Foroni, L.; Secker-Walker, L.M.; Cleary, M.L. Two Types of Genomic Rearrangements Create Alternative E2A-HLF Fusion Proteins in t(17;19)-ALL. Blood 1994, 83, 2970–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Seidel, M.G.; Wu, W.; Kamizono, S.; Ferrando, A.A.; Bronson, R.T.; Iwasaki, H.; Akashi, K.; Morimoto, A.; Hitzler, J.K.; et al. Slug, a Highly Conserved Zinc Finger Transcriptional Repressor, Protects Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells from Radiation-Induced Apoptosis in Vivo. Cancer Cell 2002, 2, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inukai, T.; Inoue, A.; Kurosawa, H.; Goi, K.; Shinjyo, T.; Ozawa, K.; Mao, M.; Inaba, T.; Look, A.T. SLUG, a Ces-1-Related Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Gene with Antiapoptotic Activity, Is a Downstream Target of the E2A-HLF Oncoprotein. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, U.; Forster, M.; Rinaldi, A.; Risch, T.; Sungalee, S.; Warnatz, H.-J.; Bornhauser, B.; Gombert, M.; Kratsch, C.; Stütz, A.M.; et al. Genomics and Drug Profiling of Fatal TCF3-HLF-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Identifies Recurrent Mutation Patterns and Therapeutic Options. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wan, X.; Yang, F.; Shi, W.; Liu, R.; Ding, L.; Tang, Y.; Luo, C.; Yang, X.; Ma, Y.; et al. Successful Treatment of TCF3-HLF–Positive Childhood B-ALL with Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, C.-H.; Relling, M.V.; Downing, J.R. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1535–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sundaresh, A.; Williams, O. Mechanism of ETV6-RUNX1 Leukemia. In RUNX Proteins in Development and Cancer; Groner, Y., Ito, Y., Liu, P., Neil, J.C., Speck, N.A., van Wijnen, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; Volume 962, pp. 201–216. ISBN 9789811032318. [Google Scholar]
- Romana, S.P.; Poirel, H.; Leconiat, M.; Flexor, M.A.; Mauchauffé, M.; Jonveaux, P.; Macintyre, E.A.; Berger, R.; Bernard, O.A. High frequency of t(12;21) in childhood B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 1995, 86, 4263–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hollenhorst, P.C.; McIntosh, L.P.; Graves, B.J. Genomic and Biochemical Insights into the Specificity of ETS Transcription Factors. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011, 80, 437–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loh, M.L.; Rubnitz, J.E. TEL/AML1-Positive Pediatric Leukemia: Prognostic Significance and Therapeutic Approaches. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2002, 9, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, S.; Downing, J.R.; Hiebert, S.W. Identification of AML-1 and the (8;21) Translocation Protein (AML-1/ETO) as Sequence-Specific DNA-Binding Proteins: The Runt Homology Domain Is Required for DNA Binding and Protein-Protein Interactions. Mol. Cell Biol. 1993, 13, 6336–6345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; van Deursen, J.; Hiebert, S.W.; Grosveld, G.; Downing, J.R. AML1, the Target of Multiple Chromosomal Translocations in Human Leukemia, Is Essential for Normal Fetal Liver Hematopoiesis. Cell 1996, 84, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiemels, J.; Cazzaniga, G.; Daniotti, M.; Eden, O.; Addison, G.; Masera, G.; Saha, V.; Biondi, A.; Greaves, M. Prenatal Origin of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia in Children. Lancet 1999, 354, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, D.; Olsen, M.; Lähnemann, D.; Stanulla, M.; Slany, R.; Schmiegelow, K.; Borkhardt, A.; Fischer, U. Five Percent of Healthy Newborns Have an ETV6-RUNX1 Fusion as Revealed by DNA-Based GIPFEL Screening. Blood 2018, 131, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Goorha, S.; Radtke, I.; Miller, C.B.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Dalton, J.D.; Girtman, K.; Mathew, S.; Ma, J.; Pounds, S.B.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of Genetic Alterations in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Nature 2007, 446, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Rapado, I.; Li, Y.; Potter, N.E.; Wedge, D.C.; Tubio, J.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Van Loo, P.; Cooke, S.L.; Marshall, J.; et al. RAG-Mediated Recombination Is the Predominant Driver of Oncogenic Rearrangement in ETV6-RUNX1 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuiper, R.P.; Schoenmakers, E.F.P.M.; van Reijmersdal, S.V.; Hehir-Kwa, J.Y.; van Kessel, A.G.; van Leeuwen, F.N.; Hoogerbrugge, P.M. High-Resolution Genomic Profiling of Childhood ALL Reveals Novel Recurrent Genetic Lesions Affecting Pathways Involved in Lymphocyte Differentiation and Cell Cycle Progression. Leukemia 2007, 21, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cavé, H.; Cacheux, V.; Raynaud, S.; Brunie, G.; Bakkus, M.; Cochaux, P.; Preudhomme, C.; Laï, J.; Vilmer, E.; Grandchamp, B. ETV6 Is the Target of Chromosome 12p Deletions in t(12;21) Childhood Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia. Leukemia 1997, 11, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raynaud, S.; Cave, H.; Baens, M.; Bastard, C.; Cacheux, V.; Grosgeorge, J.; Guidal-Giroux, C.; Guo, C.; Vilmer, E.; Marynen, P.; et al. The 12;21 translocation involving TEL and deletion of the other TEL allele: Two frequently associated alterations found in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 1996, 87, 2891–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stams, W.A.G.; Beverloo, H.B.; den Boer, M.L.; de Menezes, R.X.; Stigter, R.L.; van Drunen, E.; Ramakers-van-Woerden, N.L.; Loonen, A.H.; van Wering, E.R.; Janka-Schaub, G.E.; et al. Incidence of Additional Genetic Changes in the TEL and AML1 Genes in DCOG and COALL-Treated t(12;21)-Positive Pediatric ALL, and Their Relation with Drug Sensitivity and Clinical Outcome. Leukemia 2006, 20, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peter, A.; Heiden, T.; Taube, T.; Körner, G.; Seeger, K. Interphase FISH on TEL/AML1 Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Relapses—Analysis of Clinical Relevance of Additional TEL and AML1 Copy Number Changes. Eur. J. Haematol. 2009, 83, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attarbaschi, A.; Mann, G.; König, M.; Dworzak, M.N.; Trebo, M.M.; Mühlegger, N.; Gadner, H.; Haas, O.A. Austrian Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster cooperative study group Incidence and Relevance of Secondary Chromosome Abnormalities in Childhood TEL/AML1+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: An Interphase FISH Analysis. Leukemia 2004, 18, 1611–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loncarevic, I.F.; Roitzheim, B.; Ritterbach, J.; Viehmann, S.; Borkhardt, A.; Lampert, F.; Harbott, J. Trisomy 21 Is a Recurrent Secondary Aberration in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with TEL/AML1 Gene Fusion. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1999, 24, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales-Rodríguez, B.; Fernández-Ramírez, F.; Núñez-Enríquez, J.C.; Velázquez-Wong, A.C.; Medina-Sansón, A.; Jiménez-Hernández, E.; Flores-Lujano, J.; Peñaloza-González, J.G.; Espinosa-Elizondo, R.M.; Pérez-Saldívar, M.L.; et al. Copy Number Alterations Associated with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Mexican Children. A Report from The Mexican Inter-Institutional Group for the Identification of the Causes of Childhood Leukemia. Arch. Med. Res. 2016, 47, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, G.; Hauer, J.; Martín-Lorenzo, A.; Schäfer, D.; Bartenhagen, C.; García-Ramírez, I.; Auer, F.; González-Herrero, I.; Ruiz-Roca, L.; Gombert, M.; et al. Infection Exposure Promotes ETV6-RUNX1 Precursor B-Cell Leukemia via Impaired H3K4 Demethylases. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 4365–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhojwani, D.; Pei, D.; Sandlund, J.T.; Jeha, S.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Raimondi, S.C.; Shurtleff, S.; Onciu, M.; Cheng, C.; et al. ETV6-RUNX1-Positive Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Improved Outcome with Contemporary Therapy. Leukemia 2012, 26, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forestier, E.; Heyman, M.; Andersen, M.K.; Autio, K.; Blennow, E.; Borgström, G.; Golovleva, I.; Heim, S.; Heinonen, K.; Hovland, R.; et al. Outcome of ETV6/RUNX1-Positive Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia in the NOPHO-ALL-1992 Protocol: Frequent Late Relapses but Good Overall Survival. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 140, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandemer, V.; Chevret, S.; Petit, A.; Vermylen, C.; Leblanc, T.; Michel, G.; Schmitt, C.; Lejars, O.; Schneider, P.; Demeocq, F.; et al. Excellent Prognosis of Late Relapses of ETV6/RUNX1-Positive Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Lessons from the FRALLE 93 Protocol. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, M.; Ishimaru, S.; Seki, M.; Yoshida, K.; Shiraishi, Y.; Chiba, K.; Kakiuchi, N.; Sato, Y.; Ueno, H.; Tanaka, H.; et al. Long-Term Outcome of 6-Month Maintenance Chemotherapy for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children. Leukemia 2017, 31, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usami, I.; Imamura, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Suenobu, S.-I.; Hasegawa, D.; Hashii, Y.; Deguchi, T.; Hori, T.; Shimada, A.; Kato, K.; et al. Discontinuation of L-Asparaginase and Poor Response to Prednisolone Are Associated with Poor Outcome of ETV6-RUNX1-Positive Pediatric B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2019, 109, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, C.-H.; Pei, D.; Raimondi, S.C.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Jeha, S.; Cheng, C.; Bowman, W.P.; Sandlund, J.T.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Rubnitz, J.E.; et al. Clinical Impact of Minimal Residual Disease in Children with Different Subtypes of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated with Response-Adapted Therapy. Leukemia 2017, 31, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, D.; Enshaei, A.; Bartram, J.; Hancock, J.; Harrison, C.J.; Hough, R.; Samarasinghe, S.; Schwab, C.; Vora, A.; Wade, R.; et al. Genotype-Specific Minimal Residual Disease Interpretation Improves Stratification in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, L. ETV6/RUNX1-Positive Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in China: Excellent Prognosis with Improved BFM Protocol. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaliova, M.; Kotrova, M.; Bresolin, S.; Stuchly, J.; Stary, J.; Hrusak, O.; Te Kronnie, G.; Trka, J.; Zuna, J.; Vaskova, M. ETV6/RUNX1-like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Novel B-Cell Precursor Leukemia Subtype Associated with the CD27/CD44 Immunophenotype. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017, 56, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilljebjörn, H.; Henningsson, R.; Hyrenius-Wittsten, A.; Olsson, L.; Orsmark-Pietras, C.; von Palffy, S.; Askmyr, M.; Rissler, M.; Schrappe, M.; Cario, G.; et al. Identification of ETV6-RUNX1-like and DUX4-Rearranged Subtypes in Paediatric B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dai, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, M.; Ouyang, W.; Huang, J.; Chen, S. Emerging Molecular Subtypes and Therapeutic Targets in B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Med. 2021, 15, 347–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-F.; Dai, Y.-T.; Lilljebjörn, H.; Shen, S.-H.; Cui, B.-W.; Bai, L.; Liu, Y.-F.; Qian, M.-X.; Kubota, Y.; Kiyoi, H.; et al. Transcriptional Landscape of B Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Based on an International Study of 1,223 Cases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11711–E11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lilljebjörn, H.; Fioretos, T. New Oncogenic Subtypes in Pediatric B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2017, 130, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.R.; Li, Z.; Tai, S.T.; Oh, B.L.Z.; Yeoh, A.E.J. Genetic Alterations in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Interactions with Clinical Features and Treatment Response. Cancers 2021, 13, 4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeha, S.; Choi, J.; Roberts, K.G.; Pei, D.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Inaba, H.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Gruber, T.A.; Raimondi, S.C.; et al. Clinical Significance of Novel Subtypes of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in the Context of Minimal Residual Disease-Directed Therapy. Blood Cancer Discov. 2021, 2, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, E.; Kuehn, H.S.; Odakir, E.; Niemela, J.E.; Ozcan, A.; Eken, A.; Rohlfs, M.; Cansever, M.; Gok, V.; Aydin, F.; et al. Common Variable Immunodeficiency, Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia, and Pancytopenia Associated with a Defect in IKAROS. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 43, e351–e357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgopoulos, K.; Bigby, M.; Wang, J.-H.; Molnar, A.; Wu, P.; Winandy, S.; Sharpe, A. The Ikaros Gene Is Required for the Development of All Lymphoid Lineages. Cell 1994, 79, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulos, K.; Moore, D.D.; Derfler, B. Ikaros, an Early Lymphoid-Specific Transcription Factor and a Putative Mediator for T Cell Commitment. Science 1992, 258, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heizmann, B.; Kastner, P.; Chan, S. The Ikaros Family in Lymphocyte Development. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 51, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y. B-Cell Deficiency: A De Novo IKZF1 Patient and Review of the Literature. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 28, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- On Behalf of the EORTC-CLG; Clappier, E.; Grardel, N.; Bakkus, M.; Rapion, J.; De Moerloose, B.; Kastner, P.; Caye, A.; Vivent, J.; Costa, V.; et al. IKZF1 Deletion Is an Independent Prognostic Marker in Childhood B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, and Distinguishes Patients Benefiting from Pulses during Maintenance Therapy: Results of the EORTC Children’s Leukemia Group Study 58951. Leukemia 2015, 29, 2154–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.H.; Blonquist, T.M.; Athale, U.H.; Clavell, L.A.; Cole, P.D.; Kelly, K.M.; Laverdiere, C.; Leclerc, J.-M.; Michon, B.; Schorin, M.A.; et al. Ikaros Gene Deletion Significantly Predicts Relapse in Pediatric B-ALL Patients with Low End-Induction Minimal Residual Disease. Blood 2015, 126, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Veer, A.; Waanders, E.; Pieters, R.; Willemse, M.E.; Van Reijmersdal, S.V.; Russell, L.J.; Harrison, C.J.; Evans, W.E.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Hoogerbrugge, P.M.; et al. Independent Prognostic Value of BCR-ABL1-like Signature and IKZF1 Deletion, but Not High CRLF2 Expression, in Children with B-Cell Precursor ALL. Blood 2013, 122, 2622–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papatriantafyllou, M. Two Versions of the Ikaros Tale. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggs, S.S.; Trevisan, M.; Patrene, K.; Geogopoulos, K. Lack of Natural Killer Cell Precursors in Fetal Liver of Ikaros Knockout Mutant Mice. Nat. Immun. 1998, 16, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, I.; Yoshida, T.; Jena, N.; Qi, X.; Zhang, J.; Van Etten, R.A.; Georgopoulos, K. Loss of Ikaros DNA-Binding Function Confers Integrin-Dependent Survival on Pre-B Cells and Progression to Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobucci, I.; Storlazzi, C.T.; Cilloni, D.; Lonetti, A.; Ottaviani, E.; Soverini, S.; Astolfi, A.; Chiaretti, S.; Vitale, A.; Messa, F.; et al. Identification and Molecular Characterization of Recurrent Genomic Deletions on 7p12 in the IKZF1 Gene in a Large Cohort of BCR-ABL1–Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients: On Behalf of Gruppo Italiano Malattie Ematologiche Dell’Adulto Acute Leukemia Working Party (GIMEMA AL WP). Blood 2009, 114, 2159–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, J.M.; van der Veer, A.; Rizopoulos, D.; Fiocco, M.; Sonneveld, E.; de Groot-Kruseman, H.A.; Kuiper, R.P.; Hoogerbrugge, P.; Horstmann, M.; Zaliova, M.; et al. Prognostic Value of Rare IKZF1 Deletion in Childhood B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: An International Collaborative Study. Leukemia 2016, 30, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trageser, D.; Iacobucci, I.; Nahar, R.; Duy, C.; von Levetzow, G.; Klemm, L.; Park, E.; Schuh, W.; Gruber, T.; Herzog, S.; et al. Pre–B Cell Receptor–Mediated Cell Cycle Arrest in Philadelphia Chromosome–Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Requires IKAROS Function. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marke, R.; van Leeuwen, F.N.; Scheijen, B. The Many Faces of IKZF1 in B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2018, 103, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanulla, M.; Cavé, H.; Moorman, A.V. IKZF1 Deletions in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Still a Poor Prognostic Marker? Blood 2020, 135, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Veer, A.; Zaliova, M.; Mottadelli, F.; De Lorenzo, P.; te Kronnie, G.; Harrison, C.J.; Cavé, H.; Trka, J.; Saha, V.; Schrappe, M.; et al. IKZF1 Status as a Prognostic Feature in BCR-ABL1–Positive Childhood ALL. Blood 2014, 123, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, R.P.; Waanders, E.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; van Reijmersdal, S.V.; Venkatachalam, R.; Scheijen, B.; Sonneveld, E.; van Dongen, J.J.M.; Veerman, A.J.P.; van Leeuwen, F.N.; et al. IKZF1 Deletions Predict Relapse in Uniformly Treated Pediatric Precursor B-ALL. Leukemia 2010, 24, 1258–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, D.; Imamura, T.; Suenobu, S.; Saito, A.; Hasegawa, D.; Deguchi, T.; Hashii, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Kawasaki, H.; Hori, H.; et al. IKZF1 Deletion Is Associated with a Poor Outcome in Pediatric B-cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Japan. Cancer Med. 2013, 2, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Hung, C.-C.; Chen, J.-S.; Lin, K.-H.; Jou, S.-T.; Hsiao, C.-C.; Sheen, J.-M.; Cheng, C.-N.; Wu, K.-H.; Lin, S.-R.; et al. IKZF1 Deletions Predict a Poor Prognosis in Children with B-Cell Progenitor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Multicenter Analysis in Taiwan. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 1874–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, L.; Albitar, F.; Castor, A.; Behrendtz, M.; Biloglav, A.; Paulsson, K.; Johansson, B. Cooperative Genetic Changes in Pediatric B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Deletions or Mutations of IKZF1: Pediatric BCP All with IKZF1 Aberrations. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2015, 54, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krentz, S.; Hof, J.; Mendioroz, A.; Vaggopoulou, R.; Dörge, P.; Lottaz, C.; Engelmann, J.C.; Groeneveld, T.W.L.; Körner, G.; Seeger, K.; et al. Prognostic Value of Genetic Alterations in Children with First Bone Marrow Relapse of Childhood B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2013, 27, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palmi, C.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Longinotti, G.; Silvestri, D.; Carrino, V.; Conter, V.; Basso, G.; Biondi, A.; Kronnie, G.T.; Cazzaniga, G. What Is the Relevance of Ikaros Gene Deletions as a Prognostic Marker in Pediatric Philadelphia-Negative B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia? Haematologica 2013, 98, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanulla, M.; Dagdan, E.; Zaliova, M.; Möricke, A.; Palmi, C.; Cazzaniga, G.; Eckert, C.; te Kronnie, G.; Bourquin, J.-P.; Bornhauser, B.; et al. IKZF1plus Defines a New Minimal Residual Disease–Dependent Very-Poor Prognostic Profile in Pediatric B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piovan, E.; Yu, J.; Tosello, V.; Herranz, D.; Ambesi-Impiombato, A.; Da Silva, A.C.; Sanchez-Martin, M.; Perez-Garcia, A.; Rigo, I.; Castillo, M.; et al. Direct Reversal of Glucocorticoid Resistance by AKT Inhibition in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evangelisti, C.; Cappellini, A.; Oliveira, M.; Fragoso, R.; Barata, J.T.; Bertaina, A.; Locatelli, F.; Simioni, C.; Neri, L.M.; Chiarini, F.; et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Inhibition Potentiates Glucocorticoid Response in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 1796–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clappier, E.; Auclerc, M.-F.; Rapion, J.; Bakkus, M.; Caye, A.; Khemiri, A.; Giroux, C.; Hernandez, L.; Kabongo, E.; Savola, S.; et al. An Intragenic ERG Deletion Is a Marker of an Oncogenic Subtype of B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with a Favorable Outcome despite Frequent IKZF1 Deletions. Leukemia 2014, 28, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaliova, M.; Zimmermannova, O.; Dörge, P.; Eckert, C.; Möricke, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Stuchly, J.; Teigler-Schlegel, A.; Meissner, B.; Koehler, R.; et al. ERG Deletion Is Associated with CD2 and Attenuates the Negative Impact of IKZF1 Deletion in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2014, 28, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hütter, G.; Kaiser, M.; Neumann, M.; Mossner, M.; Nowak, D.; Baldus, C.D.; Gökbuget, N.; Hoelzer, D.; Thiel, E.; Hofmann, W.-K. Epigenetic Regulation of PAX5 Expression in Acute T-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia Res. 2011, 35, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebral, K.; König, M.; Harder, L.; Siebert, R.; Haas, O.A.; Strehl, S. Identification of PML as Novel PAX5 Fusion Partner in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 139, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, D.; Powell, S.K.; Plummer, R.S.; Young, K.P.; Ruggeri, B.A. PAX Genes: Roles in Development, Pathophysiology, and Cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souabni, A.; Jochum, W.; Busslinger, M. Oncogenic Role of Pax5 in the T-Lymphoid Lineage upon Ectopic Expression from the Immunoglobulin Heavy-Chain Locus. Blood 2007, 109, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Medvedovic, J.; Ebert, A.; Tagoh, H.; Busslinger, M. Pax5. In Advances in Immunology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 111, pp. 179–206. ISBN 9780123859914. [Google Scholar]
- Shahjahani, M.; Norozi, F.; Ahmadzadeh, A.; Shahrabi, S.; Tavakoli, F.; Asnafi, A.A.; Saki, N. The Role of Pax5 in Leukemia: Diagnosis and Prognosis Significance. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Familiades, J.; Bousquet, M.; Lafage-Pochitaloff, M.; Béné, M.-C.; Beldjord, K.; De Vos, J.; Dastugue, N.; Coyaud, E.; Struski, S.; Quelen, C.; et al. PAX5 Mutations Occur Frequently in Adult B-Cell Progenitor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and PAX5 Haploinsufficiency Is Associated with BCR-ABL1 and TCF3-PBX1 Fusion Genes: A GRAALL Study. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1989–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotta, S.; Nutt, S.L. Losing B Cell Identity. Bioessays 2008, 30, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, J.; Wei, L.; de Ridder, J.; Su, X.; Rust, A.G.; Roberts, K.G.; Payne-Turner, D.; Cheng, J.; Ma, J.; Qu, C.; et al. PAX5 Is a Tumor Suppressor in Mouse Mutagenesis Models of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2015, 125, 3609–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.-F.; Wang, B.-Y.; Zhang, W.-N.; Huang, J.-Y.; Li, B.-S.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, L.; Li, J.-F.; Wang, M.-J.; Dai, Y.-J.; et al. Genomic Profiling of Adult and Pediatric B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. EBioMedicine 2016, 8, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nebral, K.; Denk, D.; Attarbaschi, A.; König, M.; Mann, G.; Haas, O.A.; Strehl, S. Incidence and Diversity of PAX5 Fusion Genes in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2009, 23, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bousquet, M.; Broccardo, C.; Quelen, C.; Meggetto, F.; Kuhlein, E.; Delsol, G.; Dastugue, N.; Brousset, P. A Novel PAX5-ELN Fusion Protein Identified in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Acts as a Dominant Negative on Wild-Type PAX5. Blood 2007, 109, 3417–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamata, N.; Ogawa, S.; Zimmermann, M.; Sanada, M.; Hemminki, K.; Yamatomo, G.; Nannya, Y.; Koehler, R.; Flohr, T.; Miller, C.W.; et al. Rearrangement and Deletion of the PAX5 Gene in Pediatric Acute B-Cell Lineage Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2007, 110, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, L.; Schroeder, M.P.; Eckert, C.; Schlee, C.; Tanchez, J.O.; Kämpf, S.; Wagner, D.L.; Schulze, V.; Isaakidis, K.; Lázaro-Navarro, J.; et al. PAX5 Biallelic Genomic Alterations Define a Novel Subgroup of B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1895–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passet, M.; Boissel, N.; Sigaux, F.; Saillard, C.; Bargetzi, M.; Ba, I.; Thomas, X.; Graux, C.; Chalandon, Y.; Leguay, T.; et al. PAX5 P80R Mutation Identifies a Novel Subtype of B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Favorable Outcome. Blood 2019, 133, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehn, J.A.; O’Connor, M.J.; White, D.L.; Yeung, D.T. DUX Hunting—Clinical Features and Diagnostic Challenges Associated with DUX4-Rearranged Leukaemia. Cancers 2020, 12, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Washington University Pediatric Cancer Genome Project; Zhang, J.; McCastlain, K.; Yoshihara, H.; Xu, B.; Chang, Y.; Churchman, M.L.; Wu, G.; Li, Y.; Wei, L.; et al. Deregulation of DUX4 and ERG in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinnerl, D.; Mejstrikova, E.; Schumich, A.; Zaliova, M.; Fortschegger, K.; Nebral, K.; Attarbaschi, A.; Fiser, K.; Kauer, M.O.; Popitsch, N.; et al. CD371 Cell Surface Expression: A Unique Feature of DUX4 -Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2019, 104, e352–e355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasuda, T.; Tsuzuki, S.; Kawazu, M.; Hayakawa, F.; Kojima, S.; Ueno, T.; Imoto, N.; Kohsaka, S.; Kunita, A.; Doi, K.; et al. Recurrent DUX4 Fusions in B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia of Adolescents and Young Adults. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaliova, M.; Potuckova, E.; Hovorkova, L.; Musilova, A.; Winkowska, L.; Fiser, K.; Stuchly, J.; Mejstrikova, E.; Starkova, J.; Zuna, J.; et al. ERG Deletions in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with DUX4 Rearrangements Are Mostly Polyclonal, Prognostically Relevant and Their Detection Rate Strongly Depends on Screening Method Sensitivity. Haematologica 2019, 104, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamoto, T.; Yamagata, T.; Sakai, R.; Ogawa, S.; Honda, H.; Ueno, H.; Hirano, N.; Yazaki, Y.; Hirai, H. CIZ, a Zinc Finger Protein That Interacts with P130 cas and Activates the Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- La Starza, R.; Aventin, A.; Crescenzi, B.; Gorello, P.; Specchia, G.; Cuneo, A.; Angioni, A.; Bilhou-Nabera, C.; Boqué, C.; Foà, R.; et al. CIZ Gene Rearrangements in Acute Leukemia: Report of a Diagnostic FISH Assay and Clinical Features of Nine Patients. Leukemia 2005, 19, 1696–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alexander, T.B.; Gu, Z.; Iacobucci, I.; Dickerson, K.; Choi, J.K.; Xu, B.; Payne-Turner, D.; Yoshihara, H.; Loh, M.L.; Horan, J.; et al. The Genetic Basis and Cell of Origin of Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukaemia. Nature 2018, 562, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shago, M.; Abla, O.; Hitzler, J.; Weitzman, S.; Abdelhaleem, M. Frequency and Outcome of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with ZNF384 Gene Rearrangements Including a Novel Translocation Resulting in an ARID1B/ZNF384 Gene Fusion. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.G.; Mullighan, C.G. The Biology of B-Progenitor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2020, 10, a034835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- From the Tokyo Children’s Cancer Study Group; Gocho, Y.; Kiyokawa, N.; Ichikawa, H.; Nakabayashi, K.; Osumi, T.; Ishibashi, T.; Ueno, H.; Terada, K.; Oboki, K.; et al. A Novel Recurrent EP300–ZNF384 Gene Fusion in B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2015, 29, 2445–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirabayashi, S.; Butler, E.R.; Ohki, K.; Kiyokawa, N.; Bergmann, A.K.; Möricke, A.; Boer, J.M.; Cavé, H.; Cazzaniga, G.; Yeoh, A.E.J.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of B-ALL with ZNF384 Rearrangements: A Retrospective Analysis by the Ponte Di Legno Childhood ALL Working Group. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3272–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, V.J.; Sharma, M.; Zhou, J.; Gennochi, D.; Fields, T.; Sharma, R.; McCarthy, E.T.; Srivastava, T.; Domen, J.; Tormo, A.; et al. Renal and Hematological Effects of CLCF-1, a B-Cell-Stimulating Cytokine of the IL-6 Family. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffith, M.; Griffith, O.L.; Krysiak, K.; Skidmore, Z.L.; Christopher, M.J.; Klco, J.M.; Ramu, A.; Lamprecht, T.L.; Wagner, A.H.; Campbell, K.M.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Analysis Reveals FLT3 Activation and a Therapeutic Strategy for a Patient with Relapsed Adult B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Exp. Hematol. 2016, 44, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, A.; Ozaki, K.; Baumann, H.; Levin, S.D.; Puel, A.; Farr, A.G.; Ziegler, S.F.; Leonard, W.J.; Lodish, H.F. Cloning of a Receptor Subunit Required for Signaling by Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.S.; Mahajan, S.; Frank, D.A. STAT Signaling in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Leukemias. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2496–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buitenkamp, T.D.; Pieters, R.; Gallimore, N.E.; van der Veer, A.; Meijerink, J.P.P.; Beverloo, H.B.; Zimmermann, M.; de Haas, V.; Richards, S.M.; Vora, A.J.; et al. Outcome in Children with Down’s Syndrome and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Role of IKZF1 Deletions and CRLF2 Aberrations. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2204–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russell, L.J.; Capasso, M.; Vater, I.; Akasaka, T.; Bernard, O.A.; Calasanz, M.J.; Chandrasekaran, T.; Chapiro, E.; Gesk, S.; Griffiths, M.; et al. Deregulated Expression of Cytokine Receptor Gene, CRLF2, Is Involved in Lymphoid Transformation in B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2009, 114, 2688–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panzer-Grümayer, R.; Köhrer, S.; Haas, O.A. The Enigmatic Role(s) of P2RY8-CRLF2. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 96466–96467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, M.; Imamura, T.; Asai, D.; Moriya-Saito, A.; Suenobu, S.; Hasegawa, D.; Deguchi, T.; Hashii, Y.; Kawasaki, H.; Hori, H.; et al. An Overall Characterization of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with CRLF2 Overexpression: Prognostic Significance of CRLF2 Overexpression in Pediatric All. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014, 53, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, R.C.; Mullighan, C.G.; Chen, I.-M.; Wharton, W.; Mikhail, F.M.; Carroll, A.J.; Kang, H.; Liu, W.; Dobbin, K.K.; Smith, M.A.; et al. Rearrangement of CRLF2 Is Associated with Mutation of JAK Kinases, Alteration of IKZF1, Hispanic/Latino Ethnicity, and a Poor Outcome in Pediatric B-Progenitor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2010, 115, 5312–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, L.J.; Jones, L.; Enshaei, A.; Tonin, S.; Ryan, S.L.; Eswaran, J.; Nakjang, S.; Papaemmanuil, E.; Tubio, J.M.C.; Fielding, A.K.; et al. Characterisation of the Genomic Landscape of CRLF2-rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017, 56, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmi, C.; Vendramini, E.; Silvestri, D.; Longinotti, G.; Frison, D.; Cario, G.; Shochat, C.; Stanulla, M.; Rossi, V.; Di Meglio, A.M.; et al. Poor Prognosis for P2RY8-CRLF2 Fusion but Not for CRLF2 over-Expression in Children with Intermediate Risk B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2245–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cario, G.; Zimmermann, M.; Romey, R.; Gesk, S.; Vater, I.; Harbott, J.; Schrauder, A.; Moericke, A.; Izraeli, S.; Akasaka, T.; et al. Presence of the P2RY8-CRLF2 Rearrangement Is Associated with a Poor Prognosis in Non–High-Risk Precursor B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children Treated According to the ALL-BFM 2000 Protocol. Blood 2010, 115, 5393–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, L.J.; Enshaei, A.; Jones, L.; Erhorn, A.; Masic, D.; Bentley, H.; Laczko, K.S.; Fielding, A.K.; Goldstone, A.H.; Goulden, N.; et al. IGH @ Translocations Are Prevalent in Teenagers and Young Adults with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Are Associated with a Poor Outcome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Chen, I.-M.; Wilson, C.S.; Bedrick, E.J.; Harvey, R.C.; Atlas, S.R.; Devidas, M.; Mullighan, C.G.; Wang, X.; Murphy, M.; et al. Gene Expression Classifiers for Relapse-Free Survival and Minimal Residual Disease Improve Risk Classification and Outcome Prediction in Pediatric B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2010, 115, 1394–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasian, S.K.; Doral, M.Y.; Borowitz, M.J.; Wood, B.L.; Chen, I.-M.; Harvey, R.C.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Willman, C.L.; Hunger, S.P.; Mullighan, C.G.; et al. Aberrant STAT5 and PI3K/MTOR Pathway Signaling Occurs in Human CRLF2-Rearranged B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2012, 120, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potthoff, M.J.; Olson, E.N. MEF2: A Central Regulator of Diverse Developmental Programs. Development 2007, 134, 4131–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Z.; Churchman, M.; Roberts, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Harvey, R.C.; McCastlain, K.; Reshmi, S.C.; Payne-Turner, D.; Iacobucci, I.; et al. Genomic Analyses Identify Recurrent MEF2D Fusions in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohki, K.; Kiyokawa, N.; Saito, Y.; Hirabayashi, S.; Nakabayashi, K.; Ichikawa, H.; Momozawa, Y.; Okamura, K.; Yoshimi, A.; Ogata-Kawata, H.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Characteristics of MEF2D Fusion-Positive B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Childhood, Including a Novel Translocation Resulting in MEF2D-HNRNPH1 Gene Fusion. Haematologica 2019, 104, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tange, N.; Hayakawa, F.; Yasuda, T.; Odaira, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Hirano, D.; Sakai, T.; Terakura, S.; Tsuzuki, S.; Kiyoi, H. Staurosporine and Venetoclax Induce the Caspase-Dependent Proteolysis of MEF2D-Fusion Proteins and Apoptosis in MEF2D-Fusion (+) ALL Cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseyenko, A.A.; Walsh, E.M.; Wang, X.; Grayson, A.R.; Hsi, P.T.; Kharchenko, P.V.; Kuroda, M.I.; French, C.A. The Oncogenic BRD4-NUT Chromatin Regulator Drives Aberrant Transcription within Large Topological Domains. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1507–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boer, J.M.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Hormann, F.M.; Antić, Ž.; Zaliova, M.; Schwab, C.; Cazzaniga, G.; Arfeuille, C.; Cavé, H.; Attarbaschi, A.; et al. Favorable Outcome of NUTM1-Rearranged Infant and Pediatric B Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in a Collaborative International Study. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2978–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormann, F.M.; Hoogkamer, A.Q.; Beverloo, H.B.; Boeree, A.; Dingjan, I.; Wattel, M.M.; Stam, R.W.; Escherich, G.; Pieters, R.; den Boer, M.L.; et al. NUTM1 Is a Recurrent Fusion Gene Partner in B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Associated with Increased Expression of Genes on Chromosome Band 10p12.31-12.2. Haematologica 2019, 104, e455–e459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- French, C. NUT Midline Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherr, C.J. Cancer Cell Cycles. Science 1996, 274, 1672–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stott, F.J. The Alternative Product from the Human CDKN2A Locus, P14ARF, Participates in a Regulatory Feedback Loop with P53 and MDM2. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 5001–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrasco Salas, P.; Fernández, L.; Vela, M.; Bueno, D.; González, B.; Valentín, J.; Lapunzina, P.; Pérez-Martínez, A. The Role of CDKN2A/B Deletions in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Pediatric Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 33, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steeghs, E.M.P.; Boer, J.M.; Hoogkamer, A.Q.; Boeree, A.; de Haas, V.; de Groot-Kruseman, H.A.; Horstmann, M.A.; Escherich, G.; Pieters, R.; den Boer, M.L. Copy Number Alterations in B-Cell Development Genes, Drug Resistance, and Clinical Outcome in Pediatric B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, C.J.; Chilton, L.; Morrison, H.; Jones, L.; Al-Shehhi, H.; Erhorn, A.; Russell, L.J.; Moorman, A.V.; Harrison, C.J. Genes Commonly Deleted in Childhood B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Association with Cytogenetics and Clinical Features. Haematologica 2013, 98, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathiravan, M.; Singh, M.; Bhatia, P.; Trehan, A.; Varma, N.; Sachdeva, M.S.; Bansal, D.; Jain, R.; Naseem, S. Deletion of CDKN2A/B Is Associated with Inferior Relapse Free Survival in Pediatric B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Kuang, P.; Liu, T. Prognostic Significance of CDKN2A/B Deletions in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: A Meta-Analysis. Ann. Med. 2019, 51, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gil, C.; Ribera, J.; Ribera, J.M.; Genescà, E. The Yin and Yang-Like Clinical Implications of the CDKN2A/ARF/CDKN2B Gene Cluster in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Genes 2021, 12, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, C.M.; Freund, J.; Oh, P.; Ndiaye-Lobry, D.; Bretz, J.C.; Strikoudis, A.; Genesca, L.; Trimarchi, T.; Kelliher, M.A.; Clark, M.; et al. Therapeutic Targeting of the Cyclin D3:CDK4/6 Complex in T Cell Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheppard, K.E.; McArthur, G.A. The Cell-Cycle Regulator CDK4: An Emerging Therapeutic Target in Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5320–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickson, M.A. Molecular Pathways: CDK4 Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3379–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rieder, H.; Schnittger, S.; Bodenstein, H.; Schwonzen, M.; Wörmann, B.; Berkovic, D.; Ludwig, W.D.; Hoelzer, D.; Fonatsch, C. Dic(9;20): A New Recurrent Chromosome Abnormality in Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 1995, 13, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.; Byatt, S.A.; Bennett, C.F.; Brama, M.; Martineau, M.; Moorman, A.V.; Roberts, K.; Secker-Walker, L.M.; Richards, S.; Eden, O.B.; et al. Monosomy 20 as a Pointer to Dicentric (9;20) in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2000, 14, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forestier, E.; Gauffin, F.; Andersen, M.K.; Autio, K.; Borgström, G.; Golovleva, I.; Gustafsson, B.; Heim, S.; Heinonen, K.; Heyman, M.; et al. Clinical and Cytogenetic Features of Pediatric Dic(9;20)(P13.2;Q11.2)-Positive B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemias: A Nordic Series of 24 Cases and Review of the Literature. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2008, 47, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachariadis, V.; Schoumans, J.; Ofverholm, I.; Barbany, G.; Halvardsson, E.; Forestier, E.; Johansson, B.; Nordenskjöld, M.; Nordgren, A. Detecting Dic(9;20)(P13.2;P11.2)-Positive B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in a Clinical Setting Using Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization. Leukemia 2014, 28, 196–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitelman, F.; Johansson, B.; Mertens, F. Mitelman Database of Chromosome Aberrations and Gene Fusions in Cancer. 2022. Available online: https://mitelmandatabase.isb-cgc.org (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- Johansson, B.; Mertens, F.; Mitelman, F. Clinical and Biological Importance of Cytogenetic Abnormalities in Childhood and Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Ann. Med. 2004, 36, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Wright, S.L.; Moorman, A.V.; Parker, H.; Griffiths, M.; Ross, F.M.; Davies, T.; Harrison, C.J.; Strefford, J.C. Heterogeneous Breakpoints in Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and the Dic(9;20)(P11~13;Q11) Show Recurrent Involvement of Genes at 20q11.21. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoumans, J.; Johansson, B.; Corcoran, M.; Kuchinskaya, E.; Golovleva, I.; Grandér, D.; Forestier, E.; Staaf, J.; Borg, A.; Gustafsson, B.; et al. Characterisation of Dic(9;20)(P11-13;Q11) in Childhood B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia by Tiling Resolution Array-Based Comparative Genomic Hybridisation Reveals Clustered Breakpoints at 9p13.2 and 20q11.2. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 135, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strefford, J.C.; Worley, H.; Barber, K.; Wright, S.; Stewart, A.R.M.; Robinson, H.M.; Bettney, G.; van Delft, F.W.; Atherton, M.G.; Davies, T.; et al. Genome Complexity in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Is Revealed by Array-Based Comparative Genomic Hybridization. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4306–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pichler, H.; Möricke, A.; Mann, G.; Teigler-Schlegel, A.; Niggli, F.; Nebral, K.; König, M.; Inthal, A.; Krehan, D.; Dworzak, M.N.; et al. Prognostic Relevance of Dic(9;20)(P11;Q13) in Childhood B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Treated with Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster (BFM) Protocols Containing an Intensive Induction and Post-Induction Consolidation Therapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 149, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lönnerholm, G.; Nordgren, A.; Frost, B.-M.; Jonsson, O.G.; Kanerva, J.; Nygaard, R.; Schmiegelow, K.; Larsson, R.; Forestier, E. Dic(9;20)(P13;Q11) in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Is Related to Low Cellular Resistance to Asparaginase, Cytarabine and Corticosteroids. Leukemia 2009, 23, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inaba, H.; Azzato, E.M.; Mullighan, C.G. Integration of Next-Generation Sequencing to Treat Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Targetable Lesions: The St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital Approach. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

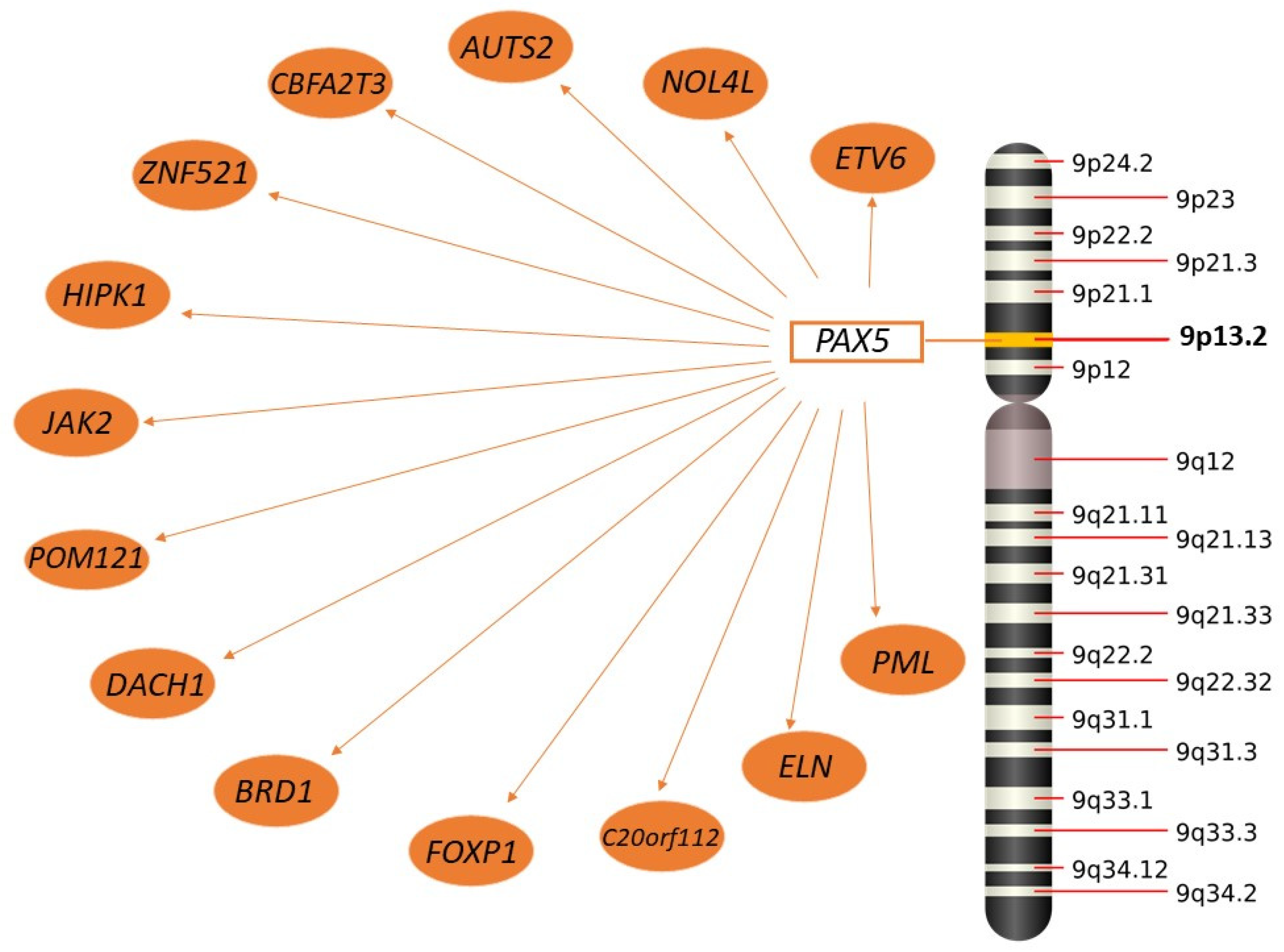
| Subtype | Genetic Alteration | Frequency in Childhood ALL | Frequency in Adult ALL | Prognosis | Targeted Therapy | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Hyperdiploidy | Aneuploidy (51–65 chromosomes) | 30% | 10% | Good prognosis | - | [23,25,27,28,29] |
| Low Hyperdiploidy | Aneuploidy (47–50 chromosomes) | 10–11% | 10–15% | Poor prognosis | - | [36,37] |
| Near Haploidy | Aneuploidy (24–31 chromosomes) | 1–2% | - | Poor prognosis | Potential use of PI3K inhibitors | [28,39,40,41,42,45] |
| Low Hypodiploidy | Aneuploidy (32–39 chromosomes) | 1–2% | 4% | Poor prognosis | Potential use of PI3K inhibitors | [28,39,40,41,42,45] |
| High hypodiploidy | Aneuploidy (40–44 chromosomes) | 2–3% | 7% | Poor prognosis | Potential use of PI3K inhibitors | [38,39,40,42] |
| iAMP21 | Amplification | 1.5–2% | 1% | Intermediate prognosis | - | [50,54] |
| BCR::ABL1 | Translocation | 3–4% | 15–20% | Poor prognosis | TKI | [59,68,69,72] |
| Ph-like ALL | Gene fusions | 15% | 20–24% | Poor prognosis | TKI, JAK2 inhibitors, JAK1/JAK3 inhibitors, TYK2 inhibitor, Crizotinib, MEK inhibitors, FAK inhibitors, FLT3 inhibitors | [77,88,89,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106] |
| TCF::PBX1 | Translocation | 6% | 6% | Intermediate prognosis | Dasatinib, ruxolitinb | [82,130,135,136,139] |
| TCF3::HLF | Translocation | <1% | <1% | Intermediate prognosis | Venetoclax | [89,90,141,142,145] |
| IKZF1 | Deletion/point mutation/gene fusion | 16–27% | 40–50% | Poor prognosis | - | [183,199,201] |
| CRLF2 | Gene fusions/point mutation | 5% | 5% | Poor prognosis | Potential use of JAK inhibitors | [81,241,247,248,249,250,251] |
| MEF2D | Gene fusions | 4% | 4% | Poor prognosis | HDAC inhibitors, staurosporine, venetoclax | [181,254,255] |
| CDKN2A | Deletion/hypermethylation | 15–35% | 30–45% | Poor prognosis | CDK4/CDK6 inhibitors | [262,266,268,269,270] |
| ETV6::RUNX1 | Translocation | 25% | <5% | Good prognosis | - | [148,167,168] |
| ETV6::RUNX1-like | Translocation | 2–3% | <1% | Poor prognosis | - | [177,180] |
| KMT2A | Translocation/inversion | 5% (70–80% in infants) | 10% | Poor prognosis | Dot1L, bromodomain, menin, BCL-2, polycomb repressive complex inhibitors | [108,119,127] |
| DUX4 | Gene fusions | 4–7% | 4–7% | Good prognosis | Possibly | [130,225,228] |
| PAX5alt | Gene fusions/deletion/amplification | 7–10% | 8–10% | Intermediate prognosis | tyrosine kinase inhibitors (NRAS, KRAS, and FLT3) | [130,177] |
| PAX5 P80R | hotspot mutation (PAX5 p.Pro80Arg mutation) | 3–4% | 1–4% | Intermediate prognosis | Potential use of Ras, JAK/STAT, FLT3, BRAF and PIK3CA inhibitors | [130,177] |
| ZNF384 | Gene fusions | 3–5% | 3–8% | Intermediate prognosis | FLT3 | [177,219,238] |
| NUTM1 | Gene fusions | 1% | - | Good prognosis | Bromodomain inhibitors | [177,257] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lejman, M.; Chałupnik, A.; Chilimoniuk, Z.; Dobosz, M. Genetic Biomarkers and Their Clinical Implications in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052755
Lejman M, Chałupnik A, Chilimoniuk Z, Dobosz M. Genetic Biomarkers and Their Clinical Implications in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(5):2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052755
Chicago/Turabian StyleLejman, Monika, Aleksandra Chałupnik, Zuzanna Chilimoniuk, and Maciej Dobosz. 2022. "Genetic Biomarkers and Their Clinical Implications in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 5: 2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052755
APA StyleLejman, M., Chałupnik, A., Chilimoniuk, Z., & Dobosz, M. (2022). Genetic Biomarkers and Their Clinical Implications in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(5), 2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052755






